13.1К
просмотров
Часто общаясь с разными интернет маркетологами и SEO специалистами, пришел к выводу, что они не придают значению 404 SOFT ошибкам. То есть, все нацелены, как всегда, на ROI, ROMI, KPI. Все хотят крутой контент. Новые посадочные под новые семантические интенты. И конечно, всем нужно крутые беклинки. Куда ж без них?
И, как ни странно, часто проходят мимо обычных технических вопросов, которые могут убить все ваше SEO—ШМЕО на корню. Один из таких технических моментов – это то, как Googlebot обходит сайт (как он краулит страницы). В данной статье поговорим про 404 SOFT ошибки и как сильно они влияют на ваше продвижение.
Давайте разбираться! Вероятно, вы уже видели страницы типа этой:
Это стандартная страница для 404 ошибки в интернет магазине f.ua.
Каждый раз, когда отображается сообщение об ошибке 404 или Not Found, сервер должен вернуть стандартный код ответа HTTP 404. Код ответа сервера 404 указывает на то, что он (сервер) не смог найти запрошенный URL.
Этот код сообщает браузеру и поисковым системам, что данная страница не существует. В результате содержимое страницы, если оно есть, не будет сканироваться поисковыми системами (это написано в справке Google).
В приведенном выше примере сервер f.ua отображает страницы 404 для всех несуществующих URL. Четко виден специально разработанный дизайн, где представлены акции магазина, чтобы пользователь не ушел с сайта мгновенно. Это стандартная практика в е-коммерсе, где важен каждый посетитель.
К сожалению, большинство специалистов, которые так или иначе вовлечены в процесс продвижения сайтов, не понимают, что сообщение «страница не найдена» – никак не связано с HTTP-ответом, который возвращает сервер. Еще раз, совсем не означает, что страница автоматически определяется, как страница 404 всего лишь по сообщению 404 File Not Found.
Ошибка «Soft 404» возникает всякий раз, когда:
– несуществующая страница (или страница, которая была удалена) не возвращает код ответа HTTP 404 по требованию пользователя или бота;
– несуществующая страница перенаправляет пользователей на нерелевантную страницу;
– когда страница пустая, на ней нет контента
Какие проблемы с 404 SOFT
Если для несуществующей страницы возвращается HTTP статус отличный от 404 (или 410), то это может негативно влиять на ранжирование всего сайта в Google поиске. Во-первых, если вы не предоставите код ответа 404, ваш сайт сообщит поисковым системам, что есть реальная страница по адресу, который они пытаются получить. В результате URL, который вы удалили, будет просканирован и проиндексирован. В итоге, вы теряете ценный бюджет краулера.
Бюджет краулинга – это концепция, согласно которой, Google ограниченное время сканирует веб-сайт прежде чем остановит процесс и перейдет на другой ресурс. Google не хочет бесконечно тратить время на сканирование контента на одном и том же сайте. Поэтому имеет смысл сделать все возможное, чтоб Google сканировал в первую очередь только новые или измененные страницы.
Исходя из концепции краулингового бюджета, процесс обхода 404 SOFT страниц неизбежно займет драгоценные лимиты сканирования. Иными словами, вместо того, чтоб сканировать нужные вам URLs, Googlebot будет сканировать Soft 404 ошибки. А это уже снижает видимость важного контента на вашем сайте. Поэтому, неудивительно, что при устранении ошибок Soft 404 наблюдается тенденция к улучшению ранжирования сайта в SERP Google.
Второе, что не менее важное – это потеря линкджуса. Как Ведущий Участник справочных форумов Google “Для веб-мастеров” и “Поиск“ наблюдал такую практику: карточку товара интернет магазина перенаправляют на главную страницу или на страницу категории (делают 301/302 редирект). Это делают для старых карточек товара, на которых есть ссылочная масса. В данном случае это совсем неуместно и будет путать поисковых роботов. Ключевой момент в том то, что удаленные или недоступные страницы должны перенаправляться только на страницы с аналогичным контентом. Если прямой замены не существует, то сервер должен возвратить 404 HTTP статус для такого типа URL
Еще одной плохой практикой является следующее: вебмастер перенаправляет удаленные или не найденные страницы на кастомную 404 страницу, которая отдает код ответа сервера 200. В данном случае прослеживается четкий интент вебмастера: желание сохранить ссылочный вес удаленных/не найденных страниц благодаря перелинковке на фейковой 404й странице. Все это приведет к тому, что Google пометить данную кастомную страницу как 404 SOFT ошибку и никакого перераспределения ссылочного веса не произойдет.
Например среди топовых интернет магазинов Украины эта болезнь у Комфи, а у Розетки дела обстоят немного хуже.
Как решать проблемы с 404 софт ошибками?
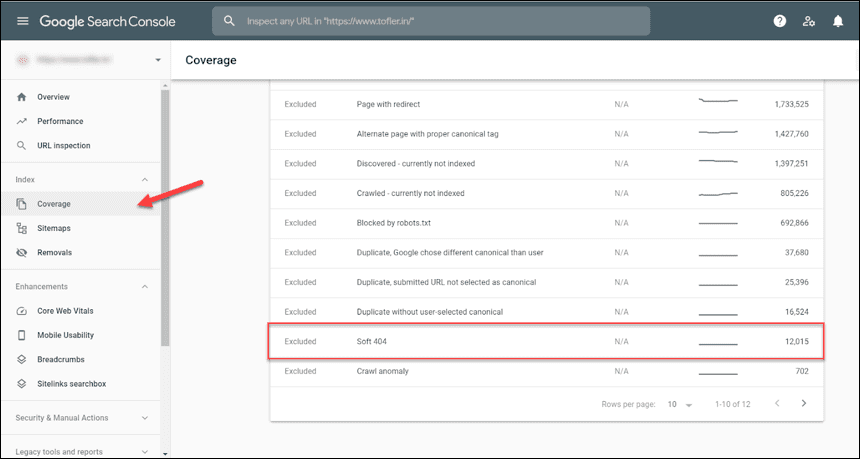
Первое, что нужно сделать – это выгрузить все 404 из Google Search Console
В приведенном выше примере сообщается о 5915 ошибках “не найдено” и 2х 404 soft ошибках. Нам понадобятся для анализа эти 2 отчета.
Google позволяет экспортировать максимум 1000 URL-адресов в Инструментах для веб-мастеров. Поэтому в таком случае работать нужно итерационно: проработайте первую 1000 – нажмите исправлено, через время Google обновит данный отчет и вы сможете проработать следующие 1000 результатов.
После того, как вы выгрузите список URL-адресов, вам нужно будет оценить, почему эти страницы помечены как 404. Google предоставляет несколько ограниченную информацию о URL-адресах, которые они выделяют как “Soft 404” (см пример ниже).
Желательно массово проверить УРЛы, чтоб понять, какой код ответа сервера они возвращают. Я использую для этих целей https://httpstatus.io/.
В большинстве случаев вы обнаружите, что такие страницы возвращают код ответа сервера 200 (OK). Это яркий пример ошибки Soft 404, поскольку код ответа HTTP указывает роботам Google, что эта страница существует и должна быть просканирована. Однако на странице нет содержимого, возвращаемого сервером.
Решение: отдавать для такого типа страниц код ответа сервера 404
Другая проблема, с которой вы можете столкнуться при диагностике основной причины ошибок Soft 404, – это неуместные 301/302 перенаправления (пример, как это может быть, описана выше).
Решение: либо отдавайте для таких страниц код ответа сервера 404 и теряйте linkjuice, либо не удаляйте такие страницы, прописывая в head документа <META NAME=»ROBOTS» CONTENT=»NOINDEX, FOLLOW«> и сохраните драгоценную вам ссылочную массу
И как вишенка на тортике (это для тех кто любит подумать и поставить эксперименты). Итак, у нас есть страницы с разным содержанием А и Б. Б – морально устарела и ее хочется удалить (что не висела в базе), но на ней много ссылок.
Что если перед удалением, мы заменим содержимое в стр Б на содержимое стр А. Отследим, когда придет бот Гугла, а после средиректим? Предлагаю обсудить это в комментариях. А также чем отличается код ответа сервера 404 от 410 и какое применение можно найти для кода ответа сервера 410?
Google search console warns publishers about 404 errors: 404 and soft 404.
While they’re both called 404, they are very different.
Consequently, it’s essential to understand the difference between the errors to fix them.
HTTP Status Codes
A webpage accessed by a browser responds with a status code that communicates whether the request was successful and, if not, why it wasn’t.
These responses are communicated with what is referred to as HTTP response codes, but officially they are called HTTP status codes.
A server provides five categories of response codes; this article is specifically about one response, the 404 page not found status code.
The Meaning Of A 404 Response Code
All codes within the 4xx series of responses mean the request could not be fulfilled because the page was not found.
The official definition is:
4xx (Client Error): The request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled
The 404 response is ambiguous as to whether the webpage might return.
Examples Of Why 404 Page Not Found Happens
- If someone mistakenly deletes a webpage, the server responds with the 404 page not found response.
- If someone links to a non-existent webpage, the server responds that the page was not found (404).
The official documentation is clear about the ambiguity of whether a page is temporarily or permanently gone:
“The 404 (Not Found) status code indicates that the origin server did not find a current representation for the target resource or is not willing to disclose that one exists.
A 404 status code does not indicate whether this lack of representation is temporary or permanent…”
To summarize, the 404 page not found code means there was an error in the browser request because the requested page could not be found.
What Is A Soft 404 Error?
A soft 404 error is not an official status code. The server does not send a soft 404 response to a browser because there is no such thing as a soft 404 status code.
Soft 404 describes a situation when the server presents a webpage and responds with a 200 OK status code, indicating success when the webpage or content is actually missing.
Four Common Reasons For A Soft 404
A webpage is missing, and a server sends 200 OK status.
This kind of soft 404 happens when a page is missing, but the server configuration redirects the missing page to the home page or a custom URL.
The page is gone, but the publisher has done something to fulfill the request for the missing page.
Content is missing or “thin.”
When content is completely missing, or there’s very little of it (a.k.a. thin content), the server will respond with a 200 status code, which means the request for the page was successful.
But for indexing webpages that are not successful webpage requests, search engines call this soft 404s.
The missing page redirects to the home page.
Some mistakenly believe that there’s something wrong with a 404 error response.
So, to stop the 404 error responses, a publisher may redirect the missing page to the homepage, even though the homepage is not what was requested.
Google calls these failed page requests soft 404s.
Missing page redirected to a custom webpage.
Sometimes, missing pages redirect to a custom-made webpage that serves a 200 status code, which results in Google labeling these pages as soft 404s.
Who Invented The Phrase Soft 404?
The concept of a soft 404 may have originated in a 2004 research paper titled, Towards an Understanding of the Web’s Decay (PDF).
The missing pages that are improperly substituted present a problem to search engines that are trying to index real pages.
Here is how the research paper frames soft 404s:
“According to the HTTP protocol when a request is made to a server for a page that is no longer available, the server is supposed to return an error code…
…in fact many servers, including most reputable ones, do not return a 404 code—instead the servers return a substitute page and an OK code (200).
…Our study shows that these type of substitutions, called “soft-404s” account for more than 15% of the dead links.”
Soft 404 Due To Coding Errors
There are cases where the page isn’t missing, but specific problems (like coding errors) have triggered Google to categorize it as a missing page.
Soft 404s are essential to investigate because they could signal broken code.
Typical coding issues:
- Missing file or include that’s supposed to populate a webpage with content.
- Database error.
- Missing JavaScript.
- Empty search results pages.
404 Errors Have Two Main Causes
- An error in the link directs users to a page that doesn’t exist.
- A link to a page that used to exist but suddenly disappeared.
Linking Error
If the cause of the 404 is a linking error, you have to fix the links.
The tricky part of this task is finding all the broken links on a site. It can be more challenging to crawl large complex sites with thousands or millions of pages.
In instances like this, crawling tools come in handy.
You have so many site crawler software options to choose from: the free Xenu and Greenflare; or paid software like Screaming Frog, DeepCrawl, Botify, Sitebulb, and OnCrawl, where several of these have free trial versions or free but limited feature versions.
A Page That No Longer Exists
When a page no longer exists, you have two options:
- Restore the page if the removal was accidental.
- 301 redirect it to the closest related page if the removal was on purpose.
First, you have to locate all the linking errors on the site. Similar to finding all errors in linking for a large-scale website, you can use crawling tools.
However, crawling tools may not find orphaned pages: pages not linked from anywhere within the navigational links or from any of the pages.
Orphaned pages can exist if they used to be part of the website, then, after a website redesign, the link going to this old page disappears, but external links from other websites might still be linking to them.
To double-check if these kinds of pages exist on your site, you can use various tools.
How To Identify 404 Response Pages
Google Search Console Reports
The Coverage report lists 404 error URLs on a website.
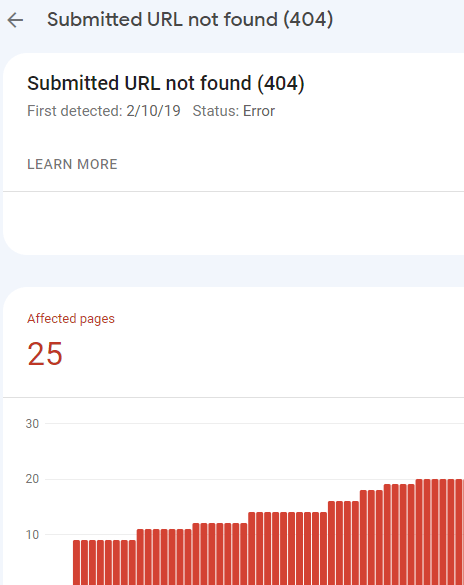
The Search Console will report 404 pages as Google crawls through all the pages it can find. This can include links from other sites to a page that used to exist on your website.
Google Analytics
You won’t find a missing page report in Google Analytics by default. However, you can track them in different ways.
For one, you can create a custom report and segment out pages with a page title mentioning Error 404 – Page Not Found.
Another way to find orphaned pages within Google Analytics is to create custom content groupings and assign all 404 pages to a content group.
Site: Operator Search Command
One cannot use the site: search command to find 404 errors because Google doesn’t index 404 webpages or soft 404 webpages.
Google’s site: search operator is useful for finding webpages on a site that contain a specific keyword phrase in the content of the webpages.
Google’s Search Console is the best source for identifying a list of soft 404s and regular 404s.
The website traffic error logs are a useful source for identifying 404 error responses.
Other Backlink Research Tools
Backlink research tools like Majestic, Ahrefs, Moz Open Site Explorer, Sistrix, Semrush, LinkResearchTools, and CognitiveSEO can also help.
Most of these tools will export a list of backlinks linking to your domain. From there, you can check all the linked pages and look for 404 errors.
How To Fix Soft 404 Errors
Crawling tools won’t detect a soft 404 because it isn’t a 404 error. But you can use crawling tools to catch something else.
Here are a few things to find:
- Thin Content: Some crawling tools report pages that have thin content along with a sortable word count. Start with pages with the least amount of words to evaluate whether the page has thin content.
- Duplicate Content: Some crawling tools are sophisticated enough to discern what percentage of the page is template content. And there are also tools made specifically for finding internal duplicate content like SiteLiner. If the main content is nearly the same as many other pages, you should look into these pages and determine why duplicate content exists on your site.
Aside from the crawling tools, you can also use Google Search Console and check under crawl errors to find pages listed under soft 404s.
Crawling an entire site to find issues that cause soft 404s allows you to locate and correct problems before Google detects them.
After detecting these soft 404 issues, you will need to correct them.
Most of the time, the solutions appear to be common sense. This can include simple things like expanding pages with thin content or replacing duplicate content with new and unique ones.
Throughout this process, here are a few things to consider:
Consolidate Pages
Sometimes, thin content is caused by being too specific with the page topic, leaving you with little to say.
Merging several thin pages into one page can be more appropriate if the topics are related. Not only does this solve thin content issues, but it can fix duplicate content issues as well.
For example, an ecommerce site selling shoes in different colors and sizes may have a different URL for each size and color combination. This leaves a large number of pages with content that is thin and relatively identical.
The more effective approach is to put this all on one page instead and enumerate the options available.
Find Technical Issues That Cause Duplicate Content
Using even the most straightforward web crawling tool like Xenu (which doesn’t look at content but only URLs, response codes, and title tags), you can still find duplicate content issues by looking at URLs.
This includes www vs. non-www URLs, HTTP and HTTPS, with index.html and without, with tracking parameters and without, etc.
404 Errors And Soft 404 Errors
The most important thing to remember about 404 errors is that if the pages are truly missing, then there is nothing to fix. It’s okay to show a 404 response for requests for pages that do not exist.
But if the pages exist but on a different URL, then that’s something to fix by redirecting a broken link to the actual URL, restoring a missing page, or redirecting the old URL to a new page that replaced it.
A soft 404 is always the result of a problem that must be diagnosed and fixed.
Understanding the difference between the 404s is essential to keeping a website operating at peak performance.
Featured Image: Paulo Bobita/Search Engine Journal
If you have ever browsed the internet, you have probably encountered a 404 error at some point.
A 404 error message can be helpful feedback for a web user, but using it in the wrong context can lead to a soft 404 error. A soft 404 error can negatively impact SEO performance, especially when a lot of them go undetected and they start to pile up.
To avoid this situation, developers should work closely with SEO experts to keep soft 404 error pages to a minimum.
Developers will want to work quickly. A soft 404 error can increasingly affect your website’s performance the longer it stays unresolved. In this guide, we will cover everything you need to know about soft 404 errors, from what the error is to how you can fix it, so that your site’s performance and rankings aren’t harmed.
What Is A Soft 404 Error?
A soft 404 error and a regular 404 error are often used interchangeably, but they mean different things.
The regular 404 error, sometimes just called a 404 error, occurs when a webpage is unavailable. In that case, a server sends the correct HTTP status code, which returns a message to display on the browser: “404 Not Found.” This code implies that the page cannot be found.
A soft 404 error, on the other hand, occurs when the server sends a “200 OK” status for the web page, but Google mistakenly interprets the message to read that a 404 error should be displayed. Although it is a mistake on the search engine’s part, it usually happens when the page looks like an error.
This is where the confusion arises. The search engine marks a page as a “404 Not Found” page, even though that’s not the webpage’s correct status. If you are experiencing soft 404 errors on your website and these errors are displayed in tools like Google Search Console, you should take an immediate step to fix them.
When a regular page gets a “200 OK” status, they are displayed in the search engine results. They can be crawled and indexed. However, pages with soft 404 errors will also appear in the search engine result and can even be indexed or crawled, unlike a true 404 error, which are neither indexed nor displayed in results.
What Is An Example Of A Soft 404 Error?
When a user searches for something on your website that does not exist, they will get a “Not Found” message, which a search engine may misinterpret. This is what happens in a soft 404 error.
With a soft 404, the server response code is “200 OK,” but the search engine still thinks that there is a query on your page. Therefore it erroneously interprets the page as a 404 error.
If you are trying to access a page that exists in the CMS, but is still not being displayed by Google, chances are it is due to a soft 404 error.
If the category page does not have any content under the category, it will likely lead to soft 404 errors. Even when the webpage exists on the website, if there is no content, Google will interpret the page as a blank and displays a 404 error.
Causes Of Soft 404s
Several situations can create soft 404s for Google. Some of the most notable causes of this error include:
The Page Has Little To No Content
This is one of the primary causes of a soft 404 error. If the page has thin content or no content at all, Google expects results pointing to a status code of “404 Not Found.”
Even when the status response is okay, Google may still display the 404 error. Some examples of a soft 404 error due to lack of content are empty product category pages, empty blog category pages or empty search result pages.
Fixing these pages or adding content to them may help you get rid of the 404 error. However, if that hasn’t solved the problem, applying the “no index directive” through the meta robots tag can be a solution.
Redirect Target Is Not Relevant Enough
If you are redirecting your URL to another URL, it must be relevant, or Google will display a “404 Not Found” message. This issue primarily occurs when developers try to redirect users from one webpage to another that is not relevant. This issue is prominent on eCommerce websites, which redirect a user to another product or category not relevant to Google’s algorithms.
You Have Accidentally Blocked Google From Rendering
Sometimes a soft 404 error can occur when you have blocked Google from accessing your JavaScript or CSS files. These files are used to render pages. If Google cannot access them it may lead to a soft 404 error.
This issue can be resolved by debugging and verifying your webpage via Google’s inspection tool. After fixing this issue, Google will be able to render your files and the 404 should be resolved.
Page Content Has 404-like Phrases
If your page has phrases that are primarily found on a 404 page, it can cause a soft 404 error.
Avoid phrases you would find on a 404 error page, such as “not in stock,” “does not exist” and “no longer available.” These phrases can be mistaken for a 404 page by Google. Removing them from your site can fix the error.
The Difference Between A 404 Not Found And A Soft 404
The primary difference between a “404 Not Found” error and a soft 404 error is the status code. The former has a status code of 404 or 410, which implies that the page cannot be found.
With a soft 404 error, the page is still not found. But instead of returning the 404 or 410 code, a “200 OK” code is returned.
404 pages are not indexed by search engines and do not appear in the search engine results. However, soft 404 pages are indexed by search engines and can appear in the search results.
How Google Sees Soft 404s
Google has changed the way it handles soft 404 detection and classifications.
Google now looks at each page by device type and assigns a soft 404 classification differently to the same URL on desktop and mobile. If Google sees a URL and accesses the same URL on desktop and mobile, it may return a soft 404 error on mobile and desktop, or vice versa.
This means Google now detects a soft 404 status on a URL, as it goes through a URL. It also does so by device type.
This can be a problem when the page works correctly on a mobile Search Console, and does not throw any alerts. Meanwhile, some of your pages may be experiencing soft 404 errors outside of the console, which can affect your website’s performance and rankings.
Why Soft 404s Are Bad For SEO
If a website returns a status OK code rather than a 404 for a page that does not exist, it can affect the website’s performance negatively in an organic search.
Therefore, if your website has high soft 404 errors, you will be negatively impacted in search results. With a soft 404 error, the website will indicate that there is a real page at the URL and that visitors can access it. Search engines will index and crawl a page that does not actually exist, draining your valuable crawl budget on non-existent pages.
Googlebot only wants to crawl a limited number of websites and it divides its efforts by crawl rate and crawl demand.
- Crawl Rate – This allows Google to not crawl pages that are too fast and can hurt the server.
- Crawl Demand – This implies the pages Google wants to crawl. This budget is based on the popularity of your pages and how old the content is. The search engine does not want to waste its time crawling content on the same website. Google assigns a budget to its web crawls before it moves on to the next website.
If your website has high soft 404 errors, the crawl budget may be spent on pages that reduce your visibility. Visitors looking at search results will not be able to access pages with actual content. A high crawl percentage also affects the performance of your website in organic search.
By reducing your soft 404 errors, you increase your site’s visibility and search performance.
How To Find Soft 404 Errors
Finding a soft 404 error is not particularly challenging. An easy way to discover the errors is to log into Google’s Search Console and check for 404 errors. Once you have identified a 404, you want to make sure that it is returning a 404 error code.
But if they are not, you should fix them immediately. These are your soft 404 errors.
Screaming Frog is another tool to find broken links within your website. It also identifies websites that have linked to pages that no longer exist. Another alternative to Screaming Frog is Xenu Link Sleuth.
How To Fix And Resolve Soft 404s
Not all 404s are bad, as there are cases when they are displayed in the correct context. When a product is not available, for example, displaying a 404 error page lets users know that the particular product is permanently removed from the website.
Soft 404 errors can be tricky, however. There can be cases when a webpage is not valid and a server still returns a “200 OK” status. In these cases, you should look at the errors and try to fix them.
Here are some solutions for addressing soft 404 errors.
Check If The Page Is Indeed A Soft 404 And Not A False Alarm
Check for false alarms. In most cases, a page incorrectly marked as a soft 404 error by Google Search Console can be audited and verified.
- Start by clicking on the “Submitted URL seems to be a soft 404” button from the Coverage Report. This returns a complete list of soft 404 pages.
- Open the URLs in new tabs.
- If the page is a valid part of your website and you want it to appear in the search results, choose the “Validate Fix” option. This will make Google crawl the page and update the status code.
- Once complete, you should inspect the page and test the live URL.
An alternative method is to select the URL and click on the “Inspect URL” option. This will give you more information about the page of interest and give you an option to “Request Indexing.”
Before doing so, test the live URL to allow Google to refresh its report. Doing this will give you the correct status of the page. In most cases, the page will function correctly and require no changes.
Improve The Affected Page And Request Indexing
If your page exists, but Google has been reporting it as a soft 404, it may be due to the page content. In this case, improve the page content and resubmit it to Google.
This is a common problem when there’s thin content. Adding more content to the page is an easy fix. Once updated, the page will become more crawable to Google, helping to eliminate the soft 404 error.
Keep The Page On Your Site But Try To De-index It From Search Engines
Another alternative to resolving a soft 404 error is to keep the page on your site, but deindex it from the search engine.
Adding a no-index directive in the header will instruct the search engine not to index that particular webpage on the site. Doing this will allow you to fix the soft 404 error, since Google will not display the page under the Error report.
Note, you will still see this page listed in the excluded report under the Soft 404 section.
Configure Your Server To Return The Proper Not Found Error Code (404/410)
If the page is not available or invalid, you should try to configure the website to return the correct status code. Once you have configured your website for the correct code, resubmit the page to Google for indexing. It should help you get rid of the soft 404 error.
Configuring your site to return a 404 code for invalid pages includes deleting the pages. Once you delete a page, the HTTP server will show a 404 code when the page is requested, allowing you to reduce your soft 404 percentage.
Redirect The Page Using A 301 Redirect
The last method to resolve the soft 404 error is by redirecting the page of interest to a valid page. You can do this by adding a 301 redirect into your .htaccess file.
This tells the search engine that the page is moved to a new location and ensures it does not display the 404 error for an existing page. Be sure to check that both of the pages have similar content before you redirect one to another.
A Word About Website Maintenance And SEO
A correct 404 error is valid and lets visitors know about pages that have been permanently deleted. However, soft 404 errors can affect the performance of your website because they’re frustrating for users and confusing for search engines.
You should keep your soft 404 percentage to a minimum to make sure that errors do not affect your search visibility and rankings. Regular site maintenance is the easiest way to ensure that soft 404 errors don’t negatively affect your site.
Frequent site check-ups will allow you to keep errors at bay and make your website accessible for visitors. Consider enlisting the help of a company trusted by Google itself to maintain your site.
Prerender can help you unlock your website’s true potential. Follow us on Twitter for more technical SEO information to keep your website running at peak performance!
Google может возвращать ложную ошибку 404 по ряду причин, например, если он считает, что страницы вашего сайта содержат мало или совсем не содержат оригинального контента. Они также могут быть вызваны техническими проблемами или если вы недавно удалили страницу со своего сайта.
Важно отметить, что ложная ошибка 404 не влияет на рейтинг других страниц. Ложные ошибки 404, которые появляются в Google Search Console, могут быть устаревшими и больше не актуальными. Ошибки, которые появляются для таких страниц, как удаленные страницы товаров или удаленные посты блога, могут отображать ложную ошибку 404; это нормальное поведение, которое со временем будет решено.
Если вы получаете сообщение о ложной ошибке 404 для URL-адреса:
Проверьте затронутые страницы:
- Если на затронутых страницах действительно есть значимый контент, используйте инструмент проверки URL-адресов, чтобы запросить переиндексацию для вашей страницы, отправив URL-адрес страницы.
- Если страницы не должны отображаться в результатах поиска (например, если вы удалили их со своего сайта), вы можете игнорировать сообщение об ошибке.
Проверьте содержимое страниц с ошибками: ложные ошибки 404 иногда возникают из-за отсутствия органического или уникального контента на странице. Это превентивная мера, выполняемая Google, чтобы страницы с более низким рейтингом не считались спамом.
Чтобы решить эту проблему, необходимо оптимизировать контент ваших страниц для SEO, гарантируя, что контент содержит уникальный и органический текст. Не забудьте добавить alt-текст изображения.
Подробнее
Every Web page on the Internet has an HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response code that is served when a browser or search-engine crawler sends a request to fetch the page. Based on the response code served, we can understand the status of the page. There is a long list of HTTP status codes and each status code defines different conditions. In this blog post, we will be explaining the difference between 404 and soft 404 errors. Read on to find out!
What is a 404 Error?
A 404 error or status code simply denotes that the requested Web page could not be found or that the page is no longer available.
Generally, 404 errors occur because of
-
An error in the URL
Errors in the URL could occur due to the user entering an incorrect URL or because a page has been linked to an incorrect URL. Incorrect URLs serve a 404 status code because they lead the user to a page that doesn’t exist at all.
-
Page removal
A page that used to exist but was taken down intentionally or unintentionally from the server will serve a 404 status code.
How to Fix 404 Errors
The first step is to identify all the URLs present on the website, which a search engine can discover, and which are throwing the 404 error. You can do this with the help of two tools – Google Search Console’s Coverage report and running crawling tools like DeepCrawl, Screaming Frog, and so on through your website. Once you compile a list of such URLs, try to understand whether the error is because the URL has an error or because the page was taken down. This step is very important because it will give you an idea of what has to be fixed.
-
Fixing Linking Errors
There may be chances that due to some error your Web pages are linking to an incorrect URL. However, finding broken links across the website is a tedious task. To make it easier, you can use crawling tools like DeepCrawl, Screaming Frog, and so on to identify broken links. Once identified, you can fix the linking errors easily.
-
Fixing Missing Pages
In case some pages were removed from the website, either erroneously or intentionally because they no longer serve a purpose, they can be fixed in two ways:
1) Restore the pages
If you think that an important page was removed by mistake, you should restore the page and submit it in Google Search Console for re-indexing. Or, you could update the sitemap. Once this is done, start validating the 404 URLs in the Search Console.
2) Redirect to the most relevant page
If the pages that throw the 404 error are of no importance, then you should redirect it to the most closely relevant page on your website. Let’s say you have an e-commerce website. If a product is no longer available and the page has been removed, then it should be redirected to the category page of the product.
For example, the 404 product URL (https://www.example.com/category/product-name) should be redirected to the category URL (https://www.example.com/category) and not the homepage.
What Is A Soft 404 Error?
A soft 404 is a page that is missing from the server. However, it serves the 200 status code instead of 404 when requested. This indicates to search engine crawlers that the page is present so that they crawl through them even though they are non-existent. In the worst-case scenario, they might get indexed as well. However, this should be strictly avoided as it causes unnecessary wastage of crawl budget.
Also, Soft 404 is not an official HTTP response code sent by a server when a Web page is requested. It is just a label that Google uses for Web pages it has discovered. You can find soft 404 pages on your website in Google Search Console’s coverage section.
Following are the reasons why Soft 404’s occur
-
Poor server configuration
Due to poor server configuration, even missing pages serve the 200 status code which misleads crawlers. Servers should be configured in such a way that missing pages should always serve a 404 status code when requested.
-
Pages with very less or no content
Sometimes live pages with very less or no content are also misidentified as soft 404 as its behaviour indicates to Google that the page does not have potential and must be a 404. As Google is not sure about it, such pages are categorised as soft 404s.
-
Issues with page rendering
If your rendered page is blank or nearly blank, there are high chances that Googlebot is not able to load the page resources. This can happen if the resources are very large in size or blocked from accessing. Such pages are also marked as soft 404 since Google is not sure if it’s actually a 404 page or not.
How To Fix Soft 404 Errors
To start with, you should extract all the URLs from the Soft 404 section in Search Console’s Coverage report. Run all the URLs through a crawling tool and identify the URLs to which the 404 error actually applies. Fix these URLs with the methods mentioned in the previous section. Now, you can proceed to fix the soft 404’s with these steps:
-
Serve correct status codes
As the title suggests, ensure that the servers serve the correct status code for each and every URL. A valid page should serve a status code 200, a missing page should serve 404 and redirected pages should either serve 301 or 302. Do not mislead Googlebot!
-
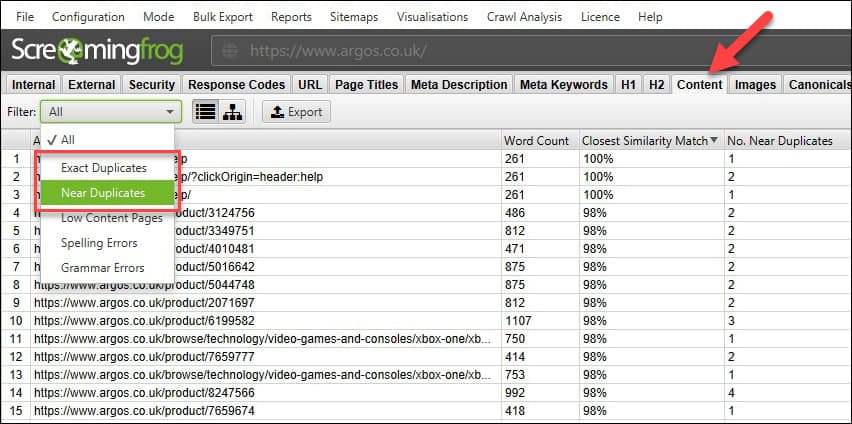
Find and fix pages with duplicate or thin content
You can run the soft 404 URLs through the Screaming Frog tool and extract the word count of the content on each page. This will give you an idea of pages with thin content on your website. Screaming Frog also helps you identify pages with Near Duplicate and Exact Duplicate content. This should help you fix the duplicate content. You can either consolidate pages with similar topics together into a single page or add unique content to them.
Along with this, you should also look at technical issues that cause duplication, such as do trailing or non-trailing slash URLs, www or non-www version of URLs, https or http version of URLs, URLs with or without “.html” resolve to the main version of the URL? If no, are proper canonicals defined for duplicate URLs? If not taken care of, these issues can cause huge duplication problems, which is not desirable.
-
Ensure Googlebot is able to render your pages
If the pages have enough content and are still marked as soft 404, then there is a possibility that the crawlers are not able to crawl or render your page efficiently. For such URLs, you should check the rendered screenshot and HTML in Search Console. If the screenshot is blank or nearly blank, then the pages surely have a rendering problem. You can analyse the rendered HTML to find which resources are causing issues. Do not block any resources for crawlers and ensure that they are not extremely large in size.
Key Takeaways
A soft 404 error is not considered the same as a 404 page. It is an indication that something is wrong with the page and the crawlers are not considering it as a legitimate page. However, just like 404 pages, if you do not fix soft 404 errors quickly, Google might start deindexing your pages which will affect your website traffic if they are important pages. The best practice is to regularly put your website through a crawling tool and check for 404 pages and thin pages. Having access to a crawling tool is essential to help you fix these errors and Screaming Frog is one of the best and most highly recommended tools available.
Have you encountered these errors? How did you fix them? Let us know in the comments section below.
Popular Searches
List of Search Engines | Top Google Searches | Importance of Digital Marketing | Importance of Website | Youtube SEO Tools | Types of SEO |Website Structure | Benefits of SEO | Cloaking |Google Sandbox | SEO Friendly Website | Blog Commenting for SEO | Server Side Rendering Vs. Client Side Rendering | Youtube Trends | Types of Sitemaps | Social Bookmarking |Off Page SEO Checklist | HTTP Status Codes | Vanity URL | SEO Vs. PPC | Best SEO Blogs | Benefits of LinkedIn Ads | Keyword Density | How to Use Keywords in Blog Posts | Website Migration | Digital Marketing Types | Search Engine Optimization | Canonical Tags | On Page SEO | What is Off Page SEO | Link Building for SEO | Image Optimization | SEO Company in Boston | Dallas SEO | SEO Company Houston