Чтобы разобраться, в чем разница между ошибками времени компиляции и ошибками времени выполнения в Java, разберемся в сути каждого вида.
Ошибки времени компиляции
Это синтаксические ошибки в коде, которые препятствуют его компиляции.
Пример
public class Test{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello")
}
}
Итог
C:\Sample>Javac Test.java
Test.java:3: error: ';' expected
System.out.println("Hello")
Ошибки времени выполнения
Исключение (или исключительное событие) – это проблема, возникающая во время выполнения программы. Когда возникает исключение, нормальный поток программы прерывается, и программа / приложение прерывается ненормально, что не рекомендуется, поэтому эти исключения должны быть обработаны.
Пример
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class FilenotFound_Demo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
File file = new File("E://file.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
}
}
Итог
C:\>javac FilenotFound_Demo.java
FilenotFound_Demo.java:8: error: unreported exception
FileNotFoundException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
^
1 error
Error is an illegal operation performed by the user which results in the abnormal working of the program. Programming errors often remain undetected until the program is compiled or executed. Some of the errors inhibit the program from getting compiled or executed. Thus errors should be removed before compiling and executing.
The most common errors can be broadly classified as follows:
1. Run Time Error:
Run Time errors occur or we can say, are detected during the execution of the program. Sometimes these are discovered when the user enters an invalid data or data which is not relevant. Runtime errors occur when a program does not contain any syntax errors but asks the computer to do something that the computer is unable to reliably do. During compilation, the compiler has no technique to detect these kinds of errors. It is the JVM (Java Virtual Machine) that detects it while the program is running. To handle the error during the run time we can put our error code inside the try block and catch the error inside the catch block.
For example: if the user inputs a data of string format when the computer is expecting an integer, there will be a runtime error. Example 1: Runtime Error caused by dividing by zero
Java
class DivByZero {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int var1 = 15;
int var2 = 5;
int var3 = 0;
int ans1 = var1 / var2;
int ans2 = var1 / var3;
System.out.println(
"Division of va1"
+ " by var2 is: "
+ ans1);
System.out.println(
"Division of va1"
+ " by var3 is: "
+ ans2);
}
}
Runtime Error in java code:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at DivByZero.main(File.java:14)
Example 2: Runtime Error caused by Assigning/Retrieving Value from an array using an index which is greater than the size of the array
Java
class RTErrorDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = new int[5];
arr[9] = 250;
System.out.println("Value assigned! ");
}
}
RunTime Error in java code:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 9
at RTErrorDemo.main(File.java:10)
2. Compile Time Error:
Compile Time Errors are those errors which prevent the code from running because of an incorrect syntax such as a missing semicolon at the end of a statement or a missing bracket, class not found, etc. These errors are detected by the java compiler and an error message is displayed on the screen while compiling. Compile Time Errors are sometimes also referred to as Syntax errors. These kind of errors are easy to spot and rectify because the java compiler finds them for you. The compiler will tell you which piece of code in the program got in trouble and its best guess as to what you did wrong. Usually, the compiler indicates the exact line where the error is, or sometimes the line just before it, however, if the problem is with incorrectly nested braces, the actual error may be at the beginning of the block. In effect, syntax errors represent grammatical errors in the use of the programming language.
Example 1: Misspelled variable name or method names
Java
class MisspelledVar {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a = 40, b = 60;
int Sum = a + b;
System.out.println(
"Sum of variables is "
+ sum);
}
}
Compilation Error in java code:
prog.java:14: error: cannot find symbol
+ sum);
^
symbol: variable sum
location: class MisspelledVar
1 error
Example 2: Missing semicolons
Java
class PrintingSentence {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String s = "GeeksforGeeks";
System.out.println("Welcome to " + s)
}
}
Compilation Error in java code:
prog.java:8: error: ';' expected
System.out.println("Welcome to " + s)
^
1 error
Example: Missing parenthesis, square brackets, or curly braces
Java
class MissingParenthesis {
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println("Printing 1 to 5 \n");
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= 5; i++ {
System.out.println(i + "\n");
}
}
}
Compilation Error in java code:
prog.java:10: error: ')' expected
for (i = 1; i <= 5; i++ {
^
1 error
Example: Incorrect format of selection statements or loops
Java
class IncorrectLoop {
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println("Multiplication Table of 7");
int a = 7, ans;
int i;
for (i = 1, i <= 10; i++) {
ans = a * i;
System.out.println(ans + "\n");
}
}
}
Compilation Error in java code:
prog.java:12: error: not a statement
for (i = 1, i <= 10; i++) {
^
prog.java:12: error: ';' expected
for (i = 1, i <= 10; i++) {
^
2 errors
Logical Error: A logic error is when your program compiles and executes, but does the wrong thing or returns an incorrect result or no output when it should be returning an output. These errors are detected neither by the compiler nor by JVM. The Java system has no idea what your program is supposed to do, so it provides no additional information to help you find the error. Logical errors are also called Semantic Errors. These errors are caused due to an incorrect idea or concept used by a programmer while coding. Syntax errors are grammatical errors whereas, logical errors are errors arising out of an incorrect meaning. For example, if a programmer accidentally adds two variables when he or she meant to divide them, the program will give no error and will execute successfully but with an incorrect result.
Example: Accidentally using an incorrect operator on the variables to perform an operation (Using ‘/’ operator to get the modulus instead using ‘%’)
Java
public class LErrorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int num = 789;
int reversednum = 0;
int remainder;
while (num != 0) {
remainder = num / 10;
reversednum
= reversednum * 10
+ remainder;
num /= 10;
}
System.out.println("Reversed number is "
+ reversednum);
}
}
Output:
Reversed number is 7870
Example: Displaying the wrong message
Java
class IncorrectMessage {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a = 2, b = 8, c = 6;
System.out.println(
"Finding the largest number \n");
if (a > b && a > c)
System.out.println(
a + " is the largest Number");
else if (b > a && b > c)
System.out.println(
b + " is the smallest Number");
else
System.out.println(
c + " is the largest Number");
}
}
Output:
Finding the largest number 8 is the smallest Number
Syntax Error:
Syntax and Logical errors are faced by Programmers.
Spelling or grammatical mistakes are syntax errors, for example, using an uninitialized variable, using an undefined variable, etc., missing a semicolon, etc.
int x, y; x = 10 // missing semicolon (;) z = x + y; // z is undefined, y in uninitialized.
Syntax errors can be removed with the help of the compiler.
Last Updated :
08 Jun, 2022
Like Article
Save Article
While working with the programming languages like executing a software program, there are many instances that we run into issues due to the run time errors or compilation errors. All these errors occur when the application is running. You might come across an instance where the application acts differently in a negative way to the requirements, then it means that a runtime error took place.
As it is one of the most common type of error that occurs during a software executive, let us get a deep idea on how to fix common types of runtime errors in Java and also the steps to be taken to resolve them on a timely basis.
Contents
- 1 Fix the 5 Most Common Types of Runtime Errors in Java
- 1.1 What is a Runtime Error in Java?
- 1.2 Differences Between Compile Time Error and Runtime Error in Java
- 1.3 Why Runtime Error Occurs in Java ?
- 1.4 1. Accessing Out of Range Value in an Array
- 1.5 2. Division by Zero Error
- 1.6 3. Less Space or Insufficient Space Memory Error
- 1.7 4. Conversion of an Invalid string into a Number
- 1.8 5. Attempting to Store an Incompatible Value to a Collection
- 1.9 How to solve Runtime Rrror in Java Programming?
Fix the 5 Most Common Types of Runtime Errors in Java
What is a Runtime Error in Java?
A runtime error in Java is referred to as an application error that comes up during the execution process of the program. This runtime error usually takes place when the syntax is corrected as expected while the issue lies during the program execution. All these errors can be detected by JVM – Java Virtual Machine and cannot be identified during the compilation time. Java is one of the most sought-after programming languages for the hiring managers across the world. So become an expert in Java through our Java Training and grab the best job opportunity.
Now, In this post, Let us discuss the top runtime errors in Java.
- Division by zero errors
- IO errors
- Out of range errors
- Undefined object errors
Differences Between Compile Time Error and Runtime Error in Java
Compile time errors are those errors in which the syntax would be incorrect in the application code. An example would be like missing semicolons, parenthesis, incorrect keywords, usage of undeclared variables, etc.
The Java compiler is capable of detecting the syntax errors during the compile time and the error message will be appearing on the screen. The compiler is also capable of preventing the code from the execution unless and until the error is resolved. Therefore it is important that these errors are addressed by making the necessary changes before the program is successfully executed.
The runtime errors occur during the program execution after the compilation has completed. Any program that is throwing a runtime error means that there are no issues with Syntax in the program.
Why Runtime Error Occurs in Java ?
Below listed are the most common types of runtime errors that occur in Java.
- Accessing an element that is out of range in an array
- Dividing a number with 0
- Less space or insufficient space memory
- Conversion of an invalid string into a number
- Attempting to store an incompatible value to a collection
When you come across such an address, you need to know that the Java compiler will be generating an error message and the program gets terminated abnormally. Runtime errors do not require to be caught explicitly. It is useful if you catch the runtime errors and resolve them to complete the program execution.
Let us review a few of the most common runtime errors in Java programming with examples to gain a deeper understanding.
1. Accessing Out of Range Value in an Array
|
public class ValueOutOfRangeErrorExample { public static void main(String[] args) { int k[] = new int[8]; System.out.println(«8th element in array: « + k[8]); } } |
In the above example, the array is initialized with 8 elements. with the above code, An element at position number 8 is trying to get access and does not exist at all, leading to the Exception java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:
Error :
|
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 8 out of bounds for length 8 at ValueOutOfRangeErrorExample.main(ValueOutOfRangeErrorExample.java:4) |
2. Division by Zero Error
Below is an example of java.lang.ArithmeticException which occurs when the user is trying to code in such a way that they perform the division by zero.
|
public class ArithmeticExceptionExample { public static void main(String[] args) { int num1 = 10, num2 = 0; System.out.println(«Result: «+ num1/num2); } } |
In the above code, the integer num1 is getting to be divided by num2 which has a value of zero, which is leading to the exception called java.lang.ArithmeticException
Below is the Error Thrown :
|
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at ArithmeticExceptionExample.main(ArithmeticExceptionExample.java:4) |
3. Less Space or Insufficient Space Memory Error
Below is an example of java.lang.OutOfMemoryError, which occurs when the user is trying to initialize an Integer array with a very large size, and due to the Java heap being insufficient to allocate this memory space, it throws an Error java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
|
public class OutOfMemory { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer[] myArray = new Integer[1000*1000*1000]; } } |
Error :
|
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space at OutOfMemory.main(OutOfMemory.java:5) |
4. Conversion of an Invalid string into a Number
Below is an example of java.lang.NumberFormatException, occurs when the user is trying to convert an alphanumeric string to an integer which leads to java.lang.NumberFormatException
|
public class NumberFormatException { public static void main(String[] args) { int a; a= Integer.parseInt(«12Mehtab»); System.out.println(a); } } |
Error :
|
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: «12Mehtab» at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:580) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:615) at NumberFormatException.main(NumberFormatException.java:6) |
5. Attempting to Store an Incompatible Value to a Collection
Below is an example where user has created the ArrayList of String but trying to store the integer value which leads to Exception java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem
|
import java.util.ArrayList; public class IncompatibleType { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> student = new ArrayList<>(); student.add(1); } } |
Error :
|
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem: The method add(int, String) in the type ArrayList<String> is not applicable for the arguments (int) at IncompatibleType.main(IncompatibleType.java:7) |
How to solve Runtime Rrror in Java Programming?
The runtime errors can be solved by using the try catch blocks in Java. Below are the steps to be followed:
- You will need to Surround the statements that are capable of throwing an exception or a runtime error in the try catch blocks.
- The next step is to catch the error.
- Based on the requirements of the court or an application, it is important to take the necessary action.
Like we discussed earlier about the ArithmeticException example, it can be corrected by making the below changes.
|
public class ArithmeticExceptionExample { public static void main(String[] args) { try { int num1 = 10, num2 = 0; System.out.println(«Result: « + num1/num2); } catch (ArithmeticException ae) { System.out.println(«Arithmetic Exception — cannot divide by 0»); } System.out.println(«Let’s continue the execution…»); } } |
As the code is surrounded in the try catch blocks, the program will continue to execute after the exception is encountered.
Result :
|
Arithmetic Exception — cannot divide by 0 Let’s continue the execution... |
In this way, it is important for you to identify the Runtime errors and also clear them without any hesitation. You can make use of the try catch blocks and many other resolutions which were helped in successful program execution. Also you will be able to track, manage and analyze the errors in real time. So this was all from this tutorial about fixing the 5 most common types of Runtime Errors in Java But still, if you have any queries, feel free to ask in the comment section. And don’t forget to stay tuned with the Tutorials field to learn this type of awesome tutorial. HAPPY CODING.
People Are Also Reading…
- How to Play Mp3 File in Java Tutorial | Simple Steps
- Menu Driven Program in Java Using Switch Case
- Calculator Program in Java Swing/JFrame with Source Code
- Registration Form in Java With Database Connectivity
- How to Create Login Form in Java Swing
- Text to Speech in Java
- How to Create Splash Screen in Java
- Java Button Click Event
- 11 Best WebSites to Learn Java Online for Free
В Java нежелательное событие, которое прерывает выполнение программы, называется ошибкой. Это происходит либо из-за синтаксических проблем, либо из-за каких-то других проблем, которые не могут быть обнаружены во время компиляции. Ошибки, которые не могут быть обнаружены во время компиляции и, следовательно, возникают во время выполнения программы, известны как ошибки времени выполнения, в то время как ошибки с синтаксическими проблемами называются временем компиляции ошибки.
В этой статье представлен подробный обзор ошибок времени выполнения в java, и в связи с этим нам необходимо понять следующие понятия:
- Что такое ошибки выполнения в Java?
- Типы ошибок выполнения в Java
- Факторы, вызывающие ошибки времени выполнения
- Примеры ошибок выполнения
- Как обрабатывать ошибки во время выполнения
Итак, приступим!
Что такое ошибки выполнения в Java?
Ошибки, возникающие во время выполнения программы, называются ошибками времени выполнения. Эти типы ошибок не могут быть обнаружены во время компиляции, поскольку в их синтаксисе нет ничего плохого. Таким образом, мы можем сказать, что программа, которая синтаксически правильная, все же выдает ошибку во время выполнения программы, называется ошибкой времени выполнения.
Типы ошибок выполнения в Java
Существует несколько типов ошибок времени выполнения, с которыми мы можем столкнуться во время выполнения программы. Некоторые часто встречающиеся ошибки во время выполнения перечислены ниже:
- Ошибки ввода-вывода
- Ошибка бесконечного цикла
- Деление на ноль ошибок
- Логические ошибки
- Ошибки вне диапазона
- Ошибка неопределенного объекта
Факторы, вызывающие ошибки времени выполнения
Существует множество факторов, вызывающих ошибки времени выполнения, среди них наиболее часто встречающиеся причины перечислены ниже:
- Деление любого числового значения на ноль приводит к ошибкам времени выполнения.
- Доступ к массиву за пределами границ.
- Передача неверных данных, например. передача числового значения в нечисловое поле.
- Передача неверных параметров/аргументов в метод.
- Несколько процессов пытаются одновременно получить доступ к одному и тому же ресурсу.
- Попытка сохранить значение несовместимого типа в коллекции.
- Ошибка нехватки места/памяти в потоках (OutOfMemoryError)
Примеры ошибок выполнения
Давайте разберемся с концепцией ошибок времени выполнения на примерах.
Пример
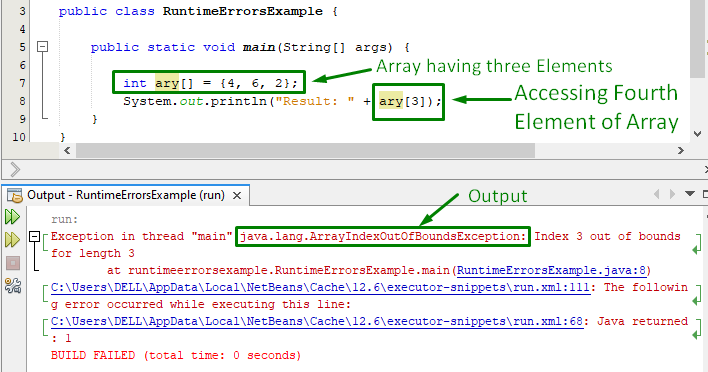
В этом примере у нас есть массив размера три:
общественныйкласс Пример выполнения {
общественныйстатическийпустота главный(Нить[] аргументы){
инт ари[]={4, 6, 2};
Система.из.печать(«Результат: «+ ари[3]);
}
}
Длина массива равна трем, и мы знали, что индексация массива начинается с нуля. Итак, указание ary[3] означает, что мы пытаемся получить доступ к четвертому элементу массива. Синтаксически в этом нет ничего плохого, так что мы не столкнулись с какой-либо ошибкой во время компиляции. Однако JVM выдаст ошибку во время выполнения:
Из приведенного выше фрагмента мы видим, что ошибка возникает во время выполнения, когда мы пытаемся получить доступ к индексу вне допустимого диапазона.
Для ясности концепции рассмотрим еще один пример:
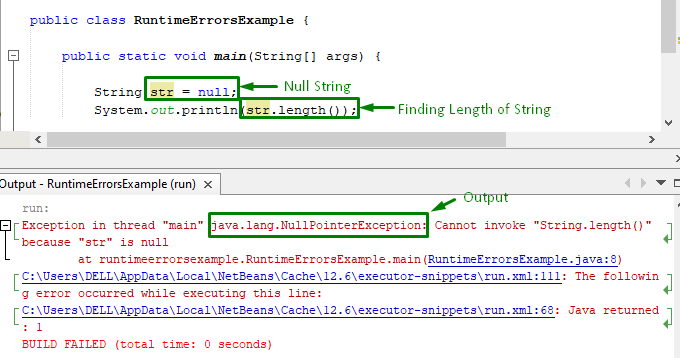
Пример
На этот раз у нас есть строка, назначенная с «нулевой» value и попробуем найти длину строки:
общественныйкласс Пример выполнения {
общественныйстатическийпустота главный(Нить[] аргументы){
Нить ул =нулевой;
Система.из.печать(ул.длина());
}
}
Ниже будет вывод для приведенного выше фрагмента кода:
Когда мы запускаем программу, мы сталкиваемся с Исключение нулевого указателя потому что строка нулевая.
Итак, как обрабатывать такие ошибки во время выполнения? Предоставляет ли java решение для устранения таких ошибок во время выполнения? Конечно, Java.
Как обрабатывать ошибки во время выполнения
В Java ошибки времени выполнения могут быть решены с помощью операторов try-catch, и для этого мы должны поместить код, который может вызвать ошибку времени выполнения, в операторы try-catch.
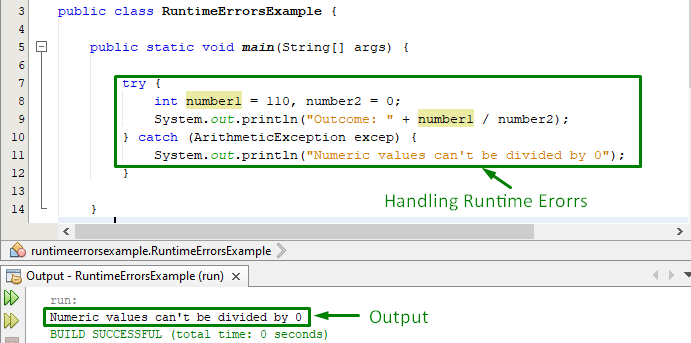
Пример
Давайте рассмотрим приведенный ниже фрагмент кода, чтобы понять, как решать ошибки времени выполнения с помощью операторов try-catch в java:
общественныйкласс Пример выполнения {
общественныйстатическийпустота главный(Нить[] аргументы){
пытаться{
инт номер 1 =110, номер 2 =0;
Система.из.печать(«Исход: «+ номер 1 / номер 2);
}ловить(Арифметическое исключение кроме){
Система.из.печать(«Числовые значения нельзя делить на 0»);
}
}
Теперь мы окружили код операторами try-catch, которые могут вызвать ошибку:
На этот раз вместо того, чтобы выдавать ошибку, JVM показывает сообщение, которое мы указали в блоке catch.
Вывод
В Java программы, которые являются синтаксически правильными, но все же выдают некоторые ошибки во время выполнения программы, называются ошибками времени выполнения. Эти ошибки возникают по разным причинам, таким как деление на ноль, доступ к массиву за пределами границ, передача неверных данных, например. передача числового значения в нечисловое поле и т. д. Эти типы ошибок можно обработать, окружив блок try-catch вокруг кода, который может вызывать ошибки времени выполнения. В этой статье объясняются различные аспекты ошибок времени выполнения, например, что такое ошибки времени выполнения, их типы, причины и способы исправления этих ошибок в java.
A runtime error in Java is an application error that occurs during the execution of a program. A runtime error occurs when a program is syntactically correct but contains an issue that is only detected during program execution. These issues cannot be caught at compile-time by the Java compiler and are only detected by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) when the application is running.
Runtime errors are a category of exception that contains several more specific error types. Some of the most common types of runtime errors are:
- IO errors
- Division by zero errors
- Out of range errors
- Undefined object errors
Runtime Errors vs Compile-Time Errors
Compile-time errors occur when there are syntactical issues present in application code, for example, missing semicolons or parentheses, misspelled keywords or usage of undeclared variables.
These syntax errors are detected by the Java compiler at compile-time and an error message is displayed on the screen. The compiler prevents the code from being executed until the error is fixed. Therefore, these errors must be addressed by debugging before the program can be successfully run.
On the other hand, runtime errors occur during program execution (the interpretation phase), after compilation has taken place. Any code that throws a runtime error is therefore syntactically correct.
Runtime Errors vs Logical Errors
A runtime error could potentially be a legitimate issue in code, for example, incorrectly formatted input data or lack of resources (e.g. insufficient memory or disk space). When a runtime error occurs in Java, the compiler specifies the lines of code where the error is encountered. This information can be used to trace back where the problem originated.
On the other hand, a logical error is always the symptom of a bug in application code leading to incorrect output e.g. subtracting two variables instead of adding them. In case of a logical error, the program operates incorrectly but does not terminate abnormally. Each statement may need to be checked to identify a logical error, which makes it generally harder to debug than a runtime error.
What Causes Runtime Errors in Java
The most common causes of runtime errors in Java are:
- Dividing a number by zero.
- Accessing an element in an array that is out of range.
- Attempting to store an incompatible type value to a collection.
- Passing an invalid argument to a method.
- Attempting to convert an invalid string to a number.
- Insufficient space in memory for thread data.
When any such errors are encountered, the Java compiler generates an error message and terminates the program abnormally. Runtime errors don’t need to be explicitly caught and handled in code. However, it may be useful to catch them and continue program execution.
To handle a runtime error, the code can be placed within a try-catch block and the error can be caught inside the catch block.
Runtime Error Examples
Division by zero error
Here is an example of a java.lang.ArithmeticException, a type of runtime exception, thrown due to division by zero:
public class ArithmeticExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10, b = 0;
System.out.println("Result: "+ a/b);
}
}In this example, an integer a is attempted to be divided by another integer b, whose value is zero, leading to a java.lang.ArithmeticException:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at ArithmeticExceptionExample.main(ArithmeticExceptionExample.java:4)
Accessing an out of range value in an array
Here is an example of a java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionthrown due to an attempt to access an element in an array that is out of bounds:
public class ValueOutOfRangeErrorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = new int[5];
System.out.println("5th element in array: " + arr[5]);
}
}In this example, an array is initialized with 5 elements. An element at position 5 is later attempted to be accessed in the array, which does not exist, leading to a java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException runtime error:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 5 out of bounds for length 5
at ValueOutOfRangeErrorExample.main(ValueOutOfRangeErrorExample.java:4)
How to Solve Runtime Errors
Runtime errors can be handled in Java using try-catch blocks with the following steps:
- Surround the statements that can throw a runtime error in try-catch blocks.
- Catch the error.
- Depending on the requirements of the application, take necessary action. For example, log the exception with an appropriate message.
To illustrate this, the code in the earlier ArithmeticException example can be updated with the above steps:
public class ArithmeticExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int a = 10, b = 0;
System.out.println("Result: " + a/b);
} catch (ArithmeticException ae) {
System.out.println("Arithmetic Exception: cannot divide by 0");
}
System.out.println("Continuing execution...");
}
}
Surrounding the code in try-catch blocks like the above allows the program to continue execution after the exception is encountered:
Arithmetic Exception: cannot divide by 0
Continuing execution…Runtime errors can be avoided where possible by paying attention to detail and making sure all statements in code are mathematically and logically correct.
Track, Analyze and Manage Errors With Rollbar

Managing errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you to proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates error monitoring and triaging, making fixing errors easier than ever. Try it today.