Когда становится скучно, то обычно чел. начинает искать себе каких-то приключений на свою пятую точку:) Вот мне на днях надоела стабильность моего локального сервера и мне захотелось какого-то «квеста» — и пошло поехало…
В линухах есть некая фича «Journaling Block Device layer» (ака JBD, процесс jbd2/sda2-8), которая на файловых системах EXT3/EXT4 занимается журналированием событий про данные с целью их дальнейшего восстановления в случае возможных сбоев в файловой системе.
На некоторых серверах, особенно со слабой скоростью доступа к диску (hdparm -t /dev/sda1), по показаниям iotop этот самый процесс jbd2/sda2-8 довольно часто дергает диск для записи в него параллельно с другими процессами выполняющими запись на диск, что вызывает всплески I/O Wait. Идея заключалась в том, чтобы полностью избавится от журнала и обслуживающего его процесса jbd2/sda2-8 (ps aux|grep jbd2).
Теоретически я знаю, что можно только сменить способ ведения журнала (data=journal, data=ordered, data=writeback), но полностью отключить журналирование и избавится от процесса jbd2/sda2-8 невозможно, но никогда не видел последствий этого замысла на практике — вот решил попробовать вовсе избавится от журнала и посмотреть чем это закончится;)
Долго ли коротко ли, вот нашелся рецепт:
Re: Resize journal on root filesystem
http://www.redhat.com/archives/ext3-users/2002-October/msg00026.html> I’ve remounted my root filesystem as ext2, but still when I ‘tune2fs -O
> ^has_journal’ I get
> —-
> The has_journal flag may only be cleared when the filesystem is
> unmounted or mounted read-only.
> —-Add the tune2fs command to rc.sysinit before the root filesystem fsck is run, then reboot the machine remotely.
В «рецепте» шла речь о изменении размера журнала на корневой файловой системе (Resize journal on root filesystem), для чего нужно его сначала удалить и создать заново с нужным размером, но создание нас не интересует — удаляем:)
{hint}
vi /etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit ... if [ -f /fastboot ] || strstr "$cmdline" fastboot ; then fastboot=yes fi tune2fs -O ^has_journal /dev/sda1 if [ -f /fsckoptions ]; then fsckoptions=`cat /fsckoptions` fi ... reboot
{/hint}
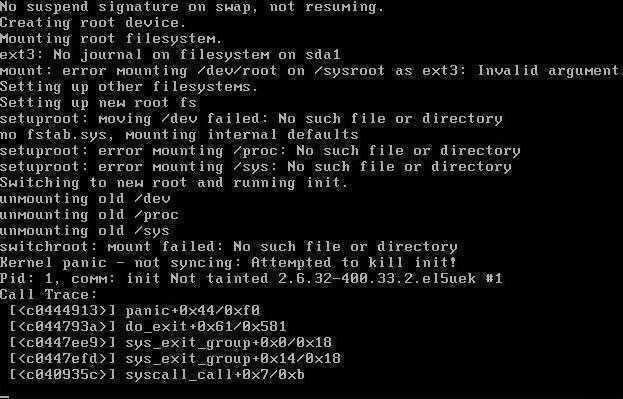
После перезагрузки всё было хорошо и CentOS работала стабильно, но вот после второго reboot-а загрузка CentOS накрылась медным тазом с сообщением «switchroot: mount failed: No such file or directory» и иже с ним «Kernel panic — not syncing: Attempted to kill init!«:
switchroot: mount failed: No such file or directory
Kernel panic — not syncing: Attempted to kill init!
Pid: 1. comm: init Not tainted 2.6.32-400.33.2.el5uek #1
CentOS перестала загружаться и в однопользовательском режиме (aka single user mode), но меня это ничуть не расстроило ибо ж за что боролись на то и напоролись. Итак.., приступим к восстановлению.
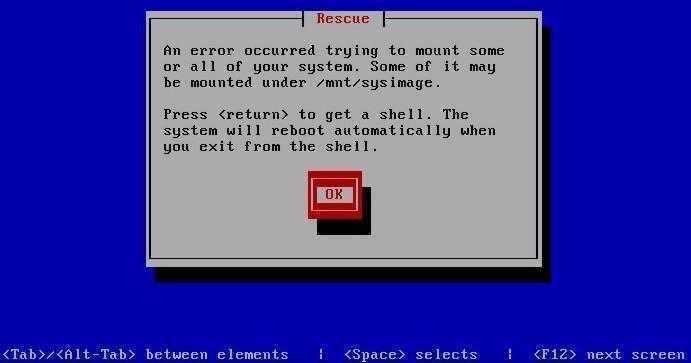
Чтобы восстановить загрузку CentOS нам потребуется восстановить журнал EXT3/EXT4, а для этого нужен загрузочный/установочный диск и его режим «Rescue mode», для входа в который набираем linux rescue и жмем <Enter>.
После запуска выбираем язык и клавиатуру по умолчанию EN, отказываемся от настройки сети, нажимаем «Continue» ради интереса или просто «Skip» чтобы сразу выйти в консоль ибо «Continue» нам здесь всё равно не поможет.
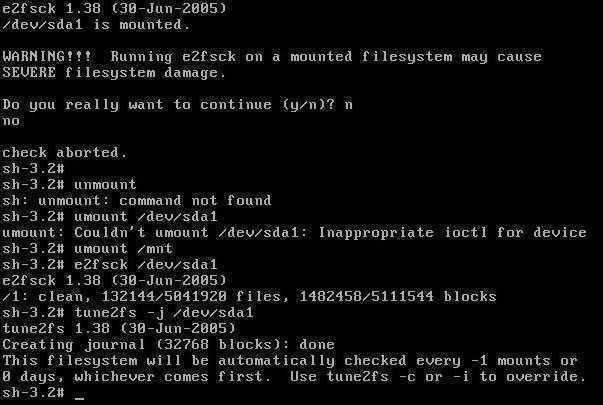
Теперь же, когда мы в консоли, выполняем набор команд:
{hint}
fdisk -l mount /dev/sda1 /mnt chroot /mnt vi /etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit # find and remove line "tune2fs -O ^has_journal /dev/sda1" exit umount /mnt tune2fs -j /dev/sda1 exit
{/hint}
Сбой в загрузке CentOS с сообщением «Kernel panic — not syncing: Attempted to kill init!» может иметь различную природу происхождения, но когда никак не получается восстановить запуск ОС, то как вариант нужно попробовать восстановить журнал EXT3/EXT4, т.е. удалить и создать заново.
Аналогичные последствия с результатом «Kernel panic — not syncing: Attempted to kill init!» будут иметь место на любых дистрибутивах Linux в случае полного удаления журнала EXT3/EXT4 или же его возможного повреждения, но в нашем случае это был CentOS GNU/Linux.
Приведённый здесь рецепт по восстановлению журнала для EXT3/EXT4 должен работать и других GNU/Linux дистрибутивах, различаться могут способы загрузки в «Rescue mode».
Ссылки по теме:
- Chapter 26. Basic System Recovery
- 26.2. Booting into Rescue Mode
- Ext3 Filesystem Documentation
- Ext4 Filesystem Documentation
Linux is a very reliable system that rules the server universe worldwide. It is fast, secure, and the way it is built makes it ideal for many environments in many parts of the world. However, it is not perfect and can be flawed in many ways, causing more than one headache for professionals in the field. Today, in this post, we will talk about a kernel panic that can ruin your day. We will talk about How to solve kernel panic not syncing error. Let’s go for it.
Contents
- What is a kernel panic?
- What can cause a kernel panic?
- What does not syncing mean in kernel panic?
- How can kernel panic issues be resolved?
- Another possible solution to the Kernel panic not syncing fatal exception error
- How to Fix kernel panic not syncing vfs: Unable to mount root Error
- Kernel panic not syncing no init found
- How do you stop kernel panic?
- How to resolve Kernel Panic Not Syncing on Mac?
- Conclusion
What is a kernel panic?
For an operating system to work efficiently, it must be synchronized with the various system units. If this does not happen, then there could be system crashes, which could lead to data loss and more severe damage. Kernel Panic is one such crash that occurs at the kernel level.
In short, a kernel panic is a serious boot-level error that is then displayed by the system. An indispensable aspect of this type of error is that the system cannot fix it by itself, preventing the system from booting. Although it provides a message explaining what it is, the reality is that these often work only for a kernel developer.
The kernel panic was introduced in an early version of Unix and hence Linux, and the basic premise is that hardware and software must work correctly. When the software or hardware fails, it results in an error that interrupts the startup of the system.
To be a bit more specific, the truth is that many error conditions can cause a kernel panic, including kernel code that attempts to access invalid memory.
Microsoft Windows users are typically familiar with the BSoD (blue screen of death) and a Kernel Panic is the Unix equivalent of this. Whereas in Windows or Unix, the system cannot continue its normal boot.
Although they are very common, the reality is that there is no specific reason for them. This means that it is not always easy to find a solution to this problem. However, the community support and the experiences gained to make it possible to find solutions.
What can cause a kernel panic?
Although it is not always easy to know the reasons why a kernel panic happens, it is possible to determine some causes.
- They can occur when the initramfs image is corrupted. This file is used during boot, so it is vital for the system, and if something happens to it, it will cause a kernel panic.
- An improper attempt by the operating system to read or write memory.
- Improper installation of RAM chips.
- A hardware issue could also cause a kernel panic. One of the possible causes of this is the missing driver needed in the kernel.
- Malware or software bugs
- Data corruption
- Damage to the hard disk or motherboard.
- When trying to read an invalid or disallowed memory address.
It is even possible to get a kernel panic due to faulty updates or corrupted packages.
Another common cause of a kernel panic is when the kernel has incompatibility flaws or has not been properly installed. This can happen when the compilation of the kernel has not been done properly. This happens when we want to compile the kernel source code ourselves.
What does not syncing mean in kernel panic?
As we have been explaining, a Kernel Panic can happen for many reasons. Specifically, the “not syncing” error happens when, at boot time, a serious error is encountered. That is, it happens as soon as the operating system is loaded from the grub. When this happens, there is not much we can do from the system as such.
The origin of this specific error may be due to hardware configuration problems. We have to remember that the kernel is the part of the system that takes care of the hardware management by the drivers that the rest of the system will take advantage of.
A frequent cause is when there is a power failure and the computer has been incorrectly disconnected, causing damage to either hardware or a boot file.
Another less common cause is that some hardware driver has been updated, and the new instructions are not properly supported by the kernel.
But in short, we are talking about a boot-time error. This makes it impossible to mount the system volumes, and therefore we have to resort to third-party solutions.
- How To Install Linux Mint Without USB?
- Best Game Engine For Linux
- How To Install VIEB on Linux?
How can kernel panic issues be resolved?
The solution to a kernel panic is very varied because it will depend on some of the factors that have caused it.
In most of these cases, it is necessary to have a rescue image of the system. The LIVE image of the system will allow us to have the same system but from a live session.
For cases where the error is a kernel panic not syncing, a possible solution is as follows.
When booting the system, instead of choosing the usual option to boot the system, you have to choose the *Advanced option for* to enter the recovery mode of the system.
Once the system has booted into recovery mode, open a terminal and edit the /etc/selinux/config file with a text editor. For example, using nano
nano /etc/selinux/config
And then add this to the end of the file
SELINUX=enforcing
Save the changes by pressing CTRL + O and close the editor by pressing CTRL + X.
After this, reboot the operating system.
reboot
Another possible solution to the Kernel panic not syncing fatal exception error
In this case, it is likely that the error is caused by initramfs. This could be because the file is either missing or corrupted.
The causes of missing or corrupted files are very varied, but in this case, what we have to do is to replace it with another one that is correct.
To achieve this, access as in the previous step to the system recovery mode. Once the system has loaded, you can use the dracut utility to generate a new one. But first, back up the old one.
cp -p /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).img /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).img.bak
And now if you generate a new initramfs with the command
dracut –f
Finally, reboot the system.
How to Fix kernel panic not syncing vfs: Unable to mount root Error
This type of kernel panic occurs when the system fails to mount the root file system. A possible workaround is as follows
Restart your computer in recovery mode or safe mode and when you get access to it, run the following command
sudo update-initramfs -u -k <kernel-version>
You have to replace <kernel-version> with the exact version of your kernel.
Then you have to run
sudo update-grub
This last command updates the entire bootloader. Finally, reboot the system.
Kernel panic not syncing no init found
In this case, we are talking about a bad installation because of the ISO image. Because the kernel is unable to mount the file system, it is because the image has been created incorrectly, and therefore the installation has been faulty.
In this case, there is nothing to do but reinstall the system and make sure that the image is well recorded. In addition to this, once the image has been downloaded, it is advisable to check its integrity.
How do you stop kernel panic?
Although we are not 100% free from suffering a kernel panic at some point, there are a few things we can do to minimize the risks:
- Do not touch any key system files, not even out of curiosity. Also, avoid installing applications that require special permissions.
- Take care of the hardware by avoiding violent, unforced shutdowns.
- Update the kernel frequently through software distribution channels.
- Avoid using kernels compiled by third parties. Since the configurations they may use will not always be compatible with ours.
- Along with the kernel, it is also a good idea to update GRUB frequently but always from the official repositories.
In addition to these recommendations, always keep an eye on your hardware and its performance to avoid any bad surprises.
How to resolve Kernel Panic Not Syncing on Mac?
macOS is a very reliable system, and this is one of the main reasons for its success. However, a kernel panic can occur from time to time. So, you are likely to see a message with the following, “You need to restart your computer. Press and hold the power button for several seconds, or press the Restart button”.
If you see it, and the system lets you reboot, you may never see the error again as stated in Apple’s documentation.
If it happens repeatedly, the device may be faulty, and you need to send it to technical support.
Lastly, there are third-party applications that can help you perform software maintenance to prevent this from happening again.
Conclusion
Linux is an incredibly stable system and that is why it dominates the server environment and more and more people use it as a working operating system. However, this does not make it bug-free. And one of the well-known ones is the kernel panic.
Throughout this post, we have developed the topic enough so that you have a clear idea about its causes, how to remedy it, and even take precautions so that you don’t have to deal with it.
В моем случае ошибка появлялась после отключения SELINUX и последующей перезагрузки.
Лечится просто:
1. При загрузке ОС нажимаем e, чтобы перейти к редактирования загрузчика GRUB.
Далее в строке загрузки ядра по-умолчанию добавляем в конец selinux=0 пример:
kernel /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.32-504.3.3.el6.x86_64 ro root=UUID=516101c3-00dd-4db6-b1ff-7214dc0baa03 rd_MD_UUID=62292ebf:38febd4a:2514de0f:1cc21698 rd_NO_LVM LANG=en_US.UTF-8 SYSFONT=latarcyrhercyrheb-sun16 crashkernel=auto rd_NO_LUKS KEYBOARDTYPE=pc KEYTABLE=us rd_NO_DM rhgb quiet selinux=0
Нажимаем Enter и затем b для продолжения загрузки.
После успешной загрузки Linux редактируем файл /etc/grub.conf и во все строки загрузки ядра добавляем selinux=0, если конечно вы все ядра планируете загружать. Обычно достаточно последнее ядро и предыдущее.
I was trying to update libc in our Ubuntu server but it failed and now when I reboot the server I get a error message:
Kernel panic — not syncing — Attempted to kill init!
and it just hangs.
What is the solution to this problem? The server is used by 10 people so I don’t want to reinstall erasing their data.
RzR
3,06829 silver badges26 bronze badges
asked Oct 12, 2012 at 21:50
6
if the full message is:
kernel panic - not syncing: Attempted to kill inint !
PId: 1, comm: init not tainted 2.6.32.-279-5.2.e16.x86_64 #1
then you should have disabled selinux and after that you have rebooted the system.
The easier way is to use a live OS and re-enable it
vim /etc/selinux/config
...
SELINUX=enforcing
...
Second choice is to disable selinux in the kernel arguments by adding selinux=0
vim /boot/grub/grub.conf
...
kernel /boot/vmlinuz-2.4.20-selinux-2003040709 ro root=/dev/hda1 nousb selinux=0
...
source kernel panic — not syncing: Attempted to kill inint !
Henry Ecker♦
34.5k18 gold badges42 silver badges59 bronze badges
answered Nov 7, 2013 at 15:07
3
- Mount the centos live cd and boot
- Go into rescue mode and wait for it load up
- Read the terminal to see where it mounted the OS
- Go into OS
- vim or nano /etc/selinux/config
- Make sure SELINUX=enforcing or disabled
answered Apr 18, 2014 at 6:42
Michael MikhjianMichael Mikhjian
2,7604 gold badges36 silver badges51 bronze badges
Solution is :-
- Restart
- Go to advanced menu and then click on ‘e'(edit the boot parameters)
- Go down to the line which starts with linux and press End
- Press space
- Add the following at the end -> kernel.panic=1
- Press F10 to restart
This basically forces your PC to restart because by default it does not restart after a kernel panic.
answered Mar 1, 2016 at 7:04
3
Booting from CD to rescue the installation and editing /etc/selinux/config: changed SELINUX from enforcing to permissive. Rebooted and system booted
/etc/selinux/config before change:
SELINUX=enforcing and SELINUXTYPE=permissive
/etc/selinux/config after change:
SELINUX=permissive and SELINUXTYPE=permissive
cubbuk
7,8004 gold badges35 silver badges62 bronze badges
answered Dec 10, 2014 at 14:27
I just came across this problem when I replaced a failing disk. I had copied over the system files to the new disk, and was good about replacing the old disk’s UUID entry with the new disk’s UUID in fstab.
However I had not replaced the UUID in the grub.conf (sometimes menu.lst) file in /boot/grub. So check your grub.conf file, and if the «kernel» line has something like
kernel ... root=UUID=906eaa97-f66a-4d39-a39d-5091c7095987
it likely has the old disk’s UUID. Replace it with the new disk’s UUID and run grub-install (if you’re in a live CD rescue you may need to chroot or specify the grub directory).
answered Apr 27, 2015 at 1:01
Ethan BrownEthan Brown
6936 silver badges11 bronze badges
Mount remount the /
Eg.
mount -o remount,rw /dev/xyz /sed -i 's/1 1/0 0/' /etc/fstabsed -i 's/1 2/0 0/' /etc/fstab- reboot
benka
4,73235 gold badges47 silver badges58 bronze badges
answered Aug 17, 2015 at 16:41
At grub screen goto boot in recovery.
As booting hold ESC
It should take you into a gui menu. Open command and fix selinux.
Also I suggest run the clean broken packages
answered Jul 25, 2016 at 0:02
1
The kernel panic not syncing error can happen for various reasons, one of which may be due to buffers not being flushed to the actual devices. This error often prevents the system from booting and may affect parts of the kernels and modules.
The dynamic loader may not be present in the root file, so when the kernel tries to execute some programs, it may not find the necessary dynamic library. While this issue can be frustrating, you can follow our detailed solutions and resolve it in no time. Keep reading to find out more.
Why Do I Keep Getting Kernel Panic Not Syncing Error
Here are some of the reasons you may be experiencing this issue:
- Missing initramfs or initrd image from the updated kernel configuration in /boot/grub/grub.conf.
- Missing initrd or initramfs file from the /boot directory.
- Incompletely installed kernel or system packages during the upgrade because of insufficient space.
- Missing third-party modules from the initrd or initramfs image. The kernel or system package wasn’t fully installed during an update.
- Insufficient disk space
- Incompatible kernel version
How Can I Fix Kernel Panic Not Syncing?
If you come across this error while using your device, do not panic. It may be due to your boot being out of space. In which case, you should take the following steps to resolve the problem.
Solution 1 – Remove the old Linux kernel to free up space in your /boot drive.
Step 1: Boot the system to grub, then select “Advanced options” from the menu.
Step 2: Select a previous kernel; this should boot without problems.
Step 3: Log in to the system and enter the command $ df. Be sure to hit enter after entering the command.
Step 4: Once that is done, check /boot directory to see if it is 100% used
Step 5: Remove old Linux kernels by entering the command: $ Sudo apt-get autoremove
How Can I Fix Kernel Panic Not Syncing on Mac?
If you are experiencing this issue on your Mac, you should try the following solutions.
Solution 1 – Disconnect all peripheral devices attached to your system
The problem may sometimes arise due to faulty or incompatible peripheral devices plugged in. Disconnect all such devices, then reboot your device. Once done, restart your device.
Solution 2 – Boot Your Device in Safe Mode
Most often, the issue with repeated kernel panic errors lies within the Mac operating system. Therefore, you need to start by rebooting your Mac in safe mode. To do that, follow this step.
Step 1: Restart your device, then hold down shift while the system boots.
Step 2: Put it in Safe mode to disable unnecessary applications running in the background, including kernel extensions.
Step 3: Check to see if the panic still happens in safe mode. If it doesn’t, the problem may be from third-party applications on your computer.
Solution 3: Update Your Outdated Apps
Suppose the previous solution fails to resolve the panic error; updating your apps should be the next step. Often, outdated applications conflict with your version of the operating system or other programs on your Mac.
Solution 4: Check your hardware
Incompatible hardware may also result in the kernel panic error you experience. To take care of this on Mac, take the following steps.
Step 1: Shut down your Mac and disconnect the external devices.
Step 2: Restart your device.
Step 3: Run a test to see if the issue still occurs. If it does not, then the issue is from one of your external devices.
How Can I Resolve Kernel Panic Not Syncing Due to Missing Initrd or Initramfs
First, you must be sure the error is due to third party modules missing from initrd or initramfs image. Here is how to check
Step 1: Create a chroot environment in the root volume of the non-booting instance.
Step 2: Use one of these three options to ascertain which module(s) are missing from the initramfs or initrd image:
Option 1: Open the system and run the Dracut -f -v command in the /boot directory. This will help you determine if the fault is from a failed rebuilding of the initrd or initramfs image and pinpoint the missing module(s). Aws Amazon
If the command doesn’t find errors, reboot the instance to check if the problem has been resolved. If the instance reboots successfully, the error has been resolved.
You should note that the Dracut -f -v command may add the missing modules to the initrd or intramifs image.
The second way to determine the missing module(s) is to run the lsinitrd initramfs-4.14.138-114.102.amzn2.x86_64.img | less command. This command allows you to view the contents of the initrd or initramfs file. Once done, you should replace initramfs-4.14.138 with the title of your image.Aws Amazon
Alternatively, you can inspect the /usr/lib/modules directory.
For these three ways, once you have verified the missing modules, you must add them back to the initrd or initramfs image to resolve the panic.
I Keep Getting the Kernel Panic Not Syncing Error on My Linux 2, What Can I Do?
dracut-initqueue[1180]: Warning: dracut-initqueue timeout – starting timeout scripts
dracut-initqueue[1180]: Warning: Could not boot.
[ OK ] Started Show Plymouth Boot Screen.
[ OK ] Reached target Paths.
[ OK ] Reached target Basic System.
dracut-initqueue[1180]: Warning: /dev/disk/by-uuid/55da5202-8008-43e8-8ade-2572319d9185 does not exist
dracut-initqueue[1180]: Warning: Boot has failed. Aws Amazon
Suppose you see any of these errors while running your Linux 2 instance on the Nitro platform; here’s how to tackle it. Debug the issue by adding “rd.shell rd.debug” to the kernel command line.
Why Do I encounter Kernel Panic Not Syncing on Mac?
The issue may plague your Mac due to
- Faulty peripheral devices
- Insufficient storage space
- Incompatibility with RAM
If you face this problem while using your Mac, you should trace the source using the tips below.
Confirm that it is not from an External Device
Sometimes, peripheral devices can be responsible for this frustrating error. To identify which one of the devices causes panic, disconnect all of such peripheral devices, and then turn off your Mac.
When you restart it, connect each external device and check if the kernel error pops up. Repeat the process until you get the kernel panic error on an external device. Once you have identified the responsible peripheral, you can have it checked out at a service center to find out why it is affecting your Mac negatively.
Check RAM
Generally, the random access memory is a reliable utility. However, it can cause MacBook kernel panic not syncing if there is any defect or incompatibility. Unfortunately, Macs are really sensitive to issues arising from RAM; thus, an extension purchased from a third-party vendor that turns out not to be a perfect fit will cause you to experience Mac panic frequently.
To avoid this, make sure you get your RAM extensions from Apple or other certified merchants. These merchants should provide you with a warranty and guarantee the RAM’s full compatibility with your Mac.
To check if your RAM is suitable for your computer, you have to determine your motherboard’s memory and specifications. Armed with this information, you can contact Apple or your RAM merchant to learn about the RAM and motherboard compatibility.
Conclusion
There are many reasons why you may be experiencing Kernel panic not syncing error on your device. One of which is missing initramfs or initrd image. While encountering this problem can be annoying, you can fix it by yourself using our solutions. Go ahead and fix your kernel panic not syncing issue today.