Пользователи интернета и владельцы сайтов периодически сталкиваются с различными ошибками на веб-страницах. Одной из самых распространенных ошибок является error 500 (ошибка 500). Поговорим в нашей статье о том, что это за ошибка и как ее исправить.
Где и когда можно встретить ошибку 500
Вы можете увидеть ошибку на любом веб-ресурсе, браузере и устройстве. Она не связана с отсутствием интернет-соединения, устаревшей версией операционной системы или браузера. Кроме того, эта ошибка не указывает на то, что сайта не существует или он больше не работает.
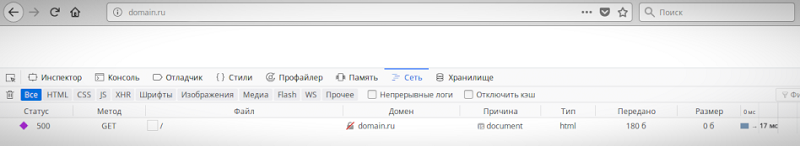
Ошибка 500 говорит о том, что сервер не может обработать запрос к сайту, на странице которого вы находитесь. При этом браузер не может точно сообщить, что именно пошло не так.
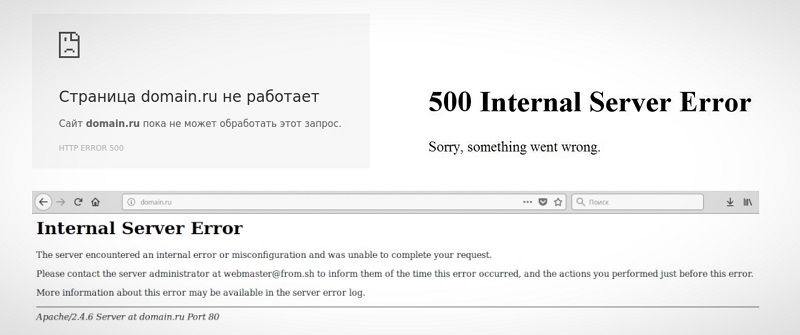
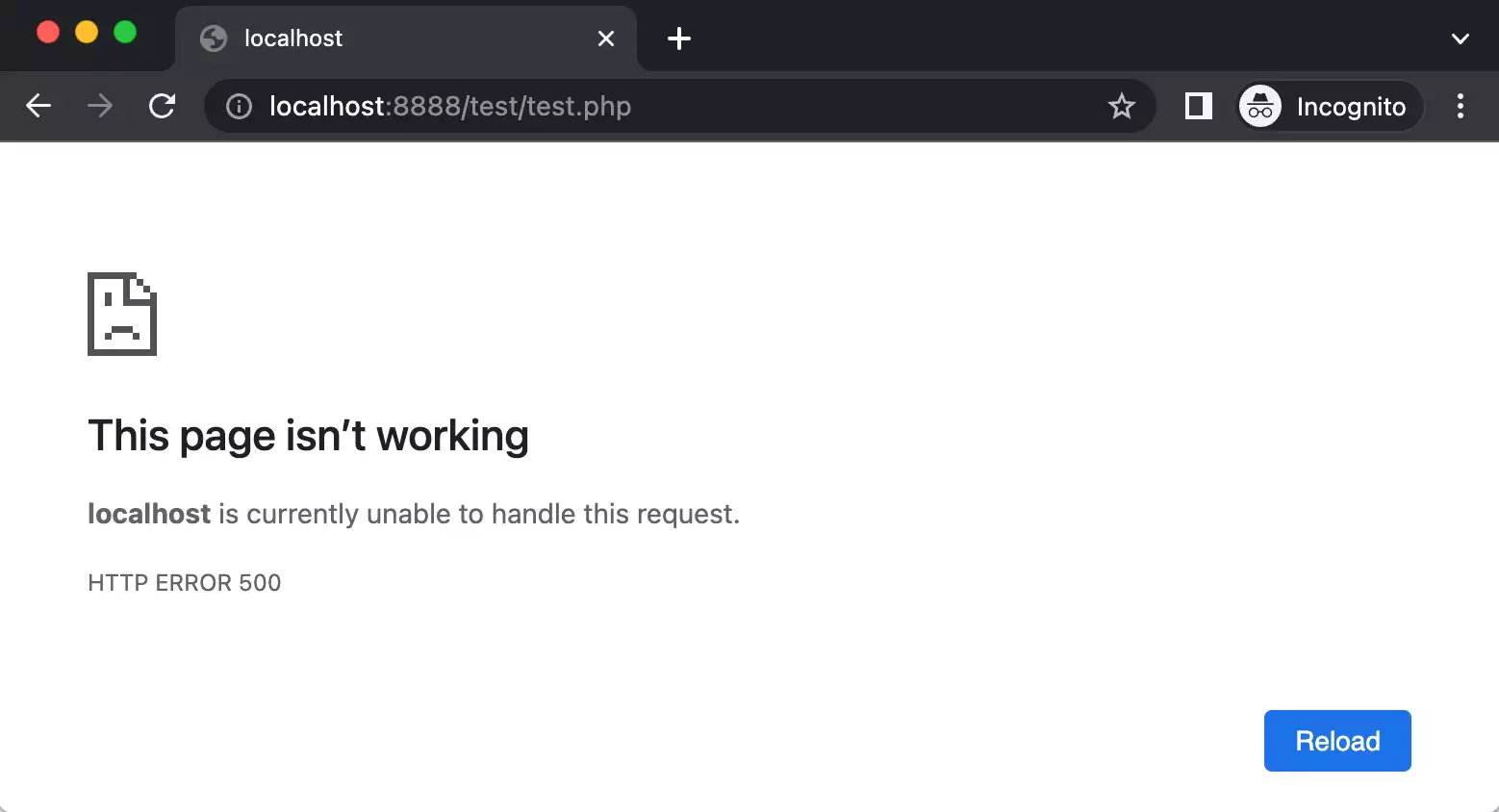
Отображаться ошибка может по-разному. Вот пример:
Если вы решили купить что-то в любимом интернет-магазине, но увидели на сайте ошибку 500, не стоит сильно огорчаться – она лишь сообщает о том, что вам нужно подождать, пока она будет исправлена.
Если ошибка появилась на вашем сайте, то нужно скорее ее исправлять. Далее я расскажу, как это можно сделать.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Как ошибка 500 влияет на SEO-продвижение
Наличие ошибки 500 напрямую влияет на продвижение сайта, ведь когда страница недоступна, это говорит о неисправностях на сайте. А если на веб-ресурсе есть что-то неладное, то это сразу звоночек для поисковых роботов. Когда они сканируют страницу и видят, что она недоступна, это негативно сказывается на всем сайте. Однако здесь важно понимать, что свое конечное решение роботы выставляют не сразу. После первого неудачного сканирования они повторно посещают страницу и проверяют, исчезла ли проблема.
Если вы исправите ошибку 500 в течение суток, то никаких проблем с SEO-продвижением случиться не должно. В противном случае либо сайт может снизиться в позициях, либо проблемные страницы исчезнут из результатов поиска. Как правило, происходит и первое, и второе.
Таким образом, чтобы минимизировать негативное влияние ошибки 500 на SEO-продвижение, необходимо следить за состоянием сервера и немедленно исправлять проблемы. Регулярный мониторинг поможет сохранить сайт доступным и улучшить его производительность и позиции в результатах поиска.
Проверить доступность страниц в поисковых системах вы можете с помощью инструментов Google Search Console и Яндекс Вебмастер.
Причины возникновения ошибки
Итак, ошибка 500 возникает, когда серверу не удается обработать запрос к сайту. Из-за этого пользователи не могут попасть на сайт, а поисковые системы полноценно с ним работать. Очевидно, что ошибка нуждается в исправлении. В первую очередь необходимо найти проблему.
Основной причиной ошибки 500 может быть:
- Неверный синтаксис файла .htaccess. htaccess – это файл, в котором можно задавать настройки для работы с веб-сервером Apache и вносить изменения в работу сайта (управлять различными перенаправлениями, правами доступа к файлам, опциями PHP, задавать собственные страницы ошибок и т.д.).
Узнать больше о файле .htaccess можно в статье «Создание и настройка .htaccess». - Ошибки в скриптах сайта, то есть сценариях, созданных для автоматического выполнения задач или для расширения функционала сайта.
- Нехватка оперативной памяти при выполнении скрипта.
- Ошибки в коде CMS, системы управления содержимым сайта. В 80% случаев виноваты конфликтующие плагины.
Год хостинга в подарок при заказе лицензии 1С-Битрикс
Выбирайте надежную CMS с регулярными обновлениями системы и профессиональной поддержкой.
Заказать
Как получить больше данных о причине ошибки
Что означает ошибка 500, мы теперь знаем. Когда она перестала быть таким загадочным персонажем, не страшно копнуть глубже — научиться определять причину ошибки. В некоторых случаях это можно сделать самостоятельно, так что обращаться за помощью к профильному специалисту не понадобится.
Отображение ошибки бывает разным. Ее внешний облик зависит от того, чем она вызвана.
Самые частые причины ошибки 500 можно распознать по тексту ошибки или внешнему виду страницы.
- Сообщение Internal Server Error говорит о том, что есть проблемы с файлом .htaccess (например, виновата некорректная настройка файла). Убедиться, что .htaccess является корнем проблемы, поможет следующий прием: переименуйте файл .htaccess, добавив единицу в конце названия. Это можно сделать с помощью FTP-клиента (например, FileZilla) или файлового менеджера на вашем хостинге (в Timeweb такой есть, с ним довольно удобно работать). После изменения проверьте доступность сайта. Если ошибка больше не наблюдается, вы нашли причину.
- Сообщение HTTP ERROR 500 или пустая страница говорит о проблемах со скриптами сайта. В случае с пустой страницей стоит учесть, что отсутствие содержимого сайта не всегда указывает на внутреннюю ошибку сервера 500.
Давайте узнаем, что скрывается за пустой страницей, обратившись к инструментам разработчика. Эта браузерная панель позволяет получить информацию об ошибках и другие данные (время загрузки страницы, html-элементы и т.д.).
Как открыть панель разработчика
- Нажмите клавишу F12 (способ актуален для большинства браузеров на Windows). Используйте сочетание клавиш Cmd+Opt+J, если используете Google Chrome на macOS. Или примените комбинацию Cmd+Opt+C в случае Safari на macOS (но перед этим включите «Меню разработки» в разделе «Настройки» -> «Продвинутые»). Открыть инструменты разработчика также можно, если кликнуть правой кнопкой мыши в любом месте веб-страницы и выбрать «Просмотреть код» в контекстном меню.
- Откройте вкладку «Сеть» (или «Network») и взгляните на число в поле «Статус». Код ответа об ошибке 500 — это соответствующая цифра.
Простыми словами: лог — это журнал, в который записывается информация об ошибках, запросах к серверу, подключениях к серверу, действиях с файлами и т.д.
Как вы видите, данных в логи записывается немало, поэтому они разделены по типам. За сведениями о нашей ошибке можно обратиться к логам ошибок (error_log). Обычно такие логи предоставляет служба поддержки хостинга, на котором размещен сайт. В Timeweb вы можете включить ведение логов и заказать необходимые данные в панели управления. Разобраться в полученных логах поможет статья «Чтение логов».
Как устранить ошибку
Теперь поговорим о том, как исправить ошибку 500. Вернемся к популярным причинам этой проблемы и рассмотрим наиболее эффективные способы решения.
Ошибки в файле .htaccess
У этого файла довольно строгий синтаксис, поэтому неверно написанные директивы (команды) могут привести к ошибке. Попробуйте поочередно удалить команды, добавленные последними, и проверьте работу сайта.
Также найти проблемную директиву можно с помощью логов ошибок (через те же инструменты разработчика в браузере). На ошибку в директиве обычно указывает фраза «Invalid command». Информацию о верном написании директивы или способе исправления ошибок в .htaccess вы можете найти в интернете. Не нужно искать, почему сервер выдает ошибку 500, просто введите в строку поиска название нужной команды или текст ошибки из логов.
Ошибки в скриптах сайта
Скрипт не запускается
Обычно это происходит, когда существует ошибка в скрипте или функция, которая не выполняется. Для успешного запуска скрипта функция должна быть верно прописана, поддерживаться сервером и выполняться от используемой версии PHP. Бывают ситуации, когда функция несовместима с определенными версиями PHP. Получить более подробную информацию о той или иной функции можно в интернете.
Не хватает оперативной памяти
Если в логах вы видите ошибку «Allowed memory size», для устранения ошибки 500 стоит оптимизировать работу скрипта. Вы можете воспользоваться специальными расширениями для анализа производительности скрипта или обратиться за помощью к специалисту, который поработает над его оптимизацией.
Если ваш сайт размещен на отдельном физическом или виртуальном сервере, можно попробовать увеличить максимальное использование оперативной памяти на процесс (memory_limit). На шаред хостинге этот параметр обычно не изменяется, но есть возможность купить хостинг помощнее.
Ошибки в CMS
Если код CMS содержит неверный синтаксис, это может вывести сайт из строя. В таком случае логи сообщат вам об ошибке 500 текстом «PHP Parse error: syntax error, unexpected». Так происходит, когда некорректно работает плагин (или тема, используемая в CMS, но реже) либо есть ошибки в коде. Ошибка может быть допущена случайно, произойти при обновлении плагина или версии CMS.
При чтении логов обратите внимание на путь, который следует за сообщением об ошибке, ведь он может указать на проблемную часть кода или плагин. Если проблема в плагине, для восстановления работы сайта переименуйте на время папку, в которой он расположен. Попробуйте обновить плагин или откатить его до прежней версии. Если ситуацию не удается исправить, от расширения стоит отказаться либо заменить его аналогом.
Информацию о других распространенных ошибках вы можете найти в статье «6 наиболее часто возникающих ошибок HTTP и способы их устранения».
Что делать, если вы пользователь
Если при посещении стороннего сайта вы столкнулись с ошибкой 500, не переживайте – вина тут лежит на стороне администратора ресурса. Здесь важно понимать, что проблема может быть кратковременной, например, из-за перегрузки сайта. В таких случаях будет достаточно просто перезагрузить страницу: сделать это можно с помощью соответствующей кнопки в браузере или клавиши F5.
Обратите внимание, что при обновлении страницы интернет-магазина могут дублироваться заказы. Например, если ошибка 500 возникает при оформлении заказа, то после перезагрузки количество товаров может удвоиться. Такое происходит редко, но помнить об этом стоит, чтобы избежать лишних покупок.
Также может быть и такое: например, вы зашли на страницу, она выдала ошибку 500, через некоторое время ее исправили специалисты, но проблема у вас осталась. Чаще всего это связано с тем, что в браузере остались старые cookie-файлы или кеш. Исправить это просто – достаточно очистить данные составляющие. Чтобы сделать это в браузере Google Chrome, необходимо нажать на троеточие в верхнем правом углу и перейти в настройки. Затем в поисковой строке ввести запрос «кеш» и нажать на кнопку «Очистить историю».
В отобразившемся окне вы можете выбрать временной диапазон. Это будет полезно, если вы хотите очищать не все данные, а только те, которые относятся к проблемному сайту.
В других браузерах очистка cookie-файлов и кеша выполняется примерно так же.
Если ни одно из вышерассмотренных действий не привело к успеху, то проблема точно на стороне администратора сайта. При желании вы можете найти его контактные данные и отправить запрос – спросить, когда будет решена проблема и с чем это связано.
Что бесполезно делать при Error 500
При ошибке 500 есть несколько вещей, которые могут быть бесполезными или непродуктивными:
- Повторные попытки обновления страницы. Вы можете сделать несколько попыток обновления страницы, надеясь, что ошибка исчезнет. Однако, если проблема связана с сервером, это не приведет к успеху.
- Перезагрузка компьютера. Ошибка 500 никак не связана с локальным компьютером, так как проблема кроется в оборудовании администратора сайта.
- Использование другого браузера. Это может помочь только в том случае, если проблема связана с кешем или cookie-файлами.
- Переустановка ПО и перезагрузка роутера. Подобные действия также не приведут к успеху.
Если вы владелец сайта, то лучше сделать так, чтобы у пользователя не возникала потребность осуществлять вышеперечисленные действия. Вы можете информировать об ошибке прямо на сайте – так человек сразу поймет, что проблема связана не с его оборудованием. Это поможет вам обеспечить качественный пользовательский опыт и поддержать хорошие показатели SEO.
Ошибка 500 на сайте, созданном на WordPress
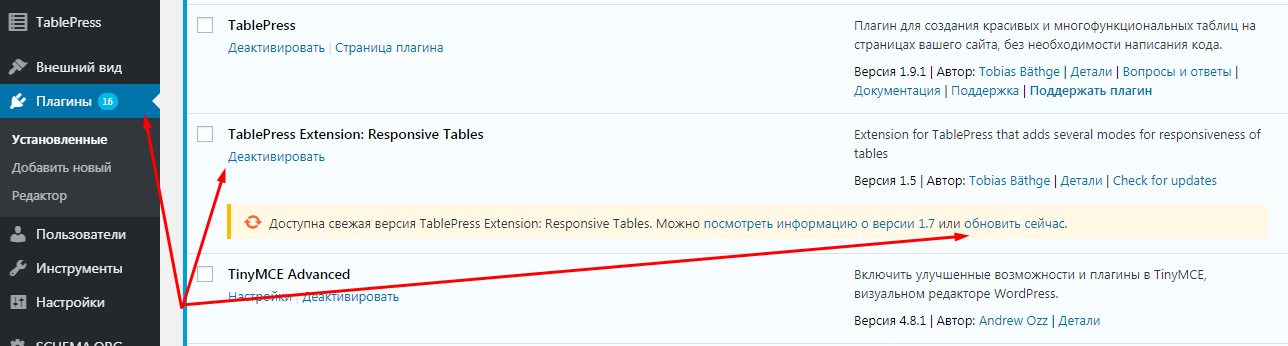
На WordPress ошибка 500 чаще всего возникает из-за установленных плагинов – как старых, так и недавно загруженных. Первым делом проверьте, нуждаются ли устаревшие инструменты в обновлении. Если же расширения обновлены, но 500 Internal Server Error до сих пор есть, попробуйте отключить все плагины. В таком случае ошибка может исчезнуть – если это произошло, то виной всему один из установленных инструментов.
Для отключения расширений перейдите в панель управления WordPress и откройте вкладку «Плагины» –> «Установленные». В отобразившемся окне нажмите на кнопку «Деактивировать», которая расположения под названием плагина.
Постепенно отключая расширения, вы сможете найти «виновника», который вызывает ошибку 500. Если же проблема кроется не в этом, то лучше обратиться за помощью к квалифицированным специалистам.
Удачи!
Summary: HTTP ERROR 500 in Exchange is displayed when the server rejects the request to establish a connection with the Exchange Server. The error prevents Exchange administrators and users from accessing the Exchange Admin Center and managing the Exchange Server. In this blog, we have discussed reasons and solutions to fix the HTTP ERROR 500 in Exchange and get access to the EAC/ECP.

Contents
- Reason for HTTP ERROR 500 in Exchange ECP/EAC
- Solutions to Fix HTTP ERROR 500 in Exchange Server
- Conclusion
Exchange Management Console (EMC) and Exchange Control Panel (ECP) were two different interfaces used in Exchange 2010 and earlier versions to manage the Exchange Servers. With Exchange 2013, Exchange Administrative Center (EAC) — a web-based management console optimized for on-premises, hybrid, and online Exchange Server deployments—replaced EMC and ECP.
And since EAC is web-based, you need to use a web browser and require the OWA/ECP virtual directory URL to access the management console. By default, you can access the ECP/EAC console using the following URLs,
Internal URL— https://<CASServerName>/ecp
It allows users to access the EAC within the organization’s firewall.
External URL— https://mail.abc.com/ecp
It provides access to users from outside of your organization’s firewall.
Administrators and users with permission can access the EAC/ECP panel by signing in using valid credentials.
However, many users have reported an HTTP ERROR 500 after they sign in to EAC/ECP.

Reason for HTTP ERROR 500 in Exchange ECP/EAC
The HTTP ERROR 500 is usually reported after upgrading or updating the Exchange Server without an elevated command prompt.
However, it may also occur due to many other reasons, such as,
- Exchange Services stopped or not working
- Damaged OWA virtual directories
- Damaged Exchange Server
- Improper configuration
- Low Resource allocation
- Corrupt or incomplete .NET framework installation
Solutions to Fix HTTP ERROR 500 in Exchange Server
Follow these solutions in the given sequence to troubleshoot and fix the HTTP 500 error in Exchange Server EAC/ECP after login.
Solution 1: Use a Different Browser
Sometimes browser cache and cookies can cause issues while accessing the Exchange Admin Center. You can reset either the web browser or use a different browser to fix the error and access the EAC/ECP.
If you still encounter the HTTP ERROR 500, proceed to the next solution.
Solution 2: Install Pending Server Updates
On your Windows Server, open the Windows Updates section and install any pending updates as they may stop certain Exchange Services resulting in HTTP ERROR 500 after EAC login.

After the update, restart the server and then try to log in to the EAC. You may disable automatic Windows Updates to prevent HTTP ERROR 500. However, it is highly recommended to install the updates to stay protected.
If there are no pending updates but the error persists, follow the next solution.
Solution 3: Reinstall Updates
If the HTTP ERROR 500 occurred after installing the Exchange Server security updates, reinstall those using the elevated command prompt. The steps are as follows,
- Open Command Prompt as administrator
- Navigate to the location where Security updates are downloaded (.msp files) using ‘cd’ command. For instance,
cd “C:\Users\UserName\Downloads\Updates\”
- Then execute the following command in the Command Prompt window,
.\UpdateName.msp
- Follow the update wizard and complete the installation process.
- Restart the server and check if you can now access the EAC/ECP.
Solution 4: Check Resource Allocation
Some users have reported that the HTTP ERROR 500 occurred simply because their Exchange VM doesn’t allocate enough CPU cores. To fix this, shut down the server VM and review the allocated resources.

Add or allocate more CPU cores and RAM, if available. Restart the server and check if EAC is accessible.
Similarly, for physical servers, upgrading the hardware may fix the error. However, we recommend you follow all the troubleshooting solutions discussed in this blog before upgrading the hardware to resolve the HTTP 500 error.
Solution 5: Update Server Configurations
Improper or outdated server configuration after the server upgrade or update can also render EAC or ECP inaccessible, causing HTTP ERROR 500 after login.
In such a case, you can run UpdateConfigFiles.ps1 and UpdateCAS.ps1 PowerShell scripts located in the Exchange Server ‘Bin’ directory (C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\Bin\) to resolve the error.

To execute these PowerShell scripts, follow these steps,
- Open PowerShell as administrator and use the ‘cd’ command to navigate the Exchange ‘Bin’ directory. For instance,
cd “C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\Bin.”

Then execute the following commands to run the PowerShell scripts to fix the configuration issues.
.\UpdateConfigFiles.ps1
.\UpdateCAS.ps1

This may take a while to finish. Once done, restart the server and check if the HTTP 500 error is resolved and ECP/EAC is accessible.
Solution 6: Recreate Virtual Directories
As a last resort, you can remove the existing OWA and ECP virtual directories and create new ones to fix the HTTP 500 error in Exchange. The steps are as follows,
- Open Exchange Management Shell (EMS) as administrator and run the following commands to remove the current OWA and ECP virtual directory
Remove-OwaVirtualDirectory –Identity “ExchangeServerName\owa (Default Web Site)”
- Press ‘a’ or ‘y’ and then press the ‘Enter’ key.

- Now execute the following command in the same EMS window to rebuild OWA virtual directory,
New-OwaVirtualDirectory –WebsiteName “Default Web Site”
The commands are case-sensitive.
This will rebuild the virtual directories and possibly fix the issue. It will also change the way you log in. Instead of the login page, you will see the following pop-up for login.

Enter username and password to log into ECP/EAC web console.
Solution 7: Repair Exchange Server
If none of the solutions worked for you, try repairing your Exchange Server. For this, you need to mount the same Cumulative Update ISO as installed on the server. Then use the following command in EMS to repair the server.
Setup /Mode:upgrade /IAcceptExchangeServerLicenseTerms

Use ‘/IAcceptExchangeServerLicenseTerms_DiagnosticDataOFF’ if your server is running on September 2021 or later Cumulative Update.
After the repair, restart the server and check if the HTTP ERROR 500 is resolved.
You may also set up a new Exchange Server if server repair fails and move your mailboxes and mail items from the old server to the new server. For this, you can use an EDB converter tool, such as Stellar Converter for EDB. The software can extract mailbox data from your faulty Exchange server with an online or offline database and export them to PST. You may also export the mailboxes from offline EDB to your new Exchange Server database to PST. The software auto-maps the source mailboxes with destination mailboxes and exports up to four mailboxes simultaneously to the target server database in a few simple steps.
Conclusion
HTTP ERROR 500 is common, especially after improper server update installation. However, it may also occur due to several other reasons, as discussed in this blog. We also discussed all possible solutions to resolve the HTTP ERROR 500 in Exchange Server 2013 and later versions. However, if the error isn’t resolved, it’s recommended to set up a new server and move your data from the faulty server to a new server using an EDB converter tool, such as Stellar Converter for EDB. The software helps you extract and move mailbox data from offline or online databases hosted on your faulty server and exports them to PST, Office 365 tenant, or Live Exchange Server. It automates the entire mailbox data migration process, saving tons of time required to manually export and import mailboxes via EMS or EAC. Moreover, the cmdlets do not work if the database is offline.
About The Author
Ravi Singh
Ravi Singh is a Senior Writer at Stellar®. He is an expert Tech Explainer, IoT enthusiast, and a passionate nerd with over 7 years of experience in technical writing. He writes about Microsoft Exchange, Microsoft 365, Email Migration, Linux, Windows, Mac, DIY Tech, and Smart Home. Ravi spends most of his weekends working with IoT (DIY Smart Home) devices and playing Overwatch. He is also a solo traveler who loves hiking and exploring new trails.
The “HTTP 500 Internal Server” error is quite general as it can be caused by a broad range of issues. Because of that, you may stumble upon it quite often.
This article will explain the “HTTP Error 500” and how to fix it.
What does “HTTP 500 Internal Server Error” mean?
Error 500, also known as the Internal Server Error, is a common HTTP status code that indicates an issue on the web server’s side. When you encounter an error 500, it means that the server has encountered an unexpected condition or configuration problem that prevents it from fulfilling the request made by the browser or client.
The HTTP status code “500 – Internal Server Error” is one of the many 5.X.X. HTTP error codes (500, 502, 503, 504, etc.). Each of them specifies a different problem but the common denominator they share is that they tell you something is wrong with the website’s server.
In other words, the hosting server can’t determine the exact problem and display a more specific message. Instead, it responds with the error “500 Internal Server Error” which means that it’s not clear what’s wrong.
You may see different message variations since many websites and web servers customize the error page.
Some variations & examples of the error message include:
- 500 Internal Server Error
- Internal Server Error 500
- HTTP Error 500
- HTTP Status 500 – Internal Server Error
- Error 500 Internal Server Error
- 500 Error
- 500. That’s an error
Apart from the text, the page’s look may vary for different websites. Below you can see a generic version of the “Internal Server Error” page.
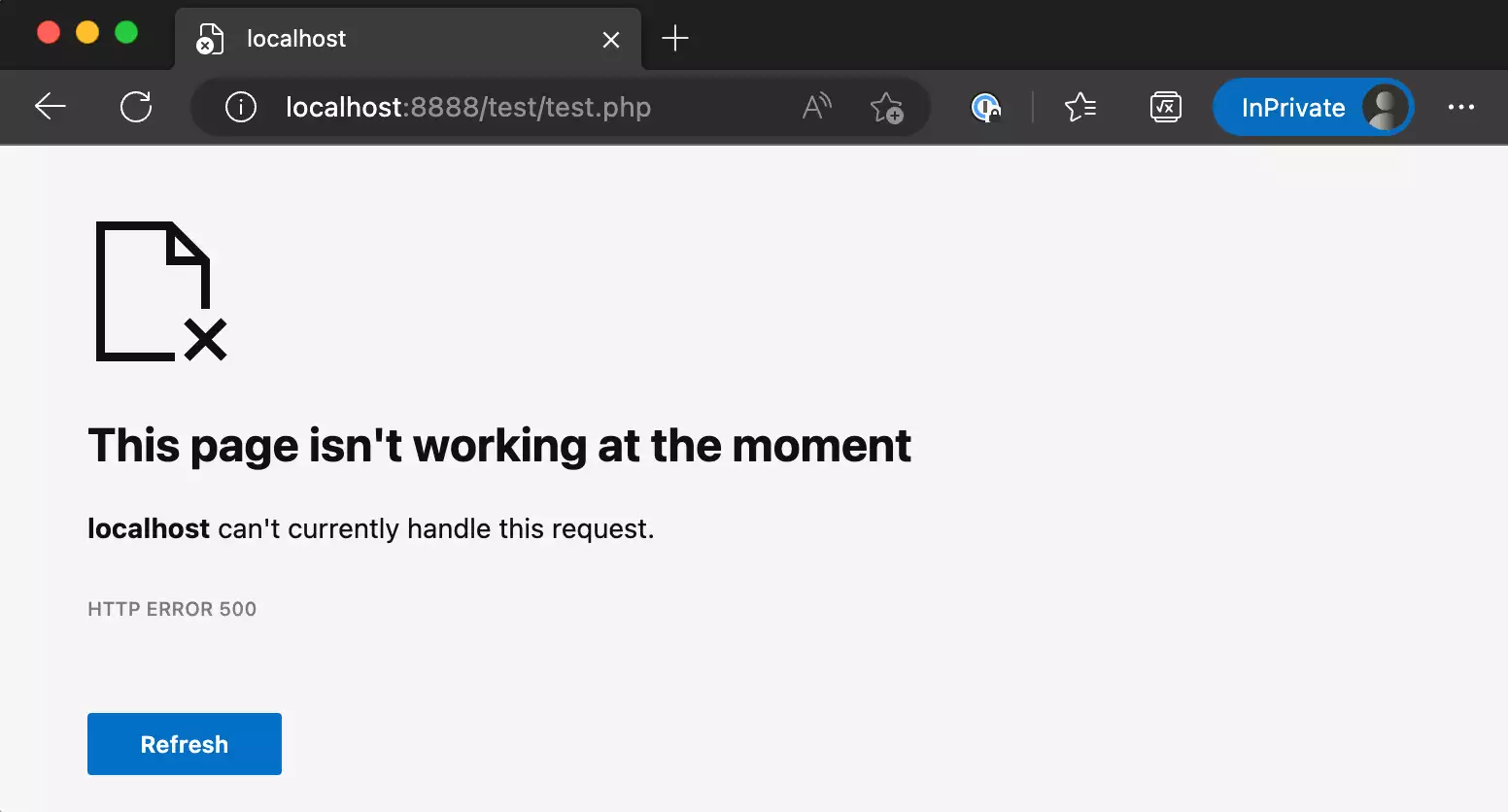
Other times, the page may have a customized design, as seen in the following image.
These are only a few examples of the error page and you can see it in countless variations. Regardless of how the page looks, it always has the same meaning – there is a problem that the server can’t pinpoint, and it prevents you from loading the website.
What are the common problems that can cause HTTP 500 Internal Server Error?
Although the error definition states the issue is from the server, that’s not always the case. Some of the common problems that can cause the error are:
- Corrupted browser cache
- Temporary connectivity issues
- Syntax errors or incorrect rules in the website’s .htaccess file
- Incorrect file and folder permissions
- Wrong PHP version for the website
- Corrupted .htaccess file
- Corrupted website’s database
- Problems with WordPress themes and plugins
- Exhausted PHP memory limit on the website
- Corrupted WordPress core files
- Large files on your website
- Problems with the MySQL server
How to Fix the “500 Internal Server” Error?
As you can see from the list above, the error’s origins are quite diverse. Since the error page will not clearly indicate the problem, you may need to troubleshoot a few of the possible causes until you find the culprit.
How to Fix 500 Internal Server – Video Tutorial
We will go over most of the eventual problems and their solutions.
How to Fix the “HTTP Error 500” as a visitor?
As a visitor, the only thing you can do is check if a connectivity issue from your end causes the error. You can also apply the following actions as a website owner since these are the quickest checks. If the error is caused by a local problem from your end, the steps below can save you a lot of time from troubleshooting.
Reload the page
The “HTTP Error 500” may be visible only for you, in case there was a brief connectivity problem. The website itself may be working fine, but you might have tried to access it when there was a momentary downtime, or your network failed to establish a connection to the website’s server.
Try reloading the page in the same browser with the Reload button or by pressing the keyboard shortcut Command+R for Mac, or F5 (Control+F5) for Windows.
If the website loads correctly, the issue was only temporary, and you can stop troubleshooting.
Clear your browser cache and cookies
When the website doesn’t open after reloading, your browser might be keeping expired or corrupted cache files and cookies. Reloading the page will not delete them, so you must clear them manually.
Read this guide on clearing cache and cookies in desktop browsers for detailed instructions.
Check these articles on deleting the cache on an Android phone or iPhone, if you use a mobile device.
Alternatively, you can test opening the page from another browser. For instance, if you use Chrome, try Firefox or vice versa.
After clearing the browser’s cache, reload the page to see if that solved the problem. If not, proceed with the next step.
Visit the website using another network
The connectivity problems causing the “HTTP 500 Error” may happen across your entire network. In this case, you will probably see the error on any device on this network.
To test if this is the problem, switch to another network. For instance, if you use a mobile phone connected to Wi-Fi, switch to mobile data.
How to Fix the HTTP 500 Internal Server Error from the website?
In the best-case scenario, the steps mentioned above will fix the problem. However, if the error persists, you may need to dig deeper into the issue since the error stems from the website itself.
As a site owner or webmaster, there are several checks you can do that can solve the “500 Internal Server Error.”
Check the Error Logs of the Website
In many cases, misconfigured files or scripts are the sources of the website’s errors. The error logs can help you identify them easier.
Typically, you should have such logs in your hosting’s control panel. SiteGround users can find the Error log in the website’s Site Tools.
To access it, navigate to the Websites section in your Client Area. Open the Site Tools of the respective site, select Statistics and click on Error Log.
You will see the most recent errors on your website that the server detected. Each error will be recorded with a few key pieces of information:
- The date and time of the error.
- Description of the error.
- Information about which folder or file is possibly generating the error.
Below, you can see an error log indicating a problem with the .htaccess file.
This record indicates that the problem is from the .htaccess file located in the root folder of the website. It also specifies that the error is related to a <IfModule> missing argument, which means there is a syntax error.
Using this information, you can navigate to the specified folder from File Manager, edit the .htaccess file and correct the syntax error.
Keep in mind that the Error log records errors related to the server configuration. Errors caused by PHP misconfiguration and scripts are not recorded, as they happen on application level.
PHP errors are recorded in php_errorlog. It is generated automatically in the folder of the offending PHP file. On SiteGround’s hosting, the PHP error log is active by default. If you have previously deactivated it or your hosting hasn’t enabled it, read this guide on how to enable error reporting in a PHP script.
To inspect the PHP error log, you can use File Manager or FTP client. Navigate to the root folder, if the error is caused by a script located in the root folder. Open the file php_errorlog, where you can examine the errors.
The php_errorlog shows general PHP errors. However, you may need a more detailed log of the problem. If you have a WordPress website, you can also enable the debug log for WordPress that can show more information. For detailed steps on how to enable the WordPress debug log, see this guide.
Reset File and Folder Permissions
Another common problem that can cause the “HTTP 500 Error” is incorrect file and folder permissions on your website. If the permissions prevent visitors from opening the critical website’s files and folders, they may see the error page.
The standard permissions are 644 for files and 755 for folders. You can change them from the File Manager in your hosting panel or from an FTP Client.
For setting the permissions for WordPress sites, SiteGround clients can use the Reset Permissions tool for WordPress in Site Tools.
If your website is using another type of application, read this guide on how to change permissions for files and folders from File Manager.
Alternatively, if your hosting’s panel doesn’t have similar tools, you can change permissions from SSH or from an FTP Client.
Change the PHP version
An incorrect PHP version on your website may cause PHP scripts to time out or produce fatal errors. As a result, the website may return the “HTTP 500 Error.”
Test switching the PHP version to an older or later version. If the error disappears, it’s an indication that the previous version was wrong. Keep the site on the newly selected one.
SiteGround users can easily switch the PHP version with only a few clicks on Site Tools. For detailed steps, check this guide on how to switch to a different PHP version in Site Tools.
Inspect or regenerate the .htaccess file
A common cause of the “Internal Server Error” is a problem within the .htaccess file. If the file is corrupted, it defines an incorrect root folder or contains syntax errors, the usual result is the “HTTP 500 Error” page.
Fix the syntax error in .htaccess
As an example of a syntax error, we can use the previously mentioned error from the error log.
<2022-05-17 14:32:40 UTC [apache][core:alert] [pid 68451] [client 35.214.177.225:57966] /home/user/www/sg-testing.com/public_html/.htaccess: <IfModule> directive requires additional argumentsTo inspect the file, open the Site Tools of the website. Then, select the section Site and open File Manager.
Navigate to the website’s root folder, which is the site name/public_html. In our example, the name is sg-testing.com, so the folder path is sg-testing.com/public_html.
In this folder, you can find the .htaccess file. Select the file and then press Edit to open the code editor.
Now, you can inspect its code. As the error log points, the problem is from the <IfModule>. The issue is a syntax error because the module is missing a forward slash in the closing tag </IfModule>.
Add the slash and then save the changes with the Save button. Reload the website and it should now load properly.
Wrong website’s root folder defined in .htaccess
Another common error in .htaccess is an incorrectly defined root folder for the website. Usually, this is a result of one of the following cases:
- You transferred the website from another hosting provider where it resided in a subfolder.
- You developed the website on a subfolder and then moved it to the main domain folder in the same hosting.
- For a WordPress website, you installed a plugin that has changed the RewriteBase in .htaccess. The plugin may need extra configuration to work with the modified code but currently, the website is inaccessible due to the “500 Internal Error”.
To illustrate the problem better, we can use the following example.
Notice the /dev path in RewriteBase. This code instructs the server to load the website from a folder named public_html/dev. Since the folder is non-existent, when you load a page from the website, it will produce the “Internal Server Error” screen.
To fix the problem, simply remove the subfolder path from RewriteBase so the code would look like this:
# BEGIN WordPress
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index\.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !/(wp-content\/uploads/.*)$
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
</IfModule>
# END WordPressThis is the default WordPress code defining the root folder for the website. Confirm the change in File Manager with the Save button and reload the website. The error shouldn’t appear anymore.
Regenerate the .htaccess file
Another standard troubleshooting scenario is to replace the .htaccess file with a new copy. To replace the file with a new copy, open File Manager, navigate to public_html, select the file .htaccess and choose Rename.
You can choose any name for the file. For example, you can name it htaccess-old and create a new .htaccess file.
If the website is WordPress, access the WordPress dashboard, navigate to the section Settings, and open Permalinks. Just click on the button Save Changes, and your website will generate a new .htaccess file with the default WordPress code.
If your website is not WordPress, find the default .htaccess code for your specific application. Use the button New File in File Manager and name the new file .htaccess. Paste the default code into .htaccess and save the changes.
After the new .htaccess file is set, reload the website again to see if the error is gone.
Repair the database or fix the database credentials
Another common problem that can cause the “500 Internal Server Error” is a corrupted database on your website. You may consider restoring the database from a backup or repairing it.
For WordPress, the error may occur if the website fails to connect to the database. Make sure that the credentials are set correctly in the wp-config.php file.
For detailed steps, read this guide on how to fix the error ‘Establishing a Database Connection’ in WordPress.
Disable plugins for your WordPress website
A misconfigured plugin can also trigger the “HTTP 500 Error” in WordPress. The standard procedure is to disable the plugins one by one until you find the culprit.
If the error is only on the front end, but you still have access to the WordPress admin dashboard, you can disable the plugins from the section Plugins. Then choose Installed plugins. From the drop-down Bulk actions menu, select Deactivate. Check the box Plugin and press Apply to deactivate all plugins.
In many cases, the error prevents you from logging into the WordPress dashboard so you may need to use an alternative way.
A popular suggestion you’ll find online is to rename the wp-content/plugins folder. We don’t recommend this method as it may fix the “HTTP 500 Error”, but cause other complications.
It is safer and more efficient to disable all plugins from Site Tools (if you are a SiteGround user) or from the database.
Read the following guides for detailed steps:
- How to disable all plugins from Site Tools
- How to disable all plugins from the website’s database
After the plugins are disabled, reload the website. If the website is fixed, it is a strong indication that the error is caused by one of the plugins.
Proceed by activating the plugins one by one. When the faulty plugin is reactivated, the error will return. You can then disable the plugins again to access the dashboard and activate all plugins apart from the problematic ones.
You may consider replacing this plugin with another one or contacting its developers to report the problem.
Change the theme for your WordPress website
A badly configured theme can also cause the “500 Internal Server Error” in WordPress. To check if the theme is the problem, you will need to replace it with another one.
Usually, you can change the theme from the website’s WordPress dashboard. However, in many cases, the ongoing “HTTP 500 Error” prevents you from logging in.
Read this guide on how to change the WordPress theme from the database for more information.
Increase the PHP Memory Limit of the Website
The “HTTP 500 Error” may also be caused by PHP scripts that exceeded the memory limit of your website. By default, the limit on all SiteGround plans is set to 512M. However, your WordPress website may be set to a lower value. To increase the memory limit, follow the steps from this guide on how to increase WP Memory Limit.
Restore a Backup of the Website
If none of the solutions helped solve the issue or you find them challenging to implement, you may consider restoring the website from a backup. Restoring the website will revert all changes that caused the error in the first place.
SiteGround users can check this detailed tutorial for the Website Backup Tool.
Check if your website contains large files
Another common reason for this error is having a very large file as a part of your website. On SiteGround’s shared hosting servers there is a size limit for files that can be opened through the web. The limit is 8GB, and if your website includes a larger file, this will result in the above error.
Check your website’s files either via SSH, FTP, or File Manager to locate the one causing the problem. Very often, these are logs with PHP errors.
On SiteGround’s servers, a log file is created automatically if your site’s PHP scripts produce any non-critical errors or warnings during their execution. The log file’s name is php_errorlog, and it is located in the same directory as the script that produced the errors. Usually, this would be your website’s root folder.
Contact the web hosting provider
Ultimately, the “500 Internal Server Error” may not be caused by your website configuration. The MySQL server may be down, or the server may be overloaded. Contact your web hosting’s support team so they can check the server’s status and help further with the problem.
Summary
The HTTP “500 Internal Server Error” can be very frustrating to deal with because of its unclear nature. The problem may originate from a local issue or an error on the website or the server.
This guide can help you narrow down the causes to fix the error more efficiently.
The “HTTP 500 Error” is one of the many error codes. Read this guide to find out more about the different error codes.
For more information about fixing other 5.X.X. status codes, read the following articles:
- How to fix the “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway Error”?
- How to fix the “HTTP 503 Service Temporarily Unavailable” error?
- What is “HTTP 504 Error” and how to fix it?
When running a web server powered by NGINX, you may encounter some errors. One such error is “NGINX 500 Internal Server Error”. This error indicates that something went wrong on the server side, preventing it from processing requests.
This error can be a headache for developers, especially in the production environment, as they break the functionality of the entire website. However, it is possible to make your server work again after identifying the causes of this error and fixing it. So, in this article, we will explore common causes of NGINX 500 Internal Server Error and provide you with potential fixes to resolve the issue.
What is the NGINX 500 internal server error?
NGINX 500 Internal Server Error is a generic HTTP status code implying an internal problem within the server. Unlike error codes that pinpoint the problem, such as Error 404 for “Not Found” or 403 for “Forbidden”, the 500 error does not reveal the exact cause of the problem.
NGINX is multipurpose software. Both reverse proxy server, load balancer or web server can cause such error. When you encounter a 500 Internal Server Error, it indicates that the NGINX server encountered an error while trying to perform its tasks.
Possible causes for the NGINX 500 internal server error
As mentioned above, this error indicates a general problem with your server that has not been detailed. However, there are some possible causes to consider that might trigger the error. Some possible causes of the NGINX 500 Internal Server Error include:
Misconfigured Server Settings
One of the primary causes of the Nginx 500 Internal Server Error is misconfigured server settings. These settings control the server’s behavior, and incorrect configurations can lead to unexpected errors. Misconfigured server configuration files may contain incompatible directives or incorrect syntax.
Insufficient Server Resources
Another potential cause of the Nginx 500 Internal Server Error is insufficient server resources, such as CPU, RAM or disk space. When these resources are exhausted, the server cannot respond to users’ requests. This causes a “bottleneck” situation. This issue can also be caused by many simultaneous users in your website, or it can be caused by malicious requests sent automatically to harm your website.
Backend Application Errors
The Nginx 500 Internal Server Error can also be a result of errors in the backend application that Nginx is proxying to. In Nginx, proxying refers to the action of forwarding client requests to another server or service. For example, Nginx can receive requests from clients and forward them to a Nodejs backend application. At this point the issue can occur if you didn’t configure the proxy connection between Nodejs and Nginx.
Insufficient File Permissions
Nginx needs the appropriate file permissions to access and serve the requested files. Nginx may not be able to access the required resources and cause a 500 Internal Server Error if you have incorrect permissions. For example, let’s say you are hosting a WordPress site, your public_html folder permissions should be set to allow your php and html files to be served.
Browser Related Problems
This cause is about client-side. You may not be seeing the 500 Internal Server Error message only because of server-related issues. If you are sure that you have configured your server well, you may be getting this error due to the caching mechanism of browsers or the extensions you have installed on your browser.
How to fix NGINX 500 internal server error
We have discussed the problems that can cause 500 Internal Server Errors. Now let’s look at the steps that can be taken to fix these problems.
Fixing Misconfigured Server Settings
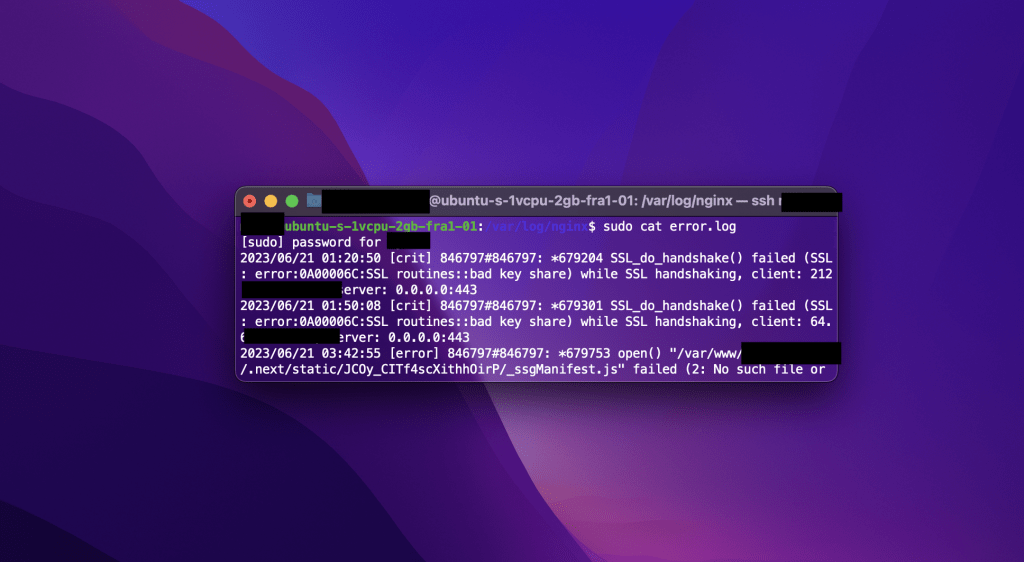
- Fix 1 – Check Nginx Error Logs
Start by checking the NGINX error log file, it can provide valuable insights into the specific configuration error. The default location for the error log is usually /var/log/nginx/error.log. So, run the following commands in Linux to access it.
cd /var/log/nginx
cat error.logThis page will show you errors affecting NGINX functionality. For example, in the image below, the error indicates that an SSL/TLS connection was not established between a client and server due to an issue with the SSL certificate.
Of course, that’s just a problem, you may find different kinds of errors in your Nginx log file. In this case, you can find the cause of your problem with a simple google search.
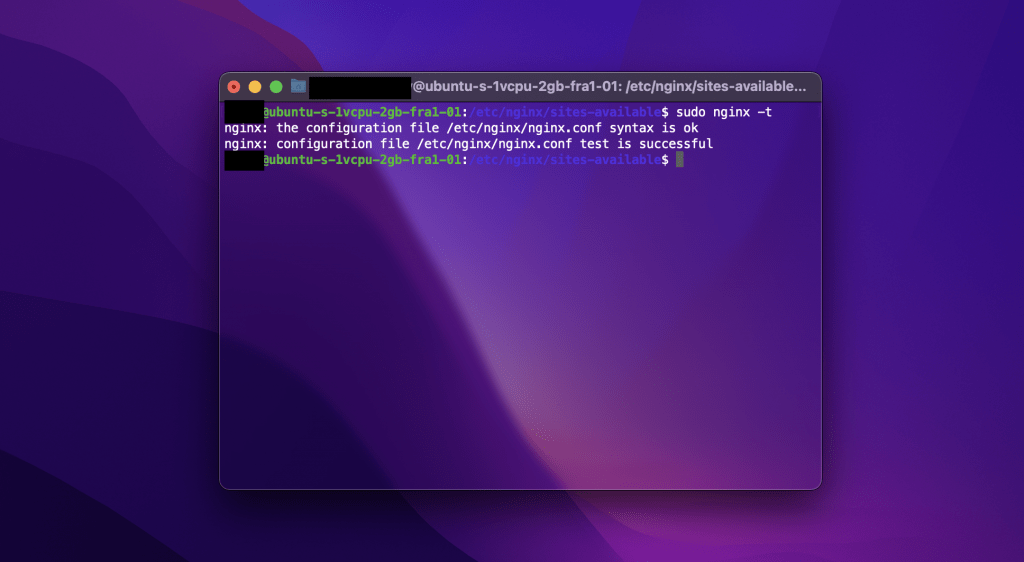
- Fix 2 – Verify the Configuration Syntax
Then, review your Nginx configuration files, paying attention to syntax errors or misplaced directives. Commands like nginx -t or nginx -t -c /path/to/nginx.conf will help you validate the syntax and detect any errors. You can simply run the following commands to navigate to the config files and detect errors.
cd /etc/nginx/sites-available
nginx -tAfter running the commands above, you should get an result as show in image below.
However, if you see a syntax error, you must fix it. Once fixed the syntax errors, restart the Nginx server using the command sudo service nginx restart or else nginx -s reload.
Fixing Insufficient Server Resources
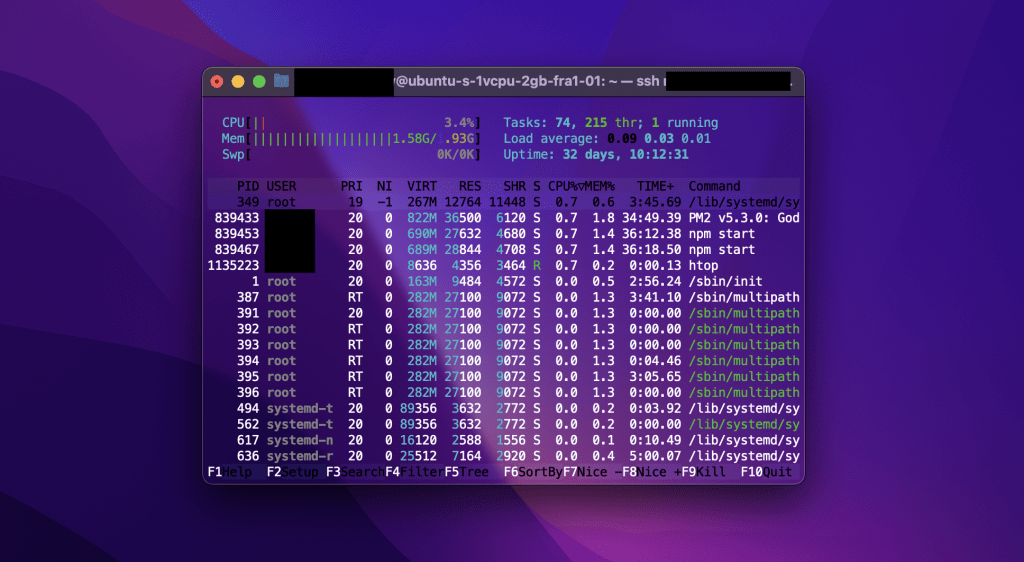
- Fix 3 – Monitor System Resources
If you suspect a lack of system resources, you firstly need to check the system’s memory usage, CPU load and disk space availability. You can achieve this using the commands like top , htop and free . Here is an example of using the htop command to see the server’s remaining resources.
Once you identify the problem in sources, you can try to remove unnecessary files, if the resource limitations persist, you should consider upgrading your server hardware or migrating to a higher-performance hosting solution.
Fixing Backend Application Errors
- Fix 4 – Check Backend Application Logs
Inspect the logs of the backend application to identify any errors or exceptions. The logs may be located in different locations depending on the application stack (e.g. /var/www/example.com/logs/error.log for WordPress or pm2 logs if you are using the pm2 package with Nodejs)
- Fix 5 – Check Proxy Configurations
Ensure that the proxy pass configuration in your Nginx server block correctly set up. You can look for the proxy_pass directive and ensure it points to the correct backend server. For example:
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend_server;
}If you’re using Nginx as a reverse proxy, issue could be related to the upstream configuration. You can check the file mostly located in the path /etc/nginx/nginx.conf on linux. For example:
upstream backend {
server backend_server1;
server backend_server2;
}backend_server1 and backend_server2 should be replaced with the actual addresses or hostnames of your backend servers and make sure each backend server is running on different ports and these ports ports do not conflict.
After making any changes, restart the Nginx service to apply the modifications using commands sudo service nginx restart or nginx -s reload .
Fixing Insufficient File Permissions
- Fix 6 – Check directory permissions
Check the permissions of the file or directory that Nginx is trying to access. You can use the chmod command to modify the permissions, typically 644 for files and 755 for directories.
- Fix 7 – Confirm ownership
Ensure that the file or directory is owned by the user running the Nginx process. You can check the ownership using the ls -l command, which will display the owner and group. If the ownership is incorrect, you can change it using the chown command. For example:
chown www-data:www-data path/to/fileAfter making changes in permissions and ownership, you should restart the Nginx using commands sudo service nginx restart or else nginx -s reload .
Fixing Browser Related Problems
- Fix 8 – Clear Browser Cache
Cached files in the browser can sometimes conflict with the server, clearing the browser cache can help resolve this issue. In Google Chrome, you can remove cached files as in shown image below.
- Fix 9 – Disable Browser Extensions
Some browser extensions, especially vpn related extensions, can block communication between the browser and the server. So, you can try disabling all extensions and then reload the webpage to see if the error persists. You can find your extensions on Google Chrome as shown below:
FAQ
Are there other less common causes for the NGINX 500 Internal Server Error?
Yes. Various factors can cause the NGINX 500 Internal Server Error. So troubleshooting the exact cause requires analyzing server logs and configuration settings. However, some common causes of the NGINX 500 server error include, i.e.:
- PHP configuration issues: If you’re using PHP with NGINX, misconfigurations in the PHP settings, such as incorrect file permissions, memory limits, or incompatible modules, can trigger a 500 error. Checking the PHP error logs and ensuring the PHP configuration aligns with the server requirements can help resolve such issues.
- Incorrect NGINX configuration: Errors in the NGINX configuration files, such as syntax errors or conflicting directives, can lead to a 500 server error. Verifying the NGINX configuration files and ensuring they are correctly written and properly structured is essential to resolve these issues.
- Insufficient file or directory permissions: NGINX may encounter a 500 error if it lacks proper permissions to access required files or directories. Ensuring that the NGINX user (usually “www-data” or “nginx”) has appropriate read, write, and execute permissions on the necessary files and directories can resolve such issues.
- Faulty upstream server: If NGINX is configured to proxy requests to an upstream server (e.g., a backend application or another web server), a 500 error may occur if the upstream server is experiencing issues. Checking the logs and health of the upstream server can help identify and address any problems.
- Resource limitations: Insufficient server resources such as CPU, memory, or disk space can cause NGINX to encounter a 500 error. Monitoring the server’s resource usage and ensuring it has adequate resources available can help prevent such errors.
It’s important to note that the 500 Internal Server Error is a generic error indicating that something went wrong on the server side, and the specific cause may vary depending on the server configuration and setup. Analyzing the NGINX error logs and consulting with server administrators or web developers can help diagnose and resolve the issue effectively.
Is NGINX a reliable web server? Or is this error frequent?
Yes, NGINX is widely regarded as a reliable and high-performance web server. It has gained popularity for its ability to handle high levels of concurrent connections and efficiently serve static and dynamic content. NGINX is known for its lightweight architecture, scalability, and robustness, making it a popular choice for websites and web applications of all sizes.
Here are some reasons why NGINX is considered a reliable web server:
NGINX is designed to handle a large number of concurrent connections and deliver content quickly. It uses an asynchronous, event-driven architecture that optimizes resource utilization and provides high-performance delivery of web content.
NGINX is highly scalable and can handle a significant amount of traffic. It efficiently distributes incoming requests across multiple worker processes or threads, enabling it to handle heavy workloads and spikes in traffic without sacrificing performance.
Stability
NGINX is known for its stability and resilience. It has a small memory footprint, efficient memory management, and effective handling of connections, which contributes to its stability under high loads. NGINX’s modular architecture also allows for easy customization and configuration to meet specific requirements.
NGINX has a reputation for reliability and uptime. It has built-in features for load balancing, fault tolerance, and high availability, which help ensure continuous service even in the event of server failures or network issues.
NGINX has a large and active community of users and developers, which provides extensive support, documentation, and resources. The NGINX community actively contributes to the development and improvement of the web server, making it reliable and well-maintained.
While no web server is entirely immune to issues or vulnerabilities like the error 500, NGINX has proven to be a dependable choice for hosting websites and serving web content due to its performance, scalability, stability, and strong community support.
Conclusion
Nginx 500 Internal Server Error indicates that there are some problems with your server. In this article, we have discussed the possible causes of these problems, how to detect them and the steps needed to fix them. Remember, such errors prevent access to your website, so you should test your application step by step both while developing and publishing it to avoid such errors in production.
Thank you for reading.
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback!
The HTTP Internal Server Error 500 typically occurs when the server encounters an unexpected condition that prevents it from fulfilling the request. This post will help you understand the causes of the error and find appropriate solutions.
Table of Contents
- What Is The 500 Internal Server Error?
- The White Screen of Death of Error 500
- Different 500 Error Messages
- 500 Internal Server Error Causes
- How To Fix The 500 Internal Error
-
How To Get More Details About The Errors In PHP
- How to show and log errors in plain PHP applications
- How to show PHP errors in WordPress
- Microsoft Internet Information Services IIS shows 500 error details
- When inspecting logs look at the right place
-
How To Get More Details About The Errors In PHP
- All HTTP Status Codes
What Is The 500 Internal Server Error?
It is considered a general error on the server side due to a non-specified problem. From the RFC Standards, we have this definition:
The 500 (Internal Server Error) status code indicates that the server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling
the request.RFC 7231: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content (rfc-editor.org)
It is not an error in your connection or browser. Rather, it means something has gone wrong with the website.
The White Screen of Death of Error 500
The “White Screen of Death” (WSOD) is a term used to describe the 500 HTTP error, and other 5XX HTTP error codes when the server cannot serve any content to the user. Some browsers like Safari or Firefox present this white screen:
Alternatively, you have browsers that translate the Internal 500 error, showing different informative messages.
Different 500 Error Messages
Although this error may appear in many ways, they all mean the same. The following displays a few examples of how you might see a 500 HTTP error.
- “500 – Internal Server Error”
- “500 Error”
- “500 Internal Server Error. Sorry, something went wrong.”
- “500 Internal Server Error”
- “500. That’s an error. There was an error. Please try again later. That’s all we know.”
- “HTTP 500 – Internal Server Error”
- “HTTP 500”
- “HTTP Error 500”
- “Internal Server Error”
- “This page isn’t working at the moment. HTTP ERROR 500.”
- “This page isn’t working. – localhost is currently unable to handle this request. – HTTP ERROR 500”
When the option to display errors to the user is enabled, and the execution is not interrupted, the server can provide more comprehensive information about errors than when the user encounters a WSOD (White Screen Of Death).
In such cases, the server may display crucial details related to the error, like the file and line number where the error occurred, a description of the error, and sometimes a stack trace.
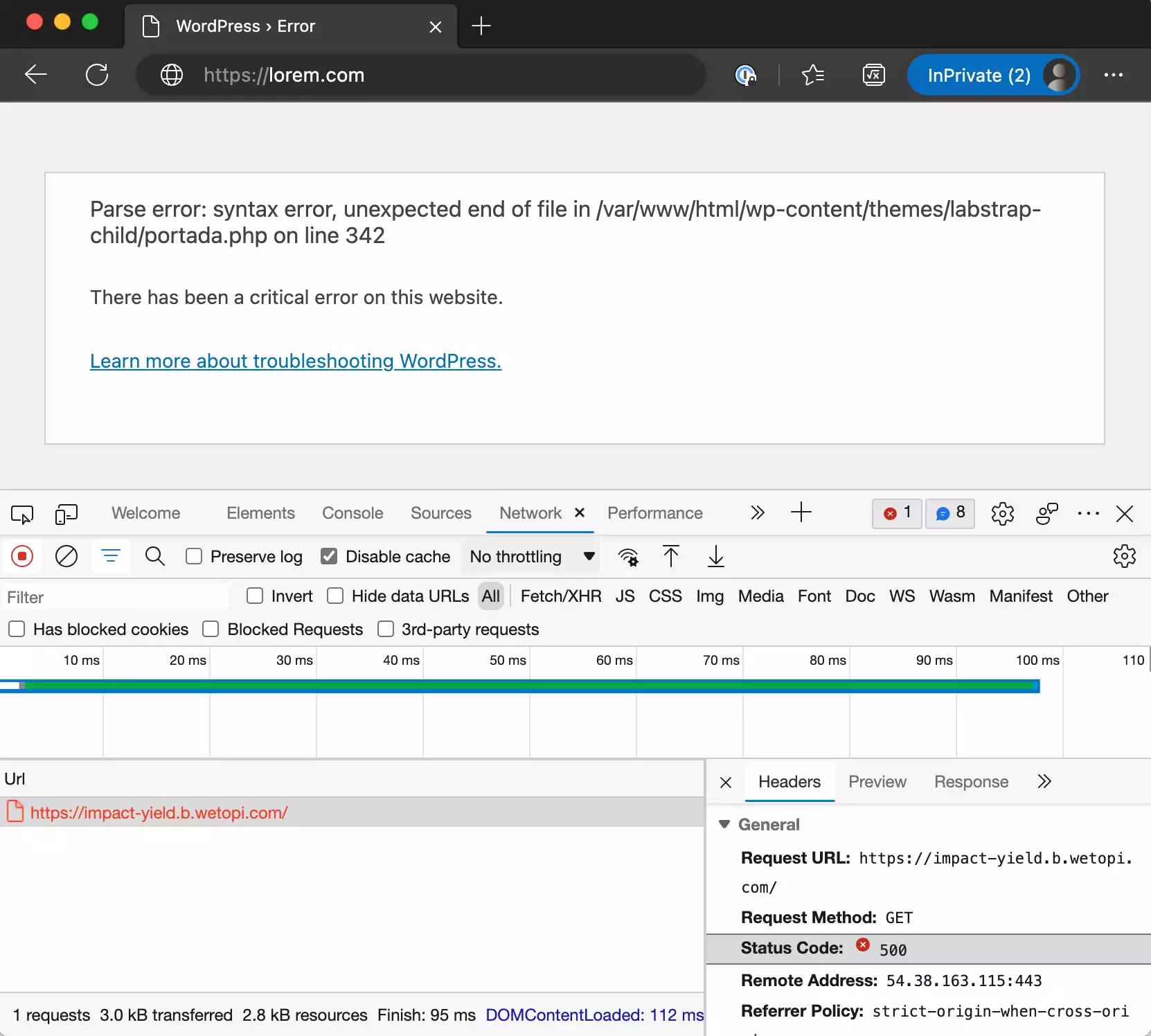
The following screenshot shows an example of this, detailing a 500 internal server error on a WordPress page:
In the following section, you will come across various scenarios that can lead to the occurrence of the 500 error.
500 Internal Server Error Causes
- A Database error while trying to retrieve data. E.g a corrupted Database, or a wrong SQL syntax.
- The application throws an error, such as a runtime error, e.g. an insufficient PHP memory, or a PHP execution timeout.
- There is an error in the application code. For instance, PHP is trying to include a nonexisting file, or a division by zero is interrupting the execution.
- Your server hardware could have a problem. For instance, you have corrupted files due to a disk failure.
- There is a server software problem. For instance,
php-fpmis misconfigured or your current version has a bug.
How To Fix The 500 Internal Error
As mentioned in the previous section, the causes of the 500 error can be diverse and not always apparent in the browser.
To solve it, check the error logs or print them in the browser for further diagnosis.
When it comes to
500 Internal Server Errors,
there’s no one-size-fits-all solution.Checking error logs can help identify the root cause.
How To Get More Details About The Errors In PHP
The answer is simple: display the errors or inspect the logs. The latter option is preferable, as a 500 internal server error can sometimes cause the execution to break, resulting in nothing but a WSOD (White Screen Of Death).
Hey, just a heads up!
If you have a WordPress website hosted on a Wetopi server,
you can easily access your logs with
just a click of your mouse.

To enable the logs here you have two options: the first one for generic PHP applications and the second one for sites running WordPress.
How to show and log errors in plain PHP applications
- Enable error reporting: add the following line to the beginning of your PHP script:
error_reporting(E_ALL); - Display errors by adding this
ini_set('display_errors', 1); - And log error setting these two options:
ini_set('log_errors', 'On');
ini_set('error_log', '/path/to/php_errors.log');
Additonally, you can also set these directives in the PHP configuration file php.ini
error_reporting = E_ALL
display_errors = On
log_errors = On
error_log = /path/to/php_errors.logHow to show PHP errors in WordPress
You can use the WP_DEBUG constant in th wp-config.php file to show PHP errors with WordPress.This will enable debug mode in WordPress and display all PHP Errors, Warnings, and Notices on the screen.
- Locate the
wp-config.phpfile: This file is in the root directory of your WordPress installation. - Open the
wp-config.phpfile: You can open this file using a text editor such as Notepad, TextEdit, or Sublime Text. - Add the WP_DEBUG constant to display the errors:
define('WP_DEBUG', true); - And or enable the debug logging to the /wp-content/debug.log with this next constant:
define( 'WP_DEBUG_LOG', true ); - Save the wp-config.php file.
You can get a more detailed explanation and refined configurations in the wordpress.org debugging documentation.
Microsoft Internet Information Services IIS shows 500 error details
If your web server is a Microsoft IIS; versions 7.0 and later have a subset of 500.XX HTTP error codes that indicate a more specific cause of error 500. This subcategory of 500 error codes will help you identify the cause of the error.
One final tip:
When inspecting logs look at the right place
When 500 internal server error occur in PHP, it is considered an Error level message rather than a Warning or Notice. Therefore, when examining logs or debugging screens for troubleshooting purposes, focus exclusively on Errors and skip Warning and Notice messages.
All HTTP Status Codes
200 OK
201 Created
202 Accepted
203 Non-Authoritative Information
204 No Content
205 Reset Content
206 Partial Content
207 Multi-Status
208 Already Reported
226 IM Used
300 Multiple Choices
301 Moved Permanently
302 Found
303 See Other
304 Not Modified
305 Use Proxy
307 Temporary Redirect
308 Permanent Redirect
400 Bad Request
401 Unauthorized
402 Payment Required
403 Forbidden
404 Not Found
405 Method Not Allowed
406 Not Acceptable
407 Proxy Authentication Required
408 Request Timeout
409 Conflict
410 Gone
411 Length Required
412 Precondition Failed
413 Payload Too Large
414 Request-URI Too Long
415 Unsupported Media Type
416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
417 Expectation Failed
418 I’m A Teapot
421 Misdirected Request
422 Unprocessable Entity
423 Locked
424 Failed Dependency
426 Upgrade Required
428 Precondition Required
429 Too Many Requests
431 Request Header Fields Too Large
444 Connection Closed Without Response
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
499 Client Closed Request
We are techies passionate about WordPress. With wetopi, a Managed WordPress Hosting, we want to minimize the friction that every professional faces when working and hosting WordPress projects.
Not a wetopi user?
Free full performance servers for your development and test.
No credit card required.