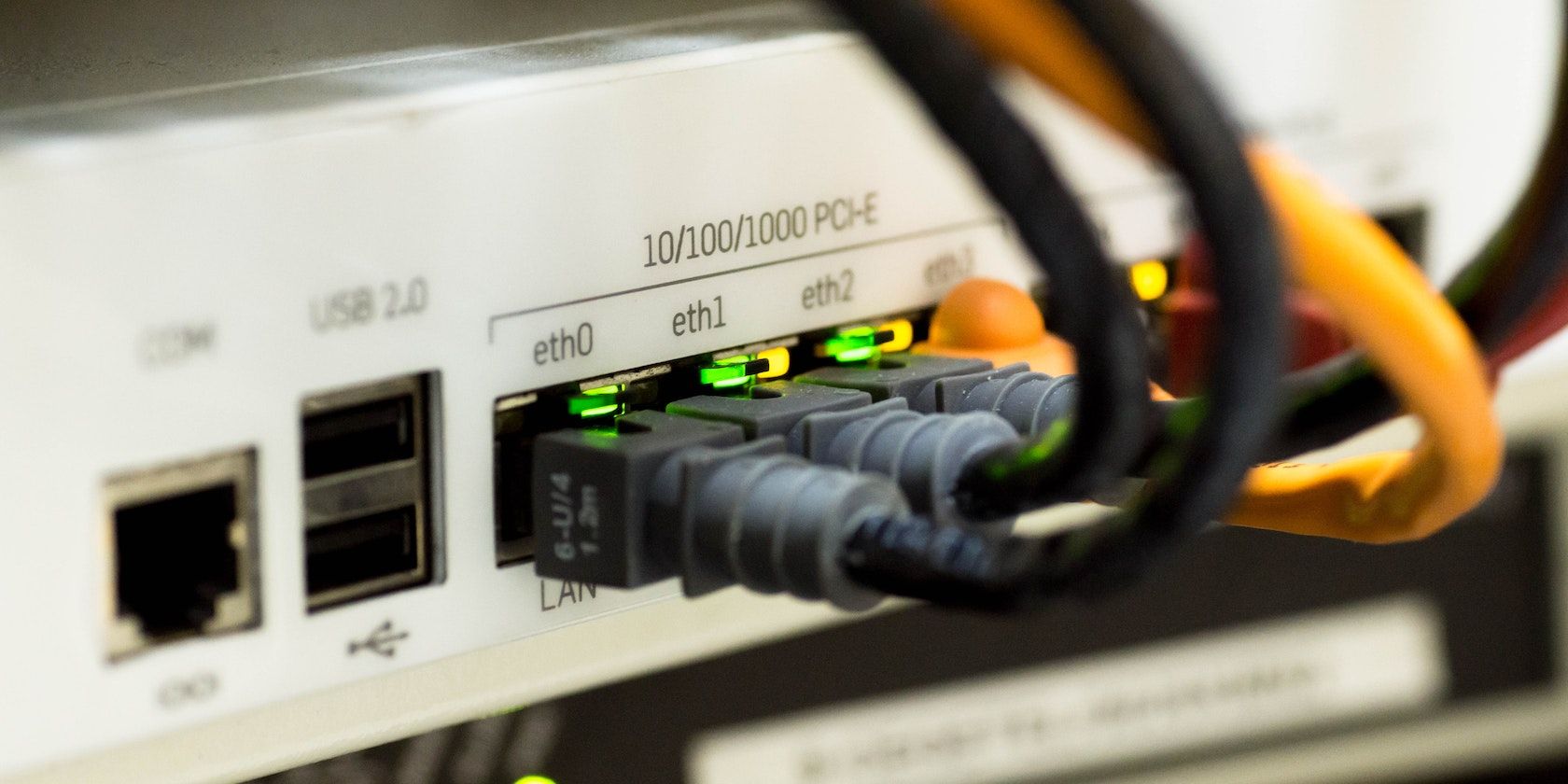
Double NAT errors can really muck up your network connection, but it’s easy to detect them on Windows.
Experiencing network problems? The problem could be down to your PC’s Network Address Translation (NAT) throwing an error. NAT errors can spoil your surfing and gameplay experience considerably, but not everyone knows what a NAT is, and how errors can ruin your fun.
If you don’t know what NAT is, we’ll help you understand its meaning and how you can fix «double NAT» errors.
What Is NAT, and What Causes a Double NAT Error?
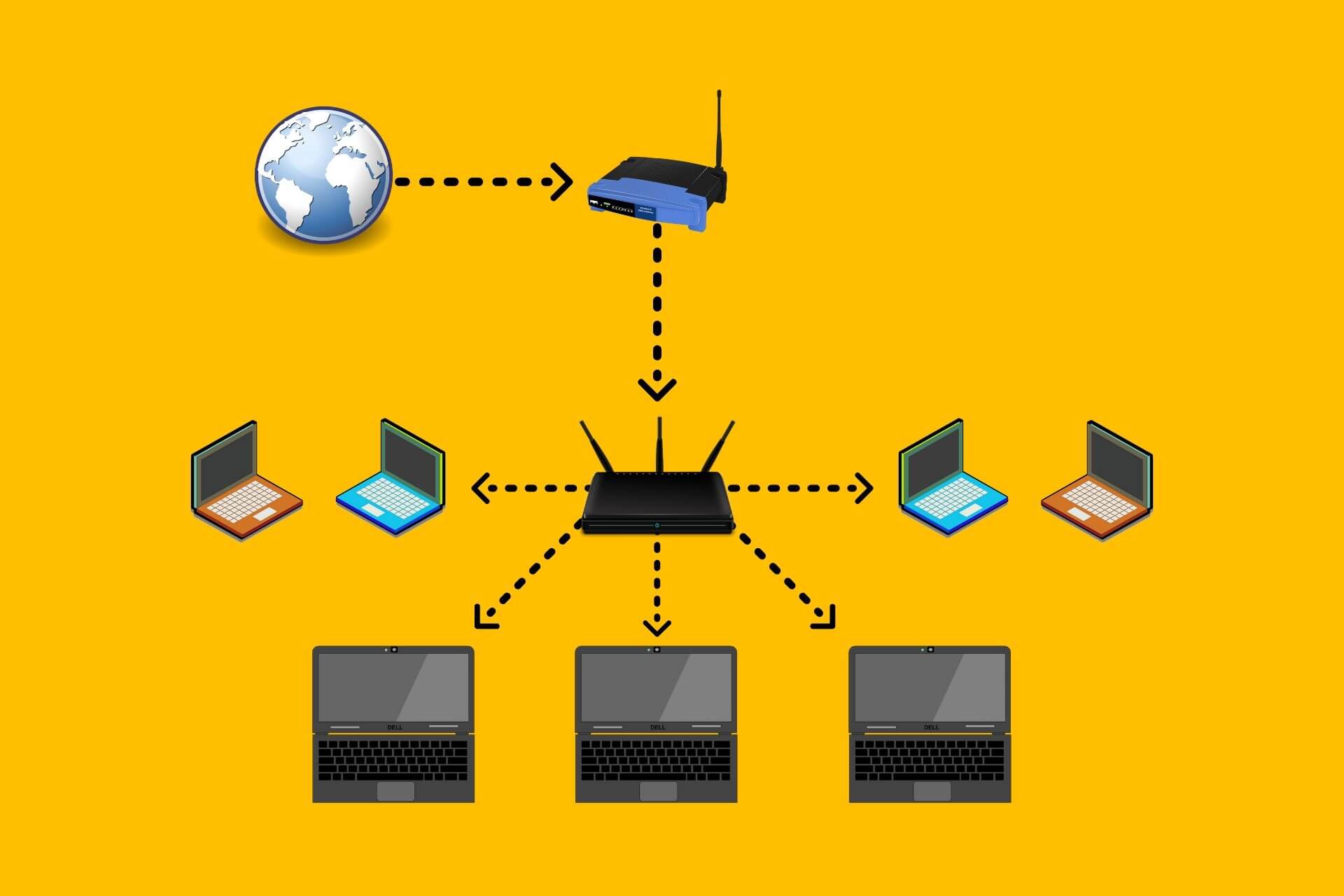
NAT is a translation method. It translates the public IP address that your Internet Service Provider (ISP) provides to a private IP address used by your local network.
The middleman in this equation is the router, which performs this translation. However, when you’re using two routers or connecting your router to an ISP gateway, the translation can go wrong and lead to double NAT errors.
Double NAT errors occur when your router is connected to another router or gateway. Since the IP address is translated twice in such setups, your network is essentially split into two different private networks. Both devices will have problems communicating with each other because of two different sets of IP addresses and firewalls.
Double NAT can cause network problems and interfere with online gaming, VPN connections, port forwarding, and port triggering. Double NAT often renders Quality-of-Service (QoS) configurations useless. It can also interfere with smart home devices like cameras and doorbells.
Essentially, double NAT can choke your network and stand in the way of effectively using many devices. Let’s talk about how to fix it.
How to Detect Double NAT on Windows
If you suspect something is wrong with your router configuration, you need to see if double NAT is currently occurring. Fortunately, you can do that from your Windows PC with a few quick steps.
To check if double NAT is the problem:
- Launch an elevated Command Prompt by pressing Win + R, typing cmd, and pressing Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
- Execute the following command:
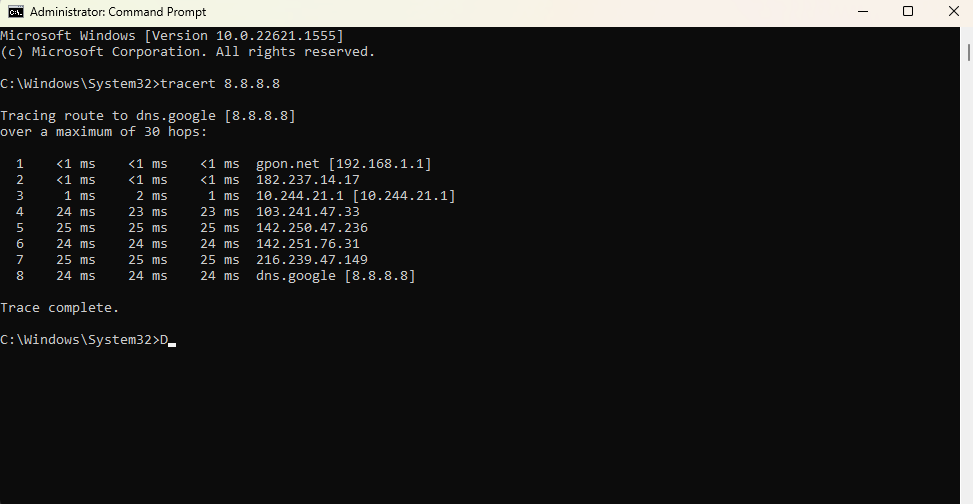
tracert 8.8.8.8
- You’ll see a list of hops. If the first two hops are private IP addresses, you have a double NAT issue.
If you’re unsure as to which IP addresses are private or public, private IP addresses are typically in specific ranges, such as:
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
- 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
If you see IP addresses that look very different from these, those are public IP addresses. In our case, for example, only the first hop shows a private IP address while the subsequent hops show public IPs. This indicates that our network doesn’t have a double NAT problem.
How to Fix Double NAT Errors
Here are some ways to fix double NAT errors:
Remove a Router
You guessed it. If your current network setup includes two routers, the easiest solution is to remove one of the two routers from the equation. If you don’t absolutely need those two routers (most regular users don’t), just use a single router provided by the ISP.
Use One Router as a Modem
If you do need to use two routers, you’ll need to use your ISP’s router as a modem. This involves plugging the ISP’s router into the second router’s WAN port.
Use Bridge Mode
Another method to fix double NAT errors is enabling bridge mode. Some routers don’t have this option so you’ll first need to check if yours does by accessing the router’s firmware.
The bridge mode turns a router into a modem that relays all the traffic that comes its way directly to the router.
When you enable bridge mode, it disables NAT and allows all traffic to pass through without translation.
The method for configuring bridge mode differs for every router. You can generally access the router firmware by typing 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1 into the browser’s URL bar and pressing Enter. Log in using the credentials provided by the ISP or the manufacturer.
If you can’t find the bridge mode settings, it’s best to contact the ISP or manufacturer.
Forward Connections Using DMZ
If bridge mode isn’t available, you can put your router in the demilitarized zone (DMZ). When you set up DMZ, you’ll create an area where all ports are forwarded to. This way, you won’t be disabling NAT, but you’ll create a port forwarding rule that says all traffic, from any port, is forwarded to a specific address.
Effectively, DMZ is a setting that bypasses DHCP, NAT, and firewall to give another router a direct connection to the internet.
Again, your router may or may not have the DMZ option.
Before you set up DMZ, you’ll need your secondary router’s IP address. This should be a static IP address, which means you can’t use DHCP mode. Once you’ve configured the router to use a static IP, go to the router firmware’s homepage or the page showing basic network details and note down the IP address.
To set up DMZ, log into the router’s firmware and locate the DMZ setting. Enable DMZ and enter the other router’s static IP address.
Eliminate Double NAT Errors and Enjoy Your Network Again
Double NAT errors be a major problem, especially for those who love online gaming. Solving the double NAT error can be as simple as removing the second router or involve some technical steps like using a static IP address and enabling DMZ.
Hopefully, you were able to resolve the double NAT issue with one of these errors. While double NAT can prevent you from joining sessions, there are other factors that can cause the game to lag even though you’re able to join the session. Of course, there are methods to fix everything when you’re a determined gamer.
For most people, a double Network Address Translation (NAT) configuration doesn’t create a noticeable effect on network performance. But some people who play online games or use port forwarding rules and Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) might prefer to avoid a double NAT configuration. Learn more about Double NAT.
To avoid a double NAT configuration on your Google Nest Wifi Pro, Nest Wifi, or Google Wifi devices, here’s what you can do:
(Recommended) Remove ISP-provided router from your network
If you have 2 separate ISP devices, a modem and router, turn off and unplug the ISP-provided router, then connect your modem directly to your Wifi device.
If your ISP-provided router is combined with the ISP’s modem in a single device, enable bridge mode on your modem/router combo to fix the Double NAT issue. When you enable bridge mode on your ISP router, it’ll turn off its NAT and allow your Wifi device to be the sole device that performs NAT.
- Connect a computer directly to your ISP-provided router with an Ethernet cable.
- Log in to your modem and router combo, then find its settings to enable bridge mode.
- To access your router’s settings, you might have to open an internet browser and enter your router’s IP address in the address bar like this:
Steps will vary depending on the device. Many ISPs and manufacturers provide instructions on how to enable bridge mode. To learn how to turn on bridge mode, check your ISP’s support website.
(Not Recommended) Enable Bridge mode on your Wifi router device
A single Wifi device that isn’t part of a mesh system can be set to bridge mode. Bridge mode disables the DHCP and routing functions so double NAT is no longer an issue. In bridge mode, this single mesh point will operate as a pure Wi-Fi access point connected over an Ethernet wire to your modem.
Note: Bridge mode on Wifi devices only works on a single Wifi device setup. If you create a mesh network with multiple Wifi devices, your primary Wifi router can’t be in bridge mode because it needs to control settings and communication within your Wi-Fi network. If your primary Wifi router is in bridge mode, in addition to losing mesh capability, you’ll also lose some functionality of your Wifi device such as:
- Family Wi-Fi, priority device, and Guest Wi-Fi will be unavailable.
- DNS and WAN settings can’t be edited.
- You won’t be able to test your mesh connection.
Additionally, bridge mode disables many of Google Wifi and Google Nest Wifi’s security protections. This is because your upstream router (the modem/router combo in the above scenario) is the one performing DNS steering, packet inspection, executable patching, and so on.
Your Wifi devices automatically install security updates to maximize your privacy and security. These protective features are most effective, and in some cases, only effective, when all traffic passes through your primary Wifi router, instead of through another router.
If you have a third-party router, you can wire your primary Wifi router to it, then mesh additional Wifi points downstream.
If you still want to turn your primary Wifi device into a bridge, you can follow the steps below:
You can’t transition your primary Wifi device into bridge mode if your WAN IP is a public IP address. To enable bridge mode, there needs to be another router between your modem and primary Wifi device. If your primary Wifi device’s WAN port has a public IP, that means it’s directly connected to your modem. In this scenario, the bridge mode option in the app will be unavailable.
Additional questions
What’s the difference between NAT and double NAT?
Your internet service provider (ISP) usually assigns your home internet connection a single public and globally unique IP address. You can view Wifi device information in the Google Home app.
Most households have multiple devices connected to its home network, with each device requiring their own IP address. Your router assigns a local IP address to each device in your home network through DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
Google Nest Wifi Pro, Nest Wifi, and Google Wifi devices transfer data that comes in or goes out from the public IP address to the device in your home network. This process of transferring data from the public IP address to the specific device local IP address is called Network Address Translation (NAT).
Internet providers usually provide a modem or gateway, which is a modem and router combo, that converts the signal that comes into your home internet connection. In many cases, the modem or gateway is set up to perform NAT. A double NAT happens if another router, for example a Nest Wifi router, is connected to the ISP modem or gateway. All this means is that data is going through a NAT process twice, which might cause a very small delay, of the order of milliseconds to data getting in and out of your home.
What other disadvantages are there in a Double NAT configuration?
You can connect 2 or more independent (non-meshed) router systems to extend the Wi-Fi coverage in your home. But when you have 2 routers, each with their own private Wi-Fi network, your personal devices can have a hard time communicating with each other because of the different sets of IP addresses and firewalls between the 2 independent router systems.
For example, let’s say you want to wirelessly print a picture from your computer. If you have 2 independent networks, it’s possible your computer is on one network while your printer is on the other. And if both networks are private, your computer won’t be able to tell your printer to print the picture.
Double NAT
A double NAT can also result in performance issues if you play online games or use port forwarding rules and UPnP.
To fix this, bridge mode lets multiple routers share one single Wi-Fi network. Here’s what that could look like:
Bridge mode
Was this helpful?
How can we improve it?
Learn what Double NAT is and how to fix it
by Vlad Constantinescu
Vlad might have a degree in Animal Husbandry and Livestock Management, but he’s currently rocking anything software related, ranging from testing programs to writing in-depth reviews about them…. read more
Updated on
- If you’ve recently upgraded your Internet connection and have two routers instead of one, it’s highly likely that you’re double NAT-ing.
- Although double NAT isn’t necessarily a bad thing, it can become troublesome, especially if you want to grant access from the outside (port forwarding) to certain devices on your private network.
If you’ve recently upgraded your Internet connection and have two routers instead of one, it’s highly likely that you’re double NAT-ing. As a novice PC user, that shouldn’t bother you too much.
Some even say that double NAT-ing is even more secure than its singular version. However, if you’re not exactly tech-savvy, you may already have a lot of questions.
You can try to use a powerful VPN service to resolve the NAT issue once and for all, making this option the easiest, but it might not be useful for all users, depending on their network setup and expectations.
In other cases, users have encountered NAT issues while using their PS4 system, which can of course cause a wide range of issues, especially if you have waited for a long time to play a game.
- What is double NAT?
- How to fix double NAT
- 1. Remove ISP router from the network
- 2. Enable Bridge mode on your ISP router
- How to port forward through double NAT
- 1. Use DMZ to forward connections
- 2. Use double router port forwarding
- 3. Set up a static IP address on Windows 10
- Bypass or disable double NAT, ultimately it’s a matter of choice
What is double NAT?
To put it simply, double NAT is the situation when you connect to the Internet through two routers. So, you connect to your router, which is behind another router. Thus, you are part of two different private networks, which might seem ideal but it isn’t.
This situation is very frequent whenever your ISP enforces the use of a proprietary router. The ISP-provided router might not be exactly powerful, so you buy an additional one, which is more to your liking.
Due to your ISP’s policy, you are now double NAT-ing, which restricts you in a bunch of ways. For instance, port forwarding becomes a distant memory, since it’s so challenging, if not downright impossible in this situation.
Sure, you could just remove the ISP-provided router, but some companies insist on you using their hardware. A more complicated situation is when you’re using fiber optics and your ISP’s router acts as a signal converter.
For many users, double NAT isn’t a problem. But it can become troublesome if you play online games, want to forward some ports on your router, use UPnP or rely on IP address assignments.
How to fix double NAT
1. Remove ISP router from the network
- Unplug and disconnect your ISP router
- Plug the network cable into the WAN port of your personal router
- Access your personal device’s interface and reconfigure it accordingly
You might need to change the way your modem handles the Internet connection. For instance, if your router only distributed dynamic IPs, you might need to change its settings so it can fill in the ISP modem’s position.
2. Enable Bridge mode on your ISP router
- Call your ISP
- Ask them to put their router in Bridge mode
- Reconfigure your personal router as needed
You will need to configure your router so it can distribute the traffic that previously ran through the first device. For instance, if the ISP router was configured for PPPoE and your personal device was in dynamic IP distribution mode, you will have to move the PPPoE settings on your personal router.
Explanation: When you put the ISP router in bridge mode, it disables the NAT feature on it. Thus, it starts functioning as a DHCP server and stops generating IP conflicts.
More so, if it’s a wireless-enabled router, it will lose its Wi-Fi capabilities and you won’t be able to access it on your network using the default gateway address.
If none of these solutions is good for you, here are a few ways you can circumvent double NAT.
How to port forward through double NAT
1. Use DMZ to forward connections
- Log into your second router (the one farthest from the Internet/closer to your PC)
- On the status page, locate the WAN/IP address and note it down
- Log into the first router (use Wi-Fi or plug your PC directly to its WAN port)
- Locate the DMZ page (if supported)
- Enable DMZ and type the IP you’ve previously noted from the second router
- Save the settings
Note that you should configure the second router in such a manner that its WAN address doesn’t change (static IP). If you use it in DHCP mode, its IP will definitely change at some point, which will render the DMZ IP you used in the first router useless.
2. Use double router port forwarding
- Log into your first router (use Wi-Fi or plug your PC straight into the WAN port)
- Forward ports to your second router’s external IP address
- Log into your second router
- Forward ports to the device where you want to run the program/service (game server, mail server, etc)
- Configure a static address for every device you want to forward ports to
- Make sure that the second router has a static IP address
If you’re not sure about setting static IP addresses for network devices, we’re going to show you how in the following section.
3. Set up a static IP address on Windows 10
- Press the Win key on your keyboard
- Type cmd and hit Enter
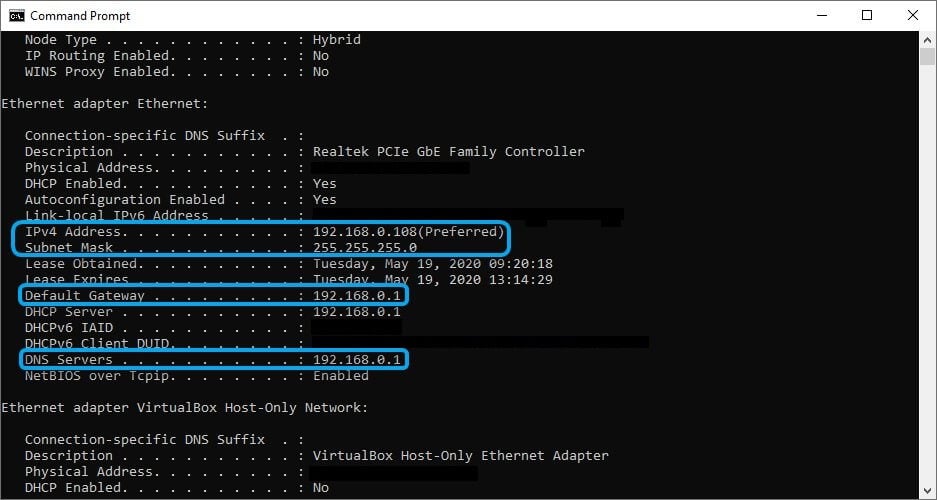
- In the Command Prompt type ipconfig /all and hit Enter on your keyboard
- Locate your main network adapter
- Note down its IPv4 Address, Subnet Mask, and DNS Servers* (check the screenshot)
- Close the Command Prompt window
- Check your router’s status page to view the DNS servers if ipconfig /all shows the same value as Default Gateway
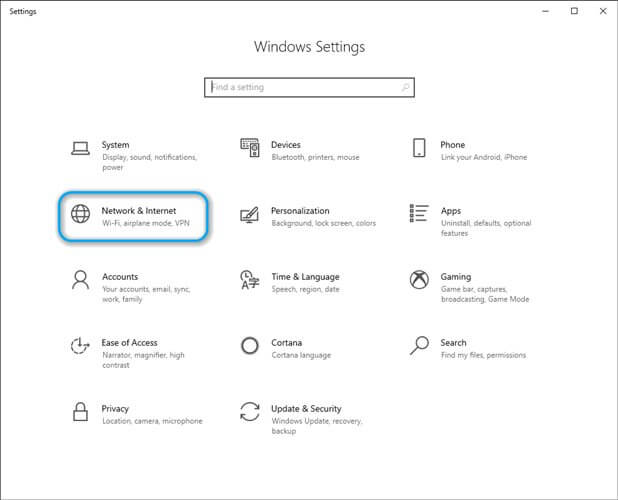
- Access the Windows 10 Settings app
- Choose Network & Internet
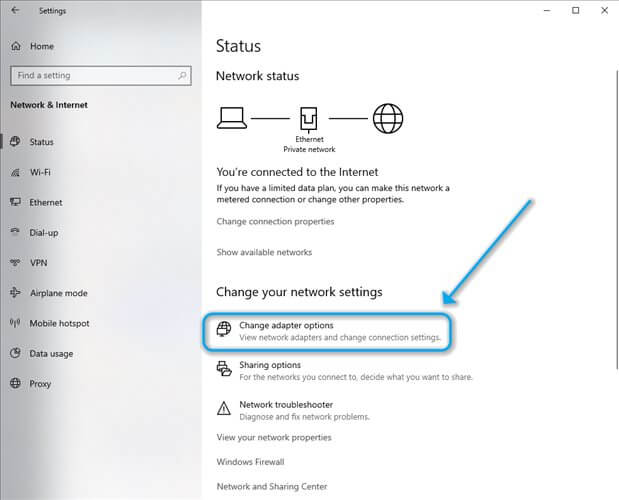
- Click the Change adapter options button
- Right-click the main adapter that you’ve used in the CMD steps above and choose Properties
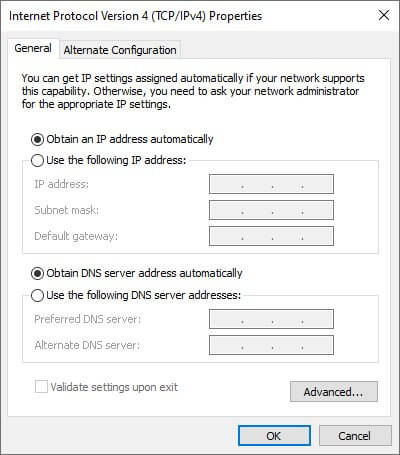
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) from the list
- Click the Properties button
- Take a screenshot of the current configuration displayed in the new window
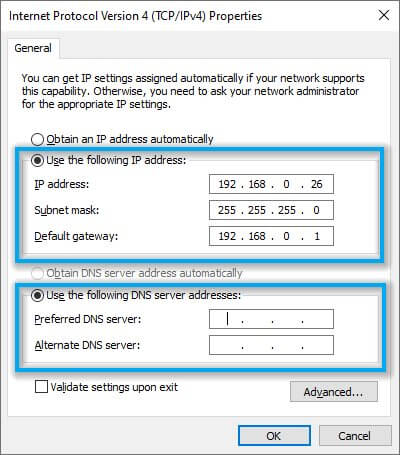
- Click the Use the following IP address radio button
- Choose an IP address for your PC (should be similar to the CMD IP above**, only the last set of digits should be different, between 1-254)
- Type the Subnet Mask and Default Gateway exactly as they appeared in the CMD window
- Click the Use the following DNS server addresses radio button
- Type the two DNS servers as they appear in your router’s status page
- Click OK
* – if you see the same DNS server as the Default Gateway, you will need to check the DNS servers displayed on your router’s status page. Alternatively, you can call your ISP and ask them what DNS servers they use, and they should be able to provide you with this information.
** – if the IP you saw in CMD is, for instance, 192.168.0.108 (our case), you can change it to any other IP like 192.168.0.xxx, where xxx = any number between 1 and 254, except 108.
If your Internet connection doesn’t work after you went through all these steps, it can be one of two things:
- You chose an invalid IP address (the same as your router’s or not in the same range)
- The DNS servers are wrong, in which case you’ll have to call your ISP and ask them to tell you what DNS servers to use
Bypass or disable double NAT, ultimately it’s a matter of choice
If you’re unfortunate enough to be trapped behind the double NAT wall, it can be quite difficult to bypass this situation if you’re a novice. However, if you follow our extensive guide, you should have no trouble.
Regardless of whether you want to eliminate Double NAT or just bypass it through various means, our guide should have you covered. Make sure you follow our instructions accordingly and not skip any step.
Понравилось? Поделитесь…
Двойные ошибки NAT могут серьезно повредить ваше сетевое соединение, но их легко обнаружить в Windows.
Возникли проблемы с сетью? Проблема может заключаться в том, что трансляция сетевых адресов (NAT) вашего ПК выдает сообщение об ошибке. Ошибки NAT могут значительно испортить ваш серфинг и игровой опыт, но не все знают, что такое NAT и как ошибки могут испортить ваше удовольствие.
Если вы не знаете, что такое NAT, мы поможем вам понять его значение и как исправить ошибку «двойной NAT.
NAT — это метод трансляции. Он преобразует общедоступный IP-адрес вашего интернет-провайдера (ISP) в частный IP-адрес, используемый вашей локальной сетью.
Посредником в этом уравнении является маршрутизатор, который выполняет это преобразование. Однако при использовании двух маршрутизаторов или подключении одного маршрутизатора к шлюзу интернет-провайдера преобразование может пойти не так и привести к двойным ошибкам NAT.
Двойные ошибки NAT возникают, когда ваш маршрутизатор подключен к другому маршрутизатору или шлюзу. Поскольку в этих настройках IP-адрес транслируется дважды, ваша сеть эффективно делится на две разные частные сети. У обоих устройств будут проблемы со связью друг с другом из-за двух разных наборов IP-адресов и брандмауэров.
Двойной NAT может вызвать проблемы с сетью и помешать онлайн-играм, VPN-подключениям, переадресации портов и срабатыванию портов. Двойной NAT часто делает бесполезными конфигурации Quality-of-Service (QoS). Он также может мешать работе умных домашних устройств, таких как камеры и дверные звонки.
По сути, двойной NAT может задушить вашу сеть и помешать эффективному использованию многих устройств. Давайте поговорим о том, как это исправить.
Как обнаружить двойной NAT в Windows
Если вы подозреваете, что с конфигурацией вашего маршрутизатора что-то не так, проверьте, не происходит ли двойной NAT. К счастью, вы можете сделать это на ПК с Windows, выполнив несколько простых шагов.
Чтобы проверить, не связана ли проблема с двойным NAT:
- Запустите командную строку с повышенными привилегиями, нажав Win + R, набрав cmd и нажав Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
- Выполните следующую команду: tracert 8.8.8.8
- Вы увидите список переходов. Если первые два прыжка являются частными IP-адресами, у вас проблема с двойным NAT.
Если вы не уверены, какие IP-адреса являются частными, а какие общедоступными, частные IP-адреса обычно находятся в определенных диапазонах, например:
- с 192.168.0.0 до 192.168.255.255
- с 172.16.0.0 по 172.31.255.255
- с 10.0.0.0 по 10.255.255.255
Если вы видите IP-адреса, которые сильно отличаются от этих, это общедоступные IP-адреса. В нашем случае, например, только первый переход показывает частный IP-адрес, а последующие переходы показывают общедоступные IP-адреса. Это указывает на то, что в нашей сети нет проблемы двойного NAT.
Как исправить ошибки двойного NAT
Вот несколько способов исправить двойные ошибки NAT :
Удалить маршрутизатор
Вы уже догадались. Если ваша текущая сетевая конфигурация включает два маршрутизатора, самым простым решением является удаление одного из двух маршрутизаторов из уравнения. Если вам вообще не нужны эти два маршрутизатора (большинству обычных пользователей они не нужны), просто используйте один маршрутизатор, предоставленный вашим интернет-провайдером.
Используйте один маршрутизатор в качестве модема
Если вам необходимо использовать два маршрутизатора, вы должны использовать маршрутизатор вашего интернет-провайдера в качестве модема. Для этого вам необходимо подключить маршрутизатор ISP к WAN-порту другого маршрутизатора.
Использовать режим моста
Еще один способ исправить двойные ошибки NAT — включить режим моста. Некоторые маршрутизаторы не имеют этой опции, поэтому вам сначала нужно проверить, есть ли она у вас, просмотрев прошивку вашего маршрутизатора.
Режим моста превращает маршрутизатор в модем, который перенаправляет весь входящий трафик непосредственно на маршрутизатор.
Когда вы включаете режим моста, он отключает NAT и позволяет всему трафику проходить без трансляции.
Метод настройки режима моста отличается для каждого маршрутизатора. Как правило, вы можете получить доступ к прошивке вашего маршрутизатора, введя 192.168.0.1 или 192.168.1.1 в адресную строку браузера и нажав Enter. Войдите в систему, используя учетные данные интернет-провайдера или производителя.
Если вы не можете найти настройки режима моста, лучше всего обратиться к поставщику услуг Интернета или производителю.
Переадресация соединений с использованием DMZ
Если режим моста недоступен, вы можете разместить маршрутизатор в демилитаризованной зоне (DMZ). Когда вы настраиваете DMZ, вы создаете область, в которую перенаправляются все порты. Таким образом, вы не отключите NAT, а создадите правило перенаправления портов, согласно которому весь трафик с любого порта перенаправляется на определенный адрес.
По сути, DMZ — это параметр, который обходит DHCP, NAT и брандмауэр, чтобы предоставить другому маршрутизатору прямое подключение к Интернету.
Опять же, ваш маршрутизатор может иметь или не иметь настройку DMZ.
Перед настройкой DMZ вам нужен IP-адрес вторичного маршрутизатора. Это должен быть статический IP-адрес, что означает, что вы не можете использовать режим DHCP. После настройки маршрутизатора на использование статического IP-адреса перейдите на домашнюю страницу встроенного программного обеспечения маршрутизатора или страницу базовой сети и запишите IP-адрес.
Чтобы настроить DMZ, войдите в маршрутизатор и прошивку № 39 и найдите настройку DMZ. Включите DMZ и введите статический IP-адрес другого маршрутизатора.
Устраните ошибки двойного NAT и наслаждайтесь сетью И снова
Двойные ошибки NAT — серьезная проблема, особенно для тех, кто любит онлайн-игры. Устранение неполадок двойного NAT может быть таким же простым, как удаление второго маршрутизатора, или включать некоторые технические шаги, такие как использование статического IP-адреса и включение DMZ.
Мы надеемся, что вы смогли решить проблему двойного NAT, используя один из маршрутизаторов с этими ошибками. Хотя двойной NAT может помешать вам присоединиться к сеансу, существуют и другие факторы, которые могут привести к задержке игры, даже если вы можете присоединиться к сеансу. Конечно, есть способы все исправить, если вы решительный игрок.
The digital world is all about IP (internet protocol) addresses. Every device needs an IP in order to communicate on the internet or within a private network. Given there’s not enough public IP addresses out there for every internet-connected device (at least with IPv4), this little thing called NAT becomes extremely important. It stands for network address translation (NAT) and is a function provided by routers to enable multiple devices to access the internet via a single public IP address.
Behind each public IP, there can be hundreds of devices with their own private IP addresses, thanks to NAT. And almost all equipment that provides the NAT function includes a firewall to protect the private IPs and devices from public IPs and devices on the internet. Other network services are also typically offered, like DHCP (dynamic host control protocol) to give out the private IP addresses to devices that connect to the local network.
How double NAT happens
Having more than one device performing NAT on a private network, however, can cause issues with that network. Some users may never notice, making it a non-issue for them. But others can run into headaches with certain applications, services, and situations. So, it’s always a good idea to eliminate double NAT if you have it.
Having more than one NAT device usually happens when you connect your own router to a gateway installed by your internet service provider (ISP) that also includes the NAT and routing functions. Some ISPs install only a simple modem that lacks the NAT and routing functions, which eliminates the problem altogether. But most ISPs assume their customers don’t have routers, however, so they’ll provide you with a combo device whether you want it or not.
If you’re unsure what the ISP has given you, take a look at the box. If there’s only one Ethernet port, it’s likely a simple modem (aka a broadband gateway). But if there’s multiple Ethernet ports or if it supports Wi-Fi connections, it’s likely performing NAT and routing as well.
The problems double NAT can cause
When there’s double NAT on your network, you might run into issues with services that require UPnP (Universal Plug-and-Play) support or manual port forwarding. This would include online gaming on computers or consoles, remote desktop into your computers, connecting to a VPN server, or accessing security camera feeds. Services like these sometimes require certain ports to be opened in the router’s firewall and directed to a particular computer or device on the network.
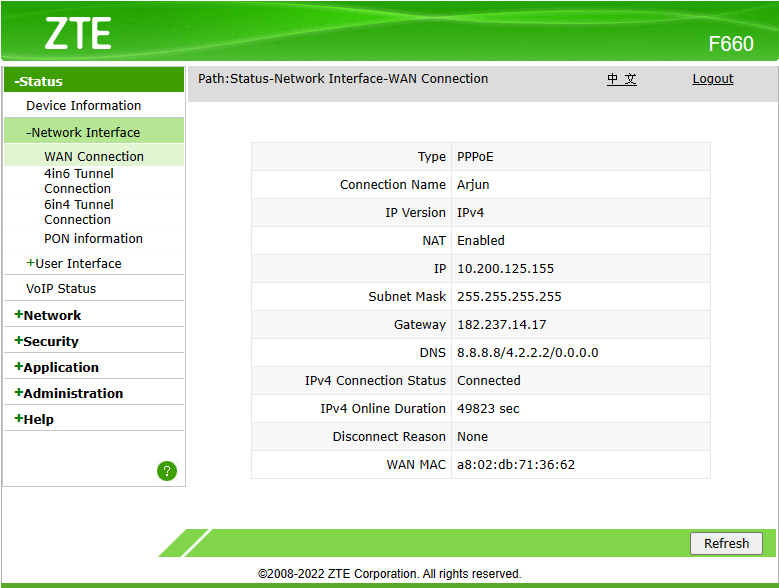
This screenshot shows how I’ve configured my router for port forwarding, so that I can use remote SSH (Secure Shell) on a server on my local network. I can’t do that if my gateway is also performing NAT (network address translation).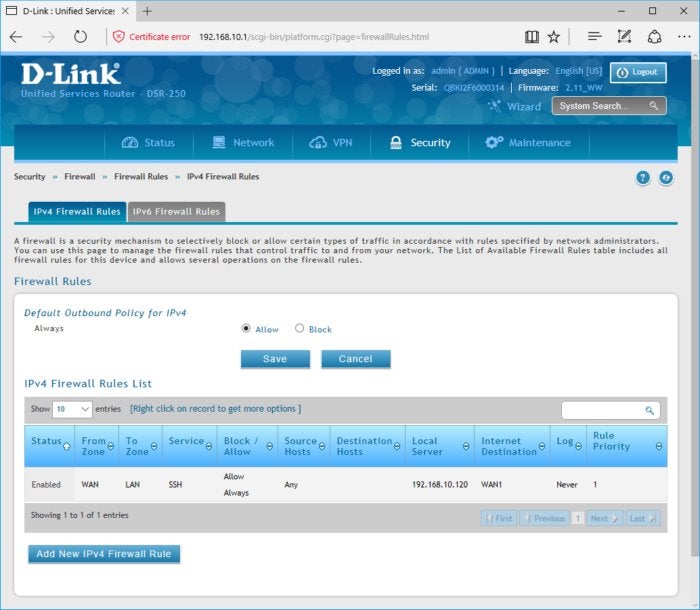
The problem with double NAT is that if the first router on your network doesn’t have the port forwards configured, incoming traffic will stop there even if you have the port forwards configured on the second router. Or even if the first router has the port forwards, it can’t forward the traffic to a device that’s connected to the second router. It might only forward traffic to computers and devices directly connected to that first router, which could be either a wireless or wired connection.
Double NAT can also complicate any manual or automatic quality-of-service (QoS) controls that prioritize traffic on your internal network to ensure lag-sensitive traffic (gaming, voice, or video) is given higher priority than data associated with file transers. This is especially the case if you have devices connected to both routers, both of which have different QoS controls.
This screenshot shows my router’s QoS (Quality of Service) controls, which I’ve configured to assign VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) top priority.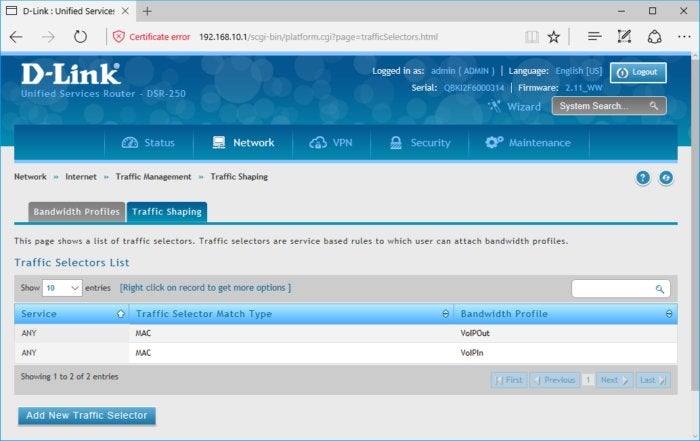
How to detect a double NAT situation
I already mentioned how to quickly tell if an ISP’s gateway has NAT and routing capabilities, but you might also want to see if double NAT is actually happening before spending time on the issue. Sometimes gateways will detect double NAT and automatically fix the issue for you. Or sometimes, if the ISP installers are knowledgeable, they might fix it when they come out to install the gateway and see that you have your own router.
For the two ways I’ll show you how to detect a double NAT situation, you’ll need to check your IP addresses and know if they’re private or public. This is easy: private addresses are usually in the 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 range, the 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 range, or the 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 range. Addresses outside of these ranges would be public (internet) addresses.
One quick way that usually shows if double NAT exists is a traceroute, which allows you to ping a server or device on the internet and see the path it takes between routers and servers. Open a Command Prompt (on a Windows PC that’s connected to the internet, click on the Start menu, type “cmd,” and hit Enter) and type “tracert 8.8.8.8“ to see the traceroute to Google’s DNS server. If you see two private IP addresses listed in the first two hops then you have double NAT. If you see only one private address and the second hop shows a public address, then you’re all good.
Here’s a traceroute showing double NAT, as evidenced by the private IP addresses in the first two hops.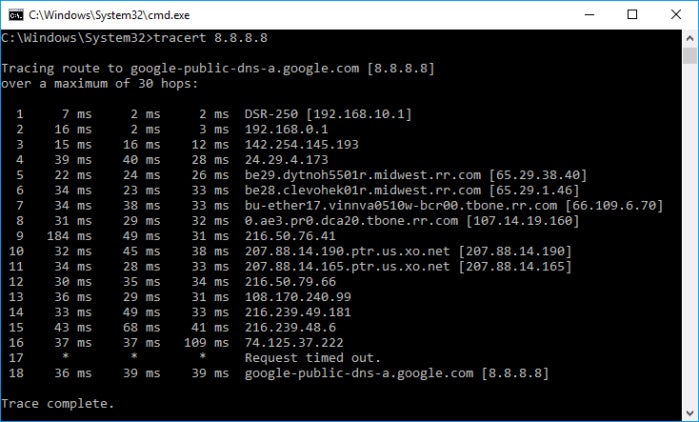
Another way to check for double NAT is to connect to your router’s web-based GUI and see if the WAN (internet) IP address is private or public. It should be a public address. If it’s a private address then you have double NAT.
More evidence of a double NAT situation: My router’s WAN IP address is private, not public.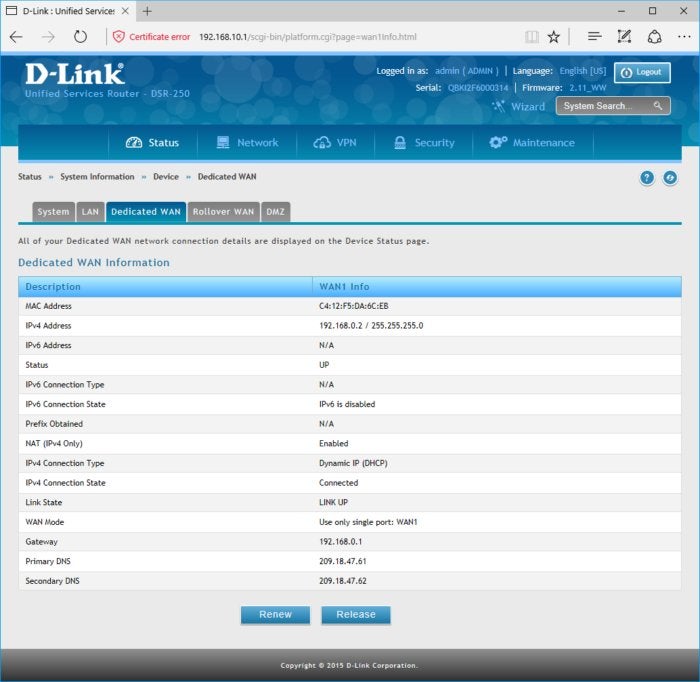
How you can fix it
If you’ve confirmed you have double NAT, there are ways to fix it. One simple way is to unplug any additional router and only use your ISP’s gateway. If you’re a power-user and you can’t part with your fancier router, then this option probably isn’t for you.
If you’d like to keep your router, see if you can put the ISP’s gateway into bridge or passthrough mode. This will disable the gateway’s NAT, firewall, and DHCP functions and reduce it to a simple internet modem. Many gateways offer these settings, but not all. Log into the web-based GUI of the gateway and check for a NAT, passthrough, or bridge mode setting, but keep in mind sometimes it’s hidden. If you don’t see it, search the internet for details on your particular model, or call your ISP’s tech support.
My Arris gateway from TimeWarner (Spectrum) has its NAT options in the LAN settings, but other vendors may have it in the WAN or another area.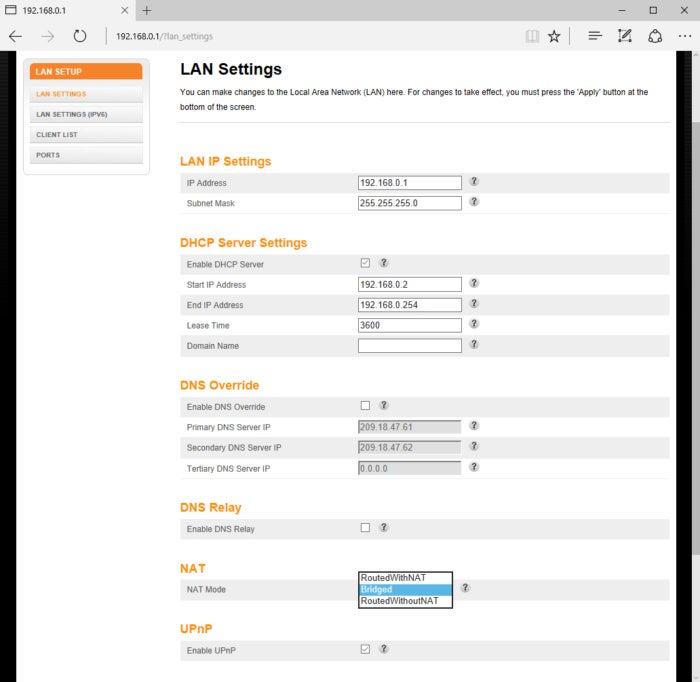
If your ISP gateway doesn’t offer any bridging functionality, consider putting your router in the DMZ (demilitarized zone) of the gateway. If the gateway has a DMZ, it will basically give the router a direct connection to the internet, bypassing the gateway’s NAT, firewall, and DHCP so that your networked devices get those values directly from your router.
To utilize the DMZ, you’d log into the web-based GUI of the gateway, find the DMZ setting, and enter the private IP address that’s assigned to your router. Furthermore, you should also see if you can establish an IP address reservation for your router, so your gateway always gives the same private IP address to your router. If the gateway doesn’t support IP address reservations, you should log into the router’s web-based GUI and manually assign it a static private IP address (the same one you configure as the DMZ host) yourself for its WAN (wide area network; i.e., the internet) connection.
My gateway has DMZ preferences in its firewall settings, as is typical for gateways.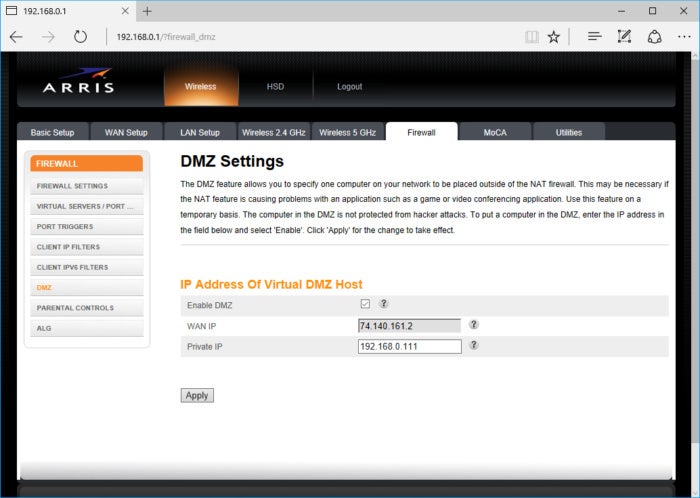
Another option for eliminating double NAT while keeping a ISP gateway and your router is to run an ethernet cable from the gateway to one of your router’s LAN ports instead of the router’s WAN (internet) port. This will basically turn your router into a switch, and any computers connecting through the router (either wired or wirelessly) will get NAT, firewall, and DHCP from the ISP’s gateway. This is a good option if you’re using a secondary router to get better Wi-Fi or because you need more ethernet ports. If, on the other hand, your desire for another router is for better port forwarding or improved QoS controls, this approach won’t help.