#статьи
-
0
Проблема на стороне пользователя или на стороне владельца сайта? Объясняем в статье.
Иллюстрация: Polina Vari для Skillbox Media
Контент подготовлен нейросетью, которая анализирует тысячи источников в режиме реального времени. Факты проверил редактор Skillbox Media.
Ошибка 404 — распространённая проблема, с которой пользователи сталкиваются при попытке получить доступ к веб-странице. Кроме того, это важный сигнал о неисправностях для владельцев сайтов и разработчиков. В статье разбираемся:
- что означает ошибка 404;
- почему она возникает;
- как последствия ошибки 404 проявляются на сайте;
- как исправить ошибку 404 со стороны пользователя;
- как исправить ошибку 404 со стороны владельца сайта;
- какие есть инструменты для отслеживания ошибки 404.
Ошибка 404, также известная как «Not Found» или «Не найдено», является стандартным HTTP-статусным кодом, который указывает на отсутствие запрашиваемого ресурса на сервере.
Ошибки 404 возникают в результате взаимодействия между клиентским устройством (например, веб-браузером) и сервером, когда клиент пытается получить доступ к странице, изображению, файлу или любому другому ресурсу. Если сервер не может найти запрашиваемый ресурс, он отправляет клиенту ответ со статусным кодом 404.
Ошибка 404 может возникать по нескольким причинам: неправильно введён URL, устарела или не работает ссылка на другом сайте, ресурс перемещён или удалён с сервера, во внутренней структуре или в серверной конфигурации сайта есть проблемы.
Для пользователей ошибка 404 означает, что запрашиваемая информация или страница временно или постоянно недоступна. Это может вызывать недовольство, особенно если пользователь ожидал найти важные сведения или материалы.
Для владельцев сайтов и разработчиков ошибка 404 является сигналом о неисправностях в системе. Она может указывать на проблемы в структуре и навигации сайта, ошибки в ссылках или отсутствие обработчиков ошибок. Исправлять ошибки 404 важно для улучшения пользовательского опыта, сохранения SEO-рейтинга и обеспечения правильной работы сайта.
В следующих разделах мы рассмотрим причины возникновения ошибки 404 подробнее и дадим рекомендации по её исправлению.
Ошибка 404 возникает, когда сервер не может найти запрашиваемый ресурс. Рассмотрим несколько распространённых причин её появления.
- Неверно введён URL. Это самая распространённая причина. Если пользователь случайно вводит неправильный адрес в адресной строке браузера, сервер не сможет найти соответствующую страницу и вернёт ошибку 404. Ошибки в адресе могут быть вызваны случайными опечатками, неправильным регистром или отсутствием необходимых символов.
- Ссылка ведёт на несуществующие страницы. Если ссылка ведёт на страницу, которая была перемещена или удалена, пользователь, кликнувший по ней, столкнётся с ошибкой 404.
- Ссылки на других сайтах устарели. Если другой сайт содержит ссылку на вашу страницу, но эта страница была удалена или перемещена, а ссылку на другом сайте не обновили, пользователь, перешедший по этой ссылке, получит ошибку 404.
- Ресурсы перемещены или удалены с сервера. Если владелец сайта переместил или удалил ресурс (например, страницу или файл), но не настроил перенаправление или обновление ссылок, клиенты, которые обращаются к этому ресурсу, получат ошибку 404.
- Есть проблемы с серверной конфигурацией. Ошибка 404 также может появляться, если сервер настроен неправильно или доступ к определённым файлам или директориям закрыт.
- Во внутренней структуре сайта есть ошибки. Например, если ссылка на страницу указывает путь неправильно, сервер не сможет найти соответствующий ресурс и вернёт ошибку 404.
Возникновение ошибки 404 может иметь негативные последствия как для пользовательского опыта, так и для поисковой оптимизации и репутации сайта. Вот несколько возможных последствий.
Вред для SEO. Если сайт содержит много неработающих ссылок, это может негативно сказаться на SEO. Разрушение внутренней и внешней ссылочной структуры приводит к потере органического трафика, ухудшению показателей SEO, затруднению навигации.
Потеря трафика и позиций в поисковых системах. Если на сайте много ошибок 404, это отражается на его позиции в поисковой выдаче. Поисковые системы принимают во внимание частоту ошибок 404 при определении качества сайта и его релевантности для пользователей. Если ошибок 404 при обращении к сайту много, сайт теряет позиции в результатах поиска.
Ухудшение репутации и уменьшение доверия. Ошибка 404 может создать впечатление непрофессионализма создателей сайта и его ненадёжности. Посетители могут начать сомневаться в качестве контента и услуг, предлагаемых на сайте, если регулярно сталкиваются с ошибками 404.
Потеря потенциальных клиентов или покупателей. Если ошибки 404 возникают на страницах с продуктами, услугами или контактами, это может привести к потере потенциальных клиентов или покупателей. Посетители начнут искать альтернативные варианты, если не смогут получить доступ к информации.
Важно принимать меры по предотвращению и исправлению ошибок, чтобы сайт функционировал эффективно.
Если вы сталкиваетесь с ошибкой 404 при посещении сайта, вы можете проверить, с вашей ли стороны проблема, и предпринять действия, чтобы её исправить. Вот несколько рекомендаций.
- Проверьте правильность написания URL. Убедитесь, что вы правильно ввели URL в адресной строке браузера. Проверьте, нет ли в нём опечаток, правильный ли использован регистр. Если есть сомнения, попробуйте переписать URL или воспользуйтесь поиском по сайту.
- Обновите страницу или повторите попытку позже. Иногда ошибка 404 может быть временной проблемой, связанной с недоступностью сервера или перегрузкой. Попробуйте обновить страницу или повторить запрос через некоторое время. Если ошибка сохраняется, перейдите к следующему шагу.
- Используйте поиск по сайту. Если на сайте есть функция поиска, воспользуйтесь ей. Это может помочь обнаружить страницу или контент, который вы ищете, даже если ссылка на него была изменена или удалена.
- Проверьте, нет ли другой ссылки на эту страницу, с помощью поискового запроса. Возможно, страница была перемещена или переименована, а запрос в поисковике приведёт вас к нужному ресурсу.
- Сообщите о проблеме владельцу сайта. Если вы уверены, что запрашиваемый ресурс должен существовать, а ошибка 404 сохраняется, свяжитесь с владельцем сайта или администратором и сообщите о проблеме. Они могут принять меры для исправления ссылки или восстановления удалённой страницы, предоставить другой путь к нужному контенту.
- Ищите альтернативные источники информации. Если вы не можете получить доступ к конкретной странице, поищите другие ресурсы по теме. Возможно, аналогичный контент доступен на других сайтах.
Несмотря на то что исправление ошибки 404 в основном зависит от владельца сайта, эти шаги могут помочь пользователю обойти проблему или найти альтернативные способы получить нужную информацию.
Если вы владелец сайта, на страницах которого возникает ошибка 404, вы можете предпринять несколько действий для исправления этой проблемы. Вот несколько рекомендаций:
- Проверьте, есть ли на вашем сервере запрашиваемый ресурс. Убедитесь, что файл или страница, на которую указывает ссылка, находится в нужном месте. Если ресурс был перемещён или удалён, возможно, его следует восстановить или предоставить пользователям альтернативу.
- Обновите ссылки и редиректы. Если вы переместили ресурс или изменили его URL, убедитесь, что все ссылки и редиректы на вашем сайте перенастроены. Обновление ссылок позволит пользователям получить доступ к нужному контенту без ошибок 404. Используйте редирект (например, 301 или 302), чтобы автоматически направлять пользователей на новый адрес.
- Создайте дизайн специальной страницы 404 с информацией и советами по навигации. На этой странице можно поместить сообщение о том, что запрошенный ресурс не найден, и предложить перейти к другим страницам сайта.
- Усовершенствуйте внутреннюю структуру сайта. Проанализируйте структуру вашего сайта и проверьте наличие сломанных или устаревших ссылок. Используйте инструменты для проверки ссылок и обновите нерабочие ссылки в меню, футере, виджетах и других разделах вашего сайта.
- Настройте поиск по сайту. Он поможет пользователям найти нужную информацию, даже если они столкнутся с ошибкой 404. Убедитесь, что поиск настроен правильно и охватывает все важные страницы. Это позволит пользователям искать нужную информацию непосредственно на вашем сайте.
- Мониторьте ошибки 404 и анализируйте их. Используйте инструменты аналитики для отслеживания и мониторинга ошибок 404 на вашем сайте. Это позволит вам получить информацию о том, какие страницы часто выдают ошибку 404, и исправить проблему. Анализ ошибок 404 позволит определить, что в структуре сайта и вашей ссылочной стратегии следует улучшить.
Исправление ошибки 404 со стороны владельца сайта требует некоторых усилий, но поможет улучшить пользовательский опыт и обеспечить более эффективную навигацию по вашему сайту.
Упростить отслеживание и управление ошибками 404 позволяют специальные инструменты. Вот несколько полезных инструментов со ссылками на их официальные сайты:
- Google Analytics. Популярный бесплатный инструмент от Google, который предоставляет подробные отчёты о посещаемости вашего сайта. Он также отслеживает ошибки 404 и предоставляет информацию о страницах, на которых возникли ошибки.
- Google Search Console. Бесплатный инструмент от Google, который позволяет отслеживать индексацию и видимость сайтов в поисковой выдаче Google. Он также предоставляет отчёты об ошибках 404 на сайте.
- Веб-мастер Яндекса. Инструмент от «Яндекса», предназначенный для анализа сайтов. Он предоставляет отчёты об ошибках 404, позволяет вам просмотреть страницы, вызывающие ошибки.
- Screaming Frog. Популярный платный инструмент для сканирования сайтов, который помогает обнаружить ошибки 404 и другие проблемы с сайтом. Он проводит аудит сайта и выдаёт подробные отчёты о неработающих ссылках, включая ссылки с ошибкой 404.
- Dead Link Checker. Онлайн-инструмент, который позволяет проверить ваш сайт на наличие неработающих ссылок. Вы можете указать URL вашего сайта, и Dead Link Checker составит отчёт о неработающих ссылках, включая ошибки 404.
- Ошибка 404 — это HTTP-код, который указывает на то, что запрашиваемый ресурс не найден на сервере. Ошибка 404 возникает, когда пользователь или поисковая система обращаются к несуществующей странице, удалённому контенту или недоступному файлу.
- Ошибка 404 может возникать по нескольким причинам: перемещение или удаление страницы или файла, неправильно введённый URL, некорректные ссылки на сайте, проблемы с сервером или недоступность ресурса из-за ошибок в программировании или конфигурации сервера. Ошибка 404 также может возникать при попытке перейти к защищённому контенту без соответствующих разрешений.
- Чтобы исправить ошибку 404, пользователю следует проверить правильность написания URL и обновить страницу или повторить попытку позже, а если это не сработало — воспользоваться функцией поиска на сайте для поиска нужной информации или ресурса.
- Для исправления ошибки 404 владельцу сайта следует проверить, есть ли нужный материал на сервере, обновить ссылки и редиректы, а также создать специальную информационную страницу для ошибки 404.
- Существуют специальные инструменты, предназначенные для отслеживания ошибок 404 на сайтах. Они позволяют провести сканирование страниц и предоставляют детальные отчёты о неработающих ссылках.

Как зарабатывать больше с помощью нейросетей?
Бесплатный вебинар: 15 экспертов, 7 топ-нейросетей. Научитесь использовать ИИ в своей работе и увеличьте доход.
Узнать больше
Ошибка 404, либо Error 404 Not Found — ошибка, которая появляется, если браузеру не удалось обнаружить на сервере указанный URL.
Сообщение об ошибке 404
Что означает ответ 404
Error 404 Not Found отображается по-разному: «HTTP 404 не найден», «Ошибка 404 Not Found», «404 Страница не найдена». Смысл надписи всегда остаётся тем же: страница отсутствует либо просто не работает. Not Found в переводе означает «не найдено».
Ошибка 404 — классический код ответа по протоколу HTTP. Он свидетельствует, что связь с сервером установлена, но данных по заданному запросу на сервере нет.
Однако если просто ввести в поисковую строку произвольный набор символов, то браузер не покажет ошибку 404 Not Found — появится сообщение, что установить соединение с конкретным сервером невозможно.
Разберёмся в техническом формировании ответа Error 404 Not Found.
Техническая сторона вопроса. При связи по HTTP браузер запрашивает указанный URL и ждёт цифрового ответа. То есть любой запрос пользователя направляется на сервер размещения искомого сайта. Когда браузеру удаётся связаться с сервером, он получает кодированный ответ. Если запрос корректный и страница найдена, отправляется ответ с кодом 200 OK, что соответствует благополучной загрузке. При отсутствии страницы отправляется ответ об ошибке.
Что значит код «404». В ответе 404 первая четвёрка указывает на то, что запрос был чрезмерно длительным или в самом адресе была ошибка. Ноль предполагает синтаксическую неточность. Завершающая цифра кода отображает конкретную причину ошибки — «4» означает отсутствие данной ссылки.
Какие ещё ошибки бывают. Ошибку 404 не нужно путать с другими ответами, которые указывают на невозможность связи с сервером. Например, ошибка 403 сообщает, что доступ к URL ограничен, а ответ «Сервер не найден» свидетельствует, что браузер не смог обнаружить место размещения сайта.
Google на 404 странице сообщает о возможных причинах ошибки
Причины ошибки
Причины, по которым HTTP возвращает ответ 404 Not Found:
- Неверный адрес. К примеру, при ручном наборе пользователь допустил опечатку в адресе либо ссылка ведёт на несуществующую страницу. При этом домен должен быть написан верно. Если пользователь ошибется в названии домена, страница вообще не загрузится (без показа ошибки).
- Битая ссылка. Это нерабочий URL, который никуда не ведёт. Данный вариант иногда возникает при внутренней перелинковке. К примеру, раньше страница существовала, а потом её удалили и забыли убрать ссылку.
- Удалённая страница. Когда пользователь попытается перейти на удалённую с сервера страницу, он также увидит ошибку 404. Ссылка для перехода может сохраниться в браузерных закладках или на сторонних ресурсах.
- Неправильный редирект на страницу с изменённым адресом. Допустим, в процессе редизайна URL изменили, но оставили без внимания связанные ссылки.
- Неполадки на сервере. Это самый редкий вариант.
В большинстве ситуаций ошибка 404 отображается, когда не удаётся обнаружить нужную страницу на доступном сервере.
Причины отсутствия страницы на сайте бывают разными
Возможные последствия для сайта
Нужно ли считать 404 ошибку опасной для сайтов? Кажется, что нет ничего плохого в том, что пользователь не смог открыть одну веб-страницу. Однако если такая ситуация будет повторяться регулярно, это чревато оттоком аудитории. Одни пользователи решат, что сайт вовсе не существует. Другие подумают, что лучше не заходить на сайт, который работает с ошибками. Третьи будут игнорировать ресурс, на котором не смогли получить обещанную информацию.
Поисковые системы относятся к Not Found более лояльно. Например, Google отмечает, что 404 страницы не влияют на рейтинг. Но если при индексации роботы будут находить все больше ошибочных страниц, вряд ли это приведёт к более высокому ранжированию.
Если вы хотите улучшить взаимодействие с посетителями, важно найти и исправить все ошибки 404 на сайте.
Как выявить ошибку
На небольшом ресурсе легко проверить работоспособность ссылок вручную. Но если на сайте сотни и тысячи страниц, без дополнительного софта не обойтись. Есть немало сервисов и программ, позволяющих находить битые ссылки. Рассмотрим некоторые из них.
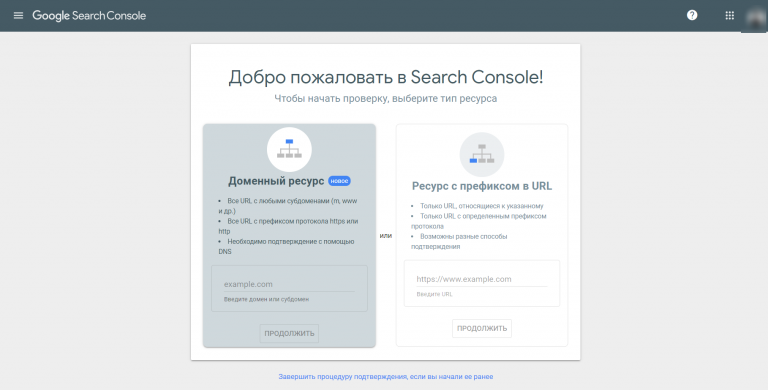
Search Console Google
Консоль поиска Google позволяет находить страницы с ошибкой 404 за несколько кликов:
- Войдите в учётную запись Google и перейдите в Search Console.
- Откройте раздел «Ошибки сканирования» → «Диагностика».
- Кликните на «Not Found».
Чтобы получить список страниц с ошибками, подтвердите права на ресурс — добавьте проверочную запись TXT в записи DNS регистратора домена. Такая запись не повлияет на работу сайта. Подробнее о процедуре подтверждения, читайте в справке Google.
Для использования Search Console Google нужно подтвердить свои права на сайт
Яндекс Вебмастер
Сервис для вебмастеров от Яндекса поможет быстро найти все ошибки 404:
- Откройте Вебмастер после авторизации в Яндекс-аккаунте.
- Выберите «Индексирование» → «Доступные для поиска страницы» → «Исключённые страницы».
- В выданном списке выберите фильтр «Ошибка HTTP: 404».
Чтобы использовать Яндекс.Вебмастер, также нужно подтвердить право владения сайтом — добавить метатег в HTML-код главной страницы.
Для входа в Вебмастер авторизуйтесь в Яндексе
Screaming Frog
Для начала загрузите и установите программу на компьютер. После запуска добавьте URL проверяемого сайта и начните поиск проблем. Неработающие ссылки можно искать даже в бесплатной версии.
Инструмент SEO-паук в Screaming Frog помогает найти технические неисправности сайта
SiteAnalyzer
Эта бесплатная десктопная программа позволяет обнаружить технические погрешности на сайте. SiteAnalyzer быстро отыщет нерабочие и несуществующие ссылки.
SiteAnalyzer бесплатно найдёт неработающие URL
Как исправить ошибку Not Found
Выбор конкретного решения зависит от причины ошибки:
- Ссылка ведёт в никуда из-за неверного URL. Для решения проблемы замените ошибочную ссылку на правильный адрес, чтобы сервер отдавал код 200 OK.
- Битая ссылка. Подобная ситуация не редкость при внутренней перелинковке страниц. К примеру, ссылка есть, а саму страницу давно удалили. Решений два: удалить ссылку или заменить её на другую.
Удалять и менять ссылки вручную удобно только на небольших сайтах. Исправление ошибок на крупных порталах лучше автоматизировать. Например, с помощью специальных плагинов для внутренней перелинковки (Terms Description, Dagon Design Sitemap Generator) и для автоматического формирования адресов страниц (Cyr-To-Lat).
Чтобы ошибки 404 появлялись как можно реже, достаточно соблюдать простые рекомендации:
- Не присваивайте сложные адреса основным разделам сайта. Это снизит число ошибок, связанных с опечатками в URL.
- Не меняйте адреса страниц слишком часто. Это неудобно для пользователей и вводит в заблуждение поисковых роботов.
- Размещайте сайт на надёжном сервере. Это предотвратит ошибки, возникающие из-за неработоспособности сервера.
Мы разобрались, как найти и исправить ошибки Not Found внутри сайта. Но неработающая ссылка может быть расположена и на стороннем ресурсе. Допустим, когда-то на другом сайте разместили рекламную публикацию со ссылкой на определённую страницу. Спустя какое-то время страницу удалили. В этом случае появится ошибка 404. Устранить её можно, связавшись с администрацией ссылающегося сайта. Если же удалить/исправить ссылку нельзя, постарайтесь использовать ошибку с выгодой.
Как сделать страницу 404 полезной
Грамотно оформленная страница с ошибкой Error 404 Not Found — действенный инструмент конвертации посетителей. Ограничений по использованию страницы с ошибкой 404 нет. При этом практически все CMS позволяют настраивать дизайн этой страницы.
Что публиковать на странице 404:
- меню с кликабельными ссылками;
- ссылку на главную страницу;
- анонс последних публикаций;
- контакты для обратной связи.
При оформлении страницы-ошибки желательно опираться на рекомендации поисковиков:
- Яндекс настоятельно рекомендует, чтобы страница контрастировала с основным содержанием сайта — иные цвета, другие графические приёмы либо их отсутствие. Необходимо чётко и понятно объяснить пользователю, что запрошенной страницы не существует и предложить другое решение.
- Google советует придерживаться единого стиля оформления. Но также рекомендует понятно рассказать об ошибке и предложить полезные материалы.
Главное — по возможности отказаться от стандартной страницы 404. Подумайте, как привлечь внимание пользователя. Расскажите ему об отсутствии искомой страницы и предложите взамен что-то полезное или интересное.
Примеры оформления страниц 404
Designzillas
Мультяшная страница креативной студии привлекает внимание и её хочется досмотреть до конца. Если прокрутить страницу, можно увидеть, как из яйца вылупится дракон. При этом на странице есть ссылки на все основные разделы сайта.
Меню на сайте Designzillas есть и на 404 странице
Domenart Studio
Веб-студия «Домен АРТ» использует красочную страницу 404, оформленную в единой стилистике ресурса. Заблудившимся пользователям предлагают попробовать ещё раз ввести адрес или перейти в нужный раздел.
Контакты, поиск, меню — и всё это на 404 странице Domenart Studio
E-co
«Эко Пауэр», дистрибьютор производителя источников питания, демонстрирует короткое замыкание как символ ошибки. Посетителям предлагают перейти на главную.
Ошибка 404 «Эко Пауэр» выглядит как страница входа
Дом со всем
Компания «Дом со всем», занимающаяся бурением скважин, разместила на странице 404 свои контакты и перечень услуг. Со страницы можно перейти в любой раздел сайта или заказать обратный звонок. С таким наполнением посетителю не нужно искать дополнительную информацию где-то ещё.
Компания «Дом со всем» предлагает заказать обратный звонок
Kualo
Страница 404 на веб-хостинге Kualo может заставить пользователя забыть, зачем он сюда пришёл. Увлекательная игра притягивает внимание. В конце игры посетителю предлагают посмотреть сайт хостинга.
На странице Kualo можно просто поиграть и заработать скидки
Рано или поздно с ошибкой 404 сталкивается большинство сайтов. При регулярной проверке можно своевременно исправить неработающие ссылки, чтобы в ответ пользователи получали код 200 OK. Но для крупного ресурса лучше настроить оригинальную страницу, которая будет отображаться при появлении ошибки Not Found и подскажет посетителям, что делать дальше.
Главные мысли
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In computer network communications, the HTTP 404, 404 not found, 404, 404 error, page not found, or file not found error message is a hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) standard response code, to indicate that the browser was able to communicate with a given server, but the server could not find what was requested. The error may also be used when a server does not wish to disclose whether it has the requested information.[1]
The website hosting server will typically generate a «404 Not Found» web page when a user attempts to follow a broken or dead link; hence the 404 error is one of the most recognizable errors encountered on the World Wide Web.
Overview
When communicating via HTTP, a server is required to respond to a request, such as a web browser request for a web page, with a numeric response code and an optional, mandatory, or disallowed (based upon the status code) message. In code 404, the first digit indicates a client error, such as a mistyped Uniform Resource Locator (URL). The following two digits indicate the specific error encountered. HTTP’s use of three-digit codes is similar to the use of such codes in earlier protocols such as FTP and NNTP. At the HTTP level, a 404 response code is followed by a human-readable «reason phrase». The HTTP specification suggests the phrase «Not Found»[1] and many web servers by default issue an HTML page that includes both the 404 code and the «Not Found» phrase.
A 404 error is often returned when pages have been moved or deleted. In the first case, it is better to employ URL mapping or URL redirection by returning a 301 Moved Permanently response, which can be configured in most server configuration files, or through URL rewriting; in the second case, a 410 Gone should be returned. Because these two options require special server configuration, most websites do not make use of them.
404 errors should not be confused with DNS errors, which appear when the given URL refers to a server name that does not exist. A 404 error indicates that the server itself was found, but that the server was not able to retrieve the requested page.
History
The origin of the 404 error code dates back to the early days of the World Wide Web. In 1992, Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the Web, and his team at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, created the first web server software, called CERN httpd.[2] This software used a simple file system to store and retrieve web pages, and it assigned a three-digit number to each type of request and response. The number 404 was chosen to indicate that the requested file was not found on the server.[3]
The term «404 Not Found» was coined by Berners-Lee himself, who explained in a 1998 interview that he wanted to make the error message «slightly apologetic».[4][3] He also said that he considered using «400 Bad Request» instead, but decided that it was too vague and technical.[4][3]
The first documented case of a 404 error appearing on a web page was in 1993, when a user tried to access a page about the Mosaic web browser on the NCSA website. The page had been moved to a different location, but the link had not been updated.[2] The user reported the error to the NCSA team, who fixed the link and added a humorous message to their 404 page: «We’re sorry, but the document you requested is not here. Maybe you should try someplace else.»[3]
Since then, 404 errors have become one of the most common and recognizable errors on the Web. Many websites have customized their 404 pages with creative designs, messages, or features to entertain or assist their visitors. For example, Google’s 404 page features a broken robot and a link to its homepage,[5] while GitHub’s 404 page shows a random image of a parallax star field and a link to its status page.[6] Some websites have also used their 404 pages to showcase their brand personality, humor, or social causes. For instance, Lego’s 404 page shows an image of a Lego character searching for a missing brick,[7] while Amazon’s 404 page displays the image of a dog with a message about conservation.[8]
Soft 404 errors
Some websites report a «not found» error by returning a standard web page with a «200 OK» response code, falsely reporting that the page loaded properly; this is known as a soft 404. The term «soft 404» was introduced in 2004 by Ziv Bar-Yossef et al.[9]
Soft 404s are problematic for automated methods of discovering whether a link is broken. Some search engines, like Yahoo and Google, use automated processes to detect soft 404s.[10] Soft 404s can occur as a result of configuration errors when using certain HTTP server software, for example with the Apache software, when an Error Document 404 (specified in a .htaccess file) is specified as an absolute path (e.g. http://example.com/error.html) rather than a relative path (/error.html).[11] This can also be done on purpose to force some browsers (like Internet Explorer) to display a customized 404 error message rather than replacing what is served with a browser-specific «friendly» error message (in Internet Explorer, this behavior is triggered when a 404 is served and the received HTML is shorter than a certain length, and can be manually disabled by the user).
There are also «soft 3XX» errors where content is returned with a status 200 but comes from a redirected page, such as when missing pages are redirected to the domain root/home page.
Proxy servers
Some proxy servers generate a 404 error when a 500-range error code would be more correct. If the proxy server is unable to satisfy a request for a page because of a problem with the remote host (such as hostname resolution failures or refused TCP connections), this should be described as a 5xx Internal Server Error, but might deliver a 404 instead. This can confuse programs that expect and act on specific responses, as they can no longer easily distinguish between an absent web server and a missing web page on a web server that is present.
Intentional 404s
In July 2004, the UK telecom provider BT Group deployed the Cleanfeed content blocking system, which returns a 404 error to any request for content identified as potentially illegal by the Internet Watch Foundation.[12] Other ISPs return a HTTP 403 «forbidden» error in the same circumstances.[13] The practice of employing fake 404 errors as a means to conceal censorship has also been reported in Thailand[14] and Tunisia.[15] In Tunisia, where censorship was severe before the 2011 revolution, people became aware of the nature of the fake 404 errors and created an imaginary character named «Ammar 404» who represents «the invisible censor».[16]
Microsoft Internet Server 404 substatus error codes
The webserver software developed by Microsoft, Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS), returns a set of substatus codes with its 404 responses. The substatus codes take the form of decimal numbers appended to the 404 status code. The substatus codes are not officially recognized by IANA and are not returned by non-Microsoft servers.
Substatus codes
Microsoft’s IIS 7.0, IIS 7.5, and IIS 8.0 servers define the following HTTP substatus codes to indicate a more specific cause of a 404 error:
- 404.0 – Not found.
- 404.1 – Site Not Found.
- 404.2 – ISAPI or CGI restriction.
- 404.3 – MIME type restriction.
- 404.4 – No handler configured.
- 404.5 – Denied by request filtering configuration.
- 404.6 – Verb denied.
- 404.7 – File extension denied.
- 404.8 – Hidden namespace.
- 404.9 – File attribute hidden.
- 404.10 – Request header too long.
- 404.11 – Request contains double escape sequence.
- 404.12 – Request contains high-bit characters.
- 404.13 – Content length too large.
- 404.14 – Request URL too long.
- 404.15 – Query string too long.
- 404.16 – DAV request sent to the static file handler.
- 404.17 – Dynamic content mapped to the static file handler via a wildcard MIME mapping.
- 404.18 – Query string sequence denied.
- 404.19 – Denied by filtering rule.
- 404.20 – Too Many URL Segments.
Custom error pages
Web servers can typically be configured to display a customised 404 error page, including a more natural description, the parent site’s branding, and sometimes a site map, a search form or 404-page widget. The protocol level phrase, which is hidden from the user, is rarely customized. Internet Explorer, however, will not display custom pages unless they are larger than 512 bytes, opting instead to display a «friendly» error page.[17] Google Chrome included similar functionality, where the 404 is replaced with alternative suggestions generated by Google algorithms, if the page is under 512 bytes in size.[18] Another problem is that if the page does not provide a favicon, and a separate custom 404-page exists, extra traffic and longer loading times will be generated on every page view.[19][20]
Many organizations use 404 error pages as an opportunity to inject humor into what may otherwise be a serious website. For example, Metro UK shows a polar bear on a skateboard, and the web development agency Left Logic has a simple drawing program.[21] During the 2015 UK general election campaign the main political parties all used their 404 pages to either take aim at political opponents or show relevant policies to potential supporters.[22] In Europe, the NotFound project, created by multiple European organizations including Missing Children Europe and Child Focus, encourages site operators to add a snippet of code to serve customized 404 error pages[23] which provide data about missing children.[24]
While many websites send additional information in a 404 error message—such as a link to the homepage of a website or a search box—some also endeavor to find the correct web page the user wanted. Extensions are available for some content management systems (CMSs) to do this.[25]
Tracking 404 errors
A number of tools exist that crawl through a website to find pages that return 404 status codes. These tools can be helpful in finding links that exist within a particular website. The limitation of these tools is that they only find links within one particular website, and ignore 404s resulting from links on other websites. As a result, these tools miss out on 83% of the 404s on websites.[26] One way around this is to find 404 errors by analyzing external links.[27]
One of the most effective ways to discover 404 errors is by using Google Search Console, Google Analytics or crawling software.
Another common method is tracking traffic to 404 pages using log file analysis.[28] This can be useful to understand more about what 404s users reached on the site. Another method of tracking traffic to 404 pages is using JavaScript-based traffic tracking tools.[29]
Causes
There are many possible causes for a page not to exist. Some of the common ones are:[30][31][32]
- The page was deleted by the owner or administrator of the website.
- The page was moved to a different location or renamed without updating the links that point to it.
- The page was never created in the first place or is still under construction.
- The page is temporarily unavailable due to maintenance or technical issues.
- The page is blocked by the user’s network or firewall settings.
- The page is restricted by the website’s privacy or security policies.
- The page contains illegal or harmful content that was removed by the authorities or the website itself.
Solutions
If a user encounters a page that doesn’t exist, there are some steps they can take to try to find the information they are looking for or to report the problem.[30][31][32]
- Check the URL of the page. Sometimes, a simple typo or spelling mistake can cause a page not to load. Make sure the correct address is entered and try again.
- Refresh the page. Sometimes, a temporary glitch or network issue can prevent a page from loading. Try reloading the page by pressing F5 or clicking on the refresh button on the browser.
- Go back to the previous page. Sometimes, a link might be broken or outdated. Try going back to the page where the link was found and see if there is an updated or alternative link to the same information.
- Use a search engine. Sometimes, a page might be indexed by a search engine even if it doesn’t exist anymore. Try searching for keywords related to the topic of the page and see if other sources of information can be found.
- Contact the website owner or administrator. Sometimes, a page might be removed or moved without notice. Try contacting the person or organization responsible for the website and ask them about the status of the page. Their contact information can usually be found on their homepage or in their footer section.
- Report the error. Sometimes, a page might not exist due to an error on the website’s part. Try reporting the error to the website owner or administrator so they can fix it as soon as possible. Their feedback form or email address can usually be found on their homepage or in their footer section.
See also
- Blue screen of death
- Funky caching
- Link rot
- List of HTTP status codes
References
- ^ a b Fielding, R.; Reschke, J. (June 2014). Fielding, R; Reschke, J (eds.). «RFC 7231, HTTP/1.1 Semantics and Content, Section 6.5.4 404 Not Found». ietf.org. doi:10.17487/RFC7231. S2CID 14399078. Retrieved 13 December 2018.
- ^ a b «404 page design: best practices and awesome examples». www.justinmind.com. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b c d «What is a 404 error and what should I do if I get one? » Internet » Windows » Tech Ease». Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b What is the world wide web? — Twila Camp, retrieved 19 May 2023
- ^ «Google 404 Error Page». Google.
- ^ «Github 404 Error Page». Github.
- ^ «LEGO 404 Error Page». Lego.
- ^ «Amazon’s 404 error page». Amazon.
- ^ Ziv Bar-Yossef; Andrei Z. Broder; Ravi Kumar; Andrew Tompkins (2004). «Sic transit gloria telae». Proceedings of the 13th international conference on World Wide Web. pp. 328–337. doi:10.1145/988672.988716. ISBN 978-1581138443. S2CID 587547.
- ^ «Why is your crawler asking for strange URLs that have never existed on my site?». Yahoo Ysearch Help page. Archived from the original on 15 July 2014. Retrieved 4 September 2013.
- ^ «Farewell to soft 404s». Google Official Blog. Retrieved 20 September 2008.
- ^ «LINX Public Affairs » Cleanfeed: the facts». Publicaffairs.linx.net. 10 September 2004. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 6 March 2011.
- ^ «DEMON – Error 403». Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- ^ Sambandaraksa, Don (18 February 2009). «The old fake ‘404 Not Found’ routine — Dead link». Bangkok Post. Retrieved 12 September 2010.
- ^ Noman, Helmi (12 September 2008). «Tunisian journalist sues government agency for blocking Facebook, claims damage for the use of 404 error message instead of 403». Open Net Initiative. Retrieved 21 November 2010.
- ^ «Anti-censorship movement in Tunisia: creativity, courage and hope!». Global Voices Advocacy. 27 May 2010. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ «Friendly HTTP Error Pages». msdn.com. 18 August 2010. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- ^ «Issue 1695: Chrome needs option to turn off «Friendly 404″ displays». bugs.chromium.org. Retrieved 25 December 2021.
- ^ Heng, Christopher (7 September 2008). «What is Favicon.ico and How to Create a Favicon Icon for Your Website». The Site Wizard. Retrieved 23 February 2011.
- ^ «The Dastardly «favicon.ico not found» Error». Internet Folks. 3 August 1999.
- ^ «From skateboarding bears to missing children: The power of the 404 Not Found error page». Metro. 6 June 2011. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ «The political Page 404 war». BBC Newsbeat. 27 April 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2018.
- ^ «Notfound.org». notfound. Archived from the original on 2 September 2014.
- ^ «Missing children messages go on 404 error pages». BBC News. 27 September 2012. Retrieved 20 September 2014.
- ^ Swenson, Sahala (19 August 2008). «Make your 404 pages more useful». Official Google Webmaster Central Blog. Google, Inc. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ «Sources Leading To 404s». SpringTrax. Retrieved 11 February 2013.
- ^ Cushing, Anne (2 April 2013). «A Data-Centric Approach To Identifying 404 Pages Worth Saving». Search Engine Land. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ^ «Tracking and Preventing 404 Errors». 404errorpages.com. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ^ «Understand 404 Errors». SpringTrax.com. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ^ a b Edgar, Matthew (11 April 2023). «How To Fix 404 Errors On Your Website». Matthew Edgar. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b Frickey, Dean (18 November 2008). «A More Useful 404». A List Apart. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b «What ‘Error 404’ means and how to fix it». IONOS Digital Guide. 31 January 2023. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
External links
- A More Useful 404
- 404 Not Found of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content specification, at the Internet Engineering Task Force
- ErrorDocument Directive – instructions on custom error pages for the Apache 2.0 web server
- 404: Not Found – an award-winning song about the error code
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is a list of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response status codes. Status codes are issued by a server in response to a client’s request made to the server. It includes codes from IETF Request for Comments (RFCs), other specifications, and some additional codes used in some common applications of the HTTP. The first digit of the status code specifies one of five standard classes of responses. The optional message phrases shown are typical, but any human-readable alternative may be provided, or none at all.
Unless otherwise stated, the status code is part of the HTTP standard (RFC 9110).
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains the official registry of HTTP status codes.[1]
All HTTP response status codes are separated into five classes or categories. The first digit of the status code defines the class of response, while the last two digits do not have any classifying or categorization role. There are five classes defined by the standard:
- 1xx informational response – the request was received, continuing process
- 2xx successful – the request was successfully received, understood, and accepted
- 3xx redirection – further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request
- 4xx client error – the request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled
- 5xx server error – the server failed to fulfil an apparently valid request
1xx informational response
An informational response indicates that the request was received and understood. It is issued on a provisional basis while request processing continues. It alerts the client to wait for a final response. The message consists only of the status line and optional header fields, and is terminated by an empty line. As the HTTP/1.0 standard did not define any 1xx status codes, servers must not[note 1] send a 1xx response to an HTTP/1.0 compliant client except under experimental conditions.
- 100 Continue
- The server has received the request headers and the client should proceed to send the request body (in the case of a request for which a body needs to be sent; for example, a POST request). Sending a large request body to a server after a request has been rejected for inappropriate headers would be inefficient. To have a server check the request’s headers, a client must send
Expect: 100-continueas a header in its initial request and receive a100 Continuestatus code in response before sending the body. If the client receives an error code such as 403 (Forbidden) or 405 (Method Not Allowed) then it should not send the request’s body. The response417 Expectation Failedindicates that the request should be repeated without theExpectheader as it indicates that the server does not support expectations (this is the case, for example, of HTTP/1.0 servers).[2] - 101 Switching Protocols
- The requester has asked the server to switch protocols and the server has agreed to do so.
- 102 Processing (WebDAV; RFC 2518)
- A WebDAV request may contain many sub-requests involving file operations, requiring a long time to complete the request. This code indicates that the server has received and is processing the request, but no response is available yet.[3] This prevents the client from timing out and assuming the request was lost. The status code is deprecated.[4]
- 103 Early Hints (RFC 8297)
- Used to return some response headers before final HTTP message.[5]
2xx success
This class of status codes indicates the action requested by the client was received, understood, and accepted.[1]
- 200 OK
- Standard response for successful HTTP requests. The actual response will depend on the request method used. In a GET request, the response will contain an entity corresponding to the requested resource. In a POST request, the response will contain an entity describing or containing the result of the action.
- 201 Created
- The request has been fulfilled, resulting in the creation of a new resource.[6]
- 202 Accepted
- The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. The request might or might not be eventually acted upon, and may be disallowed when processing occurs.
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information (since HTTP/1.1)
- The server is a transforming proxy (e.g. a Web accelerator) that received a 200 OK from its origin, but is returning a modified version of the origin’s response.[7][8]
- 204 No Content
- The server successfully processed the request, and is not returning any content.
- 205 Reset Content
- The server successfully processed the request, asks that the requester reset its document view, and is not returning any content.
- 206 Partial Content
- The server is delivering only part of the resource (byte serving) due to a range header sent by the client. The range header is used by HTTP clients to enable resuming of interrupted downloads, or split a download into multiple simultaneous streams.
- 207 Multi-Status (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The message body that follows is by default an XML message and can contain a number of separate response codes, depending on how many sub-requests were made.[9]
- 208 Already Reported (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The members of a DAV binding have already been enumerated in a preceding part of the (multistatus) response, and are not being included again.
- 226 IM Used (RFC 3229)
- The server has fulfilled a request for the resource, and the response is a representation of the result of one or more instance-manipulations applied to the current instance.[10]
3xx redirection
This class of status code indicates the client must take additional action to complete the request. Many of these status codes are used in URL redirection.[1]
A user agent may carry out the additional action with no user interaction only if the method used in the second request is GET or HEAD. A user agent may automatically redirect a request. A user agent should detect and intervene to prevent cyclical redirects.[11]
- 300 Multiple Choices
- Indicates multiple options for the resource from which the client may choose (via agent-driven content negotiation). For example, this code could be used to present multiple video format options, to list files with different filename extensions, or to suggest word-sense disambiguation.
- 301 Moved Permanently
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI.
- 302 Found (Previously «Moved temporarily»)
- Tells the client to look at (browse to) another URL. The HTTP/1.0 specification (RFC 1945) required the client to perform a temporary redirect with the same method (the original describing phrase was «Moved Temporarily»),[12] but popular browsers implemented 302 redirects by changing the method to GET. Therefore, HTTP/1.1 added status codes 303 and 307 to distinguish between the two behaviours.[11]
- 303 See Other (since HTTP/1.1)
- The response to the request can be found under another URI using the GET method. When received in response to a POST (or PUT/DELETE), the client should presume that the server has received the data and should issue a new GET request to the given URI.
- 304 Not Modified
- Indicates that the resource has not been modified since the version specified by the request headers If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match. In such case, there is no need to retransmit the resource since the client still has a previously-downloaded copy.
- 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1)
- The requested resource is available only through a proxy, the address for which is provided in the response. For security reasons, many HTTP clients (such as Mozilla Firefox and Internet Explorer) do not obey this status code.
- 306 Switch Proxy
- No longer used. Originally meant «Subsequent requests should use the specified proxy.»
- 307 Temporary Redirect (since HTTP/1.1)
- In this case, the request should be repeated with another URI; however, future requests should still use the original URI. In contrast to how 302 was historically implemented, the request method is not allowed to be changed when reissuing the original request. For example, a POST request should be repeated using another POST request.
- 308 Permanent Redirect
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI. 308 parallel the behaviour of 301, but does not allow the HTTP method to change. So, for example, submitting a form to a permanently redirected resource may continue smoothly.
4xx client errors
This class of status code is intended for situations in which the error seems to have been caused by the client. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. These status codes are applicable to any request method. User agents should display any included entity to the user.
- 400 Bad Request
- The server cannot or will not process the request due to an apparent client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, size too large, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
- 401 Unauthorized
- Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is required and has failed or has not yet been provided. The response must include a WWW-Authenticate header field containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. See Basic access authentication and Digest access authentication. 401 semantically means «unauthorised», the user does not have valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
- Some sites incorrectly issue HTTP 401 when an IP address is banned from the website (usually the website domain) and that specific address is refused permission to access a website.[citation needed]
- 402 Payment Required
- Reserved for future use. The original intention was that this code might be used as part of some form of digital cash or micropayment scheme, as proposed, for example, by GNU Taler,[14] but that has not yet happened, and this code is not widely used. Google Developers API uses this status if a particular developer has exceeded the daily limit on requests.[15] Sipgate uses this code if an account does not have sufficient funds to start a call.[16] Shopify uses this code when the store has not paid their fees and is temporarily disabled.[17] Stripe uses this code for failed payments where parameters were correct, for example blocked fraudulent payments.[18]
- 403 Forbidden
- The request contained valid data and was understood by the server, but the server is refusing action. This may be due to the user not having the necessary permissions for a resource or needing an account of some sort, or attempting a prohibited action (e.g. creating a duplicate record where only one is allowed). This code is also typically used if the request provided authentication by answering the WWW-Authenticate header field challenge, but the server did not accept that authentication. The request should not be repeated.
- 404 Not Found
- The requested resource could not be found but may be available in the future. Subsequent requests by the client are permissible.
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- A request method is not supported for the requested resource; for example, a GET request on a form that requires data to be presented via POST, or a PUT request on a read-only resource.
- 406 Not Acceptable
- The requested resource is capable of generating only content not acceptable according to the Accept headers sent in the request. See Content negotiation.
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
- The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy.
- 408 Request Timeout
- The server timed out waiting for the request. According to HTTP specifications: «The client did not produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time.»
- 409 Conflict
- Indicates that the request could not be processed because of conflict in the current state of the resource, such as an edit conflict between multiple simultaneous updates.
- 410 Gone
- Indicates that the resource requested was previously in use but is no longer available and will not be available again. This should be used when a resource has been intentionally removed and the resource should be purged. Upon receiving a 410 status code, the client should not request the resource in the future. Clients such as search engines should remove the resource from their indices. Most use cases do not require clients and search engines to purge the resource, and a «404 Not Found» may be used instead.
- 411 Length Required
- The request did not specify the length of its content, which is required by the requested resource.
- 412 Precondition Failed
- The server does not meet one of the preconditions that the requester put on the request header fields.
- 413 Payload Too Large
- The request is larger than the server is willing or able to process. Previously called «Request Entity Too Large» in RFC 2616.[19]
- 414 URI Too Long
- The URI provided was too long for the server to process. Often the result of too much data being encoded as a query-string of a GET request, in which case it should be converted to a POST request. Called «Request-URI Too Long» previously in RFC 2616.[20]
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
- The request entity has a media type which the server or resource does not support. For example, the client uploads an image as image/svg+xml, but the server requires that images use a different format.
- 416 Range Not Satisfiable
- The client has asked for a portion of the file (byte serving), but the server cannot supply that portion. For example, if the client asked for a part of the file that lies beyond the end of the file. Called «Requested Range Not Satisfiable» previously RFC 2616.[21]
- 417 Expectation Failed
- The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field.[22]
- 418 I’m a teapot (RFC 2324, RFC 7168)
- This code was defined in 1998 as one of the traditional IETF April Fools’ jokes, in RFC 2324, Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol, and is not expected to be implemented by actual HTTP servers. The RFC specifies this code should be returned by teapots requested to brew coffee.[23] This HTTP status is used as an Easter egg in some websites, such as Google.com’s «I’m a teapot» easter egg.[24][25][26] Sometimes, this status code is also used as a response to a blocked request, instead of the more appropriate 403 Forbidden.[27][28]
- 421 Misdirected Request
- The request was directed at a server that is not able to produce a response (for example because of connection reuse).
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
- The request was well-formed but was unable to be followed due to semantic errors.[9]
- 423 Locked (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The resource that is being accessed is locked.[9]
- 424 Failed Dependency (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The request failed because it depended on another request and that request failed (e.g., a PROPPATCH).[9]
- 425 Too Early (RFC 8470)
- Indicates that the server is unwilling to risk processing a request that might be replayed.
- 426 Upgrade Required
- The client should switch to a different protocol such as TLS/1.3, given in the Upgrade header field.
- 428 Precondition Required (RFC 6585)
- The origin server requires the request to be conditional. Intended to prevent the ‘lost update’ problem, where a client GETs a resource’s state, modifies it, and PUTs it back to the server, when meanwhile a third party has modified the state on the server, leading to a conflict.[29]
- 429 Too Many Requests (RFC 6585)
- The user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time. Intended for use with rate-limiting schemes.[29]
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large (RFC 6585)
- The server is unwilling to process the request because either an individual header field, or all the header fields collectively, are too large.[29]
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons (RFC 7725)
- A server operator has received a legal demand to deny access to a resource or to a set of resources that includes the requested resource.[30] The code 451 was chosen as a reference to the novel Fahrenheit 451 (see the Acknowledgements in the RFC).
5xx server errors
The server failed to fulfil a request.
Response status codes beginning with the digit «5» indicate cases in which the server is aware that it has encountered an error or is otherwise incapable of performing the request. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and indicate whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. Likewise, user agents should display any included entity to the user. These response codes are applicable to any request method.
- 500 Internal Server Error
- A generic error message, given when an unexpected condition was encountered and no more specific message is suitable.
- 501 Not Implemented
- The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfil the request. Usually this implies future availability (e.g., a new feature of a web-service API).
- 502 Bad Gateway
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable
- The server cannot handle the request (because it is overloaded or down for maintenance). Generally, this is a temporary state.[31]
- 504 Gateway Timeout
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
- The server does not support the HTTP version used in the request.
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates (RFC 2295)
- Transparent content negotiation for the request results in a circular reference.[32]
- 507 Insufficient Storage (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The server is unable to store the representation needed to complete the request.[9]
- 508 Loop Detected (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The server detected an infinite loop while processing the request (sent instead of 208 Already Reported).
- 510 Not Extended (RFC 2774)
- Further extensions to the request are required for the server to fulfil it.[33]
- 511 Network Authentication Required (RFC 6585)
- The client needs to authenticate to gain network access. Intended for use by intercepting proxies used to control access to the network (e.g., «captive portals» used to require agreement to Terms of Service before granting full Internet access via a Wi-Fi hotspot).[29]
Unofficial codes
The following codes are not specified by any standard.
- 218 This is fine (Apache HTTP Server)
- Used by Apache servers. A catch-all error condition allowing the passage of message bodies through the server when the
ProxyErrorOverridesetting is enabled. It is displayed in this situation instead of a 4xx or 5xx error message.[34] - 419 Page Expired (Laravel Framework)
- Used by the Laravel Framework when a CSRF Token is missing or expired.[citation needed]
- 420 Method Failure (Spring Framework)
- A deprecated response used by the Spring Framework when a method has failed.[35]
- 420 Enhance Your Calm (Twitter)
- Returned by version 1 of the Twitter Search and Trends API when the client is being rate limited; versions 1.1 and later use the 429 Too Many Requests response code instead.[36] The phrase «Enhance your calm» comes from the 1993 movie Demolition Man, and its association with this number is likely a reference to cannabis.[citation needed]
- 430 Request Header Fields Too Large (Shopify)
- Used by Shopify, instead of the 429 Too Many Requests response code, when too many URLs are requested within a certain time frame.[37]
- 450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft)
- The Microsoft extension code indicated when Windows Parental Controls are turned on and are blocking access to the requested webpage.[38]
- 498 Invalid Token (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 498 indicates an expired or otherwise invalid token.[39]
- 499 Token Required (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 499 indicates that a token is required but was not submitted.[39]
- 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded (Apache Web Server/cPanel)
- The server has exceeded the bandwidth specified by the server administrator; this is often used by shared hosting providers to limit the bandwidth of customers.[40]
- 529 Site is overloaded
- Used by Qualys in the SSLLabs server testing API to signal that the site can’t process the request.[41]
- 530 Site is frozen
- Used by the Pantheon Systems web platform to indicate a site that has been frozen due to inactivity.[42]
- 598 (Informal convention) Network read timeout error
- Used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network read timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.[43]
- 599 Network Connect Timeout Error
- An error used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network connect timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.
Internet Information Services
Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) web server expands the 4xx error space to signal errors with the client’s request.
- 440 Login Time-out
- The client’s session has expired and must log in again.[44]
- 449 Retry With
- The server cannot honour the request because the user has not provided the required information.[45]
- 451 Redirect
- Used in Exchange ActiveSync when either a more efficient server is available or the server cannot access the users’ mailbox.[46] The client is expected to re-run the HTTP AutoDiscover operation to find a more appropriate server.[47]
IIS sometimes uses additional decimal sub-codes for more specific information,[48] however these sub-codes only appear in the response payload and in documentation, not in the place of an actual HTTP status code.
nginx
The nginx web server software expands the 4xx error space to signal issues with the client’s request.[49][50]
- 444 No Response
- Used internally[51] to instruct the server to return no information to the client and close the connection immediately.
- 494 Request header too large
- Client sent too large request or too long header line.
- 495 SSL Certificate Error
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has provided an invalid client certificate.
- 496 SSL Certificate Required
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when a client certificate is required but not provided.
- 497 HTTP Request Sent to HTTPS Port
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has made a HTTP request to a port listening for HTTPS requests.
- 499 Client Closed Request
- Used when the client has closed the request before the server could send a response.
Cloudflare
Cloudflare’s reverse proxy service expands the 5xx series of errors space to signal issues with the origin server.[52]
- 520 Web Server Returned an Unknown Error
- The origin server returned an empty, unknown, or unexpected response to Cloudflare.[53]
- 521 Web Server Is Down
- The origin server refused connections from Cloudflare. Security solutions at the origin may be blocking legitimate connections from certain Cloudflare IP addresses.
- 522 Connection Timed Out
- Cloudflare timed out contacting the origin server.
- 523 Origin Is Unreachable
- Cloudflare could not reach the origin server; for example, if the DNS records for the origin server are incorrect or missing.
- 524 A Timeout Occurred
- Cloudflare was able to complete a TCP connection to the origin server, but did not receive a timely HTTP response.
- 525 SSL Handshake Failed
- Cloudflare could not negotiate a SSL/TLS handshake with the origin server.
- 526 Invalid SSL Certificate
- Cloudflare could not validate the SSL certificate on the origin web server. Also used by Cloud Foundry’s gorouter.
- 527 Railgun Error
- Error 527 indicates an interrupted connection between Cloudflare and the origin server’s Railgun server.[54]
- 530
- Error 530 is returned along with a 1xxx error.[55]
AWS Elastic Load Balancing
Amazon Web Services’ Elastic Load Balancing adds a few custom return codes to signal issues either with the client request or with the origin server.[56]
- 460
- Client closed the connection with the load balancer before the idle timeout period elapsed. Typically when client timeout is sooner than the Elastic Load Balancer’s timeout.[56]
- 463
- The load balancer received an X-Forwarded-For request header with more than 30 IP addresses.[56]
- 464
- Incompatible protocol versions between Client and Origin server.[56]
- 561 Unauthorized
- An error around authentication returned by a server registered with a load balancer. You configured a listener rule to authenticate users, but the identity provider (IdP) returned an error code when authenticating the user.[56]
Caching warning codes (obsoleted)
The following caching related warning codes were specified under RFC 7234. Unlike the other status codes above, these were not sent as the response status in the HTTP protocol, but as part of the «Warning» HTTP header.[57][58]
Since this «Warning» header is often neither sent by servers nor acknowledged by clients, this header and its codes were obsoleted by the HTTP Working Group in 2022 with RFC 9111.[59]
- 110 Response is Stale
- The response provided by a cache is stale (the content’s age exceeds a maximum age set by a Cache-Control header or heuristically chosen lifetime).
- 111 Revalidation Failed
- The cache was unable to validate the response, due to an inability to reach the origin server.
- 112 Disconnected Operation
- The cache is intentionally disconnected from the rest of the network.
- 113 Heuristic Expiration
- The cache heuristically chose a freshness lifetime greater than 24 hours and the response’s age is greater than 24 hours.
- 199 Miscellaneous Warning
- Arbitrary, non-specific warning. The warning text may be logged or presented to the user.
- 214 Transformation Applied
- Added by a proxy if it applies any transformation to the representation, such as changing the content encoding, media type or the like.
- 299 Miscellaneous Persistent Warning
- Same as 199, but indicating a persistent warning.
See also
- Custom error pages
- List of FTP server return codes
- List of HTTP header fields
- List of SMTP server return codes
- Common Log Format
Explanatory notes
- ^ Emphasised words and phrases such as must and should represent interpretation guidelines as given by RFC 2119
References
- ^ a b c «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry». Iana.org. Archived from the original on December 11, 2011. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ Fielding, Roy T. «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 10.1.1 «Expect»«.
- ^ Goland, Yaronn; Whitehead, Jim; Faizi, Asad; Carter, Steve R.; Jensen, Del (February 1999). HTTP Extensions for Distributed Authoring – WEBDAV. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2518. RFC 2518. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «102 Processing — HTTP MDN». 102 status code is deprecated
- ^ Oku, Kazuho (December 2017). An HTTP Status Code for Indicating Hints. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8297. RFC 8297. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ Stewart, Mark; djna. «Create request with POST, which response codes 200 or 201 and content». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.3.4».
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 7.7».
- ^ a b c d e Dusseault, Lisa, ed. (June 2007). HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV). IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4918. RFC 4918. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Delta encoding in HTTP. IETF. January 2002. doi:10.17487/RFC3229. RFC 3229. Retrieved February 25, 2011.
- ^ a b «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.4 «Redirection 3xx»«.
- ^ Berners-Lee, Tim; Fielding, Roy T.; Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk (May 1996). Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.0. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1945. RFC 1945. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «The GNU Taler tutorial for PHP Web shop developers 0.4.0». docs.taler.net. Archived from the original on November 8, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2017.
- ^ «Google API Standard Error Responses». 2016. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ «Sipgate API Documentation». Archived from the original on July 10, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ «Shopify Documentation». Archived from the original on July 25, 2018. Retrieved July 25, 2018.
- ^ «Stripe API Reference – Errors». stripe.com. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 413». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 414». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 416». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ TheDeadLike. «HTTP/1.1 Status Codes 400 and 417, cannot choose which». serverFault. Archived from the original on October 10, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Larry Masinter (April 1, 1998). Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol (HTCPCP/1.0). doi:10.17487/RFC2324. RFC 2324.
Any attempt to brew coffee with a teapot should result in the error code «418 I’m a teapot». The resulting entity body MAY be short and stout.
- ^ I’m a teapot
- ^ Barry Schwartz (August 26, 2014). «New Google Easter Egg For SEO Geeks: Server Status 418, I’m A Teapot». Search Engine Land. Archived from the original on November 15, 2015. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ «Google’s Teapot». Retrieved October 23, 2017.[dead link]
- ^ «Enable extra web security on a website». DreamHost. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ «I Went to a Russian Website and All I Got Was This Lousy Teapot». PCMag. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Nottingham, M.; Fielding, R. (April 2012). «RFC 6585 – Additional HTTP Status Codes». Request for Comments. Internet Engineering Task Force. Archived from the original on May 4, 2012. Retrieved May 1, 2012.
- ^ Bray, T. (February 2016). «An HTTP Status Code to Report Legal Obstacles». ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ alex. «What is the correct HTTP status code to send when a site is down for maintenance?». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Holtman, Koen; Mutz, Andrew H. (March 1998). Transparent Content Negotiation in HTTP. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2295. RFC 2295. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk; Leach, Paul; Lawrence, Scott (February 2000). An HTTP Extension Framework. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2774. RFC 2774. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «218 This is fine — HTTP status code explained». HTTP.dev. Retrieved July 25, 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Enum HttpStatus». Spring Framework. org.springframework.http. Archived from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «Twitter Error Codes & Responses». Twitter. 2014. Archived from the original on September 27, 2017. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Status Codes and SEO: what you need to know». ContentKing. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ «Screenshot of error page». Archived from the original (bmp) on May 11, 2013. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ a b «Using token-based authentication». ArcGIS Server SOAP SDK. Archived from the original on September 26, 2014. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Error Codes and Quick Fixes». Docs.cpanel.net. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved October 15, 2015.
- ^ «SSL Labs API v3 Documentation». github.com.
- ^ «Platform Considerations | Pantheon Docs». pantheon.io. Archived from the original on January 6, 2017. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ^ «HTTP status codes — ascii-code.com». www.ascii-code.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2017. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^
«Error message when you try to log on to Exchange 2007 by using Outlook Web Access: «440 Login Time-out»«. Microsoft. 2010. Retrieved November 13, 2013. - ^ «2.2.6 449 Retry With Status Code». Microsoft. 2009. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved October 26, 2009.
- ^ «MS-ASCMD, Section 3.1.5.2.2». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 26, 2015. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «Ms-oxdisco». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «The HTTP status codes in IIS 7.0». Microsoft. July 14, 2009. Archived from the original on April 9, 2009. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
- ^ «ngx_http_request.h». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on September 19, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «ngx_http_special_response.c». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «return» directive Archived March 1, 2018, at the Wayback Machine (http_rewrite module) documentation.
- ^ «Troubleshooting: Error Pages». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Error 520: web server returns an unknown error». Cloudflare.
- ^ «527 Error: Railgun Listener to origin error». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on October 13, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ «Error 530». Cloudflare. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e «Troubleshoot Your Application Load Balancers – Elastic Load Balancing». docs.aws.amazon.com. Retrieved May 17, 2023.
- ^ «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Caching». datatracker.ietf.org. Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- ^ «Warning — HTTP | MDN». developer.mozilla.org. Retrieved August 15, 2021.
Some text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.5 Generic (CC BY-SA 2.5) license.
- ^ «RFC 9111: HTTP Caching, Section 5.5 «Warning»«. June 2022.
External links
- «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15 «Status Codes»«.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry at the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
- HTTP status codes at http-statuscode.com
- MDN status code reference at mozilla.org
О чем сообщает? Ошибка 404 – распространенная заглушка для сайта. Она появляется, если пользователь хотел открыть какую-то страницу по ссылке, а ее там уже не существует. Владелец ресурса удалил ее намеренно, или произошел сбой.
Что с ней делать? Подобные ошибки нужно периодически искать на сайте и удалять. Однако никто не может предсказать, когда произойдет очередной баг. Поэтому на такие случаи страница с ошибкой 404 должна нести пользу для посетителей.
В статье рассказывается:
- Что означает ошибка 404
- Причины ошибки
- Вред от ошибки 404 на сайте
- Как выявить ошибку 404
- Как исправить ошибку 404 Not Found
- Как улучшить страницу с ошибкой 404
-
Пройди тест и узнай, какая сфера тебе подходит:
айти, дизайн или маркетинг.Бесплатно от Geekbrains
Каждый из нас неоднократно сталкивался с ошибкой 404, так что же это значит? Данная неполадка возникает в том случае, если не получается найти страницу по запросу пользователя.
Иными словами, ошибка 404 означает, что, несмотря на стабильное соединение, серверу не удалось отыскать запрашиваемую информацию.
О данной ошибке браузер может сообщить несколькими способами:
- 404 error.
- 404 page not found.
- Error 404.
- HTTP 404.
- The requested URL was found on web server.
- 404 file and directory was not found.
Топ-30 самых востребованных и высокооплачиваемых профессий 2023
Поможет разобраться в актуальной ситуации на рынке труда
Подборка 50+ бесплатных нейросетей для упрощения работы и увеличения заработка
Только проверенные нейросети с доступом из России и свободным использованием
ТОП-100 площадок для поиска работы от GeekBrains
Список проверенных ресурсов реальных вакансий с доходом от 210 000 ₽
Уже скачали 22618
Код этой ошибки складывается из двух составляющих:
- первая цифра «4» говорит о том, что это проблема в работе устройства клиента, а не сервера;
- цифры «04» определяют спецификацию ошибки.
Для ошибки подключения 404 характерен определенный интерфейс экрана, который разработчики создают при написании кода будущего сайта.
Пожалуй, до сих пор это один из самых распространенных багов, с которым сталкиваются пользователи. Однако, справедливости ради, в наши дни ошибка 404 (сервер не найден) возникает гораздо реже, чем в конце 90-х годов и начале нулевых. Это обусловлено следующими факторами.
- Специалисты технической поддержки крупных сайтов отлично понимают, что подобные баги ухудшают конверсию и портят пользовательский опыт, перенаправляя потенциальную аудиторию на другие страницы, содержащие похожую информацию.
- Веб-разработчики создают кастомные площадки ошибок, чтобы удержать посетителей ресурса.
Причины ошибки
Ошибка 404 not found возникает по ряду причин.
- Неверный адрес или ссылка, которая ведет к несуществующей странице. В частности, пользователь может допустить опечатку при вводе в поисковую строку. Если домен написан верно, то на экране появится уведомление о том, что страница не найдена. В случае если название будет указано неправильно, сайт даже не откроется.
- Битая ссылка (неактивный URL, который никуда не ведет). Иногда при внутренней перелинковке разработчики забывают убрать пути к удаленным площадкам.
- Удаленная с сервера страница. Порой ссылка для перехода остается в закладках браузера или на сторонних ресурсах (например, форумах и т. д.). Если пользователь попытается воспользоваться таким адресом, на экране возникнет сообщение об ошибке сервера 404.
Читайте также
- Неверно настроенная автоматическая переадресация с одного URL на другой. Например, в компании было принято решение о том, что нужно изменить адрес сайта. А в процессе редизайна веб-разработчики, заменив URL на новый, забыли про связанные ссылки.
- Технические проблемы на сервере (крайне редкий случай).
Данная ошибка чаще всего появляется, если не получается найти запрошенную пользователем страницу.
Вред от ошибки 404 на сайте
Ошибка 404 на сайте, вероятнее всего, приведет к тому, что пользователь закроет страницу и больше никогда не вернется, решив, что компания не работает. Все дело в том, что сообщение о баге неинформативно для посетителей ресурса.
Пустая белая страница с непонятным текстом (без навигации, логотипа, корпоративных цветов и юмора) не заставит пользователя, даже если он заинтересован в продукте или услугах компании, вернуться на сайт еще раз. Он закроет вкладку и начнет просматривать предложения конкурентов.
Часто данная ошибка ухудшает трафик и приводит к снижению продаж.
SEO
Если абсолютное большинство страниц сайта выдают ошибку 404, это может плохо повлиять на его рейтинг. Однако, если багов не так много, поисковики просто не будут их индексировать (это никак не отразится на SEO).
Скачать
файл
E-commerce
Если пользователь решил приобрести какой-либо товар или услугу, он это сделает в любом случае. Неполадки на сайте заставят его уйти к конкурентам, из-за чего компания потеряет прибыль.
Мотивы потенциального покупателя в этом случае объясняются максимально просто.
- Он загорелся какой-либо вещью и зашел на сайт интернет-магазина.
- Подобрал в каталоге подходящий товар.
- Кликнув на него мышкой, открывает страницу и видит ошибку https 404.
- Вполне справедливо предполагает, что товара нет в наличии или просто сайт глючит.
- Уходит на площадку конкурентов, которые продают похожие продукты.
Таким образом, чтобы не портить пользовательский опыт и улучшить коммуникацию с посетителями сайта, крайне важно своевременно выявлять и исправлять все ошибки 404.
Как выявить ошибку 404
Если сайт небольшой, не составит труда проверить работоспособность всех ссылок вручную. Однако если он состоит из огромного количества страниц, для этих целей потребуется специальный софт.
Популярные сервисы и программы, которые помогают находить битые ссылки, перечислены ниже.
Search Console Google
Чтобы найти страницы с ошибкой 404 с помощью данной консоли, потребуется несколько простых действий.
- Войти в учетную запись Google и перейти в Search Console.
- Сначала открыть раздел «Ошибки сканирования», а затем – «Диагностика».
- Кликнуть мышкой на «Not Found».
Чтобы получить доступ к списку страниц, которые содержат ошибку, необходимо подтвердить права на сайт. Для этого нужно добавить проверочную запись TXT в записи DNS регистратора домена. Данная операция никак не повлияет на работу ресурса.
«Яндекс.Вебмастер»
Этот специализированный сервис от компании «Яндекс» существенно облегчает процесс поиска ошибок 404 в онлайн-режиме.
Найти проблемные страницы можно всего в несколько кликов.
- Пройти авторизацию в Яндекс-аккаунте и отрыть «Вебмастер».
- Сначала выбрать «Индексирование», потом «Доступные для поиска страницы», а затем «Исключенные страницы».
- В сформированном списке выставить фильтр «Ошибка HTTP: 404».
insert_bn id=»all»]
Для того чтобы пользоваться сервисом «Яндекс.Вебмастер», необходимо подтвердить права владения сайтом. Для этого нужно добавить метатег в HTML-код главной страницы.
Screaming Frog
Сначала требуется скачать программу и установить ее на компьютер. Затем можно приступать к поиску ошибок 404 по URL проверяемого сайта. Огромный плюс этой утилиты в том, что битые ссылки определяются даже в бесплатной версии.
Это бесплатное Desktop-приложение позволяет оперативно найти нерабочие и несуществующие ссылки.
Как исправить ошибку 404 Not Found
Сначала необходимо выяснить, почему возникла ошибка 404. Самые распространенные причины перечислены ниже.
- Ссылка ведет к несуществующей странице из-за ошибки в URL. Чтобы решить проблему, достаточно ввести правильный адрес, чтобы сервер отдавал код «200 ОК».
- Битая ссылка. Как уже упоминалось выше, часто подобные адреса появляются при внутренней перелинковке сайта (страницу удалили, а путь остался). В этом случае есть два варианта: удалить ссылку или заменить ее другой.
Только до 25.09
Скачай подборку материалов, чтобы гарантированно найти работу в IT за 14 дней
Список документов:
ТОП-100 площадок для поиска работы от GeekBrains
20 профессий 2023 года, с доходом от 150 000 рублей
Чек-лист «Как успешно пройти собеседование»
Чтобы получить файл, укажите e-mail:
Введите e-mail, чтобы получить доступ к документам
Подтвердите, что вы не робот,
указав номер телефона:
Введите телефон, чтобы получить доступ к документам
Уже скачали 52300
Как исправить ошибку 404? Вручную удалять и менять адреса удобно лишь в том случае, если сайт небольшой. Если же речь идет о крупном ресурсе, данный процесс стоит автоматизировать. Для этих целей подходят специальные плагины для внутренней перелинковки (например, Terms Description, Dagon Design Sitemap Generator и др.) и сервисы для автоматического формирования адресов страниц (в частности, Cyr-To-Lat).

Читайте также
Чтобы посетители сайта реже встречались с ошибкой 404 (не найдено), можно воспользоваться полезными советами от опытных веб-разработчиков.
- Не стоит присваивать основным разделам сайта сложные адреса. Это позволит снизить количество опечаток в URL.
- Не надо часто менять адреса страниц. Это не только создает неудобства пользователям, но и «путает» поисковые алгоритмы.
- Для размещения сайта важно выбрать надежный сервер. Это поможет избежать технических неисправностей, связанных с проблемами в его работе.
Итак, ошибки клиента с кодом состояния «404» можно найти и исправить без особых затруднений, если они возникли внутри сайта. Однако битая ссылка может быть размещена и на сторонних ресурсах. Например, некоторое время назад на партнерской площадке была выложена рекламная публикация, содержащая путь к одной из страниц, которую впоследствии удалили.
Чтобы исправить ошибку, необходимо связаться с технической поддержкой того сайта, на котором до сих пор висит ссылка, ведущая по несуществующему адресу. Если удалить или исправить ее невозможно, можно попробовать обыграть ситуацию в свою пользу.
Как улучшить страницу с ошибкой 404
Чтобы посетители судорожно не закрывали вкладки, гадая, почему сайт выдает ошибку 404, важно успокоить пользователей, дав понять, что все под контролем. Просто возникли небольшие проблемы, над устранением которых уже трудятся специалисты.
Совет из практики: интерфейс страницы с ошибкой должен быть выполнен в фирменном стиле компании и визуально соответствовать остальным разделам сайта.
Чтобы не портить пользовательский опыт, необходимо реализовать несколько важных шагов.
Шаг 1. Донести до посетителей сайта, что все под контролем.
Безликое стандартное «Not Found» – пустой звук для большинства пользователей. Поэтому, чтобы объяснить, что произошло, лучше выбрать простые и понятные формулировки. Например:
- «Нам не удалось найти страницу».
- «Похоже, такой страницы не существует» и т. п.
Хорошая идея – можно более детально объяснить посетителям сайта, почему они столкнулись с ошибкой 404. К примеру:
- «Возможно, вы допустили ошибку, когда вводили или копировали адрес».
- «Владелец сайта удалил или переместил эту страницу. Давайте вернемся на главную».
Шаг 2. Перенаправить пользователя в другой раздел.
Несмотря на временные неисправности, важно удержать посетителя на сайте, чтобы он не ушел искать аналогичные товары и услуги у конкурентов. Для этих целей подходит призыв к действию – можно предложить перейти в другие разделы:
- на главную страницу;
- на площадку с актуальным контентом, релевантным запросу;
- в блок навигации, где можно самостоятельно выбрать интересующую страницу;
- в чат службы технической поддержки или отдела продаж, чтобы проконсультироваться со специалистами компании и оформить заказ другим способом.
Вполне логично, что, если не будет призыва к действию, не будет и отклика от посетителя сайта. Потенциальный клиент уйдет к конкурентам.
Желательно на страницу с ошибкой 404 добавить контакты специалистов технической поддержки, чтобы у пользователя была возможность связаться с администратором сайта.
Шаг 3. Сгладить негатив с помощью юмора.
Забавные шутки и сленг, понятные пользователям, позволят разрядить обстановку. Нужно постараться, чтобы каждый посетитель узнал в юморе себя – после этого он, вероятнее всего, сменит гнев на милость.
Итак, подводя итог, стоит отметить, что современные компании прикладывают максимум усилий, чтобы не только привлечь целевую аудиторию, но и удержать посетителей на сайте. Обидно терять потенциальных клиентов из-за временных неисправностей. Поэтому крайне важно разработать страницу, которая не только сообщает об ошибке 404, но и доступным языком объясняет пользователям, что произошло и что делать дальше. Это значительно повышает шансы, что они задержатся на сайте и все же совершат покупку.