Содержание
- Mozilla Thunderbird не отправляет сообщения
- Не приходят сообщения в Mozilla Thunderbird
- Не работают ссылки в сообщениях
Пользователи Mozilla Thunderbird иногда сталкиваются с неполадками, устранение которых не всегда имеет очевидные пути решения. Ошибки Mozilla Thunderbird возникают по ряду факторов, не всегда обусловленных действиями пользователя. В этой инструкции рассмотрим наиболее известные из них.
В случае, если возникает ошибка отправления сообщения Mozilla Thunderbird, в первую очередь следует проверить настройки SMTP для исходящей корреспонденции. Выберите учетную запись, которая не работает, кликните на ней правой кнопкой мыши и выберите пункты «Параметры» — «Сервер исходящей почты». Убедитесь, что параметры сервера, указанные в нижней части панели, совпадают с настройками провайдера, предоставляющего услугу.
Узнать актуальные настройки сервера можно на сайте https://support.mozilla.org/ru/ в соответствующем разделе.
Если там информации нет, ее можно найти на официальном сайте почтового провайдера – как правило, в разделе поддержки пользователей.
Убедитесь, что используется корректный SMTP-сервер. Кликните по кнопке главного меню, затем выберите «Настройки» — «Параметры учетной записи».
Важно помнить, что службы одного провайдера не отправляют корреспонденцию другого – например, SMTP-сервер Яндекса не работает с почтой Gmail и наоборот.
Проверьте настройки файервола, сетевого экрана или антивирусного ПО – они могут запретить Mozilla Thunderbird доступ в интернет. Отключите на короткое время всю защиту и попробуйте отправить тестовое письмо.
Уточните, вдруг Mozilla Thunderbird не работает из-за блокировок на стороне вашего интернет-провайдера. Известно, что многие провайдеры в целях безопасности блокируют 25-й порт, поэтому приходится использовать другие. Информацию о блокировках можно уточнить в техподдержке провайдера.
Если перечисленные методы не помогают, попробуйте удалить пароль SMTP и поменять его на другой. Не забудьте установить такой же пароль в настройках почтового ящика.
Не приходят сообщения в Mozilla Thunderbird
Когда возникают ошибки Mozilla Thunderbird с получением корреспонденции, следует выполнить все вышеперечисленное. Как правило, в большинстве случаев эти методы работают. Однако если проблему решить не удалось, рекомендуется предпринять следующие шаги:
- Проверить наличие и работоспособность интернет-соединения – проблема может быть на стороне провайдера;
- Если веб-интерфейс провайдера электронной почты работает корректно, неполадки связаны с неправильными настройками Mozilla Thunderbird;
- Убедитесь, что пароль учетной записи провайдера почты не изменен вами или посторонними;
- Если Mozilla Thunderbird недавно обновлялась, доступ может быть запрещен антивирусом или брандмауером.
Если вы получаете не всю корреспонденцию, а по пути где-то теряются важные письма, проверьте настройки антиспам-фильтров вашего почтового провайдера. Возможно, почтовые службы попросту не пропускают такие сообщения из-за содержащихся в них ссылок или вложений определенного формата. Кроме того, проверьте настройку антиспама в самом Mozilla Thunderbird, особенно если вы создавали собственные дополнительные фильтры или блокировали некоторых респондентов.
Не работают ссылки в сообщениях
В отличие от некоторых аналогичных программ, Mozilla Thunderbird вставляет при создании сообщений кликабельных ссылок, по которым можно перейти. При вставке ссылки она будет оформлена соответственно (то есть выделена цветом и подчеркнута), но при клике по ней ничего не произойдет. При наборе ссылки в теле письма она появляется в виде обычного неформатированного текста. Такое решение принято разработчиками Mozilla Thunderbird специально из-за особенностей редактирования ссылок. Активируются они только после отправки сообщения или сохранения его в черновиках.
При клике на полученную ссылку она должна автоматически открываться в браузере. Если этого не происходит, проверьте, установлен ли на вашей ОС браузер по молчанию. Как найти эту информацию на примере Windows 7.
Перейти по пути «Пуск» — «Панель управления» — «Программы по умолчанию».
Нажать кнопку «Задание программ по умолчанию».
Проверить в списке, какой из браузеров используется по умолчанию (и используется ли вообще).
Если этот метод не помогает, следует проверить, не являются ли причиной такой ошибки Mozilla Thunderbird установленные плагины. Для этого необходимо запустить почтовый клиент в безопасном режиме (перезапустите и удерживайте Shift при старте приложения). В появившемся окне установите флажок «Отключить все дополнения».
Если в безопасном режиме ссылки открываются, а в обычном нет, корректно не работает Mozilla Thunderbird из-за одного из дополнений. Осталось определить, из-за какого именно. Для этого можно отключать их по очереди в панели управления дополнениями, проверяя работоспособность ссылок.
Thunderbird 24.2.0 has a -mail command-line parameter, with which a specific mail can be opened from the command line:
$ thunderbird --help
-mail <URL> Open the message specified by this URL.
I know that one can use this function to open a specific email by an imap:// URI, but I would like to be able to open a specific mail by its unique Message-ID, no matter which folder contains it. Is this possible, and if so, what does the URI look like?
The thunderlink add-on ( https://addons.mozilla.org/en-us/thunderbird/addon/thunderlink/ ) can create message-id based links to emails and then open these with the -thunderlink parameter, but I would still like to know if this can be done with just the -mail parameter.
asked Jan 15, 2014 at 8:10
2
Update 2021-03-18: The bug mentioned below has been fixed with Thunderbird version 78.8.1. No adjustments are necessary to open mails from the command line using thunderbird.exe -mail <URL>.
Opening messages with the -mail command line parameter is still possible with a current Thunderbird version (tested on Windows 10 with version 78.6.0, 32-bit).
However, this requires a small change of the module MailNewsCommandLineHandler.jsm, because otherwise a getter-only error occurs when calling the -mail command. The error can be traced via the Thunderbird error console (see below).
Adjusting the module:
-
Copy the file
c:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Thunderbirdomni.jainto a temporary directory, rename the file toomni.zipand unpack it. -
Open MailNewsCommandLineHandler.jsm, insert
set _messenger(value) { return value; },after line 22 and save the file.
-
Repack all files using the following parameters:
zip.exe -0DXqr omni.ja *. Rename the original file toomni.ja.bakand copy the repacked file toc:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Thunderbird. -
Messages can then be opened using the following command lines:
thunderbird.exe -mail "mailbox-message://<folderLocation>#<messageKey>" (for local folders) thunderbird.exe -mail "imap-message://<folderLocation>#<messageKey>" (for IMAP folders)
Finding the right URL:
-
Error console: Open TB, select a message and open the error console (Ctrl + Shift + J). Enter the line
var hdr = gFolderDisplay.selectedMessage; alert(hdr.folder.getUriForMsg(hdr));and press enter. This will open a window with the URL for the selected message.
-
SQLite database: If you plan to build your own search tool (e.g. by writing a Python plugin for the Wox desktop launcher), it is perhaps best to create the URLs dynamically.
The Thunderbird database can be found under
%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfiles<profile>global-messages-db.sqlite. The tables messagesText_content, messages and folderLocations contain all information needed to assemble the URL strings.A simple Python script that can be used to generate the URLs might look something like this:
import sqlite3 import re import sys import os import json # Replace db_path with your profile location # (Help > Troubleshooting Information > Open Folder) db_path = r"%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfilesxxxxxxxx.default" con = sqlite3.connect(os.path.join(db_path, "global-messages-db.sqlite")) cursor = con.cursor() query = """ SELECT messagesText_content.*, strftime('%Y-%m-%d, %H:%M', DATETIME(messages.date/1000000, "unixepoch", "localtime")), messages.folderID, messages.messageKey FROM messagesText_content JOIN messages ON messages.id=messagesText_content.docid WHERE messagesText_content.c3author NOT LIKE "%daemon%" OR messagesText_content.c3author NOT LIKE "%DAEMON%" ORDER BY messages.date DESC """ def get_messages(): messages = [] cursor.execute(query) for i in cursor: messages.append({ "text": i[1] if i[1] else "", "subject": i[2], "attachments": f'attach:{i[3]}' if i[3] else "", "sender": i[4], "receiver": i[5], "date": i[6], "folder_id": i[7], "message_key": i[8] }) return messages def get_folders(): cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM folderLocations") return {i[0]: i[1:] for i in cursor.fetchall()} def collect_urls(terms): r1 = "(mailbox|imap)(?=://)" r2 = "-message" messages = get_messages() folders = get_folders() results = {} for msg in messages: msg_str = str(msg.values()).lower() if all(i.lower() in msg_str for i in terms): folder = folders.get(msg["folder_id"])[0] url = re.sub(r1, r2, folder) url = f'{url}#{msg["message_key"]}' msg["text"] = msg["text"][:50] results.update({url: msg}) return json.dumps( results, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False ) if __name__ == "__main__": if len(sys.argv) > 1: print(collect_urls(sys.argv[1:]))Just use it like so:
<C:>python collect_urls.py search terms test message { "imap-message://a%40b.cd@imap.provider.com/INBOX#28649": { "text": "Test message contains search terms", "subject": "Test message", "attachments": "", "sender": "John Doe <e@f.gh>", "receiver": "i@j.kl", "date": "2022-10-02, 14:20", "folder_id": 607, "message_key": 28649 } }
answered Jan 2, 2021 at 23:40
4
… for anyone still searching for a solution…
The following command worked for me (thunderbird 102.6.1):
thunderbird mid:<the message ID>
To make this nice and easy:
- make sure the «thunderbird» command is in PATH (e.g. you can execute it in a terminal)
- install copy message ID AddOn
- in the preferences add the following prefix:
thunderbird mid:
(make sure that there are no spaces before and after!) - open an email and click the
Copy Message IDbutton - run the copied command in a terminal to open the mail
answered Jan 10 at 16:11
Thunderbird 24.2.0 has a -mail command-line parameter, with which a specific mail can be opened from the command line:
$ thunderbird --help
-mail <URL> Open the message specified by this URL.
I know that one can use this function to open a specific email by an imap:// URI, but I would like to be able to open a specific mail by its unique Message-ID, no matter which folder contains it. Is this possible, and if so, what does the URI look like?
The thunderlink add-on ( https://addons.mozilla.org/en-us/thunderbird/addon/thunderlink/ ) can create message-id based links to emails and then open these with the -thunderlink parameter, but I would still like to know if this can be done with just the -mail parameter.
asked Jan 15, 2014 at 8:10
2
Update 2021-03-18: The bug mentioned below has been fixed with Thunderbird version 78.8.1. No adjustments are necessary to open mails from the command line using thunderbird.exe -mail <URL>.
Opening messages with the -mail command line parameter is still possible with a current Thunderbird version (tested on Windows 10 with version 78.6.0, 32-bit).
However, this requires a small change of the module MailNewsCommandLineHandler.jsm, because otherwise a getter-only error occurs when calling the -mail command. The error can be traced via the Thunderbird error console (see below).
Adjusting the module:
-
Copy the file
c:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Thunderbirdomni.jainto a temporary directory, rename the file toomni.zipand unpack it. -
Open MailNewsCommandLineHandler.jsm, insert
set _messenger(value) { return value; },after line 22 and save the file.
-
Repack all files using the following parameters:
zip.exe -0DXqr omni.ja *. Rename the original file toomni.ja.bakand copy the repacked file toc:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Thunderbird. -
Messages can then be opened using the following command lines:
thunderbird.exe -mail "mailbox-message://<folderLocation>#<messageKey>" (for local folders) thunderbird.exe -mail "imap-message://<folderLocation>#<messageKey>" (for IMAP folders)
Finding the right URL:
-
Error console: Open TB, select a message and open the error console (Ctrl + Shift + J). Enter the line
var hdr = gFolderDisplay.selectedMessage; alert(hdr.folder.getUriForMsg(hdr));and press enter. This will open a window with the URL for the selected message.
-
SQLite database: If you plan to build your own search tool (e.g. by writing a Python plugin for the Wox desktop launcher), it is perhaps best to create the URLs dynamically.
The Thunderbird database can be found under
%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfiles<profile>global-messages-db.sqlite. The tables messagesText_content, messages and folderLocations contain all information needed to assemble the URL strings.A simple Python script that can be used to generate the URLs might look something like this:
import sqlite3 import re import sys import os import json # Replace db_path with your profile location # (Help > Troubleshooting Information > Open Folder) db_path = r"%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfilesxxxxxxxx.default" con = sqlite3.connect(os.path.join(db_path, "global-messages-db.sqlite")) cursor = con.cursor() query = """ SELECT messagesText_content.*, strftime('%Y-%m-%d, %H:%M', DATETIME(messages.date/1000000, "unixepoch", "localtime")), messages.folderID, messages.messageKey FROM messagesText_content JOIN messages ON messages.id=messagesText_content.docid WHERE messagesText_content.c3author NOT LIKE "%daemon%" OR messagesText_content.c3author NOT LIKE "%DAEMON%" ORDER BY messages.date DESC """ def get_messages(): messages = [] cursor.execute(query) for i in cursor: messages.append({ "text": i[1] if i[1] else "", "subject": i[2], "attachments": f'attach:{i[3]}' if i[3] else "", "sender": i[4], "receiver": i[5], "date": i[6], "folder_id": i[7], "message_key": i[8] }) return messages def get_folders(): cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM folderLocations") return {i[0]: i[1:] for i in cursor.fetchall()} def collect_urls(terms): r1 = "(mailbox|imap)(?=://)" r2 = "-message" messages = get_messages() folders = get_folders() results = {} for msg in messages: msg_str = str(msg.values()).lower() if all(i.lower() in msg_str for i in terms): folder = folders.get(msg["folder_id"])[0] url = re.sub(r1, r2, folder) url = f'{url}#{msg["message_key"]}' msg["text"] = msg["text"][:50] results.update({url: msg}) return json.dumps( results, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False ) if __name__ == "__main__": if len(sys.argv) > 1: print(collect_urls(sys.argv[1:]))Just use it like so:
<C:>python collect_urls.py search terms test message { "imap-message://a%40b.cd@imap.provider.com/INBOX#28649": { "text": "Test message contains search terms", "subject": "Test message", "attachments": "", "sender": "John Doe <e@f.gh>", "receiver": "i@j.kl", "date": "2022-10-02, 14:20", "folder_id": 607, "message_key": 28649 } }
answered Jan 2, 2021 at 23:40
4
… for anyone still searching for a solution…
The following command worked for me (thunderbird 102.6.1):
thunderbird mid:<the message ID>
To make this nice and easy:
- make sure the «thunderbird» command is in PATH (e.g. you can execute it in a terminal)
- install copy message ID AddOn
- in the preferences add the following prefix:
thunderbird mid:
(make sure that there are no spaces before and after!) - open an email and click the
Copy Message IDbutton - run the copied command in a terminal to open the mail
answered Jan 10 at 16:11
Вопрос:
Я работаю над расширением Thunderbird и, к сожалению, не могу разобраться в том, что все еще актуально, а что нет. Там много материала в Интернете, но большинство из них больше не применимо к недавнему Thunderbird.
-
Как минимум, мне нужен способ просмотра сообщений журнала с расширением, поэтому я вижу, что работает, а что нет. В идеале, мне нужна полная консоль отладки. Существует ссылка на Stackoverflow на Thunderbird Developer Tools, но, похоже, нет способа загрузить их.
-
Я также хотел бы иметь возможность запускать Javascript, который может ссылаться на мое расширение через консоль. Когда я пробую это через консоль Thunderbird, я получаю сообщения об ошибках. Я получаю это даже при использовании других расширений для людей, поэтому я должен предположить, что расширения не входят в область консоли
Как я могу получить видимость и взаимодействие с новым расширением Thunderbird?
Лучший ответ:
Содержание
- протоколирование сообщений
- Инструменты разработчика Thunderbird
- выполнить Javascript, который может ссылаться на мое расширение
протоколирование сообщений
Как описано в https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Debugging_JavaScript, в Gecko есть 3 разных консоли. Наиболее доступным в Thunderbird является Консоль ошибок. Вы можете писать сообщения через nsIConsoleService. Если вы не против, чтобы сообщения журнала отображались как ошибка, вы также можете просто использовать Components.utils.reportError().
Другой способ – войти в (собственную) консоль, из которой запускается Thunderbird. Это делается через dump().
Самый новый способ записи сообщений – это Log.jsm. Это очень хорошая обложка вокруг различных методов ведения журнала, и мой предпочтительный способ регистрации сообщений в Thunderbird.
Инструменты разработчика Thunderbird
Поскольку вы не привязаны к ссылке, я не уверен на 100%, но я думаю, что вы имеете в виду возможность удаленно отлаживать Thunderbird через Firefox. Вам не нужно скачивать что-либо, чтобы использовать это, оно уже интегрировано в Thunderbird.
выполнить Javascript, который может ссылаться на мое расширение
Отладка Thunderbird удаленно через Firefox дает также доступ к консоли и Scratchpad в Инструментах разработчика. Оба должны иметь доступ к надстройке.
Вы также можете посмотреть Tiny JavaScript Debugger. Он также позволяет выполнять произвольный код во время отладки.
<< Back to MailNews:Home Page
Logs provide data to help developers and triagers understand what is causing an issue. Please provide a log file when requested. If you have difficulty or questions, please ask for help.
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Thunderbird Logging
- 2.1 Thunderbird Logging Types
- 2.2 Setting a Preference
- 3 Gecko Logging
- 3.1 Thunderbird Module Names
- 3.2 Environment Variables to set
- 3.2.1 MOZ_LOG_FILE
- 3.2.2 MOZ_LOG
- 3.2.2.1 Logging Level
- 3.3 Generating a Gecko Log
- 3.3.1 Windows
- 3.3.2 Mac OS X
- 3.3.3 Linux/unix
- 3.4 Missing Log File
- 4 NSPR Logging Options
- 5 Enhancement Ideas
- 6 Logging prior to Thunderbird 55.0a1 / SeaMonkey 2.52a1
Introduction
Logging in recent years has evolved in:
- where logging is enabled — possibilities include command line, and Thunderbird preferences
- location of log data — possibilities include logging to a file, and logging to the Error Console
Also, we have two types of logging:
- Thunderbird logging, for calendar, chat, gloda indexing and seach, ldap, nntp (news), pop, and smtp (sending mail)
- Gecko logging, which uses case senstive module names, such as IMAP and IMAPAutoSync
Thunderbird Logging
Modern logging is specified by setting a preference in Thunderbird.
Unless otherwise specified, logging output goes to the Error Console, at Tools > Developer > Error Console or use the hotkey Control+Shift+J (Command+Shift+J on macOS).
Thunderbird Logging Types
Log settings of type string are Case Sensitive. For example, use All, not ALL.
- Calendar — set both
calendar.debug.logandcalendar.debug.log.verbosetotrue, and reload calendar pane. Reference: Calendar/Calendar logging - Chat —
purple.debug.loglevelset to [1]- 0 Show all libpurple messages (PURPLE_DEBUG_ALL)
- 1 Very verbose (PURPLE_DEBUG_MISC)
- 2 Verbose (PURPLE_DEBUG_INFO)
- 3 Show warnings (PURPLE_DEBUG_WARNING)
- 4 Show errors (PURPLE_DEBUG_ERROR)
- 5 Show only fatal errors (PURPLE_DEBUG_FATAL)
- Chat Off-The-Record (OTR) protocol for exchanging encrypted chat messages —
chat.otr.traceboolean preference - Gloda Indexing (global search) activity to Error Console
- imap —
mailnews.imap.loglevelstring, set toAll(if you have set mailnews.imap.jsmodule=true, Daily channel builds only) - ldap —
mailnews.ldap.loglevel, string, set toAll - NNTP —
mailnews.nntp.loglevel, string, set toAll - OpenPGP/e2ee — logging is described at OpenPGP Debugging
- pop3 —
mailnews.pop3.loglevel, string, set toAll - smtp —
mailnews.smtp.loglevel, string, set toAll
Setting a Preference
To configure logging via a Thunderbird Preference, you must create a hidden Thunderbird preference, not an environment variable. In Thunderbird :
- do Settings > General
- in the search field type
config editor - click
Config Editorin the search results - in the search field paste or type the preference name, for example
mailnews.pop3.loglevel - if you are presented with choices of Boolean, Number, String
- choose Boolean for true or false settings, otherwise choose String
- click the
+(plus sign) to add the preference
- change the preferences’ value to the desired logging value
- for string preferences click the pencil icon, change the value, then click the check mark
- for boolean preferences click the double headed arror to switch between
trueandfalse
Logging is permanent until you reset or delete a preference (by clicking the trash can).
It is not necessary to restart Thunderbird — logging starts immediately.
You can view the output at Tools > Developer > Error Console. To expose timestamp, click the gear icon in top-right of the Error Console, turn on «Show Timestamps».
Gecko Logging
Gecko logging using module names is the classic method of getting log data. Gecko logging may be enabled via preferences (not discussed in this document), or command line, which is discussed here.
Thunderbird gets its module logging capabilities from Firefox core aka Gecko. Gecko logging capabilities are thoroughly documented in this excellent reference.
Thunderbird Module Names
All names are CASE SENSITIVE.
- AbOutlookDirectory (before Thunderbird version 59: nsAbOutlookDirectoryLog)
- AbWinHelper (before Thunderbird version 59: nsAbWinHelperLog)
- BayesianFilter
- CMS (for S/MIME)
- Filters
- IMAP
- IMAP_CS (for CONDSTORE)
- IMAP_KW (for keyword (tag) processing)
- IMAPAutoSync (before Thunderbird version 59: ImapAutoSync)
- IMAPCache (for IMAP caching of messages in no-sync folders)
- IMAPOffline (before Thunderbird version 59: IMAPOFFLINE)
- Import (before Thunderbird version 59: IMPORT)
- ldap (After Thunderbird 90 use Thunderbird logging)
- Mailbox (before Thunderbird version 59: MAILBOX)
- MailDirStore
- MAPI
- MAPIAddressBook
- MIME
- MsgBiff
- MsgCompose (before Thunderbird version 59: msgcompose)
- MsgCopyService (3.3a4 nightly builds starting 5/2/2011)
- MsgDB (level 1=opens/closes, level 5 lists open db’s on close, number of msg hdrs in use) (before Thunderbird version 59: MSGDB)
- MsgPurge
- NNTP (After Thunderbird 95 use Thunderbird logging)
- pop3 (After Thunderbird 98 use Thunderbird logging)
- smtp (After Thunderbird 90 use «Thunderbird logging)
Notes:
- The current, full list of Thunderbird module names is seen in this searchfox query.
- Gecko modules potentially useful to Thunderbird users:
- nsHostResolver (for DNS)
- GetAddrInfo (for DNS)
- nsSocketTransport (basic networking)
- negotiateauth (authentication)
- Version 59 bug 1353919 changed these options to be mixed case. The old, inconsistent case options are in parenthesis above.
- Deprecated:
- Movemail
- AbOutlookDirFactory (before Thunderbird version 59: nsAbOutlookDirFactoryLog)
- WABAddressBook
Environment Variables to set
NOTE — do not use this section for ldap, nntp, pop3 and smtp, which are configured per Thunderbird logging.
Two variables must be set, MOZ_LOG and MOZ_LOG_FILE as local environment variables in a batch file/script (described below) or on a command line. (using global system environment variables is not recommended)
MOZ_LOG_FILE
MOZ_LOG_FILE is the path and file name to the log file. An extension of .moz_log will be added to the file name (since Thunderbird 70). If MOZ_LOG_FILE is not set, then the output will be logged to the console/terminal (stdout) where the application was launched.
Example:
set MOZ_LOG_FILE=thunderbird-log-file
Note:
- The log file is written over every time you re-launch the application.
- You must have write access to the directory of the log file. The user’s desktop directory or system temp directory are often a good choices.
- If you run multiple applications at the same time, such as Firefox and Thunderbird, then might both write to the log file and possibly wipe out the other’s log entries. Workarounds:
- Run only one application at a time
- Use the
appendoption - Force logging to the console by setting MOZ_LOG_FILE to null,
MOZ_LOG_FILE=.
MOZ_LOG
MOZ_LOG syntax is a list of terms, separated by commas. There are two types of terms:
- A CASE SENSITIVE module name and its log level, separated by a colon (:), such as example_module:5 to enable the module example_module at logging level 5 (verbose).
- Optional special strings (switches) to configure the logging behaviour. Some configuration switches take an integer parameter, in which case the integer is separated from the string by a colon (:). Most switches only apply in a specific output context. Full documentation at [2].
Example module and loglevel: IMAP:4,IMAPAutoSync:5,timestamp
,timestamp adds a timestamp to all log lines — generally recommended, and required for all timeouts and issues which need to be correlated to an action at a given time of day
Logging Level
NOTE — do not use this section for ldap, nntp, pop3 and smtp, which are configured per Thunderbird logging.
The number in MOZ_LOG specifies the level of logging to be used. A lower number reduces the amount of information being logged. Use «5» unless requested otherwise.
- 0 = Disabled /* Indicates logging is disabled. Progammers should not use this directly in code. */
- 1 = Error /* An error occurred. Also generally something a programmer would consider asserting in a debug build. */
- 2 = Warning /* A warning often indicates an unexpected state. */
- 3 = Info /* An informational message, which often indicates the current program state. */
- 4 = Debug /* A debug message, which is useful for debugging but too verbose to be turned on normally. */
- 5 = Verbose /* A message that will be printed a lot, useful for debugging program flow and will probably impact performance. */ Verbose is not recommended for IMAP.
Some modules may not work exactly according to the log levels noted above. Very few modules actually have more than one logging level.
Generating a Gecko Log
NOTE — do not use this section for ldap, nntp, pop3 and smtp, which are configured per Thunderbird logging.
For Gecko logging, use module names.
Windows
Create a batch file by copying the lines below and paste them into the notepad application, and save the file as «create_log.bat». Variables MOZ_LOG and MOZ_LOG_file must not contain quotation marks.
set MOZ_LOG=moduleName:5,timestamp set MOZ_LOG_FILE=%USERPROFILE%Desktoplog_file "%ProgramFiles(x86)%Mozilla Thunderbirdthunderbird.exe"
- On versions with User Account Control (UAC), the batch file must be run with administrator privileges. Right click on the batch file and select «Run as administrator». Otherwise the log file will not be created and no UAC warnings will be generated.
- XP and Vista users should specify %ProgramFiles% instead of %ProgramFiles(x86)% (which is for Windows 7) — assuming Thunderbird was installed to it’s default location.
Now run the batch file. The example puts the log file on your desktop:
You can set up the batch file to be run using of these methods: double click the batch file, create a shortcut, add it to start menu, from a command window prompt, or from the start>run dialog.
Logging commands can also typed directly in the command prompt instead of running a batch file. On Windows 2000, XP, 2003 Server: Start>Programs>Accessories>Command Prompt. On later windows versions, you may type «cmd» and press enter in the launch dialog of the Start button.
Mac OS X
To generate an log, create a text file that contains the desired commands in a text editor such as BBEdit:
#!/bin/sh export MOZ_LOG=moduleName:5,timestamp export MOZ_LOG_FILE=$HOME/Desktop/log_file /Applications/Thunderbird.app/Contents/MacOS/thunderbird-bin &
If on MacOS 10.5, change the last line to arch -arch i386 /Applications/Thunderbird.app/Contents/MacOS/thunderbird-bin &
Save this file with a filename ending in .command, add execute permission by typing «chmod a+x filename» in a Terminal window, then double-click it.
Alternatively, you can setup a file so that the protocol tracing will always be in effect. (Not recommended if you use both Firefox and Thunderbird) To do this open a Terminal window, cd into the .MacOSX directory under your login directory and create a file named environment.plist containing the following. Non-unix users can use the «pico» editor which I think is available on OS X by default:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple Computer//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd"> <plist version="1.0"> <dict> <key>MOZ_LOG_FILE</key> <string>/tmp/log_file.txt</string> <key>MOZ_LOG</key> <string>moduleName:5,timestamp</string> </dict> </plist>
Note, line starting with «<!DOCTYPE» should be oneline all the way to «dtd», but I’m not sure if that makes a difference.
Linux/unix
To generate a log, run the following commands before running the application from the command line:
# For bash shell (the default shell on most GNU/Linux systems): export MOZ_LOG=moduleName:5,timestamp export MOZ_LOG_FILE=/tmp/log_file
# For tcsh / csh (which is not as common): setenv MOZ_LOG moduleName:5,timestamp setenv MOZ_LOG_FILE /tmp/log_file
Missing Log File
If your log file is empty or missing, review this document again, and check for these common problems:
- Are you logging ldap, nntp, pop3, or smtp? You must use Thunderbird logging, not Gecko module logging using environment variables.
- Do you have write access to the directory specified in MOZ_LOG_FILE?
- Did you shut down the application? (the log file is buffered in memory until the application is closed)
- Did you restart your mailnews application, and wipe out the log of the session you wanted to debug? (every restart wipes out the previous log)
- If you used a batch file on Windows, is the batch file set to run with administrator privileges?
- Do your log variables contain quotation marks or other invalid characters?
- Are your log module names correctly CASE SENSITIVE? (meaning mixed case, or camel case which is not all upper case, nor all lower case)
NSPR Logging Options
NSPR also has logging. Miscellaneous NSPR Reference (logging).
Enhancement Ideas
- bug 492620 — better, easier logging/diagnostics for Thunderbird [meta]
- bug 193873 — Add Mozilla logging to UI / Thunderbird:Logging_UI
- bug 697522 — precise logging of message filter runs and actions
Logging prior to Thunderbird 55.0a1 / SeaMonkey 2.52a1
Around April 5, 2017, via bug 1222244 and blockers of bug 1219461, changes were merged to the Mozilla trunk which impacted logging functionality. Prior to these changes, the variable names used to configure logging were NSPR_LOG_MODULES and NSPR_LOG_FILE rather than MOZ_LOG and MOZ_LOG_FILE. If you are working with an older version, use the old variable names.
In addition, some log module names changed. The old names are documented below, but will eventually be removed (along with this section) when enough time has past that it is no longer necessary for most people to debug older versions of the applications. Of course, the obsolete documentation will remain accessible in the history of this page.
Note that log module names are CASE SENSITIVE.
This article is about troubleshooting techniques for advanced users who are investigating problems with servers. It applies to all of the server types that Thunderbird connects to:
-
POP3 For getting mail IMAP For getting mail SMTP For sending mail NNTP For usenet news HTTP For RSS feeds LDAP For address books
These methods are only useful for investigating problems that occur after Thunderbird establishes a connection to a server. If Thunderbird cannot connect to the server, then it is pointless trying to log the connection—in these cases, see: Network tools for server connections
To use these methods for investigating secure authentication, you will need additional tools depending on the authentication method.
Contents
- 1 Methods for logging
- 1.1 Using Thunderbird
- 1.1.1 Sample batch files for Windows
- 1.1.2 Other types of problems you can solve
- 1.2 Using a proxy
- 1.3 Using a packet sniffer
- 1.1 Using Thunderbird
- 2 Interpreting a connection log
- 2.1 POP3 connection states
- 2.2 SMTP connection states
- 2.3 NNTP connection states
- 3 Examples
- 4 Rich logging using Gloda
- 5 See also
- 6 External links
Methods for logging
There are three methods for logging server connections:
- Thunderbird itself
- A logging proxy
- A packet sniffer
Using Thunderbird
Thunderbird can create a log file for the server types POP3, IMAP, SMTP, NNTP and HTTP, and MIME and LDAP protocols.
When you use Thunderbird to log a connection:
- You do not see all the authentication information, so you might not be able to investigate authentication problems in detail.
- You can log secure (SSL and TLS) connections.
To create the log file, follow the instructions on the Mozilla web page linked below. Use log level 5, and remember to specify POP3:5, IMAP:5, SMTP:5, NNTP:5, nsHttp:5, MIME:5 or LDAP:5, depending on which type of server or protocol you are investigating. (The module nsHttp is not mentioned on the linked page.)
- MailNews Logging
Exiting Thunderbird usually does not close any existing connections to a mail server, it can take 5-10 minutes for them to time out. It’s much easier to debug a problem when you can also log it making a new connection. For example, if you enabled IMAP logging and the connection to the AIM mail server was still open you would see something roughly like:
- 0[34988]: 2310cc0:imap.cs.com:NA:SetupWithUrl: clearing IMAP_CONNECTION_IS_OPEN
If the log file is empty that normally means you either didn’t configure the logging correctly (you need to specify POP3:5 , not POP:5 for example) or you couldn’t make a TCP-IP connection to the mail server for some reason. You could use netstat to list your connections. Run it from a console window/DOS box.
Its recommended that you add a timestamp. A combination like
- MOZ_LOG=imap:5,timestamp
would add the time of an event to each entry.
Sample batch files for Windows
The environmental variables NSPR_LOG_MODULES and NSPR_LOG_FILE are being replaced with MOZ_LOG and MOZ_LOG_FILE starting with Thunderbird 55.0a1. These sample batch files use both so that they should work with any version.
To enable logging for a IMAP account create a imap.bat file at %APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfiles (enter that string in the Windows search box and press Enter to go there using Windows Explorer) using a text editor such as Notepad. This is the default location that profiles are created in (as child directories). The log file will be created in the same directory as the imap.bat file.
Double click on the batch file and it will start Thunderbird with IMAP logging enabled. Duplicate the problem and exit Thunderbird. Afterwards open the imap.log log file with a text editor to view the log. The log file is usually too long to post in the forums. If you are asking for help in the forums it is suggested that you log into https://pastebin.com , https://www.dropbox.com or https://docs.google.com/document/ , upload the log file and then post a link to it in the forum. The log file does not contain passwords. It will contain some strings that use portions of your email address but it is garbled, so that spammers using a spider to collect email addresses should ignore it.
For a IMAP account create the following imap.bat file:
set MOZ_LOG=IMAP:5,timestamp set MOZ_LOG_FILE=%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfilesimap.log set NSPR_LOG_MODULES=IMAP:5,timestamp set NSPR_LOG_FILE=%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfilesimap.log "%ProgramFiles(x86)%Mozilla Thunderbirdthunderbird.exe"
For a POP account create the following pop.bat file instead:
set MOZ_LOG=POP3:5,timestamp set MOZ_LOG_FILE=%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfilespop.log set NSPR_LOG_MODULES=POP3:5,timestamp set NSPR_LOG_FILE=%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfilespop.log "%ProgramFiles(x86)%Mozilla Thunderbirdthunderbird.exe"
To log sending a email message (SMTP) create the following smtp.bat file instead:
set MOZ_LOG=SMTP:5,timestamp set MOZ_LOG_FILE=%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfilessmtp.log set NSPR_LOG_MODULES=SMTP:5,timestamp set NSPR_LOG_FILE=%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfilessmtp.log "%ProgramFiles(x86)%Mozilla Thunderbirdthunderbird.exe"
You can replace %APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfiles with %USERPROFILE%Desktop if you want to display the log file on your desktop instead. Or replace it with any path you want.
The logging is not account specific, it will log everything for that type of account. It is usually a good idea to temporarily disable checking for new mail in the other accounts by unchecking «check for new mail on startup» etc. before using the batch file, and not selecting any of the other accounts folders in the folder pane while duplicating the problem. Otherwise not only will it log everything for every account of that type, but it may intermingle the logging (making it much harder to read).
Other types of problems you can solve
You can also log memory usage using MSGDB:5 to help diagnose memory usage problems. If you build a debug version of Thunderbird there are other logging options such as MAPI, msgcompose, imapoffline etc. that may be useful for debugging.
Using a proxy
A logging proxy is an additional program that logs a specific connection.
When you use a proxy:
- You can log any server type.
- You do not see Thunderbird’s connection states. This simplifies the log, but it might make some problems more difficult to discover.
- You see the raw data with no explanatory information.
- You see all the authentication information. However, investigating secure authentication requires additional tools.
- You cannot successfully log a secure (SSL) connection, nor a TLS connection after the initial negotiation.
To configure a proxy, either change Thunderbird’s server settings, or use Thunderbird’s proxy settings to specify localhost (your own computer, where the proxy is running) as the proxy server. By changing settings in Thunderbird, you risk changing the nature of the problem that you are investigating. If possible, check the proxy configuration with a working server before you use it with the server you are investigating.
To change Thunderbird’s server settings, point Thunderbird at the server localhost and point the logging proxy at the real server.
To change Thunderbird’s proxy settings, choose: Tools – Options… – General – Connection Settings…, choose «Manual proxy configuration», set the HTTP proxy to localhost, and check the box «Use this proxy server for all protocols». Use whatever port you have configured in the proxy—for example, 80. Point the logging proxy at the real server and port.
Some examples of logging proxies that you can download are:
- Trivial Proxy (Windows only)
- TCPreen (cross-platform)
Using a packet sniffer
A packet sniffer is an additional program that logs network traffic. You usually configure the packet sniffer to filter the log, so that you only see the parts that interest you. The resulting log contains information similar to a proxy log, but it might be presented in a much more complex way, depending on the sniffer and on how you configure it.
When you use a packet sniffer:
- You can log any server type.
- You do not change any settings in Thunderbird.
- You see the raw data with no explanatory information.
- You do not see Thunderbird’s connection states. This simplifies the log, but it might make some problems more difficult to discover.
- You see all the authentication information. However, investigating secure authentication requires additional tools.
- You cannot successfully log a secure (SSL) connection, nor a TLS connection after the initial negotiation.
Configuring a packet sniffer depends on the sniffer.
Some examples of packet sniffers that you can download are:
- Wireshark (cross-platform) (was Ethereal)
- tcpdump (cross-platform)
- Snort (cross-platform)
Interpreting a connection log
To interpret a connection log, you need to understand something about how the server works and how Thunderbird works.
The server specifications are Internet standards published as RFCs.
There are some links to them in the External links section below.
For POP3, SMTP and NNTP, Thunderbird works by computing a connection state that tells it what to expect from the server and what to do next. These connection states are internal to Thunderbird. They might be different in different releases of Thunderbird. To understand the connection states in detail, you might have to read Thunderbird’s C++ source code.
POP3 connection states
|
|
|
SMTP connection states
|
|
|
NNTP connection states
|
|
|
Examples
Here is a proxy log of a connection to a POP3 server. There are no messages on the server:
+OK Hello there. AUTH -ERR Invalid command. CAPA +OK Here's what I can do: SASL LOGIN CRAM-MD5 CRAM-SHA1 TOP USER LOGIN-DELAY 10 PIPELINING UIDL IMPLEMENTATION Courier Mail Server . AUTH LOGIN + VXNlcm5hbWU6 anVzdC50ZXN0aW5nQGV4YW1wbGUubmV0DQo= + UGFzc3dvcmQ6 Zm9vYmFyMTIzDQo= +OK logged in. STAT +OK 0 0 QUIT +OK Bye-bye.
The base64 strings that you see are:
-
VXNlcm5hbWU6 Username: anVzdC50ZXN0aW5nQGV4YW1wbGUubmV0DQo= just.testing@example.net (the username) UGFzc3dvcmQ6 Password: Zm9vYmFyMTIzDQo= foobar123 (the password)
Here is a Thunderbird log of the same connection:
0[ef1790]: Entering NET_ProcessPop3 18 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 1 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 2 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 4 0[ef1790]: RECV: +OK Hello there. 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 29 0[ef1790]: SEND: AUTH 0[ef1790]: Entering NET_ProcessPop3 23 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 3 0[ef1790]: RECV: -ERR Invalid command. 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 30 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 31 0[ef1790]: SEND: CAPA 0[ef1790]: Entering NET_ProcessPop3 142 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 3 0[ef1790]: RECV: +OK Here's what I can do: 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 32 0[ef1790]: RECV: SASL LOGIN CRAM-MD5 CRAM-SHA1 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 32 0[ef1790]: RECV: TOP 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 32 0[ef1790]: RECV: USER 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 32 0[ef1790]: RECV: LOGIN-DELAY 10 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 32 0[ef1790]: RECV: PIPELINING 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 32 0[ef1790]: RECV: UIDL 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 32 0[ef1790]: RECV: IMPLEMENTATION Courier Mail Server 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 32 0[ef1790]: RECV: . 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 33 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 35 0[ef1790]: SEND: AUTH LOGIN 0[ef1790]: Entering NET_ProcessPop3 16 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 3 0[ef1790]: RECV: + VXNlcm5hbWU6 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 36 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 5 0[ef1790]: SEND: anVzdC50ZXN0aW5nQGV4YW1wbGUubmV0DQo= 0[ef1790]: Entering NET_ProcessPop3 16 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 3 0[ef1790]: RECV: + UGFzc3dvcmQ6 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 34 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 6 0[ef1790]: Logging suppressed for this command (it probably contained authentication information) 0[ef1790]: Entering NET_ProcessPop3 16 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 3 0[ef1790]: RECV: +OK logged in. 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 34 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 7 0[ef1790]: SEND: STAT 0[ef1790]: Entering NET_ProcessPop3 9 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 3 0[ef1790]: RECV: +OK 0 0 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 8 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 22 0[ef1790]: SEND: QUIT 0[ef1790]: Entering NET_ProcessPop3 14 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 3 0[ef1790]: RECV: +OK Bye-bye. 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 43 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 23 0[ef1790]: POP3: Entering state: 25
Rich logging using Gloda
The global database (gloda) has been enhanced to support additional logging and context information. Logsploder is a XULRunner application that supports using these features. See logsploder, circa a year+ ago for more information. This functionality isn’t useful for most users, its intended mainly to support unit testing.
See also
- Connection errors — POP3
- Connection errors — SMTP
External links
Wikipedia articles (including links to RFCs):
- Post Office Protocol (POP3)
- Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP)
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Protocol guides (they focus on the actual commands and which RFC applies to a specific protocol command):
- Post Office Protocol (POP3)
- Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
- List of registered CAPABILITY names for IMAP
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP)
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Sometimes its useful to compare session logs for another email client and Thunderbird.
- How to enable and interpret the Outlook Express Pop3.log File
- How to enable and interpret the Outlook Express Smtp.log File
Additional information on how the logging works:
- Thunderbird:Backend Hacking Guide For Newbies describes several frameworks used by Thunderbird, such as NSPR. NSPR performs the logging.
- IMAP — MozillaWiki helps you understand the calls to various methods that are logged in the IMAP log file. It has more than just a IMAP protocol trace.
- NSPR logging
- Web Site Quality Assurance Testing using Mozilla describes NSPR JavaScript, Cookie and HTTP logging in release builds.
- MozillaZine thread about complete list of protocols/modules for NSPR_LOG_MODULES
- Error Console. The simplest is to open the Thunderbird Error Console. You can open it from the menu Tools→Developer Tools→Error Console.
- OpenPGP log. Open menu Edit→Preferences→General, find the Config Editor. Add a new preference of the name temp.openpgp.logDirectory and set it to a string value, which must be the full name …
- Enigmail 2.2.x Add-on log. If you’re trying to analyze a problem in the migration process that is performed by the Enigmail 2.2.x Add-on, please set the additional preference extensions.enigmail.logDirectory — …
- RNP log. Advanced users may attempt to view internal error messages produced by the OpenPGP cryptographic engine that Thunderbird uses (the RNP library).
Error console can be shown using the shortcut Ctrl+Shift+J or via the Thunderbird tools menu under Developer Tools &aq Error Console.
Full
Answer
Where is the Thunderbird profile located?
Oct 28, 2017 · 1. To begin the Thunderbird in Safe mode, perform the following steps: If Thunderbird is not running: you can press & hold the Shift key and open Thunderbird in a safe mode. If Thunderbird is running: Go to the Help option from the Menu and choose Restart with Add-ons Disabled… option. After that, click on the Restart button from the dialog box 2.
How to fix Thunderbird not responding?
Mar 08, 2013 · Hi All, Does Thunderbird have an log somewhere? I am getting a pop up that informs me of an issue, but it disappears too fast for me to read.
Where is the Thunderbird folder in Linux?
Nov 01, 2013 · theme* of Thunderbird and it is located within the folder «extensions». But normally there is no chrome.manifest in the /%7B972ce4c6-7e08-4474-a285-3208198ce6fd%7D/ extension file. I have no…
Where can I find the Error Console?
Feb 02, 2021 · Restart Thunderbird. Please check something for me and then post info/results. Menu app icon > Options > General Scroll down to the bottom and click on ‘Config Editor’ button It will say beware In search type: »’resist»’ Look for …
How do I debug in Thunderbird?
Setting up Thunderbird All that needs to be done in Thunderbird is enabling the debugger server. This can be done using Tools from the Menu Bar (alt + Tools) and selecting Allow Remote Debugging . By default, a debugger server will be started on port 6000.
Does Thunderbird have a log file?
Turn Logging off in Mozilla Thunderbird Traffic logging is enabled only for the session you start from the command line. You do not have to turn it off.Feb 11, 2020
David E. Ross
Did you try looking at the Error Console? On the menu bar, go to [Tools
Todd and Margo Chester
On 03/08/2013 09:23 PM, David E. Ross wrote:
>> Does Thunderbird have an log somewhere? I am getting a pop
>> >up that informs me of an issue, but it disappears too fast
>> >for me to read. Nuts!
>> >
>> >Many thanks,
>> >-T
>> >
> Did you try looking at the Error Console? On the menu bar, go to [Tools
>> >Error Console].
Emails displaying wrong time
Ive been searching all over for a solution to this today and can find nothing new on this since the early 2000s. The emails displayed in Thunderbird are all displaying UTC and until today, it had the correct time (Central).
All Replies (7)
Windows 10 has the method of adjusting date time etc. Typically you would type in search ‘Date’ and select ‘Date & Time Settings’. Those setting I’m presuming are correct as computer is showing correct time.
What is the profile folder in Thunderbird?
The profile folder is the location where Mozilla Thunderbird keeps all data. This folder consists of address books, message-oriented data, and other settings required for Thunderbird configuration. However, Thunderbird’s single profile can keep single or more than single account details within RSS, news, mail etc.
How to find out if you have multiple Thunderbird accounts?
Click on the OK tab, the Windows explorer wizard will be investigated. Open Thunderbird within this Window then clicks on the Profiles option. If the multiple folders are showing within this tab then, it means you have Thunderbird multiple accounts within the system. And locate account which is required.
Popular Posts:
Q: What OS are you using ?
Q: What version of Thunderbird?
Q: What VPN provider?
Please post information on current setup.
- Help > Troubleshooting Information
- Do not select the checkbox that says ‘Include account names’.
- Click on on ‘Copy Text to clipboard’
- Paste the info into this forum question.
re :all of a sudden it stopped working this morning.
Q: Did you get any updates for Thunderbird or Anti-Virus etc?
When you start Thunderbird, what does it say in the bottom Status bar about connecting to server?
Q: Do you get any error messages ?
If yes, post image or state word for word what error you get.
- Tools > Developer Tools > Error console
- Click on the ‘Bin’ icon to clear.
- Exit Error console
- Exit Thunderbird
- STart Thunderbird
- open ‘error console’ again
Q: What does it contain ? Post image.
If you are using it at home, this could be a VPN issue.
Perform Test: Restart computer in ‘Safe Mode with Networking’ and then start Thunderbird.
Q: What was the result of the test?
If this works ok then you know the issue is possibly with the Anti-Virus.
As the Anti-virus may also control the Firewall, check the Firewall is not blocking ports.
If an update in Thunderbird occured, it is possible the Firewall thinks this is a different program. The Firewall should list Thunderbird as an allowed program.
TEST Firewall settings:
- Exit Thunderbird.
- Access Firewall.
- If Thunderbird is not listed then add to list.
- If it is already listed and allowed, then block/remove, ok it. Access Firewall again and allow Thunderbird and ok it.
This is just to ensure, Firewall is allowing current Thunderbird.
Start Thunderbird.
Q: What was the result of the test?
It is also important to make sure the VPN provider is also not blocking the ports you need to access the mail server.
With the introduction of the rewritten mail send there has been a huge
uptick in the number of folk having issues sending mail from
Thunderbird. The changes have also brought with them a new way of
logging the sending of mail in Thunderbird to provide diagnostic
information.
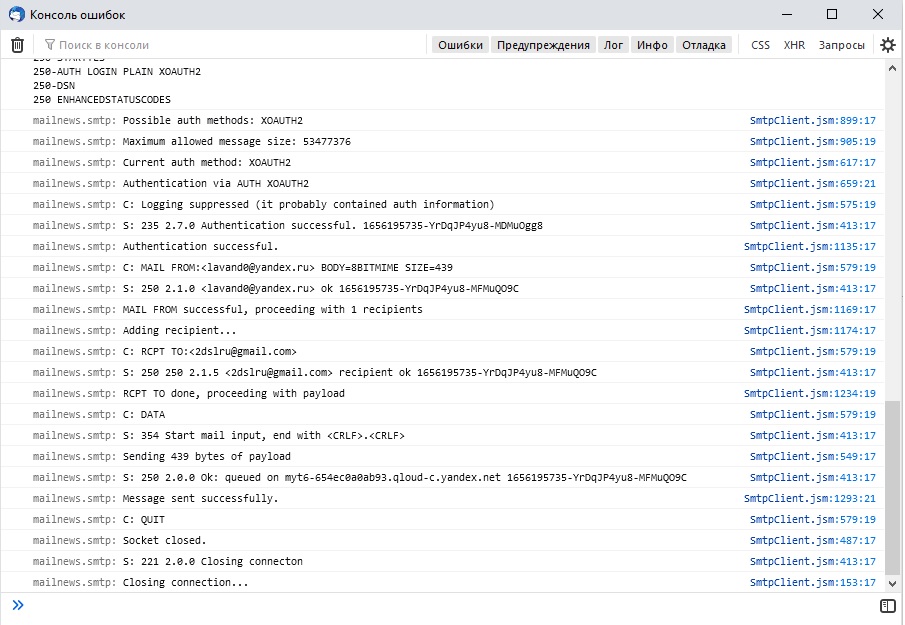
Logging is now done using the error console (Ctrl+Shift+J) in the
developer tools, but for this to occur you need to enable logging using
the config editor. Modify/set the preference mailnews.smtp.loglevel to All using the linked config editor instructions
Now open the Error Console and clear any existing entries by clicking on the trash icon.
Send a mail, debug logs should show up in the Console tab looking something like what is shown below.
If you have been asked to supply a log, or are seeking support somewhere with failures in sending then the following will provide a text file with the log in it.
Right click the console/log window and select all from the menu.
Right click again and select the rather oddly named «copy message»
Open windows notepad.(Windows key+R type notepad and press enter)
Save the file to your documents and either copy and paste or upload the file to provide the log to others. Be aware that the From and To addresses in the email are in the log you are sharing.
—-ooo00O00ooo—-
This part will certainly not work in versions after 91.
Again using the config editor set the preference mailnews.smtp.jsmodule to false. This will invoke the old mail sending code that has been replaced and already removed from Thunderbird from V93 onwards. This will allow the diagnosis of the problems to ensure it is the new send code that is at issue. It will also allow a few months of using the old code while bugs are fixed. Please file bug in bugzilla if you identify a bug in the new code.
Содержание
- Mozilla Thunderbird не отправляет сообщения
- Не приходят сообщения в Mozilla Thunderbird
- Не работают ссылки в сообщениях
Пользователи Mozilla Thunderbird иногда сталкиваются с неполадками, устранение которых не всегда имеет очевидные пути решения. Ошибки Mozilla Thunderbird возникают по ряду факторов, не всегда обусловленных действиями пользователя. В этой инструкции рассмотрим наиболее известные из них.
В случае, если возникает ошибка отправления сообщения Mozilla Thunderbird, в первую очередь следует проверить настройки SMTP для исходящей корреспонденции. Выберите учетную запись, которая не работает, кликните на ней правой кнопкой мыши и выберите пункты «Параметры» — «Сервер исходящей почты». Убедитесь, что параметры сервера, указанные в нижней части панели, совпадают с настройками провайдера, предоставляющего услугу.
Узнать актуальные настройки сервера можно на сайте https://support.mozilla.org/ru/ в соответствующем разделе.
Если там информации нет, ее можно найти на официальном сайте почтового провайдера – как правило, в разделе поддержки пользователей.
Убедитесь, что используется корректный SMTP-сервер. Кликните по кнопке главного меню, затем выберите «Настройки» — «Параметры учетной записи».
Важно помнить, что службы одного провайдера не отправляют корреспонденцию другого – например, SMTP-сервер Яндекса не работает с почтой Gmail и наоборот.
Проверьте настройки файервола, сетевого экрана или антивирусного ПО – они могут запретить Mozilla Thunderbird доступ в интернет. Отключите на короткое время всю защиту и попробуйте отправить тестовое письмо.
Уточните, вдруг Mozilla Thunderbird не работает из-за блокировок на стороне вашего интернет-провайдера. Известно, что многие провайдеры в целях безопасности блокируют 25-й порт, поэтому приходится использовать другие. Информацию о блокировках можно уточнить в техподдержке провайдера.
Если перечисленные методы не помогают, попробуйте удалить пароль SMTP и поменять его на другой. Не забудьте установить такой же пароль в настройках почтового ящика.
Не приходят сообщения в Mozilla Thunderbird
Когда возникают ошибки Mozilla Thunderbird с получением корреспонденции, следует выполнить все вышеперечисленное. Как правило, в большинстве случаев эти методы работают. Однако если проблему решить не удалось, рекомендуется предпринять следующие шаги:
- Проверить наличие и работоспособность интернет-соединения – проблема может быть на стороне провайдера;
- Если веб-интерфейс провайдера электронной почты работает корректно, неполадки связаны с неправильными настройками Mozilla Thunderbird;
- Убедитесь, что пароль учетной записи провайдера почты не изменен вами или посторонними;
- Если Mozilla Thunderbird недавно обновлялась, доступ может быть запрещен антивирусом или брандмауером.
Если вы получаете не всю корреспонденцию, а по пути где-то теряются важные письма, проверьте настройки антиспам-фильтров вашего почтового провайдера. Возможно, почтовые службы попросту не пропускают такие сообщения из-за содержащихся в них ссылок или вложений определенного формата. Кроме того, проверьте настройку антиспама в самом Mozilla Thunderbird, особенно если вы создавали собственные дополнительные фильтры или блокировали некоторых респондентов.
Не работают ссылки в сообщениях
В отличие от некоторых аналогичных программ, Mozilla Thunderbird вставляет при создании сообщений кликабельных ссылок, по которым можно перейти. При вставке ссылки она будет оформлена соответственно (то есть выделена цветом и подчеркнута), но при клике по ней ничего не произойдет. При наборе ссылки в теле письма она появляется в виде обычного неформатированного текста. Такое решение принято разработчиками Mozilla Thunderbird специально из-за особенностей редактирования ссылок. Активируются они только после отправки сообщения или сохранения его в черновиках.
При клике на полученную ссылку она должна автоматически открываться в браузере. Если этого не происходит, проверьте, установлен ли на вашей ОС браузер по молчанию. Как найти эту информацию на примере Windows 7.
Перейти по пути «Пуск» — «Панель управления» — «Программы по умолчанию».
Нажать кнопку «Задание программ по умолчанию».
Проверить в списке, какой из браузеров используется по умолчанию (и используется ли вообще).
Если этот метод не помогает, следует проверить, не являются ли причиной такой ошибки Mozilla Thunderbird установленные плагины. Для этого необходимо запустить почтовый клиент в безопасном режиме (перезапустите и удерживайте Shift при старте приложения). В появившемся окне установите флажок «Отключить все дополнения».
Если в безопасном режиме ссылки открываются, а в обычном нет, корректно не работает Mozilla Thunderbird из-за одного из дополнений. Осталось определить, из-за какого именно. Для этого можно отключать их по очереди в панели управления дополнениями, проверяя работоспособность ссылок.
Thunderbird 24.2.0 has a -mail command-line parameter, with which a specific mail can be opened from the command line:
$ thunderbird --help
-mail <URL> Open the message specified by this URL.
I know that one can use this function to open a specific email by an imap:// URI, but I would like to be able to open a specific mail by its unique Message-ID, no matter which folder contains it. Is this possible, and if so, what does the URI look like?
The thunderlink add-on ( https://addons.mozilla.org/en-us/thunderbird/addon/thunderlink/ ) can create message-id based links to emails and then open these with the -thunderlink parameter, but I would still like to know if this can be done with just the -mail parameter.
asked Jan 15, 2014 at 8:10
2
Update 2021-03-18: The bug mentioned below has been fixed with Thunderbird version 78.8.1. No adjustments are necessary to open mails from the command line using thunderbird.exe -mail <URL>.
Opening messages with the -mail command line parameter is still possible with a current Thunderbird version (tested on Windows 10 with version 78.6.0, 32-bit).
However, this requires a small change of the module MailNewsCommandLineHandler.jsm, because otherwise a getter-only error occurs when calling the -mail command. The error can be traced via the Thunderbird error console (see below).
Adjusting the module:
-
Copy the file
c:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Thunderbirdomni.jainto a temporary directory, rename the file toomni.zipand unpack it. -
Open MailNewsCommandLineHandler.jsm, insert
set _messenger(value) { return value; },after line 22 and save the file.
-
Repack all files using the following parameters:
zip.exe -0DXqr omni.ja *. Rename the original file toomni.ja.bakand copy the repacked file toc:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Thunderbird. -
Messages can then be opened using the following command lines:
thunderbird.exe -mail "mailbox-message://<folderLocation>#<messageKey>" (for local folders) thunderbird.exe -mail "imap-message://<folderLocation>#<messageKey>" (for IMAP folders)
Finding the right URL:
-
Error console: Open TB, select a message and open the error console (Ctrl + Shift + J). Enter the line
var hdr = gFolderDisplay.selectedMessage; alert(hdr.folder.getUriForMsg(hdr));and press enter. This will open a window with the URL for the selected message.
-
SQLite database: If you plan to build your own search tool (e.g. by writing a Python plugin for the Wox desktop launcher), it is perhaps best to create the URLs dynamically.
The Thunderbird database can be found under
%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfiles<profile>global-messages-db.sqlite. The tables messagesText_content, messages and folderLocations contain all information needed to assemble the URL strings.A simple Python script that can be used to generate the URLs might look something like this:
import sqlite3 import re import sys import os import json # Replace db_path with your profile location # (Help > Troubleshooting Information > Open Folder) db_path = r"%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfilesxxxxxxxx.default" con = sqlite3.connect(os.path.join(db_path, "global-messages-db.sqlite")) cursor = con.cursor() query = """ SELECT messagesText_content.*, strftime('%Y-%m-%d, %H:%M', DATETIME(messages.date/1000000, "unixepoch", "localtime")), messages.folderID, messages.messageKey FROM messagesText_content JOIN messages ON messages.id=messagesText_content.docid WHERE messagesText_content.c3author NOT LIKE "%daemon%" OR messagesText_content.c3author NOT LIKE "%DAEMON%" ORDER BY messages.date DESC """ def get_messages(): messages = [] cursor.execute(query) for i in cursor: messages.append({ "text": i[1] if i[1] else "", "subject": i[2], "attachments": f'attach:{i[3]}' if i[3] else "", "sender": i[4], "receiver": i[5], "date": i[6], "folder_id": i[7], "message_key": i[8] }) return messages def get_folders(): cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM folderLocations") return {i[0]: i[1:] for i in cursor.fetchall()} def collect_urls(terms): r1 = "(mailbox|imap)(?=://)" r2 = "1-message" messages = get_messages() folders = get_folders() results = {} for msg in messages: msg_str = str(msg.values()).lower() if all(i.lower() in msg_str for i in terms): folder = folders.get(msg["folder_id"])[0] url = re.sub(r1, r2, folder) url = f'{url}#{msg["message_key"]}' msg["text"] = msg["text"][:50] results.update({url: msg}) return json.dumps( results, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False ) if __name__ == "__main__": if len(sys.argv) > 1: print(collect_urls(sys.argv[1:]))Just use it like so:
<C:>python collect_urls.py search terms test message { "imap-message://a%40b.cd@imap.provider.com/INBOX#28649": { "text": "Test message contains search terms", "subject": "Test message", "attachments": "", "sender": "John Doe <e@f.gh>", "receiver": "i@j.kl", "date": "2022-10-02, 14:20", "folder_id": 607, "message_key": 28649 } }
answered Jan 2, 2021 at 23:40
4
… for anyone still searching for a solution…
The following command worked for me (thunderbird 102.6.1):
thunderbird mid:<the message ID>
To make this nice and easy:
- make sure the «thunderbird» command is in PATH (e.g. you can execute it in a terminal)
- install copy message ID AddOn
- in the preferences add the following prefix:
thunderbird mid:
(make sure that there are no spaces before and after!) - open an email and click the
Copy Message IDbutton - run the copied command in a terminal to open the mail
answered Jan 10 at 16:11
Thunderbird 24.2.0 has a -mail command-line parameter, with which a specific mail can be opened from the command line:
$ thunderbird --help
-mail <URL> Open the message specified by this URL.
I know that one can use this function to open a specific email by an imap:// URI, but I would like to be able to open a specific mail by its unique Message-ID, no matter which folder contains it. Is this possible, and if so, what does the URI look like?
The thunderlink add-on ( https://addons.mozilla.org/en-us/thunderbird/addon/thunderlink/ ) can create message-id based links to emails and then open these with the -thunderlink parameter, but I would still like to know if this can be done with just the -mail parameter.
asked Jan 15, 2014 at 8:10
2
Update 2021-03-18: The bug mentioned below has been fixed with Thunderbird version 78.8.1. No adjustments are necessary to open mails from the command line using thunderbird.exe -mail <URL>.
Opening messages with the -mail command line parameter is still possible with a current Thunderbird version (tested on Windows 10 with version 78.6.0, 32-bit).
However, this requires a small change of the module MailNewsCommandLineHandler.jsm, because otherwise a getter-only error occurs when calling the -mail command. The error can be traced via the Thunderbird error console (see below).
Adjusting the module:
-
Copy the file
c:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Thunderbirdomni.jainto a temporary directory, rename the file toomni.zipand unpack it. -
Open MailNewsCommandLineHandler.jsm, insert
set _messenger(value) { return value; },after line 22 and save the file.
-
Repack all files using the following parameters:
zip.exe -0DXqr omni.ja *. Rename the original file toomni.ja.bakand copy the repacked file toc:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Thunderbird. -
Messages can then be opened using the following command lines:
thunderbird.exe -mail "mailbox-message://<folderLocation>#<messageKey>" (for local folders) thunderbird.exe -mail "imap-message://<folderLocation>#<messageKey>" (for IMAP folders)
Finding the right URL:
-
Error console: Open TB, select a message and open the error console (Ctrl + Shift + J). Enter the line
var hdr = gFolderDisplay.selectedMessage; alert(hdr.folder.getUriForMsg(hdr));and press enter. This will open a window with the URL for the selected message.
-
SQLite database: If you plan to build your own search tool (e.g. by writing a Python plugin for the Wox desktop launcher), it is perhaps best to create the URLs dynamically.
The Thunderbird database can be found under
%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfiles<profile>global-messages-db.sqlite. The tables messagesText_content, messages and folderLocations contain all information needed to assemble the URL strings.A simple Python script that can be used to generate the URLs might look something like this:
import sqlite3 import re import sys import os import json # Replace db_path with your profile location # (Help > Troubleshooting Information > Open Folder) db_path = r"%APPDATA%ThunderbirdProfilesxxxxxxxx.default" con = sqlite3.connect(os.path.join(db_path, "global-messages-db.sqlite")) cursor = con.cursor() query = """ SELECT messagesText_content.*, strftime('%Y-%m-%d, %H:%M', DATETIME(messages.date/1000000, "unixepoch", "localtime")), messages.folderID, messages.messageKey FROM messagesText_content JOIN messages ON messages.id=messagesText_content.docid WHERE messagesText_content.c3author NOT LIKE "%daemon%" OR messagesText_content.c3author NOT LIKE "%DAEMON%" ORDER BY messages.date DESC """ def get_messages(): messages = [] cursor.execute(query) for i in cursor: messages.append({ "text": i[1] if i[1] else "", "subject": i[2], "attachments": f'attach:{i[3]}' if i[3] else "", "sender": i[4], "receiver": i[5], "date": i[6], "folder_id": i[7], "message_key": i[8] }) return messages def get_folders(): cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM folderLocations") return {i[0]: i[1:] for i in cursor.fetchall()} def collect_urls(terms): r1 = "(mailbox|imap)(?=://)" r2 = "1-message" messages = get_messages() folders = get_folders() results = {} for msg in messages: msg_str = str(msg.values()).lower() if all(i.lower() in msg_str for i in terms): folder = folders.get(msg["folder_id"])[0] url = re.sub(r1, r2, folder) url = f'{url}#{msg["message_key"]}' msg["text"] = msg["text"][:50] results.update({url: msg}) return json.dumps( results, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False ) if __name__ == "__main__": if len(sys.argv) > 1: print(collect_urls(sys.argv[1:]))Just use it like so:
<C:>python collect_urls.py search terms test message { "imap-message://a%40b.cd@imap.provider.com/INBOX#28649": { "text": "Test message contains search terms", "subject": "Test message", "attachments": "", "sender": "John Doe <e@f.gh>", "receiver": "i@j.kl", "date": "2022-10-02, 14:20", "folder_id": 607, "message_key": 28649 } }
answered Jan 2, 2021 at 23:40
4
… for anyone still searching for a solution…
The following command worked for me (thunderbird 102.6.1):
thunderbird mid:<the message ID>
To make this nice and easy:
- make sure the «thunderbird» command is in PATH (e.g. you can execute it in a terminal)
- install copy message ID AddOn
- in the preferences add the following prefix:
thunderbird mid:
(make sure that there are no spaces before and after!) - open an email and click the
Copy Message IDbutton - run the copied command in a terminal to open the mail
answered Jan 10 at 16:11
Вопрос:
Я работаю над расширением Thunderbird и, к сожалению, не могу разобраться в том, что все еще актуально, а что нет. Там много материала в Интернете, но большинство из них больше не применимо к недавнему Thunderbird.
-
Как минимум, мне нужен способ просмотра сообщений журнала с расширением, поэтому я вижу, что работает, а что нет. В идеале, мне нужна полная консоль отладки. Существует ссылка на Stackoverflow на Thunderbird Developer Tools, но, похоже, нет способа загрузить их.
-
Я также хотел бы иметь возможность запускать Javascript, который может ссылаться на мое расширение через консоль. Когда я пробую это через консоль Thunderbird, я получаю сообщения об ошибках. Я получаю это даже при использовании других расширений для людей, поэтому я должен предположить, что расширения не входят в область консоли
Как я могу получить видимость и взаимодействие с новым расширением Thunderbird?
Лучший ответ:
Содержание
- протоколирование сообщений
- Инструменты разработчика Thunderbird
- выполнить Javascript, который может ссылаться на мое расширение
протоколирование сообщений
Как описано в https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Debugging_JavaScript, в Gecko есть 3 разных консоли. Наиболее доступным в Thunderbird является Консоль ошибок. Вы можете писать сообщения через nsIConsoleService. Если вы не против, чтобы сообщения журнала отображались как ошибка, вы также можете просто использовать Components.utils.reportError().
Другой способ – войти в (собственную) консоль, из которой запускается Thunderbird. Это делается через dump().
Самый новый способ записи сообщений – это Log.jsm. Это очень хорошая обложка вокруг различных методов ведения журнала, и мой предпочтительный способ регистрации сообщений в Thunderbird.
Инструменты разработчика Thunderbird
Поскольку вы не привязаны к ссылке, я не уверен на 100%, но я думаю, что вы имеете в виду возможность удаленно отлаживать Thunderbird через Firefox. Вам не нужно скачивать что-либо, чтобы использовать это, оно уже интегрировано в Thunderbird.
выполнить Javascript, который может ссылаться на мое расширение
Отладка Thunderbird удаленно через Firefox дает также доступ к консоли и Scratchpad в Инструментах разработчика. Оба должны иметь доступ к надстройке.
Вы также можете посмотреть Tiny JavaScript Debugger. Он также позволяет выполнять произвольный код во время отладки.
This article is about Thunderbird’s profile folder. See also Profile folder — Firefox and Profile folder — SeaMonkey.
Thunderbird stores all personal data such as messages, address books and configuration settings in an OS folder called the profile. A profile can contain one or more account for mail, RSS, news, etc. The first time you start Thunderbird it will automatically create a profile in a default location if it does not already exist. You can also use the Profile Manager to create a profile wherever you want (but don’t create it in the Thunderbird program directory) or to delete or rename one.
It is a good idea to periodically backup your profile to a safe location. Thunderbird doesn’t delete a profile when uninstalling, upgrading or re-installing (it is stored in a directory outside of your program directory), but to avoid any risk of accidentally affecting or deleting it as a side effect of an update it is a good idea to back it up before taking such actions.
Thunderbird does not let you switch profiles without exiting, unlike Outlook Expresses identities. However, the profile switcher extension will let you switch profiles.
Contents
- 1 Finding your profile
- 1.1 Windows 2000 and XP
- 1.2 Windows Vista, 7, 8.1 and 10
- 1.3 Linux and Unix
- 1.4 Mac OS X
- 1.5 Other methods of finding a profile
- 1.5.1 Searching for a file
- 1.5.2 Using the Error Console
- 2 Profiles.ini
- 3 Files and folders in the profile
- 3.1 Folders
- 3.2 Files
- 3.3 Files without specific names
- 4 Portable Thunderbird
- 5 Miscellaneous information
- 6 See also
- 7 External links
Finding your profile
Profile folders default to a standard location but are named randomly for additional security. You can set a custom location using other methods mentioned below.
The installation directory includes a folder named «profile» (for example, C:Program FilesMozilla Thunderbirddefaultsprofile on Windows), but this folder contains program defaults, not your user profile data. On Windows 2000/XP/Vista and on Linux, the folder containing your user profile data is hidden by default and you will need to show hidden files and folders to navigate to the profile folder.
The easiest way to find your profile is to click on the «Show Folder» button in Help -> Troubleshooting Information. That launches windows explorer (or the equivalent file manager for your operating system) with the profile folder selected. That feature was added in Thunderbird 5.0.
Windows 2000 and XP
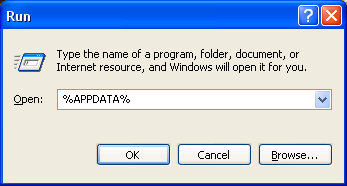
- Choose Start → Run
- Type in %APPDATA%
- Press OK. A Windows Explorer window will appear.
- In the Windows Explorer window, choose Thunderbird → Profiles. Each folder in this folder is a profile on your computer.
You can also navigate directly to your profile folder at the following path:
- C:Documents and Settings<Windows user name>Application DataThunderbirdProfiles<Profile name>
The Application Data folder is a hidden folder; to show hidden folders, open Windows Explorer and choose «Tools → Folder Options → View (tab) → Show hidden files and folders».
Windows Vista, 7, 8.1 and 10

- Open the Windows Start menu
- In the the «Start Search» box, type in %APPDATA% [1]
- Click the «Roaming» item that appears on the menu.
- In the Windows Explorer window that opens, choose Thunderbird → Profiles. Each folder in this folder is a profile on your computer.
You can also navigate directly to your profile folder at the following path:
- C:Users<Windows user name>AppDataRoamingThunderbirdProfiles<Profile name>
…or by using Thunderbird menu path Help->Troubleshooting information->click on the «Show Folder» button.
The AppData folder is folder is a hidden folder; to show hidden folders, open a Windows Explorer window and choose «Organize → Folder and Search Options → Folder Options → View (tab) → Show hidden files and folders».
Linux and Unix
Profile folders are located here:
- ~/.thunderbird/<Profile name>/
However, if you’re using a third party build from Debian or Ubuntu, those builds store your profile folder here:
- ~/.mozilla-thunderbird<Profile name>.
Both are hidden folders. See this article for more information. To show hidden files in Nautilus (Gnome desktop’s default file browser), choose «View -> Show Hidden Files».
Mac OS X
Profile folders are located here:
- ~/Library/Thunderbird/Profiles/<Profile name>/
The tilde character (~) refers to the current user’s Home folder, so ~/Library is the /Macintosh HD/Users/<username>/Library folder.
Other methods of finding a profile
Searching for a file
Every Thunderbird (or SeaMonkey) profile will have an «abook.mab» file, even if you’ve configured it to store messages outside of the profile. You could find a profile by doing a file search for that file. However, you need to include hidden files and folders in the search:
- Windows 2000: In Windows Explorer (or My Computer) choose Tools → Folder Options → View (tab) → Show hidden files and folders
- Windows XP: Click «Start → Search». In the Search Results window, scroll down and click «More advanced options». Check the boxes, «Search system folders», «Search hidden files and folders» and «Search subfolders»
- Windows Vista: From the Windows Start menu, click «Search». In the «Advanced Search» area, select «Include non-indexed, hidden, and system files (might be slow)»
Using the Error Console
You can also use Thunderbird to find the location of whatever profile it is using. In Thunderbird, go to «Tools -> Error Console» and then copy and paste the following code in the field near the top of the Error Console and click on the Evaluate button. It is one very long line ending in path — make sure that you get all of it:
Components.classes["@mozilla.org/file/directory_service;1"].getService( Components.interfaces.nsIProperties).get("ProfD", Components.interfaces.nsIFile).path
The console should display the location of the profile that is currently in use. If you don’t see it, select «All» in the toolbar.
Profiles.ini
Thunderbird uses the profiles.ini file to find the location of your profiles, and to determine which profile is the default profile. If you’re using Windows the file is located in the parent of the «Profiles» folder. It can be edited to move your profile. If it’s deleted, a new profiles.ini file will be created and a new default profile folder created when Thunderbird starts.
This file is the reason why you can’t just copy a profile into the «profiles» folder and have Thunderbird discover it.
Files and folders in the profile
Folders
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Attachments | Used when attachments aren’t stored in the folder or the desktop. It may not exist as the settings for where attachments should be stored are frequently ignored. |
| calendar-data | Used by the Lightning extension. |
| Cache | Used by the optional disk cache added in Thunderbird 3.0 |
| crashes | |
| chrome | Optional. Mainly used for the optional userChrome.css and userContent.css files. |
| extensions | Installed extensions and themes. |
| ImapMail | Mail from IMAP accounts. |
| lwtheme | Another directory used by personas (light weight themes). |
| Contains subfolders with: — POP accounts and pop mail storage. They’re normally named after the mail server so if you had a Gmail POP account it would use a pop.gmail.com subdirectory — Local Folders mail storage (including Global Inbox) — Feeds or News & Blogs for RSS subscriptions and feeds — smart mailboxes for Unified Folders/Smart Folders (virtual folders). It’s typically called «smart mailboxes -1» |
|
| minidumps | Dump files (*.dmp) created by the crash reporter |
| News | News accounts and newsgroups |
| OfflineCache | «app cache» according to the More About add-on.. |
| safebrowsing | |
| personas | Stores light weight themes (personas). Used by the Personas Plus add-on. It requires Thunderbird 3.0 or later |
| searchplugins | Optional. Used if you added additional search provider such as DuckDuckGo to OpenSearch. |
| startupCache | Precompiled startup cache stored in a startupCache.4.little file. Not clear what it caches other than system font data but some Firefox add-on developers delete the equivalent file in a Firefox profile while developing add-ons. [2][3][4] |
| TestPilotExperimentFiles | Obsolete. Used by the optional TestPilot add-on. It runs user studies on how Thunderbird is used, and is used to submit answers to surveys. It requires Thunderbird 8.0 or later. |
| WebmailData | Obsolete. Used by the Webmail extension. |
All of the messages for an account are stored in a subdirectory named after the mail server. For example if you have a Gmail POP account it would create a pop.gmail.com subdirectory in Mail. Your messages would be stored in text files with names of the folders shown in Thunderbird and with no file extension called mbox files. For example, the inbox folder would be called «Inbox.». There would also be a inbox.msf file (a index file, it doesn’t have any messages) and there might be a inbox.sbd subdirectory. The .sbd subdirectories are used to store the folders in a hierarchy, as there is no master list describing how the folders should be organized.
If you use a add-on to make a webmail account emulate a POP account the mail server is typically 127.0.0.1 (or localhost). If you have more than one account with the same mail server Thunderbird adds a suffix. So your second yahoo webmail account might be stored in 127.0.0.1-1. The same thing occurs if you have multiple accounts with the same POP or IMAP servers, though thats less common.
Files
None of these files should be read-only. If they are that might be a side effect of dragging and dropping or backing up files to removable media, and then using them to restore your profile.
See Files and folders in the profile — Thunderbird for a more complete list.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| abook.mab | Personal Address Book |
| cert8.db | Security certificates |
| cookies.txt | Cookies RSS_cookies_(Thunderbird) |
| downloads.rdf | Download history. Can be deleted to resolve slow downloads or program hangs (Bug 159107) |
| extensions.rdf | Installed extension information. It can be deleted to remove «ghost» entries from the extension list [5] and to resolve various other issues. |
| history.mab | Collected addresses |
| key3.db | Key database |
| localstore.rdf | Toolbar and window layout size/position settings. It can be deleted to resolve various issues. (Replaced by xulstore.json in latest versions of Thunderbird.) |
| mailviews.dat | Defines your current message view (you can customize it) |
| mimeTypes.rdf | Action to perform when downloading certain types of files. Can be deleted to reset download actions. |
| msgFilterRules.dat in ImapMail, Mail, News | Message filters |
| panacea.dat | Mail folder cache. Deleting it sometimes helps get rid of Phantom folders |
| popstate.dat in Mail | Keeps track of which messages have been downloaded and left on the POP3 server |
| prefs.js | All non-default preferences. See: Modify Thunderbird settings |
| secmod.db | Security module database |
| signons.sqlite | Encrypted saved passwords, requires key3.db to work. It used to use signons.txt or signons3.txt. |
| training.dat | Custom training for Junk Mail Controls |
| user.js (does not exist by default) |
User-set overriding preferences |
Files without specific names
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| *. in ImapMail, Mail, and News | Mbox files. They are text files that contain all of the messages for that folder. |
| *.mab other than abook.mab and history.mab | User-created or imported address books. |
| *.msf in ImapMail, Mail, and News | Index files for mail messages. Playback information for offline operations and incomplete online operations. |
Portable Thunderbird
Portable Thunderbird is a popular third party build of Thunderbird that is installed on a USB drive along with the profile. It’s designed for roaming users. The profile is not specified by a profiles.ini file on the boot disk, it’s always in a Dataprofile directory within the programs directory. It can have only one profile and doesn’t support the profile manager.
The profile has the same layout and files as Thunderbird.
Miscellaneous information
The channel-prefs.js file in the defaultspref directory in the Thunderbird program directory
specifies what update channel you are using. That determines what type of builds auto-update looks for. app.update.channel is normally set to «release». If you installed a beta that would set it to «beta». If you want to stop getting beta and release candidate updates change it to «release».
The application.ini file was added to the Thunderbird program directory with Thunderbird 3.0. It’s mainly used to control whether the migration assistant , crash reporter and extension manager are enabled.
The mailviews.dat file in the defaultsmessenger directory in the Thunderbird program directory specifies the default custom views. Views are selected using the View list box in the toolbar. You can add it to the toolbar by right clicking on the toolbar, selecting customize, dragging and dropping the View control to the toolbar and pressing the Done button.
Icons are normally available both as a resource within Thunderbird and at
chrome/icons/default/messengerWindow.ico in the program directory. If you don’t like the icon in the current version you could copy that file from an older version and modify the shortcut to point to it.
See also
- Empty folders
- Profile backup
- Protecting the contents of the profile
- Move a profile to Portable Thunderbird
- Moving_your_profile_folder
- Recovering a profile that suddenly disappeared
- Sharing a profile between Windows and Linux
- Starting Thunderbird with a specific profile
- Using a profile stored on a USB drive
External links
- Mozilla’s web page on how to manage Thunderbird profiles
- Bug report about profiles should be stored under «Mozilla/Thunderbird» not «Thunderbird»
- Postbox profile locations
У меня есть следующий код в моем загруженном файле дополнения Thunderbird main.js:
exports.main = function() {
console.log("abc");
};
Когда я запускаю этот код в FireFox в Add-on Builder, я получаю это сообщение, отображаемое в консоли ошибок FireFox:
info: vladp: abc
Однако, когда я запускаю свое расширение в Thunderbird, ничего не отображается. Я настроил среду разработки, как описано здесь: https://developer.mozilla.org/ en-US / docs / Setting_up_extension_development_environment
Как заставить его работать в консоли ошибок Thunderbird? Или есть какой-нибудь другой способ записать некоторую отладочную информацию, кроме «dump ()»?
ОБНОВЛЕНИЕ 1
Как было предложено speedball2001, я изменил свой код на:
exports.main = function() {
var Application = Components.classes["@mozilla.org/steel/application;1"].getService(Components.interfaces.steelIApplication);
Application.console.log('Bam!');
};
Однако, когда я запускаю Thunderbird, я получаю следующую ошибку в консоли ошибок:
Timestamp: 2013.05.22. 16:39:07
Error: myfirstext: An exception occurred.
ReferenceError: Components is not defined
resource://jid0-7yp22cmsooypei7nicamg3n0ha0-at-jetpack/myfirstext/lib/main.js 57
Как мне это исправить?
1 ответ
Лучший ответ
Thunderbird предоставляет интерфейс Application, который, помимо прочего, помогает вести журнал:
var {Cc, Ci} = require("chrome");
var Application = Cc["@mozilla.org/steel/application;1"]
.getService(Ci.steelIApplication);
Application.console.log('Bam!');
4
Martin Pecka
13 Мар 2014 в 00:24
Вначале было слово. Потом появились логи. Разработчики почтового клиента Thunderbird почему-то решили, что по умолчанию смотреть на работу протокола SMTP — вещь обычному пользователю не особо нужная и затолкали отображение логов далеко под корку настроек. К счастью, наша археологическая экспедиция нашла способ быстро это исправить.
Заходим в «Настройки» и скроллим в самый низ до кнопки «Редактор настроек»
Вбиваем в поиск параметр mailnews.smtp.loglevel и меняем его с помощью кнопки редактирования (карандаша) в конце строки на All (по умолчанию стоит warn)
После этого в консоли ошибок (ctrl+shift+j, либо через «Инструменты» -> «Инструменты разработчика») мы увидим логи SMTP при отправке сообщения:
SMTPThunderbirdСети
Todd and Margo Chester
unread,
Mar 9, 2013, 12:36:14 AM3/9/13
to
Hi All,
Does Thunderbird have an log somewhere? I am getting a pop
up that informs me of an issue, but it disappears too fast
for me to read. Nuts!
Jay Garcia
unread,
Mar 9, 2013, 3:23:41 AM3/9/13
to
Todd and Margo Chester
unread,
Mar 9, 2013, 4:30:52 AM3/9/13
to
On 03/08/2013 03:23 PM, Jay Garcia wrote:
> On 08.03.2013 14:36, Todd and Margo Chester wrote:
>
> — Original Message —
>
>> Hi All,
>>
>> Does Thunderbird have an log somewhere? I am getting a pop
>> up that informs me of an issue, but it disappears too fast
>> for me to read. Nuts!
>>
>> Many thanks,
>> -T
>
> No, but you can create your own protocol log:
>
> https://wiki.mozilla.org/MailNews:Logging#Windows
>
Thank you!
David E. Ross
unread,
Mar 9, 2013, 9:23:21 AM3/9/13
to
Todd and Margo Chester
unread,
Mar 9, 2013, 9:51:28 AM3/9/13
to
On 03/08/2013 09:23 PM, David E. Ross wrote:
>> Does Thunderbird have an log somewhere? I am getting a pop
>> >up that informs me of an issue, but it disappears too fast
>> >for me to read. Nuts!
>> >
>> >Many thanks,
>> >-T
>> >
> Did you try looking at the Error Console? On the menu bar, go to [Tools
>> >Error Console].
That is what I was looking for. Thank you!
-T
Axel Grude
unread,
Mar 12, 2013, 7:26:01 PM3/12/13
to
Make sure to install console2 for better filtering options (and to be able to copy
multiple messages to clipboard).
Содержание
- Mozilla Thunderbird не отправляет сообщения
- Не приходят сообщения в Mozilla Thunderbird
- Не работают ссылки в сообщениях
Пользователи Mozilla Thunderbird иногда сталкиваются с неполадками, устранение которых не всегда имеет очевидные пути решения. Ошибки Mozilla Thunderbird возникают по ряду факторов, не всегда обусловленных действиями пользователя. В этой инструкции рассмотрим наиболее известные из них.
В случае, если возникает ошибка отправления сообщения Mozilla Thunderbird, в первую очередь следует проверить настройки SMTP для исходящей корреспонденции. Выберите учетную запись, которая не работает, кликните на ней правой кнопкой мыши и выберите пункты «Параметры» — «Сервер исходящей почты». Убедитесь, что параметры сервера, указанные в нижней части панели, совпадают с настройками провайдера, предоставляющего услугу.
Узнать актуальные настройки сервера можно на сайте https://support.mozilla.org/ru/ в соответствующем разделе.
Если там информации нет, ее можно найти на официальном сайте почтового провайдера – как правило, в разделе поддержки пользователей.
Убедитесь, что используется корректный SMTP-сервер. Кликните по кнопке главного меню, затем выберите «Настройки» — «Параметры учетной записи».
Важно помнить, что службы одного провайдера не отправляют корреспонденцию другого – например, SMTP-сервер Яндекса не работает с почтой Gmail и наоборот.
Проверьте настройки файервола, сетевого экрана или антивирусного ПО – они могут запретить Mozilla Thunderbird доступ в интернет. Отключите на короткое время всю защиту и попробуйте отправить тестовое письмо.
Уточните, вдруг Mozilla Thunderbird не работает из-за блокировок на стороне вашего интернет-провайдера. Известно, что многие провайдеры в целях безопасности блокируют 25-й порт, поэтому приходится использовать другие. Информацию о блокировках можно уточнить в техподдержке провайдера.
Если перечисленные методы не помогают, попробуйте удалить пароль SMTP и поменять его на другой. Не забудьте установить такой же пароль в настройках почтового ящика.
Не приходят сообщения в Mozilla Thunderbird
Когда возникают ошибки Mozilla Thunderbird с получением корреспонденции, следует выполнить все вышеперечисленное. Как правило, в большинстве случаев эти методы работают. Однако если проблему решить не удалось, рекомендуется предпринять следующие шаги:
- Проверить наличие и работоспособность интернет-соединения – проблема может быть на стороне провайдера;
- Если веб-интерфейс провайдера электронной почты работает корректно, неполадки связаны с неправильными настройками Mozilla Thunderbird;
- Убедитесь, что пароль учетной записи провайдера почты не изменен вами или посторонними;
- Если Mozilla Thunderbird недавно обновлялась, доступ может быть запрещен антивирусом или брандмауером.
Если вы получаете не всю корреспонденцию, а по пути где-то теряются важные письма, проверьте настройки антиспам-фильтров вашего почтового провайдера. Возможно, почтовые службы попросту не пропускают такие сообщения из-за содержащихся в них ссылок или вложений определенного формата. Кроме того, проверьте настройку антиспама в самом Mozilla Thunderbird, особенно если вы создавали собственные дополнительные фильтры или блокировали некоторых респондентов.
Не работают ссылки в сообщениях
В отличие от некоторых аналогичных программ, Mozilla Thunderbird вставляет при создании сообщений кликабельных ссылок, по которым можно перейти. При вставке ссылки она будет оформлена соответственно (то есть выделена цветом и подчеркнута), но при клике по ней ничего не произойдет. При наборе ссылки в теле письма она появляется в виде обычного неформатированного текста. Такое решение принято разработчиками Mozilla Thunderbird специально из-за особенностей редактирования ссылок. Активируются они только после отправки сообщения или сохранения его в черновиках.
При клике на полученную ссылку она должна автоматически открываться в браузере. Если этого не происходит, проверьте, установлен ли на вашей ОС браузер по молчанию. Как найти эту информацию на примере Windows 7.
Перейти по пути «Пуск» — «Панель управления» — «Программы по умолчанию».
Нажать кнопку «Задание программ по умолчанию».
Проверить в списке, какой из браузеров используется по умолчанию (и используется ли вообще).
Если этот метод не помогает, следует проверить, не являются ли причиной такой ошибки Mozilla Thunderbird установленные плагины. Для этого необходимо запустить почтовый клиент в безопасном режиме (перезапустите и удерживайте Shift при старте приложения). В появившемся окне установите флажок «Отключить все дополнения».
Если в безопасном режиме ссылки открываются, а в обычном нет, корректно не работает Mozilla Thunderbird из-за одного из дополнений. Осталось определить, из-за какого именно. Для этого можно отключать их по очереди в панели управления дополнениями, проверяя работоспособность ссылок.
The Mozilla Crash Reporter sends your crash report to a collection system, which assigns a crash ID. You will want to post your crash ID(s) in your bug report or support request. Also, Thunderbird developers use this crash report to make future versions of Thunderbird crash less frequently. (The Mozilla Crash Reporter comes up because Thunderbird crashes; the reporter does not cause Thunderbird to crash.)
For suggestions on how to prevent Thunderbird from crashing, see Thunderbird Crashes.
Table of Contents
- 1 When Thunderbird crashes
- 2 Viewing crash reports
- 2.1 Viewing reports outside of Thunderbird
- 3 If you don’t get a crash report
When Thunderbird crashes
After Thunderbird crashes, the Mozilla Crash Reporter window should be displayed where you can supply additional information, then click Quit or Restart to submit the report. Please submit all crashes, including repeats, with your email address so developers can reach you if needed. Also, provide your crash report ID in your support and bug postings.
Tell Mozilla about this crash so they can fix it: If this box is checked, the Mozilla Crash Reporter will send crash data to Mozilla. Uncheck this box if you don’t want to send the report.
Details…: Shows some information that will be submitted with crash data. But don’t post «details» in support requests — support requests need your crash ID, which is created after submitting your crash report by enabling «Tell Mozilla …» and then clicking Quit or Restart.
Add a comment: Use this box to write details about what you were doing when Thunderbird crashed. Note: the comments you provide are public and can be read by anyone.
Allow Mozilla to contact me about this report: Check this box if you are willing to receive emails from Mozilla should they need more information from you about this crash, or have important information for you. Enter your email address in the next field. Note: Mozilla will not contact you automatically. They will contact you only if follow up is needed.
Enter your email address here: The email address to be used if you chose above to help our development staff get information and reproduce this crash.
Note: Your email address is NOT publicly viewable.
Quit Thunderbird: Submit the crash report and close the dialog, but don’t start Thunderbird.
Restart Thunderbird: Submit the crash report and close the dialog, and start Thunderbird.
If Thunderbird crashes again on startup, see Thunderbird Crashes for suggestions on how to prevent Thunderbird from crashing. Also, please submit all your crashes.
Viewing crash reports
Skip to Viewing reports outside of Thunderbird if you can’t start Thunderbird, or it crashes on startup.
If you are able to start Thunderbird, to view your crash reports:
- In Thunderbird, open More Troubleshooting Information from the menu, and scroll to the «Crash Reports» section.
- Crashes are listed by date and time.
- Successfully submitted crashes start with the characters «bp-«. In the screenshot below, the report ID is «bp-24b627a1-1416-4c09-a4ab-d7f502100331».
- Unsubmitted crashes do not start with «bp-«. Click the number to submit the crash report.
- Click on a Report ID to view the report.
- Please post the ‘bp-…’ crash report ID or full URL to the crash report in a bug report or support forum. (As a text string please, not a screenshot.)
If you don’t get a crash report, see If you don’t get a crash report described later in this article.
Viewing reports outside of Thunderbird
You can find crash information in the Crash Reports folder on your computer without starting Thunderbird.
- Press
+R on the keyboard. A Run dialog will open.
- In the Run dialog, type %APPDATA%\Thunderbird\Crash Reports\ and press Enter.
Crash reports are stored in ~/Library/Thunderbird/Crash Reports/ (show hidden folders, on Mac OS X 10.7 and above, by holding down the Option key while opening the Go menu in Finder and then selecting Library).
Crash reports are stored in ~/.thunderbird/Crash Reports/.
The folder contains two subfolders, pending and submitted:
- pending folder contains files for crashes that have not been received by the crash report database. There are two files for each crash, one is the crash dump, and one is the crash details. You must submit your crashes for developers to be able to view them. If you have not been submitting crashes, please reproduce your crash and when the crash reporter appears please be sure to submit the crash by chosing the restart or quit buttons.
- submitted folder contains reports that have been received by the crash report database where it can be viewed by a developer. Each file name is a crash ID starting with the characters «bp-«, and these IDs are what a developer may request when investigating your crash. If you are receiving help in a bug or support forum, please give them your crash report ID(s) as a text string, not a screenshot.
If you don’t get a crash report
If you don’t get a crash report either because crash reporter failed or it doesn’t work with your OS or distribution, you can get a stacktrace by using How to get a stacktrace for a bug report.
These fine people helped write this article:
Volunteer
Grow and share your expertise with others. Answer questions and improve our knowledge base.
Learn More
Вначале было слово. Потом появились логи. Разработчики почтового клиента Thunderbird почему-то решили, что по умолчанию смотреть на работу протокола SMTP — вещь обычному пользователю не особо нужная и затолкали отображение логов далеко под корку настроек. К счастью, наша археологическая экспедиция нашла способ быстро это исправить.
Заходим в «Настройки» и скроллим в самый низ до кнопки «Редактор настроек»
Вбиваем в поиск параметр mailnews.
После этого в консоли ошибок (ctrl+shift+j, либо через «Инструменты» -> «Инструменты разработчика») мы увидим логи SMTP при отправке сообщения:
SMTPThunderbirdСети