Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
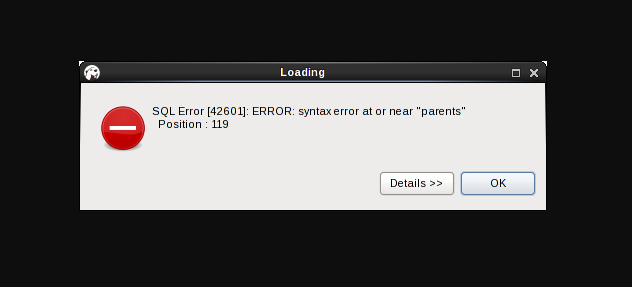
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:
Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
Хочу апдейтить число работников d.number_employees исходя из агрегированной таблицы employees, но постгрес пишет ошибку
SQL Error [42601]: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: ",")
Сам запрос вот:
UPDATE departaments AS d,
(SELECT department, COUNT(*) AS numb
FROM employees
GROUP BY department) AS e
SET d.number_employees = e.numb
WHERE d.departament_name = e.department;
задан 8 ноя 2022 в 13:06
3
У меня получилось так. Дело оказалось не во вложенном запросе, а в алиасе, по какой-то причине posgresql не взлюбил его.
UPDATE departaments
SET number_employees = empl.cnt
FROM (SELECT departament, COUNT(*) AS cnt FROM employees GROUP BY departament) AS empl
WHERE departament_name = empl.departament;
ответ дан 8 ноя 2022 в 16:36
восстановить базу из дампа:
--
-- PostgreSQL database dump
--
-- Dumped from database version 10.19 (Ubuntu 10.19-0ubuntu0.18.04.1)
-- Dumped by pg_dump version 10.19 (Ubuntu 10.19-0ubuntu0.18.04.1)
SET statement_timeout = 0;
SET lock_timeout = 0;
SET idle_in_transaction_session_timeout = 0;
SET client_encoding = 'UTF8';
SET standard_conforming_strings = on;
SELECT pg_catalog.set_config('search_path', '', false);
SET check_function_bodies = false;
SET xmloption = content;
SET client_min_messages = warning;
SET row_security = off;
--
-- Name: plpgsql; Type: EXTENSION; Schema: -; Owner:
--
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS plpgsql WITH SCHEMA pg_catalog;
--
-- Name: EXTENSION plpgsql; Type: COMMENT; Schema: -; Owner:
--
COMMENT ON EXTENSION plpgsql IS 'PL/pgSQL procedural language';
--
-- Name: attribute_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE SEQUENCE public.attribute_id_seq
START WITH 1
INCREMENT BY 1
NO MINVALUE
NO MAXVALUE
CACHE 1;
ALTER TABLE public.attribute_id_seq OWNER TO bender;
SET default_tablespace = '';
SET default_with_oids = false;
--
-- Name: attribute; Type: TABLE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE TABLE public.attribute (
attribute_id integer DEFAULT nextval('public.attribute_id_seq'::regclass) NOT NULL,
name character varying(30) NOT NULL,
attribute_type_id integer NOT NULL
);
ALTER TABLE public.attribute OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: attribute_type_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE SEQUENCE public.attribute_type_id_seq
START WITH 1
INCREMENT BY 1
NO MINVALUE
NO MAXVALUE
CACHE 1;
ALTER TABLE public.attribute_type_id_seq OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: attribute_type; Type: TABLE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE TABLE public.attribute_type (
attribute_type_id integer DEFAULT nextval('public.attribute_type_id_seq'::regclass) NOT NULL,
name character varying(50) NOT NULL
);
ALTER TABLE public.attribute_type OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: film_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE SEQUENCE public.film_id_seq
START WITH 1
INCREMENT BY 1
NO MINVALUE
NO MAXVALUE
CACHE 1;
ALTER TABLE public.film_id_seq OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: film; Type: TABLE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE TABLE public.film (
film_id integer DEFAULT nextval('public.film_id_seq'::regclass) NOT NULL,
name character varying(50) NOT NULL
);
ALTER TABLE public.film OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: film_attributes_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE SEQUENCE public.film_attributes_id_seq
START WITH 1
INCREMENT BY 1
NO MINVALUE
NO MAXVALUE
CACHE 1;
ALTER TABLE public.film_attributes_id_seq OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: film_attributes; Type: TABLE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE TABLE public.film_attributes (
film_attributes_id integer DEFAULT nextval('public.film_attributes_id_seq'::regclass) NOT NULL,
attribute_id integer NOT NULL,
film_id integer NOT NULL,
value_text character varying,
value_integer integer,
value_float double precision,
value_boolean boolean,
value_timestamp timestamp with time zone
);
ALTER TABLE public.film_attributes OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: film_attributes_values; Type: VIEW; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE VIEW public.film_attributes_values AS
SELECT
NULL::character varying(50) AS name,
NULL::character varying(50) AS attribute_type,
NULL::character varying(30) AS attribute_name,
NULL::character varying AS attribute_value;
ALTER TABLE public.film_attributes_values OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: film_tasks; Type: VIEW; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE VIEW public.film_tasks AS
SELECT
NULL::character varying(50) AS name,
NULL::character varying[] AS today_tasks,
NULL::character varying[] AS twenty_days_tasks;
ALTER TABLE public.film_tasks OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Data for Name: attribute; Type: TABLE DATA; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
COPY public.attribute (attribute_id, name, attribute_type_id) FROM stdin;
1 Рецензии 3
3 Премия Оскар 2
4 Премия Ника 2
5 Премия Золотой Глобус 2
10 Описание фильма 3
11 Длительность (мин.) 1
12 Длительность проката (дней) 1
2 Рейтинг 7
6 Премьера в мире 6
7 Премьера в России 6
8 Старт продажи билетов 6
9 Старт проката 6
13 Окончание проката 6
\.
--
-- Data for Name: attribute_type; Type: TABLE DATA; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
COPY public.attribute_type (attribute_type_id, name) FROM stdin;
1 integer
2 boolean
3 text
4 date
5 numeric
6 timestamp
7 float
\.
--
-- Data for Name: film; Type: TABLE DATA; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
COPY public.film (film_id, name) FROM stdin;
1 Spoiler-man: No Way
2 Matrix 4
\.
--
-- Data for Name: film_attributes; Type: TABLE DATA; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
COPY public.film_attributes (film_attributes_id, attribute_id, film_id, value_text, value_integer, value_float, value_boolean, value_timestamp) FROM stdin;
1 1 1 Годный фильм, распинаюсь про сюжет, пишу про игру актеров, все круто \N \N \N \N
2 1 2 Джон Уик уже не тот, сестры Вачовски сбрендили, полная фигня \N \N \N \N
5 3 1 f \N \N \N \N
7 6 2 \N \N \N \N 2021-12-10 00:00:00+03
9 7 2 \N \N \N \N 2021-12-30 00:00:00+03
10 8 1 \N \N \N \N 2021-12-10 00:00:00+03
11 8 2 \N \N \N \N 2021-12-07 00:00:00+03
12 12 1 \N 21 \N \N \N
13 12 2 \N 14 \N \N \N
14 9 1 \N \N \N \N 2021-12-15 00:00:00+03
15 9 2 \N \N \N \N 2021-12-15 00:00:00+03
16 13 1 \N \N \N \N 2022-01-04 00:00:00+03
17 13 2 \N \N \N \N 2022-01-04 00:00:00+03
18 3 2 t \N \N \N \N
6 6 1 \N \N \N \N 2021-12-15 00:00:00+03
8 7 1 \N \N \N \N 2022-01-04 00:00:00+03
\.
--
-- Name: attribute_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE SET; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
SELECT pg_catalog.setval('public.attribute_id_seq', 13, true);
--
-- Name: attribute_type_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE SET; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
SELECT pg_catalog.setval('public.attribute_type_id_seq', 6, true);
--
-- Name: film_attributes_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE SET; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
SELECT pg_catalog.setval('public.film_attributes_id_seq', 18, true);
--
-- Name: film_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE SET; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
SELECT pg_catalog.setval('public.film_id_seq', 2, true);
--
-- Name: attribute attribute_pkey; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.attribute
ADD CONSTRAINT attribute_pkey PRIMARY KEY (attribute_id);
--
-- Name: attribute_type attribute_type_name_key; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.attribute_type
ADD CONSTRAINT attribute_type_name_key UNIQUE (name);
--
-- Name: attribute_type attribute_type_pkey; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.attribute_type
ADD CONSTRAINT attribute_type_pkey PRIMARY KEY (attribute_type_id);
--
-- Name: attribute attribute_unq; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.attribute
ADD CONSTRAINT attribute_unq UNIQUE (name);
--
-- Name: film_attributes film_attributes_pkey; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.film_attributes
ADD CONSTRAINT film_attributes_pkey PRIMARY KEY (film_attributes_id);
--
-- Name: film film_pkey; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.film
ADD CONSTRAINT film_pkey PRIMARY KEY (film_id);
--
-- Name: film film_unq; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.film
ADD CONSTRAINT film_unq UNIQUE (name);
--
-- Name: attribute_index; Type: INDEX; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE INDEX attribute_index ON public.attribute USING btree (name COLLATE "C.UTF-8" varchar_ops);
--
-- Name: film_index; Type: INDEX; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE INDEX film_index ON public.film USING btree (name COLLATE "C.UTF-8");
--
-- Name: attribute attribute_type_fkey; Type: FK CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.attribute
ADD CONSTRAINT attribute_type_fkey FOREIGN KEY (attribute_type_id) REFERENCES public.attribute_type(attribute_type_id) NOT VALID;
--
-- Name: film_attributes film_attribute_attribute_fkey; Type: FK CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.film_attributes
ADD CONSTRAINT film_attribute_attribute_fkey FOREIGN KEY (attribute_id) REFERENCES public.attribute(attribute_id);
--
-- Name: film_attributes film_attribute_film_fkey; Type: FK CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.film_attributes
ADD CONSTRAINT film_attribute_film_fkey FOREIGN KEY (film_id) REFERENCES public.film(film_id);
--
-- PostgreSQL database dump complete
--
ERROR: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: "1")
LINE 180: 1 Рецензии 3
^
SQL state: 42601
Character: 4115Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:
Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
Содержание
- PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
- What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
- How we fix the error?
- Conclusion
- PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
- 10 Comments
PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
by Sijin George | Sep 12, 2019
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:
Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
SELECT * FROM long_term_prediction_anomaly WHERE + “‘Timestamp’” + ‘”BETWEEN ‘” +
2019-12-05 09:10:00+ ‘”AND’” + 2019-12-06 09:10:00 + “‘;”)
Hello Joe,
Do you still get PostgreSQL errors? If you need help, we’ll be happy to talk to you on chat (click on the icon at right-bottom).
У меня ошибка drop table exists “companiya”;
CREATE TABLE “companiya” (
“compania_id” int4 NOT NULL,
“fio vladelca” text NOT NULL,
“name” text NOT NULL,
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_8” PRIMARY KEY (“compania_id”)
);
CREATE TABLE “filial” (
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
“street” text NOT NULL,
“house” int4 NOT NULL,
“city” text NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_5” PRIMARY KEY (“id_filial”)
);
CREATE TABLE “login” (
“id_name” int4 NOT NULL,
“name” char(20) NOT NULL,
“pass” char(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (“id_name”)
);
CREATE TABLE “operator” (
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“obrabotka obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“konsultirovanie” text NOT NULL,
“grafick work” date NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_2” PRIMARY KEY (“id_operator”)
);
CREATE TABLE “polsovateli” (
“id_user” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_companiya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_oshibka” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_6” PRIMARY KEY (“id_user”)
);
CREATE TABLE “reklama” (
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“tele-marketing” text NOT NULL,
“soc-seti” text NOT NULL,
“mobile” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_3” PRIMARY KEY (“id_reklama”)
);
CREATE TABLE “tex-specialist” (
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“grafik” date NOT NULL,
“zarplata” int4 NOT NULL,
“ispravlenie oshibok” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_7” PRIMARY KEY (“id_tex-specialist”)
);
CREATE TABLE “uslugi” (
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“vostanavlenia parola” int4 NOT NULL,
“poterya acaunta” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_4” PRIMARY KEY (“id_uslugi”)
);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_operator_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_operator”) REFERENCES “operator” (“id_operator”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_uslugi_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_uslugi”) REFERENCES “uslugi” (“id_uslugi”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_filial_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_filial”) REFERENCES “filial” (“id_filial”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_reklama_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_reklama”) REFERENCES “reklama” (“id_reklama”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_tex-specialist_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_tex-specialist”) REFERENCES “tex-specialist” (“id_tex-specialist”);
ALTER TABLE “polsovateli” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_polsovateli_companiya_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_companiya”) REFERENCES “companiya” (“compania_id”);
ERROR: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: “”companiya””)
LINE 1: drop table exists “companiya”;
^
Источник
@YohDeadfall — I understand that part about it, but this is not script that I am creating or even code that I am creating. This is all created under the hood by Npsql/EntityFramework. My quick guess is that I am extending my DbContext from IdentityDbContext<IdentityUser> which wants to create all of the tables for roles, users, claims, etc. If I change this to just extend from DbContext, then everything works as advertised.
Below is the script that EF is trying to use created from dotnet ef migrations script — please be aware that I have removed my custom part of the script for brevity.
You can see there are two specific calls that are being made where [NormalizedName] and [NormalizedUserName] are being used.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "__EFMigrationsHistory" ( "MigrationId" varchar(150) NOT NULL, "ProductVersion" varchar(32) NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK___EFMigrationsHistory" PRIMARY KEY ("MigrationId") ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetRoles" ( "Id" text NOT NULL, "ConcurrencyStamp" text NULL, "Name" varchar(256) NULL, "NormalizedName" varchar(256) NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetRoles" PRIMARY KEY ("Id") ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUsers" ( "Id" text NOT NULL, "AccessFailedCount" int4 NOT NULL, "ConcurrencyStamp" text NULL, "Email" varchar(256) NULL, "EmailConfirmed" bool NOT NULL, "LockoutEnabled" bool NOT NULL, "LockoutEnd" timestamptz NULL, "NormalizedEmail" varchar(256) NULL, "NormalizedUserName" varchar(256) NULL, "PasswordHash" text NULL, "PhoneNumber" text NULL, "PhoneNumberConfirmed" bool NOT NULL, "SecurityStamp" text NULL, "TwoFactorEnabled" bool NOT NULL, "UserName" varchar(256) NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUsers" PRIMARY KEY ("Id") ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetRoleClaims" ( "Id" int4 NOT NULL, "ClaimType" text NULL, "ClaimValue" text NULL, "RoleId" text NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetRoleClaims" PRIMARY KEY ("Id"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetRoleClaims_AspNetRoles_RoleId" FOREIGN KEY ("RoleId") REFERENCES "AspNetRoles" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUserClaims" ( "Id" int4 NOT NULL, "ClaimType" text NULL, "ClaimValue" text NULL, "UserId" text NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUserClaims" PRIMARY KEY ("Id"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserClaims_AspNetUsers_UserId" FOREIGN KEY ("UserId") REFERENCES "AspNetUsers" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUserLogins" ( "LoginProvider" text NOT NULL, "ProviderKey" text NOT NULL, "ProviderDisplayName" text NULL, "UserId" text NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUserLogins" PRIMARY KEY ("LoginProvider", "ProviderKey"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserLogins_AspNetUsers_UserId" FOREIGN KEY ("UserId") REFERENCES "AspNetUsers" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUserRoles" ( "UserId" text NOT NULL, "RoleId" text NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUserRoles" PRIMARY KEY ("UserId", "RoleId"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserRoles_AspNetRoles_RoleId" FOREIGN KEY ("RoleId") REFERENCES "AspNetRoles" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE, CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserRoles_AspNetUsers_UserId" FOREIGN KEY ("UserId") REFERENCES "AspNetUsers" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUserTokens" ( "UserId" text NOT NULL, "LoginProvider" text NOT NULL, "Name" text NOT NULL, "Value" text NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUserTokens" PRIMARY KEY ("UserId", "LoginProvider", "Name"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserTokens_AspNetUsers_UserId" FOREIGN KEY ("UserId") REFERENCES "AspNetUsers" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE INDEX "IX_AspNetRoleClaims_RoleId" ON "AspNetRoleClaims" ("RoleId"); CREATE UNIQUE INDEX "RoleNameIndex" ON "AspNetRoles" ("NormalizedName") WHERE [NormalizedName] IS NOT NULL; CREATE INDEX "IX_AspNetUserClaims_UserId" ON "AspNetUserClaims" ("UserId"); CREATE INDEX "IX_AspNetUserLogins_UserId" ON "AspNetUserLogins" ("UserId"); CREATE INDEX "IX_AspNetUserRoles_RoleId" ON "AspNetUserRoles" ("RoleId"); CREATE INDEX "EmailIndex" ON "AspNetUsers" ("NormalizedEmail"); CREATE UNIQUE INDEX "UserNameIndex" ON "AspNetUsers" ("NormalizedUserName") WHERE [NormalizedUserName] IS NOT NULL; INSERT INTO "__EFMigrationsHistory" ("MigrationId", "ProductVersion") VALUES ('20180514204732_initial', '2.0.3-rtm-10026');
Пытаюсь создать табличку, вот такую
CREATE TABLE screens_items ( screenitemid bigint NOT NULL, screenid bigint NOT NULL, resourcetype integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, resourceid bigint DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, width integer DEFAULT '320' NOT NULL, height integer DEFAULT '200' NOT NULL, x integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, y integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, colspan integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, rowspan integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, elements integer DEFAULT '25' NOT NULL, valign integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, halign integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, style integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, url varchar(255) DEFAULT '' NOT NULL, dynamic integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, sort_triggers integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, application varchar(255) DEFAULT '' NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (screenitemid) );
Получаю
Error: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: "application")
psql --version psql (PostgreSQL) 9.4.9
Вроде слово «application» не зарезервировано?