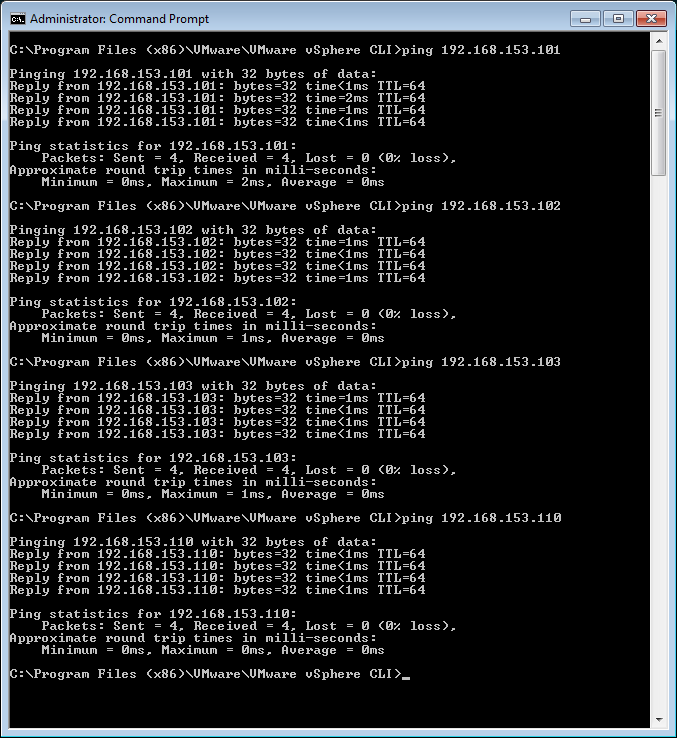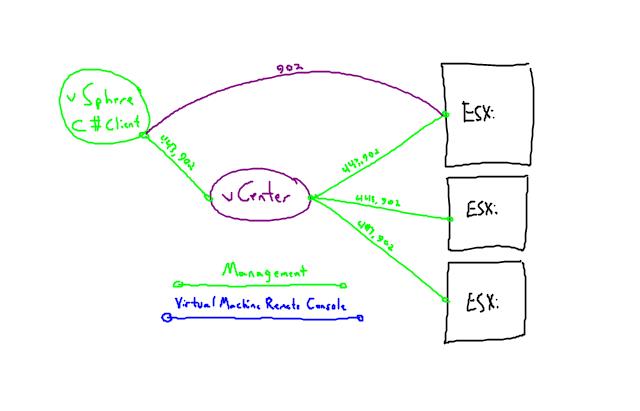
Q: Does your client have Layer 2 connectivity to your ESXi Hosts? Another way of saying this is: If your ESXi Hosts and vCenter are on 172.20.0.0/16, is the system where the client app is installed also on 172.20.0.0/16?
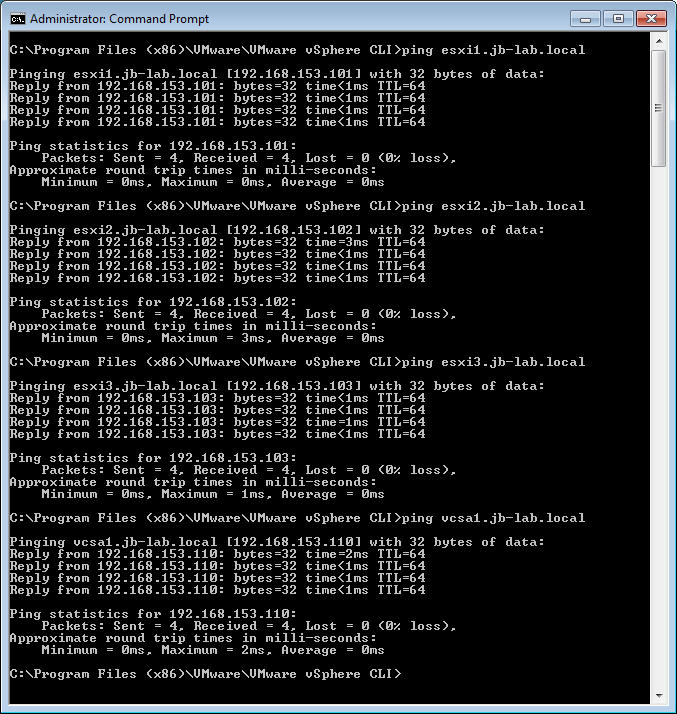
Q: Can you ping your vCenter and all your ESXi Hosts by IP address from the client system?
Q: Can you ping your vCenter and all your ESXi Hosts by hostname from the client?
Problems connecting to the Remote Console of VMware vSphere Virtual Machines can usually be divided into one of three problem areas:
Problem One: Layer 3 (Firewall/Gateway) issues
The VMRC connection exists between the EXSi Host of the VM and the Client, even in environments which are managed by a vCenter Server. This means that if the client is on a different network (Layer 3) from the ESXi Hosts, the client must be able to resolve and connect to all ESXi hosts!
It is a misnomer and wives-tale that firewalls/routers which exist between vSphere client networks and vSphere Management networks need only route ports 443 & 902 between the client and the vCenter. Those sort of Layer 3 relationships need route to ports 443 & 902 between the client and all of the ESXi Hosts!
You can diagnose issues simply with a ping. If you can ping all of your ESXi Hosts and by IP, it is likely not a problem with Layer 3 connectivity. If you can not ping vSphere, it may just be ICMP that is blocked, go ahead and use telnet or a port-scanner.
A more conclusive, diagnosis would be to use telnet or a port-scanner to check for connectivity on ports 443 & 902 from your client to all of your ESXi hosts. If you were able to connect to 443 & 902 on everything, you could rule Layer 3 problems out conclusively.
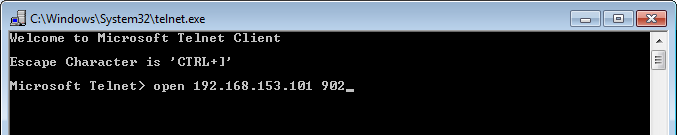
Run: telnet <ESXi IP address> 902
This is the message you should see:
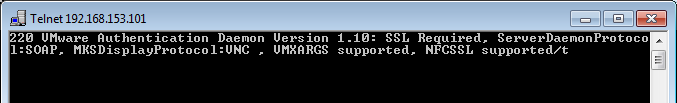
If you run: telnet <ESXI IP address> 443 you should see:
Resolution:
Fix Layer 3 connectivity issues between the client system and all of vSphere (ESXi and vCenter)
Workaround:
One potential workaround to Layer 3 issues with the VMRC would to build a Windows/Linux Desktop VM inside the vSphere Management Network and simply RDP to that! Instead of potentially compromising the security of the vSphere Management Network by opening up all of those ports, just allow 3260 (RDP), connect to that and initiate your Virtual Machine Remote Console there.
Problem Two: DNS Name resolution issues
If the PC running the vSphere Client (or Web Client) is not able to resolve the hostname of the ESXi Host of the VM, then the VMRC can not connect.
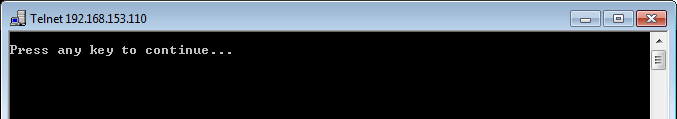
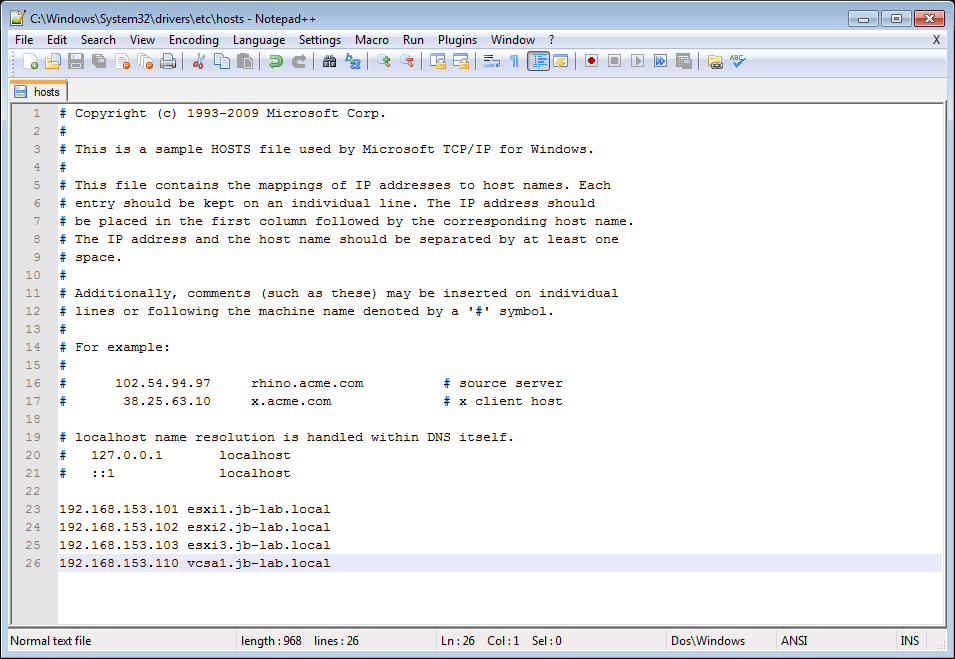
In this case, a ping by hostname to all of the ESXi hosts will determine that name resolution for one or all of these entities is not working for the client or does not exist.
This image represents a correctly configured system where the VMRC should be able to connect:
It may be a simple matter that the client PC served by a different DNS server than the vSphere Management Network, or the client PC may have no DNS resolution at all
Fix:
Make sure that the vSphere Management Network DNS is resolvable from the client PC.
NOTE: on corporate AD domains, using the workaround of creating a hosts file may be more desirable than changing the DNS of the client PC as the hosts file has no impact on authentication issues!
Workaround:
Create a hosts file on the client PC which contains the A-records for the vCenter and all of the ESXi Hosts. Be sure to run the editor as administrator. I highly recommend Notepad ++
Problem Three: vSphere 6 issues
I have noticed that, beginning with vSphere 6, when an ESXi Host is added to vCenter, and that host contains running Virtual Machines (like vCenter itself), the VMRC of those VMs will fail with a generic MKS error until the VMs are fully powered-off or vMotion-ed to another ESXi Host.
The diagnosis for this would be MKS issues that exist when there are no port issues and DNS resolution is working perfectly! In other words, if it’s not Problem One or Problem Two, then it’s probably problem Three!
Resolution:
None that I know of – please feel free to provide one!
Workaround:
As this symptom only occurs to running VMs that were on an ESXi Host at the time it was added to a vCenter, it is relatively uncommon and will only happen once in a given environment. Simply vMotion the VMs or power them off and back on once!
When was the last time you tried to remote console to a VM only to be greeted with the annoying Unable to connect to the MKS or similar message? Some of the causes leading to this issue range from firewalls blocking the required ports, badly configured DNS, and ESXi services in need of a restart. Today’s post explores a number of ways you can use to remote console to a VMware virtual machine and what you can do when remote connections fail, and you are unable to connect to the MSK.
Speaking of firewalls, adding a persistent firewall rule to ESXi can be daunting. I discuss how to do this in How to create persistent firewall rules on ESXi.
What is MKS?
MKS stands for Mouse, Keyboard and Screen. In vSphere, you can remote console to VMs using the standard vSphere clients and products such as VMware Workstation.
In pre-6.5 vSphere releases, you can use the legacy vSphere client which has now been deprecated for a long time. As shown next, just highlight the virtual machine you want to connect to and click on the Console tab. Alternatively, right-click on the VM and select Open Console. The latter method opens a stand-alone console window for you.
Remote console using the vSphere Client
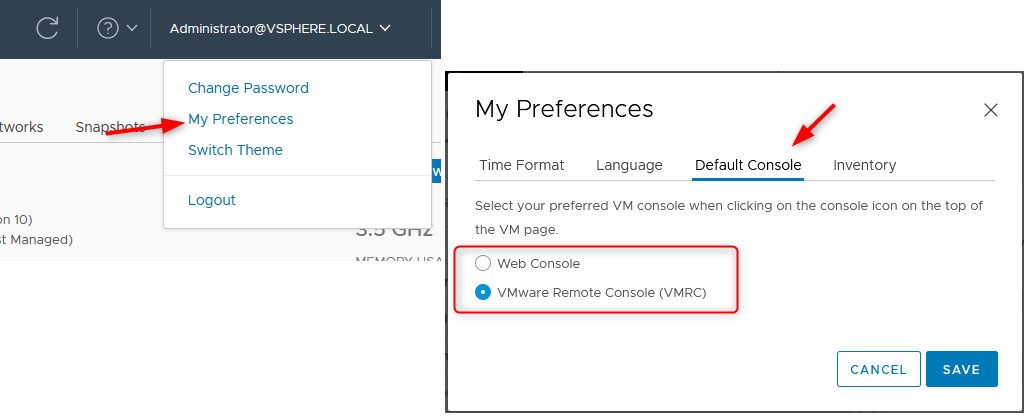
If you have vCenter installed, the vSphere Web Client provides you with two remote console options, these being VMRC (the standalone VMware Remote Console) and the Web Console.
You can change the default virtual console by clicking on your user in the top right corner > My Preferences > Default Console > You can then select the web or vmrc as your default console.
You also get both options directly underneath the preview of the VM screen in the VM view. VMRC is installed by following the link given in vSphere client or by downloading it from here.
NOTE: Users who have VMware Workstation installed will have noticed that selecting Launch Remote Console brings up Workstation’s VMRC instead of the standalone one. To override this behavior, uninstall the standalone VMRC and reinstall it back.
Back to vSphere Web Client, clicking on the VM’s console screen or selecting Open Console from the VM’s context menu will launch the default remote console.
Choose between the web console and VMRC.
Remote console using the host client (ESXi embedded)
Interestingly, you can configure a virtual machine such that you connect to it using a remote client such as tightVNC. To do this, add the following lines to the VM’s configuration (Edit Settings -> VM Options tab -> Advanced Settings -> Edit Configuration). You must disable the ESXi firewall for this to work or add a rule to allow 5900 through, this being the default VNC port. If memory serves me right, this worked with ESXi 5.x versions but to be honest, I had little time to try it out on 6.x. With ESXi 6.5, I manage to establish a connection but it keeps asking for a password regardless of the one specified in the VM’s configuration.
Configuring a VM to accept remote connections from VNC
What can go wrong and how to fix it
Some of the MKS errors (for instance, vmware unable to connect to the mks internal error) you might see are as follows:
-
- Error connecting: Host address lookup for server <SERVER> failed: The requested name is valid and was found in the database, but it does not have the correct associated data being resolved for.
-
- Error connecting: cannot connect to host <host>: A connection attempt failed because the connected party did not properly respond after a period of time, or established connection failed because the connected host has failed to respond.
-
- Error connecting: You need to execute access in order to connect with the VMware console. Access denied for config file.
-
- Unable to connect to MKS: Failed to connect to server IP:903.
1. Firewalls
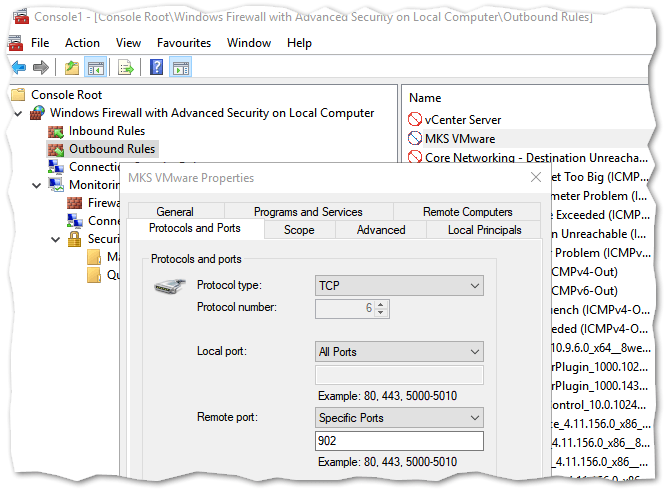
Depending on the version of ESXi / vCenter Server installed, TCP ports 902, 903, 443 and 9443 need to be reachable when using the web based and standalone remote consoles. With vSphere 6.5, I managed to replicate a common problem where a personal firewall, or one sitting between the client computer and ESXi networks, is blocking one or more ports especially 902. To do this, I enabled the Windows firewall and created an outbound rule blocking 902 as shown.
Managing Microsoft Windows firewall rules
When the firewall rule is enabled, the following is what you get when trying to remote console to a virtual machine. The error message might differ slightly depending at which point the connection is dropped.
Remote console connection errors due to a firewall blocking ports 902 and 9443
Changing the firewall rule to Allow from Block fixes the “unable to connect to the mks” issue. Often, the lost ability to remote console occurs right after someone installs or rolls out security software incorporating a personal firewall. From my experience, other primary suspects include updates to group policies governing the Windows firewall and unannounced changes to ACLs on switches / routers. If you’re not the one administering the latter, talk to your colleagues to try and narrow down the source of the problem.
You can use netstat to verify that connections on port 902 are being established when you remote console to a VM. If you don’t see any entries, the issue is definitely firewall / network related. Another trick you can use is to telnet <ESXi IP> 902 from a command prompt or terminal. If you get a reply, it means that ESXi is listening on the port and ready for connections.
Using netstat to inspect network connections
If you’re not running a personal firewall, SSH to ESXi and temporarily disable the ESXi firewall by running esxcli network firewall set –enabled false. Verify that you can connect. If not, it’s a firewall sitting in between the management station and ESXi that’s dropping the connection.
If the problem persists after having ruled out firewalling as a problem source, move on to the next check.
2. DNS
Connection to remote console can also be impeded if ESXi and vCenter Server hostnames do not resolve correctly. To determine correct DNS resolution, use ping <ESXi hostname> or nslookup to verify that your ESXi and vCenter Server hostnames are resolving to the correct IP addresses and, likewise, to the correct hostnames. If the issues persists, try adding your ESXi hosts and IP addresses to \windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts, run ipconfig /flushdns and retry.
192.168.10.10 ESX65-a.lab.local
192.168.10.11 ESX65-b.lab.local
192.168.10.12 ESX65-c.lab.local
3. Free Disk Space
If firewalling and DNS are not the culprit, verify that the partition where /var lives has enough free disk space. To do this, run df -h from an SSH session on the ESXi hosting the VM you’re trying to remote console to. Make sure that the partition where /var is located is not full.
Checking for free disk space on ESXi
Another command you could use is vdh -h.
Making sure /var has free disk space using the vdf -h command
4. Permissions
Verify that the permissions set on the VM’s VMX file are set correctly (755). To check the permissions, run the command:
ls -l *.vmx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3995 Aug 18 10:00 Windows 7.vmx
We can see that the permissions are correctly set for the VMX file of a VM called Window 7.
-
- rwx = 111 = 7
-
- r-x = 101 = 5
-
- r-x = 101 = 5
If the VMX file permissions are not set to 755, run the following command:
chmod 755 ‘Windows 7.vmx’
Note: On ESXi 6.5, setting the permissions to read only had no effect so the permissions issues might only apply to older versions of ESXi.
5. If nothing else works!
If none of the above worked, try doing the following:
-
- Check that the time on ESXi is set correctly and in sync with the rest of the infrastructure.
-
- vMotion the VM you’re unable to remote console to, to another ESXi host and retry.
-
- Restart the management agents on ESXi as per the following KB.
-
- Reboot the VM.
-
- Reboot ESXi.
Note: Sometimes to fix if vmware remote console is unable to connect to the mks is as trivial as pressing a key while the focus is given to the console window. This was common with older versions of the legacy client and vSphere releases where nothing is displayed in the VM’s console window. Hitting Enter or another key usually brings the console back to life. An alternative fix is to launch the console in its own window by right-clicking on it and selecting Open Console.
Conclusion
Being able to remote console to a virtual machine is, of course, an integral part of any admin’s job. Seeing the dreaded “Unable to connect to the MKS” message and being able to console can be highly frustrating more so when you need to fix something fast. In most cases, the problem lies with a firewall blocking one or more required ports and missing or bad DNS entries. For the rest, it’s usually enough to vMotion a VM to another host or restart the management agent on ESXi.
If you enjoyed reading this post, why not have a look at The Complete List of VMware Articles.
@linanwang wrote:
Even after you properly setup the SSL certification, you may still see the error if connect from local network, as the VMRC tries to use local ip to connect. Local ip will not match any domain name from your certification. Try to add an entry in you local machine host name resolve, for Windows edit c:windowssystem32driversetchosts by add a line of «<local ip> <domain name of server>», for example:
192.168.1.10 vm.mydomain.net
I’m sorry, I am just playing with Esxi so I don’t have a full understanding of how it all works. My ESXi host must have a self signed SSL because port 80 is blocked on my connection, but I can access everything through port 443. (It’s run from home off a residential ISP connection). My ESXi acts a little weird and I don’t leave it accessible unless I know I’m going somewhere and need to access it. I think I should setup a VPN for that. ESXi doesn’t load the login screen the first time, it just goes to a blue screen, then you refresh it and the login will actually show up, then it works like normal everywhere except for VMRC. I get the SSL error when I try to use it. I’m behind cloudflare and a kemp load balancer that holds certificates. I thought this was happening because I didn’t use any of the ssl pem and key files from letsencrypt on ESXi, but if that was the reason causing VMRC to fail, why can I access everything else under SSL?
I will definitely try entering that code. Is there something I can edit on a Ubuntu machine that would associate the internal IP to the domain also?
Содержание
- Vmrc ошибка подключения не удалось согласовать ssl подключение
- Как исправить ошибки безопасности SSL в браузере
- Что такое SSL
- Причины появления ошибок SSL
- Время и дата
- Настройки антивируса и брандмауэра
- Браузер и операционная система
- Заражение компьютерными вирусами
- Почему возникают ошибки SSL-соединения и как их исправить?
- Что такое SSL?
- Причины возникновения ошибок SSL-соединения
- Проблемы с датой и временем
- Ненадежный SSL-сертификат
- Брандмауэр или антивирус, блокирующие сайт
- Включенный экспериментальный протокол QUIC
- Отсутствие обновлений операционной системы
- Использование SSL-сертификата версии 3.0
- Ошибки «Invalid CSR» при генерации сертификата из панели управления облачного провайдера
Vmrc ошибка подключения не удалось согласовать ssl подключение
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
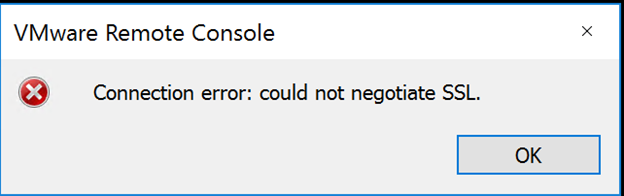
Ever since I updated the VMWare Remote Console from 10.x to 11.0 I am getting the following error message when trying to connect to a VM:
Connection error: could not negotiate SSL.
Everything works fine with remote console versions pre 11.0.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Please check all your certificates. Here is another thread with a similar issue: Black screen when launching VM Remote Console from vCloud Director 9.5
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Even after you properly setup the SSL certification, you may still see the error if connect from local network, as the VMRC tries to use local ip to connect. Local ip will not match any domain name from your certification. Try to add an entry in you local machine host name resolve, for Windows edit c:windowssystem32driversetchosts by add a line of » «, for example:
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Even after you properly setup the SSL certification, you may still see the error if connect from local network, as the VMRC tries to use local ip to connect. Local ip will not match any domain name from your certification. Try to add an entry in you local machine host name resolve, for Windows edit c:windowssystem32driversetchosts by add a line of » «, for example:
I’m sorry, I am just playing with Esxi so I don’t have a full understanding of how it all works. My ESXi host must have a self signed SSL because port 80 is blocked on my connection, but I can access everything through port 443. (It’s run from home off a residential ISP connection). My ESXi acts a little weird and I don’t leave it accessible unless I know I’m going somewhere and need to access it. I think I should setup a VPN for that. ESXi doesn’t load the login screen the first time, it just goes to a blue screen, then you refresh it and the login will actually show up, then it works like normal everywhere except for VMRC. I get the SSL error when I try to use it. I’m behind cloudflare and a kemp load balancer that holds certificates. I thought this was happening because I didn’t use any of the ssl pem and key files from letsencrypt on ESXi, but if that was the reason causing VMRC to fail, why can I access everything else under SSL?
I will definitely try entering that code. Is there something I can edit on a Ubuntu machine that would associate the internal IP to the domain also?
Источник
При открытии сайтов в браузере иногда возникают ошибки – домен в адресной строке выделяется красным с зачеркиванием или ресурс вообще не открывается. Типовая причина скрывается в сбоях работы сертификата SSL. Исправить их может только администратор сайта, но перед обращением к нему стоит проверить собственный компьютер.
Текущие тенденции сайтостроения предполагают высокую безопасность соединения пользователя с веб-ресурсом. Это необходимо для защиты персональных данных, секретных номеров банковских карт и информации о проводимых сделках. Организуется безопасность подключением протокола шифрования Secure Sockets Layer (сокращенно SSL).
- Сертификат выпускается доверенным центром Certification Authority (CA).
- После выдачи он подключается к домену средствами провайдера хостинга.
- Срок его действия ограничен 1 годом, после чего требуется продление.
Работа сайта возможна и без SSL, но поисковые системы «не доверяют» таким ресурсам и помечают их в браузере как неблагонадежные. Поэтому лучше разобраться, как решить проблему с защитой и полноценно пользоваться протоколом HTTPS. Сертификат актуален на сайтах, где присутствует регистрация, предлагается покупка товаров или онлайн-оплата различных сервисов.
При появлении любых сомнений в исправности защиты регистрироваться на сайте или вводить ранее выданные логин и пароль не рекомендуется. Тем более не стоит осуществлять онлайн-оплату с банковских карт или электронных кошельков, ведь не исключено, что проблема возникла из-за взлома ресурса злоумышленниками.
Причины появления ошибок SSL
Существует всего две причины, почему браузер отображает ошибку сертификата SSL со стороны сервера. Первая заключается в окончании срока активации, вторая – это покупка сертификата у поставщика без достаточных полномочий для выдачи «полноценной защиты». Например, виной может быть выбор самоподписанного сертификата, лишь эмулирующего работу реального протокола.
Остальные проблемы обычно скрываются на локальном компьютере:
- Произошел сброс системного времени.
- Неправильно настроена антивирусная программа.
- Сбоит браузер или установленное расширение.
- Срабатывает вредоносный скрипт.
Чтобы выяснить настоящую причину, пользователю браузера рекомендуется проверить все перечисленные факторы. При том же заражении компьютерными вирусами возможно проявление сразу нескольких симптомов – от изменения текущего времени и блокировки антивирусом до подключения перенаправления страниц в браузере и других неприятностей.
Изредка встречаются ситуации, когда проблема возникла со стороны администратора, если он ошибся при подключении нового сертификата или забыл продлить его действие. Обычно такие неполадки устраняются быстро, потому что после активации сайт проверяется и, в случае неработоспособности сертификата, проводится повторное подключение вплоть до получения положительного результата.
Время и дата
Сертификат SSL имеет четко обозначенный срок действия с датой активации и деактивации. Такой подход отчасти дает дополнительную защиту, потому что в случае технического сбоя в системных часах компьютера сайты перестают открываться. Сброс времени обычно происходит «назад», на дату изготовления материнской платы, на что и реагирует система.
Варианты исправления ситуации:
- Вручную внести корректную дату и время, после чего обновить страницу в браузере.
- Воспользоваться функцией синхронизации через интернет, встроенной в Windows.
- Заменить батарейку на памяти BIOS. При первом запуске ПК нужно внести корректные данные.
Каждый раз после изменения времени рекомендуется ручное обновление страницы или перезапуск браузера. Такой шаг активирует повторное соединение с сервером и позволяет зайти на сайт «с нуля», но уже с правильным временем, соответствующим сроку действия сертификата SSL (после активации и до ее завершения).
Настройки антивируса и брандмауэра
Программы для защиты компьютера от вирусов и хакерских атак иногда блокируют и «полезные» соединения, например, определенные домены или сразу весь протокол HTTPS, используемый при подключении сертификата SSL. Большинство антивирусов и брандмауэров проверяют его работу, и это становится причиной блокировки сайта как «злоумышленника, пытающего украсть данные».
Варианты исправления ситуации:
- Отключить режим «проверка протокола HTTPS». После этого зайти на сайт заново.
- Полностью выключить антивирусную программу. Перезагрузить ПК, открыть страницу.
- Сбросить настройки брандмауэра. Опять проводится перезапуск компьютера и веб-ресурса.
Функция временного отключения имеется в любой защитной программе, даже интегрированной в операционную систему Windows. Но это не гарантирует полную деактивацию приложения. В этом случае разобраться в ситуации поможет открытие сайта на другом компьютере или запуск безопасного режима (актуально для проводного подключения к интернету).
Браузер и операционная система
Наличие проблемы с браузером проще всего определить открытием сайта на другом устройстве или в другой программе. Иногда решение заключается в банальном обновлении версии приложения до актуальной. То же относится к операционной системе, если используется интегрированный браузер вроде Edge. Пакеты обновлений для того и выпускаются, чтобы устранять неполадки в ПО.
Варианты исправления ситуации:
- Полностью очистить историю браузера вместе с кэшем и другими данными.
- Временно отключить все ранее установленные и активные расширения.
- Переустановить программу после ее полной деинсталляции.
Остается еще один вариант – сбросить настройки браузера до состояния «по умолчанию». Способ аналогичен переустановке, но экономит время. Правда, он неэффективен, если проблема возникла из-за сбоя в одном из служебных файлов программы. Отдельное внимание стоит уделить расширению, выполняющему функции антивирусной защиты, ведь оно часто блокирует даже безопасное соединение.
Заражение компьютерными вирусами
Выдачей ошибки SSL браузер, вероятно, предупреждает о попытке его подмены, переадресации на сайт-клон или иной угрозе. В это случае рекомендуется провести полную проверку компьютера на наличие вирусов. Если присутствуют другие признаки заражения, стоит скачать парочку программ со свежими антивирусными базами (например, CureIt).
Варианты исправления ситуации:
- Временно отключить все программы из автозагрузки.
- Провести очистку диска от временных файлов.
- Перезагрузить компьютер после предыдущих шагов.
Выполняются перечисленные действия программами типа CCleaner. Они дают прямой доступ как к автозагрузке операционной системе, так и к списку расширений установленных браузеров. Также в таких программах обычно есть функция удаления ненужных системных файлов, в которых запросто может быть тело компьютерного вируса.
Если предложенные способы устранения ошибки SSL не помогли, остается ждать, пока проблему устранит администратор, или воспользоваться любым другим тематическим сайтом с аналогичным контентом.
Источник
Почему возникают ошибки SSL-соединения и как их исправить?
Зачастую после установки SSL-сертификатов многие пользователи сталкиваются с ошибками, которые препятствуют корректной работе защищенного протокола HTTPS.
Предлагаем разобраться со способами устранения подобных ошибок.
Что такое SSL?
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) — это интернет-протокол для создания зашифрованного соединения между пользователем и сервером, который гарантирует безопасную передачу данных.
Когда пользователь заходит на сайт, браузер запрашивает у сервера информацию о наличии сертификата. Если сертификат установлен, сервер отвечает положительно и отправляет копию SSL-сертификата браузеру. Затем браузер проверяет сертификат, название которого должно совпадать с именем сайта, срок действия сертификата и наличие корневого сертификата, выданного центром сертификации.
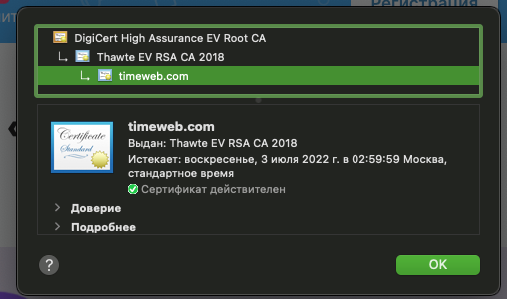
Причины возникновения ошибок SSL-соединения
Когда сертификат работает корректно, адресная строка браузера выглядит примерно так:
Но при наличии ошибок она выглядит несколько иначе:
Существует множество причин возникновения таких ошибок. К числу основных можно отнести:
- Некорректную дату и время на устройстве (компьютер, смартфон, планшет и т.д.);
- Ненадежный SSL-сертификат;
- Брандмауэр или антивирус, блокирующие сайт;
- Включенный экспериментальный интернет-протокол QUIC;
- Отсутствие обновлений операционной системы;
- Использование SSL-сертификата устаревшей версии 3.0;
- Появление ошибки «Invalid CSR» при генерации сертификата из панели управления облачного провайдера.
Давайте рассмотрим каждую из них подробнее.
Проблемы с датой и временем
Если на устройстве установлены некорректные дата и время, ошибка SSL-соединения неизбежна, ведь при проверке сертификата происходит проверка срока его действия. Современные браузеры умеют определять такую ошибку самостоятельно и выводят сообщение о неправильно установленной дате или времени.
Для исправления этой ошибки достаточно установить на устройстве актуальное время. После этого необходимо перезагрузить страницу или браузер.
Ненадежный SSL-сертификат
Иногда при переходе на сайт, защищенный протоколом HTTPS, появляется ошибка «SSL-сертификат сайта не заслуживает доверия».
Одной из причин появления такой ошибки, как и в предыдущем случае, может стать неправильное время. Однако есть и вторая причина — браузеру не удается проверить цепочку доверия сертификата, потому что не хватает корневого сертификата. Для избавления от такой ошибки необходимо скачать специальный пакет GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority, содержащий корневые сертификаты. После скачивания переходим к установке. Для этого:
- Нажимаем сочетание клавиш Win+R и вводим команду certmgr.msc, жмем «Ок». В Windows откроется центр сертификатов.
- Раскрываем список «Доверенные корневые центры сертификации» слева, выбираем папку «Сертификаты», кликаем по ней правой кнопкой мышки и выбираем «Все задачи — импорт».
- Запустится мастер импорта сертификатов. Жмем «Далее».
- Нажимаем кнопку «Обзор» и указываем загруженный ранее сертификат. Нажимаем «Далее»:
- В следующем диалоговом окне указываем, что сертификаты необходимо поместить в доверенные корневые центры сертификации, и нажимаем «Далее». Импорт должен успешно завершиться.
После вышеперечисленных действий можно перезагрузить устройство и проверить отображение сайта в браузере.
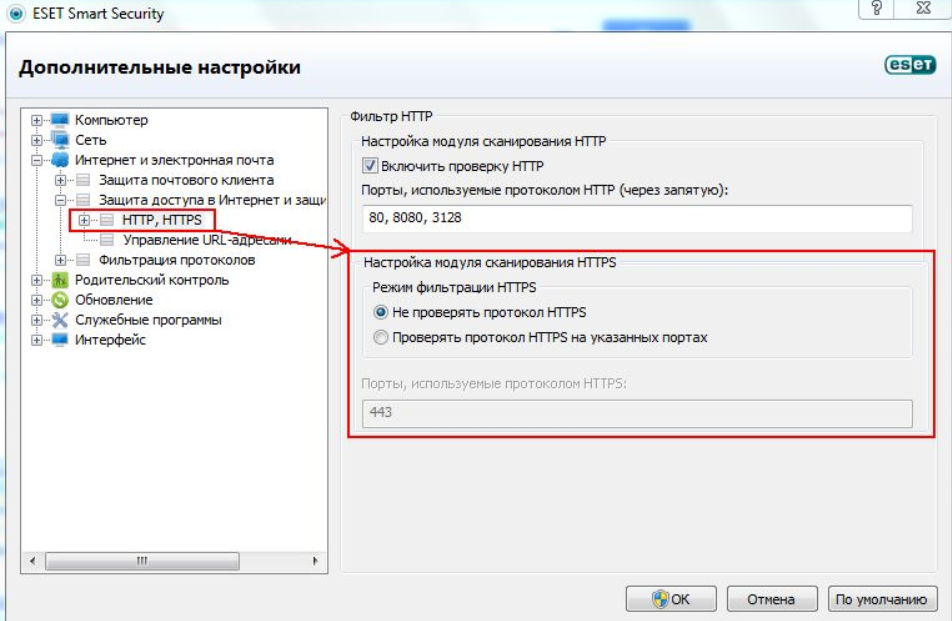
Брандмауэр или антивирус, блокирующие сайт
Некоторые сайты блокируются брандмауэром Windows. Для проверки можно отключить брандмауэр и попробовать зайти на нужный сайт. Если SSL-сертификат начал работать корректно, значит дело в брандмауэре. В браузере Internet Explorer вы можете внести некорректно работающий сайт в список надежных и проблема исчезнет. Однако таким образом вы снизите безопасность своего устройства, так как содержимое сайта может быть небезопасным, а контроль сайта теперь отключен.
Также SSL может блокировать антивирусная программа. Попробуйте отключить в антивирусе проверку протоколов SSL и HTTPS и зайти на сайт. При необходимости добавьте сайт в список исключений антивируса.
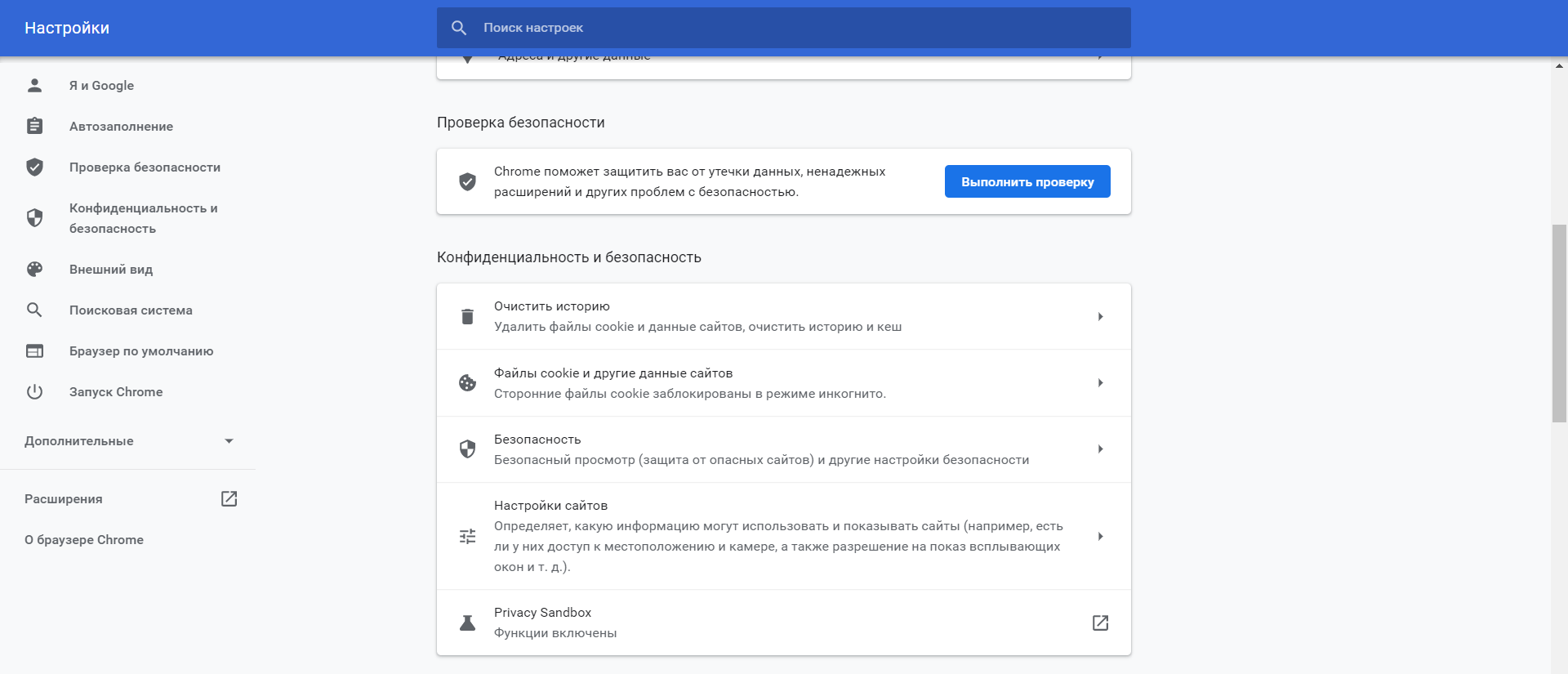
Включенный экспериментальный протокол QUIC
QUIC — это новый экспериментальный протокол, который нужен для быстрого подключения к интернету. Основная задача протокола QUIC состоит в поддержке нескольких соединений. Вы можете отключить этот протокол в конфигурации вашего браузера.
Показываем как отключить QUIC на примере браузера Google Chrome:
- Откройте браузер и введите команду chrome://flags/#enable-quic;
- В появившемся окне будет выделен параметр: Experimental QUIC protocol (Экспериментальный протокол QUIC). Под названием этого параметра вы увидите выпадающее меню, в котором нужно выбрать опцию: Disable.
- После этого просто перезапустите браузер.
Этот способ работает и в Windows и в Mac OS.
Отсутствие обновлений операционной системы
Проблемы с SSL-сертификатами могут возникать и из-за того, что на вашей операционной системе давно не устанавливались обновлений. Особенно это касается устаревших версий Windows (7, Vista, XP и более ранние). Установите последние обновления и проверьте работу SSL.
Использование SSL-сертификата версии 3.0
Некоторые сайты используют устаревший SSL-протокол версии 3.0, который не поддерживают браузеры. По крайней мере, по умолчанию. Чтобы браузер поддерживал устаревший SSL необходимо сделать следующее (на примере браузера Google Chrome):
- Откройте браузер и перейдите в раздел «Настройки».
- Прокрутите страницу настроек вниз и нажмите «Дополнительные».
- В разделе «Система» найдите параметр «Настройки прокси-сервера» и кликните на него.
- Откроется окно. Перейдите на вкладку «Дополнительно».
- В этой вкладке вы увидите чекбокс «SSL 3.0».
- Поставьте галочку в чекбоксе, нажмите кнопку «Ок» и перезагрузите браузер.
Ошибки «Invalid CSR» при генерации сертификата из панели управления облачного провайдера
В процессе активации сертификата можно столкнуться с ошибкой «Invalid CSR». Такая ошибка возникает по следующим причинам:
Источник
After upgrading my home lab to VMware Cloud Director 10.3, I started having Remote Console issues. While searching online, it sounds to affect many others and though I will share the two issues I have and how to resolve them.
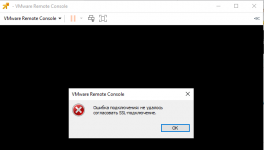
The first one, I kept getting the following error when trying to access VMware Remote Console “Connection error: could not negotiate SSL.”, as shown below:
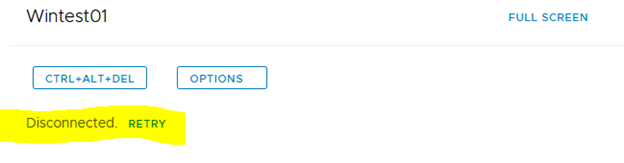
For those who are more of a Web Console users, I just kept getting a disconnected error every time I try to connect using it as shown below.
Alright, so now you have the same problem. How to resolve it? It sounds like in the later versions of VMware Cloud Director, it is becoming more restrictive on SSL Certificates and without a signed certificates the Remote Console does not seem to work properly. This was done to enhance security.
As I have found a very well written and detailed a blog post on how to replace your certs with Lets Encrypt Wildcard SSL certificates by Marc Roeleveld, I have decided against writing my own on the subject and point you to his excellent post that can be found at the link below. By the way, it’s worth mentioning that Lets Encrypt certificates are free of charge, and quite easy to get, so no excuse not to install a signed certificate even for your home lab.
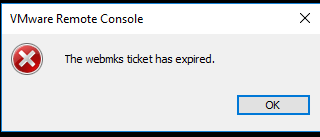
After installing the certs on my VMware Cloud Director, I kept getting the same disconnected error on the Web Console, but I had a new error on the VMware Remote Console. The message of the new error was: “The webmks ticket has expired.”. Here is a screenshot of the actual error as well:
The resolution for this issue was to easily change the port number on the Console Proxy Public URL to 8443 instead of 443. That seems to resolve the issue. You can do this by going to: Administration ==> Public Addresses ==> Console Proxy. Below is a screenshot of how mine looks like after the change.
Hope this resolve your VMware Remote Console issue. Please share in the comments if this has fixed your issue or what else did you have to do to fix it.
Vmware remote console ошибка подключения не удалось согласовать ssl подключение
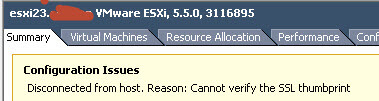
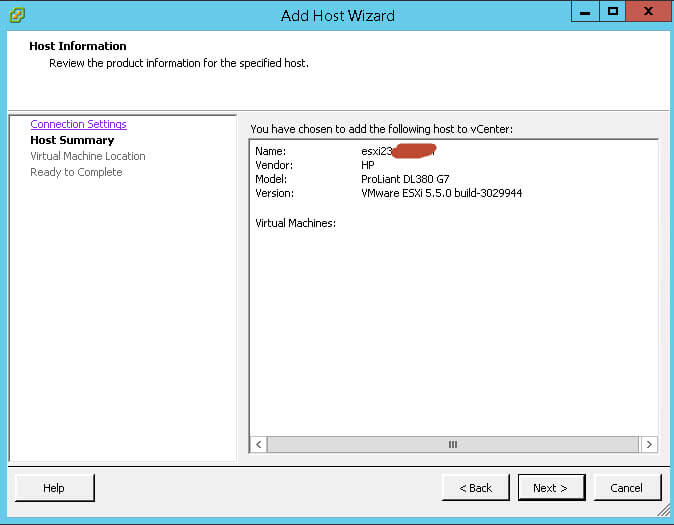
Всем привет сегодня хочу рассказать, как решается ошибка cannot verify the ssl thumbprint в VMware ESXI 5.5. Данная неприятность у меня выскочила после того, как я в тестовой среде переустанавливал VMware ESXI хост. Можете заметить, что ваш сервер, не может проверить SSL сертификат, при подключении. Смотрим как это решить и понять первоисточник проблемы. На все работы у вас уйдет не более 10 минут вашего рабочего времени.
Вот как более подробно выглядит данная ошибка cannot verify the ssl thumbprint. Данная ошибка возникает, когда у вас устарел или поменялся SSL сертификат, в моем случае была переустановка системы с последующим, тем же именем.
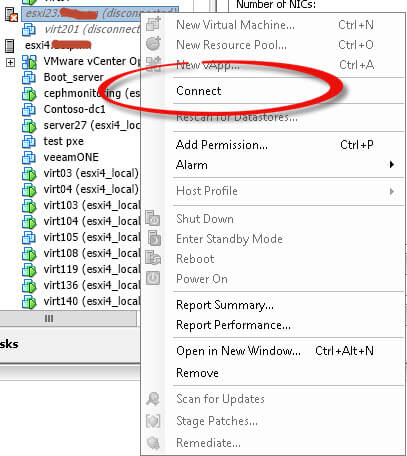
Щелкаем правым кликом по нужному хосту ESXi и выбираем Connect
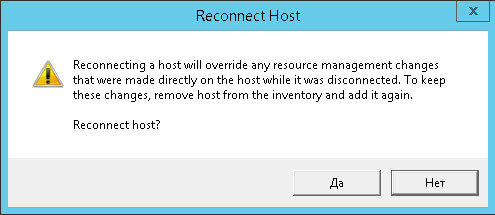
Вас спросят хотите ли вы произвести reconnect, жмем Да.
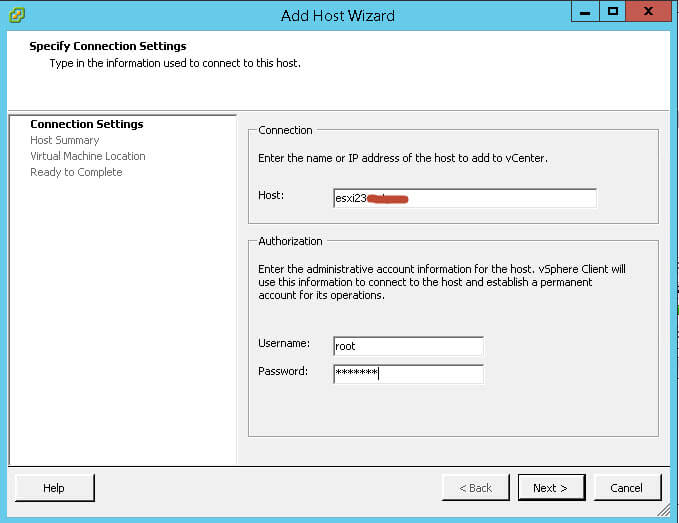
Задаем логин и пароль для доступа и жмем next.
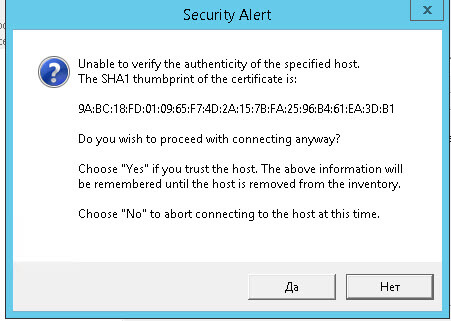
Вас предупредят, что будет заменен SSl сертификат
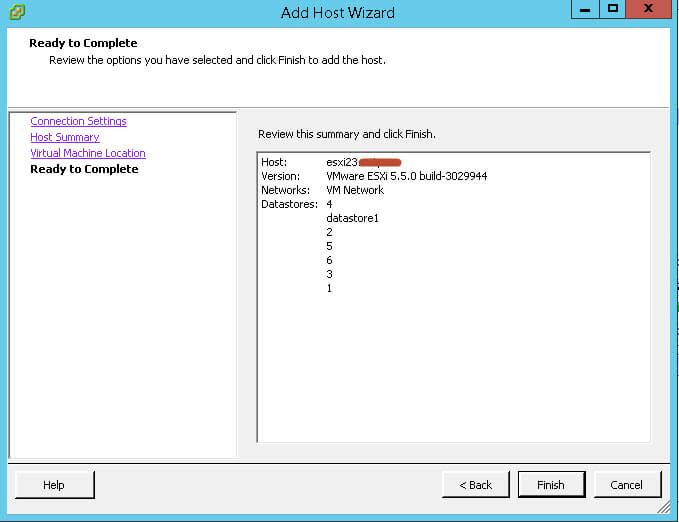
Далее жмем next.
Finish, на этом все
Ваш хост успешно добавится и вы сможете продолжить работу с ним.
Источник
vmware remote console and SSL session to remote host
I installed vcenter ver6.0 today and got surprise when i launched the remote console.
It did pop up with «failed to initialize SSL session to remote host» message.
I researched into this issue and found that we have to shut down the server to fix.
We are not allowed to shut down the server.
Is there any fixes for this without shutting it down?
Enter to win a $250 GC, 5 Solar Powered battery banks
Semi off-topic, but why are you running vCenter on a «production» server that you can’t touch?
I meant to say that I am trying to launch the remote console to a live server which is managed by this vcenter server.
Brand Representative for VMware
I don’t know any means of fixing this without a reboot of the server.
Let me know if you need anything else.
This topic has been locked by an administrator and is no longer open for commenting.
To continue this discussion, please ask a new question.
Read these next.

SpiceQuest October (2022) — On Frankenstein and Failure
Welcome to another SpiceQuest! In this series, we call out current holidays and give you the chance to earn the monthly SpiceQuest badge! (Each task can be done at any time. They don’t have to be completed on a certain holiday.) This month w.
Stupid Friday ?’s | 9/30/2022
EDIT: Apparently it is » Ask a Stupid Question Day». My time has come.Wake up any Green Day fans you know, September is just about done. I am just glad I can wear my favorite jackets and hoodies again. Here are some pre-weekend questions that are quite.
Snap! Exchange 0-Day x2, Brave browser, Hyperjacking, Ask a Stupid Question Day
Your daily dose of tech news, in brief. Not only are we on the last day of September 2022, but today is the last day for SpiceWorld 2022! It feels like it takes too long for SpiceWorld to come around each year, and it also flies by way too fast onc.
Spark! Pro Series — September 30th 2022
It is with a bit of sadness that I write this Spark today. I should have heard the news sooner, but then I have not visited my childhood friend much as the years passed. I would pass him in the grocery store but nev.
Источник
Vmware remote console ошибка подключения не удалось согласовать ssl подключение
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Email to a Friend
- Report Inappropriate Content
I have VMware ESXi open in a Safari browser on macOS Sierra and have VMRC installed.
After an update last week to Version 9.0.0 (4288332) the console does not want to open with the message»
«Failed to initialize SSL session to remote host.»
The following does not solve the problem:
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Email to a Friend
- Report Inappropriate Content
I have the same problem.
With Firefox.
I think Mac OS Sierra is the problem. VMRC asks for the certificate every time.
With another Macbook (OS EL Capitan) or Windows notebook version 9 works without problems.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Email to a Friend
- Report Inappropriate Content
Mac OS Sierra is not the problem. I had this problem before I upgraded to Sierra.
The problem started with the upgrade to V9.0.0 as indicated in my original thread.
So by the way, are the VMware developers reading these threads?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Email to a Friend
- Report Inappropriate Content
I’m in the same boat. However, I did install macOS Sierra first and then VMRC 9.0 after that in an attempt to fix the problem. The same «Failed to initialize SSL session to remote host.» appears in VMRC 9 and VMware Fusion 8.5.0 after upgrading to Sierra. Also, I can confirm that the macOS Sierra 10.12.1 upgrade did not change this behavior.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Email to a Friend
- Report Inappropriate Content
Do you see this with the web console as well? Do the conditions in the ESXi 6.0 Update 2 Release Notes apply to you?:
Unable to open VM console connection to the powered on VMs from vSphere Web Access
When you add an ESXi host with powered on VMs to the vCenter Server or when you switch the host from one vCenter Server to another, the vSphere Web Access is unable to open console connection to the VMs. Error messages similar to the following are observed with this issue:
Web console error message:
The console has been disconnected. Close this window and re-launch the console to reconnect.
Standalone VMware Remote Console error message:
Failed to initialize SSL session to remote host.
VI client console error message:
unable to connect to the mks: internal error
Error message in the vmware.log file:
SOCKET 6 (150) Error during authd-VNC negotiation: (1) Asyncsocket error.
This issue is resolved in this release.
The notes don’t mention a workaround. Disclaimer: I’m not a vSphere expert. Power cycling the VM may help. Hopefully you don’t need to re-add the host to vCenter with the VM powered down.
Источник
Diagnosing and fixing Virtual Machine Remote Console MKS problems

Q: Does your client have Layer 2
Q: Can you ping your vCenter and all your ESXi Hosts by IP address from the client system?
Q: Can you ping your vCenter and all your ESXi Hosts by hostname from the client?
Problems connecting to the Remote Console of VMware
Problem One: Layer 3 (Firewall/Gateway) issues
The VMRC connection exists between the EXSi Host of the VM and the Client, even in environments which are managed by a vCenter Server. This means that if the client is on a different network (Layer 3) from the ESXi Hosts, the client must be able to resolve and connect to all ESXi hosts!
It is a misnomer and wives-tale that firewalls/routers which exist between vSphere client networks and vSphere Management networks need only route ports 443 & 902 between the client and the vCenter. Those sort of Layer 3 relationships need route to ports 443 & 902 between the client and all of the ESXi Hosts!
You can diagnose issues simply with a ping. If you can ping all of your ESXi Hosts and by IP, it is likely not a problem with Layer 3 connectivity. If you can not ping vSphere, it may just be ICMP that is blocked, go ahead and use telnet or a port-scanner.
A more conclusive, diagnosis would be to use telnet or a port-scanner to check for connectivity on ports 443 & 902 from your client to all of your ESXi hosts. If you were able to connect to 443 & 902 on everything, you could rule Layer 3 problems out conclusively.
This is the message you should see:
If you run: telnet ESXI IP address> 443 you should see:
Fix Layer 3 connectivity issues between the client system and all of vSphere (ESXi and vCenter)
One potential workaround to Layer 3 issues with the VMRC would to build a Windows/Linux Desktop VM inside the vSphere Management Network and simply RDP to that! Instead of potentially compromising the security of the vSphere Management Network by opening up all of those ports, just allow 3260 (RDP), connect to that and initiate your Virtual Machine Remote Console there.
Problem Two: DNS Name resolution issues
In this case, a ping by hostname to all of the ESXi hosts will determine that name resolution for one or all of these entities is not working for the client or does not exist.
This image represents a correctly configured system where the VMRC should be able to connect:
It may be a simple matter that the client PC served by a different DNS
Make sure that the vSphere Management Network DNS is resolvable from the client PC.
NOTE: on corporate AD
Create a hosts file on the client PC which contains the A-records for the vCenter and all of the ESXi Hosts. Be sure to run the editor as administrator. I highly recommend Notepad ++
Problem Three: vSphere 6 issues
I have noticed that, beginning with vSphere 6, when an ESXi Host is added to vCenter, and that host contains running Virtual Machines (like vCenter itself), the VMRC of those VMs will fail with a generic MKS error until the VMs are fully powered-off or vMotion
The diagnosis for this would be MKS issues that exist when there are no port issues and DNS resolution is working perfectly! In other words, if it’s not Problem One or Problem Two, then it’s probably problem Three!
None that I know of – please feel free to provide one!
As this symptom only occurs to running VMs that were on an ESXi Host at the time it was added to a vCenter, it is relatively uncommon and will only happen once in a given environment. Simply vMotion the VMs or power them off and back on once!
About: John Borhek
John Borhek is the CEO and Lead Solutions Architect at VMsources Group Inc. John has soup-to-nuts experience in Mission Critical Infrastructure, specializing in hyper-convergence and Cloud Computing, engaging with organizations all over the United States and throughout the Americas.
Источник
Обновлено 22.06.2017
Всем привет сегодня хочу рассказать, как решается ошибка cannot verify the ssl thumbprint в VMware ESXI 5.5. Данная неприятность у меня выскочила после того, как я в тестовой среде переустанавливал VMware ESXI хост. Можете заметить, что ваш сервер, не может проверить SSL сертификат, при подключении. Смотрим как это решить и понять первоисточник проблемы. На все работы у вас уйдет не более 10 минут вашего рабочего времени.
Вот как более подробно выглядит данная ошибка cannot verify the ssl thumbprint. Данная ошибка возникает, когда у вас устарел или поменялся SSL сертификат, в моем случае была переустановка системы с последующим, тем же именем.
Щелкаем правым кликом по нужному хосту ESXi и выбираем Connect
Вас спросят хотите ли вы произвести reconnect, жмем Да.
Задаем логин и пароль для доступа и жмем next.
Вас предупредят, что будет заменен SSl сертификат
Далее жмем next.
next
Finish, на этом все
Ваш хост успешно добавится и вы сможете продолжить работу с ним.
Материал сайта pyatilistnik.org
Июн 22, 2017 09:41
ESXi и vCenter Server поддерживают стандартные X.509 v3 сертификаты для криптования соединения через SSL (Secure Socet Layer). Проверка сертификатов включена по умолчанию и SSL сертификаты используются для шифрования сетевого трафика. Тем не менее, при использовании ESXi и vCenter Server сертификаты автоматически генерируются при установке и хранятся на серверной системе. Эти сертификаты уникальны и уже позволяют получить доступ к серверу через SSL, но они непроверяемы и не подписаны “доверенным центром сертификации”. Таким образом, сертификаты по умолчанию являются уязвимыми.
Для того, чтобы получить наибольшую безопасность при использовании SSL-соединения (особенно, если вы собираетесь использовать соединение из-вне) необходимо сгенерировать новые подписанные сертификаты. Если сертификаты не установлены, связь между сервером и vCenter vSphere клиентами зашифрована с использованием самозаверенного сертификата, которого недостаточно для безопасной аутентификации в производственной среде.
Сертификат состоит из двух файлов:
rui.crt — непосредственно сам сертификат,
rui.key — “скрытый” ключ.
Дефолтное расположение сертификатов следующее:
- Для ESXi5.0/6.0: /etc/vmware/ssl/
- Для vCenter Server в Windows 2008/2012:
C:Program DataVMwareVMware VirtualCenterSSL
Использование сертификатов в vCenter Server.
В vCenter Server проверка сертификатов включена по умолчанию. Для того, чтобы убедиться подключитесь к vCenter Server с помощью vSphere Client и выберите:
Administration > vCenter Server Settings
Затем проверьте SSL Settings на левой панели и убедитесь, что выбран пункт Check host certificates.
Создание нового сертификата для ESXi.
Если вы изменили имя хоста ESXi, удалили сертификаты, или возникли какие-то другие обстоятельства, при которых необходимо сгенировать новые выполните следующие действия:
1. Подключитесь к вашему ESXi хосту через SSH и получите root-привилегии.
2. Создайте резервную копию существующих сертификатов командами:
# cd /etc/vmware/ssl # mv rui.crt orig.rui.crt # mv rui.key orig.rui.key
3. Для генерации новых сертификатов:
# /sbin/generate-certificates
По завершению вы получите предупреждение:
WARNING: can’t open config file: /usr/ssl/openssl.cnf
или
WARNING: can’t open config file: /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf
Предупреждение можно проигнорировать — новые сертификаты созданы. Выполнив команду:
# ls -la
можно сравнить время создания файлов сертификатов.
4. Восстанавливаем атрибуты для созданных файлов сертификатов:
# chmod +t rui.crt # chmod +t rui.key
5. Перезагружаем хост ESXi.
Создание подписанных сертификатов для ESXi.
В качестве центра сертификации (CA) можно использовать OpenSSL. И хотя шаги для создания сертификатов в различных операционных системах могут несколько отличаться, общий принцип един, поскольку vSphere использует X.509 v3 SSL сертификаты.
ВНИМАНИЕ! Перед началом убедитесь, что вы используете OpenSSL версии 0.9.8, иначе работа SSL не гарантируется.
Для упрощения установки OpenSSL в ОС Windows можно воспользоваться Shining Light Installer’ом, в то время как во FreeBSD и в большинстве Linux-дистрибутивов этот пакет уже установлен по умолчанию. В Windows так же потребуется установить Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 Redistributable Package (x86).
Перед тем, как приступить к конфигурированию OpenSSL, создайте бэкап openssl.cfg:
В Windows:
> cd C:OpenSSL-Win32bin > copy openssl.cfg.txt openssl.cfg.bak
Во FreeBSD и Debian:
# cd /etc/ssl/ # cp openssl.cnf openssl.cnf.backup
В CentOS:
# cd /etc/pki/tls/ # cp openssl.cnf openssl.cnf.backup
В других Linux-дистрибутивах расположение файла может отличаться.
Теперь непосредственно сам конфиг, который нужно привести к следующему виду:
[ req ] default_bits = 2048 default_keyfile = rui.key distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name encrypt_key = no prompt = no string_mask = nombstr req_extensions = v3_req
[ v3_req ] basicConstraints = CA:FALSE keyUsage = digitalSignature, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth, clientAuth subjectAltName = DNS:esxi5, IP:172.1.0.10, DNS:esxi5.domain.com
[ req_distinguished_name ] countryName = RU stateOrProvinceName = SPB localityName = Saint-Petersburg 0.organizationName = VMWare organizationalUnitName = vCenterInventoryService commonName = esxi5.domain.com
Жирным выделенные поля для заполнения. Если вы не укажете эти параметры можете ввести их при создании сертификата. Следующая команда создаст rui.csr:
openssl req -new -nodes -out rui.csr -keyout rui-orig.key -config openssl.cfg
или для Windows:
openssl req -new -nodes -out rui.csr -keyout rui-orig.key -config openssl.cfg.txt
Теперь конвертируем ключ в RSA-формат следующей командой:
openssl rsa -in rui-orig.key -out rui.key
После того, как создан “запрос” должен быть сгенерирован непосредственно сам “ответ”, то есть ответная составляющая сертификата.
Для коммерческих центров сертифицирования:
Созданный запрос необходимо направить в центр сертифицирования (CA) и полученный ответный ключ установить на сервер vCenter Server.
Для центра сертифицирования Microsoft:
Обратите внимание, что для Windows Server 2003 CA требуется версия Enterprise, так как другие редакции не имеют шаблонов для экспорта SSL-сертификатов.
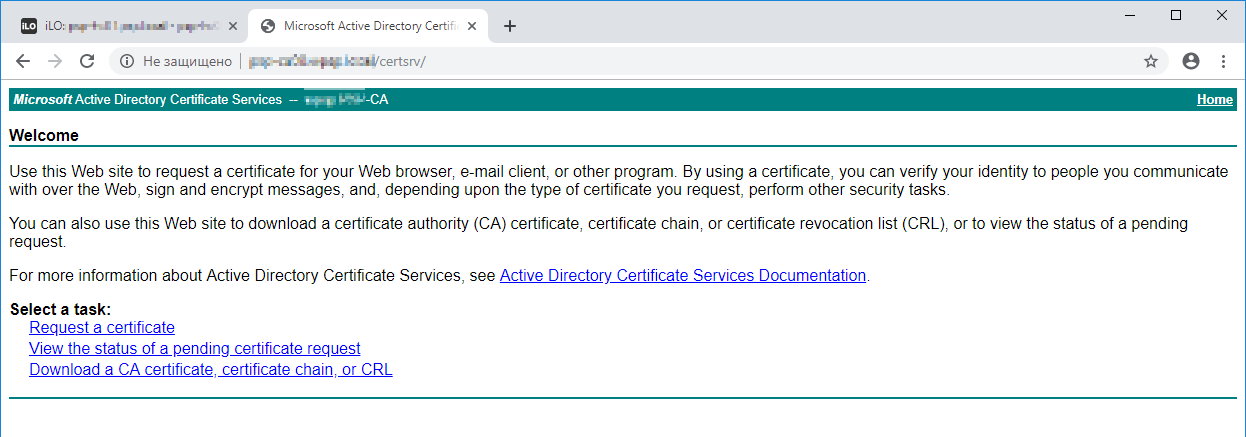
1. Откройте в веб-интерфейс центра сертифицирования Microsoft ( Microsoft CA certificate authority web interface). По умолчанию: http://servername/CertSrv/
2. Перейдите: Request a certificate > advanced certificate request.
3. Нажмите Submit a certificate request by using a base-64-encoded CMC or PKCS #10 file, или submit a renewal request by using a base-64-encoded PKCS #7 file.
4. Используя текстовый редактор скопируйте контент:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE REQUEST-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE REQUEST-----
5. Далее следуйте:
Web Server > Submit > Base 64 encoded > Download Certificate
Сохраните созданный сертификат rui.crt и перейдите к этапу его установки.
Для самоподписанных (self-signed) сертификатов:
Следующая команда создаст сертификат с помощью OpenSSL:
openssl req -x509 -sha256 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout rui.key -config openssl.cfg -out rui.crt -days 3650
Установка подписанных сертификатов для хоста ESXi.
- Подключитесь к хосту ESXi используя vSphere Client и переведите хост в Maintance Mode (не обязательно).
- Включите доступ по SSH к вашему хосту используя vSphere, или по нажатию F2 в Direct Console User Interface (DCUI): Troubleshooting options > Enable SSH.
- Подключитесь к хосту по SSH, перейдите в папку /etc/vmware/ssl и создайте бэкап сертификатов, как было описано выше.
- Скопируйте в эту директорию созданные rui.crt и rui.key в ASCII-формате. Откройте в текстовом редакторе vi и убедитесь, что нет посторонних символов (никаких ошибочных символов ^M в конце строк быть не должно). Для загрузки сертификатов в Windows можно использовать WinSCP.
- В DCUI выберите: Troubleshooting Options > Restart Management Agents. Нажмите F11 и по необходимости выведите хост из Maintenance Mode.
По завершению хост будет готов для присоединения к кластеру, однако потребуется выполнить следующие шаги для каждого из хостов, где требовалось сменить сертификат:
- Войдите в vCenter Server, переведите хост в Maintance Mode и правым кликом на хосте выберите Disconnect.
- Удалите отсоединенный хост из кластера, по правому клику выберите Connect и добавьте заново хост в кластер.

Q: Does your client have Layer 2 connectivity to your ESXi Hosts? Another way of saying this is: If your ESXi Hosts and vCenter are on 172.20.0.0/16, is the system where the client app is installed also on 172.20.0.0/16?
Q: Can you ping your vCenter and all your ESXi Hosts by IP address from the client system?
Q: Can you ping your vCenter and all your ESXi Hosts by hostname from the client?
Problems connecting to the Remote Console of VMware vSphere Virtual Machines can usually be divided into one of three problem areas:
Problem One: Layer 3 (Firewall/Gateway) issues
The VMRC connection exists between the EXSi Host of the VM and the Client, even in environments which are managed by a vCenter Server. This means that if the client is on a different network (Layer 3) from the ESXi Hosts, the client must be able to resolve and connect to all ESXi hosts!
It is a misnomer and wives-tale that firewalls/routers which exist between vSphere client networks and vSphere Management networks need only route ports 443 & 902 between the client and the vCenter. Those sort of Layer 3 relationships need route to ports 443 & 902 between the client and all of the ESXi Hosts!
You can diagnose issues simply with a ping. If you can ping all of your ESXi Hosts and by IP, it is likely not a problem with Layer 3 connectivity. If you can not ping vSphere, it may just be ICMP that is blocked, go ahead and use telnet or a port-scanner.
A more conclusive, diagnosis would be to use telnet or a port-scanner to check for connectivity on ports 443 & 902 from your client to all of your ESXi hosts. If you were able to connect to 443 & 902 on everything, you could rule Layer 3 problems out conclusively.
Run: telnet <ESXi IP address> 902
This is the message you should see:
If you run: telnet <ESXI IP address> 443 you should see:
Resolution:
Fix Layer 3 connectivity issues between the client system and all of vSphere (ESXi and vCenter)
Workaround:
One potential workaround to Layer 3 issues with the VMRC would to build a Windows/Linux Desktop VM inside the vSphere Management Network and simply RDP to that! Instead of potentially compromising the security of the vSphere Management Network by opening up all of those ports, just allow 3260 (RDP), connect to that and initiate your Virtual Machine Remote Console there.
Problem Two: DNS Name resolution issues
If the PC running the vSphere Client (or Web Client) is not able to resolve the hostname of the ESXi Host of the VM, then the VMRC can not connect.
In this case, a ping by hostname to all of the ESXi hosts will determine that name resolution for one or all of these entities is not working for the client or does not exist.
This image represents a correctly configured system where the VMRC should be able to connect:
It may be a simple matter that the client PC served by a different DNS server than the vSphere Management Network, or the client PC may have no DNS resolution at all
Fix:
Make sure that the vSphere Management Network DNS is resolvable from the client PC.
NOTE: on corporate AD domains, using the workaround of creating a hosts file may be more desirable than changing the DNS of the client PC as the hosts file has no impact on authentication issues!
Workaround:
Create a hosts file on the client PC which contains the A-records for the vCenter and all of the ESXi Hosts. Be sure to run the editor as administrator. I highly recommend Notepad ++
Problem Three: vSphere 6 issues
I have noticed that, beginning with vSphere 6, when an ESXi Host is added to vCenter, and that host contains running Virtual Machines (like vCenter itself), the VMRC of those VMs will fail with a generic MKS error until the VMs are fully powered-off or vMotion-ed to another ESXi Host.
The diagnosis for this would be MKS issues that exist when there are no port issues and DNS resolution is working perfectly! In other words, if it’s not Problem One or Problem Two, then it’s probably problem Three!
Resolution:
None that I know of – please feel free to provide one!
Workaround:
As this symptom only occurs to running VMs that were on an ESXi Host at the time it was added to a vCenter, it is relatively uncommon and will only happen once in a given environment. Simply vMotion the VMs or power them off and back on once!
Привет, сегодня решим проблему с установкой корпоративного SSL сертификата на ESXi host. Проблема в том, что хост управляется через vCenter.
Нашёл интересную статью:
https://kb.vmware.com/s/article/2113926
Мне показалось, что инструкция в данной статье чересчур сложная. Сделаем всё сами, быстрее, проще и без простоя виртуальных машин.
Заходим в UI ESXi хоста:
Видим, что на хосте установлен самоподписанный сертификат. Логинимся под root.
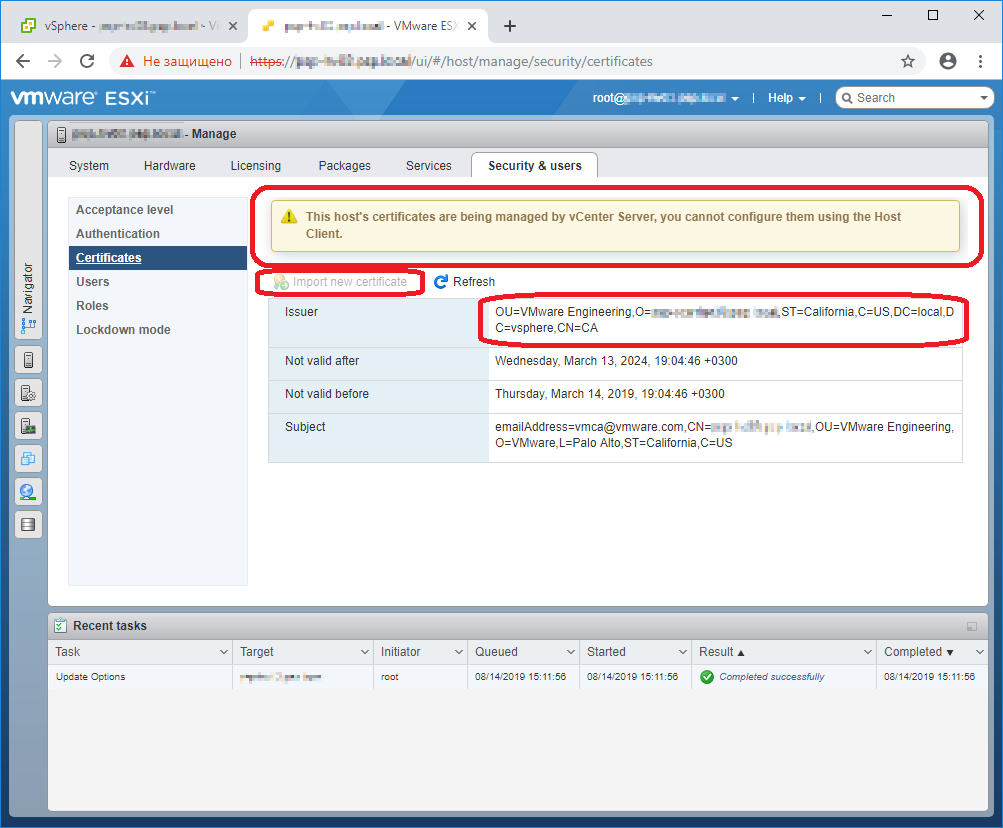
Переходим в раздел Manage > Security $ users > Certificates.
Видим ошибку:
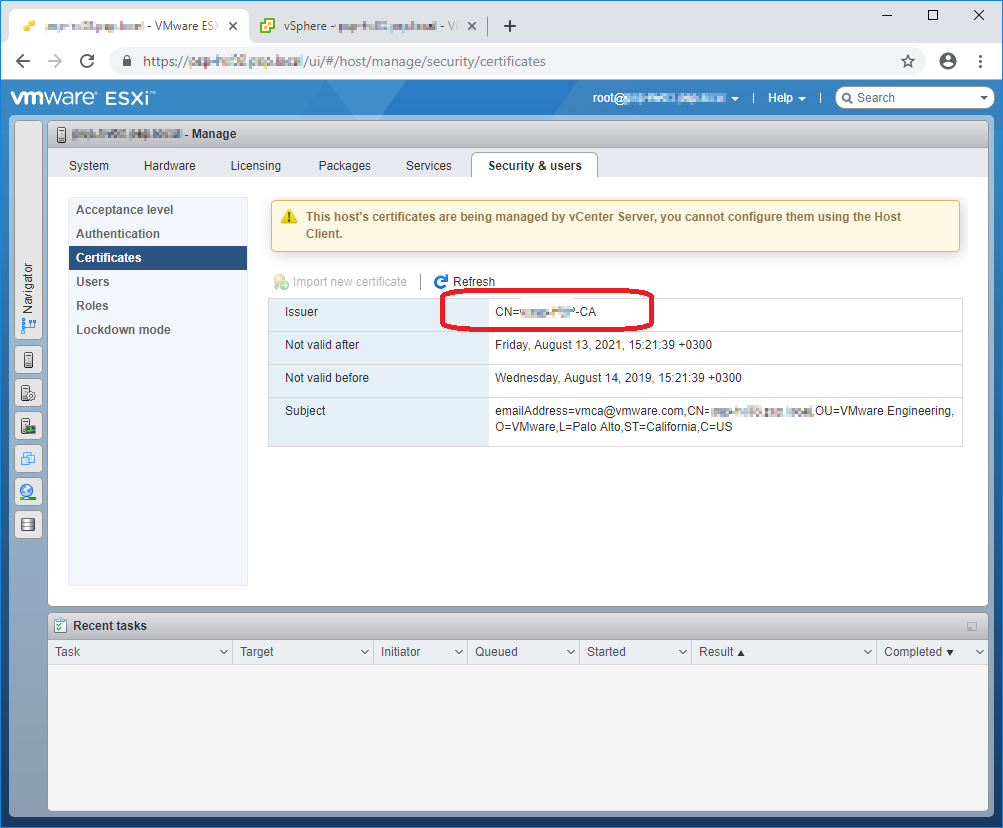
This host’s certificates are being managed by vCenter Server, you cannot configure them using the Host Client.
Из-за того, что хост прикреплён к vCenter, нельзя с него управлять сертификатами. Кнопка Import new certificate не активна. Сертификат самоподписанный.
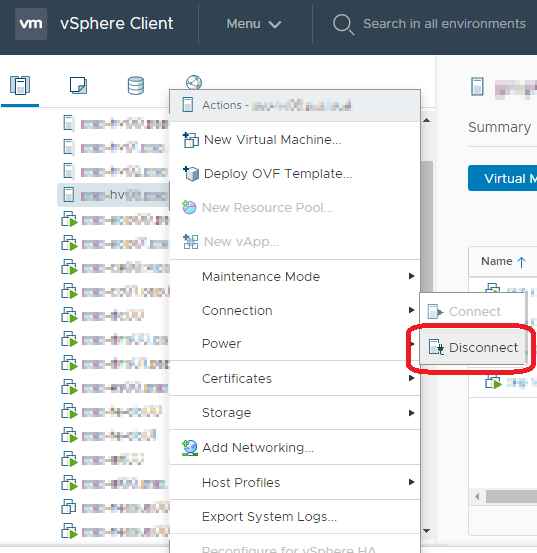
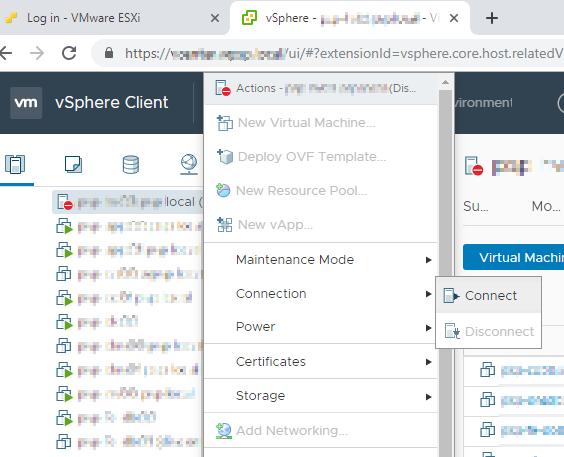
Заходим в vCenter, выбираем хост, на который будем устанавливать сертификат и делаем ему Disconnect. Виртуальные машины продолжают работать.
Обновляем другую вкладку с UI хоста.
Ошибка пропала, кнопка Import new certificate активна, нажимаем на неё.
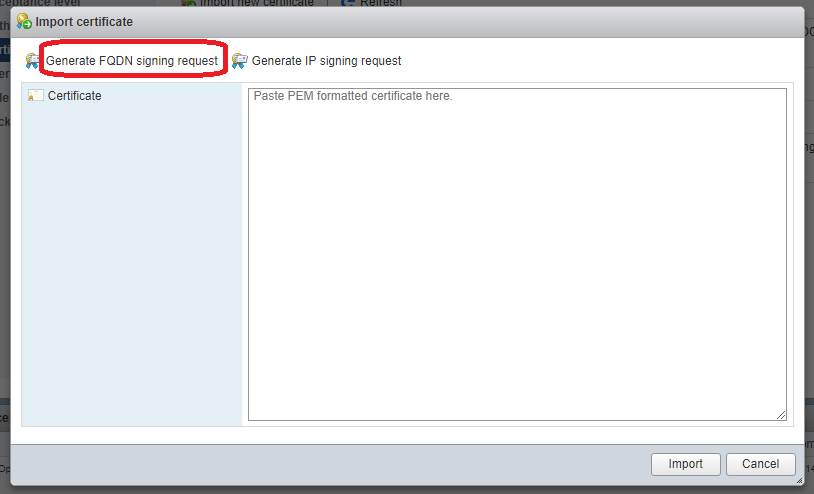
Открывается окно импорта сертификата. Генерируем CSR, нажимаем Generate FQDN signing request.
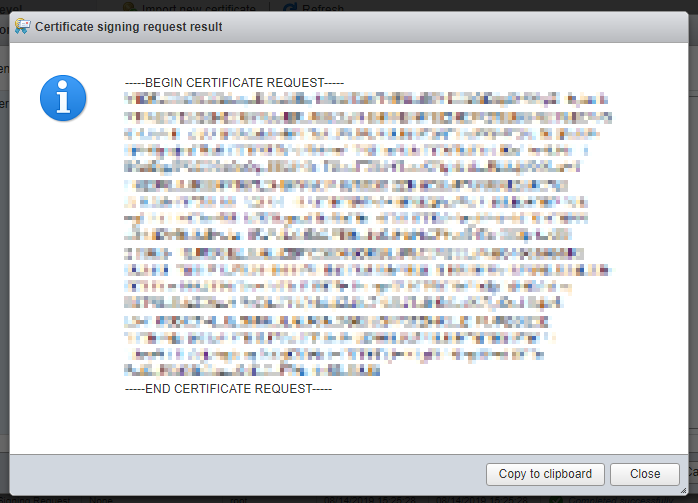
Копируем в буфер сгенерированный код CSR. Close.
Открываем центр сертификации.
Request a certificate.
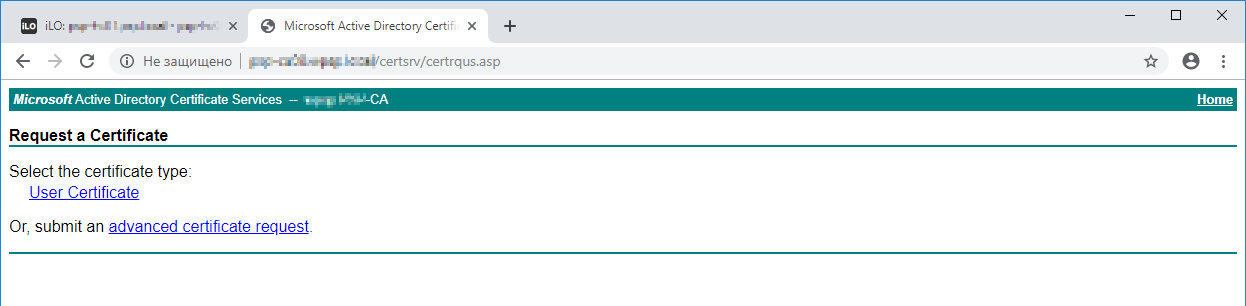
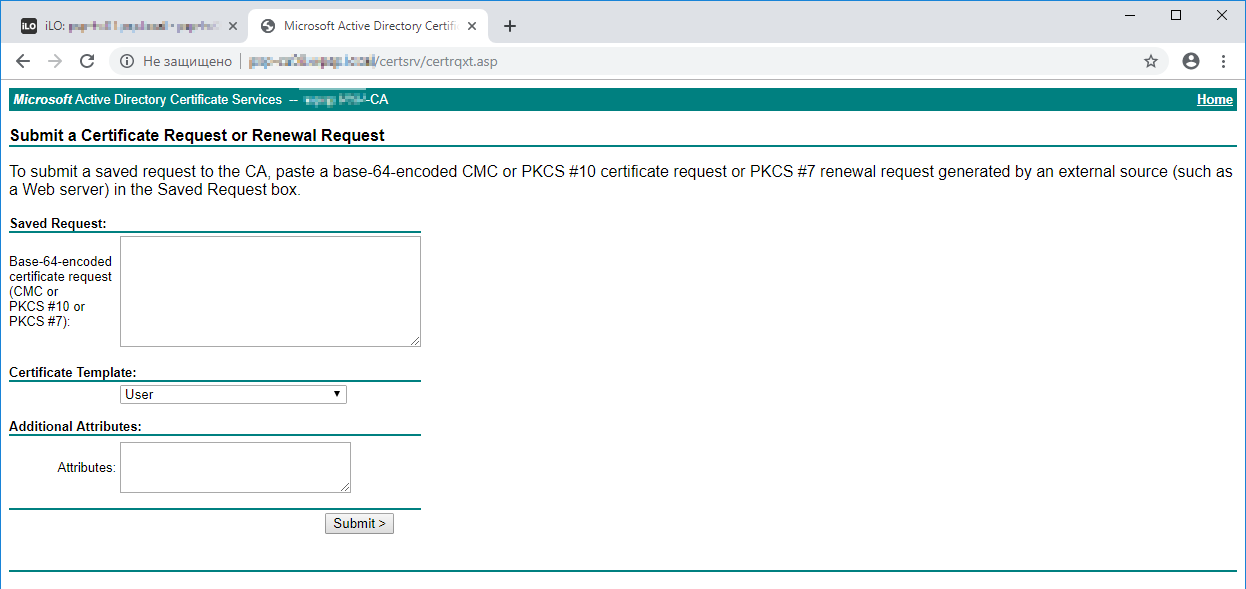
Advanced certificate request.
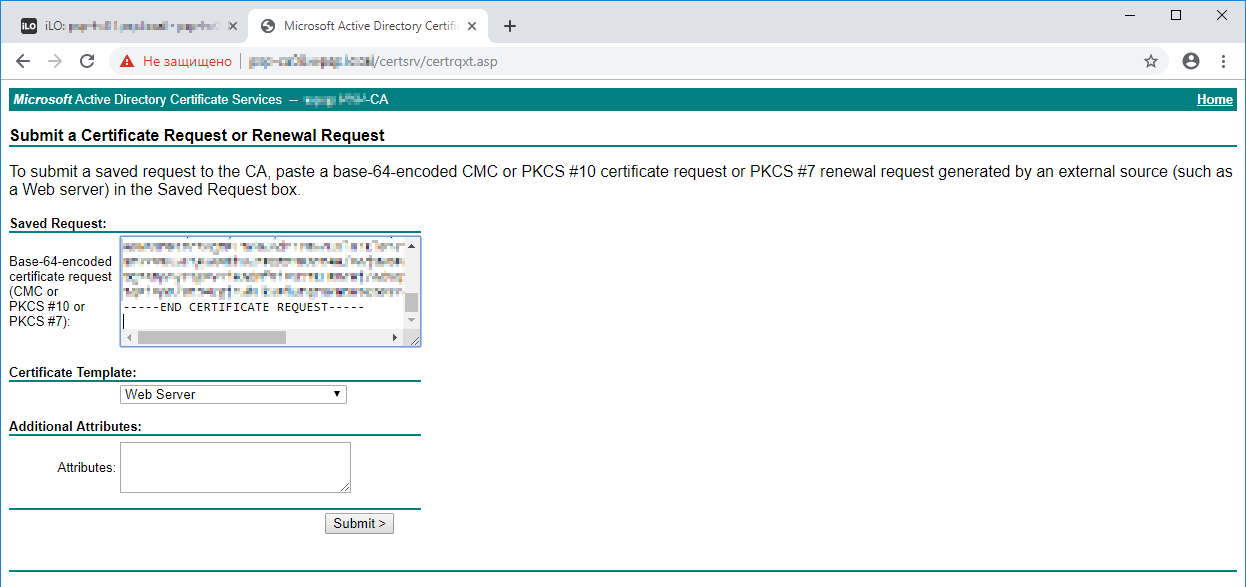
В Saved Request вставляем скопированный base64 код. Certificate Template меняем на Web Server.
Submit.
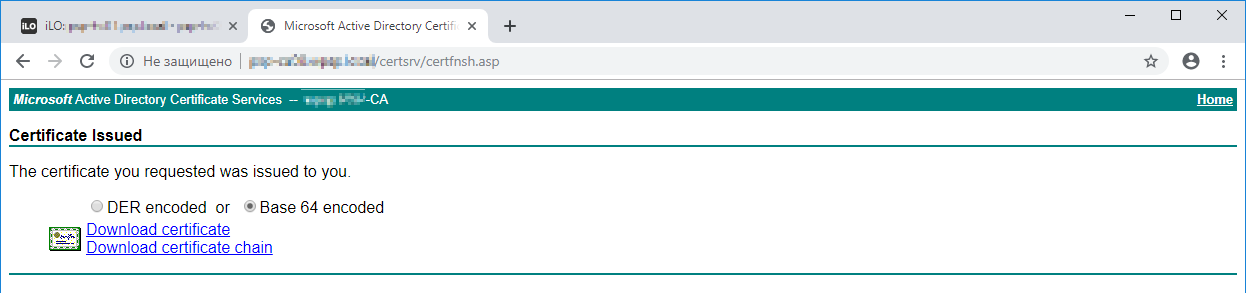
Устанавливаем галку Base 64 encoded и скачиваем сертификат Download certificate.
Открываем сертификат блокнотом, копируем содержимое.
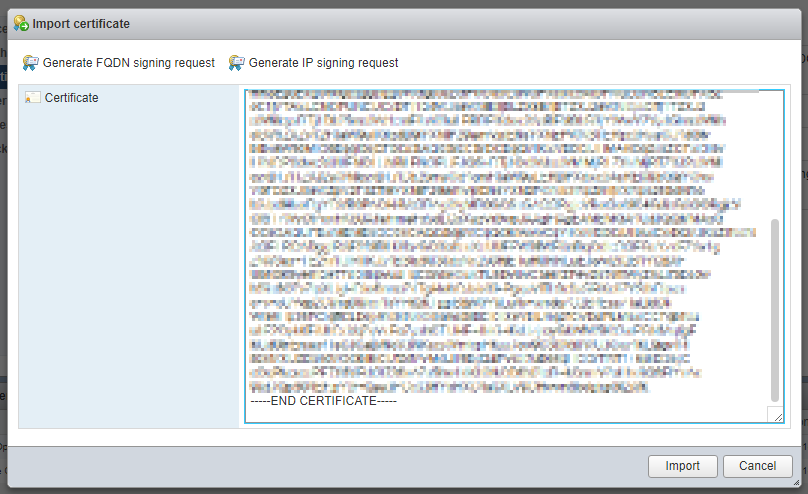
Возвращаемся в UI ESXi хоста.
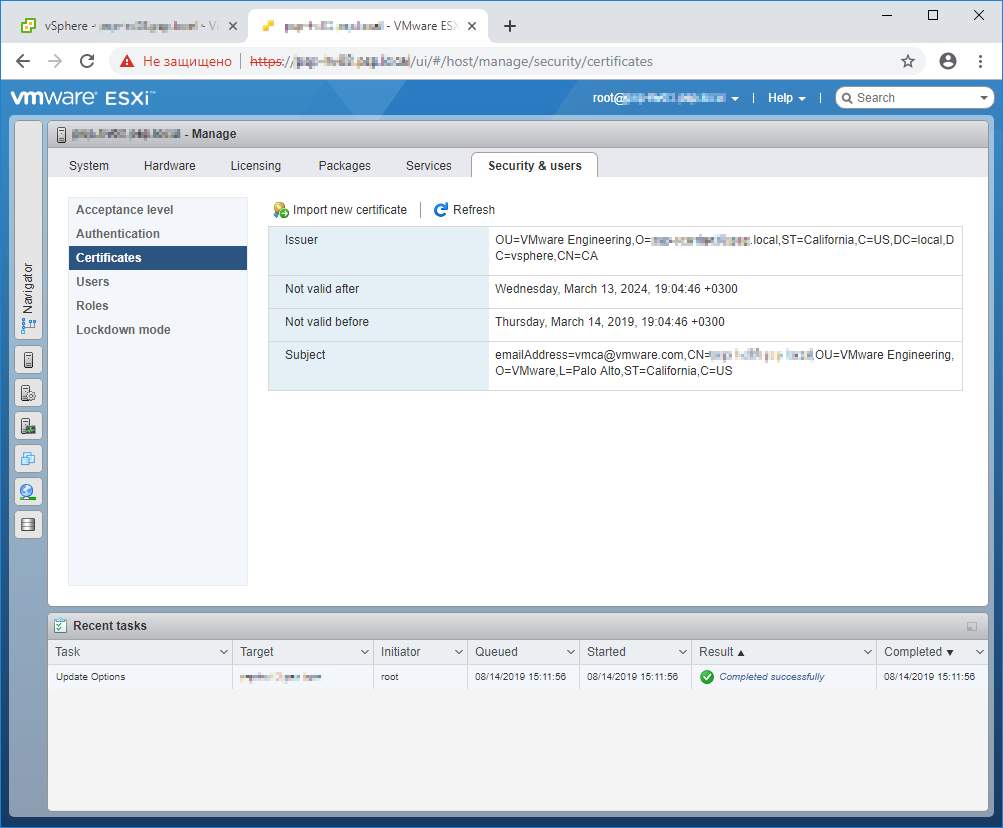
Вставляем код сертификата, нажимаем Import.
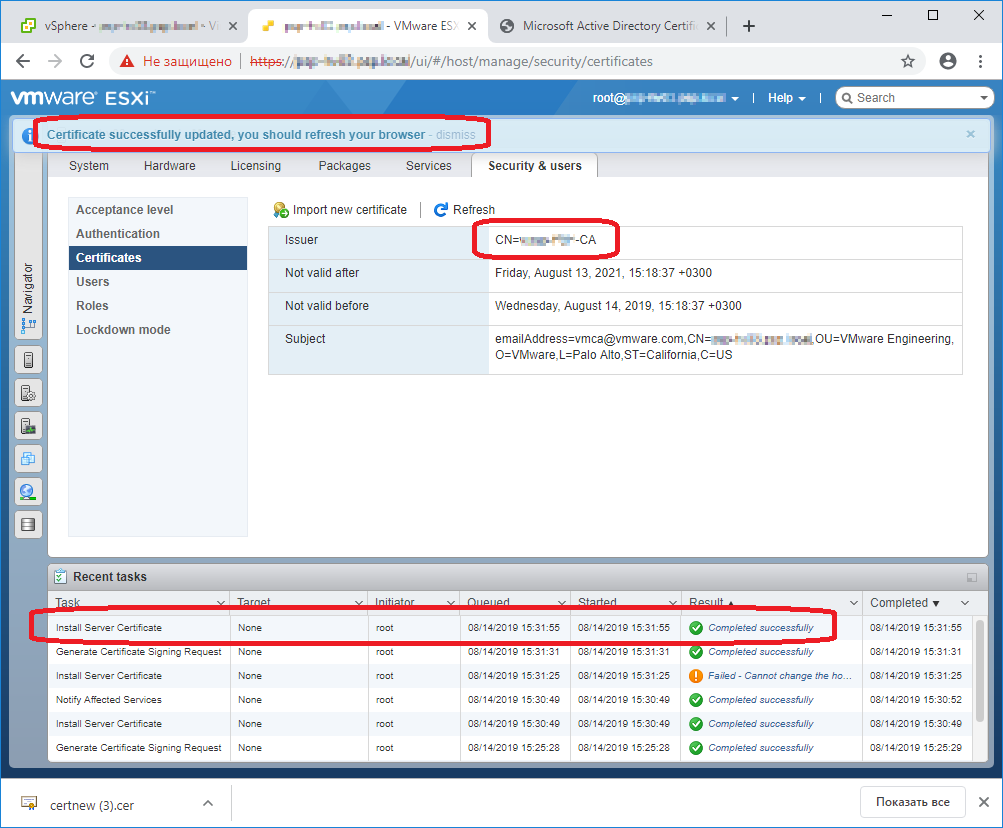
Certificate successfully updated, you should refresh your browser
Сертификат установлен. Нам предлагают перезапустить браузер. Перезапускаем браузер и открываем окно UI ESXi хоста.
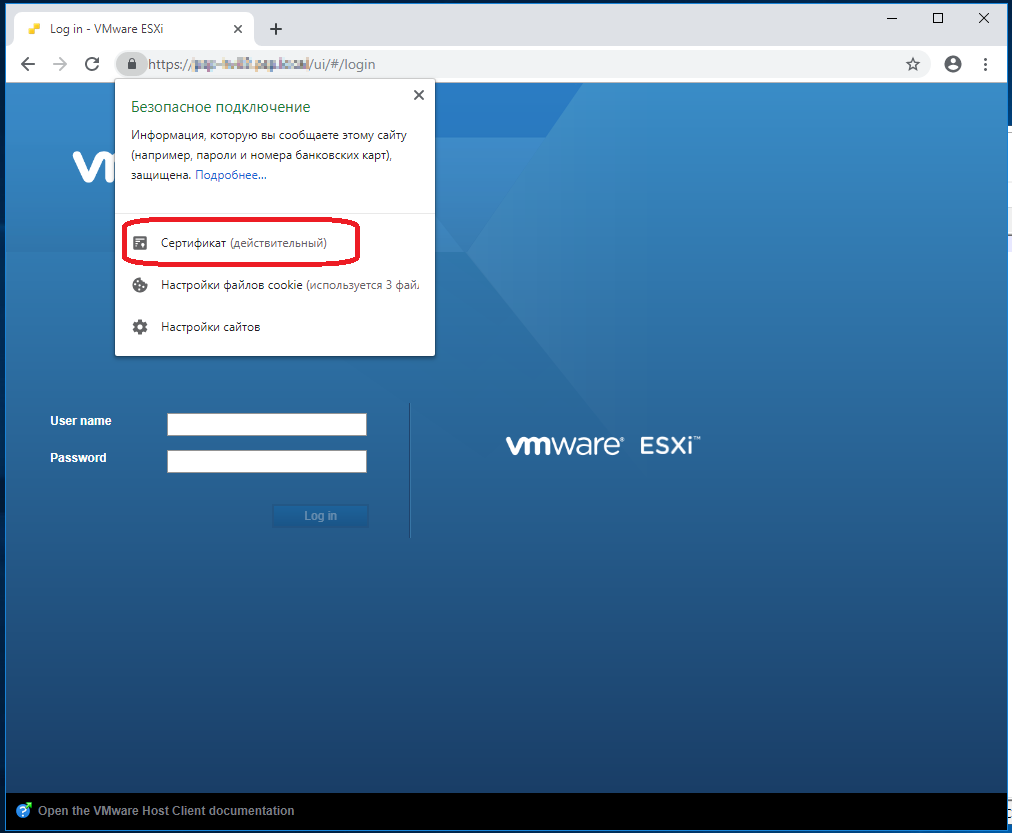
Сертификат действительный.
Заходим в vCenter, выбираем ранее отключенный хост, делаем ему Connect.
Хост снова управляется через vCenter, однако, сертификат уже — корпоративный.
After upgrading my home lab to VMware Cloud Director 10.3, I started having Remote Console issues. While searching online, it sounds to affect many others and though I will share the two issues I have and how to resolve them.
The first one, I kept getting the following error when trying to access VMware Remote Console “Connection error: could not negotiate SSL.”, as shown below:
For those who are more of a Web Console users, I just kept getting a disconnected error every time I try to connect using it as shown below.
Alright, so now you have the same problem. How to resolve it? It sounds like in the later versions of VMware Cloud Director, it is becoming more restrictive on SSL Certificates and without a signed certificates the Remote Console does not seem to work properly. This was done to enhance security.
As I have found a very well written and detailed a blog post on how to replace your certs with Lets Encrypt Wildcard SSL certificates by Marc Roeleveld, I have decided against writing my own on the subject and point you to his excellent post that can be found at the link below. By the way, it’s worth mentioning that Lets Encrypt certificates are free of charge, and quite easy to get, so no excuse not to install a signed certificate even for your home lab.
After installing the certs on my VMware Cloud Director, I kept getting the same disconnected error on the Web Console, but I had a new error on the VMware Remote Console. The message of the new error was: “The webmks ticket has expired.”. Here is a screenshot of the actual error as well:
The resolution for this issue was to easily change the port number on the Console Proxy Public URL to 8443 instead of 443. That seems to resolve the issue. You can do this by going to: Administration ==> Public Addresses ==> Console Proxy. Below is a screenshot of how mine looks like after the change.
Hope this resolve your VMware Remote Console issue. Please share in the comments if this has fixed your issue or what else did you have to do to fix it.
-
#1
Добрый день! Подскажите при подключении к облаку vCloud Director перестала открываться консоль vmware. Показывает ошибку —
VmWare Remote Console — Ошибка подключения: не удалось согласовать SSL подключение
Подскажите как вылечить ??
-
#2
Even after you properly setup the SSL certification, you may still see the error if connect from local network, as the VMRC tries to use local ip to connect. Local ip will not match any domain name from your certification. Try to add an entry in you local machine host name resolve, for Windows edit c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts by add a line of «<local ip> <domain name of server>», for example:
192.168.1.10 vm.mydomain.net
After upgrading my home lab to VMware Cloud Director 10.3, I started having Remote Console issues. While searching online, it sounds to affect many others and though I will share the two issues I have and how to resolve them.
The first one, I kept getting the following error when trying to access VMware Remote Console “Connection error: could not negotiate SSL.”, as shown below:
For those who are more of a Web Console users, I just kept getting a disconnected error every time I try to connect using it as shown below.
Alright, so now you have the same problem. How to resolve it? It sounds like in the later versions of VMware Cloud Director, it is becoming more restrictive on SSL Certificates and without a signed certificates the Remote Console does not seem to work properly. This was done to enhance security.
As I have found a very well written and detailed a blog post on how to replace your certs with Lets Encrypt Wildcard SSL certificates by Marc Roeleveld, I have decided against writing my own on the subject and point you to his excellent post that can be found at the link below. By the way, it’s worth mentioning that Lets Encrypt certificates are free of charge, and quite easy to get, so no excuse not to install a signed certificate even for your home lab.
After installing the certs on my VMware Cloud Director, I kept getting the same disconnected error on the Web Console, but I had a new error on the VMware Remote Console. The message of the new error was: “The webmks ticket has expired.”. Here is a screenshot of the actual error as well:
The resolution for this issue was to easily change the port number on the Console Proxy Public URL to 8443 instead of 443. That seems to resolve the issue. You can do this by going to: Administration ==> Public Addresses ==> Console Proxy. Below is a screenshot of how mine looks like after the change.
Hope this resolve your VMware Remote Console issue. Please share in the comments if this has fixed your issue or what else did you have to do to fix it.