Обновлено 02.01.2021

Описание ошибки 1311
У меня есть два домена Active Directory, корневой root и дочерний child, все в рамках одного дерева и леса. В какой-то момент в логах Windows на контроллерах домена я обнаружил ошибку:
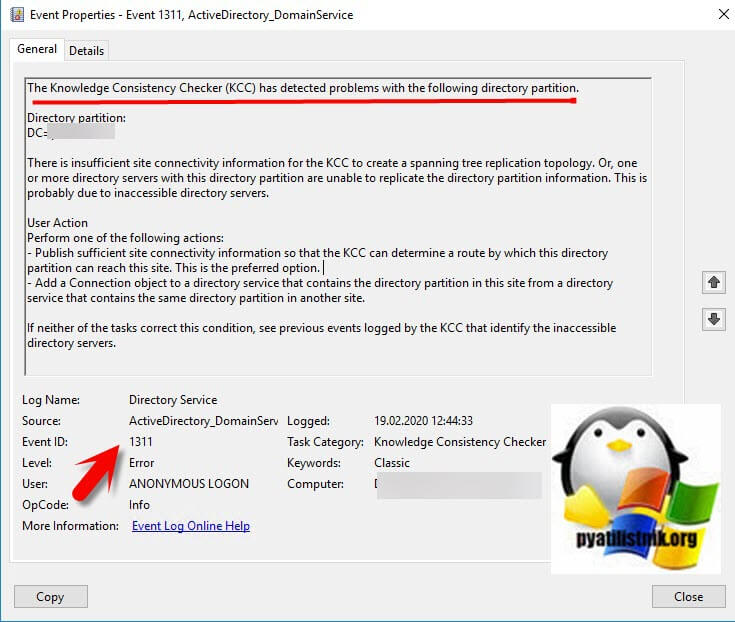
Event ID 1311: The Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC) has detected problems with the following directory partition.
Directory partition:
DC=child,DC=pyatilistnik,DC=org
There is insufficient site connectivity information for the KCC to create a spanning tree replication topology. Or, one or more directory servers with this directory partition are unable to replicate the directory partition information. This is probably due to inaccessible directory servers.
User Action
Perform one of the following actions:
— Publish sufficient site connectivity information so that the KCC can determine a route by which this directory partition can reach this site. This is the preferred option.
— Add a Connection object to a directory service that contains the directory partition in this site from a directory service that contains the same directory partition in another site.
If neither of the tasks correct this condition, see previous events logged by the KCC that identify the inaccessible directory servers.
Данная ошибка появляется каждые 15 минут.
Причины ошибки 1311
Одна из самых печально известных ошибок репликации — это событие с кодом 1311, оно может быть вызвано рядом причины:
- Один или несколько контроллеров домена недоступны по сети или один или несколько контроллеров домена находятся в автономном режиме.
- Один или несколько сайтов не могут взаимодействовать друг с другом из сетевых ошибок, например один или несколько сайтов не содержатся в ссылке на сайт.
- Ссылки сайта содержат все сайты, но ссылки сайта не связаны между собой. Это условие известно как несвязанные ссылки на сайте.
- Контроллеры домена-плацдарма подключены, но возникают ошибки при попытке репликации необходимого раздела каталога между сайтами Active Directory.
- Предпочтительные серверы-плацдармы, определенные администратором, подключены к сети, но на них не размещен необходимый раздел каталога. Наиболее распространенная неправильная конфигурация — это определение серверов не глобального каталога в качестве серверов-плацдармов.
- Предпочтительные плацдармы правильно определены администратором, но в настоящее время они отключены.
- Сервер-плацдарм перегружен, поскольку сервер не производительный, слишком много сайтов филиалов пытаются реплицировать изменения с одного и того же контроллера домена-концентратора, или расписание репликации на сайтах слишком частое.
- Средство проверки согласованности знаний (KCC) создало альтернативный путь для обхода межсайтового соединения, но продолжает повторять попытку сбойного соединения каждые 15 минут.
- Мост включен в сайтах и службах Active Directory, но сеть не позволяет подключаться к сети между любыми двумя контроллерами домена в лесу.
- Предпочитаемый сервер-плацдарм настроен и отключен
- Ошибка разрешения DNS-имени
- Ошибка 1311 может быть просто результатом другой, более серьезной проблемы и исчезнет, когда эта проблема будет решена.
Диагностика и устранение ошибки 1311
KCC — это специальный процесс, который выполняется абсолютно на всех контроллерах домена и создает топологию репликации для Active Directory леса. KCC создает отдельные топологии репликации в зависимости от того, выполняется ли репликация на сайте (внутрисайтовая) или между сайтами (межсайтовой). KCC также динамически корректирует топологию, чтобы она соответствовала добавлению новых контроллеров домена, удалению существующих контроллеров домена, перемещению контроллеров домена на сайты, изменяющимся затратам и расписаниям, а также к контроллерам домена, временно недоступен или находится в состоянии ошибки.
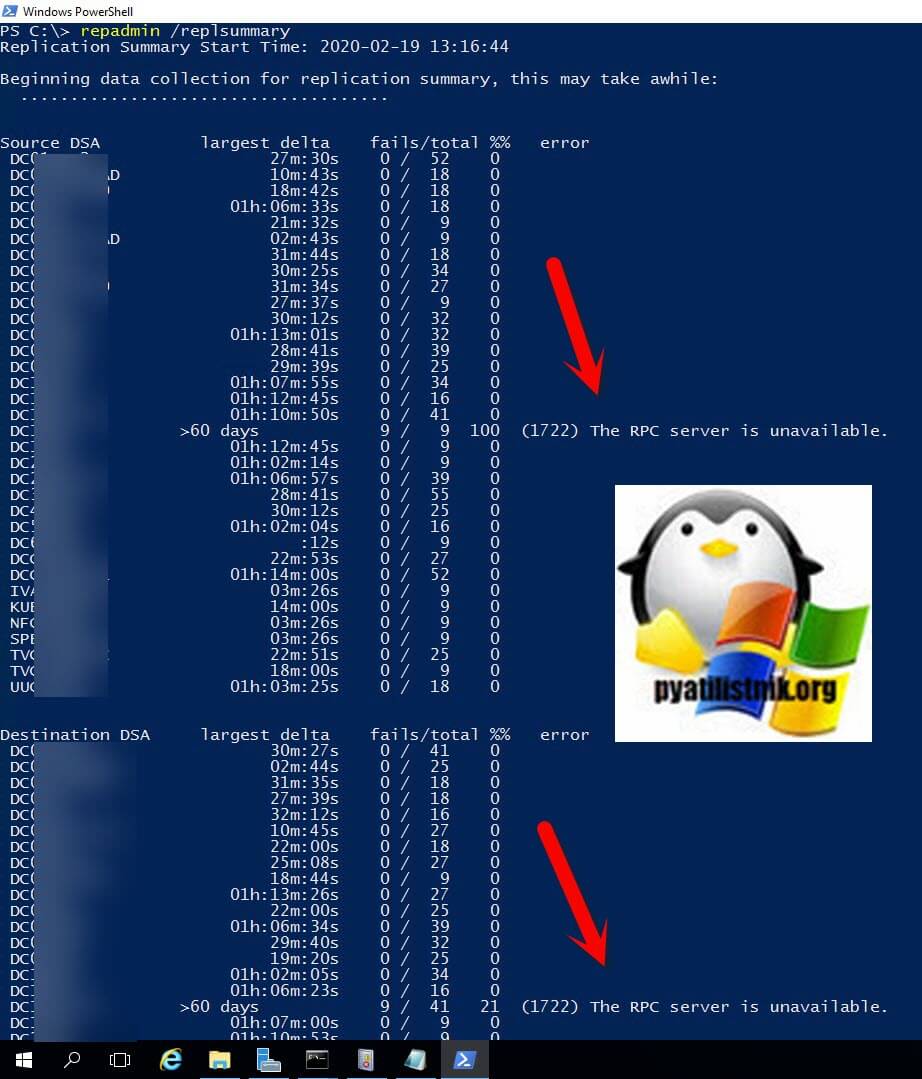
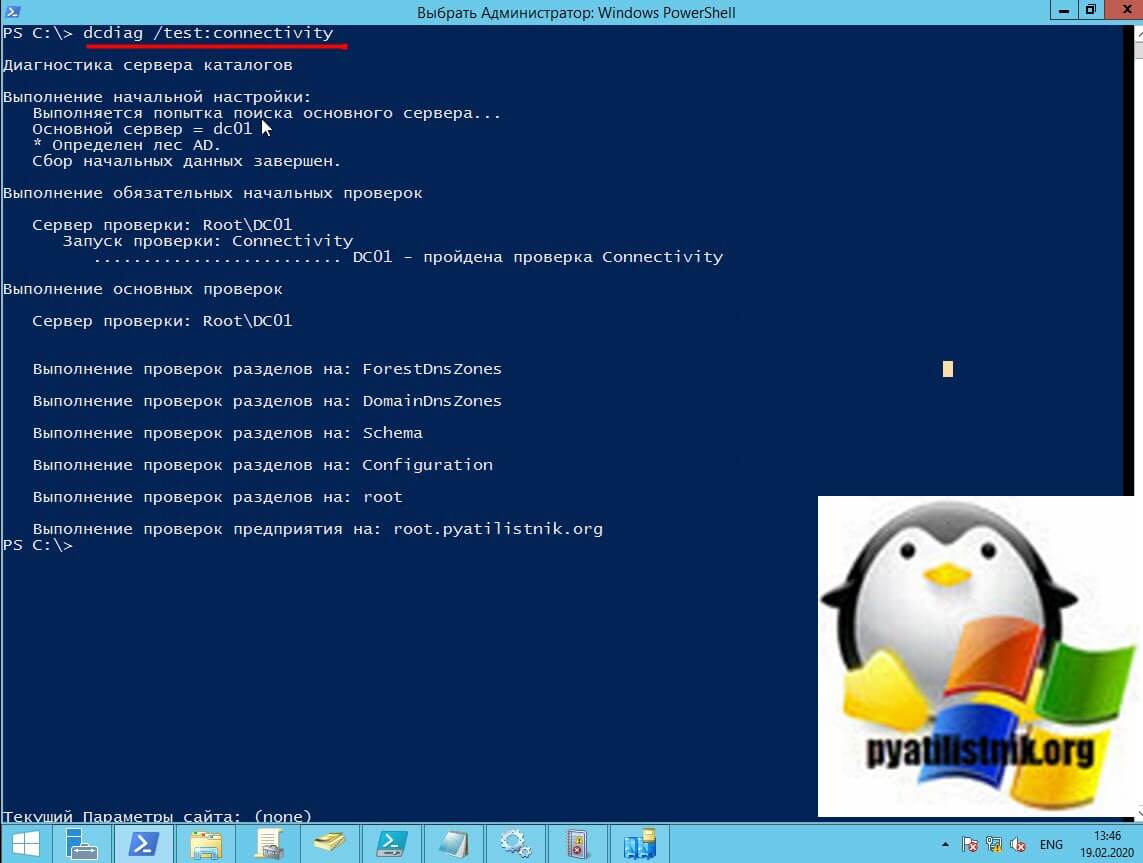
Если вы подробно еще раз посмотрите ошибку 1311, то там нет точного упоминания какой именно контроллер домена является проблемным. Для этого мы с вами можем воспользоваться уже знакомой утилитой Repadmin по проверке репликации Active Directory. Выполните команду:
Несмотря на то, что 1311 может не отображаться здесь, для него характерно сопряжение с событием «1722 Сервер RPC недоступен (The RPC server is unavailable)» (что в основном означает отсутствие физической связи). Тут же я вижу, что контроллер недоступен более 60 дней.
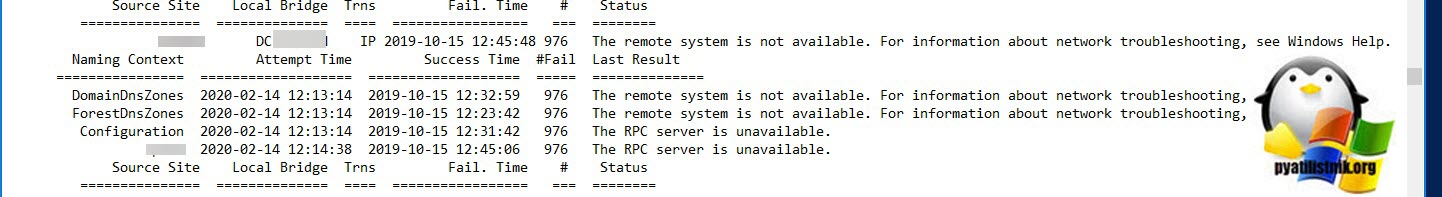
так же полезно будет выполнить команду, которая покажет подробную топологию по сайтам:
Вот вам пример, когда отсутствует связь с контроллером домена «The remote system is not available. For information about network troubleshooting».
Элементарно проверить сетевую доступность нужного контроллера домена можно с помощью утилит командной строки ping и tracert. Убедитесь, что у вас правильные настройки ip адреса на недоступном контроллере, правильные маршруты, нет блокировок на уровне брандмауэра, разрешены порты Active Directory.
Если по сети контроллер отвечает, то нужно убедиться, что существует адекватное подключение к сайту. Выполните следующую процедуру на каждом контроллере домена, на котором размещен раздел, для которого KCC сообщает, что путь репликации не может быть вычислен. Начните с контроллера домена, который сообщает об этой проблеме. Для выполнения этой процедуры у вас должно быть членство в группе «Администраторы домена» или вам должны быть делегированы соответствующие полномочия. Чтобы убедиться, что контроллеры домена, на которых размещен указанный раздел каталога, доступны откройте командную строку в режиме администратора и введите:
dcdiag /test:connectivity
Эта команда проверяет, доступны ли контроллеры домена и правильно ли они зарегистрированы на серверах системы доменных имен (DNS). Устраните все проблемы, обнаруженные при запуске этого теста.
Более подробную диагностическую информацию можно получить из команды представленной ниже, единственное необходимо в рамках леса иметь права администратора предприятия.
Если вы видите ошибки в топологии сайтов, то вы можете проверить вот такие вещи:
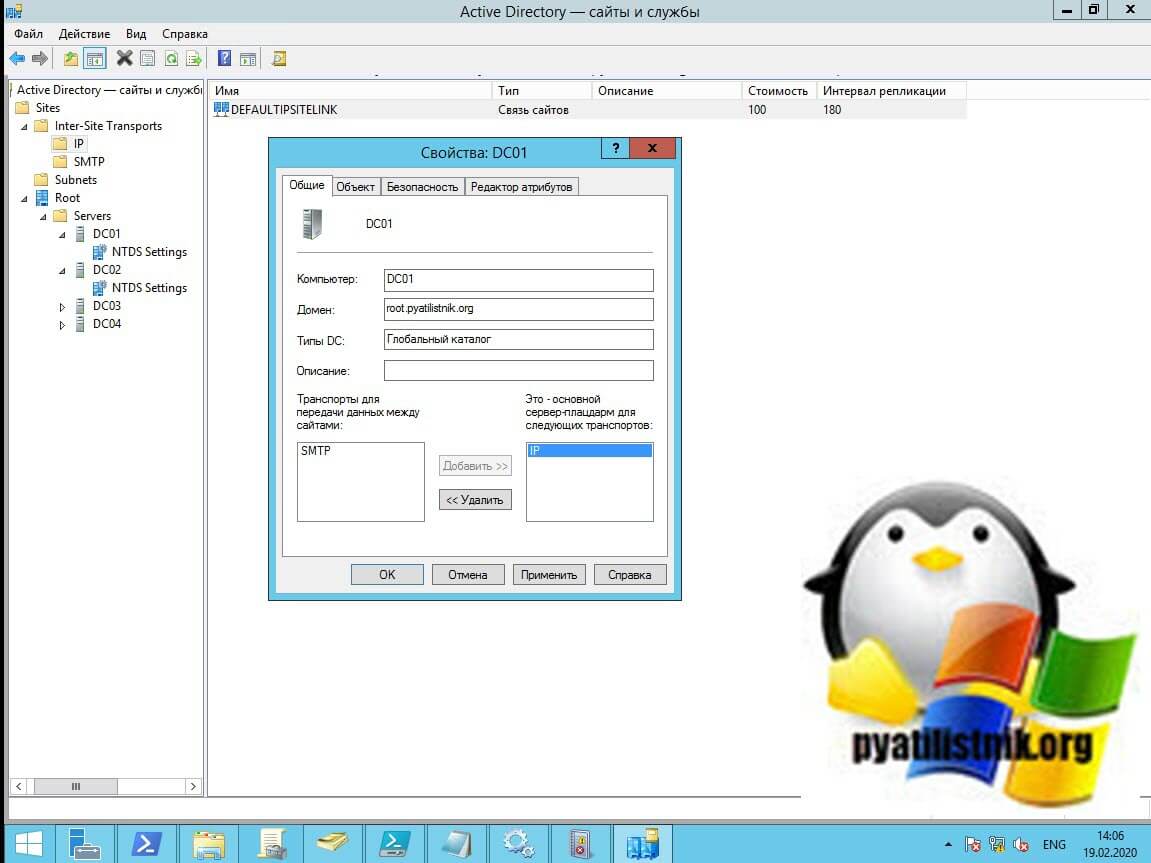
- Настройте предпочтительный сервер-плацдарм. В Windows 2003 и выше все контроллеры домена рандомизируются в качестве серверов-плацдармов вместо того, чтобы иметь один единственный, как требуется для Windows 2000. При установке этого значения один контроллер домена становится сервером-плацдармом — и, если вы установите только один, и он будет не доступен, то проверка согласованности знаний (KCC) не найдет других партнеров? Просто скажи нет на этом. Если у вас есть какие-либо из них, отмените их, сняв флажок в оснастке «Сайты и службы».
- Убедитесь, что все сайты определены в ссылках сайта — это может показаться очевидным, но вы будете удивлены, насколько часто это проблема. В одном случае администратор сообщил, что один регион, содержащий несколько сайтов AD, вообще не реплицировался. После проверки я обнаружил, что на сайте хаба в этом регионе не было ссылок на сайты, определенные для какого-либо сайта. Я был поражен, что они не обнаружили это раньше, так как не было никакой репликации на любой другой DC вообще.
Осиротевшие объекты
Однажды один сервер глобального каталога был понижен в должности, но нетерпеливый администратор хотел ускорить очистку Active Directory, поэтому он сократил значение времени tombstonelifetime и затем принудительно запустил сборку мусора. К сожалению, он сделал это до того, как удаление сервера глобального каталога (GC) было отреплицировано на все DC и GC в лесу. Я получал ошибку 1311 вместе с множеством других, заявляющих, что Active Directory пытается реплицировать объект, у которого нет родителя, но он не идентифицирует родителя. В итоге я включал подробное ведение журнала и наконец определил GUID проблемного объекта. Используя инструмент LDP.exe, я смог удалить этот объект и остановить события 1311.
Ошибки DNS
Поскольку репликация AD зависит от разрешения имен DNS, чтобы найти контроллеры домена для репликации, в случае поломки DNS может привести к возникновению событий 1311. Здесь полезно то, что если виновником является DNS, то в событии 1311 фраза «Ошибка поиска DNS» будет включена в описание. Если вы видите эту фразу, то у вас абсолютно точно есть проблема с DNS, которую нужно исправить. Я никогда не видел, чтобы эта ошибка оказалась ложной. Обратите внимание, что это не обязательно будет регистрировать событие в журнале DNS, и вы увидите это и в других событиях. Помните, что отсутствие значительных ошибок в журнале событий DNS не означает, что DNS исправен.
Если вернуться конкретно к моему случаю, то у меня контроллер домена отсутствовал уже более 60 дней, и очень глупо его включать, так как это приведет к другим проблемам. Проще такой контроллер домена удалить и по необходимости развернуть новый. Даже если контроллер домена недоступен его можно корректно удалить.
Так же не забывайте проверить, что у вас контроллер удалился с сайта, и если он был в нем один, то лучше удалить сам сайт, если он не используется. Убедитесь, что теперь команды репликации не показывают ошибок 1722 или 1311. На этом у меня все с вами был Иван Семин, автор и создатель IT портала Pyatilistnik.org.
Дополнительно
- https://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/windows-server/identity/ad-ds/get-started/replication/active-directory-replication-concepts
- https://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/1375.event-id-1311-microsoft-windows-activedirectory-domainservice.aspx
Event ID 1311 — Microsoft-Windows-ActiveDirectory_DomainService
Table of Contents
- Applies To
- Event Details
- Resolve
- Allow the KCC to compute the replication path
- Ensure that the domain controllers that host the identified directory partition are accessible
- Ensure that adequate site connectivity exists
- Allow the KCC to compute the replication path
- Verify
- Related Management Information
Event ID 1311 — KCC Replication Path Computation
Applies To
Windows Server 2008
The Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC) is a component of Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) that is responsible for generating the replication topology between domain controllers. Generating an efficient and fault-tolerant replication topology is
an integral part of achieving data consistency between domain controllers.
Event Details
| Product: | Windows Operating System |
| Event ID: | 1311 |
| Source: | Microsoft-Windows-ActiveDirectory_DomainService |
| Version: | 6.0 |
| Symbolic Name: | DIRLOG_KCC_NO_SPANNING_TREE |
| Message: | The Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC) has detected problems with the following directory partition.
Directory partition: %1 There is insufficient site connectivity information for the KCC to create a spanning tree replication topology. Or, one or more directory servers with this directory partition are unable to replicate the directory partition information. This is probably due User Action Perform one of the following actions: — Publish sufficient site connectivity information so that the KCC can determine a route by which this directory partition can reach this site. This is the preferred option. — Add a Connection object to a directory service that contains the directory partition in this site from a directory service that contains the same directory partition in another site. If neither of the tasks correct this condition, see previous events logged by the KCC that identify the inaccessible directory servers. |
Resolve
Allow the KCC to compute the replication path
To make it possible for the Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC) to compute the replication path:
- Ensure that the domain controllers that host the identified directory partition are accessible.
- Ensure that adequate site connectivity exists.
Ensure that the domain controllers that host the identified directory partition are accessible
Perform the following procedure on each domain controller that hosts the partition for which the KCC is reporting that a replication path cannot be computed. Start with the domain controller that is reporting this issue.
To perform this procedure, you must have membership in Domain Admins, or you must have been delegated the appropriate authority.
To ensure that the domain controllers that host the identified directory partition are accessible:
- Open a command prompt as an administrator. To open a command prompt as an administrator, click
Start. In Start Search, type Command Prompt. At the top of the
Start menu, right-click Command Prompt, and then click
Run as administrator. If the User Account Control dialog box appears, confirm that the action it displays is what you want, and then click
Continue. - Run the command dcdiag /test:connectivity. If you are running the command remotely, you can add the command line switch /s:computername to the command to target a specific computer (substitute the name of the computer you want to query
for computername). This command tests whether the domain controllers are available and properly registered with the domain name system (DNS) servers. Resolve any issues that you find when you run this test. Look in the System Log in Event Viewer on the affected
domain controller if you have reason to believe that there is a network connectivity issue with the domain controller.
Note: This situation also can occur if there are domain controllers in the directory that no longer exist. If a domain controller was removed and the metadata for the server was not properly cleaned up, see Clean up server metadata (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=104231).
Ensure that adequate site connectivity exists
One of the issues that may cause this error is that not all the sites have adequate connectivity. You can use the Active Directory Sites and Services snap-in to ensure that sites, site links, and bridges are configured correctly. This section walks you through
a quick check of your sites and site link bridges in Active Directory Sites and Services. For more information, see the Step-by-Step Guide to Active Directory Sites and Services (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=104532).
To perform these procedures, you must have membership in Enterprise Admins, or you must have been delegated the appropriate authority.
To ensure that adequate site connectivity exists:
- If you are not currently logged on with an account that has membership in the Enterprise Admins group, you can use the
runas command to open a command prompt with elevated credentials. To do this, click
Start in Start Search, type runas /user:domain\account cmd, and then press ENTER. Substitute the actual domain name and user account name of an account that is a member of the Enterprise
Admins group for domain and user. Type the password for the account when you are prompted. A command prompt opens under the security context of the account that you provided. - To open Active Directory Sites and Services, at the command prompt type
dssite.msc, and then press ENTER. - In the console tree, ensure that Sites is expanded.
- For each site that has servers hosting the partition that is referred to in the event message text, expand the site object and the server objects that it contains.
- Expand Inter-Site Transports. Two subordinate objects are revealed:
IP and SMTP. - Click the intersite transport that your network uses to replicate. If you are not sure which intersite transport your network uses, click both intersite transports until you see site link objects. If only one intersite transport, IP or SMTP, has site link
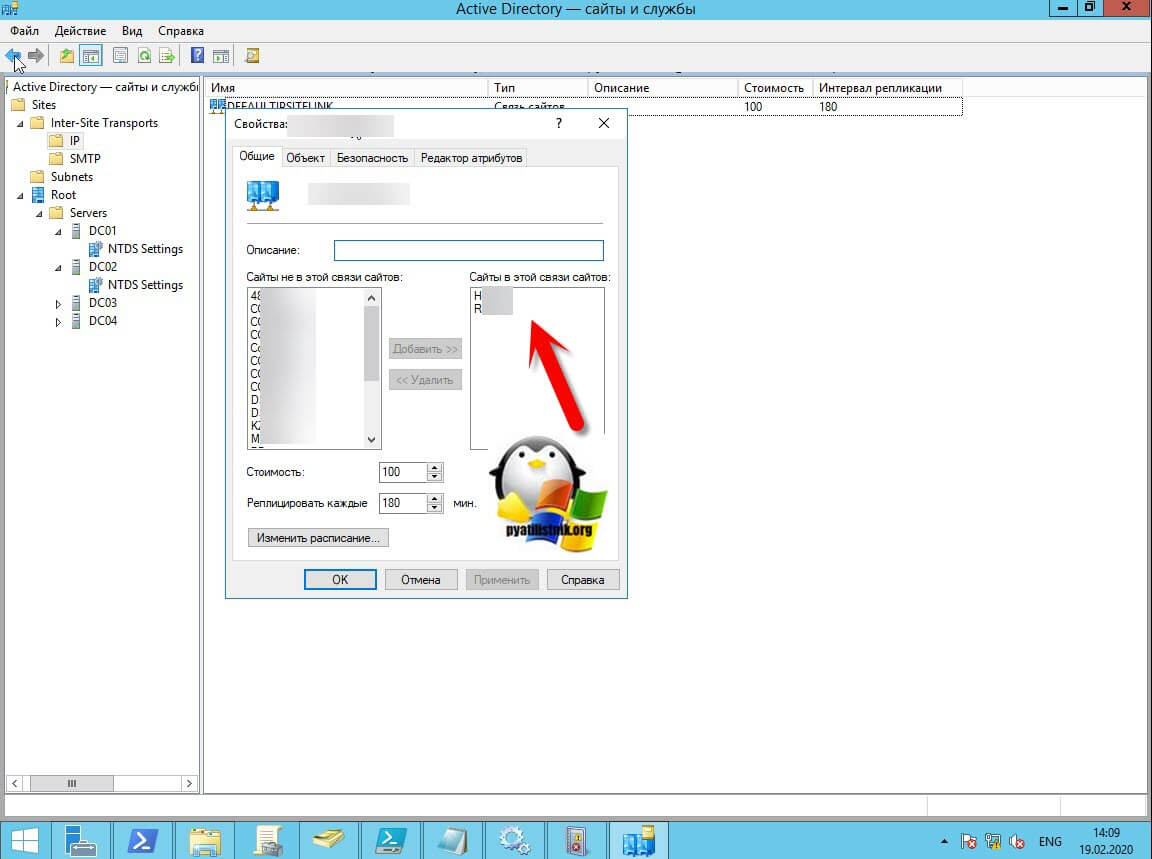
objects, that is the transport that is in use. Select that object. If both intersite transports have site link objects, both of them are probably in use. In that case, check both intersite transport objects as you complete the following steps. - In the details pane, right-click each site link, and then click Properties.
- Note the sites that are listed under Sites in this site link. Ensure that all sites are appropriately connected. Repeat this and the previous two steps until you have confirmed that all sites are connected to one another through site links.
If necessary, create additional site links to ensure that all sites are connected appropriately. - Right-click the appropriate intersite transport object (IP or SMTP), and then click
Properties. Note whether the Bridge all site links check box is selected. If the check box is selected, you do not have to configure site link bridges for the transport. If the check box is not selected, configure appropriate
site link bridges or select the Bridge all site links check box. - Click OK. If necessary, create additional site link bridges to ensure that all site links are connected appropriately.
For additional information about resolving Event ID 1865, see article 944351 in the Microsoft Knowledge Base (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=109266).
For additional information about resolving Event ID 1311, see article 307593 in the Microsoft Knowledge Base (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=109273).
Verify
Perform the following procedure on the domain controller on which you want to verify that the Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC) is functioning.
To perform this procedure, you must have membership in Domain Admins, or you must have been delegated the appropriate authority.
To verify that the KCC is computing replication paths:
- Open a command prompt as an administrator. To open a command prompt as an administrator, click
Start. In Start Search, type Command Prompt. At the top of the
Start menu, right-click Command Prompt, and then click
Run as administrator. If the User Account Control dialog box appears, confirm that the action it displays is what you want, and then click
Continue. - Run the command repadmin /kcc. This command starts KCC translation of domain controllers, to which the local domain controller replicates.
Check Event Viewer to see if there are any failure messages that are related to the KCC. If there are no error events that are related to the KCC, it is functioning properly. If there are error events, use the additional information in them to resolve the
issue.
Related Management Information
KCC Replication Path Computation (TechNet Library)
Active Directory (TechNet Library)
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests…
Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
Disclaimer
I am writing this blog and others to explain how things work and some ways deployment and operational tasks can be handled. In other words, these postings are for demonstration purposes only. Since I am not familiar with your organization or environment I do not know if these steps are applicable to your environment or are even safe to perform in your environment. It is recommended that you contact Microsoft Support prior to making changes in your environment to ensure that these steps are applicable to your environment, and are safe to perform in your environment. By writing this blog I am in no way recommending that you perform these steps in your own environment. If you choose to follow the steps outlined in this or other blog postings on this site, you are assuming the risk for your actions.
1.1 Repadmin.exe
Repadmin is a tool for checking replication status and troubleshooting replication issue. Below is a table highlighting commonly used syntax of the repadmin tool.
| Syntax | Usage |
| Repadmin /replsummary | The replsummary operation quickly and concisely summarizes the replication state and relative health of a forest. |
| Repadmin /replsummary /bysrc /bydest /sort: delta | The replsummary operation quickly and concisely summarizes the replication state and relative health of a forest. |
| Repadmin /showrepl <DC Name> | Displays the replication partners for each directory partition on the specified domain controller. Helps the administrator build a visual representation of the replication topology and see the role of each domain controller in the replication process. |
| Repadmin /showutdvec | Displays the highest Update Sequence Number (USN) for the specified domain controller. This information shows how up-to-date a replica is with its replication partners. |
| Repadmin /showobjmeta <DC> <DN of object> | Displays the replication metadata for a specified object stored in Active Directory, such as attribute ID, version number, originating and local Update Sequence Number (USN), and originating server’s GUID and Date and Time stamp. By comparing the replication metadata for the same object on different domain controllers, an administrator can determine whether replication has taken place. |
| Repadmin /showconn | Displays the connection objects for a specified domain controller. Default is local site. |
| Repadmin /replsingleobj <DC List> <Source DSA Name> <Object DN> | Replicates a single object between any two domain controllers that have partitions in common. The two domain controllers do not have a replication agreement. Replication agreements can be shown by using the Repadmin /showrepl command. |
| Repadmin /replicate <Destination_DC_List> <Naming Context> | Starts a replication event for the specified directory partition between the source and destination domain controllers. The source UUID can be determined when viewing the replication partners by using the Repadmin showrepl operation. |
| Repadmin /syncall <DC> | Synchronizes a specified domain controller with all replication partners. |
| Repadmin /queue | Displays tasks waiting in the replication queue. |
| Repadmin /showmsg <Error> | Displays the error message for a given error number. |
| Repadmin /viewlist <DC_List> | Displays a list of domain controllers. |
| Repadmin /showctx <DC_List> | Displays a list of computers that have opened sessions with a specified domain controller. |
| Repadmin /showcert | Displays the server certificates loaded on a specified domain controller. |
| Repadmin /removelingeringobjects <Dest_DC_List> <Source DC GUID> <NC> [/ADVISORY_MODE] | Uses an authoritative domain controller to compare the directory of a domain controller (destination) that is suspected of having lingering objects against the directory of a domain controller (source) that is designated as a reference source for up-to-date values for the domain of the destination. When the advisory mode parameter is used, this command provides a list of found lingering objects. When the advisory mode parameter is not used, this command removes lingering objects from the destination domain controller. |
Additional information on Repadmin.exe is available here: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc736571(v=ws.10).aspx
1.2 Repadmin /replsummary
As seen in the screenshot below repadmin /replsummary will give statistics for replication with replication partners. The output also lists any errors that were encountered with replication. This is useful for getting an overview of any replication issues the DC is having.
You can also sort the output. In the example below, the output is sorted by the largest delta since last replication.
1.3 Repadmin /showrepl
As seen below repadmin /showrepl shows the replication status with all of the DCs replication partners and is sorted by the Naming Context that is being replicated.
One trick that can be used to get a more manageable output is to use repadmin to send its output to a CSV and the use PowerShell to convert the CSV to a GridView. The command to do this is repadmin /showrepl * /csv | ConvertFrom-CSV | Out-GridView
The resulting output is in a manageable GUI.
In GridView you can sort and filter. Below is an example of filtering on Number of Failures, so that I can easily see what failed.
1.4 Repadmin /showutdvec
Replications changes are tracked through incrementing numbers called USNs. There are times where you will want to know what knowledge each DC has about other DCs current state. The up-to-dateness vector is the knowledge that a DC as about the current state of other DCs. This information can be useful when trying to troubleshoot replication issues such as USN Rollback. USN Rollback is when a DC is restored from an unsupported method such as a snapshot. In that case the up-to-dateness vector would be much larger than the actual USN of the DC. Since, there is going to be some delay in replication you will notice some differences but the numbers should be relatively close. For example, if you compare the up-to-dateness vector for DC01 across DCs you will notice the following: for itself DC01 has USN of 17347, DC02 has a USN of 17346 for DC01, and DC03 has a USN of 17346 for DC01. So, we can see the numbers are relatively close and that DC01 potentially has one change that it needs to replicate to DC02 and DC03.
1.5 Repadmin /showobjmeta
The /showobjmeta switch shows detailed information for attributes of an object. It is most commonly used when comparing the output of the command from 2 DCs to see if they are in sync and the current status of the attributes. Differences can be used to identify replication problems.
1.6 Repadmin /syncall
Repadmin /syncall is used to force replication between domain controllers. You can easily view options for the /syncall switch with the following command: repadmin /syncall /?
A normal use of repadmin /syncall is with the /AeP switch
1.7 Repadmin /showmsg
The /showmsg switch is used to convert an error message you may receive as the result of a repadmin command and converts it to human readable text.
1.8 Repadmin /viewlist
Repadmin /viewlist is used to get a list of domain controllers.
1.9 PowerShell
PowerShell is an object oriented scripting language that allows enterprises to automate IT tasks.
Below is a conversion table that shows the PowerShell command that can be used in place of the Repadmin command. So, why would you choose to use PowerShell? The output of PowerShell commands are objects those objects can be filtered with properties, piped through other PowerShell commands and manipulated to many useful things including great control in how the data is presented to the user.
| Command | PowerShell Cmdlet |
| Repadmin /FailCache | Get-ADReplicationFailure |
| Repadmin /Queue | Get-ADReplicationQueueOperation |
| Repadmin /ReplSingleObj | Sync-ADObject |
| Repadmin /ShowConn | Get-ADReplicationConnection |
| Repadmin /ShowObjMeta | Get-ADReplicationAttributeMetadata |
| Repadmin /ReplSummary | Get-ADReplicationPartnerMetadata |
| Repadmin /Showutdvec | Get-ADReplicationUpToDatenessVectorTable |
| Repadmin /SiteOptions | Set-ADReplicationSite |
| Repadmin /ShowAttr | Get-ADObject |
| Repadmin /Set Attr | Set-ADObject |
Get-ADReplicationParnerMetadata is very similar to running repadmin /showrepl. Without passing the output through another cmdlet the formatting is a bit different then to what you get with repadmin.
However, the advantage is that the output of the command are objects. You can constrain your views to certain properties.
The other advantage is that you can pass objects through other cmdlets. As seen here I am passing the output of Get-ADReplicationPartnerMetadata through Output-GridView.
Once in GridView you have the ability to sort and filter the data.
Here is another example of the usefulness of using PowerShell over repadmin. In this example I take the output of Get-ADReplicationPartnerMetadata then passing it through Select-Object so that we can then limit what objects are presented in GridView.
Here we see the output of that command.
1.10 Replication Errors
Here is a list of replication errors you may come across in either the Directory Services event log or while running repadmin.
| Event ID | Replication Error | Issue |
| 1388 | Lingering Objects | |
| 1988 | Lingering Objects | |
| 2042 | Lingering Objects | |
| 1925 | DNS Lookup Issues or Connectivity Problems | |
| 2087 | DNS Lookup Issues | |
| 2088 | DNS Lookup Issues | |
| 1311 | Replication Topology Issues | |
| 8614 | Tombstone lifetime exceeded | |
| 8524 | DNS Lookup failure | |
| 8456 | Server is currently rejecting replication requests | |
| 8457 | Server is currently rejecting replication requests | |
| 8453 | Access was denied | |
| 8452 | The naming context is in the process of being removed or is not replicated from the specified server | |
| 5 | Access is denied | |
| -21468930222 | The target principal name is incorrect | |
| 1753 | There are no more endpoints available from the endpoint mapper | |
| 1722 | The RPC server is unavailable | |
| 1396 | Logon Failure The Target account name is incorrect | |
| 1256 | The remote system is not available | |
| 1127 | While accessing the hard disk, a disk operation failed even afer retries | |
| 8451 | The replication operation encountered a database error | |
| 8606 | Insufficient attributes were given to create an object |
2 Troubleshooting Steps for Common Replication Issues
2.1 Troubleshooting -21468930222 (The target principal name is incorrect)
On the DC that is the cause of the error, perform the following steps:
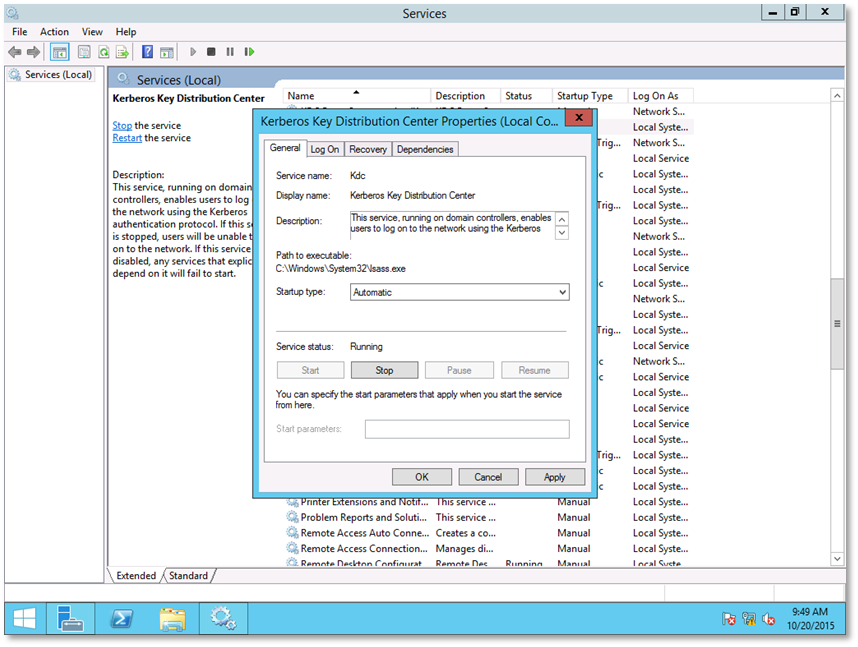
Step 1: Open Services.msc
Step 2: Configure KDC Service for Manual
Step 3: Stop the Service
Step 4: Restart the Domain Controller
Step 5: Open PowerShell as an Administrator
Step 6: Run: $cred = Get-Credential
Step 7: Enter Credentials and click OK
Step 8: Run, Reset-ComputerMachinePassword –Server <ServerName> -Credential $cred
Step 9: Restart the server
Step 10: Set the KDC service to Automatic, Start the service and click OK.
2.2 Troubleshoot Replication Error 8606, Event ID 1388, and Event ID 1988
These issues are caused by lingering objects. Lingering objects can be caused when a domain controller is taken offline for an extended period of time, does not replicate for longer than the tombstone lifetime, or is restored from a backup that is older than the tombstone lifetime.
When an object is deleted it is put in a tombstone state. After the tombstone lifetime passes (typically 180 days), DC run garbage collection and those tombstone objects are deleted. If a DC was offline for the entire TSL and then were brought back online they may have objects that have since been deleted, tombstoned, and garbage collected. Any objects that were deleted will still exist on that DC. These objects go unnoticed until a change is made to that object then the DC attempts to replicate that object, and at that point that is where it is either re-introduced into the environment or if strict replication consistency is enabled, blocked.
2.2.1 How to Determine TSL
Run the following command: dsquery * “cn=directory service,cn=windows nt,cn=services,cn=configuration,<Forest DN>” –scope base –attr tombstonelifetime
2.2.2 How to Remove Lingering Objects
2.2.2.1 Repadmin /removelingeringobjects
One way to remove lingering objects is to user repadmin with the /removelingeringobjects switch. First you must identify a clean source of the partition. The syntax of the command is repadmin /removelingeringobjects <Dest DC Name> <Source DC Guid> <Naming Context>. So, in other words you need to identify the source DCs guid and the Naming Context you want to clean. The naming context will be available in the Event 1388 or 1988 you receive in the event long. Once you find a clean source you can obtain the guid by opening DNS Manager and opening up the _msdcs Zone and obtaining the CName record for the DC in question.
Below is an example of running the repadmin /removelingeringobjects command
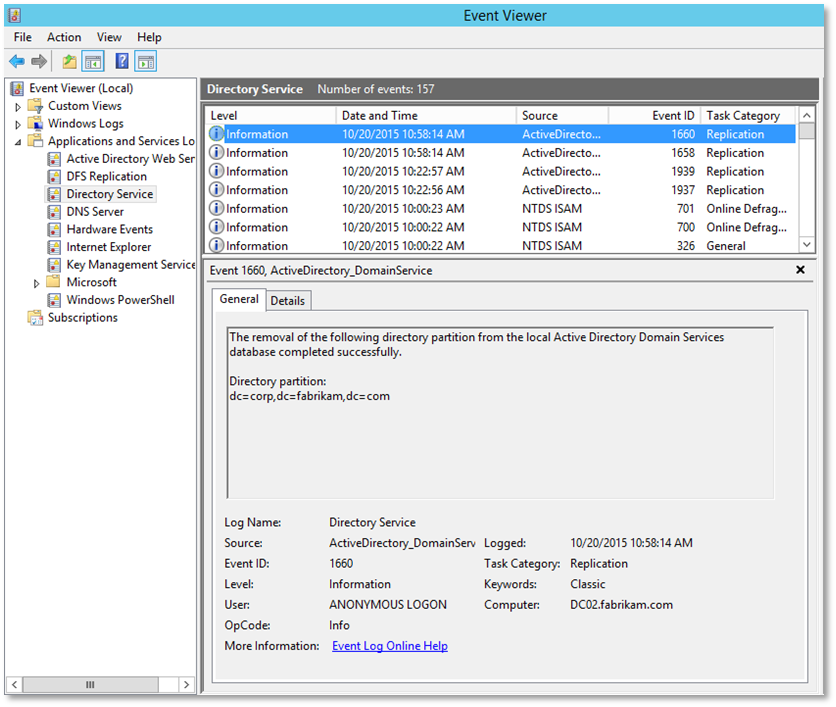
You will receive an Event 1937 when the removal of lingering objects begins.
You will then receive an Event 1939 when removal completes.
2.2.2.2 Repadmin /rehost
An alternative to using repadmin /removelingeringobjects command is to unhost the partition so that the domain controller no longer has that partition and then rehosting the entire partition with a good source.
The repadmin syntax for unhosting the partition is repadmin /unhost <DC Name> <Partition Name>
You will receive an event an event 1658 when the removal begins.
You will receive an event 1660 when the removal completes
The syntax for rehosting the partition is: repadmin /rehost <Dest DC Name> <Partition> <Source DC Name>
2.3 Troubleshooting Event ID 2042
Review event log for any 1988 or 1388 errors. If found use the previous section to remove the lingering objects from the domain controller.
Option 1: Re-hosting the partition that has not replicated
If the partition is a GC partition consider unhosting and rehosting the partition. Instructions for unhosting and rehosting are in the previous section called Repadmin /rehost
Option 2: Removing and then re-adding the domain controller to Active Directory
Another option is removing the DC from Active Directory and Re-promoting the Domain Controller
Step 1: Run Import-Module ADDSDeployment
Step 2: Run: Uninstall-ADDSDomainController –DemoteOperationMasterRole:$true –Force:$true
Step 3: Enter and confirm the new local password
Step 4: Next you will need to run the Install –ADDSDomainController cmdlet. Below is a sample that you can use. You will need to modify the template to meet the requirements of your environment.
Install-ADDSDomainController –NoGlobalCatalog:$false –CreateDnsDelegation:$false –CriticalReplicationOnly:$false –DatabasePath “C:\Windows\NTDS” –DomianName “fabrikam.com” –InstallDNS:$true –LogPath “C:\Windows\NTDS” –ReBootOnCompletion:$false –ReplicationSourceDC “DC01.fabrikam.com” –SiteName “Default-First-Site-Name” –SysvolPath “C:\Windows\SYSVOL” –Force:$true
Option 3: Enabling Replication with Divergent and Corrupt Partner
Due to the risk of adding lingering objects to Active Directory the final consideration should be enabling the following setting: Allow Replication With Divergent and Corrupt Partner.
Step 1: To enable this setting run the following command on the domain controller:
repadmin /regkey <hostname> +allowDivergent
Step 2: Let replication complete
Step 3: Disable the setting with the following command: repadmin /regkey <hostname> -allowDivergent
2.4 Troubleshooting Event ID 1311
Event 1311 is caused when there is not complete connectivity between domain controllers. There are a number of reasons there may not be complete connectivity.
2.4.1 ISTG
The Inter-Site Topology Generator (ITSG) is responsible for building the replication topology. So to determine what the scope of the connectivity issues it is important to identify the ISTGs that are logging 1311.
To find the ISTGs in your environment you need to use ldp.exe
Below are the steps for locating the ISTGs:
Step 1: Launch ldp.exe
Step 2: When LDP opens, select Connection and then Connect…
Step 3: In the Connect dialog box, enter the name of a Domain Controller for the Server you want to connect to and then click OK
Step 4: Click on Connection and then click Bind…
Step 5: In the Bind dialog box, click OK
Step 6: Select the Browse menu and then select Search
Step 7: In the search enter the following:
Base DN: CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,<DN of Forest Root> (example: CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=fabrikam,DC=com)
Filter: (CN=NTDS Site Settings)
Scope: Subtree
Attributes: Append the following to the attributes that are already listed: ;interSiteTopologyGenerator
Step 8: Click Run
Step 9: For each site you will then need to look for interSiteTopologyGenerator to determine the ITSG for each site.
2.4.2 BASL
By default, Bridge All Site Links (BASL) is enabled in Active Directory. If your environment is not fully routed, then you will want to disable BASL. By fully routed we mean each site can contact every other site. If BASL is configured on a network which is not fully routed, the KCC will generate site bridges that cannot actually be reached. To determine if BASL is enabled launch Active Directory Sites and Services (dssite.msc).
Expand Sites, then Inter-site Transports.
Right-click on IP and select Properties from the context menu
If Bridge all site links is enabled, there will be a check box next to it. To disable BASL, uncheck the checkbox and click OK.
2.4.3 Site Link Bridges
If you disable BASL you can still bridge site links. You would do that if you wanted two spoke sites to communicate directly if they could not communicate with the hub site. In a hub and spoke configuration the cost of crossing to site links (bridging a site link) will typically be a higher then just connecting directly to the hub site. So, ordinarily you would not have to worry about the Site Link Bridge being used instead of a direct site link. That being said, there are not a whole lot of scenarios where you would need to create Site Link bridges.
The following steps will allow you to bridge two site links.
Step 1: Open the Active Directory Sites and Services MMC.
Step 2: Expand Sites and then expand Inter-site Transports
Step 3: Select New Site Link Bridge… from the context menu
Add at least two sites to the Site Link Bridge, give it a Name, and click OK
And the Site Link Bridge has been completed.
2.4.4 Verify that all Sites are in a Site Link
Step 1: Run the following command in a PowerShell Console: Get-ADObject –LDAPFilter ‘(objectClass=site)’ –SearchBase (Get-ADRootDSE).ConfigurationNamingContext –Property Name | Format-Table Name
Step 2: In another PowerShell Console run: Get-ADObject –LDAPFilter ‘(objectClass=sitelink)’ –SearchBase (Get-ADRootDSE).ConfigurationNamingContext –Property Name, Cost, Description, Sitelist | Format-List Name, Sitelist
Step 3: Verify that each site that was listed in Step 1 exists in one of the site lists returned in Step 2
If not all sites are contained in a site link that you need to determine what site link that site needs to be added to or if a new site link needs to be created.
And that is all I have for replication troubleshooting for today.
-Chris
При возникновении этой ошибки в процессе диагностики отказа репликации можно делать вывод о нарушении в работе сети или о неправильных параметрах сети. Если для ускорения работы Active Directory используются сайты, их топология обычно повторяет топологию подключений в глобальной сети.
Если топология подключений через глобальную сеть меняется, необходимо перенастроить связи между сайтами и, возможно, серверы-плацдармы, чтобы они соответствовали новой топологии физической сети. При возникновении такой проблемы необходимо проверить следующие условия.
- Один или несколько контроллеров домена недоступны.
- Один или несколько сайтов находятся за пределами связей между сайтами.
- Предпочтительный сервер-плацдарм настроен неправильно.
- Предпочтительный сервер-плацдарм недоступен.
Для решения этой проблемы необходимо убедиться, что сайты, связи между сайтами и подсети настроены в соответствии с рекомендациями компании Microsoft. Если это так, то можно воспользоваться утилитами ping и pathping для определения проблемы в сети или на одном из маршрутизаторов.
Если настроены предпочтительные серверы-плацдармы, убедитесь, что они доступны. Если сеть не поддерживает полную маршрутизацию, убедитесь, что флажок Установить мост для всех связей сайтов (Bridge all site links) сброшен (этот флажок находится в диалоговом окне Свойства (Properties) связи между сайтами).
После создания связей между сайтами необходимо убедиться в соответствии между связями и топологией сетевых подключений предприятия. Это необходимо, так как домены в разных сайтах должны иметь возможность репликации. Все сайты должны принадлежать как минимум одной связи между сайтами.
Все несоседние сайты должны иметь как минимум одну общую связь. Например, если организация имеет три филиала: в Нью-Йорке, Чикаго и Лос Анджелесе, можно настроить две связи между сайтами: между Нью-Йорком и Чикаго, а также между Чикаго и Лос Анджелесом.
Пока обе связи между сайтами остаются открытыми достаточно долго (не блокируются расписанием) для репликации данных из Нью-Йорка в Лос Анджелес, в конфигурации связей между сайтами не должно возникать проблем.