PhpStorm analyses code in the files that are opened in the editor and highlights problematic code as you type. Additionally, you can run the necessary inspection or a set of inspections on the selected scope of files manually. In this case, you will get a comprehensive report of all problems detected in the files.
Instant analysis of the current file
The IDE continuously checks your code and searches for problems. The widget in the top-right corner of the editor displays the number of problems of each severity detected in the current file:
Click the widget to open the list of problems on the File tab of the Problems tool window. You can also access the Problems tool window by selecting or by pressing Alt+6.
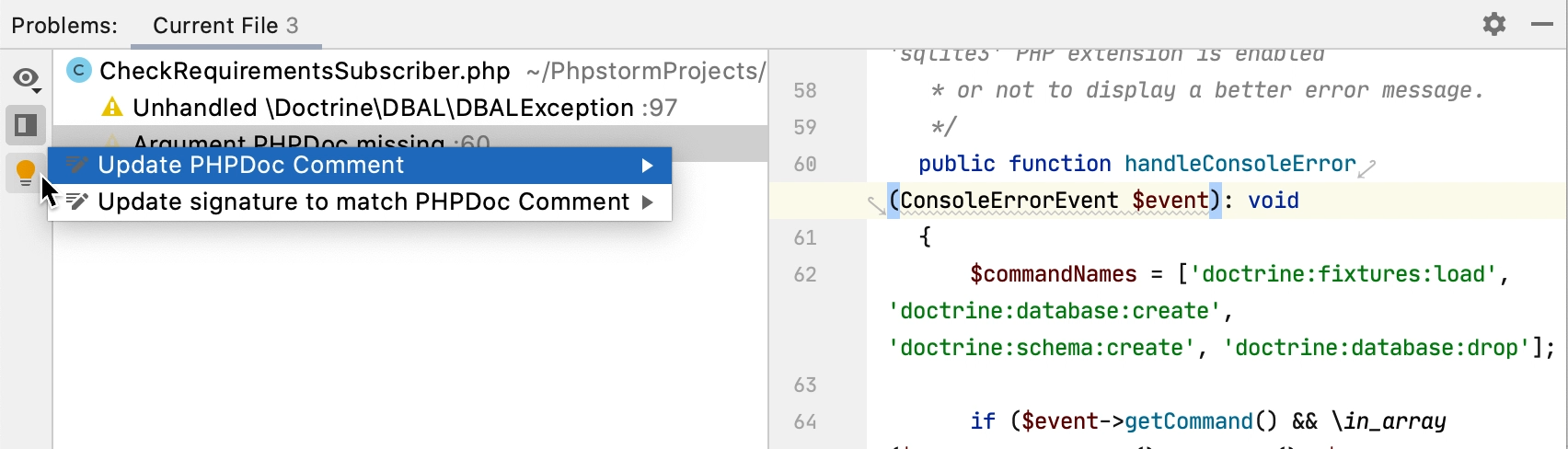
For each problem, you can see the suggested quick-fix by pressing Alt+Enter or by clicking 
Alternatively, click 
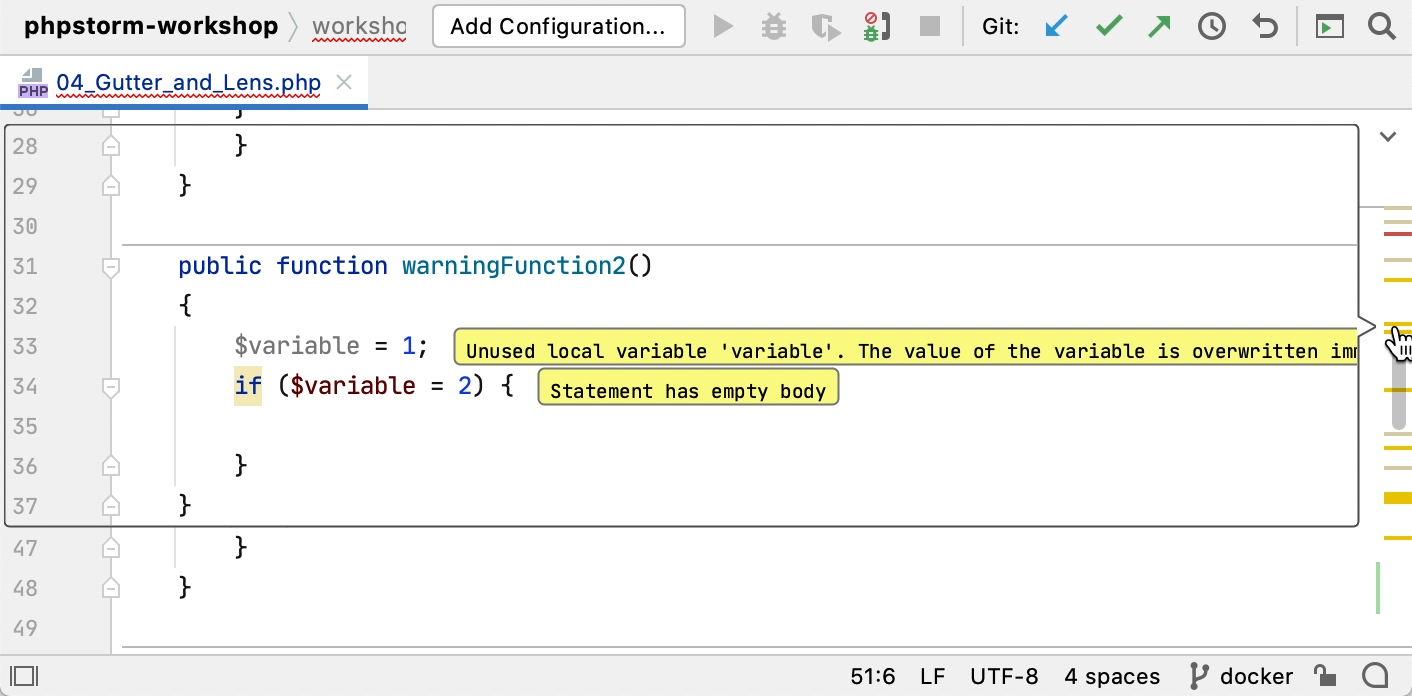
The color stripe in the scrollbar also marks the detected code problems and helps you quickly access the corresponding lines without scrolling the file. Hover over a mark on the stripe to see the detected problem in a tooltip. Click a mark to jump to the corresponding line.
Navigate to detected problems
You can jump from one highlighted problem to another within a file by clicking 

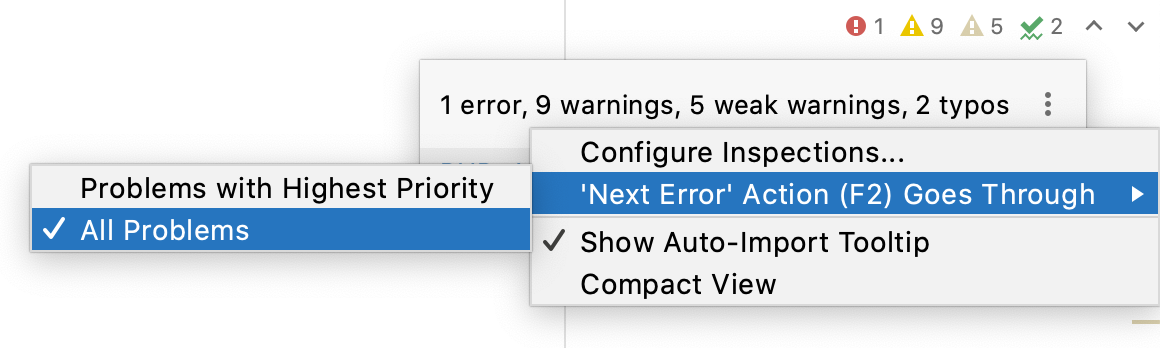
You can configure PhpStorm to take you through the problems one by one regardless of their severity. Hover over the widget in top-right corner of the editor, click 
Run inspections manually
Some inspections require global code analysis, and that is why they are disabled in the editor. These inspections are listed in . Click 
If you want to get a full report of all detected problems, run inspections manually.
Run all inspections
-
Go to .
-
Select the scope of files that you want to analyze.
Click the
icon to configure a new scope.
-
Select the inspection profile that you want to apply.
To create a new profile or modify one of the existing profiles, click Configure.
-
Click Analyze to start the analysis.

Specify Inspection Scope dialog
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Whole project |
Inspect the whole project. |
|
Module <name> |
Inspect the module that is currently selected in the Project tool window. |
|
File <name> |
Inspect the file that is currently selected in the Project tool window or opened in the editor. |
|
Selected files |
Inspect the files that are currently selected in the Project tool window. |
|
Uncommitted files |
This scope is only available for the projects under version control. Inspect only the files that have not been committed to the version control system. |
|
Directory |
Inspect the directory that is currently selected in the Project tool window. |
|
Custom scope |
Inspect a custom scope of files. Select a pre-defined scope from the list, or click |
|
Include test sources |
Inspect the test sources included in the analysis scope. |
|
Inspect injected code |
Inspect pieces of code in other languages embedded in your code. |
|
Inspection profile |
Select a profile that you want to use to inspect your code. If the required profile is not in the list, click Configure and create a new profile. |
Run a single inspection
Running a single inspection is useful in case you want to track a specific problem. If you find a warning in a file, you can inspect your entire project, or the necessary scope of files, to ensure that there are no more such warnings in your code base.
-
Go to or press Control+Alt+Shift+I.
-
Type the inspection name in the popup. Use CamelHumps to match camel case words and white spaces with initial letters of the words. The suggestion list will show you inspections that match your search request.
If you are not sure that you are selecting the correct inspection, you can view its description. To do so, select an inspection in the popup and press Control+Q.
-
Double-click the necessary inspection to open its settings.
-
In the dialog that opens, select the scope of files that you want to analyze.
The File mask(s) option helps you narrow down the number of files that will be inspected.
Select the checkbox and specify a pattern of characters and wildcards that matches the names of files you want to analyze. Use a comma to separate multiple file masks.
-
Some inspections might have additional options that you will be prompted to configure.
These settings will only be applied to this run, and will not affect this inspection’s configuration in your current profile.
The IDE will show you the inspection results in the dedicated tool window tool window. There you can examine and fix detected problems.
Analyze code before committing it to Git
If your project is under Git or Mercurial version control, you can configure the IDE to analyze modified files before committing them.
-
Press Command K or select from the main menu.
-
In the Commit tool window, click
and in the Commit Checks area, select the Analyze code checkbox.
-
Click Choose profile and select the required inspection profile from which the IDE will run inspections.
-
Click Commit.
PhpStorm analyzes the code from the modified files by running inspections from the selected profile.
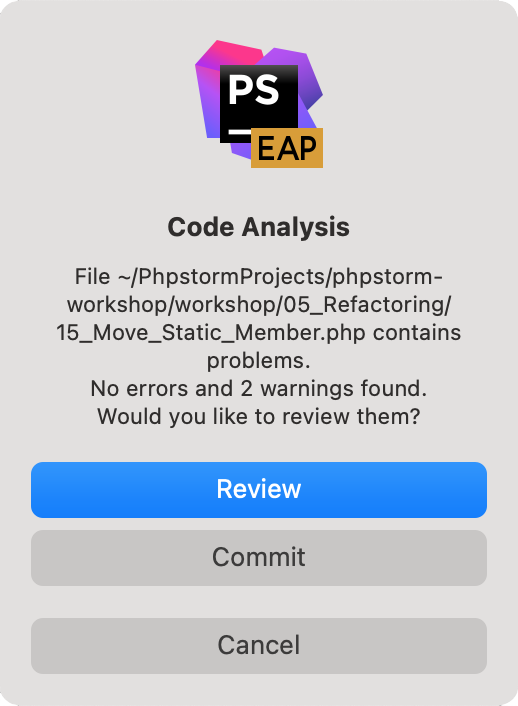
If any errors or warnings are detected, you will see a notification.
-
In the notification, click Review code analysis to see the list of the detected problems in the Messages tool window. Click Ignore to commit your changes without fixing the detected problems.
Run code inspection with Qodana
which is bundled and enabled in PhpStorm by default. If the relevant features aren’t available, make sure that you didn’t disable the plugin. For more information, refer to Open plugin settings.
You can inspect your code locally or remotely using Qodana. The main use case for Qodana is to perform resource-intensive code analysis remotely, on a CI/CD server. However, you can also run the same analysis in the IDE to make sure that you have the same results, and to be able to locate the detected issues in your source code.
-
Go to .
-
Select where you want to run inspections: locally or on your CI/CD server.
To run inspections on the server, you need to set up Qodana on your CI first.
-
The Qodana configuration file opens. In this file, you can specify Qodana inspection profile, enable or disable specific inspections, and specify a list of plugins that should be installed before the analysis.
Click Run.
Once the analysis is finished, the report will be displayed in the Problems tool window on the Server-Side Analysis tab. You can work with the results locally or send them to Qodana Cloud.
The reports of all local runs of Qodana analysis are saved and available from the main menu: . The currently opened report has a checkmark next to it, you can click it to close the report.
For more information about Qodana, refer to its documentation.
Run inspections offline
In addition to running code inspections from the IDE, you can launch inspections from the command line without actually running PhpStorm. The inspection results will be stored in an XML file. For more information, refer to Run code inspections from the command line.
Change the order of scopes
By default, all enabled code inspections analyze all files in your project. Depending on your needs, you can run the same inspection in more than one scope of files with different settings.
If one file is included in two or more scopes, and you enable an inspection in these scopes, PhpStorm will process them according to their order in the list of scopes — the uppermost scope will have the highest priority, and therefore, it will be analyzed first.
-
In the Settings dialog (Control+Alt+S), select .
-
Select any inspection from the list.
-
From the In All Scopes list, select Edit Scopes Order.
-
Select the necessary scope, and use
and
to move it up and down the list.
-
If needed, create a new scope. To do so, click
(Edit Scopes), specify scope settings, and select the files and folders that you want to include in it. For more information, refer to Scopes and file colors.
Last modified: 08 September 2023
The Problems tool window displays problems that PhpStorm detects in your project using several tabs.
You can select any problem in the window and press F4 or double-click it to jump to the corresponding line in the editor.
When the design-time code inspection is enabled, this tab lists all code issues found in the current file. The list is updated as you switch between files in the editor.
Toolbar
|
Item |
Tooltip and shortcut |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
View Options |
Filter out code issues by their severity and configure their sorting. When no grouping or sorting options are selected, the issues are listed in the order they appear in the file. |
|
|
Show Quick-Fixes Alt+Enter |
Show quick-fixes available for the selected problem. |
|
|
Open Editor Preview |
Open the preview pane to view the selected issue in its source context right in the Problems window. Note that this preview is a normal editor where you can change the code and apply available quick-fixes. |
|
Item |
Shortcut |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Show Quick-Fixes |
Alt+Enter |
Show quick-fixes available for the selected problem. |
|
Copy Problem Description |
Control+C |
Copy the problem description to the clipboard. |
|
Jump to Source |
F4 |
Open the code containing the problem in the editor. |
|
Show Error Details |
Open error details in a separate dialog. |

Toolbar
|
Item |
Tooltip and shortcut |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
View Options |
Filter out code issues by their severity and configure their sorting. When no grouping or sorting options are selected, the issues are listed in the order they appear in the file. |
|
|
Show Quick-Fixes Alt+Enter |
Show quick-fixes available for the selected problem. |
|
|
Open Editor Preview |
Open the preview pane to view the selected issue in its source context right in the Problems window. Note that this preview is a normal editor where you can change the code and apply available quick-fixes. |
|
|
Expand All |
Expand all nodes. |
|
|
Collapse All |
Collapse all nodes. |
|
Item |
Shortcut |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Copy Problem Description |
Control+C |
Copy the problem description to the clipboard. |
|
Jump to Source |
F4 |
Open the code containing the problem in the editor. |
|
Show Error Details |
Open error details in a separate dialog. |
This tab displays code problems detected with Qodana. Qodana allows you run inspections locally including your IDE, and as a part of CI/CD pipelines.
Toolbar
|
Item |
Tooltip and shortcut |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Log in to Qodana |
Log in to Qodana Cloud. This action is a prerequisite for linking your project with Qodana Cloud-based reports. Alternatively, you can do it from the main menu: . For more information, refer to Qodana Cloud. |
|
|
Logged in to Qodana |
You are logged in to Qodana Cloud. You can link your project with Qodana Cloud. |
|
|
Link Project with Cloud |
Link your project and upload the report to Qodana Cloud. Alternatively, you can do it from the main menu: . For more information, refer to Open report from Qodana Cloud. |
|
|
Linked with Cloud |
Your project is linked with Qodana Cloud. By clicking this button, you can open the inspection report in the cloud or unlink your project from Qodana Cloud. |
|
|
Refresh Cloud Report |
Refresh the current cloud report. |
|
|
View Options |
Filter out code issues by their severity and configure their sorting. When no grouping or sorting options are selected, the issues are listed in the order they appear in the file. |
|
|
Open Editor Preview |
Open the preview pane to view the selected issue in its source context right in the Problems window. Note that this preview is a normal editor where you can change the code and apply available quick-fixes. |
|
|
Expand All Control+NumPad-+ |
Expand all nodes. |
|
|
Collapse All Control+NumPad-- |
Collapse all nodes. |
|
|
Show Qodana in Browser |
Open the results of the analysis in your default browser. An interactive report opens allowing you to examine the problems in detail and navigate between the report and the IDE. |
|
Item |
Shortcut |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Show Quick-Fixes |
Alt+Enter |
Show quick-fixes available for the selected problem. |
|
Jump to Source |
F4 |
Open the code with the problem in the editor. |
|
Show Error Details |
Learn more in formation about the detected problem in a popup. |
|
|
qodana.yaml |
Modify the qodana.yaml configuration file by excluding from the analysis certain files, folders, or inspections. |

Toolbar
|
Item |
Shortcut |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Control+F5 |
Run the inspection and show the results on the same tab. |
|
|
Control+Alt+ArrowUp |
Navigate to the previous problem. |
|
|
Control+Alt+ArrowDown |
Navigate to the next problem. |
|
|
Alt+Enter |
Resolve the problem for the selected inspection item by choosing one of the available quick fixes from the list. |
|
|
Change the settings for the selected inspection or group of inspections in the Errors dialog. |
|
|
|
Group or filter found problems according to the selected option:
|
|
|
|
Control+NumPad-+ |
Expand all nodes. |
|
|
Control+NumPad-- |
Collapse all nodes. |
|
|
Export the inspection results into XML , Sarif, or HTML format. |
|
Item |
Shortcut |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Jump to Source |
F4 |
Open the file that contains the selected problem in the editor and place the caret at the beginning of the corresponding code fragment. |
|
Exclude |
Delete |
Exclude the selected items from further examination. Excluded nodes are shown strikethrough. If the filter toggle |
|
Include |
Insert |
Include previously excluded items in the list of results. All nested elements are included too. |
|
|
Alt+Enter |
Select one of the suggested solutions. |
|
Suppress problem |
Suppress the inspection for the selected problem or the selected class. |
|
|
Edit Settings |
Change the settings for the selected inspection or group of inspections in the Errors dialog. |
|
|
Disable inspection |
Disable alerts for the selected inspection in the active tab of results. If the filter toggle |
|
|
Run inspection on |
Rerun the selected inspection and display the results on a new tab. |
Inspection report
The inspection report is shown in the right pane of the results tab when an inspection node is selected in the left pane. The report may include the following:
-
Problem resolution: A button for each of the available solutions. Clicking a button invokes the corresponding fix. If no buttons are present, you have to fix the problem yourself.
-
Suppress: Click this button to reveal the list of inspection suppress options.
-
Problem synopsis: A brief description of the problem.
-
Disable inspection: Disable alerts for the selected inspection in the active tab of results. If the filter toggle
is on, the nodes for disabled inspections are hidden.
-
Run inspection on: Rerun the selected inspection and display the results on a new tab.
Last modified: 07 September 2023
PhpStorm analyses code in the files that are opened in the editor and highlights problematic code as you type. Additionally, you can run the necessary inspection or a set of inspections on the selected scope of files manually. In this case, you will get a comprehensive report of all problems detected in the files.
Instant analysis of the current file
The IDE continuously checks your code and searches for problems. The widget in the top-right corner of the editor displays the number of problems of each severity detected in the current file:
Click the widget to open the list of problems on the Current File tab of the Problems tool window. You can also access the Problems tool window by selecting or by pressing Alt+6.
For each problem, you can see the suggested quick-fix by pressing Alt+Enter or by clicking 
Alternatively, click 
The color stripe in the scrollbar also marks the detected code problems and helps you quickly access the corresponding lines without scrolling the file. Hover over a mark on the stripe to see the detected problem in a tooltip. Click a mark to jump to the corresponding line.
Navigate to detected problems
You can jump from one highlighted problem to another within a file by clicking 

You can configure PhpStorm to take you through the problems one by one regardless of their severity. Hover the mouse over the widget in top-right corner of the editor, click 
Run inspections manually
Some inspections require global code analysis, and that is why they are disabled in the editor. These inspections are listed in . Click 
If you want to get a full report of all detected problems, run inspections manually.
Run all inspections
-
From the main menu, select .
-
Select the scope of files that you want to analyze.
Click the
icon to configure a new scope.
-
Select the inspection profile that you want to apply.
To create a new profile or modify one of the existing profiles, click Configure.
-
Click Analyze to start the analysis.
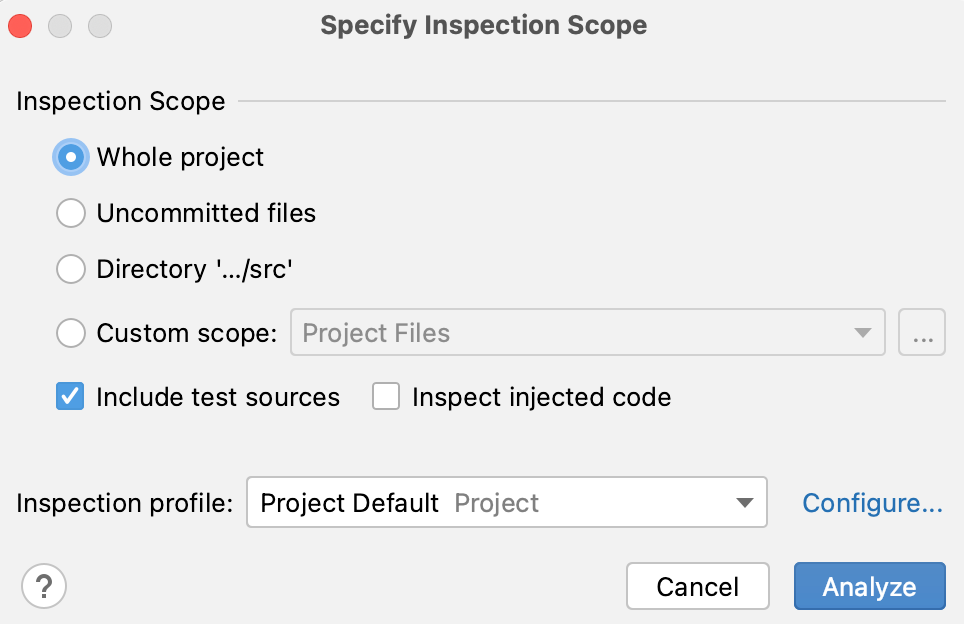
Specify Inspection Scope dialog
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Whole project |
Inspect the whole project. |
|
Module <name> |
Inspect the module that is currently selected in the Project tool window. |
|
File <name> |
Inspect the file that is currently selected in the Project tool window or opened in the editor. |
|
Selected files |
Inspect the files that are currently selected in the Project tool window. |
|
Uncommitted files |
This scope is only available for the projects under version control. Inspect only the files that have not been committed to the version control system. |
|
Directory |
Inspect the directory that is currently selected in the Project tool window. |
|
Custom scope |
Inspect a custom scope of files. Select a pre-defined scope from the list, or click |
|
Include test sources |
Inspect the test sources included in the analysis scope. |
|
Inspect injected code |
Inspect pieces of code in other languages embedded in your code. |
|
Inspection profile |
Select a profile that you want to use to inspect your code. If the required profile is not in the list, click Configure and create a new profile. |
Run a single inspection
Running a single inspection is useful in case you want to track a specific problem. If you find a warning in a file, you can inspect your entire project, or the necessary scope of files, to ensure that there are no more such warnings in your code base.
-
From the main menu, select or press Ctrl+Alt+Shift+I.
-
Type the inspection name in the popup. Use CamelHumps to match camel case words and white spaces with initial letters of the words. The suggestion list will show you inspections that match your search request.
If you are not sure that you are selecting the correct inspection, you can view its description. To do so, select an inspection in the popup and press Ctrl+Q.
-
Double-click the necessary inspection to open its settings.
-
In the dialog that opens, select the scope of files that you want to analyze.
The File mask(s) option helps you narrow down the number of files that will be inspected.
Select the checkbox and specify a pattern of characters and wildcards that matches the names of files you want to analyse. Use a comma to separate multiple file masks.
-
Some inspections might have additional options that you will be prompted to configure.
These settings will only be applied to this run, and will not affect this inspection’s configuration in your current profile.
The IDE will show you the inspection results in the dedicated tool window tool window. There you can examine and fix detected problems.
Analyze code before committing it to Git
If your project is under Git version control, you can configure the IDE to analyze modified files before committing them.
-
Press Ctrl+K or select from the main menu.
-
In the Commit tool window, click
and in the Commit Checks area, select the Analyze code checkbox.
-
Click Choose profile and select the required inspection profile from which the IDE will run inspections.
-
Click Commit.
PhpStorm analyzes the code from the modified files by running inspections from the selected profile.
If any errors or warnings are detected, you will see a notification.
-
In the notification, click Review code analysis to see the list of the detected problems in the Messages tool window. Click Commit to commit your changes without fixing the detected problems.
Run inspections offline
In addition to running code inspections from the IDE, you can launch inspections from the command line without actually running PhpStorm. The inspection results will be stored in an XML file. For more information, refer to Run code inspections from the command line.
Change the order of scopes
By default, all enabled code inspections analyze all files in your project. Depending on your needs, you can run the same inspection in more than one scope of files with different settings.
If one file is included in two or more scopes, and you enable an inspection in these scopes, PhpStorm will process them according to their order in the list of scopes — the uppermost scope will have the highest priority, and therefore, it will be analyzed first.
-
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), select .
-
Select any inspection from the list.
-
From the In All Scopes list, select Edit Scopes Order.
-
Select the necessary scope, and use
and
to move it up and down the list.
-
If needed, create a new scope. To do so, click
(Edit Scopes), specify scope settings, and select the files and folders that you want to include in it. See Scopes and file colors for details.
Last modified: 28 April 2023
2 Answers
To get the list of all files with errors and warnings use Code | Inspect Code. It’s possible to specify what inspection profile to use, which directories to scan. Custom Scope provides a flexible way to include/exclude certain directories or files from the inspection results.
answered Oct 3, 2012 at 17:32
CrazyCoderCrazyCoder
390k172 gold badges990 silver badges906 bronze badges
Slightly off-topic, but may be helpful. If you need to jump through all the errors in a file (for example, CSS file), open up the file and and hit the F2 button on the keyboard. Repeat it to cycle through all the errors. To navigate back to the previous error, hit Shift + F2
answered Mar 30, 2017 at 8:45
DevnerDevner
6,85511 gold badges63 silver badges104 bronze badges
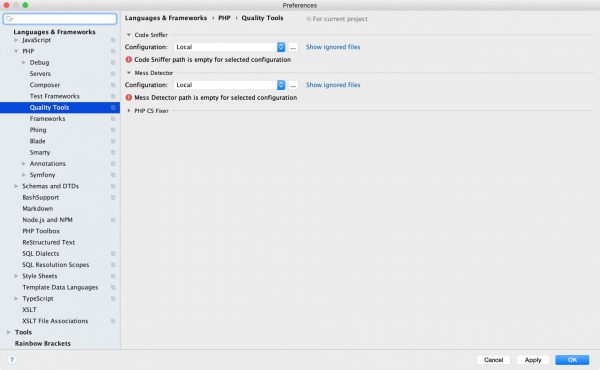
Устанавливаем модули для проверки PHP кода в PhpStorm — Code Sniffer, Mess Detector.
Устанавливаем PHP Code Sniffer
Устанавливаем через composer
composer global require «squizlabs/php_codesniffer=*»
Затем заходим в Quality Tools
Заходим внутрь настроек Code Sniffer и выбираем путь до файлов phpcs (проверка) и phpcbf (автоматическое исправление):
~/.composer/vendor/squizlabs/php_codesniffer/bin/phpcs
Отмечаем в Inspections, что хотим авто-проверку:
И наслаждаемся результатом:
Более подробно здесь
https://www.jetbrains.com/help/phpstorm/using-php-code-sniffer.html
Устанавливаем Mess Detector
Делаем все по аналогии для Mess Detector.
Устанавливаем:
composer global require ‘phpmd/phpmd=*’
Заходим в папку куда установили и выбираем файл phpmd:
~/.composer/vendor/phpmd/phpmd/src/bin/phpmd
Более подробно:
https://www.jetbrains.com/help/phpstorm/using-php-mess-detector.html
CS Fixer
CS Fixer расшифровывается как PHP Coding Standards fixer.
Установка CS Fixer
composer global require friendsofphp/php-cs-fixer
Выбираем директорию установки в PhpStorm
~/.composer/vendor/friendsofphp/php-cs-fixer/php-cs-fixer
Также по аналогии выделаем в Editors->Insepctions
Для ручного запуска:
/Users/Dream/.composer/vendor/friendsofphp/php-cs-fixer/php-cs-fixer fix file
Подробнее:
https://www.jetbrains.com/help/phpstorm/using-php-cs-fixer.html
PHPLOC
Статистика для PHP кода.
Установка:
composer global require ‘phploc/phploc=*’
Проверить папку с кодом:
/Users/Dream/.composer/vendor/phploc/phploc/phploc directory
где folder название папки следующее за тем местом, откуда вызывается код, но можно указать и абсолютные пути. Кому что больше нравится.
Dead Code Detector (DCD)
Находит мертвый код в проекте.
Установка:
composer global require ‘sebastian/phpdcd=*’
Используем:
/Users/Dream/.composer/vendor/sebastian/phpdcd/phpdcd directory
Copy/Paste Detector (CPD)
Находит дублирование кода в проекте.
Установка:
composer global require ‘sebastian/phpcpd=*’
Используем:
/Users/Dream/.composer/vendor/sebastian/phpcpd/phpcpd directory


 icon to configure a new scope.
icon to configure a new scope. and in the
and in the 


 and
and  to move it up and down the list.
to move it up and down the list.
 (
(













 is on, the excluded nodes are hidden.
is on, the excluded nodes are hidden.

 icon to configure a new scope.
icon to configure a new scope.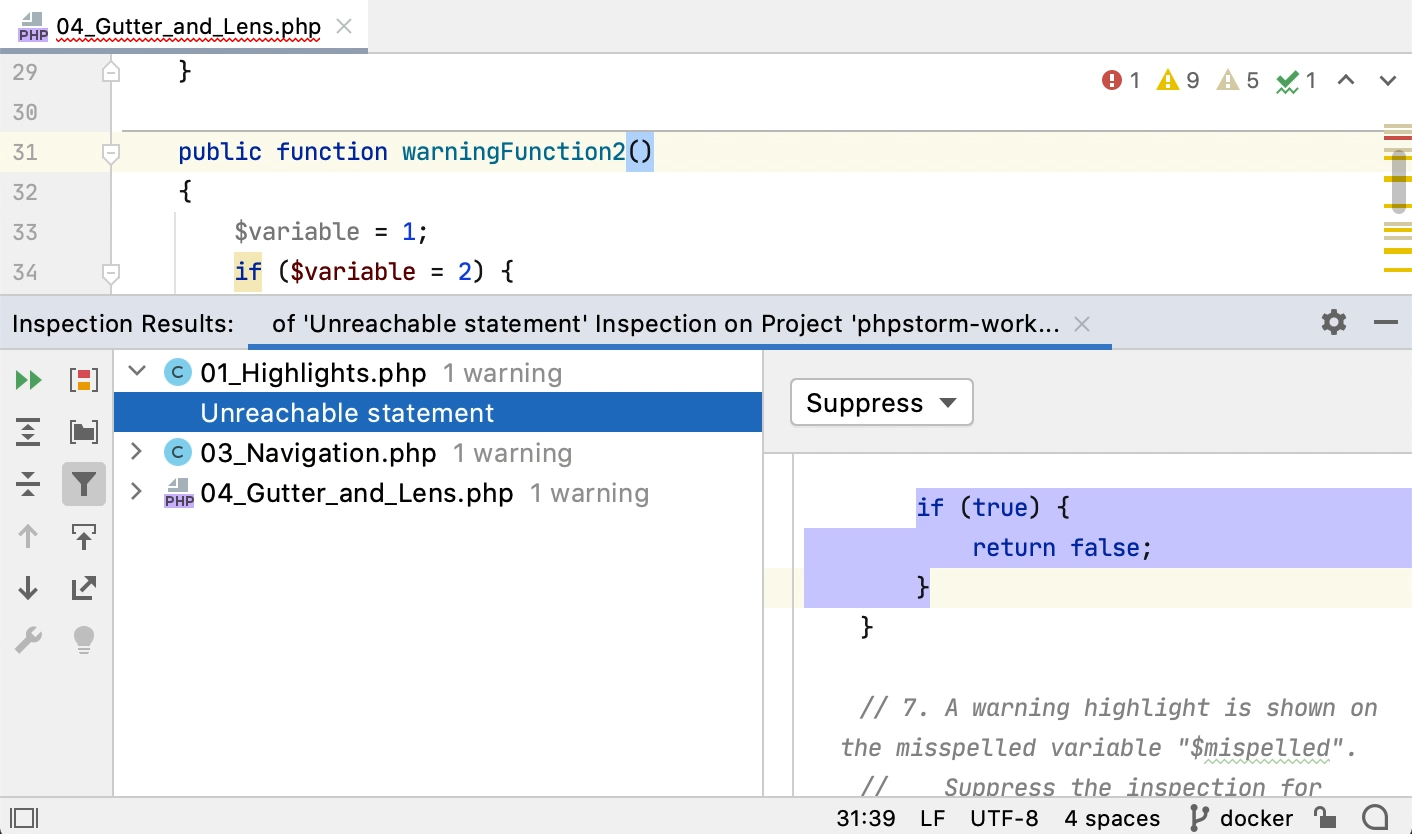
 and in the
and in the 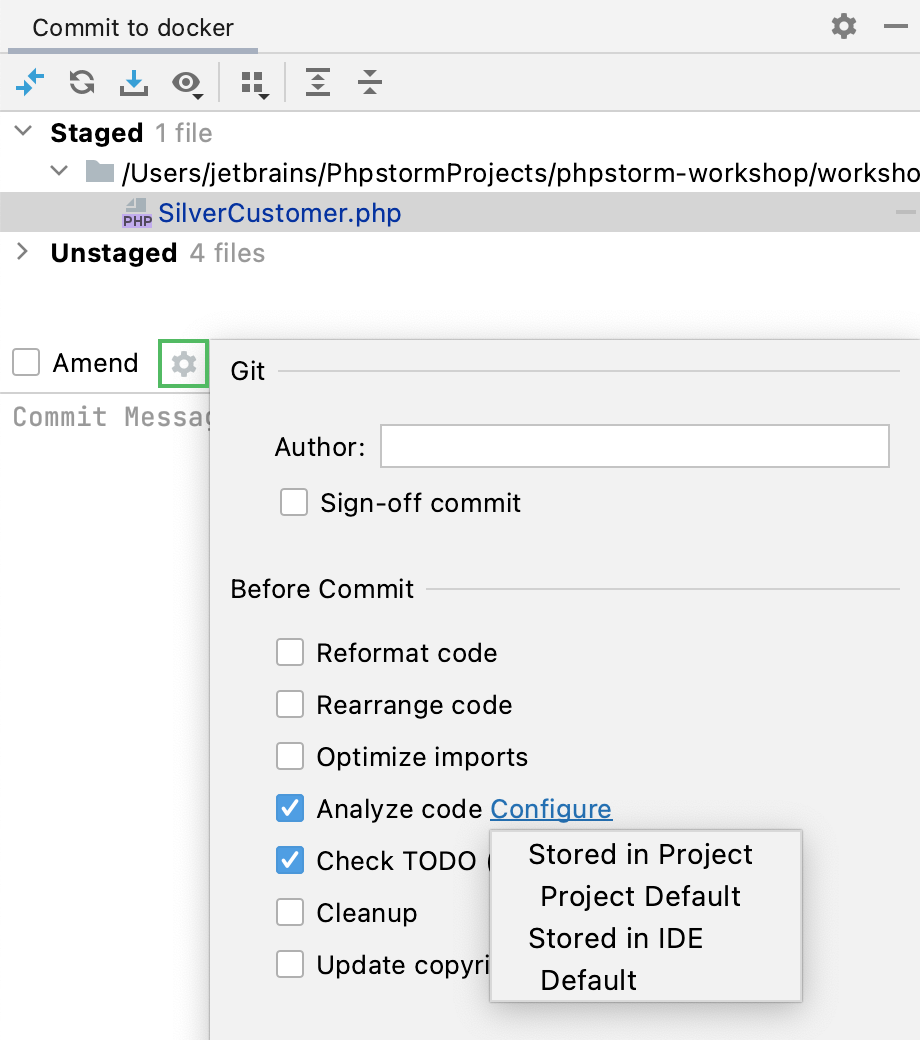
 and
and  to move it up and down the list.
to move it up and down the list.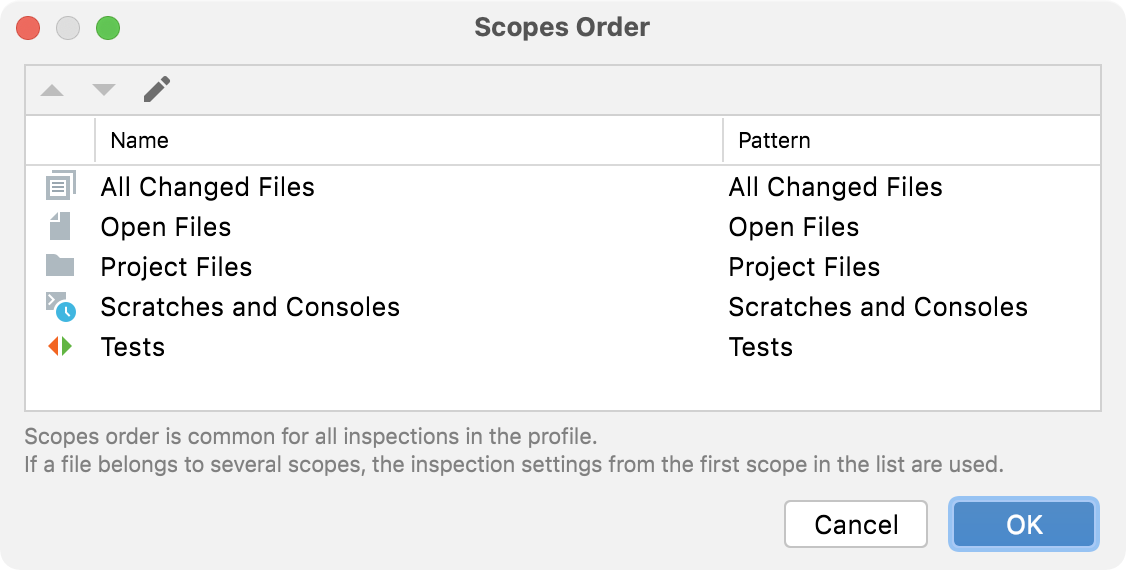
 (
(