Компании, внедрившие продукты компании SAP потратили большое количество ресурсов на клиентскую доработку решений. Однако не привносят ли эти разработки дополнительные риски в ваши бизнес-процессы? Компания SAP гарантирует качество кода в своих приложениях благодаря ручному аудиту поставляемого кода и использованию самых современных механизмов статистического и динамического анализа своих продуктов на различные уязвимости.
Было проведено исследование в университете города Саарбрюккен (Германия), целью которого являлся анализ кодов продуктов SAP (решения по электронной коммерции) самыми современными инструментами статистического анализа. Выводы были таковы — качество кода достаточно высокое.
Программный код компании SAP проходит ручной и автоматизированный анализ, тысячи специальных тест-кейсов. Клиентский программный код зачастую не может быть так полно проанализирован, особенно в условиях сжатых сроков проектов, в которых приходится работать. Стоит задуматься о качестве клиентского кода в ваших системах.
Система SAP упрощает ведение бизнеса на системном уровне, а также проводит анализ и аналитику деятельности. Но если в программном коде Компании есть * ошибки SAP *, то они должны быть исправлены немедленно для правильной работы программы и, соответственно, бизнеса.
Важно понимать, что проверка авторизации пользователя (синоним безопасности SAP для многих предприятий) не поможет предотвратить использование такого рода ошибок, так как пользователь, использующий ошибки в коде, выходит за рамки полномочий, определённых системным администратором.
Рассмотрим ошибки, которые могут присутствовать в клиентском коде.
Инъекция кода
Оставленная возможность инъекции кода — одна из самых распространённых и самых опасных уязвимостей по классификации OWASP. Большинство широко известных уязвимостей, включая OpenSSL Heartbleed и взлом площадки Ebay связаны с непреднамеренно оставленной возможностью инъекции пользовательского ввода внутрь программы.
Опасность такого рода ошибок заключается в практически непредсказуемых результатах исполнения уязвимых программ. Результатом инъекции SQL кода может быть, как утечка паролей, так и полное удаление всех данных системы.
Дополнительная проблема, связанная с такими уязвимостями, заключается в сложности их поиска автоматизированными средствами. Поиск на основе правил и паттернов не даст положительного результата из-за большого количества ошибочно сформулированных предположений.
Единственным по-настоящему эффективным способом поиска ошибок может быть статический анализ потока данных, проступающего в программу. Статический анализ потока данных позволяет проследить, какие данные поступают в потенциально опасные точки предположения о наличии или отсутствии уязвимости инъекции кода.
Обход каталога
Другой опасной ошибкой программного кода является непреднамеренно оставленная возможность подмены данных ввода, которая позволяет обход каталога.
Атакующий, использующий такую уязвимость, получает возможность считывать или записывать данные, находящиеся вне предопределённого каталога. Таким образом, могут быть считаны критичные системные настройки или перезаписаны конфигурационные файлы, что может вывести систему из строя на достаточно долгий промежуток времени.
Возможны достаточно специфические варианты использования этой ошибки. Например, вызов оператора OPEN DATASET dset FILTER iv_filter, открывающего файл на чтение, в системе Unix поставляет данные из считываемого файла в предопределённый процесс, который может осуществлять непредусмотренные действия на уровне операционной системы.
Таким образом, некорректная конфигурация ОС и уязвимый код, не имеющие ошибок по отдельности, могут приводить к критическим последствиям работая совместно.
Ошибки авторизации
Руководствуются ли ваши программисты концепцией полномочий в разработке своих приложений? В соответствии с этой концепцией, доступ к любому функциональному блоку программы должен быть запрещён до тех пор, пока не определено обратное.
Исследуйте свой бизнес -потенциал: Откройте для себя нашего диапазона преобразующих курсов сегодня!
Раскрыть силу знаний с нашим разнообразным набором курсов, от оперативных закупок в S/4HANA до SEO Essentials. Повысьте свой опыт и успешны в своих деловых предприятиях.
Получите свой курс
К сожалению, на многих проектах, разграничение доступа происходит на уровне транзакций, что делает возможным комбинирование различных существующих полномочий с целью доступа к запрещённой информации. Например, использование оператора CALL TRANSACTION (который массово используется разработчиками) на проектах с разграничением доступа на уровне транзакций является небезопасным. Без указания WITH AUTHORITY-CHECK оператор CALL TRANSACTION позволяет переходить по любой другой транзакции.
Возможен также случай, когда проверка авторизации есть, но сделана она неправильно. Такие случаи также надо находить и исправлять.
Бэкдоры
До этого мы рассмотрели некоторые случаи уязвимостей, когда программисты совершили непреднамеренные ошибки, в результате чего код стал уязвимым. Однако, возможны также и случаи, когда программист намеренно изменяет ход исполнения программы для определённых пользователей («недокументированные возможности»), либо вообще не оставляет так называемый бэкдор, который позволяет обходить все проверки, выставленные системой.
Разработчик может делать бэкдор и без злонамеренных целей, как например получение полномочий SAP_ALL для более «эффективной» работы на проекте внедрения. Очевидно, что это не умаляет тех рисков, которые привносит наличие бэкдоров.
В сети существует большое количество примеров таких бэкдоров, которые могут быть просто скопированы и перенесены в продуктивную систему. Отловить наличие недокументированных возможностей и бэкдоров очень сложно, во-первых, из-за огромного количества клиентского кода, во-вторых из-за особенностей языка программирования SAP. ABAP позволяет исполнять код на лету и хранится в СУБД, то есть может быть запрятан очень и очень глубоко.
Существует несколько различных способов поиска уязвимостей в коде, наиболее совершенным из которых является статический анализ потока данных.
В SAP Netweaver AS присутствует модуль, реализующий анализ потока данных на наличие или отсутствие уязвимостей (Code Vulnerability Analysis). Есть сертифицированные партнёрские решения, позволяющие сканировать код приложений на наличие уязвимостей.
SAP Code Vulnerability Analysis (CVA) основан на инструменте Code Inspector, который уже много лет позволяет проверять клиентский код на наличие потенциально опасных конструкций, но в отличие от Code Inspector, использует в своей работе анализ потока данных. Наиболее целесообразным является использование CVA с первой же стадии проекта — сто стадии разработки (до переноса разработок далее по ландшафту), так как внесение исправлений позже (например, при продуктивной эксплуатации) является более сложным и затратным.
Внедрение CVA подразумевает не только поиск и исправление ошибок, но изменение самого подхода к стандартам разработки на предприятии.
Внесение любой новой разработки в продуктивную систему должно быть санкционировано экспертом, руководствующимся в своей работе самыми современными инструментами анализа разработок.
Одним из способов для поиска ошибок есть такой инструмент. Не всем известно о том, что SAP содержит более одного миллиона сообщений об ошибках. Можно использовать этот простой, а главное бесплатный инструмент, чтобы быстро найти любой код ошибки и сообщение SAP.
В специальное окно необходимо ввести код сообщения об ошибке SAP, например АА729, или ключевое слово, например, актив, чтобы найти все связанные сообщения об ошибках SAP.
Часто Задаваемые Вопросы
- Что означает «обход каталогов»?
- Это ошибка программирования SAP о том, что непреднамеренно оставляют входные подделки, чтобы разрешить прохождение каталога. Это может считывать настройки критических систем или перезаписать файлы конфигурации, которые могут снизить систему в течение довольно длительного периода времени.
If you have been working with SAP for more than a few weeks, you know that sooner or later, you will run into an error message. Maybe you tried to run a transaction and received an authorization error (saying that you are not authorized for this SAP transaction). Or maybe you tried to post a document and then received a warning message about missing or incorrect system settings or configuration.
The list of possible errors in SAP is truly endless, and it is always a frustrating experience when things in SAP don’t go as you want them to.
We developed an elegant tool to let you search for all SAP messages and keywords…but first, let’s take a look at the components that make up an SAP error message:
- The error message code
- The error message text
- The error message long text
SAP Error Message Code
An SAP message code typically looks like this: AA001 (or sometimes shown as AA 001). The first part is the Message Class, which indicates the functional area of the messages. It is a way to group messages by logical category. In our example, message class AA is used for all messages related to Asset Accounting.
Here are a few other SAP error message classes:
- class FH is used for General Ledger messages
- FC is used for FI Configuration messages
- FI is for Treasury Funds Management messages
- ME is for General Purchasing messages
- VS is used for SD Master Data messages
Following the message class is the actual message number (in our example: 001). Message numbers can range from 000 – 999.
Whenever you see a message in SAP and want to tell someone about it, always make sure to share both the message class and message number to identify the correct error.
There are about 16,000 different message classes in SAP S/4HANA – each of these classes can contain up to 1000 individual messages…that’s a lot of messages. I’ll let you do the math.
SAP Error Message Text
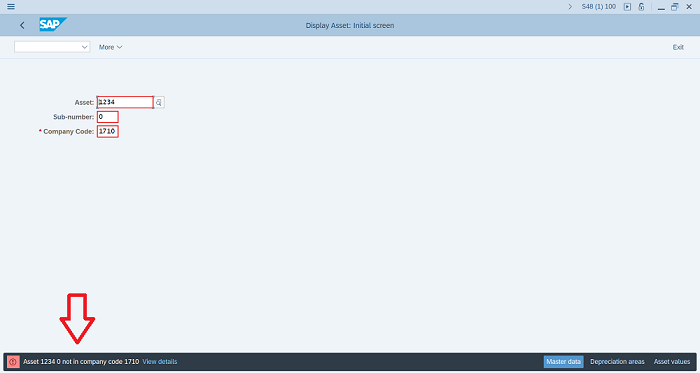
The message text is the (short) description of the issue and is displayed in the status bar in your SAP window. The message text can be up to 73 characters long. In our example, message AA001 says: Asset & & not in company code &.
The ampersand characters (&) are placeholders for the actual assets numbers and company code. In other words, the real message you would see in your SAP screen would say something like this: Asset 1000 0 not in company code 3000.
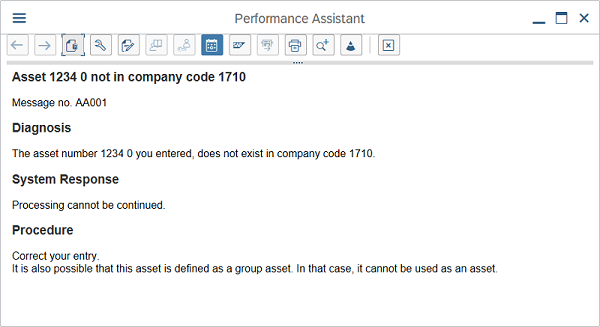
SAP Error Message Long Text
Unfortunately, these messages are not always self-explanatory – in fact, many times they can be quite cryptic. Luckily, most messages also have a Long Text, which you can display by double-clicking the error message. In our example, the long text says:
The Long Text typically includes useful information about how to fix the error. It might even include direct links to a configuration transaction (if specific configuration settings are missing, for example).
Now, one of our most popular blog articles is this one: Download all SAP transaction codes – a handy Excel list of all the available Tcodes in the SAP system. Thus, I thought I’ll create a similar tool to lookup all of SAP’s error messages.
How To Lookup An SAP Error Message
You can look up SAP error messages in the SAP system directly using transaction SE91 – however, this is considered a Basis / System Admin transaction and you might not have access to it. Therefore, we created our online lookup tool here:
Search SAP Error Messages
Lookup All SAP Error Messages
You can look up SAP error messages by message class, message number, or even keyword to find messages quickly.
By the way, do you know how many SAP error messages exist? Before I wrote this article, I had no idea either. Well, it turns out there are about 1 million error messages (in English) in the system!
I hope this tool will be useful for you! Please share this with your coworkers.
Cheers,
Thomas
Did you know that SAP contains over 1 million error messages?
You can use this easy and free tool to quickly look up any SAP error code and message. Simply enter an SAP error message code (i.e. AA729) or keyword (i.e. asset) to find all related SAP error messages.
How to search for SAP error messages
You can search using keywords (for example: asset, purchase order, accounting period), SAP error message codes (i.e. AA729, MM005, etc.) or just an SAP message class (i.e. AA, FI, MM, etc.).
Our algorithm will search through millions of SAP messages in your selected language. Once you find the message you are looking for, you can save it to your favorites (premium subscribers only) so that you don’t have to look for it again in the future.
Types of SAP messages
SAP messages fall into 3 different categories:
- Error messages (message type = E)
- Warnings (W)
- Informational (I) messages
An error message will prevent you from continuing your work — it is a hard stop and you need to fix the error before you can proceed. A warning message will stop your work, however, you can then bypass the warning by pressing the Enter key on your keyboard. That said, it is still good practice to investigate the cause of the warning message and address it. An information message will not stop your work and is truly just for informational purposes.
Click on this link to search all SAP messages.
The following list is taken from SAP Note 320991 – Error codes during logon (list). You might want to refer to https://itsiti.com/how-to-handle-the-error-codes-during-sap-logon/ for the resolution steps.
Explanation of the Error Codes/Return Codes
| Return Code | Error Message |
|---|---|
| 0 | No error – successful logon |
| 1 | Incorrect logon data (client / user name / password) |
| 2 | User account is locked |
| 3 | Incorrect logon data; for SAPGUI: connection closed |
| 4 | (Successful) Logon using emergency user SAP* (see SAP Note 2383) |
| 5 | Error when constructing the user buffer (==> possible follow-on error) |
| 6 | User exists only in the central user administration (CUA) |
| 7 | Invalid user type |
| 8 | User account outside validity period |
| 9 | SNC name and specified user/client do not match |
| 10 | Logon requires SNC (Secure Network Communication) |
| 11 | No ABAP user with this SNC name exists in the system |
| 12 | ACL entry for SNC-secured server-server link is missing |
| 13 | No suitable SAP account found for the SNC name |
| 14 | Ambiguous assignment of SNC names to ABAP users |
| 15 | Unencrypted SAP GUI connection refused |
| 16 | Unencrypted RFC connection refused |
| 20 | Logon using logon/assertion ticket is generally deactivated |
| 21 | Syntax error in received logon/assertion ticket or reentrance ticket not valid |
| 22 | Digital signature check for logon/assertion ticket fails |
| 23 | Logon ticket/assertion issuer is not in the ACL table |
| 24 | Logon/assertion ticket is no longer valid |
| 25 | Assertion ticket receiver is not the addressed recipient |
| 26 | Logon/assertion ticket contains no/an empty ABAP user ID |
| 27 | Reauthorization check: ticket does not match current user |
| 28 | Ticket logon denied by security policy |
| 30 | Logon using X.509 certificate is generally deactivated |
| 31 | Syntax error in the received X.509 certificate |
| 32 | X.509 certificate does not originate from the Internet Transaction Server |
| 34 | No suitable ABAP user found for the X.509 certificate |
| 35 | Ambiguous assignment of X.509 certificate to ABAP users |
| 36 | 36 Certificate is older than the date entered as «min. date» (USREXTID) |
| 41 | No suitable ABAP user found for the external ID |
| 42 | Ambiguous assignment of external ID to ABAP users |
| 50 | Password logon was generally deactivated or denied by security policy |
| 51 | Initial password has not been used for too long |
| 52 | User does not have a password |
| 53 | Password lock active (too many failed logons) |
| 54 | Productive password has not been used for too long |
| 60 | SPNego logon denied by security policy |
| 61 | Invalid SPNego token (syntax) |
| 62 | NTLM token received instead of SPNego token |
| 63 | Missing/incorrect Kerberos keytab entry |
| 64 | Invalid SPNego token (time) |
| 65 | SPNego replay attack detected |
| 66 | SPNego: Error when creating the SNC name |
| 67 | SPNego: No suitable SAP account found for the SNC name |
| 68 | SPNego: Ambiguous assignment of SNC names to ABAP users |
| 69 | Reauthentication check: SPNego token does not match current user |
| 100 | Client does not exist |
| 101 | Client is currently locked for logons |
| 102 | External WebSocket RFC communication is not allowed (RFC runtime) |
| 103 | External WebSocket RFC communication requires alias user (RFC runtime) |
| 104 | System is in maintenance mode and locked against logons |
| 110 | Tenant was stopped (runlevel STOPPED) |
| 111 | Tenant cannot be used generally (runlevel ADMIN) |
| 112 | No authorization to log on to the current logon category |
| 120 | Server does not allow logon |
| 121 | No special rights for logon on this server |
| 300-399 | OpenID connect (OIDC) error; see SAP Note 3111813 |
| 1001 | Password is initial/has expired – interactive change required (RFC/ICF) |
| 1002 | Trusted system logon failed (no S_RFCACL authorization) |
| 3000 | Reauthorization check: SAML bearer assertion is not compatible with current user |
| 3001 | Internal SAML bearer assertion verification error |
| 3002 | SAML bearer assertion could not be parsed |
| 3003 | SAML bearer assertion was already used (replay) |
| 3004 | SAML bearer assertion could not be assigned to a user |
| 3005 | Issuer of SAML bearer assertion is not trusted |
| 3006 | NameID format of SAML bearer assertion is not supported |
| 3007 | Signature of SAML bearer assertion is not valid |
| 3008 | SAML bearer assertion is not valid or is no longer valid |
| 3009 | SAML is not activated or SAML bearer assertion provider is not activated |
Explanations for “access” (access types):
| Return Code | Error Message |
|---|---|
| A | Dialog logon (SAP GUI) |
| B | Background processing (batch) |
| C | CPIC |
| F | RFC (as of 4.6C: internal RFC) |
| R | RFC (as of 4.6C: external RFC) |
| I | RFC system call (internal SRFC) |
| S | RFC system call ( [external]* SRFC) – *see SAP Note 2590963 |
| U | User switch (internal call) |
| H | HTTP |
| u | Restore session (ABAP class CL_USERINFO_DATA_BINDING) |
| » « | API call (such as SUSR_CHECK_LOGON_DATA) |
| M | SMTP authentication (MTA): Password check |
| P | ABAP push channel (APC)/WebSockets |
| E | Establishment of a shared memory area (internal call) |
| O | AutoABAP (internal call) |
| T | Server startup procedure (internal call) |
| V | SAP start service (internal call) |
| J | Java Virtual Machine (internal call) |
| W | BGRFC watchdog (internal call) |
| G | ABAP Resource Manager (internal call) |
| r | RFC via WebSockets (external) |
Explanations for “auth” (authentication types):
| Return Code | Error Message |
|---|---|
| P | Password-based authentication |
| T | Logon ticket |
| t | Assertion ticket |
| X | Certificate-based logon (X.509 / https) |
| S | SNC (Secure Network Communication) |
| R | Internal RFC or trusted system RFC |
| A | Internal call via background processing for example |
| E | External authentication (PAS / SAML / …) |
| U | Inverse user switch (ABAP class CL_USER_POC) |
| s | HTTP security session |
| 2 | SAML2 |
| 1 | SAML1 |
| o | OAuth2 |
| N | SPNego |
| a | APC session (WebSockets) |
| B | SAML bearer |
| r | Reentrance ticket |
| D | OIDC logon |
| d | OIDC bearer |
During our day to day activities we see many HTTP status code, so below is the List of common HTTP status code we see in SAP.
HTTP Response Status Codes
Every HTTP request that is received by a server is responded to with a 3-digit HTTP status code. They are grouped into five classes.
The class of a status code can be quickly identified by its first digit:
1xx: Informational
2xx: Success
3xx: Redirection
4xx: Client Error
5xx: Server Error
**Note: HTTP errors are often caused by incorrect URLs, interconnected proxy servers, or by slow processing in a system**
1xx Informational:
Request received, continuing process.
This class of status code indicates a provisional response, consisting only of the Status-Line and optional headers, and is terminated by an empty line. Since HTTP/1.0 did not define any 1xx status codes, servers must not send a 1xx response to an HTTP/1.0 client except under experimental conditions.
2xx Successful:
This class of status codes indicates the action requested by the client was received, understood, accepted and processed successfully.
200 -OK
The requested resource retrieval is successful, and a full payload of the requested resource is returned.
201 -Created
The request has been fulfilled and resulted in a new resource being created.
202 -Accepted
The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed.
204 -No Content
The server successfully processed the request, but is not returning any content. Usually used as a response to a successful delete request.
3xx Redirection:
This class of status code indicates the client must take additional action to complete the request. Many of these status codes are used in URL redirection.A user agent may carry out the additional action with no user interaction only if the method used in the second request is GET or HEAD. A user agent should not automatically redirect a request more than five times, since such re-directions usually indicate an infinite loop.
300 -Multiple Choices
Indicates multiple options for the resource that the client may follow.
301 -Moved Permanently
This and all future requests should be directed to the given URL.
Client Errors (4xx):
Client errors, or HTTP status codes from 400 to 499, are the result of HTTP requests sent by a HTTP client. Even though these types of errors are client-related, it is often useful to know which error code a user is encountering to determine if the potential issue can be fixed by server configuration.
400 -Bad Request
The 400 status code, or Bad Request error, means the HTTP request that was sent to the server has invalid syntax.
401 -Unauthorized
The 401 status code, or an Unauthorized error, means that the user trying to access the resource has not been authenticated or has not been authenticated correctly. This means that the user must provide credentials to be able to view the protected resource. An example scenario where a 401 Unauthorized error would be returned is if a user tries to access a resource that is protected by HTTP authentication if enters invalid username and password.
403 -Forbidden
The 403 status code, or a Forbidden error, means that the user made a valid request but the server is refusing to serve the request, due to a lack of permission to access the requested resource.
404 -Not Found
The 404 status code, or a Not Found error, means that the user is able to communicate with the server but it is unable to locate the requested resource.
405 -Method Not Allowed
The method specified in the Request Line is not allowed for the resource identified by the Request URI.
407 -Proxy Authentication Required
The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy.
408 -Request Timeout
The server timed out waiting for the request. According to HTTP specifications: “The client did not produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time.”
409 -Conflict
There is an internal access conflict to the specified resource.
410 -Gone
Indicates that the resource requested is no longer available and will not be available again. This should be used when a resource has been intentionally removed and the resource should be purged.
429 -Too Many Requests
The user has sent too many requests in a given period of time. This error message is typically encountered if API rate limits, set to protect against DoS attacks and to preserve server responsiveness, have been exceeded..
Server Errors (5xx):
Server errors, or HTTP status codes from 500 to 599, are returned by server when it is aware that an error has occurred or is otherwise not able to process the request.
500 -Internal Server Error
The 500 status code, or Internal Server Error, means that server cannot process the request for an unknown reason.
501 -Not Implemented
The server does not support the functionality required to fulfill the request.
502 -Bad Gateway
The 502 status code, or Bad Gateway error, means that the server is a gateway or proxy server, and it is not receiving a valid response from the backend servers that should actually fulfill the request.
503 -Service Unavailable
The 503 status code, or Service Unavailable error, means that the server is overloaded or under maintenance. This error implies that the service should become available at some point.
504 -Gateway Timeout
The 504 status code, or Gateway Timeout error, means that the server is a gateway or proxy server, and it is not receiving a response from the backend servers within the allowed time period.
505 -HTTP Version Not Supported
The server does not support the HTTP protocol version used in the request.
507 -Insufficient Storage
The server is unable to store the representation needed to complete the request.
599 -Network connect timeout error (Unknown)
This status code is not specified in any RFCs, but is used by Microsoft HTTP proxies to signal a network connect timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.
Hope this will help you guys.