Editor’s note: php-fpm uses the term “master” to describe its primary process. Datadog does not use this term. Within this blog post, we will refer to this as “primary,” except for the sake of clarity in instances where we must reference a specific process name.
This post is part of a series on troubleshooting NGINX 502 Bad Gateway errors. If you’re not using PHP-FPM, check out our other article on troubleshooting NGINX 502s with Gunicorn as a backend.
PHP-FastCGI Process Manager (PHP-FPM) is a daemon for handling web server requests for PHP applications. In production, PHP-FPM is often deployed behind an NGINX web server. NGINX proxies web requests and passes them on to PHP-FPM worker processes that execute the PHP application.

NGINX will return a 502 Bad Gateway error if it can’t successfully proxy a request to PHP-FPM, or if PHP-FPM fails to respond. In this post, we’ll examine some common causes of 502 errors in the NGINX/PHP-FPM stack, and we’ll provide guidance on where you can find information that can help you resolve these errors.
Explore the metrics, logs, and traces behind NGINX 502 Bad Gateway errors using Datadog.
Some possible causes of 502s
In this section, we’ll describe how the following conditions can cause NGINX to return a 502 error:
- PHP-FPM is not running
- NGINX can’t communicate with PHP-FPM
- PHP-FPM is timing out
If NGINX is unable to communicate with PHP-FPM for any of these reasons, it will respond with a 502 error, noting this in its access log (/var/log/nginx/access.log) as shown in this example:
access.log
127.0.0.1 - - [31/Jan/2020:18:30:55 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 502 182 "-" "curl/7.58.0"NGINX’s access log doesn’t explain the cause of a 502 error, but you can consult its error log (/var/log/nginx/error.log) to learn more. For example, here is a corresponding entry in the NGINX error log that shows that the cause of the 502 error is that the socket doesn’t exist, possibly because PHP-FPM isn’t running. (In the next section, we’ll look at how to detect and correct this problem.)
error.log
2020/01/31 18:30:55 [crit] 13617#13617: *557 connect() to unix:/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock failed (2: No such file or directory) while connecting to upstream, client: 127.0.0.1, server: localhost, request: "GET / HTTP/1.1", upstream: "fastcgi://unix:/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock:", host: "localhost"PHP-FPM isn’t running
Note: This section includes a process name that uses the term “master.” Except when referring to specific processes, this article uses the term “primary” instead.
If PHP-FPM isn’t running, NGINX will return a 502 error for any request meant to reach the PHP application. If you’re seeing 502s, first check to confirm that PHP-FPM is running. For example, on a Linux host, you can use a ps command like this one to look for running PHP-FPM processes:
PHP-FPM organizes its worker processes in groups called pools. The sample output below shows that the PHP-FPM primary process is running, as are two worker processes in the default pool (named www):
root 29852 0.0 2.2 435484 22396 ? Ssl 16:27 0:00 php-fpm: master process (/etc/php/7.2/fpm/php-fpm.conf)
www-data 29873 0.0 1.5 438112 15220 ? Sl 16:27 0:00 php-fpm: pool www
www-data 29874 0.0 1.6 438112 16976 ? Sl 16:27 0:00 php-fpm: pool wwwIf the output of the ps command doesn’t show any PHP-FPM primary or pool processes, you’ll need to get PHP-FPM running to resolve the 502 errors.
In a production environment, you should consider using systemd to run PHP-FPM as a service. This can make your PHP application more reliable and scalable, since the PHP-FPM daemon will automatically start serving your PHP app when your server starts or when a new instance launches. PHP-FPM is included in the PHP source code, so you can add PHP-FPM as a systemd service when you configure PHP.
Once your PHP-FPM project is configured as a service, you can use the following command to ensure that it starts automatically when your server starts up:
sudo systemctl enable php7.2-fpm.serviceThen you can use the list-unit-files command to see information about your service:
sudo systemctl list-unit-files | grep -E 'php[^fpm]*fpm'On a PHP 7.2 server that has PHP-FPM installed (even if it is not running), the output of this command will be:
php7.2-fpm.service enabledTo see information about your PHP-FPM service, use this command:
sudo systemctl is-active php7.2-fpm.serviceThis command should return an output of active. If it doesn’t, you can start the service with:
sudo service php7.2-fpm startNGINX can’t access the socket
When PHP-FPM starts, it creates one or more TCP or Unix sockets to communicate with the NGINX web server. PHP-FPM’s worker processes use these sockets to listen for requests from NGINX.
To determine whether a 502 error was caused by a socket misconfiguration, confirm that PHP-FPM and NGINX are configured to use the same socket. PHP-FPM uses a separate configuration file for each worker process pool; these files are located at /etc/php/7.2/fpm/pool.d/. Each pool’s socket is defined in a listen directive in the pool’s configuration file. For example, the listen directive below configures a pool named mypool to use a Unix socket located at /run/php/mypool.sock:
mypool.conf
listen = /run/php/mypool.sockIf NGINX can’t access the socket for a particular pool, you can determine which worker pool is involved in the issue by checking which socket is named in the NGINX error log entry. For example, if PHP-FPM had failed to start the mypool worker pool, NGINX would return a 502 and its error log entry would include:
error.log
connect() to unix:/run/php/mypool.sock failed (2: No such file or directory)Check your nginx.conf file to ensure that the relevant location block specifies the same socket. The example below contains an include directive that loads some general configuration information for PHP-FPM, and a fastcgi_pass directive that specifies the same Unix socket named in the mypool.conf file, above.
nginx.conf
location / {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/mypool.sock;
}Unix sockets are subject to Unix file system permissions. The PHP-FPM pool’s configuration file specifies the mode and ownership of the socket, as shown here:
www.conf
listen.owner = www-data
listen.group = www-data
listen.mode = 0660Make sure these permissions allow the user and group running NGINX to access the socket. If the permissions on the socket are incorrect, NGINX will log a 502 error in its access log, and a message like the one shown below in its error log:
error.log
2020/02/20 17:12:03 [crit] 3059#3059: *4 connect() to unix:/run/php/mypool.sock failed (13: Permission denied) while connecting to upstream, client: 127.0.0.1, server: localhost, request: "GET / HTTP/1.1", upstream: "fastcgi://unix:/run/php/mypool.sock:", host: "localhost"Note that the default values of listen.owner and listen.group match the default owner and group running NGINX, and listen.mode defaults to 0660. Using these defaults, NGINX should be able to access the socket.
If PHP-FPM is listening on a TCP socket, the pool conifguration’s listen directive will have a value in the form of address:port, as shown below:
Just as with a Unix socket, you can prevent 502 errors by confirming that the location of this socket matches the one specified in the NGINX configuration.
PHP-FPM is timing out
If your application is taking too long to respond, your users will experience a timeout error. If PHP-FPM’s timeout—which is set in the pool configuration’s request_terminate_timeout directive (and defaults to 20 seconds)—is less than NGINX’s timeout (which defaults to 60 seconds), NGINX will respond with a 502 error. The NGINX error log shown below indicates that its upstream process—which is PHP-FPM—closed the connection before sending a valid response. In other words, this is the error log we see when PHP-FPM times out:
error.log
2020/02/20 17:17:12 [error] 3059#3059: *29 recv() failed (104: Connection reset by peer) while reading response header from upstream, client: 127.0.0.1, server: localhost, request: "GET / HTTP/1.1", upstream: "fastcgi://unix:/run/php/mypool.sock:", host: "localhost"In this case, the PHP-FPM log (which by default is located at /var/log/php7.2-fpm.log) shows a correlated message which provides further information:
php7.2-fpm.log
[20-Feb-2020 17:17:12] WARNING: [pool mypool] child 2120, script '/var/www/html/index.php' (request: "GET /index.php") execution timed out (25.755070 sec), terminatingYou can raise PHP-FPM’s timeout setting by editing the pool’s configuration file, but this could cause another issue: NGINX may time out before receiving a response from PHP-FPM. The default NGINX timeout is 60 seconds; if you’ve raised your PHP-FPM timeout above 60 seconds, NGINX will return a 504 Gateway Timeout error if your PHP application hasn’t responded in time. You can prevent this by also raising your NGINX timeout. In the example below, we’ve raised the timeout value to 90 seconds by adding the fastcgi_read_timeout item to the http block of /etc/nginx/nginx.conf:
nginx.conf
http {
...
fastcgi_buffers 8 16k;
fastcgi_buffer_size 32k;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 90;
fastcgi_send_timeout 90;
fastcgi_read_timeout 90;
}Reload your NGINX configuration to apply this change:
Next, to determine why PHP-FPM timed out, you can collect logs and application performance monitoring (APM) data that can reveal causes of latency within and outside your application.
Collect and analyze your logs
To troubleshoot application errors, you can collect your logs and send them to a log management service. In addition to the NGINX logs we examined above, PHP can log errors and other events that might be valuable to you. See our PHP logging guide for more information.
When you bring your PHP and NGINX logs into a log management service, combined with logs from relevant technologies like caching servers and databases, you can analyze logs from throughout your web stack in a single platform.
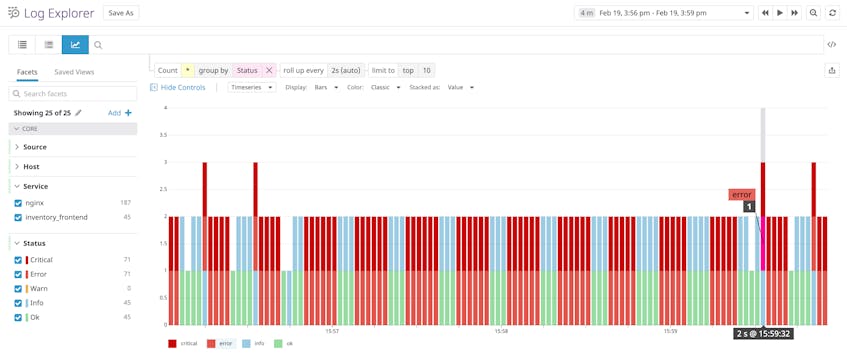
Collect APM data from your web stack
APM can help you identify bottlenecks and resolve issues, like 502 errors, which affect the performance of your app. The screenshot below shows NGINX’s APM data visualized in Datadog. This view summarizes request volume, error rates, and latency for an NGINX-based service and helps you investigate performance problems like 502 errors.
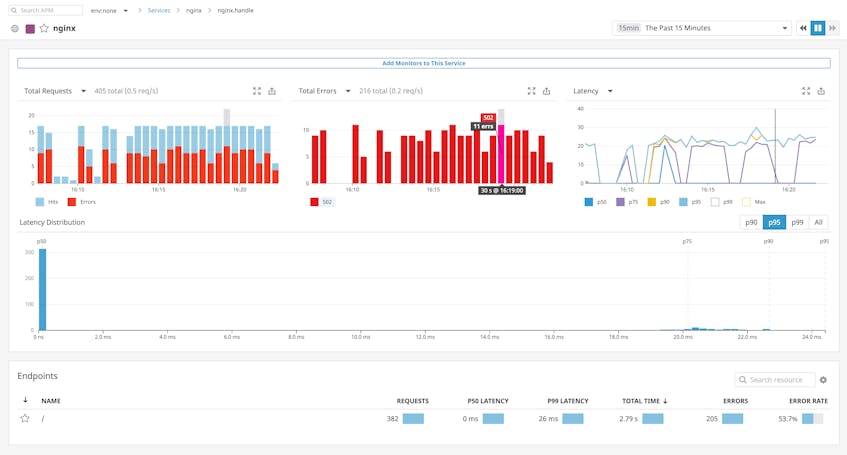
200 OK
The faster you can diagnose and resolve your application’s 502 errors, the better. Datadog allows you to analyze metrics, traces, logs, and network performance data from across your infrastructure. If you’re already a Datadog customer, you can start monitoring NGINX, PHP-FPM, and more than
600 other technologies. If you don’t yet have a Datadog account, sign up for a 14-day free trial and get started in minutes.
Configuration
- Ubuntu Server 11.10 64 bit
- Amazon AWS, Ec2, hosted on the cloud
- t1.micro instance
Before I write anything else, I’d like to state that I’ve checked both nginx 502 bad gateway and Nginx + PHP-FPM 502 Bad Gateway threads, which unfortunately haven’t helped me in this regard.
The issue appears to be rather common: a misconfiguration of nginx or php-fpm can lead to a 502 Bad Gateway error, which is something that I haven’t been able to get rid of. Note that this appears even when I go to my domain root, without specifying any particular directory.
I’m running an Amazon EC2 webserver, with port 9000 enabled, port 80 open, etc.
The question in particular is, how can I get rid of this nasty error? Or, better yet, how can I get php5-fpm to actually work.
What I Have Attempted so Far
Mostly consistent editing of configuration files, notably php-fpm.conf and nginx.conf.
i. php-fpm.conf
I’ve added the following, which hasn’t quite helped much:
;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Fpm Start ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;
;pm.start_servers = 20
;pm.min_spare_servers = 5
;pm.max_spare_servers = 35
Now, afterward I tried including my configuration files:
include=/etc/php5/fpm/*.conf
Which only screwed me even further.
Full Configuration
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; FPM Configuration ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; All relative paths in this configuration file are relative to PHP's install
; prefix (/usr). This prefix can be dynamicaly changed by using the
; '-p' argument from the command line.
; Include one or more files. If glob(3) exists, it is used to include a bunch of
; files from a glob(3) pattern. This directive can be used everywhere in the
; file.
; Relative path can also be used. They will be prefixed by:
; - the global prefix if it's been set (-p arguement)
; - /usr otherwise
;include=/etc/php5/fpm/*.conf
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Global Options ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
[global]
; Pid file
; Note: the default prefix is /var
; Default Value: none
pid = /var/run/php5-fpm.pid
; Error log file
; Note: the default prefix is /var
; Default Value: log/php-fpm.log
error_log = /var/log/php5-fpm.log
; Log level
; Possible Values: alert, error, warning, notice, debug
; Default Value: notice
log_level = notice
; If this number of child processes exit with SIGSEGV or SIGBUS within the time
; interval set by emergency_restart_interval then FPM will restart. A value
; of '0' means 'Off'.
; Default Value: 0
;emergency_restart_threshold = 0
; Interval of time used by emergency_restart_interval to determine when
; a graceful restart will be initiated. This can be useful to work around
; accidental corruptions in an accelerator's shared memory.
; Available Units: s(econds), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays)
; Default Unit: seconds
; Default Value: 0
emergency_restart_interval = 0
; Time limit for child processes to wait for a reaction on signals from master.
; Available units: s(econds), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays)
; Default Unit: seconds
; Default Value: 0
;process_control_timeout = 0
; Send FPM to background. Set to 'no' to keep FPM in foreground for debugging.
; Default Value: yes
daemonize = no
;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Fpm Start ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;
;pm.start_servers = 20
;pm.min_spare_servers = 5
;pm.max_spare_servers = 35
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Pool Definitions ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Multiple pools of child processes may be started with different listening
; ports and different management options. The name of the pool will be
; used in logs and stats. There is no limitation on the number of pools which
; FPM can handle. Your system will tell you anyway :)
; To configure the pools it is recommended to have one .conf file per
; pool in the following directory:
include=/etc/php5/fpm/pool.d/*.conf
ii. nginx.conf
In all honesty this configuration is a smattering of a few websites I’ve visited, but I can tell you that before this 502 Bad Gateway business, the server was running fine (without PHP working. Period.).
The issue primarily lies in the fact that something is terribly, terribly wrong. And now, when I try to do a service php5-fpm restart, it hangs in what I’m guessing is an infinite loop or something, which I can’t even CTRL—C out of.
Full Configuration
user www-data;
worker_processes 1;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 64;
# multi_accept on;
}
http {
##
# Basic Settings
##
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush off;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
# server_tokens off;
# server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
# server_name_in_redirect off;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
##
# Logging Settings
##
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
##
# Gzip Settings
##
gzip on;
gzip_disable "msie6";
# gzip_vary on;
# gzip_proxied any;
# gzip_comp_level 6;
# gzip_buffers 16 8k;
# gzip_http_version 1.1;
# gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/x-javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;
##
# Virtual Host Configs
##
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
server {
listen 80;
server_name ec2-xx-xx-xx-xx.compute-x.amazonaws.com;
location ~ ^(.+\.php)(.*)$ {
root /home/wayvac/public;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php5-fpm.pid;
#fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; #Un-comment this and comment "fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php-fpm/php-fpm.sock;" if you are not using php-fpm.
fastcgi_index index.php;
set $document_root2 $document_root;
if ($document_root2 ~ "^(.*\\\\).*?[\\\\|\/]\.\.\/(.*)$") { set $document_root2 $1$2; }
if ($document_root2 ~ "^(.*\\\\).*?[\\\\|\/]\.\.\/(.*)$") { set $document_root2 $1$2; }
if ($document_root2 ~ "^(.*\\\\).*?[\\\\|\/]\.\.\/(.*)$") { set $document_root2 $1$2; }
if ($document_root2 ~ "^(.*\\\\).*?[\\\\|\/]\.\.\/(.*)$") { set $document_root2 $1$2; }
if ($document_root2 ~ "^(.*\\\\).*?[\\\\|\/]\.\.\/(.*)$") { set $document_root2 $1$2; }
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(.*)$;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root2$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
fastcgi_param PATH_TRANSLATED $document_root2$fastcgi_path_info;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $document_root2;
}
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
location / {
root /home/wayvac/public;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
}
location ~* \.(?:ico|css|js|gif|jpe?g|png)$ {
# Some basic cache-control for static files to be sent to the browser
expires max;
add_header Pragma public;
add_header Cache-Control "public, must-revalidate, proxy-revalidate";
}
#include drop.conf;
#include php.conf;
}
}
502 Bad Gateway is an error website visitors see relatively rarely. However, since it can prevent the users from interacting with the website or the hosted application, website owners should make rectifying this error their top priority.
This error typically occurs when a server acting as a gateway or proxy receives an invalid response from an upstream server. Since NGINX is a popular proxy server, users often see error messages like “502 Bad Gateway” and the active NGINX version.
The NGINX 502 Bad Gateway is a common issue website visitors encounter. There are several possible causes for this error and several solutions. This post will examine the most likely reasons and how site owners and developers can resolve the error.
Let’s start with a short introduction to the error.
Table of Content
- What Does the Error Code 502 Bad Gateway in NGINX Mean?
- What is PHP-FPM & How Does It Work?
- The Top Six Possibilities Behind 502 Bad Gateway in NGINX (And How to Fix Them)
- Reason # 1: NGINX is Not Running
- Examine the NGINX Status
- Examine the NGINX Configuration
- Check the Port Bindings
- Check for Conflicting Services
- Examine the NGINX Error Logs
- Examine The System Resources
- Reason # 2: PHP-FPM Isn’t Working
- Examine the NGINX and PHP-FPM Configurations
- Check the Status of PHP-FPM
- Restart NGINX and PHP-FPM
- Examine the Socket or Address and Port Settings
- Examine PHP-FPM Error Logs
- Examine the File Permissions
- Test Configurations With a Simple PHP Script
- Reason # 3: The PHP-FPM Timeout Has Expired
- Increase the Value of the Timeout
- Restart PHP-FPM Service
- Improve Your PHP Code
- Check for Resource Constraints
- Reason # 4: NGINX Requests Denied by the Firewall
- Examine the Firewall Rules
- Temporarily Disable the Firewall
- Examine the Firewall Logs
- Allow NGINX Through the Firewall
- Test Connectivity
- Reason # 5: A Domain Name is Not Permitted
- Check the server_name Directive
- Examine DNS Resolution
- Reason # 6: Bugs In Web Applications
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What Does the Error Code 502 Bad Gateway in NGINX Mean?
502 Bad Gateway indicates that the server you are trying to reach has encountered an error while communicating with another server. This occurs when one server serves as a proxy to receive data from other servers in the setup. The 502 error occurs when a server returns an error when attempting to connect to another server.
The exciting aspect of this discussion is the several ways to indicate that a 502 error has occurred. Here’re a few ways you’ll find this error being mentioned on various websites:
- 502 Bad Gateway NGINX
- HTTP 502
- HTTP Error 502 – Bad Gateway
- 502 Service Temporarily Overloaded
- Temporary Error (502)
- 502 Bad Gateway
- 502 Proxy Error
- Error 502
As with the 404 Not Found error, developers can customize the appearance of the 502 error page to match the current website design.
Before going into the probable reasons for the 502 Bad Gateway error in NGINX, let’s discuss PHP-FPM and its role in NGINX performance.
What is PHP-FPM & How Does It Work?
PHP applications deployed on a server use PHP-FPM (PHP-FastCGI Process Manager) as a tool for handling web requests. When combined with NGINX, PHP-FPM can make websites run faster and use fewer resources for responding to requests.
If you use PHP-FPM, PHP works as a separate service, and the web requests are handled through a TCP/IP port. NGINX only handles HTTP requests in this configuration, while PHP-FPM reads PHP code. This arrangement ensures a faster response by distributing the workload over two services.
Now that you have a good idea about the 502 Bad Gateway error in NGINX, let’s discuss why this error occurs.
The Top Six Possibilities Behind 502 Bad Gateway in NGINX (And How to Fix Them)
Here’re the six reasons users might encounter the 502 Bad Gateway error.
Reason # 1: NGINX is Not Running
If you receive a “502 Bad Gateway” error, first, you should check whether NGINX is up and running. Here’s how you can debug this problem:
Examine the NGINX Status
Start by confirming that NGINX is up and operating. For this, launch the terminal and enter the following command:
$ sudo service nginx status or systemctl status nginx
As you can see, this command will display the NGINX web server’s current status. If it isn’t running, you’ll see a message saying that NGINX isn’t running.
If that’s the case, you can try restarting it with the following command that restarts NGINX and attempts to bind it to the designated ports:
$ sudo service nginx restart
Examine the NGINX Configuration
An error in the NGINX configuration file can likely stop it from functioning correctly. To verify this, use the following command to verify the configuration syntax:
$ sudo nginx -t
This command checks the NGINX configuration file for syntax issues. If there are any errors, it will specify the exact problem.
You can rectify the mistakes by editing the configuration file (/etc/nginx/nginx.conf or /etc/nginx/conf.d/*). If the syntax is okay, you will see a similar message:
Check the Port Bindings
If NGINX is working correctly, you should next check that NGINX is bound to the adequately designated ports. NGINX listens on port 80 for HTTP and port 443 for HTTPS by default.
Open the NGINX configuration file (/etc/nginx/nginx.conf or /etc/nginx/conf.d/*) and look for the listen directives within the server blocks. Here you should check that the ports are correctly specified.
Check for Conflicting Services
If NGINX does not start because of port conflicts, the main reason is that another service may be already mapped to the same port. You can use the following command to identify any conflicting services:
$ sudo netstat -tuln | grep LISTEN
This command displays all the services currently listening on specific ports. Look for any services that use ports 80 or 443. If you discover any conflicts, you must stop or adjust those services to free up ports for NGINX.
Examine the NGINX Error Logs
When investigating the 502 error, the NGINX logs can help determine what went wrong with the reverse proxy server. Typically, error logs are stored at /var/log/nginx/error.log. We recommend examining these log files for any error messages that may point to the source of the problem.
Examine The System Resources
Verifying that your server has sufficient resources (CPU, RAM, and disc space) to support NGINX operations is always a good idea. Insufficient resources can prevent NGINX from booting up or cause it to crash. We recommend using system monitoring tools or command-line utilities such as htop to examine resource consumption.
Reason # 2: PHP-FPM Isn’t Working
If you’re getting a 502 Bad Gateway error because NGINX and PHP-FPM aren’t “cooperating”, you can troubleshoot the problem by doing the following:
Examine the NGINX and PHP-FPM Configurations
Start by checking that NGINX and PHP-FPM are both correctly configured and functioning.
Open the NGINX configuration file (/etc/nginx/nginx.conf or /etc/nginx/conf.d/*) and verify that the location block for PHP scripts is correctly set up. It should have directives like fastcgi_pass, which points to the PHP-FPM socket or address and port, and fastcgi_param parameters.
Similarly, review the PHP-FPM configuration file (/etc/php-fpm.conf or /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf) to ensure all settings are correctly set up.
Check the Status of PHP-FPM
Check to see if PHP-FPM is currently operational.
For this, launch the terminal or command prompt and type the following command:
$ sudo service php-fpm status
This command displays PHP-FPM’s current status. If it isn’t up, you’ll receive a message that PHP-FPM isn’t running.
Restart NGINX and PHP-FPM
If NGINX and PHP-FPM are running but not communicating correctly, you can try restarting both services.
To restart them, use the following commands:
$ sudo service nginx restart
$ sudo service php-fpm restart
Examine the Socket or Address and Port Settings
Check that the fastcgi_pass directive in the NGINX configuration file is correctly pointing to the PHP-FPM socket or IP and port.
Here’s what a properly formatted directive looks like:
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
If you use a TCP address and port, it should appear like this:
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
Check that the socket or address and port correspond to the PHP-FPM settings. After modifying the configuration, remember to restart both NGINX and PHP-FPM.
Examine PHP-FPM Error Logs
PHP-FPM logs provide essential insight into any PHP script execution issues. Typically, the log file is located in /var/log/php-fpm.log.
Examine the log file for error messages that may illuminate the problem. While you’re at it, we suggest checking NGINX’s error log (/var/log/nginx/error.log) for any relevant error messages.
Examine the File Permissions
An overlooked reason behind PHP-FPM and NGINX-related issues is misconfigured file permissions.
You should confirm that the PHP files and directories have the necessary permissions and ownership so that NGINX can access them and PHP-FPM can execute them.
Typically, PHP files should be readable by the NGINX user, and folders should have appropriate execution rights. Use the chown and chmod commands to change ownership and permissions, if necessary.
Test Configurations With a Simple PHP Script
Write a simple PHP script (we highly recommend printing info.php) to test NGINX and PHP-FPM operations. For this, we suggest the following:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Put this line in a file named info.php and save the file in the web root directory (for example, /var/www/html). Now, visit it using your browser (for example, http://your-domain.com/info.php).
If you can see the PHP information page, the NGINX, and PHP-FPM are working successfully together. If not, it could point to a problem with PHP-FPM settings or communication between NGINX and PHP-FPM.
Reason # 3: The PHP-FPM Timeout Has Expired
The error “The PHP-FPM timeout has expired” usually means that a PHP script executed by PHP-FPM took longer to complete than the timeout value mentioned in the config file.
When PHP-FPM receives a request to execute a PHP script, a worker process is launched to fulfill the request. PHP-FPM terminates the process and returns the timeout error if the script execution exceeds the timeout setting defined in the PHP-FPM configuration.
You can resolve this problem by taking the following steps:
Increase the Value of the Timeout
In the PHP-FPM configuration file (typically /etc/php-fpm.conf or /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf), change the request_terminate_timeout setting directive.
We suggest increasing the value of request_terminate_timeout to allow PHP scripts to run for extended periods.
For instance, in the following example, the timeout is set to 300 seconds (5 minutes):
request_terminate_timeout = 300s
We suggest adjusting the value to meet the needs of your application.
Restart PHP-FPM Service
If you change the PHP-FPM configuration file, you must restart the PHP-FPM service to implement the modifications.
The command may differ depending on your operating system and how PHP-FPM is installed. Here is an example of the restart commands:
$ sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
Improve Your PHP Code
If your PHP script takes too long to execute, you may need to optimize your code to improve its execution time frame. You should focus on finding and optimizing bottlenecks like database requests, intensive computations, or inefficient algorithms.
Check for Resource Constraints
Executing PHP scripts requires server resources. Time-out errors might also occur when a script gets stuck while waiting for the resources to continue execution.
As such, you should ensure that your server has sufficient resources to handle PHP script execution.
Reason # 4: NGINX Requests Denied by the Firewall
If you receive a “502 Bad Gateway” error in NGINX and think that the firewall is blocking requests, try the following ideas to troubleshoot the problem:
Examine the Firewall Rules
Start by checking the firewall rules to ensure it is not blocking inbound requests to NGINX.
Depending on your firewall solution ( iptables, UFW, or Firewalld), the rule syntax about port 80 for HTTP or port 443 for HTTPS might differ. You should check and allow inbound traffic to NGINX, and modify the rules accordingly.
Temporarily Disable the Firewall
As a first step in troubleshooting, temporarily disable the firewall and see if the 502 Bad Gateway error persists. This helps you narrow down the firewall as the source of the problem.
However, you should re-enable the firewall immediately to maintain security.
Examine the Firewall Logs
Check the firewall logs to see whether entries are linked to disallowed requests. In addition, firewall logs can give information about blocked traffic and the reasons for denials. The location of the firewall logs differs depending on the firewall solution. We suggest checking /var/log/iptables.log, /var/log/ufw.log, and /var/log/firewalld.log for the logs.
Allow NGINX Through the Firewall
We recommend allowing NGINX through the firewall to eliminate firewall-related causes of the NGINX 502 Bad Gateway error.
Start by configuring the necessary rules to allow NGINX through the firewall. Make changes to the firewall rules to allow inbound connections on the NGINX ports 80 and 443. The particular instructions or configuration procedures vary depending on the firewall solution.
Here are a couple of examples:
iptables
Use the following commands to whitelist ports 80 and 443 in iptables:
$ sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
$ sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT
UFW (Simplified Firewall)
Use the following commands to whitelist ports 80 and 443 in UFW:
$ sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
$ sudo ufw allow 443/tcp
Firewalld
Use the following commands to whitelist ports 80 and 443 in Firewalld:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=https --permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Test Connectivity
After modifying the firewall rules and validating the NGINX configuration, see if you can connect to NGINX.
Use programs such as Telnet or curl to verify connectivity locally and from remote systems. For example, to test NGINX’s response, use the following command:
# curl -I http://localhost/
If the connection is successful and the expected response is received, the firewall rules allow traffic to the NGINX reverse proxy server.
Reason # 5: A Domain Name is Not Permitted
If you get a “502 Bad Gateway” error message in NGINX with the message “A domain name is not permitted,” it usually means that NGINX received a request for a domain name not configured or allowed in the configuration file.
You can troubleshoot this problem by doing the following:
Check the server_name Directive
Start by checking the server_name directive to see if the domain name causing the problem is included in the directive block. The path should be: /etc/nginx/sites-available/domainname.conf
For example,
server_name example.com www.example.com;
If the domain name is missing or incorrect, add or change the server_name directive.
Examine DNS Resolution
Check that the domain name correctly resolves to the NGINX server’s IP address. You can do DNS lookups with tools like nslookup or dig to ensure the domain name resolves to the correct IP address. Here’s a sample lookup command:
# nslookup example.com
If the domain name does not resolve correctly, you may need to adjust your DNS configuration or contact your DNS provider.
Reason # 6: Bugs In Web Applications
Errors at the application level can (rarely) cause the 502 Bad Gateway error.
If your web server logs contain loading errors similar to the following, the application code may be incompatible with the server version and configuration.
[notice] child pid xxxxx exit signal Segmentation fault (11)
You must examine your application’s software needs and re-configure the services to meet the requirements.
Conclusion
The 502 Bad Gateway in NGINX error usually happens when NGINX runs as a reverse proxy and can’t connect to services on either side of the server setup. This error could occur because of a server crash, a network error, a problem with the NGINX setup, or domain-related issues.
Here at Redswitches, we offer The perfect platform for setting up NGINX as a Reverse Proxy server.
Optimizing a reverse proxy can make it run faster and handle calls more efficiently. Remember that the right configurations and optimizations may differ based on how you use the system and what you expect from the NGINX server. Redswitches is a one-stop solution for all of your website hosting needs.
FAQs
Q. What does the NGINX 502 Bad Gateway error indicate?
The 502 Bad Gateway error means an upstream server sent no or malformed response to the NGINX server in a reverse proxy server role. It usually happens when NGINX can’t connect to the backend server or when the backend server gives an invalid or unexpected response.
Q. Can too much traffic cause a 502 Bad Gateway?
Too much traffic can overwhelm the backend servers or the proxy infrastructure, causing the 502 Bad Gateway problem. In these situations, you may need to optimize your server resources, change timeouts, or use load balancers to handle the extra traffic.
Q. Can DNS problems result in a 502 Bad Gateway error?
Yes, a “502 Bad Gateway” error can be caused by trouble with DNS resolution. Ensure that the upstream server’s IP address can be found by resolving the domain name used in the NGINX setup.
Q. Can a PHP-FPM misconfiguration cause a 502 Bad Gateway error in NGINX?
A 502 Bad Gateway problem in NGINX can happen if PHP-FPM is set up incorrectly. To avoid these errors, ensure that NGINX is set up correctly to talk to PHP-FPM using the correct socket, address, and port. Check the PHP-FPM configuration file (php-fpm.conf or www.conf) to ensure it conforms to the proper NGINX configuration settings.
Nginx is one of the fast performing web servers on the internet. Nginx and php-fpm are the most used combinations on the internet to server PHP websites. Sometimes we came across a very bad Nginx 502 Bad Gateway error generated by Nginx server and it is not very easy to identify the problem and fix. Here are some quick solutions to fix Nginx 502 Bad Gateway error on a web-server.
How Nginx 502 Bad Gateway Error happens and what is its connection with php-fpm
Common 502 errors include the following messages from Nginx server
- “502 Bad Gateway”
- “502 Bad Gateway NGINX”
- “502 Proxy Error”
- “502 Service Temporarily Overloaded”
- “Error 502”
- “HTTP Error 502 – Bad Gateway”
- “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway”
These errors point to the same situation of Nginx server and the error came across below situations
- Nginx server running with php-fpm service
- Nginx is running as a reverse proxy to Apache server
- Nginx running as a gateway to other services like Python, Ruby, etc.
- Bad configuration of cache or timeout.
Now the error says there is a “BAD GATEWAY”. That means Nginx server is trying to communicate to another service through a gateway and it is not getting any answer from that gateway. This is Nginx 502 Bad Gateway error situation.
So Nginx and another service (Apache, php-fpm, other services) running. Both are communicating through a gateway and Nginx is not getting any answer from the gateway. To solve 502 Bad Gateway Error the other service running with Nginx must answer through the gateway.
Usually, this happens due to a misconfiguration in the configuration files of the server. Or the other service is not running properly with Nginx. So to solve this problem a two-step check is required.
- Step 1: Check the other server status, whether it is running perfectly, is it giving the desired output?
- Step 2: Is the configuration correct? Is the second service configured to answer the gateway perfectly?
Nginx 502 Bad Gateway Error with PHP-FPM
The problem occurs due to the following conditions
- PHP-FPM won’t get started
- PHP-FPM not running
- NGINX can’t communicate with PHP-FPM server
- NGINX is timing out
- PHP-FPM is timing out with requests
Check whether php-fpm is running or not
service php-fpm status
or
systemctl status php-fpm.service
will tell you about the current situation of php-fpm server
Just restart the php-fpm server to solve this problem
service php-fpm restart
or
systemctl restart php-fpm.service
for php5 the name of service may be php5-fpm, for PHP 7 it may be php7.0-fpm or php7.1-fpm or php7.2-fpm check accordingly.
Php-fpm is not communicating with Nginx and causing a 502 Bad Gateway Error
This is caused due to the misconfiguration of the php-fpm server or the misconfiguration of Nginx server.
Check the following configuration files in the worker pool configuration (the file is in /etc/php/fpm/pool.d/www.conf, this may vary with installation) and verify these lines ( www-data is the owner of the web server process, that is nginx)
user = www-data
group = www-data
listen = /var/run/php7-fpm.sock
listen.owner = www-data
listen.group = www-datathen restart the php-fpm service.
If the Nginx server and php-fpm are running and still getting a 502 Bad Gateway error then it is the problem with communicating the gateway. The problem is happening due to the misconfiguration in the file /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default, by default or the file name in the name of the website called /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/mywebsite.com.conf
Look at the segment where the fastcgi_pass configuration. It must be the same as the listen in the above configuration
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php7-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_nam$
include fastcgi_params;
}See
listen = /var/run/php7-fpm.sock
and
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php7-fpm.sock
must be the same.
Then restart both Nginx and php-fpm servers. Now check the website whether it is serving properly.
502 Bad Gateway Error due to Nginx is timing out
if php-fpm is running and serving the requests properly then there will be a chance of Nginx is timing out. That is php-fpm do not respond to NGINX in a timely manner will cause a 502 because NGINX couldn’t wait any longer for a response from php-fpm.
In this case, increasing the maximum execution time of the application and NGINX’s timeout window would be the best solution.
To get this we need two changes:
First, increase the maximum execution time of the php-fpm server. To do this open PHP-FPM’s configuration file
sudo nano /etc/php7/fpm/php.ini
find the following line and increase the number to a higher value. Usually 60 or 120.
max_execution_time = 30
The value depends upon the expected execution time of the application running in the php-fpm server. Add some extra buffer time to get rid of the situation again.
Exceptionally large execution time will affect the server performance and it may lead to a dead server process in the memory.
Second, edit the NGINX config
sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
add the following within the HTTP block to increase timeout windows, buffers, and buffer sizes:
http {
...
fastcgi_buffers 8 16k;
fastcgi_buffer_size 32k;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
}
Save the changes to the file and exit. Now restart Nginx and php-fpm
service php-fpm restart
or
systemctl restart php-fpm.service and
service nginx restart
systemctl restart nginx.service
502 Bad Gateway Error due to PHP-FPM is timing out
if the php-fpm server is timing out upon execution of an exceptionally long PHP script or the script is blocked by a large MySQL query process then these solutions may not work. In that situation, you could temporarily extend PHP’s execution time limit by invoking the set_time_limit() function from within the PHP application, but if you are continuously reaching into the execution timeout limit then as a long-term solution like profiling or increasing PHP-FPM’s timeout may be more appropriate to get rid of a 502 error more safely. These things must be done after an extensive research of the execution time of the corresponding PHP function or MySQL query. Take a look at the memory and system load during the execution is a must for a smooth operation of this server.
Nginx 502 Bad Gateway Error when Nginx as Proxy for Apache
In this situation, the gateway service is Apache and the Nginx is a proxy for Apache. If apache server dies or it’s not well configured, it can cause this 502 Bad Gateway error. How to fix the apache error? Most of the times, restarting apache web server will get rid of this, but you must check the log files to know why exactly this was caused.
Nginx with other services/apps and 502 Bad Gateway Error
In this situation, the app is gone not responding. Try restarting the other service behind Nginx server and check the logs created by the application to find the exact reason why a 502 Error happened.
Check the status codes HTTP Status Codes on W3C for more details.
"My WordPress site is getting lot of bad gateways when trying to edit the back end. Please fix."
Recently, we were contacted by a customer who was getting PHP 502 bad gateway error when trying to update his website.
In our role as Technical Support Services for web hosting companies, configuring and managing the web servers for best performance, is a major task we do.
Resolving web server errors forms a part of this service. Today, we’ll see how we fix 502 gateway errors in our customers’ servers.
What is PHP 502 bad gateway error?
A gateway in a server denotes a connection point between two services in it. Gateway errors happen when front-end web server does not get a response from back-end web server.
502 gateway error usually happens in these scenarios: Nginx or Apache is front-end web server & Apache, PHP-FPM or other services is in back-end.
When the front-end server is unable to establish a proper connection to the back-end server, the websites served by these web server starts showing PHP 502 bad gateway errors.
The easiest way to resolve this error is to restart the services. But that is only a band-aid fix and you will soon find the same error recurring in your sites.
In the servers that we manage, we examine the service related logs and website logs to figure out what exactly is causing this error, and then proceed to fix it.
PHP 502 bad gateway error – Major causes
In our experience dealing with gateway errors, we’ve come across a number of causes that turn out to be the culprits behind the error.
1. Service errors
The first step we do is to verify the status of the back-end service. If the service is not running or not giving the desired results, gateway errors pop up.
That back-end service can be Apache, PHP-FPM or other services such as Perl, Python, etc. 502 errors also occur when the service is overloaded or keeps crashing.
2. Configuration issues
Most often, even if the back-end service is in running status, it may not be configured adequately to serve the front-end web server purpose.
Certain websites are very demanding and with huge traffic. But the website specific service configuration may not be adequate to handle this demand.
If the configuration is not proper, services such as PHP-FPM or Nginx can time out handling the web server requests. This leads to PHP 502 bad gateway errors.
3. Mod-security restrictions
Mod-security is a web application firewall (WAF) configured to protect websites from attacks. This WAF is configured based on rules that filter incoming traffic.
Some of these rules can create unwanted complications and disrupt the service functioning. We have noticed 502 gateway errors in websites due to some messy Mod-security rules.
4. Cloudflare settings
Cloudflare is a CDN service that offers DDOS protection to websites. But for sites with too many redirects, this causes 502 errors at times, if not configured correctly.
5. Port or permission issues
In a gateway setup, there would be two services connecting to each other. These services would be running in separate ports.
For instance, in a server where reverse proxy is configured, Nginx (front-end server) would be listening on port 80 and Apache (back-end server) would be on port 8080.
These ports can be further changed for security reasons. If the ports are not allowed for connections in the server firewall, the connectivity can fail and lead to gateway errors.
Services such as PHP-FPM can also be configured to bind to socket files in the server. If the ownership, permissions or path to the socket file in the configuration file is improper, errors can occur.
6. Software bugs
In cases where custom software or some third party applications are configured as back-end services, any bugs in these software can lead to 502 errors.
7. High server load
Server load can spike when the website traffic is high or when a DOS attack occurs to the server. Peak traffic or malware files in the server can contribute to this high server load.
Certain 3rd party applications or not optimised website code can hog the server resources such as CPU and memory, and cause high load. This can lead to timeout issues and website errors.
Solutions for PHP 502 bad gateway error
Finding the root cause of the 502 error and resolving it, is the key to prevent intermittent website down times. The solution for the error varies based on the issue noted in the logs.
- In cases where the underlying service itself is not running, our primary focus is to figure out the problem and fix the service. This is done with the help of service or application or website logs.
- If the service is working fine, but logs show timeout errors, then we increase the execution time, buffer size and timeout settings of the service or application. But this value should not be increased blindly, as it can hog the server resources.
- The configuration file for the service is examined and settings such as socket path, port, user and group etc. are confirmed to be correct. Reviewing the website specific settings is also vital to pinpoint the issue.
- The port connectivity, firewall rule or related socket file is checked and proper access rights and permissions are granted for its functioning.
- Problem aspects such as APC cache, Cloudflare settings, redirect rules, mod-security configuration, etc. are reviewed, and issues, if any, are sorted out.
- To prevent a single process from hogging the entire server memory, we set memory limits of processes and services and tweak them to use the maximum allotted memory for that service.
- At times, a problematic web code or a query can tie up the resources, take a lot of time to complete execution, and cause errors. We identify such problem-makers and take actions to fix them.
- We review the number of processes configured for services such as PHP-FPM and Nginx or Apache. By tweaking these process count to the ideal values supported by server resources, we ensure that service errors are fixed.
Conclusion
Today we’ve discussed how our Support Engineers fix PHP 502 bad gateway in the servers we manage, and ensure error-free websites for our customers.
In our customers’ servers, monitoring the server resources periodically and conducting periodic server audits and tweaks enable us to prevent such bad gateway errors to a great extent.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
SEE SERVER ADMIN PLANS
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;


