На чтение 7 мин Просмотров 13.9к.
Рассмотрим подробнее
- Техническое описание и расшифровка ошибки P0093
- Симптомы неисправности
- Причины возникновения ошибки
- Как устранить или сбросить код неисправности P0093
- Диагностика и решение проблем
- Давление топлива, а также топливный насос
- Топливная система высокого давления
- Топливные магистрали и регулятор
- Датчик давления топлива
- На каких автомобилях чаще встречается данная проблема
- Видео
Код ошибки P0093 звучит как «обнаружена большая утечка в топливной системе». Часто, в программах, работающих со сканером OBD-2, название может иметь английское написание «Fuel System Leak Detected – Large Leak».
Техническое описание и расшифровка ошибки P0093
Этот диагностический код неисправности (DTC) является общим кодом. Ошибка P0093 считается общим кодом, поскольку применяется ко всем маркам и моделям транспортных средств. Хотя конкретные этапы ремонта могут несколько отличаться в зависимости от модели.
Чтобы извлечь максимальную мощность из каждой капли топлива, она должна быть достаточно распылена внутри цилиндра, чтобы ее можно было эффективно воспламенить. Поэтому двигатель внутреннего сгорания сжигает не жидкое топливо, а его пары.
Для достижения достаточного воспламенения топлива, большинство систем впрыска топлива работают при умеренном давлении 2-5 атмосфер. Давление и распыление в сочетании с высокими температурами впуска и цилиндров помогают топливу испаряться еще лучше. Это обеспечивает лучшую выходную мощность и экономию топлива.
Дизельные двигатели и некоторые современные бензиновые используют другую форму впрыска топлива, впрыскивая его непосредственно в цилиндр. В этом случаи топливо впрыскивается в такте сжатия, когда давление в цилиндре приближается к максимальному. Поэтому топливные форсунки должны работать при гораздо более высоком давлении.
Топливный насос, установленный в топливном баке, подает топливо к механическому топливному насосу, обычно установленному непосредственно на двигателе. Механический насос повышает давление в системе прямого впрыска. Большинство систем с прямым впрыском бензина (GDI) работают под давлением до 170 атмосфер. А системы с впрыском дизельного топлива под давлением более 270 атмосфер.
Чтобы правильно измерять впрыск топлива, модуль управления двигателем (ЕСМ) внимательно отслеживает и регулирует систему высокого давления даже между импульсами форсунки.
Если контроллер обнаруживает неожиданное падение давления на стороне высокого давления топливной системы. В любом месте, между механическим топливным насосом и топливными форсунками.
Модуль управления устанавливает диагностический код неисправности (DTC) P0093, который означает, что в топливной системе обнаружена большая утечка топлива. Также, после этого, загорается контрольная лампа двигателя (MIL), на панели приборов.
Симптомы неисправности
Основным симптомом появления ошибки P0093 для водителя является подсветка MIL (индикатор неисправности). Также его называют Check engine или просто «горит чек».
Также они могут проявляться как:
- Загорится контрольная лампа «Check engine» на панели управления (код будет записан в память как неисправность).
- Двигатель может запустить аварийный режим и полностью выключиться.
- Большая потеря мощности под нагрузкой.
- Двигатель глохнет либо плохо заводится.
- Повышенный расход топлива.
- Запах топлива из-под капота.
- Снижение давления топлива.
Ошибка P0093 является довольно серьезной, так как при ее появлении могут возникнуть проблемы с двигателем и управляемостью автомобиля. При обнаружении данного кода рекомендуется как можно скорее обратиться к квалифицированному специалисту для диагностирования и устранения ошибки.
Причины возникновения ошибки
Код P0093 может означать, что произошла одна или несколько следующих проблем:
- Неисправность топливной форсунки.
- Утечка в топливной магистрали.
- Износ или повреждение шлангов, относящихся к топливной системе.
- Неисправен датчик давления топлива.
- Потеря мощности у топливного насоса в связи с поломкой.
- Короткое замыкание в жгуте проводов форсунок или блока управления двигателем.
- Забит топливный фильтр, что приводит к уменьшению объема топливопровода.
- Неисправность регулятора давления топлива.
- Вышел из строя датчик давления топлива.
- Иногда причиной является неисправный модуль PCM.
Как устранить или сбросить код неисправности P0093
Некоторые предлагаемые шаги для устранения неполадок и исправления кода ошибки P0093:
- Осмотрите форсунки на предмет утечек.
- Проверьте давление топлива.
- Протестируйте топливный насос.
- Осмотрите топливные магистрали.
- Убедитесь в нормальной работе регулятора на топливной рампе.
- Обратите внимание на датчик давления топлива.
Диагностика и решение проблем
Когда причина ошибки, в данном случае P0093 лежит на поверхности и легко исправима, это одно дело. Но иногда случается так, что причину очень трудно обнаружить, поэтому пройдемся по наиболее значимым местам.
Давление топлива, а также топливный насос
Давление топлива можно проверить с помощью механического манометра, прикрепленного к топливной рампе. Если давление находится в пределах заводских спецификаций, может быть неисправность датчика давления топлива, выдающего ложные показания для PCM / ECM.
При невозможности добраться манометром до места проверки, можно соединить несколько фитингов между топливопроводами и топливной рампой. Также для проверки можно использовать диагностический прибор, который покажет результаты в реальном времени.
Проверьте топливный насос на достаточную мощность, найдя жгут проводов. Замерьте напряжение аккумулятора на положительной клемме топливного насоса с помощью цифрового вольтомметра.
Если мощности недостаточно, протестируйте проводку к топливному насосу. Проследите, есть ли чрезмерное сопротивление, ослабленные провода или неисправные соединения.
Топливная система высокого давления
Проверьте все разъемы и жгуты проводов. Убедитесь, что на них нет погнутых или вывернутых контактов или коррозии. При необходимости замените или отремонтируйте.
Обратите внимание на драйвер топливной форсунки (FID). Если драйвер или топливная форсунка были заменены, FID должен запустить программу повторного обучения. Которая настраивает его на насос высокого давления и топливные форсунки.
Осмотрите систему на предмет утечки топлива, также проверьте уровень масла. Если уровень масла выше нормы и пахнет топливом, ищите утечку в топливной форсунке. Особенно если у вас также присутствуют коды неисправности топливной коррекции или пропуски зажигания.
Если вы не можете найти какие-либо проблемы с топливной системой высокого давления. Но у вас есть другие коды неисправности, связанные с топливной системой. Диагностируйте и устраните их, прежде чем возвращаться к ошибке P0093.
Топливные магистрали и регулятор
Ищите физические повреждения или перегибы топливных магистралей, которые могут вызвать затруднения в подающей или обратной магистрали. Может потребоваться снять топливный фильтр, чтобы определить его на забитость и не нуждается ли он в замене.
Топливо должно свободно течь по направлению потока, указанном стрелкой на топливном фильтре. На некоторых автомобилях фильтр расположен на входе в сам топливный насос, необходимо будет снять модуль. Чтобы определить, много ли в баке, что также может ограничить подачу топлива к насосу.
На автомобилях, оборудованных топливной системой обратного типа, регулятор обычно расположен на самой топливной рампе. Регулятор давления топлива имеет вакуумную линию, которая механически ограничивает подачу топлива в зависимости от величины разрежения, создаваемого двигателем.
Проверьте, нет ли поврежденных или ослабленных вакуумных шлангов к регулятору. Если в вакуумном шланге находится топливо, в регуляторе может быть внутренняя утечка, что приведет к потере давления.
В безвозвратных системах регулятор давления топлива может быть расположен внутри бензобака на модуле топливного насоса, и может потребоваться замена модуля топливного насоса в сборе.
Датчик давления топлива
Проверьте датчик давления топлива, сняв разъем и проверив сопротивление на клеммах, используя вольтомметр. Сопротивление должно быть в пределах заводских спецификаций. Проверить опорное напряжение к датчику давления топлива, оно должно быть около 5 вольт, в зависимости от автомобиля.
Если напряжение не соответствует техническим характеристикам, осмотрите проводку, чтобы определить, есть ли чрезмерное сопротивление в проводе. Оно должно быть очень низким, близким к 0 Ом. Если присутствует сопротивление, возможно, произошло замыкание на массу, и необходимо будет отследить проводку, чтобы определить место замыкания.
Выполнив проверку по этим пунктам, у вас должно получится определить проблему появления ошибки P0093. А после определения, решить ее, не составит труда.
На каких автомобилях чаще встречается данная проблема
Проблема с кодом P0093 может встречаться на различных машинах, но всегда есть статистика, на каких марках эта ошибка присутствует чаще. Вот список некоторых из них:
- Citroen (Ситроен С4, С5)
- Fiat (Фиат Дукато)
- Ford (Форд Рейнджер)
- Hyundai (Хендай HD78)
- Isuzu (Исузу NPR 75)
- Mazda (Мазда БТ 50, MPV)
- Mitsubishi (Митсубиси Паджеро, L200)
- Nissan (Ниссан Кабстар, Навара, Патфайндер)
- Opel (Опель Астра, Мерива)
- Peugeot (Пежо 407, 4007, Боксер, Партнер)
- Toyota (Тойота Авенсис, Ленд Крузер, Прадо, Рав4, Хайлюкс)
- Газель Некст
С кодом неисправности Р0093 иногда можно встретить и другие ошибки. Наиболее часто встречаются следующие: P0087, P0094, P1113, P1351, P3003.
Видео
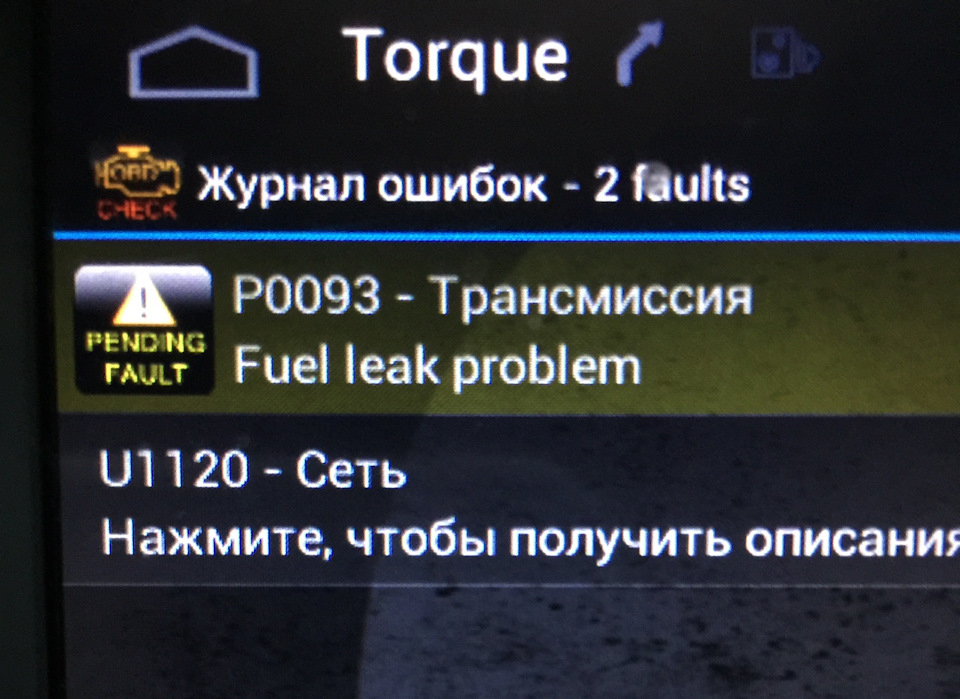
На КАД, прямо на скорости загорелась ошибка — проверка двигателя и машина перестала реагировать на педаль газа.
Отъехал на обочину, заглушил мотор, завёл заново и поехал.
Через несколько километров опять.
Свернул с КАД, поехал через город, срабатываний больше не было.
Подключил OBD-II, в программе Torque видна ошибка 93 — утечка топлива.
Далее последовала замена клапана ТНВД.
Пробег: 114 000 км
Войдите или зарегистрируйтесь, чтобы писать комментарии, задавать вопросы и участвовать в обсуждении.
Все комментарии
OPERATION
- Refer to Code No. P0191: Rail Pressure Sensor Range/performance Problem
.
FUNCTION
- The engine-ECU monitors the signals input from the rail pressure sensor.
- The engine-ECU controls the suction control valve so that necessary fuel pressure
can be obtained before fuel injection. - The engine-ECU compares the fuel pressure immediately before fuel injection and
the fuel pressure after injection to check whether. The pressure drop greatly exceeds the expected range
determined based on fuel consumption. The engine-ECU detects fuel leaks in this way
TROUBLE JUDGEMENT
Check Conditions
- Battery positive voltage is 8 — 16 V.
- 2 seconds later after the ignition switch has been in «ON» position or the engine
has started up. - The engine speed is 600 r/min or more.
- Rail pressure sensor is normal.
Judgement Criterion
- The fuel discharge rate of the supply pump continues to exceed its threshold value
against the fuel injection rate.
FAIL-SAFE AND BACKUP FUNCTION
- The rail pressure is controlled to be 100 MPa or less.
- The fuel injection amount is restricted (Output restriction).
- The open angle of the accelerator pedal is restricted.
- The throttle valve is closed (Fixed opening degree).
- The EGR control is stopped (fully closed).
- The DPF regeneration is prohibited.
- The AS&G control is prohibited.
PROBABLE CAUSES
- Fuel leakage or fuel line blocked
- Failed injector
- Failed suction control valve
- Failed rail pressure sensor
- Harness damage in rail pressure sensor circuit or loose connector contact.
- Failed fuel pressure limiter valve
- Failed engine-ECU
DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURE |
STEP 1. M.U.T.-III diagnosis code. |
Q.
|
 Go to Step 2. Go to Step 2. |
|
STEP 2. Detection of fuel line leakage. |
|
Q.
|
 Go to Step 3. Go to Step 3. |
|
 Replace the parts of an abnormal location. Replace the parts of an abnormal location. |
|
STEP 3. Release the air from the fuel line. |
|
Q.
|
 Go to Step 4. Go to Step 4. |
|
 The check is end. The check is end. |
|
STEP 4. Engine oil level check. |
|
Q.
|
 Go to Step 6. Go to Step 6. |
|
 Go to Step 5. Go to Step 5. |
|
STEP 5. Fuel leakage from injector check. |
|
Q.
|
STEP 6. Rail pressure sensor output signal check. |
|
| OK: The rail pressure of 0 kPa is shown. |
Q.
|
 Go to Step 11. Go to Step 11. |
|
 Go to Step 7. Go to Step 7. |
|
STEP 7. Check harness between rail pressure sensor connector terminal
|
|
Q.
|
 Go to Step 8. Go to Step 8. |
|
 Repair or replace the connector, or repair the damaged harness wire. Repair or replace the connector, or repair the damaged harness wire. |
|
STEP 8. Check harness between rail pressure sensor connector terminal
|
|
Q.
|
 Go to Step 9. Go to Step 9. |
|
 Repair or replace the connector, or repair the damaged harness wire. Repair or replace the connector, or repair the damaged harness wire. |
|
STEP 9. Check harness between rail pressure sensor connector terminal
|
|
Q.
|
 Go to Step 10. Go to Step 10. |
|
 Repair or replace the connector, or repair the damaged harness wire. Repair or replace the connector, or repair the damaged harness wire. |
|
STEP 10. Replace the common rail assembly and fuel injection tubes. |
|
Q.
|
 Replace the engine-ECU. Replace the engine-ECU. |
|
 The check is end. The check is end. |
|
STEP 11. Rail pressure check. |
| Connect the M.U.T.-III to check the following data list items. |
|
Q.
|
 Go to Step 12. Go to Step 12. |
|
STEP 12. Fuel pressure limiter valve function check. |
|
| OK: The rail pressure should be approximately 200 MPa to be stabilized. |
Q.
|
 Go to Step 13. Go to Step 13. |
|
 Replace the common rail assembly. Replace the common rail assembly. |
|
STEP 13. M.U.T.-III diagnosis code. |
|
Q.
|
 Replace the engine-ECU. Replace the engine-ECU. |
|
MMC-Manuals.ru
| Code | Fault Location | Probable Cause |
|---|---|---|
| P0094 | Fuel system leak -small leak detected (Buy Part On Amazon) |
Wiring, fuel pressure sensor, mechanical fault |
We recommend Torque Pro
Table of Contents
- What Does Code P0094 Mean?
- What are the common causes of code P0094 ?
- What are the symptoms of code P0094 ?
- How do you troubleshoot code P0094 ?
- Codes Related to P0094
- Get Help with P0094
What Does Code P0094 Mean?
OBD II fault code P0094 is defined as “Fuel System Leak Detected Small Leak”, and is set when the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) detects an unexpected decrease in the fuel pressure in the high-pressure part of the fuel injection system. Note that code P0094 is most commonly encountered in diesel injection systems.
Diesel engines require very high fuel pressures to work efficiently, and any drop in the fuel pressure will set the code, and illuminate the CHECK ENGINE light. In many cases, this code will cause the PCM to command a fail-safe or limp mode, which mode reduces power, and may prevent gear shifts. In some cases though, the engine may be shut down completely.
The image below shows a leaking diesel injector. This type of leak is typical of code P0094, although there are many other possible sites on a diesel engine at which fuel may leak.
What are the common causes of code P0094 ?
Common causes of this code include the following-
- Burnt, damaged, shorted, or otherwise damaged wiring and/or connectors.
-
Ruptured fuel lines; two common causes of steel fuel lines failing are rubbing, or chafing against engine components, and weaknesses induced by vibration in lines that are not properly secured.
-
Split or otherwise damaged fuel rails.
- Component failure in high pressure pumps.
- Loose connections in high pressure fuel lines.
-
Damage to return lines. Although the return pressure is only a fraction of the working pressure, the volume of fuel delivered by the pump is too small to compensate for the volume of fuel lost through a leak.
-
Defective fuel pressure sensor or pressure regulator; however, unless the fuel pressure sensor and/or fuel pressure regulator is actually leaking fuel, these components have their own dedicated fault codes meaning that a failure of one, or both of these components is unlikely to set code P0094.
-
A defective PCM may cause the code to be stored, but this is a rare event. Therefore, the code must be investigated thoroughly before any controller is replaced.
NOTE: Intermittent leaks in high pressure diesel injection systems are rare. One a leak path has opened, the high pressure in the system will keep it open, which will continually set the code until the problem has been resolved.
What are the symptoms of code P0094 ?
The symptoms of code P0094 can appear suddenly, and may be dramatic in some cases. Common symptoms may include the following-
- Sudden loss of power as the engine enters limp mode
- Inability to accelerate, and the transmission may refuse to shift
- The engine may shut off unexpectedly, with the accompanying loss of power steering and vacuum assistance for the brakes
- Smoke may be visible from under the hood
- Depending on the site of the leak, engine fires may result
- The strong smell of diesel fuel may be present
- Depending on the size and site of the leak, the engine may not start.
How do you troubleshoot code P0094 ?
WARNING: While gasoline engines generally work with fuel pressures of well under 100 psi, the fuel pressure on diesel engines could be anywhere from 4 000 psi to as high as 30 000 psi. Therefore, extreme care must be exercised when working on diesel injection systems, since serious personal injury or even death can result from following incorrect testing procedures.
Diagnosing and repairing diesel fuel systems requires proper training and more than a working knowledge of the system- thus; do NOT attempt this repair if you are not knowledgeable, or feel uncomfortable working on high pressure fuel injection systems.
NOTE #1: A repair manual for the system being worked on, as well as a dedicated diesel fuel pressure gauge is required to diagnose and test any diesel fuel injection system.
NOTE #2: Although defective fuel pressure regulators can cause a drop in fuel pressure (including intermittent drops) this type of issue has its own dedicated trouble code(s), such as P1280 and others that may be make and model specific.
Step 1
NOTE: Make sure the engine is cold and that there is no risk of fire before starting the diagnostic procedure. Depending on the site of the leak, fuel may have sprayed all over the engine compartment, and there may be pooled fuel present on the engine. To eliminate the risk of fire, be sure to remove all visible liquid fuel before starting the diagnostic/repair procedure.
Record all fault codes present, as well as all available freeze frame data, but only after the vehicle has been made safe to work on.
Step 2
If the site of the leak is not immediately apparent, start the diagnostic process by thoroughly inspecting all wiring associated with the fuel injection system, since burnt, shorted, or damaged wiring and connectors can also set code P0094. Repair all wiring issues found, clear the code(s), and test the vehicle to see if the code returns.
Step 3
If no obvious wiring issues are found, perform resistance, reference voltage, and ground checks on all wiring in the system. Pay particular attention to the reference voltage on the fuel pressure sensor and/or regulator; on most applications, the reference voltage will be 5 volts, but be sure to consult the manual to confirm this value.
Make the repairs required to ensure that all input voltages, reference voltages, and resistance/ continuity values fall within the manufacturer’s specification. Note that if damaged wiring is found, the better option is always to replace the entire (relevant) harness, as opposed to making repairs that could cause continuity/resistance issues later on.
NOTE: Be sure to disconnect the control system from the PCM before starting continuity checks to prevent damage to the controller. Consult the manual to determine the location, function, routing, and color-coding of each wire in the control system to prevent accidental short circuits.
Step 4
If all electrical values fall within the manufacturer’s specifications, clear all codes and rescan the system to see if the fault returns. However, this may require that the engine be cranked, which offers an excellent opportunity to try and spot the site of the leak.
If the leak is not spotted immediately, enlist the help of an assistant to crank the engine. Likely sites of leaks are failed/cracked injectors (rare, but not impossible) loose connections in high pressure fuel lines, split fuel rails, and failed seals on regulators and pressure sensors. Note that while leaks on pressure pumps are relatively rare, they do happen, so check the pump for outward signs of leaks as well.
TIP: Since many engine compartments are so crowded, it is sometimes almost impossible to spot leaks in fuel systems. A great tool to have is a small mirror with a moveable head mounted on a telescopic handle. The smaller the mirror, the easier it is too get it behind fixed fuel lines to inspect parts of fuel lines that cannot be inspected in any other way.
If the leak is found, make suitable repairs, but resist the temptation to repair high pressure fuel lines; the better option is always to replace failed and/or suspect lines with OEM parts. Also be sure to tighten all connections in fuel lines properly to prevent a recurrence of the problem.
Note that high pressure fuel lines are secured to the engine for a reason; vibrations of the engine can cause steel fuel lines to weaken at certain spots, so make sure that all retaining devices are in place, and that all securing bolts/screws are in place and tightened properly to prevent vibration- induced leaks in fuel lines.
NOTE: Small leaks in diesel injection systems will rarely squirt a jet of liquid fuel; the extremely high pressures involved will more likely expel the fuel in a fine mist that might look like smoke. If what appears to be smoke is found, hold a sheet of paper against it, and move it toward the origin of the mist/smoke to narrow down the search field until the exact site of the leak is identified. The paper will get progressively wetter with fuel the closer to the site of the leak it gets.
Step 5
After repairs had been made, clear all codes and retest the system to see if the code returns.
If the wiring checks out OK, and no leaks are found on the fuel lines but the code has returned, it is entirely possible that the pressure pump is leaking fuel into the engine. However, internal fuel leaks are unlikely to be visible. Since the pressure pump is lubricated by engine oil, the leaking fuel is likely to mix with the pump’s lubricating oil, which effectively renders the leak invisible.
This is a relatively rare event but it does happen: if it established that there are no leaks on the visible parts of the high pressure system, the pump is the only remaining source of the leak. If this is suspected, the best option is to refer the vehicle to a diesel injection specialist. This type of repair requires specialist knowledge, training, and equipment. Do NOT attempt DIY repairs on a high pressure diesel pump.
Step 6
Once all repairs had been made, clear all codes and consult the manual on the correct procedure to test the fuel pressure in the system with the engine running. However, take extreme care to follow the directions in the manual exactly- serious personal injury can result from mistakes during this test.
Compare the test result with the values stated in the manual, which if all repairs had been successful, should match the stated values exactly, or be very close to stated values.
P0093 – Relates to “Fuel System Leak Detected Large Leak”
Help Us Help You
Please comment below describing your issue as well as the specifics of your vehicle (make, model, year, miles, and engine),
and one of our mechanics will respond as soon as possible. We appreciate a $9.99 donation via the payment button below.
Skip to content
P0093 Fuel System Leak Detected – Large Leak: Causes, Symptoms, Solutions, and Conclusion
P0093 Fuel System Leak Detected – Large Leak: Causes, Symptoms, Solutions, and Conclusion
Introduction:
The OBD-II diagnostic trouble code P0093 indicates a large leak detected in the fuel system. This code suggests that there is a significant leak in the fuel system, leading to potential issues with fuel efficiency and performance. In this article, we will provide a detailed explanation of the code, possible causes, symptoms, solutions, and conclude with essential insights.
Detailed Explanation:
The fuel system in a vehicle is responsible for delivering the appropriate amount of fuel to the engine for combustion. The OBD-II system monitors the fuel system for leaks and issues. When a large leak is detected, it triggers the P0093 code.
Possible Causes:
Several factors can contribute to the occurrence of the P0093 code. These include:
- Faulty fuel cap: A loose, damaged, or improperly installed fuel cap can result in a large leak in the fuel system.
- Leaking fuel lines or connections: Damaged or deteriorated fuel lines, connectors, or fittings can cause significant fuel leaks.
- Faulty fuel pressure regulator: A malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator can lead to excessive fuel pressure, resulting in leaks.
- Fuel injector issues: Leaking or malfunctioning fuel injectors can cause fuel to escape from the system.
- Damaged fuel tank: A damaged fuel tank can result in large fuel leaks.
- EVAP system problems: Issues with the evaporative emissions (EVAP) system, such as a malfunctioning purge valve or canister, can lead to fuel system leaks.
Symptoms:
When the P0093 code is present, the following symptoms may be observed:
- Check Engine Light: The most common symptom is the illumination of the Check Engine Light on the vehicle’s dashboard.
- Strong fuel odor: A noticeable smell of fuel inside or outside the vehicle may indicate a large fuel leak.
- Decreased fuel efficiency: The vehicle may experience a decrease in fuel efficiency due to the excessive fuel leaking from the system.
- Poor engine performance: Leaking fuel can result in engine misfires, hesitation, or rough idling.
- Visible fuel leaks: In some cases, fuel leaks may be visible underneath the vehicle or around the fuel system components.
Solutions:
To address the P0093 code, follow these steps:
- Code diagnosis: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the trouble code and confirm that it is P0093.
- Visual inspection: Inspect the fuel cap and ensure it is properly tightened. Inspect fuel lines, connections, and components for any visible signs of leaks or damage.
- Check fuel pressure regulator: Test the fuel pressure regulator for proper functionality. If found faulty, replace it with a new one.
- Inspect fuel injectors: Check the fuel injectors for leaks or malfunctions. Replace any faulty injectors.
- Inspect the fuel tank: Examine the fuel tank for any visible damage or leaks. Repair or replace the tank if necessary.
- Check the EVAP system: Inspect the EVAP system components, such as the purge valve and canister, for proper operation. Replace any malfunctioning parts.
- Clear the code: After performing the necessary repairs, use the OBD-II scanner to clear the trouble code and reset the Check Engine Light.
Conclusion:
The P0093 code indicates a large leak detected in the fuel system, which can lead to fuel inefficiency and performance issues. Timely diagnosis and resolution of the underlying causes are crucial to ensure proper fuel system performance. By inspecting and repairing or replacing components such as the fuel cap, fuel lines, fuel pressure regulator, fuel injectors, fuel tank, and EVAP system, you can rectify the large leak problem.
Regular maintenance and periodic checks of the fuel system can help prevent issues that may trigger the P0093 code. By addressing fuel system leaks promptly, you can ensure optimal fuel efficiency, engine performance, and safety.
If you are unsure or unable to diagnose and fix the issue yourself, it is recommended to consult a qualified mechanic or automotive technician for assistance.





