Your function would work like this:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount int)
LANGUAGE plpgsql AS
$func$
BEGIN
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH v_tb_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM v_tb_person WHERE nome LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM v_tb_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;
END
$func$;
Call:
SELECT * FROM prc_tst_bulk($$SELECT a AS name, b AS nome, c AS gender FROM tbl$$)
You cannot mix plain and dynamic SQL the way you tried to do it. The whole statement is either all dynamic or all plain SQL. So I am building one dynamic statement to make this work. You may be interested in the chapter about executing dynamic commands in the manual.
The aggregate function count() returns bigint, but you had rowcount defined as integer, so you need an explicit cast ::int to make this work.
I use dollar quoting to avoid quoting hell.
However, is this supposed to be a honeypot for SQL injection attacks or are you seriously going to use it? For your very private and secure use, it might be ok-ish — though I wouldn’t even trust myself with a function like that. If there is any possible access for untrusted users, such a function is a loaded footgun. It’s impossible to make this secure.
Craig (a sworn enemy of SQL injection) might get a light stroke when he sees what you forged from his answer to your preceding question. 
The query itself seems rather odd, btw. The two SELECT terms might be merged into one. But that’s beside the point here.
| Error Code | Condition Name |
|---|---|
| Class 00 — Successful Completion | |
00000 |
successful_completion |
| Class 01 — Warning | |
01000 |
warning |
0100C |
dynamic_result_sets_returned |
01008 |
implicit_zero_bit_padding |
01003 |
null_value_eliminated_in_set_function |
01007 |
privilege_not_granted |
01006 |
privilege_not_revoked |
01004 |
string_data_right_truncation |
01P01 |
deprecated_feature |
| Class 02 — No Data (this is also a warning class per the SQL standard) | |
02000 |
no_data |
02001 |
no_additional_dynamic_result_sets_returned |
| Class 03 — SQL Statement Not Yet Complete | |
03000 |
sql_statement_not_yet_complete |
| Class 08 — Connection Exception | |
08000 |
connection_exception |
08003 |
connection_does_not_exist |
08006 |
connection_failure |
08001 |
sqlclient_unable_to_establish_sqlconnection |
08004 |
sqlserver_rejected_establishment_of_sqlconnection |
08007 |
transaction_resolution_unknown |
08P01 |
protocol_violation |
| Class 09 — Triggered Action Exception | |
09000 |
triggered_action_exception |
| Class 0A — Feature Not Supported | |
0A000 |
feature_not_supported |
| Class 0B — Invalid Transaction Initiation | |
0B000 |
invalid_transaction_initiation |
| Class 0F — Locator Exception | |
0F000 |
locator_exception |
0F001 |
invalid_locator_specification |
| Class 0L — Invalid Grantor | |
0L000 |
invalid_grantor |
0LP01 |
invalid_grant_operation |
| Class 0P — Invalid Role Specification | |
0P000 |
invalid_role_specification |
| Class 0Z — Diagnostics Exception | |
0Z000 |
diagnostics_exception |
0Z002 |
stacked_diagnostics_accessed_without_active_handler |
| Class 20 — Case Not Found | |
20000 |
case_not_found |
| Class 21 — Cardinality Violation | |
21000 |
cardinality_violation |
| Class 22 — Data Exception | |
22000 |
data_exception |
2202E |
array_subscript_error |
22021 |
character_not_in_repertoire |
22008 |
datetime_field_overflow |
22012 |
division_by_zero |
22005 |
error_in_assignment |
2200B |
escape_character_conflict |
22022 |
indicator_overflow |
22015 |
interval_field_overflow |
2201E |
invalid_argument_for_logarithm |
22014 |
invalid_argument_for_ntile_function |
22016 |
invalid_argument_for_nth_value_function |
2201F |
invalid_argument_for_power_function |
2201G |
invalid_argument_for_width_bucket_function |
22018 |
invalid_character_value_for_cast |
22007 |
invalid_datetime_format |
22019 |
invalid_escape_character |
2200D |
invalid_escape_octet |
22025 |
invalid_escape_sequence |
22P06 |
nonstandard_use_of_escape_character |
22010 |
invalid_indicator_parameter_value |
22023 |
invalid_parameter_value |
22013 |
invalid_preceding_or_following_size |
2201B |
invalid_regular_expression |
2201W |
invalid_row_count_in_limit_clause |
2201X |
invalid_row_count_in_result_offset_clause |
2202H |
invalid_tablesample_argument |
2202G |
invalid_tablesample_repeat |
22009 |
invalid_time_zone_displacement_value |
2200C |
invalid_use_of_escape_character |
2200G |
most_specific_type_mismatch |
22004 |
null_value_not_allowed |
22002 |
null_value_no_indicator_parameter |
22003 |
numeric_value_out_of_range |
2200H |
sequence_generator_limit_exceeded |
22026 |
string_data_length_mismatch |
22001 |
string_data_right_truncation |
22011 |
substring_error |
22027 |
trim_error |
22024 |
unterminated_c_string |
2200F |
zero_length_character_string |
22P01 |
floating_point_exception |
22P02 |
invalid_text_representation |
22P03 |
invalid_binary_representation |
22P04 |
bad_copy_file_format |
22P05 |
untranslatable_character |
2200L |
not_an_xml_document |
2200M |
invalid_xml_document |
2200N |
invalid_xml_content |
2200S |
invalid_xml_comment |
2200T |
invalid_xml_processing_instruction |
22030 |
duplicate_json_object_key_value |
22031 |
invalid_argument_for_sql_json_datetime_function |
22032 |
invalid_json_text |
22033 |
invalid_sql_json_subscript |
22034 |
more_than_one_sql_json_item |
22035 |
no_sql_json_item |
22036 |
non_numeric_sql_json_item |
22037 |
non_unique_keys_in_a_json_object |
22038 |
singleton_sql_json_item_required |
22039 |
sql_json_array_not_found |
2203A |
sql_json_member_not_found |
2203B |
sql_json_number_not_found |
2203C |
sql_json_object_not_found |
2203D |
too_many_json_array_elements |
2203E |
too_many_json_object_members |
2203F |
sql_json_scalar_required |
2203G |
sql_json_item_cannot_be_cast_to_target_type |
| Class 23 — Integrity Constraint Violation | |
23000 |
integrity_constraint_violation |
23001 |
restrict_violation |
23502 |
not_null_violation |
23503 |
foreign_key_violation |
23505 |
unique_violation |
23514 |
check_violation |
23P01 |
exclusion_violation |
| Class 24 — Invalid Cursor State | |
24000 |
invalid_cursor_state |
| Class 25 — Invalid Transaction State | |
25000 |
invalid_transaction_state |
25001 |
active_sql_transaction |
25002 |
branch_transaction_already_active |
25008 |
held_cursor_requires_same_isolation_level |
25003 |
inappropriate_access_mode_for_branch_transaction |
25004 |
inappropriate_isolation_level_for_branch_transaction |
25005 |
no_active_sql_transaction_for_branch_transaction |
25006 |
read_only_sql_transaction |
25007 |
schema_and_data_statement_mixing_not_supported |
25P01 |
no_active_sql_transaction |
25P02 |
in_failed_sql_transaction |
25P03 |
idle_in_transaction_session_timeout |
| Class 26 — Invalid SQL Statement Name | |
26000 |
invalid_sql_statement_name |
| Class 27 — Triggered Data Change Violation | |
27000 |
triggered_data_change_violation |
| Class 28 — Invalid Authorization Specification | |
28000 |
invalid_authorization_specification |
28P01 |
invalid_password |
| Class 2B — Dependent Privilege Descriptors Still Exist | |
2B000 |
dependent_privilege_descriptors_still_exist |
2BP01 |
dependent_objects_still_exist |
| Class 2D — Invalid Transaction Termination | |
2D000 |
invalid_transaction_termination |
| Class 2F — SQL Routine Exception | |
2F000 |
sql_routine_exception |
2F005 |
function_executed_no_return_statement |
2F002 |
modifying_sql_data_not_permitted |
2F003 |
prohibited_sql_statement_attempted |
2F004 |
reading_sql_data_not_permitted |
| Class 34 — Invalid Cursor Name | |
34000 |
invalid_cursor_name |
| Class 38 — External Routine Exception | |
38000 |
external_routine_exception |
38001 |
containing_sql_not_permitted |
38002 |
modifying_sql_data_not_permitted |
38003 |
prohibited_sql_statement_attempted |
38004 |
reading_sql_data_not_permitted |
| Class 39 — External Routine Invocation Exception | |
39000 |
external_routine_invocation_exception |
39001 |
invalid_sqlstate_returned |
39004 |
null_value_not_allowed |
39P01 |
trigger_protocol_violated |
39P02 |
srf_protocol_violated |
39P03 |
event_trigger_protocol_violated |
| Class 3B — Savepoint Exception | |
3B000 |
savepoint_exception |
3B001 |
invalid_savepoint_specification |
| Class 3D — Invalid Catalog Name | |
3D000 |
invalid_catalog_name |
| Class 3F — Invalid Schema Name | |
3F000 |
invalid_schema_name |
| Class 40 — Transaction Rollback | |
40000 |
transaction_rollback |
40002 |
transaction_integrity_constraint_violation |
40001 |
serialization_failure |
40003 |
statement_completion_unknown |
40P01 |
deadlock_detected |
| Class 42 — Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation | |
42000 |
syntax_error_or_access_rule_violation |
42601 |
syntax_error |
42501 |
insufficient_privilege |
42846 |
cannot_coerce |
42803 |
grouping_error |
42P20 |
windowing_error |
42P19 |
invalid_recursion |
42830 |
invalid_foreign_key |
42602 |
invalid_name |
42622 |
name_too_long |
42939 |
reserved_name |
42804 |
datatype_mismatch |
42P18 |
indeterminate_datatype |
42P21 |
collation_mismatch |
42P22 |
indeterminate_collation |
42809 |
wrong_object_type |
428C9 |
generated_always |
42703 |
undefined_column |
42883 |
undefined_function |
42P01 |
undefined_table |
42P02 |
undefined_parameter |
42704 |
undefined_object |
42701 |
duplicate_column |
42P03 |
duplicate_cursor |
42P04 |
duplicate_database |
42723 |
duplicate_function |
42P05 |
duplicate_prepared_statement |
42P06 |
duplicate_schema |
42P07 |
duplicate_table |
42712 |
duplicate_alias |
42710 |
duplicate_object |
42702 |
ambiguous_column |
42725 |
ambiguous_function |
42P08 |
ambiguous_parameter |
42P09 |
ambiguous_alias |
42P10 |
invalid_column_reference |
42611 |
invalid_column_definition |
42P11 |
invalid_cursor_definition |
42P12 |
invalid_database_definition |
42P13 |
invalid_function_definition |
42P14 |
invalid_prepared_statement_definition |
42P15 |
invalid_schema_definition |
42P16 |
invalid_table_definition |
42P17 |
invalid_object_definition |
| Class 44 — WITH CHECK OPTION Violation | |
44000 |
with_check_option_violation |
| Class 53 — Insufficient Resources | |
53000 |
insufficient_resources |
53100 |
disk_full |
53200 |
out_of_memory |
53300 |
too_many_connections |
53400 |
configuration_limit_exceeded |
| Class 54 — Program Limit Exceeded | |
54000 |
program_limit_exceeded |
54001 |
statement_too_complex |
54011 |
too_many_columns |
54023 |
too_many_arguments |
| Class 55 — Object Not In Prerequisite State | |
55000 |
object_not_in_prerequisite_state |
55006 |
object_in_use |
55P02 |
cant_change_runtime_param |
55P03 |
lock_not_available |
55P04 |
unsafe_new_enum_value_usage |
| Class 57 — Operator Intervention | |
57000 |
operator_intervention |
57014 |
query_canceled |
57P01 |
admin_shutdown |
57P02 |
crash_shutdown |
57P03 |
cannot_connect_now |
57P04 |
database_dropped |
57P05 |
idle_session_timeout |
| Class 58 — System Error (errors external to PostgreSQL itself) | |
58000 |
system_error |
58030 |
io_error |
58P01 |
undefined_file |
58P02 |
duplicate_file |
| Class 72 — Snapshot Failure | |
72000 |
snapshot_too_old |
| Class F0 — Configuration File Error | |
F0000 |
config_file_error |
F0001 |
lock_file_exists |
| Class HV — Foreign Data Wrapper Error (SQL/MED) | |
HV000 |
fdw_error |
HV005 |
fdw_column_name_not_found |
HV002 |
fdw_dynamic_parameter_value_needed |
HV010 |
fdw_function_sequence_error |
HV021 |
fdw_inconsistent_descriptor_information |
HV024 |
fdw_invalid_attribute_value |
HV007 |
fdw_invalid_column_name |
HV008 |
fdw_invalid_column_number |
HV004 |
fdw_invalid_data_type |
HV006 |
fdw_invalid_data_type_descriptors |
HV091 |
fdw_invalid_descriptor_field_identifier |
HV00B |
fdw_invalid_handle |
HV00C |
fdw_invalid_option_index |
HV00D |
fdw_invalid_option_name |
HV090 |
fdw_invalid_string_length_or_buffer_length |
HV00A |
fdw_invalid_string_format |
HV009 |
fdw_invalid_use_of_null_pointer |
HV014 |
fdw_too_many_handles |
HV001 |
fdw_out_of_memory |
HV00P |
fdw_no_schemas |
HV00J |
fdw_option_name_not_found |
HV00K |
fdw_reply_handle |
HV00Q |
fdw_schema_not_found |
HV00R |
fdw_table_not_found |
HV00L |
fdw_unable_to_create_execution |
HV00M |
fdw_unable_to_create_reply |
HV00N |
fdw_unable_to_establish_connection |
| Class P0 — PL/pgSQL Error | |
P0000 |
plpgsql_error |
P0001 |
raise_exception |
P0002 |
no_data_found |
P0003 |
too_many_rows |
P0004 |
assert_failure |
| Class XX — Internal Error | |
XX000 |
internal_error |
XX001 |
data_corrupted |
XX002 |
index_corrupted |
I have a table address_all and it is inherited by several address tables. address_history inherits from parent table history_all and keeps current address information. I am creating new table which inherits address_all table and copies information from address_history to new table.
My stored procedure is like this below. I am having some error when I call it. To better explain error I am using line number.
1 CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION somefunc()
2 RETURNS void AS
3 $BODY$
4 DECLARE
5 year_id INTEGER;
6 month_id INTEGER;
7 week_id INTEGER;
8 addresstablename text;
9 backupdays text;
10 BEGIN
11 week_id := EXTRACT(DAY FROM TIMESTAMP 'now()');
12 month_id := EXTRACT(MONTH FROM TIMESTAMP 'now()');
13 year_id := EXTRACT(YEAR FROM TIMESTAMP 'now()');
14 addresstablename := 'address_history_' || week_id || '_' || month_id || '_' || year_id;
15 backupdays:= date_trunc('hour',CURRENT_TIMESTAMP - interval '7 days');
16 EXECUTE 'create table ' || addresstablename || '() INHERITS (address_all)';
17 EXECUTE 'insert into ' || addresstablename || ' select * from address_history where address_timestamp >= ' || backupdays || ''; --AS timestamp without time zone);
18 END;
19 $BODY$
20 LANGUAGE 'plpgsql' VOLATILE;
When I run:
select somefunc()
I get this error:
ERROR: syntax error at or near "12"
LINE 1: ...story where address_timestamp >= 2012-07-31 12:00:00-0...
^
QUERY: insert into address_history_7_8_2012 select * from address_history where address_timestamp >= 2012-07-31 12:00:00-04
CONTEXT: PL/pgSQL function "somefunc" line 14 at EXECUTE statement
********** Error **********
ERROR: syntax error at or near "12"
SQL state: 42601
Context: PL/pgSQL function "somefunc" line 14 at EXECUTE statement
asked Aug 7, 2012 at 16:24
Try this largely simplified form:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION somefunc()
RETURNS void AS
$func$
DECLARE
addresstablename text := 'address_history_' || to_char(now(), 'FMDD_MM_YYYY');
BEGIN
EXECUTE
'CREATE TABLE ' || addresstablename || '() INHERITS (address_all)';
EXECUTE
'INSERT INTO ' || addresstablename || '
SELECT *
FROM address_history
WHERE address_timestamp >= $1'
USING date_trunc('hour', now() - interval '7 days');
END
$func$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
Major points:
-
You can assign variables in plpgsql at declaration time. Simplifies code.
-
Use
to_char()to format your date. Much simpler. -
now()andCURRENT_TIMESTAMPdo the same. -
Don’t quote
'now()', usenow()(without quotes) if you want the current timestamp. -
Use the
USINGclause withEXECUTE, so you don’t have to convert thetimestamptotextand back — possibly running into quoting issues like you did. Faster, simpler, safer. -
In
LANGUAGE plpgsql,plpgsqlis a keyword and should not be quoted. -
You may want to check if the table already exists with
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS, available since PostgreSQL 9.1.
answered Aug 7, 2012 at 17:05
Erwin BrandstetterErwin Brandstetter
608k145 gold badges1083 silver badges1232 bronze badges
1
Apparently you need to quote backupdays, or it is not seen as a string from where to parse a timestamp.
answered Aug 7, 2012 at 16:27
LSerniLSerni
55.7k10 gold badges65 silver badges107 bronze badges
0
You’re building SQL using string manipulation so you have to properly quote everything just like in any other language. There are a few functions that you’ll want to know about:
quote_ident: quote an identifier such as a table name.quote_literal: quote a string to use as a string literal.quote_nullable: asquote_literalbut properly handles NULLs as well.
Something like this will server you better:
EXECUTE 'create table ' || quote_ident(addresstablename) || ...
EXECUTE 'insert into ' || quote_ident(addresstablename) || ... || quote_literal(backupdays) ...
The quote_ident calls aren’t necessary in your case but they’re a good habit.
answered Aug 7, 2012 at 17:07
mu is too shortmu is too short
427k70 gold badges834 silver badges801 bronze badges
5
Добрый вечер. Есть выражение:
$this->insertStmt = $this->connection->getPdo()->prepare("
INSERT INTO files (
real_name,
virtual_name,
album,
size,
resolution,
duration,
comment,
path,
user
) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
");Которое вызывается как обычно:
protected function doInsert(object $object)
{
$values = [
$object->getRealName(),
$object->getVirtualName(),
$object->getAlbum(),
$object->getSize(),
$object->getResolution(),
$object->getDuration(),
$object->getComment(),
$object->getPath(),
$object->getUser(),
];
$this->insertStmt->execute($values);
}Примерное содержание $values:
array(9) {
[0]=> string(15) "BvrK9z6UPxY.jpg"
[1]=> string(16) "1265dde1c67abc1c"
[2]=> string(23) "По умолчанию"
[3]=> int(54973)
[4]=> string(7) "720x430"
[5]=> NULL
[6]=> string(0) ""
[7]=> string(108) "files/id5cd487313a93a/По умолчанию/2019-05-10/1265dde1c67abc1c.jpg"
[8]=> string(15) "id5cd487313a93a"
}Сообщение ошибки:
Type: PDOException
Code: 42601
Message: SQLSTATE[42601]: Syntax error: 7 ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: "user") LINE 11: user ^С точки зрения синтаксиса вроде все верно, много раз перепроверил, IDE ни на что не ругается. В чем трабл, господа?
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
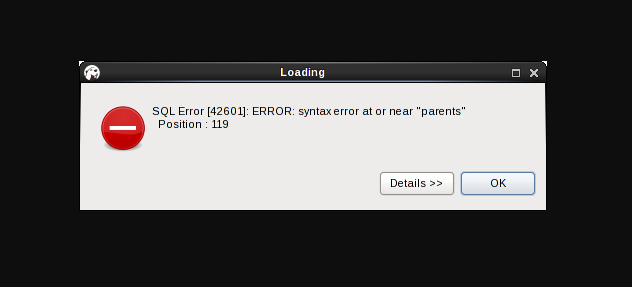
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:
Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
Содержание
- PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
- What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
- How we fix the error?
- Conclusion
- PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
- 10 Comments
PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
by Sijin George | Sep 12, 2019
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:
Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
SELECT * FROM long_term_prediction_anomaly WHERE + “‘Timestamp’” + ‘”BETWEEN ‘” +
2019-12-05 09:10:00+ ‘”AND’” + 2019-12-06 09:10:00 + “‘;”)
Hello Joe,
Do you still get PostgreSQL errors? If you need help, we’ll be happy to talk to you on chat (click on the icon at right-bottom).
У меня ошибка drop table exists “companiya”;
CREATE TABLE “companiya” (
“compania_id” int4 NOT NULL,
“fio vladelca” text NOT NULL,
“name” text NOT NULL,
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_8” PRIMARY KEY (“compania_id”)
);
CREATE TABLE “filial” (
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
“street” text NOT NULL,
“house” int4 NOT NULL,
“city” text NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_5” PRIMARY KEY (“id_filial”)
);
CREATE TABLE “login” (
“id_name” int4 NOT NULL,
“name” char(20) NOT NULL,
“pass” char(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (“id_name”)
);
CREATE TABLE “operator” (
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“obrabotka obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“konsultirovanie” text NOT NULL,
“grafick work” date NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_2” PRIMARY KEY (“id_operator”)
);
CREATE TABLE “polsovateli” (
“id_user” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_companiya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_oshibka” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_6” PRIMARY KEY (“id_user”)
);
CREATE TABLE “reklama” (
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“tele-marketing” text NOT NULL,
“soc-seti” text NOT NULL,
“mobile” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_3” PRIMARY KEY (“id_reklama”)
);
CREATE TABLE “tex-specialist” (
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“grafik” date NOT NULL,
“zarplata” int4 NOT NULL,
“ispravlenie oshibok” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_7” PRIMARY KEY (“id_tex-specialist”)
);
CREATE TABLE “uslugi” (
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“vostanavlenia parola” int4 NOT NULL,
“poterya acaunta” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_4” PRIMARY KEY (“id_uslugi”)
);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_operator_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_operator”) REFERENCES “operator” (“id_operator”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_uslugi_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_uslugi”) REFERENCES “uslugi” (“id_uslugi”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_filial_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_filial”) REFERENCES “filial” (“id_filial”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_reklama_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_reklama”) REFERENCES “reklama” (“id_reklama”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_tex-specialist_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_tex-specialist”) REFERENCES “tex-specialist” (“id_tex-specialist”);
ALTER TABLE “polsovateli” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_polsovateli_companiya_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_companiya”) REFERENCES “companiya” (“compania_id”);
ERROR: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: “”companiya””)
LINE 1: drop table exists “companiya”;
^
Источник
@YohDeadfall — I understand that part about it, but this is not script that I am creating or even code that I am creating. This is all created under the hood by Npsql/EntityFramework. My quick guess is that I am extending my DbContext from IdentityDbContext<IdentityUser> which wants to create all of the tables for roles, users, claims, etc. If I change this to just extend from DbContext, then everything works as advertised.
Below is the script that EF is trying to use created from dotnet ef migrations script — please be aware that I have removed my custom part of the script for brevity.
You can see there are two specific calls that are being made where [NormalizedName] and [NormalizedUserName] are being used.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "__EFMigrationsHistory" ( "MigrationId" varchar(150) NOT NULL, "ProductVersion" varchar(32) NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK___EFMigrationsHistory" PRIMARY KEY ("MigrationId") ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetRoles" ( "Id" text NOT NULL, "ConcurrencyStamp" text NULL, "Name" varchar(256) NULL, "NormalizedName" varchar(256) NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetRoles" PRIMARY KEY ("Id") ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUsers" ( "Id" text NOT NULL, "AccessFailedCount" int4 NOT NULL, "ConcurrencyStamp" text NULL, "Email" varchar(256) NULL, "EmailConfirmed" bool NOT NULL, "LockoutEnabled" bool NOT NULL, "LockoutEnd" timestamptz NULL, "NormalizedEmail" varchar(256) NULL, "NormalizedUserName" varchar(256) NULL, "PasswordHash" text NULL, "PhoneNumber" text NULL, "PhoneNumberConfirmed" bool NOT NULL, "SecurityStamp" text NULL, "TwoFactorEnabled" bool NOT NULL, "UserName" varchar(256) NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUsers" PRIMARY KEY ("Id") ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetRoleClaims" ( "Id" int4 NOT NULL, "ClaimType" text NULL, "ClaimValue" text NULL, "RoleId" text NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetRoleClaims" PRIMARY KEY ("Id"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetRoleClaims_AspNetRoles_RoleId" FOREIGN KEY ("RoleId") REFERENCES "AspNetRoles" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUserClaims" ( "Id" int4 NOT NULL, "ClaimType" text NULL, "ClaimValue" text NULL, "UserId" text NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUserClaims" PRIMARY KEY ("Id"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserClaims_AspNetUsers_UserId" FOREIGN KEY ("UserId") REFERENCES "AspNetUsers" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUserLogins" ( "LoginProvider" text NOT NULL, "ProviderKey" text NOT NULL, "ProviderDisplayName" text NULL, "UserId" text NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUserLogins" PRIMARY KEY ("LoginProvider", "ProviderKey"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserLogins_AspNetUsers_UserId" FOREIGN KEY ("UserId") REFERENCES "AspNetUsers" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUserRoles" ( "UserId" text NOT NULL, "RoleId" text NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUserRoles" PRIMARY KEY ("UserId", "RoleId"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserRoles_AspNetRoles_RoleId" FOREIGN KEY ("RoleId") REFERENCES "AspNetRoles" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE, CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserRoles_AspNetUsers_UserId" FOREIGN KEY ("UserId") REFERENCES "AspNetUsers" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUserTokens" ( "UserId" text NOT NULL, "LoginProvider" text NOT NULL, "Name" text NOT NULL, "Value" text NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUserTokens" PRIMARY KEY ("UserId", "LoginProvider", "Name"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserTokens_AspNetUsers_UserId" FOREIGN KEY ("UserId") REFERENCES "AspNetUsers" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE INDEX "IX_AspNetRoleClaims_RoleId" ON "AspNetRoleClaims" ("RoleId"); CREATE UNIQUE INDEX "RoleNameIndex" ON "AspNetRoles" ("NormalizedName") WHERE [NormalizedName] IS NOT NULL; CREATE INDEX "IX_AspNetUserClaims_UserId" ON "AspNetUserClaims" ("UserId"); CREATE INDEX "IX_AspNetUserLogins_UserId" ON "AspNetUserLogins" ("UserId"); CREATE INDEX "IX_AspNetUserRoles_RoleId" ON "AspNetUserRoles" ("RoleId"); CREATE INDEX "EmailIndex" ON "AspNetUsers" ("NormalizedEmail"); CREATE UNIQUE INDEX "UserNameIndex" ON "AspNetUsers" ("NormalizedUserName") WHERE [NormalizedUserName] IS NOT NULL; INSERT INTO "__EFMigrationsHistory" ("MigrationId", "ProductVersion") VALUES ('20180514204732_initial', '2.0.3-rtm-10026');