11 764
Обнаружены пропуски воспламенения в 2 цилиндре
Возможные причины в автомобиле Volkswagen:
- Не отрегулированные клапана
- Неисправна свеча 2 цилиндра
- Забит или неисправен инжектор 2 цилиндра
- Неисправна катушка зажигания 2 цилиндра
- Обрыв или замыкание проводки форсунки 2 цилиндра
- Неисправность разъема проводки форсунки 2 цилиндра
- Обрыв или замыкание проводки катушки зажигания 2 цилиндра
- Неисправность разъема катушки зажигания 2 цилиндра
- Низкая компрессия в втором цилиндре
- Неправильное давление топлива
- Подсос воздуха впускного коллектора
Код P0302 означает, что в втором цилиндре автомобиля Фольксваген были обнаружены пропуски воспламенения зажигания или случайные пропуски. Диагностику лучше проводить в следующий последовательности – первое проверить впускной тракт на наличие подсоса воздуха, если поступления лишнего воздуха нет, то следующий шаг это замена свечи зажигания в втором цилиндре. Если проблема не удалось решить этими двумя пунктами, то необходимо провести дополнительную диагностику , которая детально описана здесь.
ВОЗМОЖНЫЕ СИМПТОМЫ ОШИБКИ P0302 Фольксваген:
- Горит сигнал «CHEK ENGINE»;
- Отсутствие/потеря мощности двигателя;
- Двигатель «трясет». Неровная работа мотора;
- Затруднен запуск двигателя. Особенно холодного.
Описание ошибки P0302 Volkswagen
При возникновении пропуска воспламенения частота вращения двигателя будет колебаться. Если изменения частоты вращения двигателя достаточны, для изменения сигнала датчика положения коленчатого вала (CKP), блок управления двигателем (ECM) определяет ошибку Volkswagen P0302 .
Ошибки (коды ошибок) полученные от прибора, сканера требуют правильной интерпретации информации, дабы не тратить время и деньги на замену работающих элементов автомобиля.
Проблема зачастую кроется намного глубже чем кажется на первый взгляд. Это& вызвано теми обстоятельствами, что информационные сообщения содержат, как было выше сказано, косвенную информацию о нарушении работы системы.
Может быть полезным для решения вопроса по устранению неисправности у Volkswagen Passat B6:
Механическая неисправность двигателя, проводка, система зажигания / топливная система, форсунка, датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости / датчик расхода воздуха (MAF), ECM
Не характерная работа двигателя проявляется рывками — краткими по времени как на малых, так и на высоких оборотах, холодном или прогретом двигателе.
Стоит знать, что детекция ошибки p0302 не всегда вызывает аварийную индикацию «Check Engine». Однако, при серьезных неисправностях или отклонениях от рабочих норм, «Check Engine» не даст запуститься двигателю.
Первоочередной список проверки узлов и компонентов на их целостность и исправность:
- Не контакт или окисление (коррозия) коннекторов, клеммных защелок, замыкания.
- Пробой изолятора модуля или высоковольтного провода.
- Неисправность свечи.
- Выход из строя катушки.
- Засорение форсунки.
- Недостаточная компрессия в блоке цилиндра.
- Воздух в подводящих топливных патрубках.
- Повреждение или износ прокладки на самой головке цилиндра.
- Некорректная работа ГРМ, износ цепи.
- Нарушение работы маслоотделителя.
- Неисправен блок ECM.
- Неисправность блока ЭБУ.
- Неисправность датчиков – детонации, коленчатого вала.
Список серьезных неисправностей при ошибке OBD-2 p0302:
- Нарушение толкателя клапана.
- Износ кулачка распределительного вала.
- Износ клапана и его торца.
- «Просадка» седла клапана.
- разбитый эллипс посадочного места толкателя.
Влияние ошибки p0302 на работу двигателя, и выброса сгораемого продукта
Следствием нагрузочных износов в первую очередь страдает цикл работы впуска и выпуска. С ростом пробега автомобиля, на впускном клапане зазор увеличивается, а на выпускном наоборот, будет уменьшаться (садится).
Из этого приходит понимание о нарушении зазора между клапаном и стаканом, а так же зазоры толкателя. Нередко встречаются случаи просадки седла клапана.
Не правильная работа воспламенения в цилиндрах приводит сгораемые продукты (выхлопной газ) к более токсичному состоянию. Не до конца отработанный продукт (топливо) завышает общую температуру на выходе из цилиндра, при этом превышая токсичность, быстрому износу и скорой поломке катализатора из-за выхода за предельно рабочую температуру – восьмисот градусов.
Дополнительно
Характер проявления подобных неисправностей (OBD-2 p0302) связан с нарушением технического предписания и несвоевременного обслуживания — за исключением аварий и других случаев.
Как пример: не качественное масло, его уровень, качество топлива, охлаждения, некорректной работы сопутствующих компонентов и узлов.
Все это по отдельности и в совокупности приводят к повышенным тепломеханическим нагрузкам — разрушающие геометрию узла, компонента, детали.
P0302 in the Volkswagen Passat is a common OBD II trouble code. It indicates that your car’s second cylinder has a misfire.
P0302 is a real drivability concern and should be dealt with right away. If it’s bad enough to cause your Passat’s check engine light to come on, you shouldn’t drive your car at all.
Repairing P0302 should be considered a high priority. Unlike a lot of the OBDII codes, this code has to do directly with engine combustion. It also can cost money to ignore it, since driving with a misfire can damage the Passat’s catalytic converter.
The most common fix for P0302 is to replace the spark plugs, coil packs, or (if equipped) plug wires.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Symptoms
- Causes
- How to Fix
- P0302 + Other Codes
- Common Questions
- Conclusion
P0302 Meaning: Cylinder 2- Misfire Detected
Cylinder 2
P0302 is a cylinder-specific misfire code, meaning it’s only the second cylinder that has a misfire. But, where is the second cylinder?
On “V” configuration engines, it’ll usually be the first cylinder on the head further back from the front of the engine. A quick google image search will confirm the correct cylinder (include your Passat’s model year and engine type).
Misfire Detected
In order for an engine to burn fuel efficiently, each cylinder needs:
- Fuel– In the right quantity (around 14.7 parts air to one part fuel).
- Air– It needs to be metered by your Passat’s mass air flow sensor or MAP sensor, so the powertrain control module (PCM) knows exactly how much air to let into the combustion chamber.
- Spark– The spark plug needs to fire at the right time and at the right temperature.
- Compression– The air-fuel mixture must be compressed during the engine’s power stroke.
If one of the above variables is off, your Passat’s second cylinder will misfire, or it won’t fire at all.
Passat P0302 OBDII Code Symptoms
Here are the most common symptoms of P0302 in the Volkswagen Passat.
- Check engine light
- The car itself may begin to run rough. It depends on how serious the misfire is.
- Your Passat may produce excess vibration, especially at lower RPM.
- Fuel mileage may suffer.
- You may smell raw gas coming from the tailpipe.
- The engine may backfire.
P0302 Trouble Code Causes: Volkswagen Passat
There are quite a few things that can cause the P0302 trouble code to trigger in the Volkswagen Passat.
Here are the most common problems that may cause misfiring. They are presented somewhat in order from most to least likely to be causing P0302:
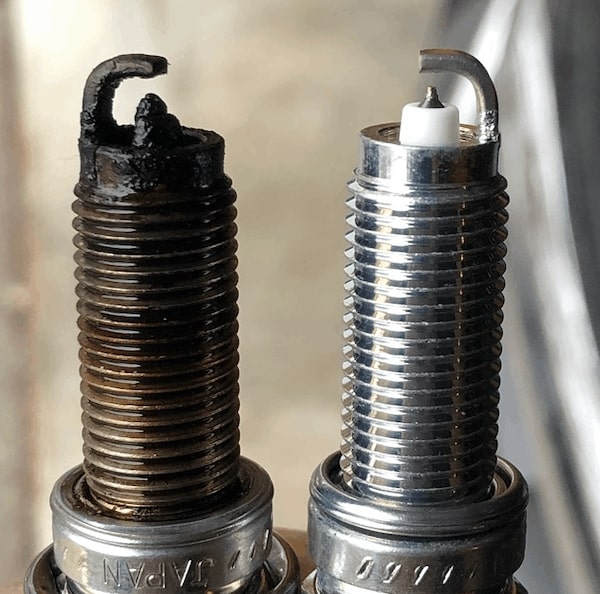
- Bad Spark Plugs– A fouled spark plug is the most common cause of P0302. Look at the electrodes and see if they are in good shape. Your Passat likely has iridium plugs that need to be changed very infrequently. That being said, a bad spark plug is the number one offender when it comes to P0302. Here’s a great video on verifying a spark plug is bad.
- Spark Plug Wires– On most modern engines, the plug wires are not nearly as long as they once were (if your car even has them), but they can still go bad. Here’s how to tell if your plug wires are bad (video).
- Coil Packs– Coil packs rarely go bad, but when they do, they can cause P0302 in your Volkswagen Passat. Replacing a set can be very expensive. Here’s how to test them.
- Bad Fuel Injector– If you have a fuel injector that has failed, it won’t be able to properly atomize fuel, and you’ll get P0302. Here’s a good video on how to diagnose an injector; it can be a little tricky. You’ll likely see P0171 and/or P0202 with a bad injector.
- Vacuum leak– If your Passat has a vacuum leak, it can be difficult for the PCM to get the right air/fuel mixture. This will cause the cylinders to misfire, and it’ll throw P0302 if the leak is around that specific cylinder on the intake manifold. Popular Mechanics: How to find a vacuum leak. You’ll likely see P0171 and P0300 when there’s a vacuum leak.
- Cam or Crank Sensors– This one is unlikely, but it does happen. If the ECU is not getting the right signal from these sensors, the vehicle’s timing will not sync up, and it’ll misfire. You’ll likely get P0300 and a cam/crank correlation code too.
- Mechanical Issue– If your Passat has a leaking head gasket, bent valve, cracked head, etc… that would cause compression to not be as high as it should be, you’re going to get P0302. You should also feel that your car is down on power as well.
If P0302 is the only code you get when you plug an OBD II scanner into your Passat, this section should help you determine what is causing the code.
If you have multiple codes with P0302, jump down a section.
1. Swap Test
Here’s a quick and easy test to determine what is causing your Passat’s second cylinder to misfire. Swap ignition parts to another cylinder. Here’s how to do it.
- Identify the second cylinder.
- Remove the spark plug.
- Swap it with the most convenient cylinder to access’s spark plug.
- Clear your Passat’s DTC codes with a scanner.
- Start the engine and wait for the check engine light to come back on. If it changed to a different P030X code, the plug was bad.
- If nothing changed, do this for the coil packs and plug wires (if equipped).
- If the code stays P0302, you’ve ruled out ignition-related issues.
2. Diagnosis
Here’s what to look for when the swap test didn’t change your car’s misfire code number.
- Check the wiring harness going to the cylinder two coil pack. If it’s damaged or loose, repair it. Ignition wiring is a common rodent damage area.
- Check for a vacuum leak.
- Verify the second injector is working (there’s a link to how to test one above).
- Do a compression test.
- Perform a leak-down test.
P0302 + Other Codes
P0302 + P0300
The most likely reason your Passat will get P0300 and P0302 simultaneously is faulty spark plugs.
P0300 in the Volkswagen Passat indicates random multiple misfiring, which means that multiple cylinders are misfiring at the same time.
If your Volkswagen Passat has P0300 and P0302 error codes, it’s best to diagnose why the second cylinder is misfiring and see if that will fix the P0302 code.
Try doing the swap test from the previous section. Make note of the condition of BOTH spark plugs as you swap them. If they look fouled, new plugs will likely clear this code.
P0302 + P0171
Look for a vacuum leak around the second cylinder or a bad fuel injector.
P0171 is one of the most common trouble codes there is. While there are many potential causes for P0171, the most prevalent is a vacuum leak.
When your Passat has P0302 and P0171 together, it’s often caused by a clogged or underperforming fuel injector.
P0302 + Other Cylinder Misfire Codes
Treat P0302 with these codes like it has P0300.
P0302 will often be accompanied by codes P0301, P0303, P0304, P0305, etc… These codes indicate a misfire in cylinders one, three, four, and five, respectively.
Treat P0302 with these codes like it has P0300. Suspect an ignition-related cause or a vacuum leak.
Common Questions
Is P0302 a serious concern?
P0302 is cause for concern and, left unfixed, can leave you stranded. Your Passat will be virtually undrivable if the second cylinder stops firing altogether. The raw fuel can also damage the catalytic converter.
Can you drive your Passat with P0302?
We do not advise driving your Passat with P0302. It can cause damage to your car.
Is P0302 hard to repair?
Most of the time, P0302 is not hard to repair, as you’ll be swapping out ignition parts. It’s a great first-time project for a shade tree mechanic. If the problem ends up not being ignition related, that’s when you might have to bring it into a shop.
Conclusion
Replacing the spark plug or coil packs is the most common fix for P0302 in the Volkswagen Passat. There are other causes, but the swap test can help narrow them down considerably.
Content
- Trouble Code P0302 OBD-II Datasheet
- What does this mean?
- Code severity P0302
- Symptoms of code P0302
- Causes of the P0302 code
- Diagnostic and repair stages
-
- It looks like this:
- HOW DOES A MECHANIC DIAGNOSTIC CODE P0302?
- COMMON ERRORS WHEN DIAGNOSING CODE P0302
- ADDITIONAL COMMENTS TO BE AWARE OF CODE P0302
-
- Need more help with the P0302 code?
Trouble Code P0302 OBD-II Datasheet
Ignition misfire detected in cylinder 2
What does this mean?
This Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is a generic transmission code, which means it applies to OBD-II equipped vehicles. Although general in nature, the specific repair steps may differ depending on the brand / model. Car brands covered by this code may include, but are not limited to, VW, Chevrolet, Jeep, Dodge, Nissan, Honda, Ford, Toyota, Hyundai, etc.
The reason the P0302 code is stored in your OBD II vehicle is because the powertrain control module (PCM) has detected a misfire in a single cylinder. P0302 refers to cylinder number 2. Consult a reliable vehicle information source for the location of cylinder number 2 for the vehicle in question.
This type of code can be caused by a fuel supply problem, a large vacuum leak, an exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system malfunction, or a mechanical engine failure, but is most often the result of an ignition system malfunction resulting in little or no spark. condition.
Almost all OBD II vehicles use a distributorless high-intensity spark ignition system, a coil-spark plug (COP) ignition system. It is controlled by the PCM to ensure accurate spark ignition and timing.
The PCM calculates inputs from the crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor, and throttle position sensor (among others, depending on the vehicle) to tune the ignition timing strategy.
In a real sense, the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position sensor are vital to the operation of the OBD II ignition system. Using inputs from these sensors, the PCM outputs a voltage signal that causes the high intensity ignition coils (usually one for each cylinder) to fire in sequential order.
Since the crankshaft rotates at about twice the speed of the camshaft (s), it is very important that the PCM knows their exact position; both in general and in relation to each other. Here’s a simple way to explain this aspect of engine performance:
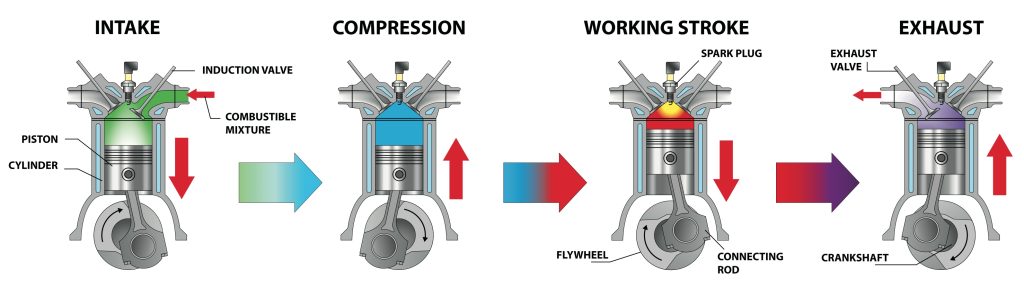
Top dead center (TDC) is the point at which the crankshaft and camshaft(s) are aligned with the piston (for cylinder number one) at its highest point and the intake valve(s) (for cylinder number one) are open. This is called the compression stroke.
During the compression stroke, air and fuel are drawn into the combustion chamber. At this point, an ignition spark is required to cause a fire. The PCM recognizes the position of the crankshaft and camshaft and provides the voltage signal required to generate a high intensity spark from the ignition coil.
Combustion in the cylinder pushes the piston back down. When the engine goes through a compression stroke and the number one piston begins to retrace to the crankshaft, the intake valve (s) close. This starts the beat of the release. When the crankshaft makes another revolution, the number one piston reaches its highest point again. Since the camshaft (s) have only made half a turn, the intake valve remains closed and the exhaust valve is open. At the top of the exhaust stroke, no ignition spark is required as this stroke is used to push the exhaust gas out of the cylinder through the opening created by the open exhaust valve (s) into the exhaust manifold.
Typical high intensity ignition coil operation is achieved with a constant supply of fused, switchable (only present when the ignition is on) battery voltage and a ground pulse supplied (at the appropriate time) from the PCM. When a ground pulse is applied to the ignition coil (primary) circuit, the coil emits a high intensity spark (up to 50,000 volts) for a fraction of a second. This high-intensity spark is transmitted through the spark plug wire or shroud and the spark plug, which is screwed into the cylinder head or intake manifold where it contacts the precise air/fuel mixture. The result is a controlled explosion. If this explosion does not occur, the RPM level is affected and the PCM detects it. The PCM then monitors camshaft position, crankshaft position, and individual coil feedback voltage inputs to determine which cylinder is currently misfiring or misfiring.
If the cylinder misfire is not persistent or severe enough, the code may appear pending and the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) may only flash when the PCM actually detects a misfire (and then goes out when it is not). The system is designed to alert the driver that an engine misfire of this degree could harm the catalytic converter and other engine components. As soon as the misfires become more persistent and severe, P0302 will be stored and the MIL will remain on.
Code severity P0302
Conditions that favor the storage of P0302 can damage the catalytic converter and / or engine. This code should be classified as serious.
Symptoms of code P0302
P0302 symptoms may include:
- Reduced engine performance
- Feeling rough or unstable from the engine (idling or slightly accelerating)
- Strange engine exhaust smell
- Flashing or steady MIL (malfunction indicator lamp)
Causes of the P0302 code
The P0302 code may mean that one or more of the following events have occurred:
- Defective ignition coil (s)
- Bad spark plugs, spark plug wires, or spark plug anthers
- Defective fuel injectors
- Faulty fuel delivery system (fuel pump, fuel pump relay, fuel injectors, or fuel filter)
- Serious engine vacuum leak
- EGR valve stuck in fully open position
- Exhaust gas recirculation ports clogged.
Diagnostic and repair stages
Diagnosing a stored (or pending) P0302 code will require a diagnostic scanner, a digital volt / ohm meter (DVOM), and a reliable source of vehicle information.
- Begin your diagnosis by visually inspecting the damaged ignition coil, spark plug, and spark plug boot.
- Fluid contaminated components (oil, engine coolant, or water) must be cleaned or replaced.
- If the recommended maintenance interval requires (all) replacement of the spark plugs, now is the time to do so.
- Inspect the primary wiring and connectors of the corresponding ignition coil and repair if necessary.
- With the engine running (KOER), check for a large vacuum leak and repair if necessary.
- If Lean Exhaust Codes or Fuel Delivery Codes accompany a misfire code, they must be diagnosed and repaired first.
- All EGR valve position codes must be corrected before a misfire code is diagnosed.
- Insufficient EGR flow codes must be eliminated before diagnosing this code.
After fixing all the above problems, connect the scanner to the vehicle diagnostic port and retrieve all stored codes and freeze frame data. I like to write this information down as it may be useful later. Now clear the codes and see if P0302 resets during an extended test drive.
If the code is cleared, use your vehicle information source to search for technical service bulletins (TSBs) that relate to the symptoms and codes in question. Since TSB lists are compiled from many thousands of repairs, the information found in the corresponding list is likely to help you in making the correct diagnosis.
Take care to find the cylinder that is leaking ignition. Once this is done, you must determine the exact cause of the problem. You can spend many hours testing individual components, but I have a simple system for this task. The described procedure applies to a vehicle equipped with an automatic transmission. Manual transmission vehicles can also be tested in this way, but this is a more complicated way.
It looks like this:
- Determine which rpm range is most likely to misfire. This can be done by test driving or checking freeze frame data.
- After determining the RPM range, start the engine and allow it to reach normal operating temperature.
- Install chocks on both sides of the drive wheels of the vehicle.
- Have an assistant sit in the driver’s seat and move the gear selector to the DRIVE position with the parking brake engaged and his foot firmly pressing the brake pedal.
- Stand close to the front of the vehicle so you can reach the engine with the hood open and secure.
- Have the assistant increase the rev level gradually by depressing the accelerator pedal until a misfire appears.
- If the engine stops working, CAREFULLY raise the ignition coil and pay attention to the degree of spark formation of a high intensity.
- The high intensity spark should be bright blue in color and have tremendous power. If not, suspect the ignition coil is faulty.
- If you are unsure of the spark produced by the coil in question, lift the known good coil from its place and observe the spark level.
- If it is necessary to replace the ignition coil, it is recommended to replace the corresponding spark plug and dust cover / wire.
- If the ignition coil is working properly, shut off the engine and insert a known good spark plug in the shroud / wire.
- Restart the engine and ask the assistant to repeat the procedure.
- Observe a strong spark from the spark plug. It should also be bright blue and rich. If not, suspect that the spark plug is faulty for the corresponding cylinder.
- If a high intensity spark (for the affected cylinder) seems normal, you can perform a similar test on the fuel injector by carefully disconnecting it to see if any difference in engine speed is found. A running fuel injector will also make an audible ticking sound.
- If the fuel injector is not working, use the assembly indicator to check the voltage and ground signal (at the injector connector) with the engine running.
In most cases, you will have found the cause of the misfires by the time you finish testing the high intensity spark.
- Exhaust gas recirculation systems that use a single cylinder exhaust gas injection system are known to cause symptoms that mimic a misfire condition. The cylinder portals of the exhaust gas recirculation are clogged and cause all the exhaust gas recirculation gases to be dumped into one cylinder, resulting in a misfire.
- Use caution when testing high intensity sparks. Voltage at 50,000 volts can be dangerous or even fatal under extreme circumstances.
- When testing a high intensity spark, keep it away from fuel sources to avoid disaster.
HOW DOES A MECHANIC DIAGNOSTIC CODE P0302?
- Uses an OBD-II scanner to collect freeze frame data and stored trouble codes from the transmission control module.
- See if DTC P0302 returns when you test drive the vehicle.
- Inspects cylinder 2 spark plug wire for frayed or damaged wires.
- Inspects spark plug housing 2 for excessive wear or damage.
- Inspects coil pack wires for frayed or damaged wires.
- Inspect the coil packs for excessive wear or damage.
- Replace damaged spark plugs, spark plug wires, coil packs, and battery wiring as needed.
- If DTC P0302 returns after replacing damaged spark plugs, batteries, spark plug wires and battery wiring, they will check the fuel injectors and fuel injector wiring for damage.
- For vehicles with a distributor cap and rotor button system (older vehicles), they will inspect the distributor cap and rotor button for corrosion, cracks, excessive wear, or other damage.
- Diagnose and correct any other related trouble codes stored in the transmission control module. Runs another test drive to see if DTC P0302 reappears.
- If DTC P0302 returns, a 2-cylinder compression system test will be performed (this is not common).
- If DTC P0302 still persists, the problem may be with the Powertrain Control Module (rare). May require replacement or reprogramming.
COMMON ERRORS WHEN DIAGNOSING CODE P0302
Visually inspect the fuel injector harness for damage before replacing spark plugs, coil packs, or spark plug and battery harnesses. If applicable, diagnose and repair any other related trouble codes present. Also remember to rule out the bad cylinder as the cause of the problem.
OBD2 коды ошибок формата P03XX — относятся к системе зажигания и системе контроля пропусков воспламенения.
Что означает ошибка P0302 на VOLKSWAGEN
Комбинация Р0302 появляется в результате появления пропусков зажигания во втором цилиндре
Цилиндр 2: обнаружен пропуск воспламенения
При обнаружении сразу нескольких ошибок, устраняйте их в порядке появления в отчете диагностического устройства.
- Повреждение свечи зажигания цилиндра 2;
- Отсутствие компрессии в цилиндре 2;
- Износ или повреждение проводов свечей зажигания и/или катушек зажигания;
- Износ или повреждение крышки распределителя (при наличии);
- Износ или повреждение бегунка распределителя зажигания (при наличии);
- Повреждение топливной форсунки;
- Засорение трубок или клапана системы рециркуляции отработавших газов;
- Обгорание клапанов;
- Неправильная установка момента зажигания;
- Утечка вакуума;
- Низкий уровень или низкое давление топлива;
- Повреждение прокладки головки блока цилиндров;
- Износ крышки распределителя;
- Неисправность датчика положения распределительного вала;
- Неисправность датчика положения коленчатого вала;
- Неисправность датчика расхода воздуха;
- Неисправность датчика кислорода;
- Неисправность датчика положения дроссельной заслонки;
- Неисправность каталитического нейтрализатора;
- Неисправность PCM;
Как исправить ошибку P0302?
- Замена изношенных или поврежденных свечей зажигания;
- Замена изношенных или поврежденных проводов свечей зажигания;
- Замена изношенных или поврежденных проводов катушек зажигания;
- Ремонт или замена засоренных трубок и/или клапана системы рециркуляции отработавших газов;
- Замена сгоревших клапанов;
- Устранение утечки вакуума;
- Ремонт или замена поврежденной прокладки головки блока цилиндров;
- Замена неисправного датчика положения распределительного вала;
- Замена неисправного датчика положения коленчатого вала;
- Замена неисправного датчика расхода воздуха;
- Замена неисправного датчика кислорода;
- Замена неисправного датчика положения дроссельной заслонки;
- Замена неисправной топливной форсунки;
- Замена неисправного каталитического нейтрализатора;
- Устранение всех присутствующих ошибок;
- Замена крышки и бегунка распределителя зажигания (при наличии);
- Ремонт неисправных внутренних компонентов двигателя;
- Замена двигателя (при повреждении цилиндра);
- В редких случаях, замена или перепрограммирование PCM;
На каких автомобилях появляется ошибка P0302?
- RENAULT
- SKODA
- RENAULT-HR16DE
- SUBARU
- SSANGYONG
- SEAT
- TOYOTA
- ВАЗ
- VOLVO
- VOLKSWAGEN
Другие ошибки на VOLKSWAGEN
- 00247
- 01500
- 07A9
- 080C
- 01107
- 00872
- 0814
- 01330
- 0416
- 449F
- 02211
- 18531
- 00172
- 00468
- 02842
- 090A
- 16826
- 02118
- 06B4
- 00DB
- 0246
- 16651
- 03D0
- 02682
- 18453
- 02688
- 01DA
- 01B9
- 02920
- 02583
- 466B
- 00E4
- 01403
- 02689
- 02457
- 02914
- 02513
- 4CF0
- 02786
- 17101
- 17942
- 01810
- 02339
- 01FB
- 16610
- 02143
- 062A
- 02F9
- 0634
- 00441
- 18045
- 4542
- 18729
- 4123
- 16952
- 19490
- 16654
- 01454
- 07F3
- 08FC
- 17713
- 4D61
- 28795
- 4D57
- 050
- 02324
- 444B
- 4ADD
- 17745
- 01736
- 46D6
- 16607
- 00309
- 0351
- 06FA
- 00302
- 005B
- 45C0
- 0A9D
- 18081
- 07EB
- 16507
- 0692
- 441B
- 01035
- 00FD
- 0A7A
- 19462
- 18342
- 19543
- 00609
- 410F
- 0985
- 0B02
- 19793
- 073B
- 17937
- 01807
- 04E7
- 00130