На чтение 4 мин Просмотров 28.6к.
Рассмотрим подробнее
- Техническое описание и расшифровка ошибки P2196
- Симптомы неисправности
- Причины возникновения ошибки
- Как устранить или сбросить код неисправности P2196
- Диагностика и решение проблем
- На каких автомобилях чаще встречается данная проблема
- Видео
Код ошибки P2196 звучит как «сигнал датчика кислорода O₂ застрял в положении слишком богатая смесь (Банк 1, Датчик 1)». Часто, в программах, работающих со сканером OBD-2, название может иметь английское написание «O2 Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 1, Sensor 1)».
Код OBD-II P2196 является общим кодом силового агрегата. Который определяется всеми автопроизводителями как «заедание сигнала датчика O₂ в положении богатой смеси (Банк 1, Датчик 1)». Где Банк 1 относится к группе цилиндров, которая содержит цилиндр № 1.
Во время нормальной работы датчик O₂ реагирует на изменения содержания кислорода в выхлопном потоке. В зависимости от типа датчика, он фиксирует изменения либо сигнального напряжения, либо электрического сопротивления. Которые PCM использует для поддержания соотношения воздух-топливо как можно ближе к идеальному соотношению 14,7:1.
Полностью работоспособный датчик кислорода не может генерировать напряжение сигнала или сопротивление, которое не изменяется. Типичный диапазон напряжения сигнала варьируется от 0,1 вольт до 0,9 вольт.
При этом значение 0,45 вольт представляет собой среднюю точку, в которой топливно-воздушная смесь максимально приближена к идеальному соотношению 14,7:1.
Таким образом, весьма маловероятно, что соотношение воздух-топливо в смеси будет оставаться постоянным в течение значительного периода времени. Поэтому, когда PCM обнаруживает отсутствие изменений в сигнальном напряжении или сопротивлении датчика. Устанавливается код P2196 и загорается сигнальная лампа.
Симптомы неисправности
Основным симптомом появления ошибки P2196 для водителя является подсветка MIL (индикатор неисправности). Также его называют Check engine или просто «горит чек».
Также они могут проявляться как:
- Загорится контрольная лампа «Check engine» на панели управления (код будет записан в память ECM как неисправность).
- Плавающие обороты, а также попытки заглохнуть на холостом ходу.
- Двигатель глохнет либо плохо заводится.
- Снижение мощности двигателя.
- Повышенный расход топлива.
- Черный дым из выхлопной трубы.
- Симптомы могут отсутствовать, кроме сохраненного кода неисправности.
Степень серьезности кода неисправности P2196 варьируется от средней до высокой. Но если не устранять его в течении длительного времени, возможен выход из строя катализатора.
Причины возникновения ошибки
Код P2196 может означать, что произошла одна или несколько следующих проблем:
- Неисправность датчика кислорода O₂ или его нагревателя.
- Обрыв или короткое замыкание в проводке.
- Проблема с давлением топлива либо с топливной форсункой.
- Утечки всасываемого воздуха или вакуума в двигателе.
- Неисправность датчика массового расхода воздуха (MAF).
- Неисправность датчика, а также регулятора давления топлива.
- Иногда причиной является неисправный модуль PCM.
Как устранить или сбросить код неисправности P2196
Некоторые предлагаемые шаги для устранения неполадок и исправления кода ошибки P2196:
- Осмотрите проводку и разъемы.
- Визуально проверьте вакуумные линии.
- Проведите испытание давления топлива.
- Протестируйте датчики на предмет выхода из строя. При необходимости замените.
- Сделайте тест модуля PCM, при необходимости, замените его.
Диагностика и решение проблем
Перед началом диагностики неисправности P2196 осмотрите проводку и разъемы, ведущие к датчику, проверьте нет ли потертостей, оплавления, при необходимости отремонтируйте. Визуально проверьте вакуумные линии. Если установлено, что проблема связана с утечкой вакуума, было бы разумно заменить все вакуумные линии.
Снимите датчик кислорода O₂ с автомобиля и осмотрите его на предмет наличия нагара, повреждений или отложений. Обратите внимание, что загрязненные или поврежденные кислородные датчики нельзя очистить или отремонтировать.
При замене датчика убедитесь, что вся проводка подключена правильно, проложена вдали от горячих компонентов выхлопной системы. Надежно закрепите, чтобы предотвратить трение или истирание о другие компоненты.
Очистите код неисправности P2196 и проведите тест драйв, чтобы проверить, вернется ли код снова, что очень маловероятно. Однако, если он все же возвращается, вполне вероятно, что замененный датчик также неисправен либо неисправны схемы мониторинга в PCM.
Проверьте актуальные бюллетени технического обслуживания (TSB) для вашего автомобиля. В некоторых случаях PCM может быть откалиброван, и проблема будет решена.
На каких автомобилях чаще встречается данная проблема
Проблема с кодом P2196 может встречаться на различных машинах, но всегда есть статистика, на каких марках эта ошибка присутствует чаще. Вот список некоторых из них:
- Audi (Ауди а3, Ауди а4, Ауди q7)
- BMW
- Citroen (Ситроен С4)
- Ford (Форд Куга, Маверик, Мустанг, Фокус, Фьюжн, Экспедишн, Эксплорер, Эскейп, E250, F-150)
- Hyundai (Хендай Элантра)
- Land Rover (Ленд Ровер Фрилендер)
- Lexus
- Lincoln LS
- Mazda (Мазда 3)
- Mercedes
- Peugeot (Пежо 308)
- Skoda (Шкода Октавия)
- Toyota (Тойота Камри, Королла, Приус, Ярис)
- Volkswagen (Фольксваген Битл, Крафтер, Пассат, Туарег, Транспортер)
- Volvo
- Лада Нива
С кодом неисправности Р2196 иногда можно встретить и другие ошибки. Наиболее часто встречаются следующие: P0011, P0102, P0113, P0132, P0171, P0172, P0174, P0191, P0202, P0300, P0355, P0420, P2096, P2106, P2195, P2197, P2198, P2270.
Видео
DTC P2195 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
DTC P2196 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Description
Monitor description
Monitor strategy
Typical enabling conditions
Typical malfunction thresholds
Confirmation driving pattern
Wiring diagram
Inspection procedure
Check any other dtcs output (in addition to p2195 or p2196)
Confirm if vehicle has run out of fuel in past
Perform confirmation driving pattern
Read value using intelligent tester (air fuel ratio sensor current)
Perform active test using intelligent tester (control the injection volume)
Check intake system
Check for exhaust gas leak
Check fuel pressure
Inspect fuel injector assembly
Replace air fuel ratio sensor
Perform confirmation driving pattern
Perform active test using intelligent tester (control the egr step position)
Inspect egr valve assembly
Replace ecm
Confirm whether malfunction has been successfully repaired
Replace air fuel ratio sensor
Perform confirmation driving pattern
Check fuel line
Description
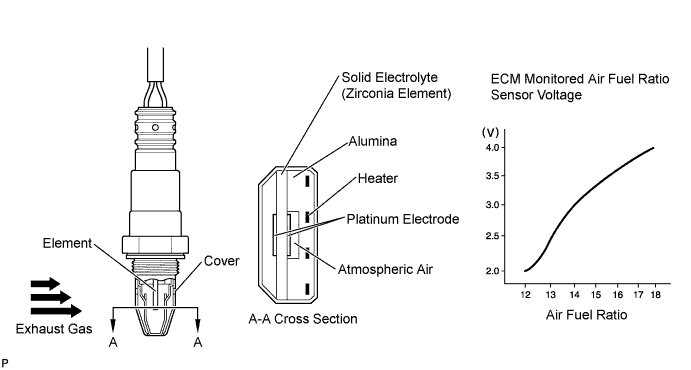
The air fuel ratio sensor generates voltage* that corresponds to the actual air fuel ratio. This sensor voltage is used to provide the ECM with feedback so that it can control the air fuel ratio. The ECM determines the deviation from the stoichiometric air fuel ratio level, and regulates the fuel injection duration. If the air fuel ratio sensor malfunctions, the ECM is unable to control the air fuel ratio accurately. The air fuel ratio sensor is a planar type with an integrated heater, which heats the solid electrolyte (zirconia element). This heater is controlled by the ECM. When the intake air volume is low (the exhaust gas temperature is low), current flows to the heater to heat the sensor, in order to facilitate accurate oxygen concentration detection. In addition, the sensor and heater portions are narrower than the conventional type. The heat generated by the heater is conducted to the solid electrolyte through the alumina, therefore the sensor activation is accelerated. A three-way catalytic converter is used in order to convert the carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbon (HC), and nitrogen oxide (NOx) into less harmful substances. To allow the three-way catalytic converter to function effectively, it is necessary to keep the air fuel ratio of the engine near the stoichiometric air fuel ratio. *: Value changes inside the ECM. Since the air fuel ratio sensor uses the current output element, the current is converted to a voltage inside the ECM. Any measurements taken at the air fuel ratio sensor or ECM connectors will show a constant voltage.
| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P2195 | Conditions (a) and (b) continue for 5 seconds or more (2 trip detection logic): (a) Air fuel ratio sensor voltage is higher than 3.8 V. (b) Heated oxygen sensor voltage is 0.21 V or higher. |
|
| While the fuel-cut operation is performed (during vehicle deceleration), the air fuel ratio sensor current is 2.2 mA or higher for 3 seconds (2 trip detection logic). |
|
|
| P2196 | Conditions (a) and (b) continue for 5 seconds or more (2 trip detection logic): (a) Air fuel ratio sensor voltage is below 2.8 V. (b) Heated oxygen sensor voltage is below 0.59 V. |
|
| While the fuel-cut operation is performed (during vehicle deceleration), the air fuel ratio sensor current is below 0.7 mA for 3 seconds (2 trip detection logic). |
|
HINT:
- When any of these DTCs are set, check the air fuel ratio sensor output voltage by entering the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / AFS Voltage B1S1.
- Short-term fuel trim values can also be read using the intelligent tester.
- The ECM regulates the voltages at the A1A+ and A1A- terminals of the ECM to a constant level. Therefore, the air fuel ratio sensor output voltage cannot be confirmed without using the intelligent tester.
- If an air fuel ratio sensor malfunction is detected, the ECM sets a DTC.
Monitor description
- Sensor voltage detection monitor Under air-fuel ratio feedback control, if the air fuel ratio sensor output voltage is below 2.8 V (very rich condition) for 5 seconds despite the heated oxygen sensor output voltage being below 0.59 V, the ECM stores DTC P2196. Alternatively, if the air fuel ratio sensor output voltage is higher than 3.8 V (very lean condition) for 5 seconds despite the heated oxygen sensor output voltage being 0.21 V or higher, DTC P2195 is stored.
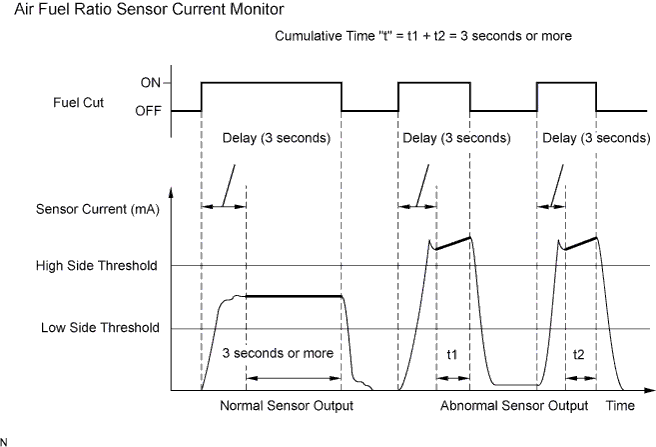
- Sensor current detection monitor A rich air-fuel mixture causes a low air fuel ratio sensor current, and a lean air-fuel mixture causes a high air fuel ratio sensor current. Therefore, the sensor output becomes low during acceleration, and it becomes high during deceleration with the throttle valve fully closed. The ECM monitors the air fuel ratio sensor current during fuel-cut and detects any abnormal current values. If the air fuel ratio sensor output is 2.2 mA or higher for more than 3 seconds of cumulative time, the ECM interprets this as a malfunction in the air fuel ratio sensor and stores DTC P2195 (stuck on high side). If the air fuel ratio sensor output is below 0.7 mA for more than 3 seconds of cumulative time, the ECM stores DTC P2196 (stuck on low side).
Monitor strategy
| Required Sensors/Components (Main) | Air fuel ratio sensor |
| Required Sensors/Components (Related) | Heated oxygen sensor |
| Frequency of Operation | Continuous: Sensor voltage detection monitor Once per driving cycle: Sensor current detection monitor |
| Duration | 3 seconds: Sensor current detection monitor 5 seconds: Sensor voltage detection monitor |
Typical enabling conditions
| Time after engine start | 30 seconds or more |
| Air fuel ratio sensor status | Activated |
| Fuel system status | Closed-loop |
| Auxiliary battery voltage | 11 V or higher |
| Engine coolant temperature | 75°C (167°F) or higher |
| Atmospheric pressure | 76 kPa (570 mmHg) or higher |
| Air fuel ratio sensor status | Activated |
| Continuous time of fuel cut | 3 to 10 seconds |
Typical malfunction thresholds
| Rear heated oxygen sensor voltage | 0.21 V or higher |
| Air fuel ratio sensor voltage | Higher than 3.8 V |
| Rear heated oxygen sensor voltage | Below 0.59 V |
| Air fuel ratio sensor voltage | Below 2.8 V |
| Air fuel ratio sensor current | 2.2 mA or higher |
| Air fuel ratio sensor current | Below 0.7 mA |
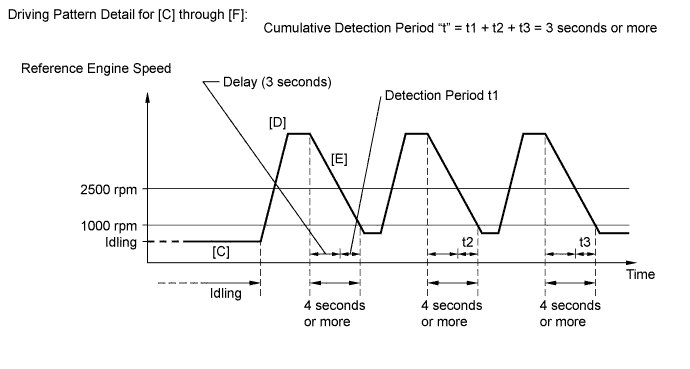
Confirmation driving pattern
HINT:
This confirmation driving pattern is used in the «Perform Confirmation Driving Pattern» procedure of the following diagnostic troubleshooting procedure.
- Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- Turn the power switch on (IG).
- Turn the tester on.
- Clear the DTCs (even if no DTCs are stored, perform the clear DTC operation).
- Turn the power switch off and wait for 30 seconds.
- Turn the power switch on (IG) and turn the tester on.
- Put the engine in inspection mode (maintenance mode) .
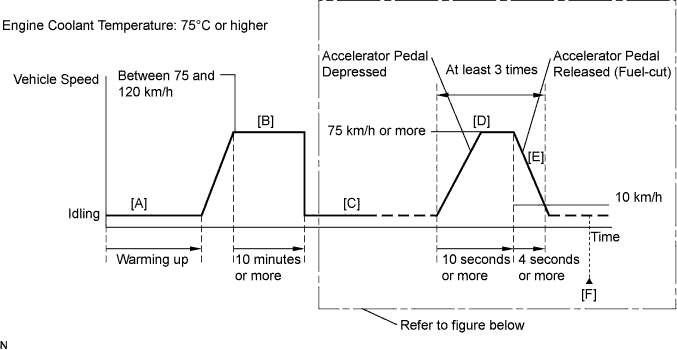
- Start the engine, and warm it up until the engine coolant temperature reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher [A].
- On the tester, enter the following menus to check the fuel-cut status: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / Idle Fuel Cut.
- Drive the vehicle at between 75 and 120 km/h (47 and 75 mph) for at least 10 minutes [B].
CAUTION:
When performing the confirmation driving pattern, obey all speed limits and traffic laws.
- Move the shift lever in B [C].
- Accelerate the vehicle to 75 km/h (47 mph) or more by depressing the accelerator pedal for at least 10 seconds [D].
- Soon after performing step [D] above, release the accelerator pedal for at least 4 seconds without depressing the brake pedal in order to execute fuel-cut control [E].
HINT:
Fuel-cut control is executed when the accelerator pedal is released while the vehicle is moving at 35 km/h (22 mph) or slower (Fuel-cut control is prohibited when the engine sped decreases to 1000 rpm or lower).
- Allow the vehicle to decelerate until the vehicle speed decreases to less than 10 km/h (6 mph).
- Repeat steps [C] through [E] above at least 3 times in one driving cycle.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC [F].
- Read the pending DTCs.
HINT:
- If a pending DTC is output, the system is malfunctioning.
- If a pending DTC is not output, perform the following procedure.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Utility / All Readiness.
- Input the DTC: P2195 or P2196.
- Check the DTC judgment result.
Tester Display Description NORMAL - DTC judgment completed
- System normal
ABNORMAL - DTC judgment completed
- System abnormal
INCOMPLETE - DTC judgment not completed
- Perform driving pattern after confirming DTC enabling conditions
UNKNOWN - Unable to perform DTC judgment
- Number of DTCs which do not fulfill DTC preconditions has reached ECU memory limit
HINT:
- If the judgment result shows NORMAL, the system is normal.
- If the judgment result shows ABNORMAL, the system has a malfunction.
- If the judgment result shows INCOMPLETE or UNKNOWN, perform steps [B] through [E].
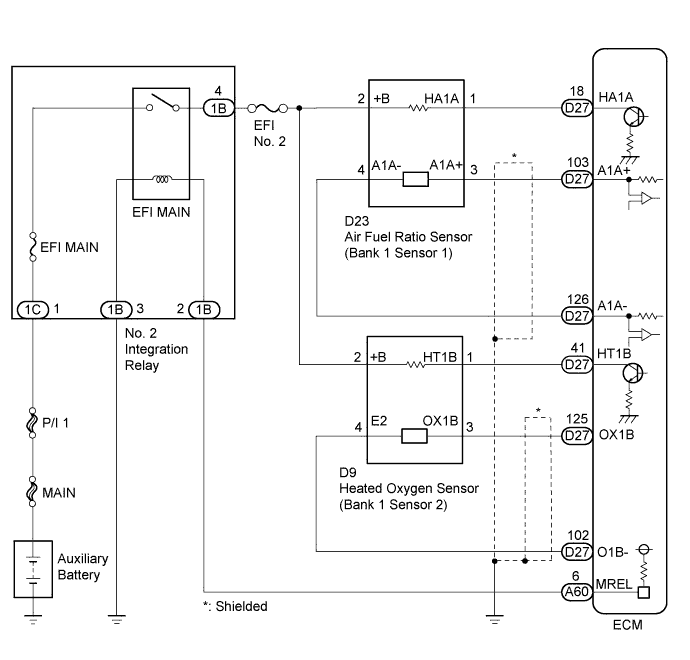
Wiring diagram
Inspection procedure
HINT:
- Although the DTC titles say oxygen sensor, these DTCs relate to the air fuel ratio sensor.
- Sensor 1 refers to the sensor mounted in front of the three-way catalytic converter and located near the engine assembly.
- Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
- A low air fuel ratio sensor voltage could be caused by a rich air fuel mixture. Check for conditions that would cause the engine to run rich.
- A high air fuel ratio sensor voltage could be caused by a lean air fuel mixture. Check for conditions that would cause the engine to run lean.
- Sensor 1 refers to the sensor closest to the engine assembly.
- Sensor 2 refers to the sensor farthest away from the engine assembly.
1.CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO P2195 OR P2196)
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the power switch on (IG).
-
Turn the tester on.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
-
Read the DTCs.
Result
Result Proceed to DTC P2195 or P2196 is output A «P2195 or P2196» and «P0136, P0137 or P0138» are output A DTC P2195 or P2196 and other DTCs are output B
HINT:
If any DTCs relating to the air fuel ratio sensor (DTCs for the air fuel ratio sensor heater or air fuel ratio sensor admittance) are output, troubleshoot those DTCs first.
2.CONFIRM IF VEHICLE HAS RUN OUT OF FUEL IN PAST
-
Has the vehicle run out of fuel in the past?
3.PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the power switch on (IG).
-
Turn the tester on.
-
Clear the DTCs .
-
Turn the power switch off and wait for 30 seconds.
-
Turn the power switch on (IG) and turn the tester on.
-
Put the engine in inspection mode (maintenance mode) .
-
Start the engine and warm it up.
-
Drive the vehicle in accordance with the driving pattern described in the Confirmation Driving Pattern.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Utility / All Readiness.
-
Input the DTC: P2195 or P2196.
-
Check the DTC judgment result.
Result
Result Proceed to NORMAL (DTC is not output) A ABNORMAL (DTC P2195 or P2196 is output) B
| A | |
|
DTC CAUSED BY RUNNING OUT OF FUEL |
4.READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR CURRENT)
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the power switch on (IG).
-
Turn the tester on.
-
Clear the DTCs .
-
Put the engine in inspection mode (maintenance mode) .
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / AFS Current B1S1.
-
Check the value of the air fuel ratio sensor output current during fuel-cut, referring to the Drive Pattern Detail for [C] through [F] in the Confirmation Driving Pattern.
HINT:
- To measure the air fuel ratio sensor current precisely, perform the fuel-cut operation as long as possible.
- If it is difficult to measure the air fuel ratio sensor current, use the snapshot function of the tester.
Result
Test Value Proceed to Within normal range (0.7 mA or higher, and below 2.2 mA) A Outside normal range (below 0.7 mA, or 2.2 mA or higher) B
5.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (CONTROL THE INJECTION VOLUME)
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the power switch on (IG).
-
Turn the tester on.
-
Put the engine in inspection mode (maintenance mode) .
-
Start the engine.
-
Warm up the air fuel ratio sensor at an engine speed of 2500 rpm for 90 seconds.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume.
-
Perform the Control the Injection Volume operation with the engine idling.
-
Monitor the output voltages of the air fuel ratio and heated oxygen sensors (AFS Voltage B1S1 and O2S B1S2) displayed on the tester.
HINT:
- Change the fuel injection volume within the range of -12.0% to +12.0%. The injection volume can be changed in fine gradations.
- The air fuel ratio sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and the heated oxygen sensor has a maximum output delay of approximately 20 seconds.
- If the sensor output voltage does not change (almost no reaction) while performing the Active Test, the sensor may be malfunctioning.
Standard
Tester Display (Sensor) Injection Volume Status Voltage AFS Voltage B1S1 (Air fuel ratio) +12.0% Rich Below 3.1 V AFS Voltage B1S1 (Air fuel ratio) -12.0% Lean Higher than 3.4 V O2S B1S2 (Heated oxygen) +12.0% Rich Higher than 0.55 V O2S B1S2 (Heated oxygen) -12.0% Lean Below 0.4 V Result
Status of AFS Voltage B1S1 Status of O2S B1S2 Air Fuel Ratio Condition and Air Fuel Ratio Sensor Condition Proceed to Lean Lean Actual air fuel ratio lean A Rich Rich Actual air fuel ratio rich A Lean Lean/Rich Air fuel ratio sensor malfunction B Rich Lean/Rich Air fuel ratio sensor malfunction B Lean/Rich Lean/Rich Normal C Lean: During the Control the Injection Volume Active Test, the air fuel ratio sensor output voltage (AFS Voltage) is consistently higher than 3.4 V, and the heated oxygen sensor output voltage (O2S) is consistently below 0.4 V. Rich: During the Control the Injection Volume Active Test, the AFS Voltage is consistently below 3.1 V, and the O2S is consistently higher than 0.55 V. Lean/Rich: During the Control the Injection Volume Active Test, the output voltage of the heated oxygen sensor alternates correctly.
HINT:
Refer to «Data List / Active Test» [AFS Voltage B1S1 and O2S B1S2] .
|
CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS |
|
-
Check the intake system for vacuum leaks .
OK:
No leaks in intake system.
|
REPAIR OR REPLACE INTAKE SYSTEM |
|
7.CHECK FOR EXHAUST GAS LEAK
-
Check for exhaust gas leaks from exhaust manifold sub-assembly and exhaust pipes..
OK:
No gas leaks.
|
REPAIR OR REPLACE EXHAUST SYSTEM |
|
-
Check the fuel pressure .
9.INSPECT FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY
-
Check the fuel injector assembly (whether fuel volume is high or low, and whether injector pattern is poor) .
|
REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY |
|
10.REPLACE AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR
-
Replace the air fuel ratio sensor .
11.PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the power switch on (IG).
-
Turn the tester on.
-
Clear the DTCs .
-
Turn the power switch off and wait for 30 seconds.
-
Drive the vehicle in accordance with the driving pattern described in the Confirmation Driving Pattern.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Utility / All Readiness.
-
Input the DTC: P2195 or P2196.
-
Check the DTC judgment result.
Result
Result Proceed to ABNORMAL (DTC P2195 or P2196 is output) A NORMAL (DTC is not output) B
12.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (CONTROL THE EGR STEP POSITION)
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the power switch on (IG).
-
Turn the tester on.
-
Put the engine in inspection mode (maintenance mode) .
-
Start the engine and warm it up until the engine coolant temperature reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher.
HINT:
The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the EGR Step Position / Data List / All Data / Throttle Idle Position and MAP.
-
Confirm that the Throttle Idle Position is ON and check the engine idling condition and MAP values in the Data List while performing the Active Test.
HINT:
- Do not leave the EGR valve open for 10 seconds or more during the Active Test.
- Be sure to return the EGR valve to step 0 when the Active Test is completed.
- Do not open the EGR valve 30 steps or more during the Active Test.
OK:
MAP and idling condition change in response to EGR step position when Throttle Idle Position is ON in Data List.
Standard:
— EGR Step Position (Active Test) 0 Steps 0 to 30 Steps Idling condition Steady idling Idling changes from steady to rough idling or stalls MAP (Data List) MAP value is 20 to 40 kPa (150 to 300 mmHg) (EGR valve is fully closed) MAP value is at least +10 kPa (75 mmHg) higher than when EGR valve is fully closed HINT:
During Active Test, if the idling condition does not change in response to EGR step position, then there is probably a malfunction in the EGR valve.
Result
Result Proceed to Outside of standard range A Within standard range B
13.INSPECT EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY
-
Remove the EGR valve assembly .
-
Check if the EGR valve is stuck open.
OK:
EGR valve us tightly closed.
|
REPLACE EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY |
|
-
Replace the ECM .
15.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the power switch on (IG).
-
Turn the tester on.
-
Clear the DTCs .
-
Turn the power switch off and wait for 30 seconds.
-
Drive the vehicle in accordance with the driving pattern described in the Confirmation Driving Pattern.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Utility / All Readiness.
-
Input the DTC: P2195 or P2196.
-
Check the DTC judgment result.
Result
Tester Display Description NORMAL - DTC judgment completed
- System normal
ABNORMAL - DTC judgment completed
- System abnormal
INCOMPLETE - DTC judgment not completed
- Perform driving pattern after confirming DTC enabling conditions
UNKNOWN - Unable to perform DTC judgment
- Number of DTCs which do not fulfill DTC preconditions has reached ECU memory limit
16.REPLACE AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR
-
Replace the air fuel ratio sensor .
17.PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the power switch on (IG).
-
Turn the tester on.
-
Clear the DTCs .
-
Turn the power switch off and wait for 30 seconds.
-
Drive the vehicle in accordance with the driving pattern described in the Confirmation Driving Pattern.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Utility / All Readiness.
-
Input the DTC: P2195 or P2196.
-
Check the DTC judgment result.
Result
Result Proceed to NORMAL (DTC is not output) A ABNORMAL (DTC P2195 or P2196 is output) B
-
Check the fuel lines for leaks or blockage.
|
REPAIR OR REPLACE FUEL LINE |
|
P2196 is a generic diagnostic trouble code that indicates that your Lexus IS 300’s first oxygen sensor on bank one is stuck rich. It does not necessarily mean that the vehicle itself is running too rich. This code is the opposite of code P2195, which indicates the oxygen sensor is stuck lean.
P2196 Definition: Oxygen Sensor – Stuck Rich (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
Oxygen Sensor
When you get P2196 it means that the voltage level being recorded by the oxygen sensor is stuck on the rich side (think like a high waveform). Your engine’s computer uses the data from the oxygen sensor to adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion. There’s information on how to test and determine if your IS 300’s oxygen sensor is bad in the diagnostic section below.
Stuck Rich
A rich condition means that there’s too much fuel in relation to air entering into the combustion chamber. When your oxygen sensor is “stuck rich” the data value that it is sending to the PCM is consistently measuring too high.
Bank 1
Bank one is the part of your IS 300’s engine with the first cylinder. You only need to concern yourself with this if there is more than one cylinder head (meaning inline-four and six engines get a pass). If there is more than one cylinder head, you’ll need to determine which bank is which.
The first cylinder is usually the furthest from the transmission (as a rule, it’s not definite for all vehicles). But, you can use this guide to help you determine where bank one.
Sensor 1
Once you find bank one, finding sensor one is pretty easy.
Sensor one would be the first sensor when tracing your IS 300’s exhaust from the combustion chamber to the exhaust pipe. It’s usually at the end of the exhaust manifold, or right where the exhaust manifold bolts up to the exhaust itself.
Usually, there are symptoms associated with P2196. Here are the most common ones:
- Black/Sooty smoke from the exhaust
- Poor MPG
- Engine runs rough or down on power
Lexus IS 300: P2196 Causes and Diagnosis
Below we have listed the most common causes of P2196, they are listed in an order of ease of diagnosis weighted with the likelihood of being the problem.
There are a lot of potential causes for P2196. Check for any other codes. If there are, they can provide valuable insight.
1. Check the Wiring Harness at the O2 Sensor
Your Lexus IS 300’s B1S1 O2 sensor has a tough life. It is right there on the hot exhaust, it also has to deal with a lot of engine vibration. The wiring harness to this sensor will fail more than almost any other automotive wiring.
Check to see if the wiring is burnt or frayed. Make sure that the pigtail that plugs into the sensor is snugged in tight and has no damage itself. You can do this pretty quickly with a flashlight. You can usually see this oxygen sensor without having to take anything apart.
You can use a multimeter to determine if there’s a short or open circuit. This article can make you an expert on the subject in no time.
2. Swap Test (Optional V6, V8 Only)
If you happen to be lucky enough to have a IS 300 with a V-8 or V6 engine, you can do something called the swap test. Basically, it involves removing the bank one sensor one oxygen(B1S1) sensor and replacing it with the bank two sensor one sensor(B2S1).
If you’re comfortable with a scan tool, you can skip this part and move straight on to capturing the short-term and long-term fuel trim values below. If you’re not comfortable with a scanner though, this test can save you a lot of time.
Here’s how to do the swap test:
- Clear the DTC codes with your scanner.
- Swap the Bank 2 Sensor 1 O2 sensor with the Bank 1 Sensor 1. It’ll be on or right after the exhaust manifold.
- Run the engine until the check engine light comes back on.
- If the code changes to P2198 (which indicates the O2 sensor on Bank 2 is stuck lean), that is enough proof that you need a new O2 sensor. Since the problem changed sides of the engine, we can be confident that the sensor is at fault.
- If the code remains P2196, you’ll need to continue pursuing your diagnosis, knowing that both O2 sensors are working fine.
3. Capture the Short/Long Term Fuel Trim Values
If you happen to have access to a scan tool, you can use it to capture the short and long-term fuel trim values. You’ll need to make sure that your IS 300’s engine is warmed up before you do this.
Doing this test will help you determine if the O2 sensor is operating within spec without having to do any looking under the hood. You’ll need to compare the values that you capture with your tool with the values the manufacturer specifies.
While this isn’t a skill most DIY mechanics have, the concept is simple, and you can learn enough to use fuel trim to your advantage by watching this 11-minute video (it’s worth it).
Related: Lexus IS 300 Bad Oxygen Sensor
4. Vacuum Leaks
Often a worn or brittle vacuum line will allow unmetered air into your IS 300’s engine. When this happens, it creates a lean condition.
You can test for a vacuum leak around the vacuum lines and the intake manifold. A common method is to spray carb cleaner around the intake/vacuum lines. When the spot is found the engine will rev higher with no throttle input.
Obviously, carb cleaner is super flammable. So be CAREFUL. Make sure you have a form of fire suppression available to you.
5. Other P2196 Causes
The steps listed above cover the most common causes of P2196. The trouble with this code though is, there are a lot of other things that can cause it as well.
Here are other things that can cause P2196:
- Bad or dirty MAF sensor
- Fuel pressure is too high (bad fuel pressure regulator usually, adds too much fuel to the air/fuel ratio)
- PCV system leak (cracked hoses going from the head to the intake)
- Bad fuel pressure sensor
- ECT Sensor
Bottom Line
In the Lexus IS 300, P2196 is usually caused by a bad oxygen sensor.
Doing your due diligence can save you a lot of time and wasted money/effort. Good luck!
Описание P2196 ошибки автомобиля Lexus. В нашем справочнике имеется следующая информация:
На русском языке:
Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 1 — сигнал постоянно богатой смеси
На английском языке:
O2 Sensor Signal Biased/Stuck Rich Bank 1 Sensor 1
Выберите модель для возможности более детального просмотра информации по этой ошибке:
Найти причину >>>
Принимая во внимание тот факт, что OBD2 ошибки работы электронных систем автомобиля не всегда на прямую указывают на неработающий элемент, а чаще дают всего лишь общую информацию о неисправности, мы пришли к следующему выводу:
В разных марках и моделях автомобилей одна и также ошибка может возникать как следствие неисправности абсолютно разных элементов.
Стало понятно, что просто необходим ресурс в котором можно найти не только общую информацию об OBD2 ошибке, а практические данные по конкретному автомобилю.
Опыт автоэлектриков показал, что если рассматривать определенную марка-модель автомобиля, то в подавляющем большинстве случаев причина возникновения какой либо ошибки одна и также.
Мы создаем, не без вашей помощи, справочник причинно-следственной связи возникновения той или иной OBD2 ошибки у конкретного автомобиля (марка и модель). Если на Ваш автомобиль не найдено описание (причинно-следственной связи) ошибки, то не стесняйтесь задавайте вопрос.
Если у вас есть опыт в устранении той или иной ошибки — делитесь опытом с другими пользователями. Так мы сможем сформировать полезный ресурс. По капле от каждого и всем будет полезно.
Возможно будет интересно:
Если ошибка указывает на неверные параметры (высокие или низкие значения) какого нибудь из датчиков или анализаторов, то вероятней всего этот элемент исправен, а проблему надо искать так сказать «выше по течению», в элементах работу которых анализирует датчик или зонд.
Если ошибка указывает на постоянно открытый или закрытый клапан, то тут надо подойти к решению вопроса с умом, а не менять бездумно этот элемент. Причин может быть несколько: клапан засорен, клапан заклинил, на клапан приходит неверный сигнал от других неисправных узлов.
Автомобили с каждым днем становятся все более сложными, но и более диагностируемыми. Наш форум создан для всех, от простых автолюбителей до профессиональных автоэлектриков.
Выполняется любое из следующих условий:
-
Условия (a) и (b) сохраняются в течение не менее 5 с (логика диагностирования за 2 поездки):
(a) Напряжение датчика состава топливовоздушной смеси превышает 3,8 В.
(b) Напряжение подогреваемого кислородного датчика превышает 0,21 В.
-
Во время прекращения подачи топлива (при замедлении автомобиля) ток датчика состава топливовоздушной смеси составляет не менее 2,2 мА в течение 3 с (логика диагностирования за 2 поездки).
-
Обрыв или короткое замыкание в цепи датчика состава топливовоздушной смеси (датчик 1)
-
Датчик состава топливовоздушной смеси (датчик 1)
-
Утечки газов из системы выпуска отработавших газов
-
Система забора воздуха
-
Давление в топливной системе
-
Топливная форсунка в сборе
-
Топливная система
-
ECM
Выполняется любое из следующих условий:
-
Условия (a) и (b) сохраняются в течение не менее 5 с (логика диагностирования за 2 поездки):
(a) Напряжение датчика состава топливовоздушной смеси менее 2,8 В.
(b) Напряжение подогреваемого кислородного датчика менее 0,69 В.
-
Во время прекращения подачи топлива (при замедлении автомобиля) ток датчика состава топливовоздушной смеси менее 0,7 мА в течение 3 с (логика диагностирования за 2 поездки).
-
Обрыв или короткое замыкание в цепи датчика состава топливовоздушной смеси (датчик 1)
-
Датчик состава топливовоздушной смеси (датчик 1)
-
Утечки газов из системы выпуска отработавших газов
-
Система забора воздуха
-
Давление в топливной системе
-
Топливная форсунка в сборе
-
Топливная система
-
ECM