In the code below: highly simplified. I get ZeroDivisionError: float division
Any value below one gives errors. Other times 5/365 gives the error.
How do I fix?
import math
def top( t):
return ((.3 / 2) * t) / (.3 * math.sqrt(t))
t = 365/365
top= top(t)
print (top)
asked Sep 20, 2011 at 2:04
MerlinMerlin
24.6k41 gold badges133 silver badges206 bronze badges
6
The problem is here:
t = 365/365
You are dividing two integers, so python is using integer division. In integer division, the quotient is rounded down. For example, 364/365 would be equal to 0. (365/365 works because it is equal to 1, which is still 1 rounded down.)
Instead, use float division, like so.
t = 365.0/365.0
answered Sep 20, 2011 at 2:10
cheekencheeken
33.7k4 gold badges35 silver badges42 bronze badges
2
In addition to cheeken’s answer, you can put the following at the top of your modules:
from __future__ import division
Doing so will make the division operator work the way you want it to i.e always perform a (close approximation of) true mathematical division. The default behaviour of the division operator (where it performs truncating integer division if the arguments happen to be bound to integers) was inherited from C, but it was eventually realised that it was not a great fit for a dynamically typed language like Python. In Python 3, this no longer happens.
In my Python 2 modules, I almost always import division from __future__, so that I can’t get caught out by accidentally passing integers to a division operation I don’t expect to truncate.
It’s worth noting that from __future__ import ... statements have to be the very first thing in your module (I think you can have comments and a docstring before it, nothing else). It’s not really a normal import statement, even though it looks like one; it actually changes the way the Python interpreter reads your code, so it can’t wait until runtime to be exectuted like a normal import statement. Also remember that import __future__ does not have any of the magic effects of from __future__ import ....
answered Sep 20, 2011 at 2:24
BenBen
68.7k20 gold badges127 silver badges174 bronze badges
1
Try this:
exponent = math.exp(-(math.pow(x-mean,2)/(2*math.pow(stdev,2))))
A ZeroDivisionError is encountered when you try to divide by zero.
Adil B
14.7k11 gold badges60 silver badges78 bronze badges
answered Oct 29, 2017 at 18:05
Замените условие на
if not b and ( c=='mod' or c=='/' or c=='div'):
print("Делеение на ноль")или лучше на
if not b and c in ['/','%', 'mod', 'div']:
print("Делеение на ноль")а так пара других вариантов
a = float(input())
b = float(input())
c = input()
z_div = 'Деление на ноль!"
OPERATORS = {
"+": a + b,
"-": a - b,
"*": a * b,
"/": a / b if b else z_div,
"mod": a % b if b else z_div,
"div": a // b if b else z_div,
"pow": a ** b
}
print(OPERATORS[c])
более понятный вариант, но придется вычислять все варианты.
Более python way :
a = float(input())
b = float(input())
c = input()
z_div = 'Деление на ноль!'
OPERATORS = {
"+": lambda x, y: x + y,
"-": lambda x, y: x - y,
"*": lambda x, y: x * y,
"/": lambda x, y: x / y if y else None,
"mod": lambda x, y: x % y if y else None,
"div": lambda x, y: x // y if y else None,
"pow": lambda x, y: x ** y
}
print(OPERATORS[c](a, b))АНАЛог с eval :
a = input()
b = input()
c = input()
OPERATORS = {
"+": "+",
"-": "-",
"*": "*",
"/": "/",
"mod": "%",
"div": "//",
"pow": "**"
}
if not float(b) and c in ['/','%', 'mod', 'div']:
print('Деление на ноль!')
else:
print(
eval(
a + OPERATORS[c] + b
)
)When working with numbers in Python, you might encounter the following error:
ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero
This error occurs when you attempt to divide a floating number with zero.
Python raises the ZeroDivisionError because dividing a number with a zero returns an infinite number, which is impossible to measure in a programming language.
This tutorial will show you an example that causes this error and how to fix it
How to reproduce this error
Suppose you have two number variables where one of them is a float and the other is zero.
When you divide the float by zero as follows:
You get this output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 4, in <module>
z = x / y
ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero
The error occurs because the y variable is zero, so the division yields an infinite number that can’t be counted.
How to fix this error
To resolve this error, you need to prevent a division by zero from happening in your code.
One way to do this is to use the if statement to check if the dividing number is zero. In this case, you have to check the value of the y variable:
x = 9.5
y = 0
if y == 0:
print("Can't perform division: the y variable is 0")
z = 0
else:
z = x / y
Or you can also use a one-line if statement as follows:
z = 0 if y == 0 else (x / y)
When the value of y is zero, then set the value of z as zero too. Otherwise, divide x by y and assign the result to z.
Other similar errors
Besides float division by zero, the ZeroDivisionError also has some alternatives:
ZeroDivisionError: integer division by zeroZeroDivisionError: integer modulo by zeroZeroDivisionError: float modulo by zero
Although the error message is slightly different, all these variants are caused by the same problem: you tried to divide or modulo the number by zero.
Here are some examples:
x = 5 / 0 # integer division by zero
y = 5 % 0 # integer modulo by zero
z = 7.5 % 0 # float modulo by zero
The solution to these errors is the same, you need to prevent the numbers from being divided or reduced using a zero.
I hope this tutorial helps you solve the error. Cheers! 🙌
If the number (positive or negative) is divided by zero in mathematics, the output will be undefined or of no value. Similarly, if the number (integer or float) is divided by zero in Python, the interpreter will throw a “ZeroDivisionError”. To resolve this error, various solutions are used in Python, such as the “if” statement and the “try-except” block.
This blog provides the reason for the error “float division by zero” with their solutions and examples. The following aspects are followed in this article:
- Reason: Dividing Floating Point Number By “0”
- Solution 1: Use if-Statement
- Solution 2: Use try-except Block
So, let’s get started!
Reason: Dividing Floating Point Number By “0”
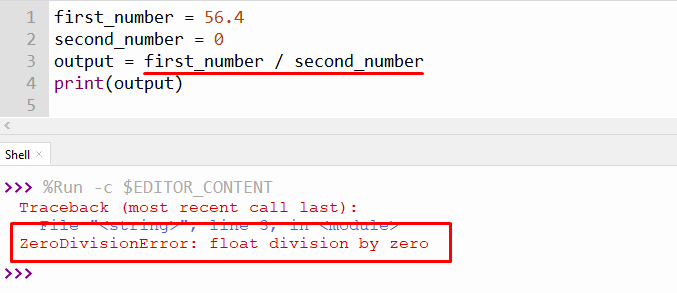
The prominent reason which causes this error in Python is when a user tries to divide the floating point number by “0” in a program. The error snippet is shown below:
The above snippet shows “ZeroDivisionError” because the floating point number is divided by “0”.
Solution 1: Use if-Statement
To resolve this error, you can use the “if” statement to check if the divisor is equal to “0” or not. Here is a code example:
Code:
first_number = 56.4
second_number = 0
if second_number!=0:
output = first_number / second_number
else:
output = 0
print(output)
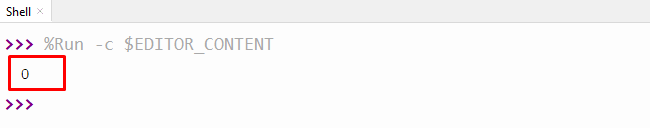
In the above code:
- The “if” statement is utilized to check whether the divisor or the number which we are dividing by is equal to zero or not.
- If the number is not equal to zero, then the “if” block statement is executed and shows the division result.
- The else block is executed when the divisor is equal to zero.
The above output shows the value “0” because the divisor number is equal to “0”.
Solution 2: Use try-except Block
Another solution to handle this particular error is using the “try-except” block in the program. Let’s understand this concept via the below-given Python program.
Code:
first_number = 56.4
second_number = 0
try:
output = first_number / second_number
except ZeroDivisionError:
output = 0
print(output)
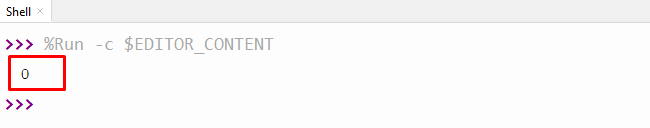
In the above code:
- The “try” block executes when the divisor is not equal to zero.
- If the dividing number/divisor is equal to zero, then the “except” block handles the “ZeroDivisionError” and assigns a “0” value to the output variable.
The output shows that the try-except block successfully resolves the stated error.
That’s it from this guide!
Conclusion
The “ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero” occurs when a user tries to divide a floating point number by the value “0” in Python. To resolve this error, you can use the “if-else” statement to check whether the input number is equal to zero or not before performing the calculation. The “try-except” block is also used to handle the “ZeroDivisionError” in Python programs. This blog explained how to resolve the “float division by zero” error in Python using appropriate examples.
By Lenin Mishra
in
python
—
Handling Zero Division exceptions in Python
A ZeroDivisionError is raised when you try to divide by 0. This is part of the ArithmeticError Exception class.
Example 1
Code/Output
# integers
1/0
>>> ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
# floats
5.3/0
>>> ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero
# complex numbers
(1+2j)/0
>>> ZeroDivisionError: complex division by zeroExample 2 — decimal library
If you are working with a decimal library and you perform the division operation with a 0, you get a DivisionByZero error.
The DivisionByZero eexception is decimal libraries own exception type that derives from the ZeroDivisionError exception.
Code
from decimal import Decimal
x = Decimal(1)
print(x/0)Output
decimal.DivisionByZero: [<class 'decimal.DivisionByZero'>]Handling ZeroDivisionError in Python
You can handle ZeroDivisionError errors by using the same exception class in your except block.
Code
# integers
try:
1/0
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
print(e)
# floats
try:
5.3/0
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
print(e)
# complex numbers
try:
(1+2j)/0
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
print(e)Output
division by zero
float division by zero
complex division by zeroHierarchy of ZeroDivisionError
The ZeroDivisionError inherits from the ArithmeticError class, which in turn inherits from the generic Exception class.
->Exception
-->ArithmeticError
--->ZeroDivisionError
So you can catch all ZeroDivisionError exceptions using the ArithmeticError exception class too.
Code
# integers
try:
1/0
except ArithmeticError as e:
print(e, e.__class__)
# floats
try:
5.3/0
except ArithmeticError as e:
print(e, e.__class__)
# complex numbers
try:
(1+2j)/0
except ArithmeticError as e:
print(e, e.__class__)Output
division by zero <class 'ZeroDivisionError'>
float division by zero <class 'ZeroDivisionError'>
complex division by zero <class 'ZeroDivisionError'>Check out other Python Built-in Exception classes in Python.