Программа: Mailwizz
Действие: импорт списков / загрузка файлов / сохранение в базу данных
Ошибка: Ошибка 400!
Невозможно определить CSRF.
Причина и решение: Ошибка происходит, когда вы загружаете файл большего размера, чем разрешено лимитом PHP, и для передачи токена CSRF нет места.
Решение состоит в том, чтобы увеличить лимит загрузки из вашего файла настроек PHP (php.ini).
Примечание:
Ошибка «Не удалось проверить токен CSRF» обычно появляется, когда вы отправляете форму, содержащую поле для загрузки файла, и выбираете файл, размер которого превышает разрешенный размер файла для загрузки на ваш сервер.
MailWizz не контролирует это поведение, размер загружаемого файла определяется вашим веб-сервером и вашими настройками PHP.
Для веб-сервера nginx прочтите эту статью .
Информацию о веб-сервере Apache с PHP см. В этой статье .
О самом PHP см. В этой статье .
Поскольку это изменение на стороне сервера, вам может потребоваться связаться с вашим хостингом, чтобы помочь вам, или нанять системного администратора, который внесет изменения за вас.
В vesta Cp обратите внимание на значение этой директивы post_max_size / upload_max_filesize и если он маленький — увеличьте его.
Обратите внимание что маленькие лимиты других директив, таких как к примеру memory_limit — так же будут влиять на работу Вашего MailWizz
-
wra
- Сообщения: 37
- Зарегистрирован: 2009.10.28, 13:48
Проблема с CSRF
Проблема при установке параметра в конфиге:
Код: Выделить всё
'request'=>array(
'enableCsrfValidation'=>true,
),
После этого невозможно удалить запись (например статью или комментарий в моем случае). Вываливает 400-ошибку: «Невозможно определить CSRF.»
Есть идеи как это решить?
-
wra
- Сообщения: 37
- Зарегистрирован: 2009.10.28, 13:48
Re: Проблема с CSRF
Сообщение
wra »
Спасибо. Идея понятна. С реализацией проблема…
Удаление идет по ссылке, на которую наверчена отправка jQuery-формы:
Код: Выделить всё
/*<![CDATA[*/
jQuery(document).ready(function() {
jQuery('#yt0').click(function(){if(confirm('Точно удалить?')) {jQuery.yii.submitForm(this,'/articles/delete/id/10',{});return false;} else return false;});
});
/*]]>*/
Подскажите каким образом сюда можно вставить скрытое поле? Или как то по другому делается?
-
Ozzy
- Сообщения: 269
- Зарегистрирован: 2009.04.02, 15:09
- Откуда: Украина, Одесса
Re: Проблема с CSRF
Сообщение
Ozzy »
Ну так это полюбому submitForm, значит где то вверху форма таки определяется?
-
wra
- Сообщения: 37
- Зарегистрирован: 2009.10.28, 13:48
Re: Проблема с CSRF
Сообщение
wra »
Вот этот:
Код: Выделить всё
/*<![CDATA[*/
jQuery(document).ready(function() {
jQuery('#yt0').click(function(){if(confirm('Точно удалить?')) {jQuery.yii.submitForm(this,'/articles/delete/id/10',{});return false;} else return false;});
});
/*]]>*/
-
samdark
- Администратор
- Сообщения: 9474
- Зарегистрирован: 2009.04.02, 13:46
- Откуда: Воронеж
- Контактная информация:
Re: Проблема с CSRF
Сообщение
samdark »
Нет, это то, что получается в итоге. Должен быть PHP-код, который это нагенерил.
-
wra
- Сообщения: 37
- Зарегистрирован: 2009.10.28, 13:48
Re: Проблема с CSRF
Сообщение
wra »
Вот генерация:
Код: Выделить всё
<li><?=CHtml::linkButton('удал',array(
'submit'=>array('articles/delete','id'=>$Article->articleId),
'confirm'=>"Точно удалить?",'class'=>'delete'))?></li>
-
wra
- Сообщения: 37
- Зарегистрирован: 2009.10.28, 13:48
Re: Проблема с CSRF
Сообщение
wra »
Добавление в linkButton:
Код: Выделить всё
'YII_CSRF_TOKEN'=>Yii::app()->request->csrfTokenдало то, что в саму ссылку дабавился этот параметр со значением. Но это не помогло создать скрытое поле (я так понимаю и не должно было). Поясните пожалуйста на примере как добавляется скрытое поле а форму, которая генерится через linkButton(). Либо если можно передавать не только через скрытое поле, то поясните как…
-
delvin
- Сообщения: 85
- Зарегистрирован: 2009.11.13, 15:29
Re: Проблема с CSRF
Сообщение
delvin »
linkButton в этом случае создает post-запрос динамически, т.е. никаких форм не создается и не отправляется.
Попробуй так:
Код: Выделить всё
<li><?=CHtml::linkButton('удал',array(
'submit'=>array('articles/delete','id'=>$Article->articleId),
'params'=>array('YII_CSRF_TOKEN' => Yii::app()->request->csrfToken,),
'confirm'=>"Точно удалить?",'class'=>'delete'))?></li>Перейти к содержимому
Такая ошибка обычно говорит, что проблема с токеном CSRF. Токена нет или токен не тот. Этот токен нужно передавать как в POST так и в AJAX запросах.
На английском эта ошибка звучит так:
Bad Request (#400): Unable to verify your data submission
Проблему можно решить тремя способами:
Два неправильных способа — отключить проверку для всего приложения в конфиге или отключить в конкретном месте. Смотрите код ниже:
|
//В файле конфигурации отключаем для всего приложения ‘components’ => [ ‘request’ => [ ... ‘enableCsrfValidation’=>false, ... ], ... ], // Отключаем в конкретном месте $this—>enableCsrfValidation = false; |
А теперь правильный способ.
Всегда передавать валидный CSRF токен! В Yii2 для этого есть все инструменты.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
//В мета тэгах вашего шаблона echo Html::csrfMetaTags(); //это добавит строки содержащие имя параметра и сам токен <meta name=«csrf-param» content=«_csrf»> <meta name=«csrf-token» content=«OTDOwBtYk-tsjYLIgTAXrqhKwU-WgneMk_TpFcbE6DwPCIu3XRPJhj202Jn0Z3TP4Ry3ecevOcC-x4ZQkKu8dg==»> //В формах <input type=«hidden» name=«_csrf» value=«OTDOwBtYk-tsjYLIgTAXrqhKwU-WgneMk_TpFcbE6DwPCIu3XRPJhj202Jn0Z3TP4Ry3ecevOcC-x4ZQkKu8dg==»> //Если форму создавать методами ActiveForm::begin() и Html:beginForm(), то input будет подставляться автоматически //Если же вы сами создаёте форму, то пишите так <input type=«hidden» name=«<?=Yii::$app—>request—>csrfParam; ?>« value=«<?=Yii::$app—>request—>getCsrfToken(); ?>« /> //Если отправляете ajax запрос, то в javascript можно получить csrf токен из метатэгов var param = $(‘meta[name=»csrf-param»]’).attr(«content»); var token = $(‘meta[name=»csrf-token»]’).attr(«content»); $.ajax({ url: ‘https://help1c.su’, type: ‘post’, dataType: ‘json’, data: {‘data1’: data1, ‘data2’: data2,....., param : token}, }); |
Напечатайонлайн.рф — печатная продукция в Иркутске
Getting Error 400: The CSRF token could not be verified. when trying to delete an item using the default delete link.
$this->menu=array(
array(‘label’=>’Create Use’, ‘url’=>array(‘create’)),
array(‘label’=>’Update Use’, ‘url’=>array(‘update’, ‘id’=>$model->use_id)),
array(‘label’=>’Delete Use’, ‘url’=>’#’, ‘linkOptions’=>array(‘submit’=>array(‘delete’,’id’=>$model->use_id,’confirm’=>’Are you sure you want to delete this item?’)),
array(‘label’=>’Manage Uses’, ‘url’=>array(‘admin’)),
);
Answer:
This problem can be solved by adding ‘csrf’ => true to the linkOptions
$this->menu=array(
array(‘label’=>’Create Use’, ‘url’=>array(‘create’)),
array(‘label’=>’Update Use’, ‘url’=>array(‘update’, ‘id’=>$model->use_id)),
array(‘label’=>’Delete Use’, ‘url’=>’#’, ‘linkOptions’=>array(‘submit’=>array(‘delete’,’id’=>$model->use_id,’confirm’=>’Are you sure you want to delete this item?’),’csrf’=>true)),
array(‘label’=>’Manage Uses’, ‘url’=>array(‘admin’)),
);
Every other day or so it seems, a new question is posted to one of the community
forums that cover ASP.NET Core Razor Pages asking why an AJAX post doesn’t
appear to work, or results in an HTTP 400 error. This article explains the most common cause, and
offers guidance on how to solve it.
The first step in diagnosing issues with AJAX requests is to actually examine
the request itself. There are many tools available for this, but the most
accessible tools are the developer tools provided by the major browsers. They are
accessible from within Chrome, IE, Edge and Firefox by pressing F12 while viewing
your web page, or Ctrl+Shift+I in Opera. This latter key combination also works for
FireFox. In all cases, a panel should open in the browser that looks something
like this:
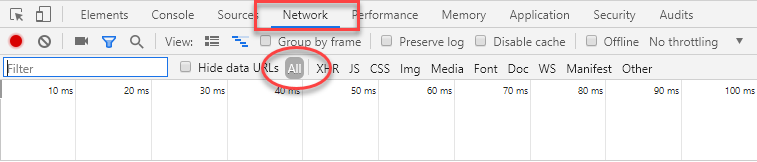
The highlighted elements are the Network tab, which is currently open and shows details of the browser’s network traffic, and the
All option which is selected by default. This option results in all network traffic being recorded and reported on. The option that sits to the right —
XHR — filters out all requests except those initiated by the XmlHttpRequest object or the browser’s Fetch API. In other words, if you select the XHR option, you will only see details of AJAX requests.
Once you have this panel open, you are in a much better position to fault
find. And the first potential point of failure to rule out is whether the AJAX
request is actually being made at all. If nothing appears in the grid, the
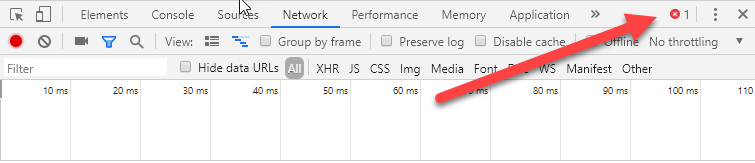
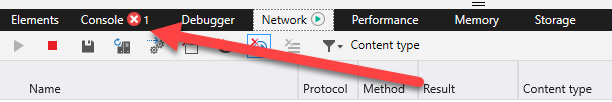
request is not being made. This could be for any number of reasons. If there is
an error in the JavaScript code, an inidcator will appear (arrowed, showing Chrome then Edge) and details will appear in the Console tab.
If there are no errors reported, but the request is still not made in
response to the trigger action, check to see if the event handler that initiates
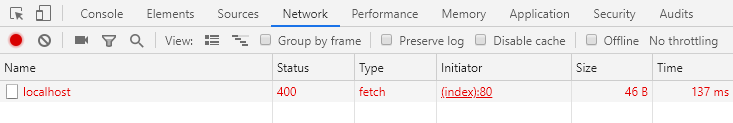
the request is wired to the trigger element correctly. If the request is made,
details will appear, hopefully accompanied by a nice 200 HTTP status code to
signify that all has gone well. However, as alluded to in the title of this
article, the status code that causes the most confusion is 400:
According to the HTTP standards:
The 400 (Bad Request) status code indicates that the server cannot or
will not process the request due to something that is perceived to be
a client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, invalid request
message framing, or deceptive request routing).
So there is an error in the way that the post request has
been constructed, but what is it? The most common cause for a 400 Bad Request
status code in Razor Pages is a missing Request Verification token.
Request Verification Tokens
Request verification is a process that ensures that post
requests received by your application originate from the application, and not
from a third party. Request verification is an important tool in the armoury
against
cross site request forgery (CSRF) attacks, and is enabled by default in Razor Pages.
A hidden form field named
__RequestVerificationToken is rendered within every form by the
form tag helper. It contains an encrypted token. The same value is included in a cookie which is sent with the form request. The presence of both of these
tokens and their values are validated when ASP.NET Core processes a POST request. If verification fails, the framework returns a
400 status code.
During normal form submission, the hidden field containing the CSRF token is automatically included in
the payload. The most common causes for failed AJAX posts resulting in a 400
status code are:
- The CSRF token was generated but the was not included in the
posted payload - The CSRF token was included in the post, but in a way
that prevented its discovery on the server. - No CSRF token was generated because the form tag helper was not used
No hidden field was generated
You need to generate a CSRF token value. While the form tag helper is the most
common means of generating the token value as a hidden field, it is not the only
means. In fact, it may not even make sense to generate form tags or hidden
fields for your scenario — espcially if you are not posting form field values.
If it does make sense to include a form in your page, then do so, but ensure
that the method attribute is set to post. CSRF
tokens are not generated for forms that use the get method.
If you don’t need a form, you can inject the IAntiforgery interface into your
page, and use it to generate a token value:
@page @model MyApp.Pages.IndexModel @inject IAntiforgery antiforgery @{ var token = antiforgery.GetAndStoreTokens(HttpContext).RequestToken; }
You will need to either use the fully qualified namespace (Microsoft.AspNetCore.Antiforgery)
to reference IAntiforgery, or add a using statement to the
_ViewImports file. The token can then be used in the AJAJX post.
Including the CSRF token in the post
You can construct the data for your AJAX post in any number of ways.
If you use jQuery, its serialize()
method will take care of ensuring that all the specified form values are
properly encoded for submission. When using the Fetch API, you can construct a
FormData object from the relevant form element, which will also
ensure that all fields, including hidden fields are included in the payload. You
may be doing this, but still your posts generate 400 codes. If so,
check to ensure that you are not stringifying your serialised form values to
JSON (using e.g. JSON.stringify) unnecessarily as this will prevent
the token being discovered by the server.
If you construct the values yourself, it is easy to overlook the verification
token.
The verification token can be included manually in the post in two ways, as part of
the request body, or in a header.
By default, the header must be named
RequestVerificationToken and the form field’s name must be __RequestVerificationToken,
although you can customise them through configuration via the
AntiforgeryOptionsConfigureServices e.g.
services.AddAntiforgery(o => o.HeaderName = "CSRF-TOKEN");
Acording to OWASP, inserting the CSRF token in the HTTP request header via JavaScript is considered more secure than adding the token in the hidden field form parameter.
If you are using jQuery, you can use the $.ajax method instead of
$.post, because it enables you access to more options, including setting headers:
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
url: "/",
data: { foo: "bar" },
headers: { "RequestVerificationToken": $('input[name="__RequestVerificationToken"]').val() },
success: function (response) {
...
Here’s how you can accomplish the same thing using Fetch:
var token = document.querySelector('input[name="__RequestVerificationToken"]').getAttribute("value"); fetch("", { method: "post", headers: { "RequestVerificationToken": token }, body: { foo: "bar" } }).then(() => { ... });
If the CSRF token is included as a form field and a header value, the header
value takes precedence. If the header value fails verification, the system will
not fall back to the form field. It will simpy return a BadRequestResult,
generating a 400 response code.
Summary
This article provides some basic guidance on troubleshooting failing AJAX
post requests, and then focuses on the most common culprit in ASP.NET Core Razor
Pages. It explains what the CSRF token is, how it is generated by Razor Pages,
and how you can generate one using the IAntiforgery API. It also
explains how to manually include the token in your AJAX post so that it can be
discovered.