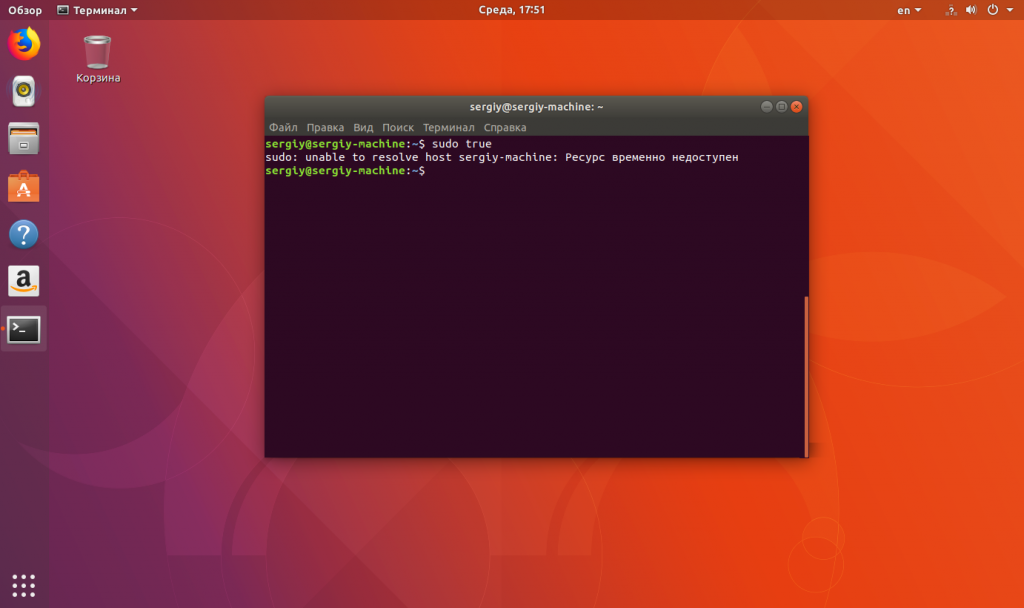
When I run sudo the terminal is stuck for a few seconds and then outputs an error message. My terminal looks like this:
ubuntu@(none):~$ sudo true
sudo: unable to resolve host (none)
What can I do to solve it?
asked Aug 31, 2011 at 19:09
Kit SundeKit Sunde
11k7 gold badges25 silver badges32 bronze badges
7
Two things to check (assuming your machine is called my-machine, you can change this as appropriate):
-
That the
/etc/hostnamefile contains just the name of the machine. -
That
/etc/hostshas an entry forlocalhost. It should have something like:127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost 127.0.1.1 my-machine
If either of these files aren’t correct (since you can’t sudo), you may have to reboot the machine into recovery mode and make the modifications, then reboot to your usual environment.
Thomas Ward♦
72.7k30 gold badges173 silver badges237 bronze badges
answered Sep 1, 2011 at 3:26
Jeremy KerrJeremy Kerr
26.8k4 gold badges48 silver badges62 bronze badges
18
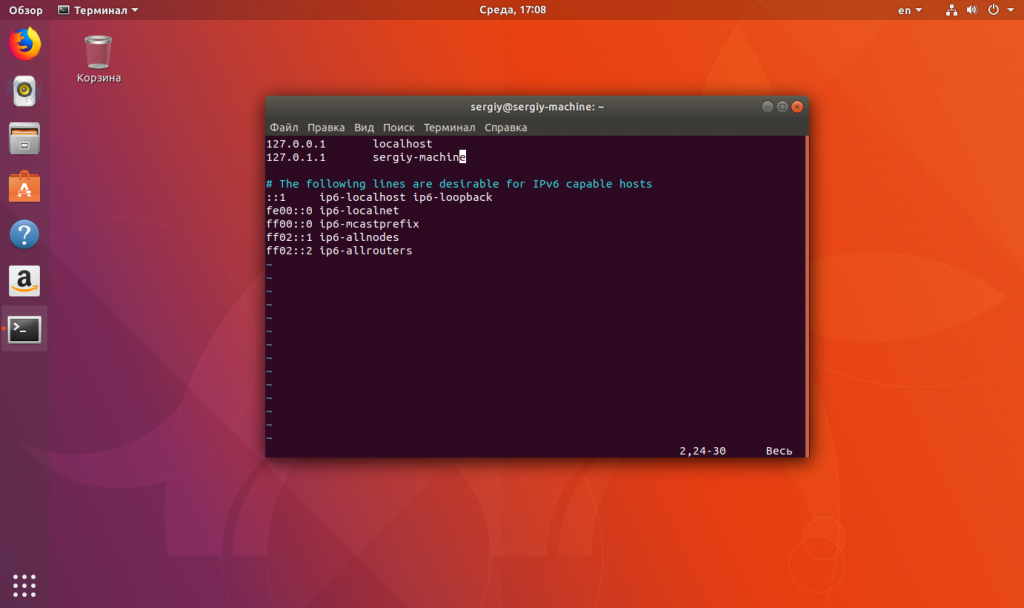
Edit /etc/hosts and append your new hostname to the 127.0.0.1 line (or create a new line if you prefer that).
Mine looks like:
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain penguin
# The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts
::1 ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
fe00::0 ip6-localnet
ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
Replace penguin in the above example by your new hostname as stated in the /etc/hostname file.
answered Apr 7, 2012 at 13:39
LekensteynLekensteyn
172k65 gold badges312 silver badges401 bronze badges
4
Add your hostname to /etc/hosts like so:
echo $(hostname -I | cut -d\ -f1) $(hostname) | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
answered Sep 15, 2014 at 16:03
Collin AndersonCollin Anderson
3,1661 gold badge17 silver badges12 bronze badges
4
Note, this is an answer to this question which has been merged with this one.
Your hostname (dave00-G31M-ES2L) is not represented in /etc/hosts. Add an L to this line:
127.0.1.1 dave00-G31M-ES2
So it becomes:
127.0.1.1 dave00-G31M-ES2L
In order to accomplish this, open a console (press Ctrl+Alt+T) and type:
sudo gedit /etc/hosts
Add the letter L as mentioned, save and exit.
answered Aug 18, 2012 at 11:02
ThorThor
3,51325 silver badges27 bronze badges
5
I had this issue when I was using ubuntu on a VPS. I solved it editing /etc/hosts file.
run this command:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
and then add:
127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost
127.0.1.1 ubuntu
I hope that will solve your issue 
PS: Remember to reboot your computer!
answered Apr 1, 2013 at 1:18
Luca D’AmicoLuca D’Amico
5541 gold badge5 silver badges14 bronze badges
3
I was having the same issue even though the hostname in my /etc/hostname file and /etc/hosts file matched.
My hostname was «staging_1». It turns out that you can’t have an underscore in your hostname, which is why I was getting this error. Changing the underscore to a hyphen fixed my problem.
answered Aug 13, 2014 at 13:50
Chris.BChris.B
2412 silver badges4 bronze badges
0
In AWS, go to your vpc and turn on «DNS Hostnames».
answered Jan 15, 2015 at 5:15
ErickErick
1371 silver badge2 bronze badges
5
The symptom given in the question may correlate strongly with this more specific problem:
$ hostname --fqdn
hostname: Temporary failure in name resolution
There are different ways that this could be resolved, one of which is to add your hostname as localhost in /etc/hosts (as shown in several other answers). This may be the right thing to do in general, but it isn’t the only possible resolution.
A «fully qualified domain name» may be supplied by an external DNS server or similar (if such is available on your network). In this case, sudo will not complain, despite the missing entry in /etc/hosts.
Note: sudo attempts to dereference the hostname, even though it isn’t necessarily required, due to optional capabilities in the sudoers file. See sudo command trying to search for hostname.
As long as the delay isn’t too long, this error message is typically harmless.
answered Sep 18, 2017 at 22:17
Brent BradburnBrent Bradburn
2,7662 gold badges29 silver badges35 bronze badges
3
Everybody advises to modify /etc/hosts. But in some cases this may not be possible (for example inside a docker container). So, I had to find a better way and I came up with this:
echo "alias sudo='sudo -h 127.0.0.1'" >> ~/.bash_aliases
source ~/.bashrc
Aliases don’t work in bash scripts, but we can use variables: sudo='sudo -h 127.0.0.1'
answered Jul 28, 2018 at 17:24
dashohoxhadashohoxha
3224 silver badges12 bronze badges
I encountered this same error message. I think this discussion thread at AWS Developer Forums is a better solution:
«Go the the VPC management console, select the VPC, click on Actions, select Edit DNS Hostnames and select Yes.»
https://forums.aws.amazon.com/thread.jspa?messageID=699718
answered Feb 13, 2016 at 11:44
user93581user93581
1171 silver badge2 bronze badges
Some terminal emulators will not update prompt with the correct hostname until you close and restart the emulator (lxterminal, I’m talking to you).
I spent 30min fighting with this error after editing my hostname and hosts files and running sudo service hostname restart until I ran sudo hostname and saw that the hostname was the new value, even though the prompt was showning the old value.
answered Jun 19, 2016 at 16:29
dagbeldagbel
611 silver badge1 bronze badge
1
In my case it was the problem, I changed the hostname to man because I wanted to know if there are some parameters you can use on hostname. Instead it changed my hostname to man and I always got the same message like you
sudo: unable to resolve host (none)
after changing the hostname back to `localhost everything worked fine again
hostname localhost
answered Jan 9, 2014 at 22:24
XandruCeaXandruCea
1531 silver badge5 bronze badges
Sorry I can’t help you much but, since it says «can’t resolve host» try running:
hostname
And see if the output is the hostname of the machine. If not, the problem is the host configuration, not sudo.
answered Aug 31, 2011 at 19:16
animaletdesequiaanimaletdesequia
8,3064 gold badges26 silver badges43 bronze badges
3
OP wrote:
It was all in /etc/hostname. On two of our sick servers it looked like
this:ubuntu@(none):~$ cat /etc/hostname linux-web-n ip-10-128-##-##While on a server without this issue we had:
ubuntu@ip-10-128-##-###:~$ cat /etc/hostname ip-10-128-##-###Removed the
linux-web-nportion, rebooted and everything was fine.
you might be getting an error if your hosts or hostname file contain illegal characters. Only these symbols are permitted: a-z, A-Z, 0-9
answered Jan 18, 2015 at 3:26
M.G.M.G.
1212 bronze badges
if you can’t sudo you CAN log in as root via su.
IE: su root (in an x-term).
then give the root password when prompted, then you can edit the files with nano. The root password in ‘buntu is the same as the password you would use for sudo.
answered Aug 24, 2016 at 15:07
1
I had this same problem! I changed my VPS’s name through the online admin control panel which did not change the machine name in the hosts file All I did was run:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
Then I edited it from this:
127.0.1.1 Megabyte Megabyte
127.0.0.1 localhost
To this:
127.0.1.1 Debian Debian
127.0.0.1 localhost
and that fixed my error! Hope this helped!
answered Jan 10, 2017 at 2:18
SynthSynth
211 bronze badge
In case your problem is that /etc/hostname file and /etc/hosts, both files have your desired hostname and still your machine is showing the error
sudo: unable to resolve host
Try, forcing the hostname
sudo hostname -F /etc/hostname
You will probably still get the same error, but try logging out and logging back in. It worked for me.
answered May 21, 2019 at 6:45
I had the same problem. I solved it by editing the /etc/hosts and /etc/hostname files… on the /etc/hosts file, just edit the top part as shown below.
#vi /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
127.0.1.1 localhost myhostname
#vi /etc/hostname
myhostname
muru
194k53 gold badges475 silver badges725 bronze badges
answered Mar 26, 2016 at 17:53
CentyCenty
211 bronze badge
2
If you are using Vagrant, then login into the guest and run
apt-get --no-install-recommends install virtualbox-guest-utils
answered Jul 13, 2017 at 7:27
tanmoytanmoy
1011 silver badge4 bronze badges
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Некоторые пользователи сталкиваются с ошибкой «sudo unable to resolve host». Обычно, эта ошибка появляется после смены имени компьютера. Это простая проблема, которую можно быстро решить.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим, почему возникает эта ошибка, что она означает, а также как её решить на примере Ubuntu.
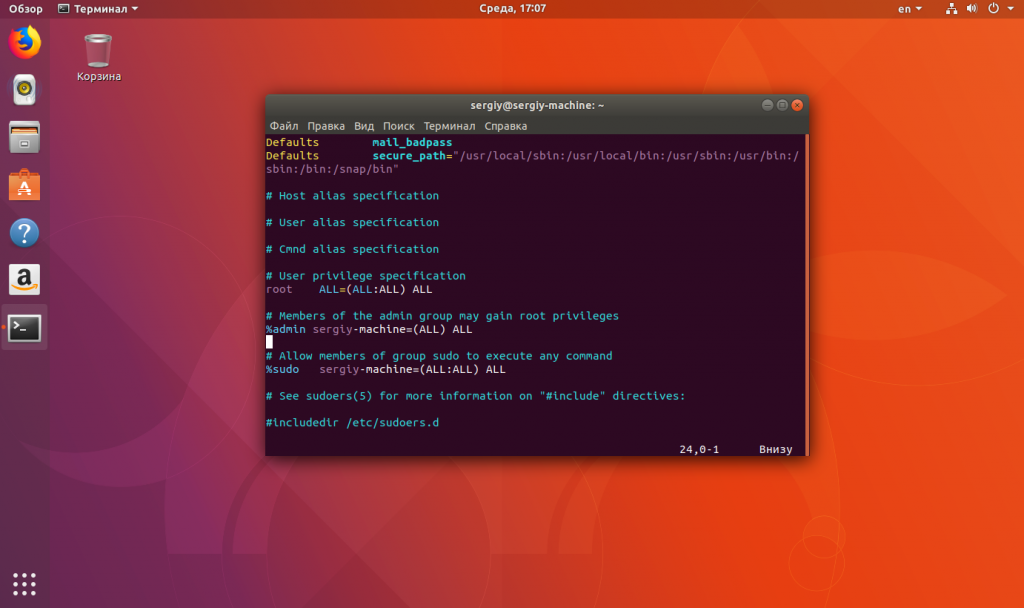
Сообщение «unable to resolve host имя_хоста» означает, что утилита не может определить IP-адрес хоста «имя_хоста«. Казалось бы, sudo — это локальная команда для повышения привилегий в системе, и ей незачем определять IP хостов. Но это не совсем так: sudo может использоваться и удалёнными пользователями, например, подключёнными по SSH, а в самом конфигурационном файле /etc/sudoers уровни доступа различных пользователей настраиваются такой строчкой:
пользователь хост=(другой_пользователь:группа) команды
Подробнее про строку настройки читайте в статье настройка sudo в linux. А сейчас нам интересно, что для каждого запроса утилите нужно определить, какой хост используется на данном компьютере.
Если кратко, то основная идея разработчиков состоит в том, что один универсальный файл /etc/sudoers будет использоваться на множестве компьютеров и на каждом из них нужно определить, какие правила предназначены для него. Таким образом, переменная host в sudoers влияет только на локальные правила.
А теперь вернёмся к нашей ошибке. Как я уже сказал, она означает, что утилита не может определить IP-адрес «имени хоста». Для домена сайта это означало бы, что такой записи нет в DNS. Но поскольку это имя нашего локального компьютера, то вполне естественно, что его нет в глобальной сети.
Как исправить ошибку
1. Решение проблемы в /etc/hosts
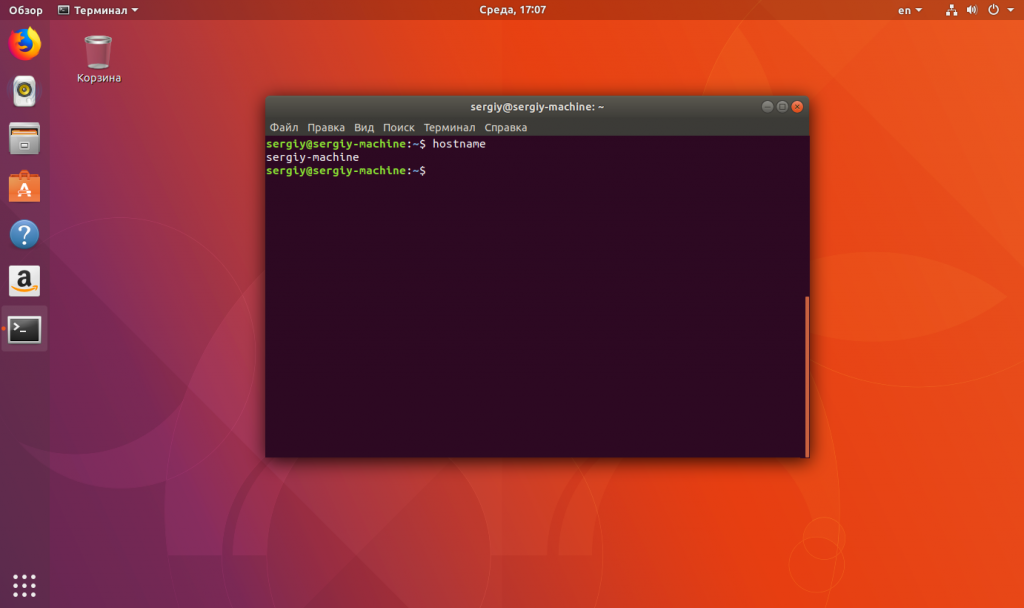
Чтобы исправить ошибку, мы можем добавить такую DNS-запись локально в файл /etc/hosts. Поскольку sudo у вас не работает, а этот файл можно редактировать только от суперпользователя, то эта простая задача становится сложнее. Сначала смотрим наше текущее имя хоста:
hostname
Дальше, если у вас установлен пароль root, вы можете авторизоваться от его имени с помощью su:
su -
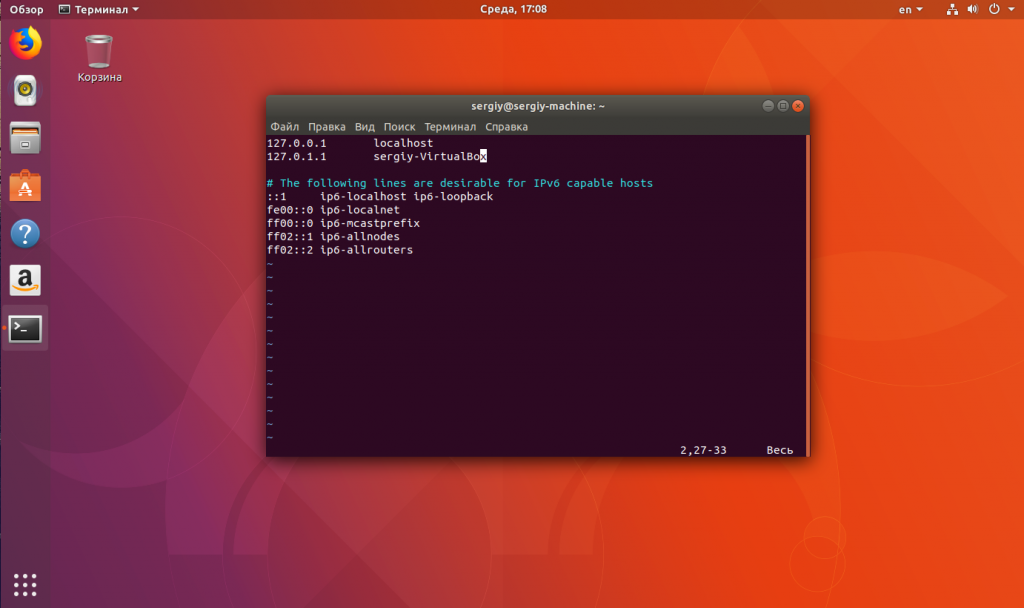
А затем добавить такую строчку в /etc/hosts:
vi /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 имя_хоста
Слова «имя_хоста» надо заменить на то имя хоста, которое вы получили с помощью команды hostname. После этого надо перезапустить компьютер или просто перезапустить сеть:
sudo systemctl restart networking
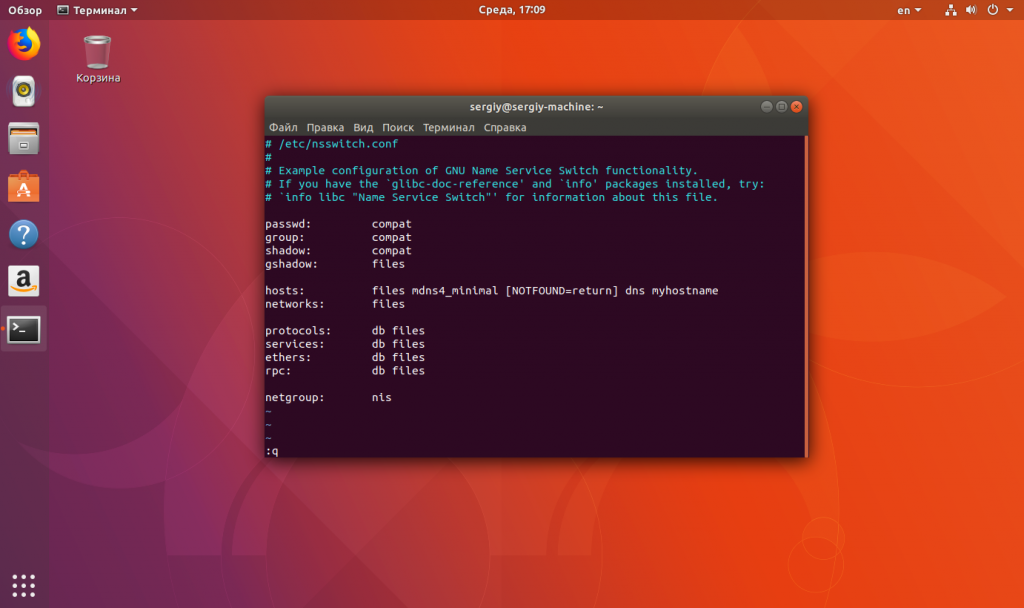
Ещё желательно убедиться, что в системной службе разрешения доменных имён включено использование файла /hosts. Откройте /etc/nsswitch.conf и найдите в строке hosts слово «files». Оно должно быть на первом месте. Если нет, перенесите его на первое место.
Если же у вас пароль для root не установлен, вам нужно загрузиться с LiveCD, примонтировать корневую файловую систему в /mnt/ и исправлять ошибку уже там.
2. Решение с помощью systemd
Есть ещё один путь. В попытках воспроизвести эту проблему в своей Ubuntu 18.04 я обнаружил, что разрешением доменных имён для локальных приложений занимается служба systemd-resolved. Если она запущена, то даже если в файле /etc/hosts нет имени вашего компьютера, всё будет работать. Поэтому, если вы случайно отключили эту службу, верните её на место и всё заработает:
sudo systemctl start systemd-resolved
sudo systemctl enable systemd-resolved
Выводы
В этой статье мы разобрали, как справиться с ошибкой «sudo cannot to resolve host». Как видите, всё достаточно логично и просто. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
Об авторе
Основатель и администратор сайта losst.ru, увлекаюсь открытым программным обеспечением и операционной системой Linux. В качестве основной ОС сейчас использую Ubuntu. Кроме Linux, интересуюсь всем, что связано с информационными технологиями и современной наукой.
When I run sudo the terminal is stuck for a few seconds and then outputs an error message. My terminal looks like this:
ubuntu@(none):~$ sudo true
sudo: unable to resolve host (none)
What can I do to solve it?
asked Aug 31, 2011 at 19:09
Kit SundeKit Sunde
11k7 gold badges25 silver badges32 bronze badges
7
Two things to check (assuming your machine is called my-machine, you can change this as appropriate):
-
That the
/etc/hostnamefile contains just the name of the machine. -
That
/etc/hostshas an entry forlocalhost. It should have something like:127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost 127.0.1.1 my-machine
If either of these files aren’t correct (since you can’t sudo), you may have to reboot the machine into recovery mode and make the modifications, then reboot to your usual environment.
Thomas Ward♦
72.7k30 gold badges173 silver badges237 bronze badges
answered Sep 1, 2011 at 3:26
Jeremy KerrJeremy Kerr
26.8k4 gold badges48 silver badges62 bronze badges
18
Edit /etc/hosts and append your new hostname to the 127.0.0.1 line (or create a new line if you prefer that).
Mine looks like:
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain penguin
# The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts
::1 ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
fe00::0 ip6-localnet
ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
Replace penguin in the above example by your new hostname as stated in the /etc/hostname file.
answered Apr 7, 2012 at 13:39
LekensteynLekensteyn
172k65 gold badges312 silver badges401 bronze badges
4
Add your hostname to /etc/hosts like so:
echo $(hostname -I | cut -d\ -f1) $(hostname) | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
answered Sep 15, 2014 at 16:03
Collin AndersonCollin Anderson
3,1661 gold badge17 silver badges12 bronze badges
4
Note, this is an answer to this question which has been merged with this one.
Your hostname (dave00-G31M-ES2L) is not represented in /etc/hosts. Add an L to this line:
127.0.1.1 dave00-G31M-ES2
So it becomes:
127.0.1.1 dave00-G31M-ES2L
In order to accomplish this, open a console (press Ctrl+Alt+T) and type:
sudo gedit /etc/hosts
Add the letter L as mentioned, save and exit.
answered Aug 18, 2012 at 11:02
ThorThor
3,51325 silver badges27 bronze badges
5
I had this issue when I was using ubuntu on a VPS. I solved it editing /etc/hosts file.
run this command:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
and then add:
127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost
127.0.1.1 ubuntu
I hope that will solve your issue 
PS: Remember to reboot your computer!
answered Apr 1, 2013 at 1:18
Luca D’AmicoLuca D’Amico
5541 gold badge5 silver badges14 bronze badges
3
I was having the same issue even though the hostname in my /etc/hostname file and /etc/hosts file matched.
My hostname was «staging_1». It turns out that you can’t have an underscore in your hostname, which is why I was getting this error. Changing the underscore to a hyphen fixed my problem.
answered Aug 13, 2014 at 13:50
Chris.BChris.B
2412 silver badges4 bronze badges
0
In AWS, go to your vpc and turn on «DNS Hostnames».
answered Jan 15, 2015 at 5:15
ErickErick
1371 silver badge2 bronze badges
5
The symptom given in the question may correlate strongly with this more specific problem:
$ hostname --fqdn
hostname: Temporary failure in name resolution
There are different ways that this could be resolved, one of which is to add your hostname as localhost in /etc/hosts (as shown in several other answers). This may be the right thing to do in general, but it isn’t the only possible resolution.
A «fully qualified domain name» may be supplied by an external DNS server or similar (if such is available on your network). In this case, sudo will not complain, despite the missing entry in /etc/hosts.
Note: sudo attempts to dereference the hostname, even though it isn’t necessarily required, due to optional capabilities in the sudoers file. See sudo command trying to search for hostname.
As long as the delay isn’t too long, this error message is typically harmless.
answered Sep 18, 2017 at 22:17
Brent BradburnBrent Bradburn
2,7662 gold badges29 silver badges35 bronze badges
3
Everybody advises to modify /etc/hosts. But in some cases this may not be possible (for example inside a docker container). So, I had to find a better way and I came up with this:
echo "alias sudo='sudo -h 127.0.0.1'" >> ~/.bash_aliases
source ~/.bashrc
Aliases don’t work in bash scripts, but we can use variables: sudo='sudo -h 127.0.0.1'
answered Jul 28, 2018 at 17:24
dashohoxhadashohoxha
3224 silver badges12 bronze badges
I encountered this same error message. I think this discussion thread at AWS Developer Forums is a better solution:
«Go the the VPC management console, select the VPC, click on Actions, select Edit DNS Hostnames and select Yes.»
https://forums.aws.amazon.com/thread.jspa?messageID=699718
answered Feb 13, 2016 at 11:44
user93581user93581
1171 silver badge2 bronze badges
Some terminal emulators will not update prompt with the correct hostname until you close and restart the emulator (lxterminal, I’m talking to you).
I spent 30min fighting with this error after editing my hostname and hosts files and running sudo service hostname restart until I ran sudo hostname and saw that the hostname was the new value, even though the prompt was showning the old value.
answered Jun 19, 2016 at 16:29
dagbeldagbel
611 silver badge1 bronze badge
1
In my case it was the problem, I changed the hostname to man because I wanted to know if there are some parameters you can use on hostname. Instead it changed my hostname to man and I always got the same message like you
sudo: unable to resolve host (none)
after changing the hostname back to `localhost everything worked fine again
hostname localhost
answered Jan 9, 2014 at 22:24
XandruCeaXandruCea
1531 silver badge5 bronze badges
Sorry I can’t help you much but, since it says «can’t resolve host» try running:
hostname
And see if the output is the hostname of the machine. If not, the problem is the host configuration, not sudo.
answered Aug 31, 2011 at 19:16
animaletdesequiaanimaletdesequia
8,3064 gold badges26 silver badges43 bronze badges
3
OP wrote:
It was all in /etc/hostname. On two of our sick servers it looked like
this:ubuntu@(none):~$ cat /etc/hostname linux-web-n ip-10-128-##-##While on a server without this issue we had:
ubuntu@ip-10-128-##-###:~$ cat /etc/hostname ip-10-128-##-###Removed the
linux-web-nportion, rebooted and everything was fine.
you might be getting an error if your hosts or hostname file contain illegal characters. Only these symbols are permitted: a-z, A-Z, 0-9
answered Jan 18, 2015 at 3:26
M.G.M.G.
1212 bronze badges
if you can’t sudo you CAN log in as root via su.
IE: su root (in an x-term).
then give the root password when prompted, then you can edit the files with nano. The root password in ‘buntu is the same as the password you would use for sudo.
answered Aug 24, 2016 at 15:07
1
I had this same problem! I changed my VPS’s name through the online admin control panel which did not change the machine name in the hosts file All I did was run:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
Then I edited it from this:
127.0.1.1 Megabyte Megabyte
127.0.0.1 localhost
To this:
127.0.1.1 Debian Debian
127.0.0.1 localhost
and that fixed my error! Hope this helped!
answered Jan 10, 2017 at 2:18
SynthSynth
211 bronze badge
In case your problem is that /etc/hostname file and /etc/hosts, both files have your desired hostname and still your machine is showing the error
sudo: unable to resolve host
Try, forcing the hostname
sudo hostname -F /etc/hostname
You will probably still get the same error, but try logging out and logging back in. It worked for me.
answered May 21, 2019 at 6:45
I had the same problem. I solved it by editing the /etc/hosts and /etc/hostname files… on the /etc/hosts file, just edit the top part as shown below.
#vi /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
127.0.1.1 localhost myhostname
#vi /etc/hostname
myhostname
muru
194k53 gold badges475 silver badges725 bronze badges
answered Mar 26, 2016 at 17:53
CentyCenty
211 bronze badge
2
If you are using Vagrant, then login into the guest and run
apt-get --no-install-recommends install virtualbox-guest-utils
answered Jul 13, 2017 at 7:27
tanmoytanmoy
1011 silver badge4 bronze badges
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
The “unable to resolve host address” error in wget occurs when the tool is unable to resolve the domain name of the host you’re trying to access.
This could be due to various reasons, such as DNS server issues, network connectivity problems, or incorrect URLs.
10 ways to fix unable to resolve host address in wget command
Here are some steps you can follow to troubleshoot and fix this issue:
Sure, here’s a more detailed explanation of each step:
- Check the URL:
Sometimes, the “Could not resolve host” error occurs due to a simple mistake in the URL.
Make sure you have entered the correct URL, including the proper protocol (e.g., “http://” or “https://”).
Additionally, ensure there are no extra spaces or special characters in the URL. - Verify the host’s DNS:
The Domain Name System (DNS) is responsible for converting domain names (e.g., example.com) into IP addresses (e.g., 192.0.2.1) that computers can understand.
If wget cannot resolve the host’s domain name to an IP address, it won’t be able to establish a connection. Use the ping command to check if your DNS is working correctly. Open your terminal/command prompt and type:
ping your-hostname.com
If you receive responses with an IP address, it indicates that your DNS is resolving correctly. If there are no responses or you get an error, it means there is an issue with DNS resolution. - Check your internet connection:
Ensure that your internet connection is active and functioning properly.
If you are on a corporate network, behind a proxy server, or have a firewall, make sure that wget is allowed to access external hosts. - Use an alternative DNS server:
Your default DNS server may experience temporary issues or outages.
You can try using a different DNS server to see if it resolves the host’s name correctly.
To change your DNS server, you can modify your network settings to use public DNS servers like Google’s DNS (8.8.8.8) or Cloudflare’s DNS (1.1.1.1). - Flush DNS cache (Windows):
On Windows systems, DNS data is cached to improve performance.
However, sometimes this cache can become corrupted or outdated. To clear the DNS cache, open the Command Prompt as an administrator and run the following command:ipconfig /flushdnsThis will clear the DNS cache and force your computer to request fresh DNS information from the configured servers.
- Restart networking service (Linux):
On Linux systems, restarting the networking service can help resolve network-related issues.
The commands to restart the networking service may vary depending on your Linux distribution.
For example, on Ubuntu, you can use:
sudo service networking restart
Alternatively, you can try restarting your computer to reset the network configuration. - Temporarily disable your firewall and antivirus:
In some cases, your firewall or antivirus software may be blocking wget from accessing the internet.
Temporarily disable them to check if they are causing the issue. If disabling them resolves the problem, you can adjust the settings to allow wget to function properly. - Check for typos and mistakes:
Carefully review the URL you are trying to access. Typos, misspellings, or incorrect domain names can lead to the “Could not resolve host” error.
Ensure there are no unnecessary spaces or special characters in the URL. - Use the IP address directly:
If all else fails and you know the IP address of the host, you can try using it directly instead of the domain name. For example:
wget http://192.0.2.1/file.txt - use curl command:
if the wget command is not available on your system, you can use the curl command as an alternative for downloading files.
curl is a versatile and widely used command-line tool that supports various protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SCP, and more.
It can perform similar tasks to wget, such as downloading files from URLs.To use curl to download a file, you can use the following command:
curl -o URLReplace <URL> with the actual URL of the file you want to download.
The -o option tells curl to save the downloaded file with the same name as the original file from the URL.
curl provides a rich set of features and options for downloading files, and it can be an excellent alternative to wget in situations where wget is not available or not installed on your system.
Wget FAQ
1. What is wget? wget stands for “web get” and is a command-line utility for downloading files from the internet. It is available on various operating systems and supports various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and more.
2. How do I use wget to download a file? You can use wget by opening a terminal or command prompt and typing wget followed by the URL of the file you want to download. For example:
wget https://example.com/file.zip
3. How do I specify the output filename with wget? By default, wget will save the downloaded file with the same name as the file on the server. To specify a different output filename, use the -O option:
wget -O my_file.zip https://example.com/file.zip
4. How can I resume a partial download with wget? To resume a partially downloaded file, use the -c or –continue option with wget:
wget -c https://example.com/large_file.zip
5. How do I limit the download rate with wget? You can limit the download rate using the –limit-rate option followed by the desired download rate in bytes per second, kilobytes per second (K), or megabytes per second (M):
wget --limit-rate=1M https://example.com/large_file.zip
6. How do I download multiple files with wget? To download multiple files, you can provide multiple URLs to wget:
wget https://example.com/file1.zip https://example.com/file2.zip
7. Can wget download recursively? Yes, wget can perform recursive downloads, allowing you to download entire directories from a web server. Use the -r or –recursive option:
wget -r https://example.com/directory/
8. How do I specify a user-agent with wget? You can set a custom user-agent string using the –user-agent option:
wget --user-agent="MyCustomUserAgent" https://example.com/file.zip
9. Can wget download over FTP? Yes, wget supports FTP downloads. Just provide the FTP URL for the file you want to download:
wget ftp://example.com/file.zip
10. Where can I find more information about wget? You can access wget documentation and additional options by typing man wget in your terminal. Alternatively, you can check online resources and tutorials for more detailed information about wget.
If none of these steps resolve the issue, it’s possible that the host you are trying to access may be temporarily down or inaccessible. You may need to wait for the host to come back online or contact the website administrator for further assistance.
Это ошибка возникает, когда Linux не может определить хост, на котором он работает. Решение проблемы — добавить хост компьютера в DNS записи. Самый простой путь — добавить строчку в /etc/hosts.
Это ошибка возникает, когда Linux не может определить хост, на котором он работает. Решение проблемы — добавить хост компьютера в DNS записи. Самый простой путь — добавить строчку в /etc/hosts.
127.0.0.1 localhost 127.0.1.1 Имя Компьютера # The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts ::1 ip6-localhost ip6-loopback fe00::0 ip6-localnet ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
Сделать это можно из учётной записи root простой командой
echo 127.0.13.37 $HOSTNAME >> /etc/hosts
Если вы не помните пароль root’а — вы можете попробовать его восстановить.