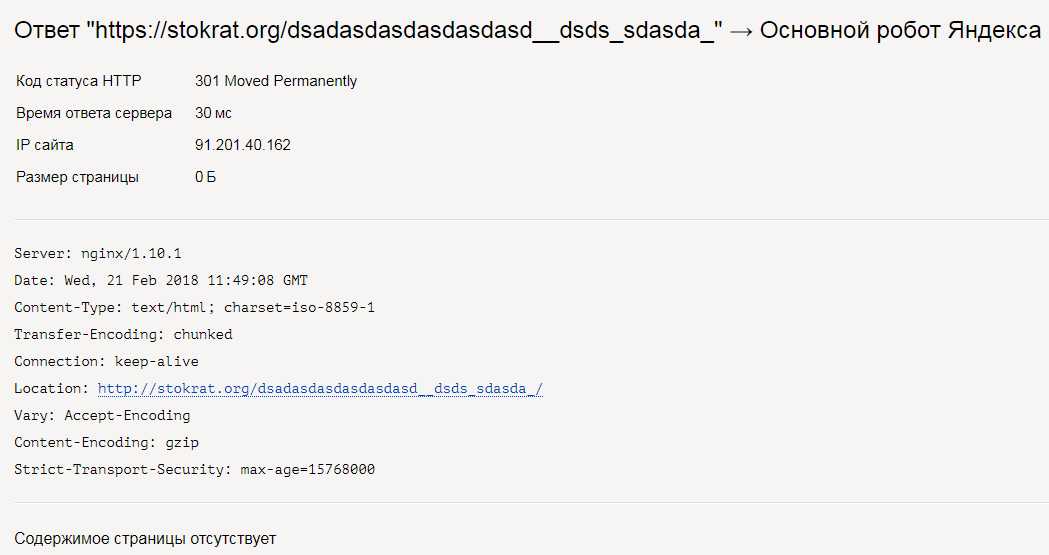
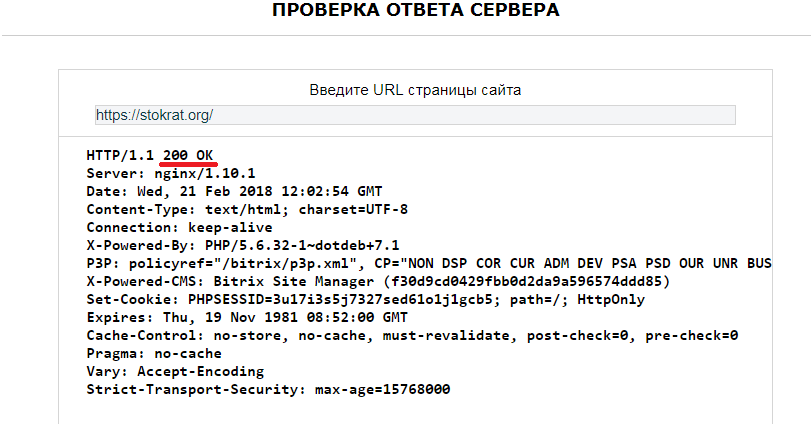
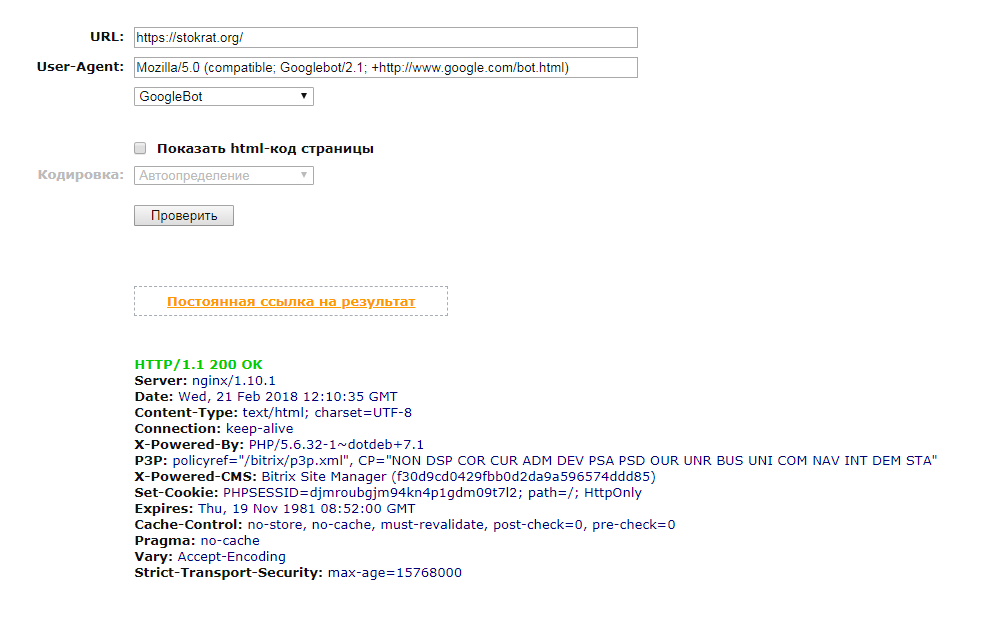
Может сейчас эта тема не особо вас волнует, однако протяжении существования вашего сайта вы будете сталкиваться с кодами ответов сервера или «списком кодов состояния HTTP», связанных с различными элементами функциональной составляющей вашего сайта. Довольно часто встречаются такие ошибки, как 404 и 301, но существует огромное множество других ошибок, с которыми вы, возможно, не знакомы. Прежде чем паниковать, лучше прочтите эту статью, призванную рассказать вам о значения кодов различных ошибок, которые могут встретиться на вашем пути.
Некоторые из них напрямую связаны с сервером или с клиентской стороной, а некоторые уже не актуальны, поэтому вы вряд ли их увидите в реальной жизни, но ради интереса и фоновых знаний я включил и их.
Ниже представлена удобная таблица, при помощи которой вы сможете быстро и просто перейти к интересующей вас ошибке, и узнать ее значение:
| 100 | 301 | 405 | 417 | 450 |
| 101 | 302 | 406 | 418 | 451 |
| 102 | 303 | 407 | 422 | 500 |
| 200 | 304 | 408 | 423 | 501 |
| 201 | 305 | 409 | 424 | 502 |
| 202 | 306 | 410 | 425 | 503 |
| 203 | 307 | 411 | 426 | 504 |
| 204 | 400 | 412 | 428 | 505 |
| 205 | 401 | 413 | 429 | 506 |
| 206 | 402 | 414 | 431 | 507 |
| 207 | 403 | 415 | 444 | 509 |
| 300 | 404 | 416 | 449 | 510 |
1xx Информационные коды
- 100 Continue Server Code
100 Continue означает «работу в штатном режиме». Он означает, что пользователем был сделан хороший запрос, и сервер принялся к обработке. Это временный код ответа, имеющий место лишь тогда, когда пользователь ожидает финального ответа от сервера, который происходит только после того, как будет отослан последний пакет данных.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Это внутренний код, и иногда он даже не генерируется, если пользователь уже получил какие-то данные от сервера. Это нечто вроде послания к серверу о том, что соединение было установлено успешно, и двери открыты. Высылай данные, но не забудь закрыть дверь, когда закончишь дела (имеется в виду код финального ответа).
Вернуться в начало
- 101 Switching Protocols
Это, наверное, один из самых простых серверных кодов, который означает, что пользователь сделал запрос на переключение типа протокола, используемого на веб-сервере, и сервер дал согласие на это.
Когда этот код может использоваться? При переключении на новую версию HTTP с протокола старого типа. Этот запрос выполняется только при наличии более подходящего протокола (иными словами, при наличии более свежей версии HTTP).
Вернуться в начало
- 102 Processing
Так как WebDAV-запрос (протокол передачи) может содержать не только один запрос, но также множество подзапросов, включая операции с файлами, он зачастую может затребовать более длительного времени для завершения запроса.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Этот код генерируется для того, чтобы оповестить пользователя и необходимости сбросить таймер и ожидать следующей команды в обычном режиме, так как процесс обработки запроса может занять длительное время.
Вернуться в начало
2xx Success
Сообщения данного класса информируют о случаях успешного принятия и обработки запроса клиента. В зависимости от статуса сервер может ещё передать заголовки и тело сообщения. Иначе говоря, данная классификация кодов обозначает, что действие, запрошенное клиентом, было успешно принято в обработку.
- 200 OK
Этот код, вероятно, является самым популярным, но при этом самым незаметным ввиду его характера. Он означает, что обмен между пользователем и сервером завершен, и все прошло так, как должно было.
- 201 Created
В результате успешного выполнения запроса был создан новый ресурс. Например, запрос пользователя привел к созданию нового ресурса вроде новой страницы. Сервер-источник должен создать ресурс перед тем, как отправлять код 201. Если ресурс не может быть создан в данный момент, то сервер вместо этого должен отобразить код 202 (accepted).
Вернуться в начало
- 202 Accepted
Запрос был принят на обработку, но она не завершена по каким-либо причинам. Запрос может и не быть выполнен до конца, в зависимости от того, был ли он отклонен в процессе обработки.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда сервер не может выполнить запрос в тот момент, в который он был сделан. Запрос изначально не рассчитан на обязательное исполнение, и клиенту не обязательно дожидаться окончательной передачи сообщения, так как может быть начат очень долгий процесс.
Вернуться в начало
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information
Сервер успешно обработал запрос, но передаваемая информация была взята не из первичного источника (резервной копии, другого сервера и т. д.) и поэтому может быть неактуальной. По сути, этот код очень похож на 200, но указывает на то, что информация была получена не из первоисточника.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Этот код может быть использован вместо 200, когда у отправителя есть причина полагать, что заголовки ответа от постороннего источника могут отличаться от того, что предоставил бы исходный сервер.
Вернуться в начало
- 204 No Content
Этот код представляет собой ответ, посланный сервером для того, чтобы сообщить, что запрос был получен и понят, но отсутствуют данные, которые можно было отправить пользователю. Это, главным образом, используется для того, чтобы разрешить запуск скриптов, не меняя при этом документ. Данный код не должен содержать тело сообщения, и включается в первую пустую строку кода сразу после заголовка.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Этот код, главным образом, используется для того, чтобы позволить осуществить ввод или какие-либо действия без необходимости обновлять документ (страницу).
Вернуться в начало
- 205 Reset Content
Сервер успешно обработал запрос, но при этом не возвращает какой-либо контент. В отличие от 204, этот ответ требует от запрашиваемого обновить документ.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Обычно он используется тогда, когда пользователь заполняет форму, а сервер посылает браузеры запрос на очистку формы. Он схож с кодом 204, но просит пользователя сбросить документ после завершения – например, очистить HTML-форму после подтверждения.
Вернуться в начало
- 206 Partial Reset
Сервер возвращает лишь часть контента, соответствующего заголовку, посланному клиентом. Обычно он используется расширенными инструментами кэширования, когда пользователь запрашивает лишь небольшую часть контента на странице, и сервер в своем ответе предоставляет данные лишь для этой области на странице.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Этот кода обычно используется вследствие запрос If-Range, который применяется в мощных валидаторах кэша. Запрос также должен включать заголовки области, которые используется в качестве параметров диапазона возвратной информации.
Вернуться в начало
- 207 Multi-Status
Сервер передаёт результаты выполнения сразу нескольких независимых операций, которые помещают в тело сообщения в виде XML-документа.
Вернуться в начало
3хх Перенаправление
Этот класс кодов состояния указывает на дальнейшие действия, которые должны быть предприняты агентом пользователя для того, чтобы завершить запрос. Действия могут производиться пользователей, либо могут включать в себя различные запросы к серверу.
- 300 Multiple Choices
В основном, этот код сообщает пользователю о том, что ресурс был перемещен, и сервер отвечает списком доступных альтернативных вариантов, среди которых пользователь может выбрать наиболее подходящий ему ресурс.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Обычно этот код можно увидеть, когда сервер считает, что предоставленный пользователем (другими словами, браузером пользователя) URL имеет недостаточно точный указатель, и предлагает дальнейший выбор. Обычно это происходит тогда, когда пользователь использует URL на директорию не самого последнего уровня, и сервер предлагает ему выбор имеющихся файлов или директорий последующего уровня.
Вернуться в начало
- 301 Moved Permanently
Это довольно распространенный пользовательский запрос. Он означает, что запросы для данного ресурса (а также все последующие запросы) должны быть перенаправлены на заданный URL.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда страница более не существует, либо ссылка, ведущая на сторонний источник, уже не работает. 301 редирект сообщает пользователю о том, что запрашиваемый ресурс был перемещен (обычно это реализуется при помощи файла .htaccess, доступного на серверах Apache).
Вернуться в начало
- 302 Found
Этот код сообщает пользователю, что расположение запрашиваемого ресурса временно изменено, и 302 код состояния должен содержать информацию о новом месторасположении, которое пользователь и должен запросить.
Когда этот код может использоваться? У этого кода есть несколько применений, многие из которых не являются тем, для чего код был изначально предназначен. Изначально он представлял собой основной способ создания временного перенаправления. Тем не менее, сегодня существуют и другие – этичные, и неэтичные – способы его применения.
Вернуться в начало
- 303 See Other
Этот код указывает пользователю на то, что запрашиваемый ресурс можно найти по URL, который отличается от указанного в запросе. Это не обязательно означает, что что-то было перемещено, это код лишь предоставляет адрес, по которому следует запрашивать подобный ответ.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Этот метод главным образом существует для того, чтобы позволить выводу данных POST-активированного скрипта перенаправить агента пользователя к выбранному ресурсу.
Вернуться в начало
- 304 Not Modified
Этот код означает, что пользователь запрашивает документ/ресурс только в том случае, если он подвергался изменениям с момента последнего обновления кэша данного документа.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Если в ответе от сервера сообщается о том, что параметры документа If-Modified-Since или If-Match не менялись с момента создания последнего кэша, то нет необходимости в повторной отправке ресурса.
Вернуться в начало
- 305 Use Proxy
Этот код сообщает пользователю, что доступ к запрашиваемому ресурсу возможен только посредством прокси, указанного в ответе.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Этот код часто отображается в связи с мерами безопасности, и предоставляет доступ к запрашиваемым URL-ресурсам.
Вернуться в начало
- 306 Switch Proxy
Этот код изначально означал «последующие запросы должны использовать указанный прокси», но в данный момент не используется и зарезервирован.
Вернуться в начало
- 307 Temporary Redirect
Этот код возвращается, если ресурс на данный момент временно доступен по другому URL, который также предоставляется в ответе. Этот код немного отличается от кода 302 – он представляет собой более определенную версию кода 302.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Он используется практически в тех же случаях, что и 302, но пользователь должен продолжить запросы по исходному URL при следующих запросах, либо до тех пор, пока не будет применен новых код ответа.
Вернуться в начало
4хх Ошибка клиента
Класс кодов 4xx предназначен для указания ошибок со стороны клиента, либо на то, что локации никогда (или уже) не существовало. Эти коды состояния применимы к любому методу запроса.
- 400 Bad Request
Запрос не может быть исполнен ввиду синтаксической ошибки.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда пользователь запрашивает информацию, но делает это, пренебрегая правилами протокола передачи гипертекста. Запрос не следует повторять без изменения синтаксиса.
Вернуться в начало
- 401 Unauthorized
Этот код связан с запросом к ресурсу, который требует авторизации. Ответ 401 указывает на то, что попытка авторизации была отклонена по тем данным, которые предоставил пользователь.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда пользователь совершает запрос к серверу, используя неправильные данные авторизации (имя пользователя и/или пароль).
Вернуться в начало
- 402 Payment Required
Зарезервирован на будущее. Тем не менее, исходное предназначение заключалось в том, что данный код мог использоваться в некоторой форме электронных денег для проведения трансакций, но этого не случилось, и коду не нашлось применения.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Старый сервис MobileMe от Apple выдавал ошибку 402, если аккаунт пользователя в MobileMe подозревался в злоупотреблении сервисом. Кроме того, Youtube использует это состояние, если конкретный IP-адрес уличен в совершении чрезмерного числа запросов, и тогда пользователю необходимо ввести CAPTHA.
Вернуться в начало
- 403 Forbidden
Пользователь пытается осуществить доступ к ресурсу, к которому у него нет доступа, и авторизация не изменит положения.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда сервер понял запрос, но он отказывается его выполнять из-за ограничений в доступе для клиента к указанному ресурсу. Обычно такое случается, когда ресурс не предназначен для публичного доступа.
Вернуться в начало
- 404 Not Found
Все знакомы с этим кодом, не так ли? Он означает, что запрошенный ресурс не может быть найден, но в будущем – когда он, возможно, там появится, – к нему можно будет осуществить доступ. Также здесь допустимы последующие запросы от клиента. Тем не менее, в большинстве таких случаев применяется код перенаправления из семейства 3хх, и пользователя перенаправляют на альтернативный ресурс или локацию.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Довольно часто, особенно если страницу переместили или удалили. Зачастую в подобных случаях сервер автоматически генерирует направляющую страницу с ошибкой 404.
Вернуться в начало
- 405 Method Not Allowed
Метод, при помощи которого совершается запрос к ресурсу, не доступен. Другими словами, ошибка возникает при попытке использовать GET на форме, которая требует ввод данных посредством POST, либо использовании метода PUT на ресурсе, который предназначен только для чтения.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Ошибки 405 встречаются в связи с конкретными объектами на веб-странице, для которых был совершен запрос. Например, когда строка запроса в скрипте отличается от пользовательского запроса, в котором подразумевается использование этого скрипта.
Вернуться в начало
- 406 Not Acceptable
Запрошенный ресурс способен генерировать только тот контент, который не применим к Accept-заголовкам в самом запросе. Браузер способен указывать серверу характеристики данных, которые данные будут принимать от сервера
Когда этот код может использоваться? Если форма файла запрошенного ресурса не совпадает с форматом, который пользователь способен распознать. Мы говорим сейчас о языке программирования, а не о французском!
Вернуться в начало
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
Как и код состояния 401, код 407 означает, что клиент сначала должен авторизоваться через прокси. Чтобы сделать это и авторизоваться, прокси должен вернуть поле с заголовком proxy-authenticate, который отвечает требованиям, представленным сервером.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда сервер думает, что запрос данных от клиента корректным, но доступ к ресурсу возможен только посредством авторизации через прокси-сервер.
Вернуться в начало
- 408 Request Timeout
Время ожидания сервером передачи от клиента истекло.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Руководствуясь спецификацией W3 HTTP: «Клиент не сделал запрос в отведенный промежуток времени, который сервер был готов ждать. Клиент МОЖЕТ повторить запрос когда угодно».
Вернуться в начало
- 409 Conflict
Указывает на то, что запрос не может быть выполнен из-за конфликтного обращения к ресурсу.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Вы можете получить такой код при загрузке файла на веб-сервер, где уже имеется более свежая версия этого файла, что приводит к конфликту в системе контроля версий.
Вернуться в начало
- 410 Gone
Такой ответ сервер посылает, если ресурс раньше был по указанному URL, но был удалён и теперь недоступен. Пользователю не следует повторять идентичный запрос.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Если более невозможно осуществить доступ к ресурсу посредством данного запроса, и сервер не владеет информацией о возможном месте расположения ресурса. Если у сервера есть подозрение, что документ в ближайшее время может быть восстановлен, то лучше клиенту передать код 404.
Вернуться в начало
- 411 Length Required
Запрос не указывает длину контента, и это было затребовано в совершенном запросе.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда браузер не определяет длину запрашиваемого контента в заголовке запроса. Сервер не примет запрос без валидного поля заголовка content-length.
Вернуться в начало
- 412 Precondition Failed
Сервер не отвечает одному из предварительных условий, которые отправитель указал в запросе. Другими словами, один или более заголовок запроса был возвращен с атрибутом false.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Если заголовок запроса, который совершает валидный запрос к ресурсу, сообщает, что этот конкретный запрос не применим к этому конкретному ресурсу.
Вернуться в начало
- 413 Request Entity Too Large
Код 413 отображается в тех случаях, когда сервер отказывается обработать запрос по причине слишком большого размера тела запроса.
Когда этот код может использоваться? При использовании в форме метода POST с контентом, по размеру большим, нежели сервер способен обработать.
Вернуться в начало
- 414 Request-URL Too Long
Этот код отображается, когда сервер не может обработать запрос из-за слишком длинного указанного URL.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда POST-запрос конвертируется в GET-запрос. POST-запрос поддерживает отправку безграничного объема данных, связывая их с самим запросом. Тем не менее, если запрос должен быть конвертирован в GET-запрос, то запрос позволяет привязать данные формы к URL, что позволяет проводить информацию в больших размерах, чем это было доступно.
Вернуться в начало
- 415 Unsupported Media-Type
Ответ 415 отправляется для указания о том, что сервер заметил, что часть запроса была сделана в неподдерживаемом формате.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда в запросе не указываются какие-либо типы медиа, которые поддерживаются ресурсом или сервером. Например, пользователь запрашивает изображение с расширением файла, которое не поддерживается сервером. Сервер знает о том, что было запрошено, но не понимает формат, в котором был запрошен ресурс.
Вернуться в начало
- 416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
Этот ответ приходит пользователю, когда тот запрашивает часть запрашиваемого ресурса, когда эта часть не может быть предоставлена.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда у сервера запрашивают XXX-YYY байтов какого-либо ресурса, но ресурс имеет меньший размер, чем указано в запросе.
Вернуться в начало
- 417 Expectation Failed
Этот ответ может быть получен, когда по каким-то причинам сервер не может удовлетворить значению поля Expect заголовка запроса.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Все вполне и так понятно. Когда один из заголовков запроса, заголовок «Expect», имеет запрос, на который сервер не может предоставить ответ.
Вернуться в начало
- 418 I’m a teapot
Этот код был создан в 1998 году как одна из традиционных первоапрельских шуток IETF, в RFC 2324, Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol, и вряд ли будет обрабатываться современными HTTP-серверами.
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
Запрос был принят и понят, но не может быть выполнен ввиду наличия семантических ошибок.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда сервер успешно принял запрос, может работать с указанным видом данных, в теле запроса XML-документ имеет верный синтаксис, но имеется какая-то логическая ошибка, из-за которой невозможно произвести операцию над ресурсом.
Вернуться в начало
- 423 Locked
Целевой ресурс из запроса заблокирован от применения к нему указанного метода. Чтобы ресурс стал доступным, необходимо снять блокировку или предоставить правильные данные авторизации.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда ресурс… закрыт. Обычно это случается из соображений безопасности.
Вернуться в начало
- 424 Failed Dependency
Указывает на то, что реализация текущего запроса может зависеть от успешности выполнения другой операции, и если она не будет успешно проведена, вся обработка запроса будет прервана.
Вернуться в начало
- 425 Unordered Collection
Этот код отображается, когда ресурс определен в черновиках «WebDAV Advanced Collections Protocol», но не присутствует в «Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning Ordered Collections Protocol».
Вернуться в начало
- 426 Upgrade Required
Этот код отображается, когда сервер указывает клиенту на необходимость обновить (переключиться на другой, более новый) протокол. Когда этот код может использоваться? Обычно когда браузер использует устаревшие протоколы.
Вернуться в начало
- 428 Precondition Required
Сервер-источник требует, чтобы в запросе были указаны предварительные условия. Этот код предназначен для того, чтобы избежать конфликта версий ресурса в тех случаях, когда клиент получает (GET) состояние ресурса, изменяет его, и отправляет (PUT) обратно на сервер, и в то же время какая-то третья сторона также изменяет положение ресурса прямо на севере, что приводит к конфликту.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Запрашивая указание условий, сервер как бы гарантирует клиентам то, что они используют корректные актуальные копии ресурс. Если же это не соответствует действительно, пользователь получит ошибку 428.
Вернуться в начало
- 429 Too Many Requests
Этот ответ посылается, если клиент попытался отправить слишком много запросов за короткое время.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда пользователь посылает слишком много запросов за короткий промежуток времени.
Вернуться в начало
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large
Происходит, когда сервер не собирается обрабатывать запрос, так как какое-то из полей заголовка (или все поля заголовков) слишком большое.
Когда этот код может использоваться? В основном тогда, когда заголовок запроса от пользователя больше, чем сервер способен обработать. Запрос может быть повторен после того, как будет уменьшен размер полей заголовков в запросе.
Вернуться в начало
- 444 No Response
Использовался в лог-файлах Nginx для указания того, что сервер не вернул информацию пользователю и закрыл соединение.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Обычно использовался в качестве сдерживающего фактора против вредоносного ПО.
Вернуться в начало
- 449 Retry With (Microsoft)
Расширение Microsoft, которое указывает на то, что запрос должен быть повторен после применения подходящего действия.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Этот код зачастую генерируется, когда выставленные параметры запроса не соответствуют тем, что может принять сервер.
Вернуться в начало
- 450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft)
Расширение Microsoft. Эта ошибка выдается, когда параметры Windows Parental Controls выставлены на блокировку доступ к определенным веб-страницам.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда родители (зная об этой функции) используют родительский контроль, и id-доступа запросил доступ к заблокированному ресурсу.
Вернуться в начало
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
Новый HTTP-код состояния для ресурсов, которые заблокированы из юридических соображений. Используется для указания на то, что доступ к запрашиваемому ресурсу был заблокирован из юридических соображений: например, цензурой, или правительством.
Вернуться в начало
5xx Ошибка сервера
Коды 5xx выделены под случаи неудачного выполнения операции по вине сервера.
Эти серверные ответы зачастую отображаются, когда пользователь делает запрос, который сервер не в состоянии обработать по той или иной причине. Сервер должен включать сообщение для браузера, которое должно быть показано пользователю – в нем сообщается, что сервер (и по каким причинам) не способен обработать запрос.
- 500 Internal Server Error
Данная ошибка говорит о любой внутренней ошибке сервера, которая не входит в рамки остальных ошибок класса.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда ресурс или ссылка создаются на сервере (вроде календаря в системе бронирования), которые технически не существуют в виде ссылки или доступного ресурса, но показывается пользователю в виде ссылки.
Вернуться в начало
- 501 Not Implemented
Сервер либо не понимает метод в запросе, либо не поддерживает возможностей, необходимых для обработки запроса
Когда этот код может использоваться? Вы можете столкнуться с этим, когда сервер не поддерживает нормальные протоколы запроса, вроде GET, OPTIONS, HEAD, POST и т.д.
Вернуться в начало
- 502 Bad Gateway
Ответ 502 отображается, когда сервер, выступая в роли шлюза или прокси-сервера, получил недействительное ответное сообщение от вышестоящего сервера.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Обычно, когда вышестоящий сервер и прокси-сервер/шлюз не согласовывают между собой протоколы, представленные в запросе, и в результате получается ошибка при обмене данных.
Вернуться в начало
- 503 Server Unavailable
Сервер временно не имеет возможности обрабатывать запросы по техническим причинам. В основном, это состоянии является временным.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда сайт пользуется чрезмерным спросом, и сервер не в состоянии обработать все запросы.
Вернуться в начало
- 504 Gateway Timeout
Сервер в роли шлюза или прокси-сервера не дождался ответа от вышестоящего сервера для завершения текущего запроса.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда для передачи данных используется прокси-сервер/шлюз, и два сервера ждут ответов.
Вернуться в начало
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
Сервер не поддерживает указанную в запросе версию протокола HTTP.
Когда этот код может использоваться? В случаях, описанных выше! Когда HTTP-протокол более старый, нежели требуется серверу, и следовательно не поддерживается.
Вернуться в начало
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates
Такой ответ посылается, когда в результате ошибочной конфигурации выбранный вариант указывает сам на себя, из-за чего процесс связывания прерывается.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда сервер настроен некорректно, и не способен обработать запрос.
Вернуться в начало
- 507 Insufficient Storage
Когда сервер не способен разместить данные, так как не хватает места для выполнения текущего запроса.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда сервер уже полностью загружен, и пользователь совершает запрос на ресурс, который сервер уже имеет в запасе. Проблема заключается в том, что на сервере нет места для того, чтобы поместить данные, которые посылаются в запросе, чтобы затем выслать запрашиваемый ресурс.
Вернуться в начало
- 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded
Этот код ответа используется при превышении веб-площадкой отведённого ей ограничения на потребление трафика.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда на сервере Apache выполняется корректное расширение, и в ISP установлен уровень пропускного канала, который скоро может быть превышен. Существует несколько опций предела.
Вернуться в начало
- 510 Not Extended
Когда на сервере отсутствует расширение, которое желает использовать клиент. Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда сервер требует больше информации в совершаемом запросе.
Вернуться в начало
- 511 Network Authentication Required
Данный код состояния отображается в случае, если клиент должен сначала авторизоваться в сети, например, ввести пароль для платной точки доступа к Интернету.
Когда этот код может использоваться? Когда пользователь предварительно должен дать свое согласие на условия использования, перед тем, как он получит доступ к интернету (например, к Wi-fi точке доступа).
Итак, надеюсь, что данный список хоть как-то окажется вам полезным. Если я упустил что-то из виду, пожалуйста, допишите информацию в комментариях, и я обязательно включу ее в статью. Пожалуйста, не забудьте поделиться этой статье с друзьями, чтобы они также были в курсе.
Вернуться в начало
Каждый раз, когда мы кликаем на какую-то ссылку или на наш сайт заходят поисковые роботы, происходит один из диалогов примерно такого содержания:
— Привет, сервер! Я поисковый робот. Могу я просканировать эту страницу?
— Привет! Конечно, заходи.
— А если вот эту страницу?
— А вот здесь пока ведутся ремонтные работы, приходи позже.
Язык ответов HTTP понимают и браузеры, и поисковые роботы, и SEO-специалисты, которым он нужен при работе с сайтом.
Если вы до сих пор путаете 301 с 302, и не знаете, зачем нужен 410 ответ — вам просто необходимо разобраться в кодах ответов HTTP, которые встречаются чаще всего. О них я и расскажу в этой статье. А еще мы узнаем, какую роль они отыграют в SEO и как не допустить ошибок в их использовании.
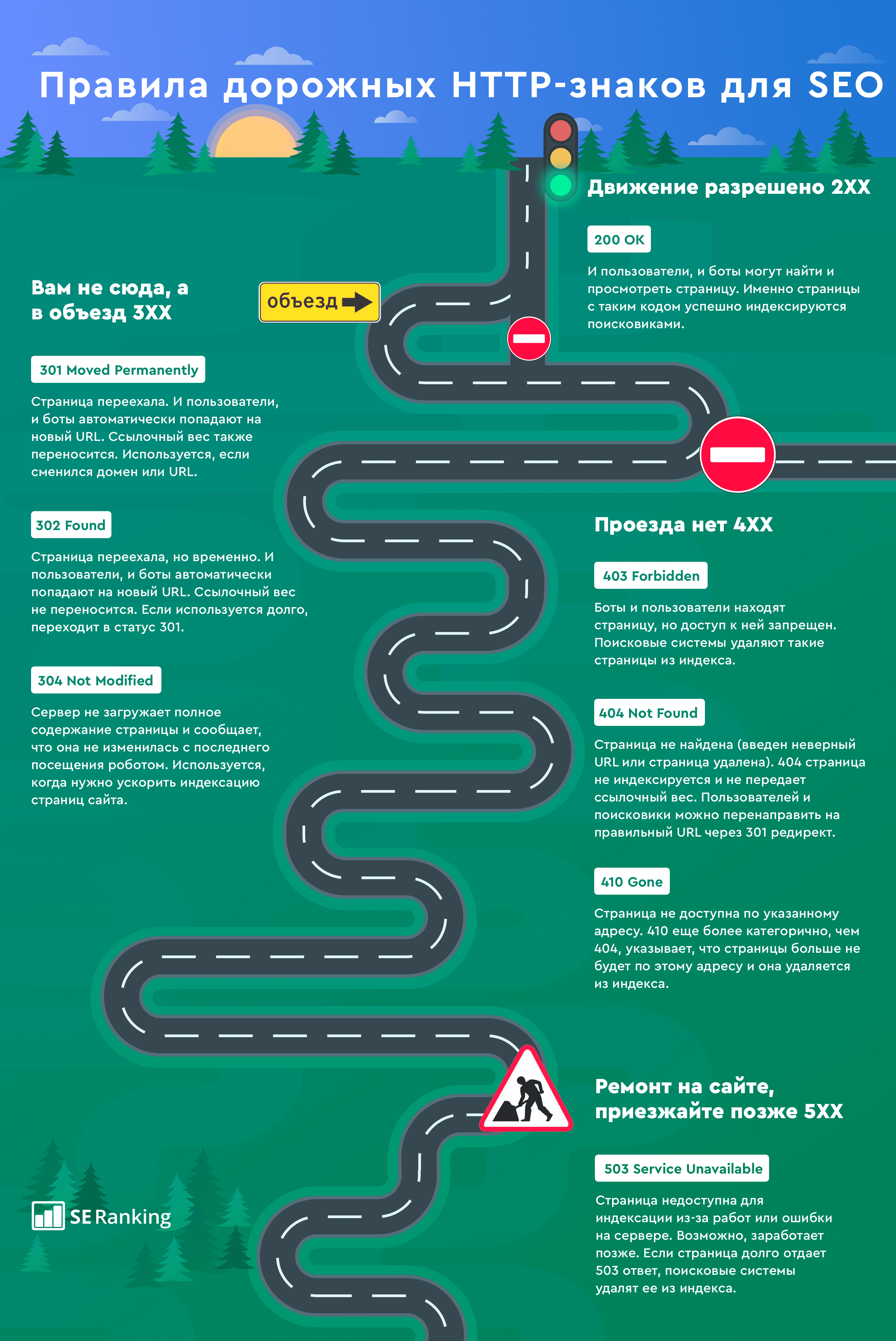
Какие ответы серверов существуют?
Начнем с того, что все коды ответов (состояния) серверов делятся на 5 классов, каждый из которых несет определенный смысл:
- 1XX. Эти информационные коды говорят о том, что запрос был понят, принят сервером и уже обрабатывается. Такие временные ответы обычно не отображаются на экране пользователей, но служат внутренними кодами для браузеров.
- 2XX. Обозначают успешную обработку полученного запроса. Они используются браузерами для подтверждения того, что запрос был принят, обработан и отражают его текущий статус.
- 3XX. Это коды перенаправления. Говорят о том, что серверу нужно выполнить дополнительные действия — например, перейти по редиректу на новый адрес.
- 4XX. Говорят об ошибке на стороне пользователя. Чаще всего появляются, если время ожидания браузера истекло или запрос был введен неправильно.
- 5XX. Говорят об ошибке сервера. Это значит, что вы запрашиваете специфический ресурс и он найден, но сервер не может дать вам к нему доступ. В конечном счете, запрос не может быть обработан.
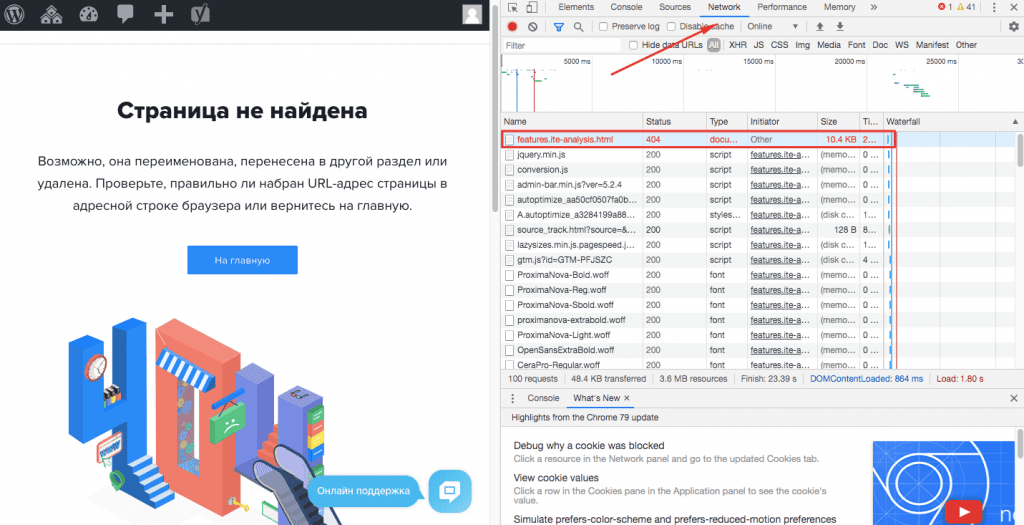
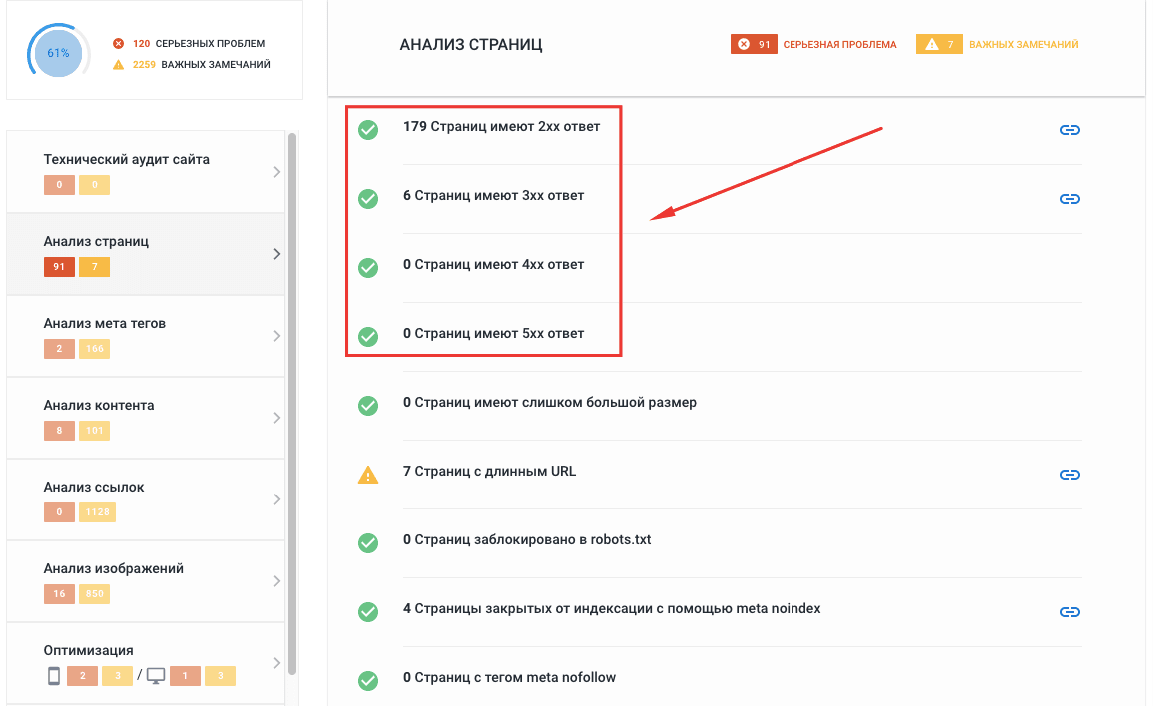
Не все ответы сервера можно увидеть прямо на экране, большинство так и остаются внутренними кодами для браузеров и поисковых роботов. Чтобы быстро узнать статус любой страницы, откройте инструменты разработчика в браузере Chrome (нажмите F12). Перейдите на вкладку Network, обновите страницу и получите список статусов каждого элемента, включая саму страницу:
Именно в этих трех цифрах в колонке Status зашифрованы данные о состоянии страницы: можно ли ее сканировать, находится ли она по этому адресу, загружается ли все ее содержимое и т. д.
Какие же коды ответов сервера встречаются чаще всего? И что они значат для оптимизации сайта? Давайте внимательно рассмотрим самые полезные для SEO ответы и способы их обработки.
Ответы серверов, которые встречаются чаще всего
На самом деле существует более 70 различных кодов состояния сервера, но, скорее всего, вы никогда не столкнетесь с большей половиной из них. Однако знать самые распространенные коды состояния HTTP очень важно, потому что ответы сервера напрямую влияют на индексацию вашего сайта, краулинговый бюджет и продвижение ресурса в поисковых системах.
301 Moved Permanently
Говорит о том, что URL был навсегда перенесен на новое место. Браузеры самостоятельно переходят по 301 переадресации — никакого действия от пользователя не требуется.

301 код ответа обычно используют при переводе сайта с HTTP на HTTPS, склейке зеркал (страниц с www и без www), настройке слеша в конце URL, а также при переносе части сайта или всех страниц на новый домен. Этот редирект идеально подходит, если вы хотите передать ссылочный вес старой страницы на новую и сохранить результаты SEO-продвижения.
Совет: Старайтесь не перенаправлять пользователей с удаленного URL на главную страницу сайта. Например, в вашем интернет-магазине есть карточка с неактуальным товаром, но с неплохой ссылочной массой. Вы хотите сохранить этот вес и ставите 301 редирект на главную. Здесь и кроется ошибка! Такой редирект воспринимается Google как 404 Soft, а это означает, что поисковик не будет передавать сигналы со старого URL на новый. В такой ситуации всегда перенаправляйте страницу на максимально похожую (или 404, если аналогичная страница отсутствует).
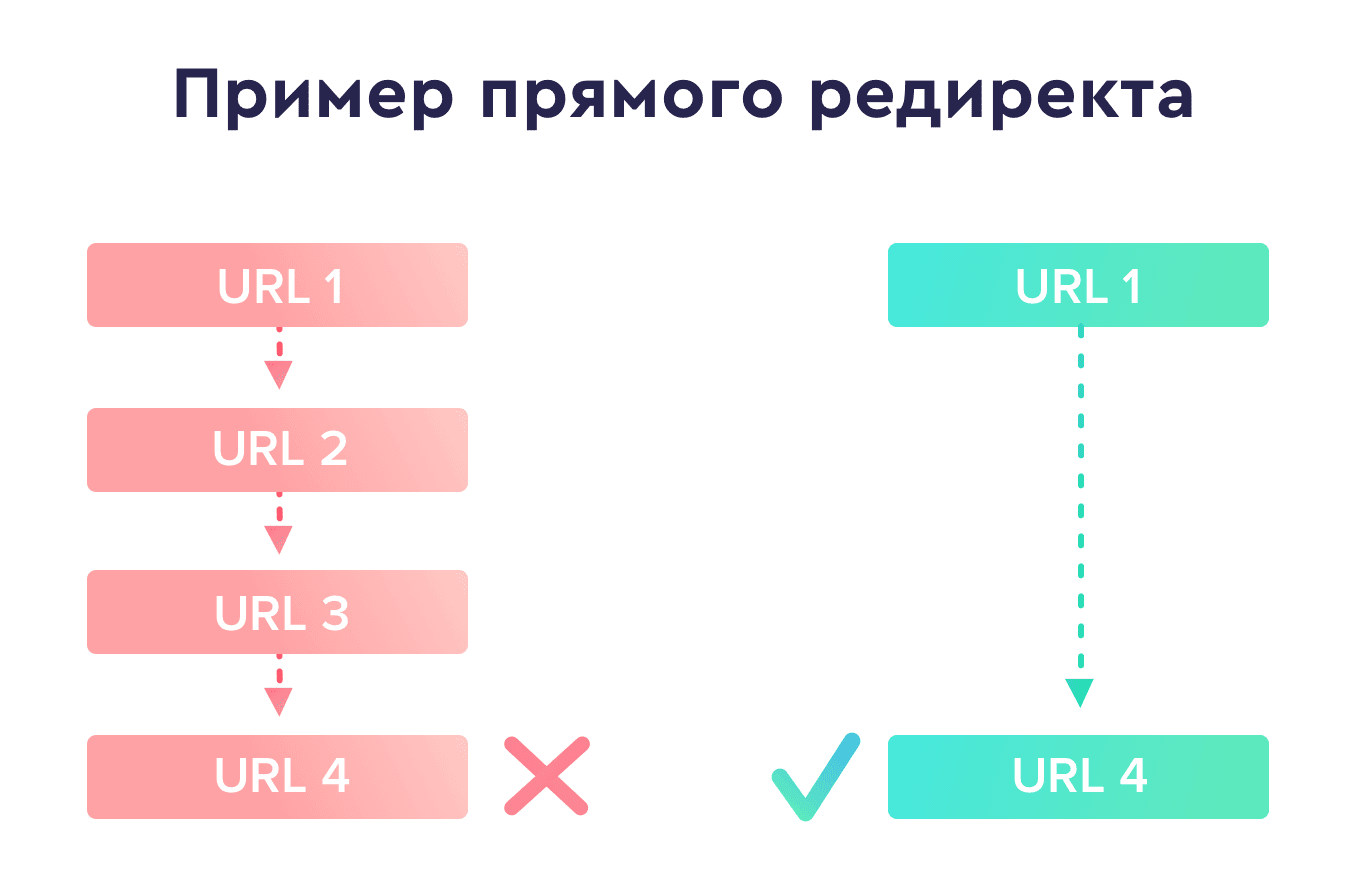
Кроме того, избегайте цепочек редиректов с двумя и больше переадресациями, так как они создают дополнительную нагрузку на сервер и даже могут помешать пользователям перейти на ваш сайт как небезопасный. Google не индексирует дальше 4-го редиректа, и после каждого теряется вес, поэтому лучше ставьте прямые редиректы (вместо 1 -> 2 -> 3, сразу 1 -> 3).
Через несколько лет можете смело удалять 301, чтобы уменьшить нагрузку на сервер.
302 Found / Moved Temporarily
В отличие от постоянного 301 редиректа, этот — временный. Он говорит о том, что страница найдена, но пока размещена по другому адресу.
Обычно его путали с 301, а после того, как Google объявил, что все 3хx редиректы передают ссылочный вес, — ситуация усугубилась. По факту, его нужно ставить, если вы точно уверены, что будете использовать старый URL снова. Как раз об этом вы и сообщаете поисковику с помощью 302 сигнала, а он в ответ оставляет весь ссылочный вес за старой страницей.

Если вы будете использовать 302 редирект на постоянной основе, Google в конечном итоге воспримет его как 301 со всеми вытекающими последствиями. Также проверьте, нет ли на вашем сайте 302 редиректов, которые на самом деле должны быть 301 — такая ошибка встречается очень часто.
304 Not Modified
Сервер отдает 304 Not Modified ответ, когда страница остается неизменной со времени последнего посещения.
Все браузеры хранят в своем кэше данные заголовка Last-Modified. В свою очередь, это позволяет им точно знать, когда страница была в последний раз изменена. И когда поисковые роботы заходят на страницу и видят, что значение заголовка совпадает с уже сохраненным в кэше, сервер возвращает 304 ответ.

Этот код можно использовать для ускорения индексации сайта. Ведь получив такой ответ, поисковый робот не будет загружать страницу, а значит, успеет проиндексировать больше других страниц.
Лучший ответ сервера для оптимизатора ― 200 ОК. Он означает, что запрос успешно обработан. Но 304 несет ту же нагрузку. Как правило, на новые страницы и первое посещение должен выдаваться ответ 200, на все последующие, если не произошло изменений — 304.
403 Forbidden
Этот код ответа говорит о том, что пользователю запрещен доступ к странице.

403 ошибка может появиться, если пользователь вошел на сайт, но у него нет разрешения для доступа к закрытой внутренней сети. Например, если я попытаюсь зайти в кабинет админа SE Ranking по прямому URL, используя пароль и логин личного аккаунта, на экране будет 403 ошибка «Нет доступа». Также 403 ошибка возникает, если индексный файл для главной указан неправильно. Он обязательно должен иметь название index и расширение: *.shtml, *.html, *.htm, *.phtml или *.php.
Кроме того, когда вы переносите сайт на HTTPS, то 403 ответ появится, когда DNS-кэш ещё не успел обновиться, а вы уже что-то от него хотите. Лучше подождите, или, если это вопрос жизни и смерти, обновите кэш принудительно.
Совет: страницы с 403 кодом ответа в конечном итоге будут удалены из индекса, поэтому Google рекомендует использовать 404 ответ вместо 403.
404 Not Found
Самая «любимая» ошибка в SEO. Говорит о том, что сервер ничего не нашел по указанному адресу, хотя соединение между сервером и клиентом прошло успешно.

Не стоит переживать, если вы увидите много 404 страниц в своей Google Search Console. Поисковик просто сообщает вам, какие страницы удалены, а вам уже решать, нужно ли их проверять. Но что стоит точно сделать — убрать все ссылки на удаленные страницы, чтобы не путать посетителей при навигации по вашему сайту.
Обычно мы видим этот код ошибки, когда вводим неправильный URL в браузер и, как следствие, пытаемся получить доступ к несуществующей странице. Или, например, владелец сайта удалил страницу без редиректа URL по новому адресу. Как результат — 404 ошибка. Чтобы решить проблему, посетителю нужно перепроверить написание URL или попробовать найти информацию на сайте самостоятельно через поиск, а владельцу ресурса ― исправить «битые» ссылки на рабочие.
404 страница не индексируется и не передает вес. Поэтому некоторые оптимизаторы грешат «мягкой 404», выдавая стандартную страницу с ответом 200 вместо 404. Но это считается плохой практикой, потому что 200 код говорит Google, что по этому URL есть реальная страница. В конечном счете, страница оказывается в индексе, и поисковик продолжает свои попытки сканировать несуществующие URL-адреса вместо сканирования ваших реальных страниц.
Как настроить 404 страницу для своего сайта
Если раньше после перехода на несуществующую страницу пользователь видел перед собой только цифру 404, то сейчас — просто море креатива. Но не стоит забывать, что он пришел с конкретным запросом и ваша задача — дать решение, а не развлечь его. Поэтому не забудьте оптимизировать 404 страницу — добавьте навигацию своего сайта или контактную форму, особенно если на 404 страницы идет трафик.
Если ваша CMS (система управления контентом) не создала 404 страницу, вы можете создать ее самостоятельно.
С помощью htaccess
Самый простой способ настроить страницу с 404 ошибкой — добавить сообщение об ошибке, например ErrorDocument 404 “<H1> Not Found </ H1>” в сам файл .htaccess.
В результате у вас должно получиться что-то вроде этого:
Через PHP
Вы можете использовать функцию заголовка и менять контент 404 страницы в зависимости от разных сценариев (например, юзер сделал ошибку в URL самостоятельно или уже перешел по «битой» ссылке с какого-то ресурса).
Детальнее — в этой инструкции.
Через WordPress
У вас есть несколько вариантов:
- Отредактируйте существующую страницу 404, которая уже есть в вашей теме.
- Добавьте свою 404 страницу, если ваша тема ее не предлагает по умолчанию.
- Используйте плагин для 404 страницы.
Подробности можно узнать здесь.
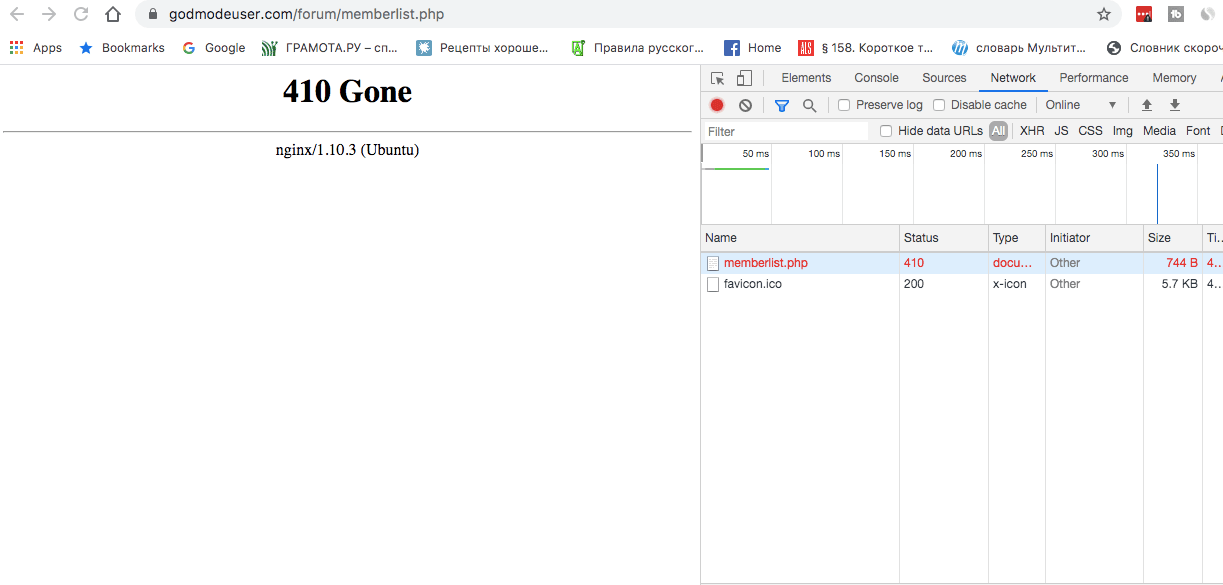
410 Gone
Этот ответ говорит о том, что страница или документ не доступны по указанному адресу и новый адрес неизвестен.
Более того, инструмент проверки URL в Google Search Console обозначает 410 ответы как 404, что приводит к еще большему количеству 404 ошибок, обнаруженных в консоли.
410 ответ чаще всего встречается на страницах с низким трастом, без ссылок или тех, что удалены безвозвратно. Например, с товаром, которого больше не будет в продаже.
Поскольку Google все-таки относится к 404 и 410 ошибкам по-разному, нужно использовать 410 код только тогда, когда вы точно знаете, что страница удалена и больше не вернется. Такой ответ по умолчанию кэшируется, поисковый робот больше не заходит на страницу, а она в свою очередь удаляется из индекса.
Совет: подумайте дважды, прежде чем удалять страницу навсегда. Если вы сомневаетесь, лучше поставить редирект на похожую страницу и получить хотя бы часть текущего трафика. Если же удаления страницы не избежать, обязательно проверьте ссылки, которые на нее ведут — как только страница будет удалена, магия ссылок закончится тоже.
503 Service Unavailable
Этот статус говорит поисковым роботам и пользователям, что в данный момент страница недоступна и, следовательно, сервер не может обработать входящий запрос.
В большинстве случаев 503 появляется, если сервер перегружен, например, превышено ограничение на число входящих запросов или сервер проходит техническое обслуживание.
Могут быть ещё такие причины:
- DDOS-атака на сайт.
- Использование большого количества скриптов и других элементов с внешних ресурсов: виджеты, картинки.
- Запросы к базе данных и извлечение оттуда информации занимают слишком много времени.
- Чрезмерное количество обращений к сайту от поисковиков, пользователей или сервисов по парсингу сайта.
Совет: в идеале в сообщении с 503 ошибкой обязательно нужно указать, что пользователю нужно вернуться на сайт через Х времени. К сожалению, так очень редко делают — обычно просят попытать удачу позже.
И последнее, но не менее важное: код состояния 503 не позволяет поисковым системам индексировать сайт. Кроме того, он сообщает, что сайт плохо обслуживается, потому что пользователи не могут попасть, куда хотели. Поэтому важно, чтобы неполадки были устранены как можно быстрее — иначе это скажется на позициях сайта.
Как настроить 503 страницу для своего сайта через PHP
Вот как выглядит код состояния 503 в PHP:
<?php
header("HTTP/1.1 503 Service Temporarily Unavailable");
header("Status: 503 Service Temporarily Unavailable");
header("Retry-After: 3600");
?>
Больше подробностей можно почитать в этой инструкции.
Как проверить коды состояния всех страниц на сайте
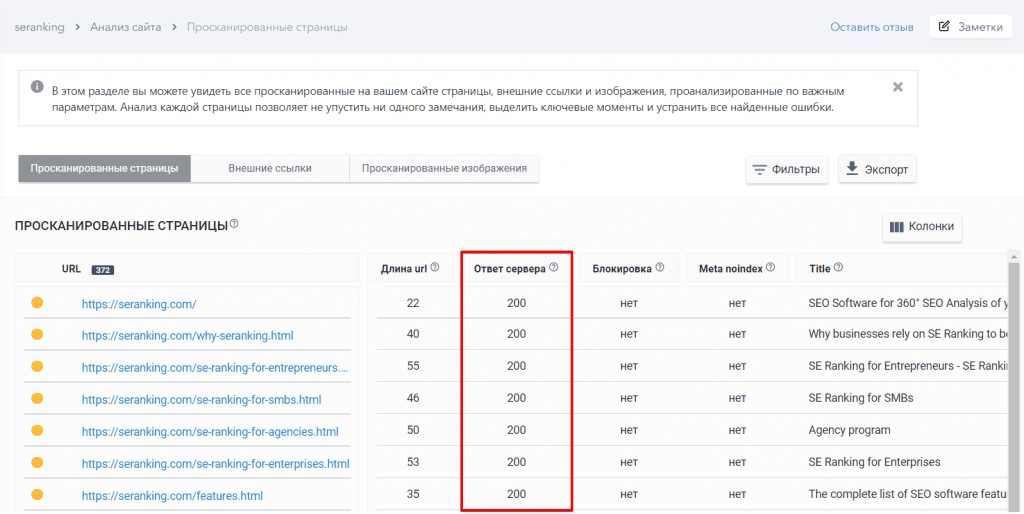
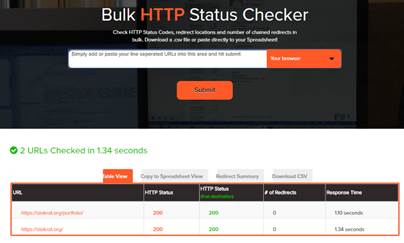
Чтобы быть в курсе всего, что происходит на вашем сайте, нужно мониторить коды состояния всех ваших страниц. Конечно, для этого можно использовать расширение Live HTTP Headers для Chrome или отчет «Покрытие» в Google Search Console, но лучше, если вы проанализируете ответы до того, как до них доберутся поисковые роботы.
Если вы хотите быстро проверить коды состояния всех страниц вашего сайта одним кликом, обязательно попробуйте наш инструмент «Аудит сайта».
Инструмент не просто проверит все страницы на вашем сайте и проанализирует ключевые параметры оптимизации, но и выполнит SEO-аудит всего ресурса по важным техническим параметрам, найдет ошибки и даже подскажет методы их решения.
Все статусы страниц вы увидите в основном отчете, в котором проанализированы технические параметры, страницы, мета-теги, ссылки и контент.
Кстати, вы можете воспользоваться бесплатной пробной версией, чтобы протестировать все основные функции аудита.
Если же вас интересуют только коды состояния всех страниц, просто перейдите на вкладку «Сканированные страницы». Все данные можно экспортировать в формате XLS для подробного изучения:
Безусловно, найти ошибки в кодах ответов это только полдела. Решать проблемы, связанные с ошибками сервера, вам все равно придется самостоятельно, но сам поиск ошибок у вас теперь будет занимать считанные минуты. Оптимизировав коды состояния своих страниц, не забудьте отправить их на повторную индексацию.
Чтобы сдать этот экзамен на отлично, мы подготовили для вас шпаргалку по правилам HTTP-знаков с лучшими SEO-советами. Теперь какой бы знак не встретился у вас на пути, вы будете знать, что делать.
Юлия — контент-маркетолог c 10-летним опытом работы в журналистике, копирайтинге, рекламе и PR.
Своим опытом и знаниями она делится, создавая полезные статьи про SEO и диджитал-маркетинг для блога SE Ranking и популярных медиа.
Когда Юлия не пишет статьи, она осваивает новые асаны, путешествует и помогает волонтерской организации YWCA.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is a list of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response status codes. Status codes are issued by a server in response to a client’s request made to the server. It includes codes from IETF Request for Comments (RFCs), other specifications, and some additional codes used in some common applications of the HTTP. The first digit of the status code specifies one of five standard classes of responses. The optional message phrases shown are typical, but any human-readable alternative may be provided, or none at all.
Unless otherwise stated, the status code is part of the HTTP standard (RFC 9110).
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains the official registry of HTTP status codes.[1]
All HTTP response status codes are separated into five classes or categories. The first digit of the status code defines the class of response, while the last two digits do not have any classifying or categorization role. There are five classes defined by the standard:
- 1xx informational response – the request was received, continuing process
- 2xx successful – the request was successfully received, understood, and accepted
- 3xx redirection – further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request
- 4xx client error – the request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled
- 5xx server error – the server failed to fulfil an apparently valid request
1xx informational response
An informational response indicates that the request was received and understood. It is issued on a provisional basis while request processing continues. It alerts the client to wait for a final response. The message consists only of the status line and optional header fields, and is terminated by an empty line. As the HTTP/1.0 standard did not define any 1xx status codes, servers must not[note 1] send a 1xx response to an HTTP/1.0 compliant client except under experimental conditions.
- 100 Continue
- The server has received the request headers and the client should proceed to send the request body (in the case of a request for which a body needs to be sent; for example, a POST request). Sending a large request body to a server after a request has been rejected for inappropriate headers would be inefficient. To have a server check the request’s headers, a client must send
Expect: 100-continueas a header in its initial request and receive a100 Continuestatus code in response before sending the body. If the client receives an error code such as 403 (Forbidden) or 405 (Method Not Allowed) then it should not send the request’s body. The response417 Expectation Failedindicates that the request should be repeated without theExpectheader as it indicates that the server does not support expectations (this is the case, for example, of HTTP/1.0 servers).[2] - 101 Switching Protocols
- The requester has asked the server to switch protocols and the server has agreed to do so.
- 102 Processing (WebDAV; RFC 2518)
- A WebDAV request may contain many sub-requests involving file operations, requiring a long time to complete the request. This code indicates that the server has received and is processing the request, but no response is available yet.[3] This prevents the client from timing out and assuming the request was lost. The status code is deprecated.[4]
- 103 Early Hints (RFC 8297)
- Used to return some response headers before final HTTP message.[5]
2xx success
This class of status codes indicates the action requested by the client was received, understood, and accepted.[1]
- 200 OK
- Standard response for successful HTTP requests. The actual response will depend on the request method used. In a GET request, the response will contain an entity corresponding to the requested resource. In a POST request, the response will contain an entity describing or containing the result of the action.
- 201 Created
- The request has been fulfilled, resulting in the creation of a new resource.[6]
- 202 Accepted
- The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. The request might or might not be eventually acted upon, and may be disallowed when processing occurs.
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information (since HTTP/1.1)
- The server is a transforming proxy (e.g. a Web accelerator) that received a 200 OK from its origin, but is returning a modified version of the origin’s response.[7][8]
- 204 No Content
- The server successfully processed the request, and is not returning any content.
- 205 Reset Content
- The server successfully processed the request, asks that the requester reset its document view, and is not returning any content.
- 206 Partial Content
- The server is delivering only part of the resource (byte serving) due to a range header sent by the client. The range header is used by HTTP clients to enable resuming of interrupted downloads, or split a download into multiple simultaneous streams.
- 207 Multi-Status (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The message body that follows is by default an XML message and can contain a number of separate response codes, depending on how many sub-requests were made.[9]
- 208 Already Reported (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The members of a DAV binding have already been enumerated in a preceding part of the (multistatus) response, and are not being included again.
- 226 IM Used (RFC 3229)
- The server has fulfilled a request for the resource, and the response is a representation of the result of one or more instance-manipulations applied to the current instance.[10]
3xx redirection
This class of status code indicates the client must take additional action to complete the request. Many of these status codes are used in URL redirection.[1]
A user agent may carry out the additional action with no user interaction only if the method used in the second request is GET or HEAD. A user agent may automatically redirect a request. A user agent should detect and intervene to prevent cyclical redirects.[11]
- 300 Multiple Choices
- Indicates multiple options for the resource from which the client may choose (via agent-driven content negotiation). For example, this code could be used to present multiple video format options, to list files with different filename extensions, or to suggest word-sense disambiguation.
- 301 Moved Permanently
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI.
- 302 Found (Previously «Moved temporarily»)
- Tells the client to look at (browse to) another URL. The HTTP/1.0 specification (RFC 1945) required the client to perform a temporary redirect with the same method (the original describing phrase was «Moved Temporarily»),[12] but popular browsers implemented 302 redirects by changing the method to GET. Therefore, HTTP/1.1 added status codes 303 and 307 to distinguish between the two behaviours.[11]
- 303 See Other (since HTTP/1.1)
- The response to the request can be found under another URI using the GET method. When received in response to a POST (or PUT/DELETE), the client should presume that the server has received the data and should issue a new GET request to the given URI.
- 304 Not Modified
- Indicates that the resource has not been modified since the version specified by the request headers If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match. In such case, there is no need to retransmit the resource since the client still has a previously-downloaded copy.
- 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1)
- The requested resource is available only through a proxy, the address for which is provided in the response. For security reasons, many HTTP clients (such as Mozilla Firefox and Internet Explorer) do not obey this status code.
- 306 Switch Proxy
- No longer used. Originally meant «Subsequent requests should use the specified proxy.»
- 307 Temporary Redirect (since HTTP/1.1)
- In this case, the request should be repeated with another URI; however, future requests should still use the original URI. In contrast to how 302 was historically implemented, the request method is not allowed to be changed when reissuing the original request. For example, a POST request should be repeated using another POST request.
- 308 Permanent Redirect
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI. 308 parallel the behaviour of 301, but does not allow the HTTP method to change. So, for example, submitting a form to a permanently redirected resource may continue smoothly.
4xx client errors
This class of status code is intended for situations in which the error seems to have been caused by the client. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. These status codes are applicable to any request method. User agents should display any included entity to the user.
- 400 Bad Request
- The server cannot or will not process the request due to an apparent client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, size too large, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
- 401 Unauthorized
- Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is required and has failed or has not yet been provided. The response must include a WWW-Authenticate header field containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. See Basic access authentication and Digest access authentication. 401 semantically means «unauthorised», the user does not have valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
- Some sites incorrectly issue HTTP 401 when an IP address is banned from the website (usually the website domain) and that specific address is refused permission to access a website.[citation needed]
- 402 Payment Required
- Reserved for future use. The original intention was that this code might be used as part of some form of digital cash or micropayment scheme, as proposed, for example, by GNU Taler,[14] but that has not yet happened, and this code is not widely used. Google Developers API uses this status if a particular developer has exceeded the daily limit on requests.[15] Sipgate uses this code if an account does not have sufficient funds to start a call.[16] Shopify uses this code when the store has not paid their fees and is temporarily disabled.[17] Stripe uses this code for failed payments where parameters were correct, for example blocked fraudulent payments.[18]
- 403 Forbidden
- The request contained valid data and was understood by the server, but the server is refusing action. This may be due to the user not having the necessary permissions for a resource or needing an account of some sort, or attempting a prohibited action (e.g. creating a duplicate record where only one is allowed). This code is also typically used if the request provided authentication by answering the WWW-Authenticate header field challenge, but the server did not accept that authentication. The request should not be repeated.
- 404 Not Found
- The requested resource could not be found but may be available in the future. Subsequent requests by the client are permissible.
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- A request method is not supported for the requested resource; for example, a GET request on a form that requires data to be presented via POST, or a PUT request on a read-only resource.
- 406 Not Acceptable
- The requested resource is capable of generating only content not acceptable according to the Accept headers sent in the request. See Content negotiation.
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
- The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy.
- 408 Request Timeout
- The server timed out waiting for the request. According to HTTP specifications: «The client did not produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time.»
- 409 Conflict
- Indicates that the request could not be processed because of conflict in the current state of the resource, such as an edit conflict between multiple simultaneous updates.
- 410 Gone
- Indicates that the resource requested was previously in use but is no longer available and will not be available again. This should be used when a resource has been intentionally removed and the resource should be purged. Upon receiving a 410 status code, the client should not request the resource in the future. Clients such as search engines should remove the resource from their indices. Most use cases do not require clients and search engines to purge the resource, and a «404 Not Found» may be used instead.
- 411 Length Required
- The request did not specify the length of its content, which is required by the requested resource.
- 412 Precondition Failed
- The server does not meet one of the preconditions that the requester put on the request header fields.
- 413 Payload Too Large
- The request is larger than the server is willing or able to process. Previously called «Request Entity Too Large» in RFC 2616.[19]
- 414 URI Too Long
- The URI provided was too long for the server to process. Often the result of too much data being encoded as a query-string of a GET request, in which case it should be converted to a POST request. Called «Request-URI Too Long» previously in RFC 2616.[20]
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
- The request entity has a media type which the server or resource does not support. For example, the client uploads an image as image/svg+xml, but the server requires that images use a different format.
- 416 Range Not Satisfiable
- The client has asked for a portion of the file (byte serving), but the server cannot supply that portion. For example, if the client asked for a part of the file that lies beyond the end of the file. Called «Requested Range Not Satisfiable» previously RFC 2616.[21]
- 417 Expectation Failed
- The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field.[22]
- 418 I’m a teapot (RFC 2324, RFC 7168)
- This code was defined in 1998 as one of the traditional IETF April Fools’ jokes, in RFC 2324, Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol, and is not expected to be implemented by actual HTTP servers. The RFC specifies this code should be returned by teapots requested to brew coffee.[23] This HTTP status is used as an Easter egg in some websites, such as Google.com’s «I’m a teapot» easter egg.[24][25][26] Sometimes, this status code is also used as a response to a blocked request, instead of the more appropriate 403 Forbidden.[27][28]
- 421 Misdirected Request
- The request was directed at a server that is not able to produce a response (for example because of connection reuse).
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
- The request was well-formed but was unable to be followed due to semantic errors.[9]
- 423 Locked (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The resource that is being accessed is locked.[9]
- 424 Failed Dependency (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The request failed because it depended on another request and that request failed (e.g., a PROPPATCH).[9]
- 425 Too Early (RFC 8470)
- Indicates that the server is unwilling to risk processing a request that might be replayed.
- 426 Upgrade Required
- The client should switch to a different protocol such as TLS/1.3, given in the Upgrade header field.
- 428 Precondition Required (RFC 6585)
- The origin server requires the request to be conditional. Intended to prevent the ‘lost update’ problem, where a client GETs a resource’s state, modifies it, and PUTs it back to the server, when meanwhile a third party has modified the state on the server, leading to a conflict.[29]
- 429 Too Many Requests (RFC 6585)
- The user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time. Intended for use with rate-limiting schemes.[29]
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large (RFC 6585)
- The server is unwilling to process the request because either an individual header field, or all the header fields collectively, are too large.[29]
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons (RFC 7725)
- A server operator has received a legal demand to deny access to a resource or to a set of resources that includes the requested resource.[30] The code 451 was chosen as a reference to the novel Fahrenheit 451 (see the Acknowledgements in the RFC).
5xx server errors
The server failed to fulfil a request.
Response status codes beginning with the digit «5» indicate cases in which the server is aware that it has encountered an error or is otherwise incapable of performing the request. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and indicate whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. Likewise, user agents should display any included entity to the user. These response codes are applicable to any request method.
- 500 Internal Server Error
- A generic error message, given when an unexpected condition was encountered and no more specific message is suitable.
- 501 Not Implemented
- The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfil the request. Usually this implies future availability (e.g., a new feature of a web-service API).
- 502 Bad Gateway
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable
- The server cannot handle the request (because it is overloaded or down for maintenance). Generally, this is a temporary state.[31]
- 504 Gateway Timeout
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
- The server does not support the HTTP version used in the request.
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates (RFC 2295)
- Transparent content negotiation for the request results in a circular reference.[32]
- 507 Insufficient Storage (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The server is unable to store the representation needed to complete the request.[9]
- 508 Loop Detected (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The server detected an infinite loop while processing the request (sent instead of 208 Already Reported).
- 510 Not Extended (RFC 2774)
- Further extensions to the request are required for the server to fulfil it.[33]
- 511 Network Authentication Required (RFC 6585)
- The client needs to authenticate to gain network access. Intended for use by intercepting proxies used to control access to the network (e.g., «captive portals» used to require agreement to Terms of Service before granting full Internet access via a Wi-Fi hotspot).[29]
Unofficial codes
The following codes are not specified by any standard.
- 218 This is fine (Apache HTTP Server)
- Used by Apache servers. A catch-all error condition allowing the passage of message bodies through the server when the
ProxyErrorOverridesetting is enabled. It is displayed in this situation instead of a 4xx or 5xx error message.[34] - 419 Page Expired (Laravel Framework)
- Used by the Laravel Framework when a CSRF Token is missing or expired.[citation needed]
- 420 Method Failure (Spring Framework)
- A deprecated response used by the Spring Framework when a method has failed.[35]
- 420 Enhance Your Calm (Twitter)
- Returned by version 1 of the Twitter Search and Trends API when the client is being rate limited; versions 1.1 and later use the 429 Too Many Requests response code instead.[36] The phrase «Enhance your calm» comes from the 1993 movie Demolition Man, and its association with this number is likely a reference to cannabis.[citation needed]
- 430 Request Header Fields Too Large (Shopify)
- Used by Shopify, instead of the 429 Too Many Requests response code, when too many URLs are requested within a certain time frame.[37]
- 450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft)
- The Microsoft extension code indicated when Windows Parental Controls are turned on and are blocking access to the requested webpage.[38]
- 498 Invalid Token (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 498 indicates an expired or otherwise invalid token.[39]
- 499 Token Required (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 499 indicates that a token is required but was not submitted.[39]
- 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded (Apache Web Server/cPanel)
- The server has exceeded the bandwidth specified by the server administrator; this is often used by shared hosting providers to limit the bandwidth of customers.[40]
- 529 Site is overloaded
- Used by Qualys in the SSLLabs server testing API to signal that the site can’t process the request.[41]
- 530 Site is frozen
- Used by the Pantheon Systems web platform to indicate a site that has been frozen due to inactivity.[42]
- 598 (Informal convention) Network read timeout error
- Used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network read timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.[43]
- 599 Network Connect Timeout Error
- An error used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network connect timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.
Internet Information Services
Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) web server expands the 4xx error space to signal errors with the client’s request.
- 440 Login Time-out
- The client’s session has expired and must log in again.[44]
- 449 Retry With
- The server cannot honour the request because the user has not provided the required information.[45]
- 451 Redirect
- Used in Exchange ActiveSync when either a more efficient server is available or the server cannot access the users’ mailbox.[46] The client is expected to re-run the HTTP AutoDiscover operation to find a more appropriate server.[47]
IIS sometimes uses additional decimal sub-codes for more specific information,[48] however these sub-codes only appear in the response payload and in documentation, not in the place of an actual HTTP status code.
nginx
The nginx web server software expands the 4xx error space to signal issues with the client’s request.[49][50]
- 444 No Response
- Used internally[51] to instruct the server to return no information to the client and close the connection immediately.
- 494 Request header too large
- Client sent too large request or too long header line.
- 495 SSL Certificate Error
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has provided an invalid client certificate.
- 496 SSL Certificate Required
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when a client certificate is required but not provided.
- 497 HTTP Request Sent to HTTPS Port
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has made a HTTP request to a port listening for HTTPS requests.
- 499 Client Closed Request
- Used when the client has closed the request before the server could send a response.
Cloudflare
Cloudflare’s reverse proxy service expands the 5xx series of errors space to signal issues with the origin server.[52]
- 520 Web Server Returned an Unknown Error
- The origin server returned an empty, unknown, or unexpected response to Cloudflare.[53]
- 521 Web Server Is Down
- The origin server refused connections from Cloudflare. Security solutions at the origin may be blocking legitimate connections from certain Cloudflare IP addresses.
- 522 Connection Timed Out
- Cloudflare timed out contacting the origin server.
- 523 Origin Is Unreachable
- Cloudflare could not reach the origin server; for example, if the DNS records for the origin server are incorrect or missing.
- 524 A Timeout Occurred
- Cloudflare was able to complete a TCP connection to the origin server, but did not receive a timely HTTP response.
- 525 SSL Handshake Failed
- Cloudflare could not negotiate a SSL/TLS handshake with the origin server.
- 526 Invalid SSL Certificate
- Cloudflare could not validate the SSL certificate on the origin web server. Also used by Cloud Foundry’s gorouter.
- 527 Railgun Error
- Error 527 indicates an interrupted connection between Cloudflare and the origin server’s Railgun server.[54]
- 530
- Error 530 is returned along with a 1xxx error.[55]
AWS Elastic Load Balancing
Amazon Web Services’ Elastic Load Balancing adds a few custom return codes to signal issues either with the client request or with the origin server.[56]
- 460
- Client closed the connection with the load balancer before the idle timeout period elapsed. Typically when client timeout is sooner than the Elastic Load Balancer’s timeout.[56]
- 463
- The load balancer received an X-Forwarded-For request header with more than 30 IP addresses.[56]
- 464
- Incompatible protocol versions between Client and Origin server.[56]
- 561 Unauthorized
- An error around authentication returned by a server registered with a load balancer. You configured a listener rule to authenticate users, but the identity provider (IdP) returned an error code when authenticating the user.[56]
Caching warning codes (obsoleted)
The following caching related warning codes were specified under RFC 7234. Unlike the other status codes above, these were not sent as the response status in the HTTP protocol, but as part of the «Warning» HTTP header.[57][58]
Since this «Warning» header is often neither sent by servers nor acknowledged by clients, this header and its codes were obsoleted by the HTTP Working Group in 2022 with RFC 9111.[59]
- 110 Response is Stale
- The response provided by a cache is stale (the content’s age exceeds a maximum age set by a Cache-Control header or heuristically chosen lifetime).
- 111 Revalidation Failed
- The cache was unable to validate the response, due to an inability to reach the origin server.
- 112 Disconnected Operation
- The cache is intentionally disconnected from the rest of the network.
- 113 Heuristic Expiration
- The cache heuristically chose a freshness lifetime greater than 24 hours and the response’s age is greater than 24 hours.
- 199 Miscellaneous Warning
- Arbitrary, non-specific warning. The warning text may be logged or presented to the user.
- 214 Transformation Applied
- Added by a proxy if it applies any transformation to the representation, such as changing the content encoding, media type or the like.
- 299 Miscellaneous Persistent Warning
- Same as 199, but indicating a persistent warning.
See also
- Custom error pages
- List of FTP server return codes
- List of HTTP header fields
- List of SMTP server return codes
- Common Log Format
Explanatory notes
- ^ Emphasised words and phrases such as must and should represent interpretation guidelines as given by RFC 2119
References
- ^ a b c «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry». Iana.org. Archived from the original on December 11, 2011. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ Fielding, Roy T. «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 10.1.1 «Expect»«.
- ^ Goland, Yaronn; Whitehead, Jim; Faizi, Asad; Carter, Steve R.; Jensen, Del (February 1999). HTTP Extensions for Distributed Authoring – WEBDAV. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2518. RFC 2518. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «102 Processing — HTTP MDN». 102 status code is deprecated
- ^ Oku, Kazuho (December 2017). An HTTP Status Code for Indicating Hints. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8297. RFC 8297. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ Stewart, Mark; djna. «Create request with POST, which response codes 200 or 201 and content». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.3.4».
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 7.7».
- ^ a b c d e Dusseault, Lisa, ed. (June 2007). HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV). IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4918. RFC 4918. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Delta encoding in HTTP. IETF. January 2002. doi:10.17487/RFC3229. RFC 3229. Retrieved February 25, 2011.
- ^ a b «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.4 «Redirection 3xx»«.
- ^ Berners-Lee, Tim; Fielding, Roy T.; Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk (May 1996). Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.0. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1945. RFC 1945. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «The GNU Taler tutorial for PHP Web shop developers 0.4.0». docs.taler.net. Archived from the original on November 8, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2017.
- ^ «Google API Standard Error Responses». 2016. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ «Sipgate API Documentation». Archived from the original on July 10, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ «Shopify Documentation». Archived from the original on July 25, 2018. Retrieved July 25, 2018.
- ^ «Stripe API Reference – Errors». stripe.com. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 413». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 414». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 416». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ TheDeadLike. «HTTP/1.1 Status Codes 400 and 417, cannot choose which». serverFault. Archived from the original on October 10, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Larry Masinter (April 1, 1998). Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol (HTCPCP/1.0). doi:10.17487/RFC2324. RFC 2324.
Any attempt to brew coffee with a teapot should result in the error code «418 I’m a teapot». The resulting entity body MAY be short and stout.
- ^ I’m a teapot
- ^ Barry Schwartz (August 26, 2014). «New Google Easter Egg For SEO Geeks: Server Status 418, I’m A Teapot». Search Engine Land. Archived from the original on November 15, 2015. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ «Google’s Teapot». Retrieved October 23, 2017.[dead link]
- ^ «Enable extra web security on a website». DreamHost. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ «I Went to a Russian Website and All I Got Was This Lousy Teapot». PCMag. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Nottingham, M.; Fielding, R. (April 2012). «RFC 6585 – Additional HTTP Status Codes». Request for Comments. Internet Engineering Task Force. Archived from the original on May 4, 2012. Retrieved May 1, 2012.
- ^ Bray, T. (February 2016). «An HTTP Status Code to Report Legal Obstacles». ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ alex. «What is the correct HTTP status code to send when a site is down for maintenance?». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Holtman, Koen; Mutz, Andrew H. (March 1998). Transparent Content Negotiation in HTTP. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2295. RFC 2295. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk; Leach, Paul; Lawrence, Scott (February 2000). An HTTP Extension Framework. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2774. RFC 2774. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «218 This is fine — HTTP status code explained». HTTP.dev. Retrieved July 25, 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Enum HttpStatus». Spring Framework. org.springframework.http. Archived from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «Twitter Error Codes & Responses». Twitter. 2014. Archived from the original on September 27, 2017. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Status Codes and SEO: what you need to know». ContentKing. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ «Screenshot of error page». Archived from the original (bmp) on May 11, 2013. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ a b «Using token-based authentication». ArcGIS Server SOAP SDK. Archived from the original on September 26, 2014. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Error Codes and Quick Fixes». Docs.cpanel.net. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved October 15, 2015.
- ^ «SSL Labs API v3 Documentation». github.com.
- ^ «Platform Considerations | Pantheon Docs». pantheon.io. Archived from the original on January 6, 2017. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ^ «HTTP status codes — ascii-code.com». www.ascii-code.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2017. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^
«Error message when you try to log on to Exchange 2007 by using Outlook Web Access: «440 Login Time-out»«. Microsoft. 2010. Retrieved November 13, 2013. - ^ «2.2.6 449 Retry With Status Code». Microsoft. 2009. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved October 26, 2009.
- ^ «MS-ASCMD, Section 3.1.5.2.2». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 26, 2015. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «Ms-oxdisco». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «The HTTP status codes in IIS 7.0». Microsoft. July 14, 2009. Archived from the original on April 9, 2009. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
- ^ «ngx_http_request.h». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on September 19, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «ngx_http_special_response.c». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «return» directive Archived March 1, 2018, at the Wayback Machine (http_rewrite module) documentation.
- ^ «Troubleshooting: Error Pages». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Error 520: web server returns an unknown error». Cloudflare.
- ^ «527 Error: Railgun Listener to origin error». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on October 13, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ «Error 530». Cloudflare. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e «Troubleshoot Your Application Load Balancers – Elastic Load Balancing». docs.aws.amazon.com. Retrieved May 17, 2023.
- ^ «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Caching». datatracker.ietf.org. Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- ^ «Warning — HTTP | MDN». developer.mozilla.org. Retrieved August 15, 2021.
Some text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.5 Generic (CC BY-SA 2.5) license.
- ^ «RFC 9111: HTTP Caching, Section 5.5 «Warning»«. June 2022.
External links
- «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15 «Status Codes»«.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry at the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
- HTTP status codes at http-statuscode.com
- MDN status code reference at mozilla.org
СОДЕРЖАНИЕ
Какие бывают http ответы сервера (сайта, страницы)?
Ответ сервера 1XX
Ответ сервера 200
Ответ сервера 301
Ответ сервера 302
Ответ сервера 404
Ответ сервера 500
Ответ сервера 502
Ответ сервера 550
Как получить коды ответа сервера (страницы) через Яндекс
Как еще узнать коды ответа сервера (сайта)?
Массовая проверка ответов сервера (сайта) онлайн
Как проверить скорость (время) ответа сервера сайта?
Долгий ответ сервера
Какое должно быть время ответа сервера?
Сокращение ответа сервера
Коды ответа http сервера (англ. HTTP status code) являются частью первой строки ответа сервера. Он представляет собой целое трехзначное число, первая цифра которого указывает на класс состояния. Вместе с кодом ответа выдается короткая англоязычная подсказка. Продвижение сайтов в сети интернет невозможно без знания ответов сервера.
Пример:
404 Not found
Дальнейшие действия зависят именно от того, какой код ответа дал сервер или страница. Ввиду того что набор кодов является стандартным для всех сайтов/страниц/серверов, действия при выдаче того или иного кода тоже будут стандартными.
На сегодняшний день выделено 5 основных классов кода ответа:
1xx: Informational (рус. Информационный) — запрос правильно воспринят, но его обработка не завершена.
2xx: Success (рус. Успешно) — запрос правильно воспринят и успешно обработан.
3xx: Redirection (рус. Перенаправление) — коды переадресации на другие страницы.
4xx: Client Error (рус. Ошибка клиента) — ошибка со стороны клиента.
5xx: Server Error (рус. Ошибка сервера) — ошибка со стороны сервера.
А теперь давайте по отдельности разберем некоторые коды состояния IANA.
Ответ сервера 1XX
100 Continue Server Code
100 Continue сообщает, что связь с сервером уже установлена, сервер принял корректный запрос и теперь ведется обмен данными между сервером и клиентом. Данный код является временным, т.е. за ним всегда следует другой. Код 100 является внутренним и не относится к ошибочным. Т.е. «дверь открыта, читай что нужно, как закончишь – закрой». Код 100 может и не генерироваться, если пользователь уже получил часть данных от сервера.
101 Switching Protocols
Данный код так же не является ошибочным. Генерируется при переключении с одного протокола на другой. Например, при запросе переключения со старой версии HTTP на более новую.
Это, один из самых простых серверных кодов. Он означает, что со стороны пользователя поступил запрос на переключение типа протокола, используемого на веб-сервере, и сервер дал согласие на это.
102 Processing
В каком-то смысле это аналог кода 100. Генерируется в том случае, когда обработка запроса может занять много времени. Для этих целей таймер ожидания сбрасывается и ожидание дальнейших команд происходит в обычном режиме. Так же не является кодом ошибки.
Ответ сервера 200 ОК
По праву занимает самое первое место по важности и популярности, т.к. именно его отдает сервер в случае успешной и правильной обработки запроса пользователя.
Ответ сервера 301
Также является одним из распространенных кодов ответа. Он сообщает, что запрашиваемая страница по данному адресу более не доступна, а затем происходит перенаправление на другой адрес. 301 редирект может применяться, например, при «переезде» сайта с протокола HTTP на HTTPS (обычно это реализуется через файл .htaccess, доступный на серверах Apache).
Ответ сервера 302
Данный код сообщает о том, что расположение запрашиваемой страницы временно изменено. Также должна быть предоставлена информация о новом местоположении запрашиваемого документа. Данный код изначально использовался в качестве основного способа перенаправления.
Ответ сервера 404
Вот уж что-что, а ошибку ответа сервера 404 не видели только те, кто еще не родился и те, кто умер до создания интернета. Данный код сообщает о том, что запрашиваемый документ по каким-то причинам на сайте отсутствует. Код ошибки ответа сервера 404 должен отдаваться только в том случае, если по указанному пользователем адресу документа никогда не было. Если документ ранее был доступен по этому адресу, а потом его удалили с сайта, то сервер должен отдавать код 410, а не 404.
Фейковые страницы 404
Большинство вебмастеров не обращает на 404-тые страницы никакого внимания, однако, это может серьезно навредить ранжированию сайта. Парадокс, но страница с сообщением 404 File Not Found далеко не всегда отдает код 404. Такие страницы принято называть «Soft 404». Причины возникновения просты – по каким-то причинам страница отдает код, отличный от 404 и 410 – например, 200. Такое вполне возможно, если страница уже создана, но контента на ней пока нет.
Ответ сервера 500
Все коды серии 5хх свидетельствуют о том, что сервер не в состоянии завершить обработку запроса. Вместе с кодом должно появляться и поясняющая подсказка (с причиной) на английском языке.
500 Internal Server Error
Код 500 отдается в случае любой внутренней ошибки сервера, за исключением остальных ошибок 5хх класса. Такая ошибка может быть отдана в том случае, когда ссылка генерируется на сервере непосредственно в момент запроса. Простейший пример – внутренний поиск по сайту: физически никакого документа по запрашиваемой ссылке нет.
Ответ сервера 502
Код 502 может отображаться в тех случаях, когда сервер играет роль шлюза или прокси, но при этом не удалось «найти общий язык» между ним и вышестоящим сервером, т.е., по сути, это просто ошибка обмена данных.
Ответ сервера 550
При возникновении ошибки 550 необходимо проверить насколько корректно прописаны MX-записи, чтобы устранить данные ошибки ответа сервера .
Для проверки необходимо перейти по ссылке (https://www.reg.ru/nettools/dig), затем прописать имя проверяемого домена, а в списке выбрать «MX». Теперь нажимаем Проверить:
На выходе будет представлена таблица.
Необходимо убедиться, что в ней прописаны необходимые записи для работы вашей почты:
|
Почта |
MX-записи |
|
Почта REG.RU на хостинге |
mx1.hosting.reg.ru и mx2.hosting.reg.ru |
|
Yandex |
mx.yandex.net |
|
Google Apps |
aspmx.l.google.com … |
|
Mail.Ru для бизнеса |
emx.mail.ru |
|
Расширенная защита от спама |
mxs1.reg.ru и mxs2.reg.ru |
|
Почта REG.RU на VPS |
mail.domain.ru |
ВАЖНО! Смешивание MX-записей недопустимо, т.е. в таблице на выдаче должны быть только те MX-записи, которые нужны именно для вашей почты. При необходимости нужно скорректировать записи, исправив ошибки и/или удалив лишнее.
Как получить коды ответа сервера (страницы) через Яндекс
Шаг 1. Проверяем код ответа сервера на страницу сайта, которая должна быть в поиске.
Открываем любую страницу Вашего сайта, находящуюся в поисковой выдаче Яндекса, затем из адресной строки копируем ее URL-адрес.
Теперь переходим в сервис Яндекса (http://webmaster.yandex.ru/server-response.xml), с помощью которого можно посмотреть на сайт глазами робота и проверить скорость ответа сервера в Яндекс панели.
Просто вставляем url-адрес интересующей нас страницы в текстовое поле и нажимаем на кнопку «Проверить». В данном случае мы получили код 200 ОК, свидетельствующий о нормальной работе страницы.
Шаг 2. Проверяем ответ сервера на заведомо несуществующую страницу.
В том же сервисе вводим имя_домена/какая-то_крокозябра
В данном случае мы получили ответ 301 Moved Permanently. Это говорит о том, что адрес страницы указан неверно и происходит переадресация на правильный адрес.
Как еще узнать коды ответа сервера (сайта)?
Mainspy
В качестве альтернативы можно пробить код ответа с помощью сервиса http://mainspy.ru. Работает аналогично сервису Яндекса: вставляем интересующий URL и жмем «Проверить». Код ответа в данном случае находится в самой первой строке:
Bertal
Bertal, в отличие от Mainspy, позволяет взглянуть на страницу не только глазами Яндекс-бота, но и глазами поисковых роботов Bing и Google, а в качестве бонуса – может эмулировать популярные браузеры. Для удобства взглянем на те же страницы глазами GoogleBot. В данном случае код ответа подсвечен зеленым.
Массовая проверка ответов сервера (сайта) онлайн
Массовая проверка кодов ответа может пригодиться для поиска неработающих сайтов, на которых были куплены ссылки (через биржи или напрямую – неважно).
Dimax.biz — http://backlinks-checker.dimax.biz/tools/proverka_otveta_servera.php – это один из лучших чекеров. Единственный минус – в бесплатном режиме можно делать не более 2 запросов по 50 ссылок каждый. Для более «серьезных» объемов придется воспользоваться платным PRO-тарифом. На выходе мы получаем список, отсортированных по коду ответа. В данном случае в сортировке нет необходимости, т.к. в списке всего 2 адреса, и оба отдают код 200.
Urlitor
Urlitor – еще один сервис, для массовой проверки кодов ответа. Сервис хорош тем, что результаты проверки сводятся в таблицу для облегчения восприятия. К слову – ссылки в таблице кликабельны.
Как проверить скорость (время) ответа сервера сайта?
Сколько таких сервисов уже развелось – не пересчитать. Рассмотрим некоторые из них.
Pingdom
Это англоязычный инструмент, анализирующий скорость по всем параметрам. С его помощью можно узнать скорость в секундах, сколько весит тестируемая страница, а также получить оценку и рекомендации для ее улучшения. Преимущество данного сервиса в том, что анализируется каждый отдельный элемент. Такой анализ позволяет выяснить, что именно затормаживает загрузку отдельно взятой страницы и/или сайта в целом.
Which Loads Faster
Основная фишка данного сервиса в том, что анализируется время загрузки одновременно двух ресурсов. Это позволяет узнать, какой из двух ресурсов работает быстрее. Единственный минус – при разных подключениях и в разных браузерах результат может отличаться.
Google PageSpeed Insights
Google PageSpeed Insights так же является одним из самых мощных инструментов для измерения скорости работы мобильной и десктопной версии. Оценка производится по 100-бальной шкале. 85 баллов и более – это хороший показатель. Плюс бонусом он выдает рекомендации по улучшению.
Долгий ответ сервера
Ответ, длительность которого составляет больше, чем полсекунды, принято называть «долгим». Поэтому, при длительной загрузке сайте вы можете видеть сообщение в браузере «превышено время ожидания ответа от сервера». Причин долгого ответа может быть уйма:
— сложная логика предоставления данных
— сервер не успевает своевременно обрабатывать поступающие запросы из-за их большого количества
— сами запросы (либо сложные, либо неоптимизированные, либо и то и другое)
— запросы к большому количеству внешних ресурсов
— большое количество исполняемых файлов
— сам веб-сервер долго обрабатывает запрос.
Самые «больные» места производительности сервера:
Используемый веб-сервер (Apache, IIS).
Ряд веб-серверов даже при выдаче статических файлов могут создавать задержки, т.к. они на архитектурном уровне не предназначены для обработки большого количества запросов и из-за этого может быть сообщения что превышено время ожидания ответа от сервера. Поэтому для нормальной работы веб-сервера имеет смысл использовать nginx (причем в связке с Apache, php-fpm, а также остальными серверами приложений для обработки серверных вычислений).
Использование OpCache.
Сократите время ответа сервера путем кэширования исполняемого кода (скриптов сайта) – оно позволяет воспользоваться уже готовым результатом вместо того, чтоб каждый раз переводить PHP-инструкции в бинарный код. Но это кэширование с кэшированием результатов выполнения PHP-скриптов не имеет вообще ничего общего.
Запросы к базе данных.
Второй шаг к быстродействию сервера — настройка таблиц (индексов) в базе данных и их структурирование, чтоб облегчить обработку запросов. Сюда же можно отнести пересчет промежуточных и кэширование наиболее часто используемых результатов в отдельные таблицы. Это снизит потребление серверных ресурсов в несколько раз и поможет сократить время ответа сервера.
Сложная логика обработки данных.
Третий шаг – упрощение серверной логики. По сути, это просто устранение ненужных операций и профилирование времени выполнения серверных скриптов.
Обращение к сторонним сервисам.
Прописанные в коде серверных скриптов запросы к сторонним сервисам – это «обычная история», способная преподнести множество сюрпризов, поскольку производительность сервисов, откуда запрашиваются данные, практически никогда и никем не проверяется. А ведь время ответа стороннего сервиса напрямую влияет на время ответа сервера. Поэтому лучше всего в серверных запросах использовать только внутренние источники, которые в любой момент можно проконтролировать на качество производительности, либо в отложенном режиме запросить данные на клиентской.
Почему скорость ответа веб сервера влияет на продвижение.
Во-первых, потому что скорость загрузки является одним из факторов ранжирования (хоть и не решающим). Google открыто заявляет, что по скорости показа страниц ранжируется менее 1% сайтов. НО…
Во-вторых, если страница слишком долго грузится — пользователь ее просто закроет. Такое поведение пользователя принято называть «отказом». К слову, «отказы» оказывают прямое влияние на позиции в поисковой выдаче. Чем выше скорость загрузки – тем ниже процент отказов и, как следствие, тем выше позиции.
Превышено время ожидания ответа от сервера.
Для начала важно понимать причину возникновения сбоя. Т.е. пользователь вводит адрес, а браузер в этот момент отправляет группу запросов, а также включает обратный секундомер на каждый из них. Если по истечении заданного времени браузер не получает ответ на свой запрос, то пользователь увидит вот такую неприятную картинку.
Основных же причин сбоя может несколько:
- Невозможно подключиться к сайту из-за нестабильной работы его серверов;
- Сбитые настройки браузера либо его захламленность;
-
Проблемы с подключением к интернету со стороны пользователя;
-
Ресурс заблокирован.
Что делать для решения?
Если сбой единичен – перезагружаем страницу с помощью комбинации Ctrl+F5. Возможно, потребуется перезагрузить страницу несколько раз. Если не помогло – проверяем подключение к интернету.
Настройки Сети.
1. Некоторые сайты иногда «капризничают». Для динамического IP решение будет простым – перезагрузить роутер через отключение питания.
2. Медленное соединение иногда провоцирует ошибку ERR_CONNECTION_TIMED_OUT. Скорость работы интернета можно проверить через Яндекс-интернетометр. Если скорость слишком низкая – следует обратиться к интернет-провайдеру.
3. Необходимо проверить «Свойства сети» на наличие посторонних DNS-адресов. Если такие адреса имеются – удалить (предварительно на всякий случай переписав их куда-нибудь) и проверить систему на вирусы с помощью установленного на ПК антивирусного ПО – NOD32, Kaspersky, AdwCleaner, MalwareBytes, Dr.Web и т.д. Лучше всего для этих целей использовать Live-загрузчики.
4. Проверить настройки самого роутера. Наиболее часто сбивается параметр MTU. Универсальных рекомендаций по настройке роутера дать невозможно, т.к. это напрямую зависит и от модели роутера, и от интернет-провайдера. Обычно MTU имеет значения 1500, 1460, 1476.
Какое должно быть время ответа сервера?
И сразу же конкретные цифры:
— самая высокая конверсия у страниц, которые полностью загружаются за 1,8 и 2,7 секунды для десктопной и мобильной версий соответственно
— самый низкий показатель отказов у страниц, которые полностью загружаются за 1 и 0.7 секунды для десктопной и мобильной версий соответственно
Данные цифры позаимствованы из исследования Akamai Technologies.
Итак, Вы проверили сайт на скорость загрузки. Но как реагировать на результаты?
-
<1 секунды – идеал
-
1-2 секунды – почти идеал
-
3-5 секунд – сносно, но имеет смысл допилить
-
5-10 секунд – плохо, нужно срочно допиливать
-
≥10 секунд – очень плохо, нужно ЭКСТРЕННО допиливать
Однако, нельзя забывать одно ультраважное правило – скорость загрузки должна быть выше, чем у конкурентов. Исследования The New York Times доказали, что разницы в 0,25 секунды может быть достаточно для того, чтоб посетители предпочли более быстрый сайт. И глазом моргнуть не успеете (в самом прямом смысле), как пользователь уйдет от Вас к конкуренту.
Сокращение ответа сервера
Оптимизация графики.
Ранее мы говорили, что некоторые чекеры предоставляют еще и рекомендации по оптимизации. Среди них можно найти адреса картинок, которые можно оптимизировать путем уменьшения.
Упростить код.
В тех же рекомендациях будет сказано, где и насколько можно подрезать коды HTML, CSS и JavaScript. Например, убрать лишние пробелы, комментарии от создателей кода, и т.д.
Использовать кеш браузера.
Браузер будет скачивать изображения к себе в кэш. Следовательно, повторная загрузка изображений с сервера уже не потребуется, а это сэкономит массу времени на загрузку.
Включить сжатие.
Актуально, если используется gzip. В итоге объем данных сокращается раза в 4, а то и в 5. Чем меньше объем передаваемых данных – тем меньше времени занимает их передача.
Сократить время ответа сервера.
С помощью сервиса Pingdom можно вычислить, сколько времени требуется серверу для того, чтоб отдать код ответа. Идеальное время – не более 0,2 секунды.
Данные инструкции помогут значительно ускорить работу сайта. Однако, есть риск навредить функциональности или внешнему виду. Поэтому перед каждым действием в обязательном порядке делать бэкапы исходных файлов. Также не помешает проконсультироваться с техническими специалистами.
HTTP status codes are three-digit responses from the server to the browser-side request. Everyone has probably gotten the classic 404 page-not-found error. That is an HTTP client error status code and there are a lot more of them.
These status codes (also called response status codes) serve as a means of communication between the server and the internet browser and there are multiple code classes based on the type of information they are communicating. The differences in classes are indicated through the first digit of the error code, for example: just like a 404, any other 4xx will mean that in some way the page or website could not be reached, while a 2xx means that your request was successfully completed.
Table of content
- What are HTTP status codes?
- How are HTTP status codes categorized?
- Complete list of HTTP Status Codes
- What does this HTTP status code mean?
- HTTP Status codes to know for SEO
- How to check the HTTP status code
- How to fix 404 errors
- How to fix 503 errors
How are HTTP status codes categorized?
HTTP status codes are split into 5 different categories. Each category will give you hints as to what the response was, even if you don’t know the specific response code.
For an explanation of each category — and each individual status code — click on the corresponding link below or go to our complete list of HTTP status codes.
- 1xx — Informational: The server has received the request and is continuing the process
- 2xx — Successful: The request was successful and the browser has received the expected information
- 3xx (Redirection): You have been redirected and the completion of the request requires further action
- 4xx (Client Error): The website or the page could not be reached, either the page is unavailable or the request contains bad syntax
- 5xx (Server Error): While the request appears to be valid, the server could not complete the request
Complete list of HTTP Status Codes
| Status code | Meaning |
| 1xx Informational | |
| 100 | Continue |
| 101 | Switching protocols |
| 102 | Processing |
| 103 | Early Hints |
| 2xx Succesful | |
| 200 | OK |
| 201 | Created |
| 202 | Accepted |
| 203 | Non-Authoritative Information |
| 204 | No Content |
| 205 | Reset Content |
| 206 | Partial Content |
| 207 | Multi-Status |
| 208 | Already Reported |
| 226 | IM Used |
| 3xx Redirection | |
| 300 | Multiple Choices |
| 301 | Moved Permanently |
| 302 | Found (Previously «Moved Temporarily») |
| 303 | See Other |
| 304 | Not Modified |
| 305 | Use Proxy |
| 306 | Switch Proxy |
| 307 | Temporary Redirect |
| 308 | Permanent Redirect |
| 4xx Client Error | |
| 400 | Bad Request |
| 401 | Unauthorized |
| 402 | Payment Required |
| 403 | Forbidden |
| 404 | Not Found |
| 405 | Method Not Allowed |
| 406 | Not Acceptable |
| 407 | Proxy Authentication Required |
| 408 | Request Timeout |
| 409 | Conflict |
| 410 | Gone |
| 411 | Length Required |
| 412 | Precondition Failed |
| 413 | Payload Too Large |
| 414 | URI Too Long |
| 415 | Unsupported Media Type |
| 416 | Range Not Satisfiable |
| 417 | Expectation Failed |
| 418 | I’m a Teapot |
| 421 | Misdirected Request |
| 422 | Unprocessable Entity |
| 423 | Locked |
| 424 | Failed Dependency |
| 425 | Too Early |
| 426 | Upgrade Required |
| 428 | Precondition Required |
| 429 | Too Many Requests |
| 431 | Request Header Fields Too Large |
| 451 | Unavailable For Legal Reasons |
| 5xx Server Error | |
| 500 | Internal Server Error |
| 501 | Not Implemented |
| 502 | Bad Gateway |
| 503 | Service Unavailable |
| 504 | Gateway Timeout |
| 505 | HTTP Version Not Supported |
| 506 | Variant Also Negotiates |
| 507 | Insufficient Storage |
| 508 | Loop Detected |
| 510 | Not Extended |
| 511 | Network Authentication Required |
HTTP Status Codes explained individually
In some cases a HTTP response code might be descriptive enough to understand its meaning. 200 OK probably means that everything went okay. But what about a 103 Early Hints, 205 Reset Content and 305 Use Proxy?
Below is an explanation for all 63 status codes, sorted in the 5 overall categories.
What does a 1xx Informational status code mean?
A 1xx Informational status code means that the server has received the request and is continuing the process. A 1xx status code is purely temporary and is given while the request processing continues. For most tasks you won’t encounter these much, as it’s not the final response to the request.
- 100 Continue
- 101 Switching protocols
- 102 Processing
- 103 Early Hints
What does 100 Continue mean?
The 100 Continue status code means that the initial part of the request has been received by the server and that the client should proceed with the request or ignore the response if the request has already finished.
What does 101 Switching protocols mean?
The 101 Switching protocols status code means that the server understands the Upgrade header field request and indicates which protocol it is switching to.
What does 102 Processing mean?
The 102 Processing status code means that the server has accepted the full request but has not yet completed it and no response is available as of yet.
What does 103 Early Hints mean?
The 103 Early hints status code is intended to be used to allow the user agent to preload resources, while the server prepares a response. It is intended to be primarily used with the Link Header.
What does a 2xx Succesful status code mean?
A 2xx Succesful status code means that the request was successful and the browser has received the expected information. This is generally the one you want to see, as it means that the request was a success and has been received, understood and accepted it. As a website owner you should make sure that all pages and resources (images, videos, etc.) all return a 2xx status code. This means that browsers can reach it successfully and that your website visitors can see and use your website.
- 200 OK
- 201 Created
- 202 Accepted
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information
- 204 No Content
- 205 Reset Content
- 206 Partial Content
- 207 Multi-Status
- 208 Already Reported
- 226 IM Used
What does 200 OK mean?
The 200 OK status code means that the request was successful, but the meaning of success depends on the request method used:
- GET: The requested resource has been fetched and transmitted to the message body.
- HEAD: The header fields from the requested resource are sent in without the message body.
- POST or PUT: A description of the result of the action is transmitted to the message body.
- TRACE: The request messages, as received by the server, will be included in the message body
When looking at things SEO-wise the 200 OK response code is the perfect status code for a functioning page, all the linked pages are working as they should. A 200 will mean that search engine crawlers can successfully crawl the page and it will be put into their search index.
What does 201 Created mean?
The 201 Created status code means that the request was successfully fulfilled and resulted in one or possibly multiple new resources being created.
What does 202 Accepted mean?
The 202 Accepted status code means that the request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been finished yet. The request may or may not be completed when the processing eventually takes place.
The 203 Non-Authoritative Information status code means that the request was successful. However, the meta-information that has been received is different from the one on the origin server and has instead been collected from a 3rd party or local copy. When not used for backups or mirrors of another resource a 200 OK response is preferable.
What does 204 No Content mean?
The 204 No Content status code means that while the server has successfully fulfilled the request, there is no available content for this request. But the user agent might want to update its currently cached headers for this resource, for the new one.
What does 205 Reset Content mean?
The 205 Reset Content status code means that the user should reset the document that sent this request.
What does 206 Partial Content mean?
The 206 Partial Content response code is a response to a Range header sent from the client when requesting only a part of the resource.
What does 207 Multi-Status mean?
The 207 Multi-Status status code conveys information about multiple resources, in situation when multiple status codes are appropriate.
What does 208 Already Reported mean?
The 208 Already Reported status code is used inside the response element DAV: propstat, in order to avoid enumerating the internal members of multiple bindings to the same collection repeatedly.
What does 226 IM Used mean?
The 226 IM response code means that the server has successfully fulfilled a GET request for the resource, and the response is a representation of the result of one or multiple instance-manipulations applied to the current instance.
What does a 3xx Redirection code mean?
A 3xx Redirection status code means that you have been redirected and the completion of the request requires further action. Redirects are a natural part of the internet and you shouldn’t be scared to have 3xx redirect status codes on your website. A redirect means that the request was received successfully, but that the resource was found elsewhere. If a webpage has changed path and you try to access it through the old path, your CMS will often redirect the user to the new path. Ultimately the request will end in a 2xx success, but first it must go through the 3xx redirection.
- 300 Multiple Choices
- 301 Moved Permanently
- 302 Found (Previously «Moved temporarily»)
- 303 See Other
- 304 Not Modified
- 305 Use Proxy
- 306 Switch Proxy
- 307 Temporary Redirect
- 308 Permanent Redirect
What does 300 Multiple Choices mean?
The 300 Multiple Choices status code means that the request has multiple possible responses and the user/user agent should choose one.
What does 301 Moved Permanently mean?
The 301 Moved Permanently response code means that the target resource has been assigned a new permanent URL and any references to this resources in the future should use one of the URLs included in the response.
When looking at things SEO-wise the 301 Permanent Redirect should be used every time a URL is moved permanently. This redirect passes your current link equity from your content to the new URL. Links that result in a status code 301 does give slightly less link equity than 200. So if you have a lot of links going through a 301 Permanent Redirect it is advised to fix these, if possible.
What does 302 Found (Previously “Moved temporarily”) mean?
The 302 Found status code, previously known as “Moved temporarily”, means that the URI of the request has been changed temporarily, and since changes can be made to the URI in the future, the effective request URI should be used for future requests.
When looking at things SEO-wise the 302 Found should only be used when making temporary changes as it does not pass the link equity the same way as a 301. If the page is not going to come back you should always use 301.
What does 303 See Other mean?
The 303 See Other response code is sent by the server in order to direct the client to get the requested resource at another URI with a GET request.
What does 304 Not Modified mean?
The 304 Not Modified response code informs the client that the response has not been modified. This means that the client can continue to use the already present, cached version of the response.
What does 305 Use Proxy mean?
The 305 Use Proxy status code instructs a client that it should connect to a proxy and then repeat the same request there. This response code is deprecated due to security concerns.
What does 306 Switch Proxy mean?
The 306 Switch proxy status code is no longer in use. It was used to inform the client that the subsequent requests should use the specified proxy.
What does 307 Temporary Redirect mean?
The 307 Temporary Redirect status code gets sent by the server in order to direct the client to the requested resource at another URI. The request method, however, must not be changed.
What does 308 Permanent Redirect mean?
The 308 Permanent Redirect status code means that the requested resource has been permanently assigned a new URI and future references to the resource should be made by using one of the enclosed URIs.
What does a 4xx Client Error mean?
A 4xx Client Error status code means that the website or the page could not be reached and either the page is unavailable or the request contains bad syntax. As a website owner you should do your best to avoid these, as it means your users will not find what they’re looking for. This can be either pages that are no longer found and are either temporarily or permanently gone. Besides giving a bad user experience, it can also hurt your SEO efforts.
- 400 Bad Request
- 401 Unauthorized
- 402 Payment Required
- 403 Forbidden
- 404 Not Found
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- 406 Not Acceptable
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
- 408 Request Timeout
- 409 Conflict
- 410 Gone
- 411 Length Required
- 412 Precondition Failed
- 413 Payload Too Large
- 414 URI Too Long
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
- 416 Range Not Satisfiable
- 417 Expectation Failed
- 418 I’m a Teapot
- 421 Misdirected Request
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
- 423 Locked
- 424 Failed Dependency
- 425 Too Early
- 426 Upgrade Required
- 428 Precondition Required
- 429 Too Many Requests
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
What does 400 Bad Request mean?
The 400 Bad Request status code means that the server could not understand the request because of invalid syntax.
What does 401 Unauthorized mean?
The 401 Unauthorized status code means that the request has not been applied because the server requires user authentication.
What does 402 Payment Required mean?
The 402 Payment Required status code is a response reserved for future use. It was originally created to be implemented in digital payment systems, however, it is rarely used and a standard convention of using it does not exist.
What does 403 Forbidden mean?
The 403 Forbidden status code means that the client request has been rejected because the client does not have rights to access the content. Unlike a 401 error, the client’s identity is known to the server, but since they are not authorized to view the content, giving the proper response is rejected by the server.
What does error 404 mean?
The 404 Not Found status code means that the server either did not find a current representation for the requested resource or is trying to hide its existence from an unauthorized client.
When looking at things SEO-wise the 404 Not Found status code pages with a high volume of traffic should be redirected using a 301 to the most relevant page possible. For some pages, however, a 404 might be necessary, for example, if the product is out of stock for an extended period of time. If you have external links pointing to a page that returns 404, you will lose the link equity those links would otherwise give.
If you need to fix 404 errors, jump to this section.
What does 405 Method Not Allowed mean?
The 405 Method Not Allowed status code means that while the server knows the request method, the method has been disabled and can not be used.
What does 406 Not Acceptable mean?
The 406 Not Acceptable status code is sent by the server when it does not find any content following the criteria given by the user agent.
What does 407 Proxy Authentication Required mean?
The 407 Proxy Authentication Required status code means that the client must first be authenticated by a proxy (similar to a 401).
What does 408 Request Timeout mean?
The 408 Request Timeout status code means that the server did not receive a complete request in the time that it prepared to wait.
What does 409 Conflict mean?
The 409 Conflict status code means that the request could not be fulfilled due to a conflict with the current state of the target resource and is used in situations where the user might be able to resubmit the request after resolving the conflict.
What does 410 Gone mean?
The 410 Gone status code means that the target resource has been deleted and the condition seems to be permanent.
When looking at things SEO-wise the 410 Gone status code is a more permanent version a 404. The page will no longer be available from the server and has no forwarding address available. If you want to completely remove a page from Googles search index, then using 410 on a page is the proper way of doing it (instead of simply 404).
What does 411 Length Required mean?
The 411 Length Required status code means that the server has rejected the request because it requires the Content-Length header field to be defined.
What does 412 Precondition Failed mean?
The 412 Precondition Failed status code means the server does not meet one or multiple preconditions that were indicated in the request header fields.
What does 413 Payload Too Large mean?
The 413 Payload Too Large status code means the server refuses to process the request because the request payload is larger than the server is able or willing to process. While the server may close the connection to prevent the client from continuing the request, it should generate a Retry-After header field and after how long can the client retry.
What does 414 URI Too Long mean?
The 414 URI Too Long status code means that the server is refusing to service the request because the request-target was longer than the server was willing to interpret.
What does 415 Unsupported Media Type mean?
The 415 Unsupported Media Type status code means that the server is rejecting the request because it does not support the media format of the requested data.
What does 416 Range Not Satisfiable mean?
The 416 Range Not Satisfiable status code means that the range specified in the Range header field of the request can’t be fulfilled. The reason might be that the given range is outside the size of the target URI’s data.
What does 417 Expectation Failed mean?
The 417 Expectation Failed status code means that the Expectation indicated by the Expect request-header field could not be met by the server.
What does 418 I’m a Teapot mean?
The 418 I’m a Teapot status code means that the server refuses to brew coffee because it is, in fact, a teapot. (It is a reference to a 1998 April Fools’ joke called »Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol»).
What does 421 Misdirected Request mean?
The 421 Misdirected Request status code means that the client request was directed at a server that is not configured to produce a response.
What does 422 Unprocessable Entity mean?
The 422 Unprocessable Entity status code means that while the request was well-formed, the server was unable to follow it, due to semantic errors.
What does 423 Locked mean?
The 423 Locked status code means that the resource that is being accessed is locked.
What does 424 Failed Dependency mean?
The 424 Failed Dependency status code means that the request failed due to the failure of a previous request.
What does 425 Too Early mean?
The 425 Too Early status code means that the server is not willing to risk processing a request that might be replayed.
What does 426 Upgrade Required mean?
The 426 Upgrade Required status code means that while the server refuses to perform the given request using the current protocol, it might be willing to do so after the client has been upgraded to a different protocol.
What does 428 Precondition Required mean?
The 428 Precondition Required status code means that the origin server requires the request to be conditional.
What does 429 Too Many Requests mean?
The 429 Too Many Requests response code means that in the given time, the user has sent too many requests.
The 431 Request Header Fields Too Large means that the server is not willing to process the request because its header fields are indeed too large, however, the request may be submitted again once the size of the request header fields is reduced.
What does 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons mean?
The 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons response code means that the user has requested an illegal resource (such as pages and sites blocked by the government).
What does a 5xx Server error mean?
A 5xx Server error status code means that while the request appears to be valid, the server could not complete the request. If you’re experiencing 5xx server errors for your website, you should immediately look at your server. If you’re hosting your own server you’ll need to start debugging to figure out why it is not responding properly. If you’re using an external hosting provider you’ll need to reach out to them, so they can look at it.
- 500 Internal Server Error
- 501 Not Implemented
- 502 Bad Gateway
- 503 Service Unavailable
- 504 Gateway Timeout
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates
- 507 Insufficient Storage
- 508 Loop Detected
- 510 Not Extended
- 511 Network Authentication Required
What does 500 Internal Server Error mean?
The 500 Internal Server Error status code means that the server has encountered a situation that it does not know how to handle.
When looking at things SEO-wise the 500 Internal Server Error indicates a problem with the server, not the actual availability of the content. Since bots and users will both be lost, the link equity will go down fast.
What does 501 Not Implemented mean?
The 501 Not Implemented response code means that the request can not be handled because it is not supported by the server.
What does 502 Bad Gateway mean?
The 502 Bad Gateway response code means that the server received an invalid response while working as a gateway to handle the response.
What does 503 Service Unavailable mean?
The 503 Service Unavailable response code means that the server is currently not ready to handle the request. This is a common occurrence when the server is down for maintenance or is overloaded.
When looking at things SEO-wise the 503 Service Unavailable status code means that the server is unavailable and the visitor, bot or human, is asked to return again at a later time. This could be because of either server maintenance or server overload and search engines know to come back and check the availability later.
If you want to fix 503 errors, jump to this section.
What does 504 Gateway Timeout mean?
The 504 Gateway Timeout response code means that the server acting as a gateway could not get a response time.
What does 505 HTTP Version Not Supported mean?
The 505 HTTP Version Not Supported response code means that the version of HTTP used in the request is not supported by the server.
What does 506 Variant Also Negotiates mean?
The 506 Variant Also Negotiates response code means that the server has the following internal configuration error: The chosen variant resource is configured to engage in transparent negotiation itself, therefore it cannot be a proper endpoint in the negotiation process.
What does 507 Insufficient Storage mean?
The 507 Insufficient Storage status code means that the method could not be performed on the resource because the server is not able to store the representation that would be needed to complete the request successfully.
What does 508 Loop Detected mean?
The 508 Loop Detected response code means that the server has detected an infinite loop while processing the request.
What does 510 Not Extended mean?
The 510 Not Extended response code means that further extensions are required for the server to be able to fulfil the request.
What does 511 Network Authentication Required mean?
The 511 Network Authentication Required response code indicates that the client needs to authenticate to gain network access.
HTTP Status Codes & SEO: Here are the ones you need to know
If you want great results with your SEO it’s important to work with technical SEO. A big part of that is handling response codes on your website to ensure that the website is properly crawled by Googlebot and that your content returns the proper response code when it is requested.
Below are the 5 status codes that you need to know as an SEO.
200 OK & SEO
This is the goal for 99 % of your content (pages, media, etc.): a successful status code that means everything works like it should. This is critical to a well-functioning website and for a great user experience.
It also gives you the reassurance that all external pointing to your website will give you link value. If all of your content returns a 200 OK status code you can rest assured that your website is working and is properly accessible for crawlers and visitors alike.
301 Moved Permanently & SEO
In a perfect world all of your content will stay on the same URL and always respond with a 200 OK. But that’s rarely how it works in the real world when managing a website.
If a page has changed its URL you will need to set up a redirect to send users and bots from the old URL to the new URL. Otherwise they will be met by a 404 page (see explanation below). In some content management systems, automatic redirect is a built-in SEO feature, while in others you’ll have to manually set it up.
You should use 301 redirects if the page is permanently gone and will not come back. This is the case for pages that have changed their URL or content that has been deleted.
If something is gone, instead of simply moved, you can either let it become a 404 or choose to redirect it to something similar on your website. This could be a product that you’re no longer going to sell, where it can make sense to redirect that page to the category page instead.
302 Found & SEO
What if the page is only gone temporarily, but will come back again later? To give a good user experience you don’t want it to become a 404 page and you also don’t want to make a permanent 301 redirect.
The solution is to use 302 Found instead of a 301. To the user it will be the same, but to search engine crawlers and bots, it will tell them to check back later on, as this redirect is only temporary. That means the old URL will keep its value while it’s gone.
This is perfect for pages that will only be unavailable temporarily. An example could be a sold-out product which is removed from the website until it is back in stock. In that case you want to make use of a 302 Found temporary redirect. Once the product is back online, you remove the redirect and the page will have kept its value (and good rankings in search engines).
Note that if the 302 redirect is there for too long, Google will consider it a 301 permanent redirect instead.
404 Not Found & SEO
If a page is no longer found it will result in a 404 page (psst, here’s some tips on how to make a great 404 page). This means, that the server tells users, crawlers and bots that the page they were looking for is not found.
These are important to keep an eye on, as they can hurt your SEO a lot if not monitored and fixed.
Firstly, if a page returns a 404 it won’t be shown in Google’s search results. While it won’t get removed instantly, it will be after a short period of time, if not fixed. So if any of the pages that give you organic traffic end up returning a 404 error, you need to fix it quickly. See some tips on how to fix 404 errors here.
Secondly, if the page had any external links pointing to it, they will no longer give any value to your website. So even if the page does not receive any organic traffic, it can hurt your SEO performance.
The easiest way to fix this problem is to set up a 301 redirect. This will give a better user experience and will pass most of the link value from external links to the new page you’re redirecting to.
410 Gone & SEO
What if you actually want a page to completely disappear from Google’s search engine index? It might be intuitive to simply let it return a 404 error, but there’s one caveat with that:
404 does not tell crawlers and bots why the page was not found. For that reason, Google still might keep thinking that the page is there, even if it encounters a 404 error. In most cases this is fine, but there’s one case where you want to make it crystal clear that the content is gone. And that’s if you have been hacked and malicious content has been added to your website.
After doing cleanup it’s not enough to let the URLs return 404. Instead you should make sure that they return the 410 Gone status code. This clearly tells crawlers and bots that the page is gone for good and that they should remove it from their index.
5xx Server errors & SEO
The last one is not directly SEO-related, but more of a good tip for troubleshooting your website.
If you see any response code that start with 5xx, you should instantly know that it is a server error. This will help you greatly when it comes to troubleshooting and fixing it.
Instead of wasting time trying to fix the problem through your CMS backend or elsewhere, you can go straight to fixing the server. No matter if you do your own hosting or if you use a hosting provider, it is helpful to know that it’s related to the server, not your website.
How to check the HTTP status code of a page
Finding the server response code for a page can be done manually in your browser or by using various tools and website crawlers.
Depending on the browser you’re using it is slightly different. Below is how to do it in Chrome (most steps will be similar in other browsers).
Checking HTTP status code in Chrome
- Open the URL your want to check with your browser
- Open the Developer tab (F12) and go to the «Network» tab
- Refresh the page
- Scroll to the top of the list of requests and find the first of type «document»
- In «Status» you can now find the HTTP response code
How to fix 404 errors
If you have seen the status code 404 Page Not found you might have been thinking «What does error 404 mean?»
HTTP status code 404 means «Page Not Found». This means that the request you sent was received by the server, but it could not find the page you were looking for.
So to fix the 404 error you first need to find the cause for it, which can be due to many things. But since you know that the server is reachable (otherwise it would have returned a 5xx error), you know that the error is client-side. Basically that means it’s your fault (not as harsh as it sounds).
Luckily it means that you can also fix the error on your end without having to debugging your server or reaching out to your hosting provider.
Run through this checklist to fix the 404 error:
- Refresh the page. It might seem simple, but a 404 error could have just been a temporary issue that is fixed simply by trying again.
- Check the URL you typed in. Did you make a mistake somewhere? If the URL you typed is not exactly right a 404 is to be expected (unless a 3xx redirect is set up)
- If no mistake was made, try again from a different device like your mobile phone or tablet. If it works from a different device it’s most likely due to browser cache and cookies. Clear the browser cache and delete cookies, then try to access the page again.
If none of the above tricks worked, it’s likely that the piece of content was deleted or some other way moved. If the content was moved, which caused it to change URL, then you should make sure to set up a redirect that points from the old URL to the new one. That way you’re sure that anyone looking for the page can still find it.
If it was deleted, then a 404 error is the right response as the page truly was not found on your website and everything is working as it should.
If you see a lot of your visitors ending up on this page, then it’s most likely due to one of 3 things:
- You have an internal link on your website pointing to the page. If that’s the case, you should remove (or change) this link so it no longer points to a page that is not found.
- External websites link to the page. This is trickier as you can’t simply change it (although you can reach out to the websites and ask them to change it). A more simple thing for you to do would be to add a 301 redirect and point from the page to a different page on your website. That way you lead people to a page that is working, while also being a SEO-friendly option.
- The page is still showing up in Google’s search results and sending traffic to your website. While this is usually short-lived, it is possible that a 404 page can stay in the search results for a while, as a 404 does not tell Googlebot whether the page is temporarily or permanently missing. If this is happening, you’ll need to get the page back quickly or redirect it to a different page, so you won’t lose your rankings in Google.
Find 404 pages in Google Analytics
Have you ever wondered if there’s a way to find 404 pages in Google Analytics?
Well, the good news is, there are ways to find them within your analytics setup. Now this can sometimes come down to how your website is configured. One way to find them is to check by page title — Your 404 page will very likely have “404” or “Page not found” in the title. It’s very easy to find the 404 page this way:
- Within your analytics tool, go to behavior → Site Content → All Pages.
- Now you can set your primary dimension to Page title and search for “404” or “Page not Found”.
- And now — you should hopefully have your 404 report.
Now this is not the only way to set it up, but there is a very good chance that you can find the pages this way.
How to fix 503 errors
The 503 response code means «Service Unavailable» and happens when a server is currently not ready to handle the request. This can be either due to the server being down for maintenance or if it is overloaded.
If this error occurs on your own website, you need to have a look at your server, as something is making it unable to process the requests made.
Unfortunately it’s not always easy and simple to fix. A 503 response code can be due to many things, but at least you know it’s server-related and not client-side like with a 404 error.
Here’s a list of steps you can go through to identify and fix a 503 error:
- Is your website still running and receiving traffic? Check your Analytics tools or server logs to see if other visitors are getting through to your website.
- If it’s no longer receiving traffic your server might be under maintenance or have crashed. If it’s under maintenance then a 503 is to be expected and everything will work fine once it’s done. If it crashed you should try restarting it.
- If you’re receiving huge amounts of website traffic, the server is most likely overloaded and returning 503 errors because it doesn’t have the resources to keep up. Before fixing such an issue you need to identify it the traffic is from real visitors or if you’re the victim of a DoS or DDoS attack.
- Identifying a DoS or DDoS attack can be hard, but the most effective ways are:
- Checking if one or more IP addresses make a lot of requests
- The TTL (time to live) on a ping request times out
- Analyzing the server logs and seeing huge spikes in traffic
- If it looks to be a DoS or DDoS attack, you’ll need to apply one or more defense techniques to stop the attack.
- If it is not a DoS or DDoS attack, then your website has most likely become more popular than your server can handle. The best way to fix such an issue is to look at connection limits, bandwidth throttling, system resources, fail-safes that might have triggered or anything that might be limiting server performance. Essentially you’ll need to upgrade your server so it has the proper resources to handle the traffic.
The above list is great for troubleshooting one-off 503 errors. But if it happens on a regular basis, then it might be a more permanent problem with your server that you should dive deeper into fixing. This can be inefficient processes using up all of your resources or your server simply not having enough allocated resources to handle the traffic your website is receiving.
What status code is returned by a website when the browser request is successful?
With all these HTTP status codes — It can be a bit daunting to figure if any of them are good. But some of them are.
A browser will return a 2xx status code if the browser request was successful. So a 2xx code is the one you want to see. The 200 status code means that the browser’s request was successful and received, understood, and accepted.