Обработка ошибок в VBA Excel с помощью оператора On Error. Синтаксис выражений с оператором On Error. Пример кода с простым обработчиком ошибок.
On Error – это оператор, который используется для отслеживания ошибок во время исполнения кода VBA. При возникновении ошибки On Error передает информацию о ней в объект Err и включает программу обработки ошибок, начинающуюся с указанной строки.
В первую очередь, обработчик ошибок нужен для пользователей файлов Excel с кодами VBA. Любая ошибка приводит к прекращению выполнения программы, открытию редактора VBA с непонятным для пользователя сообщением или даже к полному зависанию приложения.
Обработчик ошибок позволяет завершить выполнение программы при возникновении ошибки и вывести сообщение пользователю с ее описанием.
Синтаксис выражений с On Error
Включает алгоритм обнаружения ошибок и, в случае возникновения ошибки, передает управление операторам обработчика ошибок с указанной в выражении строки. Stroka – это метка, после которой расположены операторы обработчика ошибок.
Включает алгоритм обнаружения ошибок и, в случае возникновения ошибки, передает управление оператору, следующему за оператором, вызвавшем ошибку.
Отключает любой включенный обработчик ошибок в текущей процедуре.
Простой обработчик ошибок
Шаблон простейшего обработчика ошибок:
|
Sub Primer() On Error GoTo Stroka ‘Блок операторов процедуры Exit Sub Stroka: MsgBox «Произошла ошибка: « & Err.Description End Sub |
Оператор On Error GoTo размещается в начале процедуры, метка и обработчик ошибок – в конце процедуры. Название метки можно сменить на другое, в том числе на кириллице.
Оператор Exit Sub обеспечивает выход из процедуры, если блок операторов выполнен без ошибок. Для вывода описания ошибки используется свойство Description объекта Err.
Примеры обработки ошибок
Пример 1
Деление на ноль:
|
Sub Primer1() On Error GoTo Инструкция Dim a As Double a = 45 / 0 Exit Sub Instr: MsgBox «Произошла ошибка: « & Err.Description End Sub |
Результат выполнения кода VBA Excel с обработчиком ошибок:
Пример 2
Выход за границы диапазона:
|
Sub Primer2() On Error GoTo Instr Dim myRange As Range Set myRange = Range(«A1:D4»).Offset(—2) Exit Sub Instr: MsgBox «Произошла ошибка: « & Err.Description End Sub |
Результат выполнения кода VBA Excel с оператором On Error GoTo:
Пример использования выражений On Error Resume Next и On Error GoTo 0 смотрите в статье: Отбор уникальных значений с помощью Collection.
“Abort, Retry, Fail?” – MS-DOS error message circa 1986
This post provides a complete guide to VBA Error Handing. If you are looking for a quick summary then check out the quick guide table in the first section.
If you are looking for a particular topic on VBA Error Handing then check out the table of contents below(if it’s not visible click on the post header).
If you are new to VBA Error Handling, then you can read the post from start to finish as it is laid out in logical order.
Contents
- 1 A Quick Guide to Error Handing
- 2 The Webinar
- 3 Download the Error Handling Library
- 4 Introduction
- 5 VBA Errors
- 5.1 Syntax Errors
- 5.2 Compilation Errors
- 5.2.1 Using Debug->Compile
- 5.2.2 Debug->Compile Error Summary
- 5.2.3 Debug->Compile Usage
- 5.3 Runtime Errors
- 5.3.1 Expected Versus Unexpected Errors
- 5.4 Runtime Errors that are not VBA Errors
- 6 The On Error Statement
- 6.1 On Error GoTo 0
- 6.2 On Error Resume Next
- 6.3 On Error GoTo [label]
- 6.4 On Error GoTo -1
- 6.5 Using On Error
- 7 Resume Next
- 8 The Err Object
- 8.1 Getting the Line Number
- 8.2 Using Err.Raise
- 8.3 Using Err.Clear
- 9 Logging
- 10 Other Error Related Items
- 10.1 Error Function
- 10.2 Error Statement
- 11 A Simple Error Handling Strategy
- 11.1 The Basic Implementation
- 12 A Complete Error Handling Strategy
- 12.1 An Example of using this strategy
- 13 Error Handling in a Nutshell
- 14 What’s Next?
A Quick Guide to Error Handing
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| On Error Goto 0 | When error occurs, the code stops and displays the error. |
| On Error Goto -1 | Clears the current error setting and reverts to the default. |
| On Error Resume Next | Ignores the error and continues on. |
| On Error Goto [Label] | Goes to a specific label when an error occurs. This allows us to handle the error. |
| Err Object | When an error occurs the error information is stored here. |
| Err.Number | The number of the error. (Only useful if you need to check a specific error occurred.) |
| Err.Description | Contains the error text. |
| Err.Source | You can populate this when you use Err.Raise. |
| Err.Raise | A function that allows you to generate your own error. |
| Error Function | Returns the error text from an error number. Obsolete. |
| Error Statement | Simulates an error. Use Err.Raise instead. |
The Webinar
Members of the Webinar Archives can access the webinar for this article by clicking on the image below.
(Note: Archive members have access to the webinar archive.)
Download the Error Handling Library
Introduction
Error Handling refers to code that is written to handle errors which occur when your application is running. These errors are normally caused by something outside your control like a missing file, database being unavailable, data being invalid etc.
If we think an error is likely to occur at some point, it is good practice to write specific code to handle the error if it occurs and deal with it.
For all other errors, we use generic code to deal with them. This is where the VBA error handling statement comes into play. They allow our application to deal gracefully with any errors we weren’t expecting.
To understand error handling we must first understand the different types of errors in VBA.
VBA Errors
There are three types of errors in VBA:
- Syntax
- Compilation
- Runtime
We use error handling to deal with runtime errors. Let’s have a look at each of these error types so that it is clear what a runtime error is.
Syntax Errors
If you have used VBA for any length of time you will have seen a syntax error. When you type a line and press return, VBA will evaluate the syntax and if it is not correct it will display an error message.
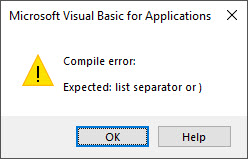
For example if you type If and forget the Then keyword, VBA will display the following error message
Some examples of syntax errors are
' then is missing If a > b ' equals is missing after i For i 2 To 7 ' missing right parenthesis b = left("ABCD",1
Syntax errors relate to one line only. They occur when the syntax of one line is incorrect.
Note: You can turn off the Syntax error dialog by going to Tools->Options and checking off “Auto Syntax Check”. The line will still appear red if there is an error but the dialog will not appear.
Compilation Errors
Compilation errors occur over more than one line. The syntax is correct on a single line but is incorrect when all the project code is taken into account.
Examples of compilation errors are:
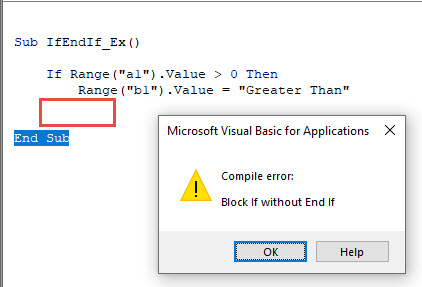
- If statement without corresponding End If statement
- For without Next
- Select without End Select
- Calling a Sub or Function that does not exist
- Calling a Sub or Function with the wrong parameters
- Giving a Sub or Function the same name as a module
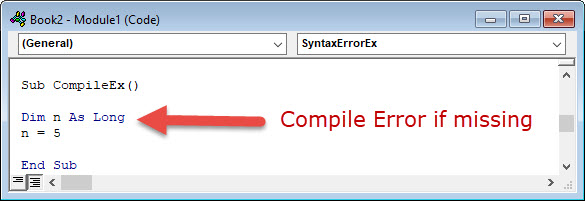
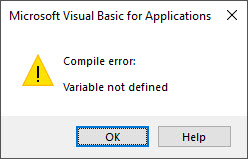
- Variables not declared(Option Explicit must be present at the top of the module)
The following screenshot shows a compilation error that occurs when a For loop has no matching Next statement.
Using Debug->Compile
To find compilation errors, we use Debug->Compile VBA Project from the Visual Basic menu.
When you select Debug->Compile, VBA displays the first error it comes across.
When this error is fixed, you can run Compile again and VBA will then find the next error.
Debug->Compile will also include syntax errors in it’s search which is very useful.
If there are no errors left and you run Debug->Compile , it may appear that nothing happened. However, “Compile” will be grayed out in the Debug menu. This means your application has no compilation errors at the current time.
Debug->Compile Error Summary
- Debug->Compile finds compilation(project wide) errors.
- It will also find syntax errors.
- It finds one error each time you use it.
- When there are no compilation errors left the Compile option will appear grayed out in the menu.
Debug->Compile Usage
You should always use Debug->Compile before you run your code. This ensures that your code has no compilation errors when you run it.
If you do not run Debug->Compile then VBA may find compile errors when it runs. These should not be confused with Runtime errors.
Runtime Errors
Runtime errors occur when your application is running. They are normally outside of your control but can be caused by errors in your code.
For example, imagine your application reads from an external workbook. If this file gets deleted then VBA will display an error when your code tries to open it.
Other examples of runtime errors are
- a database not being available
- the user entering invalid data
- a cell containing text instead of a number
As we have seen, the purpose of error handling is to deal with runtime errors when they occur.
Expected Versus Unexpected Errors
When we think a runtime error could occur we put code in place to handle it. For example, we would normally put code in place to deal with a file not being found.
The following code checks if the file exists before it tries to open it. If the file does not exist then a user friendly message is displayed and the code exits the sub.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub OpenFile() Dim sFile As String sFile = "C:\docs\data.xlsx" ' Use Dir to check if file exists If Dir(sFile) = "" Then ' if file does not exist display message MsgBox "Could not find the file " & sFile Exit Sub End If ' Code will only reach here if file exists Workbooks.Open sFile End Sub
When we think an error is likely to occur at some point, it is good practice to add code to handle the situation. We normally refer to these errors as expected errors.
If we don’t have specific code to handle an error it is considered an unexpected error. We use the VBA error handling statements to handle the unexpected errors.
Runtime Errors that are not VBA Errors
Before we look at the VBA Handling there is one type of error we must mention. Some runtime errors are not considered errors by VBA but only by the user.
Let me explain this with an example. Imagine you have an application that requires you to add the values in the variables a and b
result = a + b
Let’s say you mistakenly use an asterisk instead of the plus sign
result = a * b
This is not a VBA error. Your code syntax is perfectly legal. However, from your requirements point of view it is an error.
These errors cannot be dealt with using error handling as they obviously won’t generate any error. You can deal with these errors using Unit Testing and Assertions. I have an in-depth post about using VBA assertions – see How to Make Your Code BulletProof.
The On Error Statement
As we have seen there are two ways to treat runtime errors
- Expected errors – write specific code to handle them.
- Unexpected errors – use VBA error handling statements to handle them.
The VBA On Error statement is used for error handling. This statement performs some action when an error occurs during runtime.
There are four different ways to use this statement
- On Error GoTo 0 – the code stops at the line with the error and displays a message.
- On Error Resume Next – the code moves to next line. No error message is displayed.
- On Error GoTo [label] – the code moves to a specific line or label. No error message is displayed. This is the one we use for error handling.
- On Error GoTo -1 – clears the current error.
Let’s look at each of these statements in turn.
On Error GoTo 0
This is the default behavior of VBA. In other words, if you don’t use On Error then this is the behavior you will see.
When an error occurs, VBA stops on the line with the error and displays the error message. The application requires user intervention with the code before it can continue. This could be fixing the error or restarting the application. In this scenario no error handling takes place.
Let’s look at an example. In the following code, we have not used any On Error line so VBA will use the On Error GoTo 0 behavior by default.
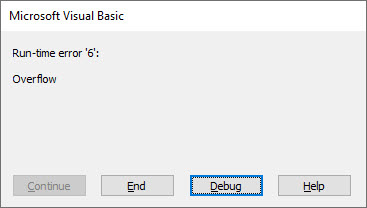
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UsingDefault() Dim x As Long, y As Long x = 6 y = 6 / 0 x = 7 End Sub
The second assignment line results in a divide by zero error. When we run this code we will get the error message shown in the screenshot below
When the error appears you can choose End or Debug
If you select End then the application simply stops.
If you select Debug the application stops on the error line as the screenshot below shows
This behaviour is fine when you are writing VBA code as it shows you the exact line with the error.
This behavior is unsuitable for an application that you are given to a user. These errors look unprofessional and they make the application look unstable.
An error like this is essentially the application crashing. The user cannot continue on without restarting the application. They may not use it at all until you fix the error for them.
By using On Error GoTo [label] we can give the user a more controlled error message. It also prevents the application stopping. We can get the application to perform in a predefined manner.
On Error Resume Next
Using On Error Resume Next tells VBA to ignore the error and continue on.
There are specific occasions when this is useful. Most of the time you should avoid using it.
If we add Resume Next to our example Sub then VBA will ignore the divide by zero error
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UsingResumeNext() On Error Resume Next Dim x As Long, y As Long x = 6 y = 6 / 0 x = 7 End Sub
It is not a good idea to do this. If you ignore the error, then the behavior can be unpredictable. The error can affect the application in multiple ways.You could end up with invalid data. The problem is that you aren’t aware that something went wrong because you have suppressed the error.
The code below is an example of where using Resume Next is valid
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub SendMail() On Error Resume Next ' Requires Reference: ' Microsoft Outlook 15.0 Object Library Dim Outlook As Outlook.Application Set Outlook = New Outlook.Application If Outlook Is Nothing Then MsgBox "Cannot create Microsoft Outlook session." _ & " The email will not be sent." Exit Sub End If End Sub
In this code we are checking to see if Microsoft Outlook is available on a computer. All we want to know is if it is available or not. We are not interested in the specific error.
In the code above, we continue on if there is an error. Then in the next line we check the value of the Outlook variable. If there has been an error then the value of this variable will be set to Nothing.
This is an example of when Resume could be useful. The point is that even though we use Resume we are still checking for the error. The vast majority of the time you will not need to use Resume.
On Error GoTo [label]
This is how we use Error Handling in VBA. It is the equivalent of the Try and Catch functionality you see in languages such as C# and Java.
When an error occurs you send the error to a specific label. It is normally at the bottom of the sub.
Let’s apply this to the sub we have been using
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UsingGotoLine() On Error GoTo eh Dim x As Long, y As Long x = 6 y = 6 / 0 x = 7 Done: Exit Sub eh: MsgBox "The following error occurred: " & Err.Description End Sub
The screenshot below shows what happens when an error occurs
VBA jumps to the eh label because we specified this in the On Error Goto line.
Note 1: The label we use in the On…GoTo statement, must be in the current Sub/Function. If not you will get a compilation error.
Note 2: When an error occurs when using On Error GoTo [label], the error handling returns to the default behaviour i.e. The code will stop on the line with the error and display the error message. See the next section for more information about this.
On Error GoTo -1
This statement is different than the other three. It is used to clear the current error rather than setting a particular behaviour.
When an error occurs using On Error GoTo [label], the error handling behaviour returns to the default behaviour i.e. “On Error GoTo 0”. That means that if another error occurs the code will stop on the current line.
This behaviour only applies to the current sub. Once we exit the sub, the error will be cleared automatically.
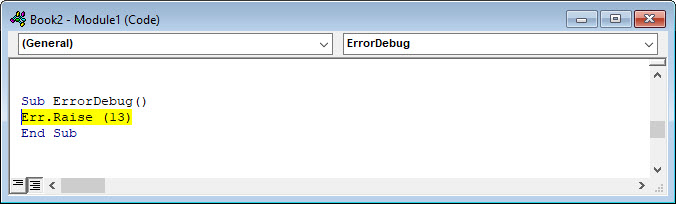
Take a look at the code below. The first error will cause the code to jump to the eh label. The second error will stop on the line with the 1034 error.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub TwoErrors() On Error Goto eh ' generate "Type mismatch" error Error (13) Done: Exit Sub eh: ' generate "Application-defined" error Error (1034) End Sub
If we add further error handling it will not work as the error trap has not been cleared.
In the code below we have added the line
On Error Goto eh_other
after we catch the first error.
This has no effect as the error has not been cleared. In other words the code will stop on the line with the error and display the message.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub TwoErrors() On Error Goto eh ' generate "Type mismatch" error Error (13) Done: Exit Sub eh: On Error Goto eh_other ' generate "Application-defined" error Error (1034) Exit Sub eh_other: Debug.Print "eh_other " & Err.Description End Sub
To clear the error we use On Error GoTo -1. Think of it like setting a mouse trap. When the trap goes off you need to set it again.
In the code below we add this line and the second error will now cause the code to jump to the eh_other label
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub TwoErrors() On Error Goto eh ' generate "Type mismatch" error Error (13) Done: Exit Sub eh: ' clear error On Error Goto -1 On Error Goto eh_other ' generate "Application-defined" error Error (1034) Exit Sub eh_other: Debug.Print "eh_other " & Err.Description End Sub
Note 1: There are probably rare cases where using On Error GoTo -1 is useful. In most cases using Resume Next is better as it clears the error and resumes the code at the next line after the error occurs.
Note 2: The Err Object has a member Clear. Using Clear clears the text and numbers in the Err object, but it does NOT reset the error.
Using On Error
As we have seen, VBA will do one of three things when an error occurs
- Stop and display the error.
- Ignore the error and continue on.
- Jump to a specific line.
VBA will always be set to one of these behaviors. When you use On Error, VBA will change to the behaviour you specify and forget about any previous behavior.
In the following Sub, VBA changes the error behaviour each time we use the On Error statement
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub ErrorStates() Dim x As Long ' Go to eh label if error On Error Goto eh ' this will ignore the error on the following line On Error Resume Next x = 1 / 0 ' this will display an error message on the following line On Error Goto 0 x = 1 / 0 Done: Exit Sub eh: Debug.Print Err.Description End Sub
Resume Next
The Resume Next statement is used to clear the error and then resume the code from the line after where the error occurred.
If your code can have multiple errors and you want to keep detecting them then this line is very useful.
For example, in the following code we want to resume the code after the error has been reported:
Private Sub Main() On Error Goto eh Dim i As Long For i = 1 To 3 ' Generate type mismatch error Error 13 Next i done: Exit Sub eh: Debug.Print i, Err.Description End Sub
We could use On Error Goto -1 to clear the code and then use a goto statement to go back to the code like this:
Private Sub Main() On Error Goto eh Dim i As Long For i = 1 To 3 ' Generate type mismatch error Error 13 continue: Next i done: Exit Sub eh: Debug.Print i, Err.Description On Error Goto -1 ' clear the error Goto continue ' return to the code End Sub
The Resume Next provides a nicer way of doing it and it always means the code is much clearer and easier to understand:
Private Sub Main() On Error Goto eh Dim i As Long For i = 1 To 3 ' Generate type mismatch error Error 13 continue: Next i done: Exit Sub eh: Debug.Print i, Err.Description ' clear the error and return to the code Resume Next End Sub
The Err Object
When an error occurs you can view details of the error using the Err object.
When an runtime error occurs, VBA automatically fills the Err object with details.
The code below will print “Error Number: 13 Type Mismatch” which occurs when we try to place a string value in the long integer total
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UsingErr() On Error Goto eh Dim total As Long total = "aa" Done: Exit Sub eh: Debug.Print "Error number: " & Err.Number _ & " " & Err.Description End Sub
The Err.Description provides details of the error that occurs. This is the text you normally see when an error occurs e.g. “Type Mismatch”
The Err.Number is the ID number of the error e.g. the error number for “Type Mismatch” is 13. The only time you really need this is if you are checking that a specific error occurred and this is only necessary on rare occasions.
The Err.Source property seems like a great idea but it does not work for a VBA error. The source will return the project name, which hardly narrows down where the error occurred. However, if you create an error using Err.Raise you can set the source yourself and this can be very useful.
Getting the Line Number
The Erl function is used to return the line number where the error occurs.
It often causes confusion. In the following code, Erl will return zero
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UsingErr() On Error Goto eh Dim val As Long val = "aa" Done: Exit Sub eh: Debug.Print Erl End Sub
This is because there are no line numbers present. Most people don’t realise it but VBA allows you to have line numbers.
If we change the Sub above to have line number it will now print out 20
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UsingErr() 10 On Error Goto eh Dim val As Long 20 val = "aa" Done: 30 Exit Sub eh: 40 Debug.Print Erl End Sub
Adding line numbers to your code manually is cumbersome. However there are tools available that will allow you to easily add and remove line numbers to a sub.
When you are finished working on a project and hand it over to the user it can be useful to add line numbers at this point. If you use the error handling strategy in the last section of this post, then VBA will report the line where the error occurred.
Using Err.Raise
Err.Raise allows us to create errors. We can use it to create custom errors for our application which is very useful. It is the equivalent of the Throw statement in Java\C#.
The format is as follows
Err.Raise [error number], [error source], [error description]
Let’s look at a simple example. Imagine we want to ensure that a cell has an entry that has a length of 5 characters. We could have a specific message for this
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Const ERROR_INVALID_DATA As Long = vbObjectError + 513 Sub ReadWorksheet() On Error Goto eh If Len(Sheet1.Range("A1")) <> 5 Then Err.Raise ERROR_INVALID_DATA, "ReadWorksheet" _ , "The value in the cell A1 must have exactly 5 characters." End If ' continue on if cell has valid data Dim id As String id = Sheet1.Range("A1") Done: Exit Sub eh: ' Err.Raise will send code to here MsgBox "Error found: " & Err.Description End Sub
When we create an error using Err.Raise we need to give it a number. We can use any number from 513 to 65535 for our error. We must use vbObjectError with the number e.g.
Err.Raise vbObjectError + 513
Using Err.Clear
Err.Clear is used to clear the text and numbers from the Err.Object. In other words, it clears the description and number.If you want the clear the actual error you can use either On Error GoTo -1 or Resume Next
It is rare that you will need to use Err.Clear but let’s have a look at an example where you might.
In the code below we are counting the number of errors that will occur. To keep it simple we are generating an error for each odd number.
We check the error number each time we go through the loop. If the number does not equal zero then an error has occurred. Once we count the error we need to set the error number back to zero so it is ready to check for the next error.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UsingErrClear() Dim count As Long, i As Long ' Continue if error as we will check the error number On Error Resume Next For i = 0 To 9 ' generate error for every second one If i Mod 2 = 0 Then Error (13) ' Check for error If Err.Number <> 0 Then count = count + 1 Err.Clear ' Clear Err once it is counted End If Next Debug.Print "The number of errors was: " & count End Sub
Note 1: Err.Clear resets the text and numbers in the error object but it does not clear the error – see Resume Next Or On Error GoTo -1 for more information about clearing the actual error.
Logging
Logging means writing information from your application when it is running. When an error occurs you can write the details to a text file so you have a record of the error.
The code below shows a very simple logging procedure
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub Logger(sType As String, sSource As String, sDetails As String) Dim sFilename As String sFilename = "C:\temp\logging.txt" ' Archive file at certain size If FileLen(sFilename) > 20000 Then FileCopy sFilename _ , Replace(sFilename, ".txt", Format(Now, "ddmmyyyy hhmmss.txt")) Kill sFilename End If ' Open the file to write Dim filenumber As Variant filenumber = FreeFile Open sFilename For Append As #filenumber Print #filenumber, CStr(Now) & "," & sType & "," & sSource _ & "," & sDetails & "," & Application.UserName Close #filenumber End Sub
You can use it like this
' Create unique error number ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Const ERROR_DATA_MISSING As Long = vbObjectError + 514 Sub CreateReport() On Error Goto eh If Sheet1.Range("A1") = "" Then Err.Raise ERROR_DATA_MISSING, "CreateReport", "Data is missing from Cell A1" End If ' other code here Done: Exit Sub eh: Logger "Error", Err.Source, Err.Description End Sub
The log is not only for recording errors. You can record other information as the application runs. When an error occurs you can then check the sequence of events before an error occurred.
Below is an example of logging. How you implement logging really depends on the nature of the application and how useful it will be:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub ReadingData() Logger "Information", "ReadingData()", "Starting to read data." Dim coll As New Collection ' add data to the collection coll.Add "Apple" coll.Add "Pear" If coll.Count < 3 Then Logger "Warning", "ReadingData()", "Number of data items is low." End If Logger "Information", "ReadingData()", "Number of data items is " & coll.Count Logger "Information", "ReadingData()", "Finished reading data." End Sub
Having a lot of information when dealing with an error can be very useful. Often the user may not give you accurate information about the error that occurred. By looking at the log you can get more accurate information about the information.
This section covers some of the other Error Handling tools that VBA has. These items are considered obsolete but I have included them as they may exist in legacy code.
Error Function
The Error Function is used to print the error description from a given error number. It is included in VBA for backward compatibility and is not needed because you can use the Err.Description instead.
Below are some examples:
' Print the text "Division by zero" Debug.Print Error(11) ' Print the text "Type mismatch" Debug.Print Error(13) ' Print the text "File not found" Debug.Print Error(53)
Error Statement
The Error statement allows you to simulate an error. It is included in VBA for backward compatibility. You should use Err.Raise instead.
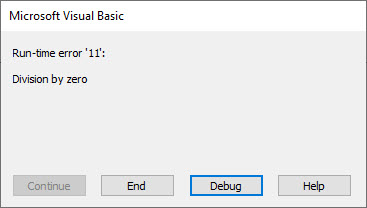
In the following code we simulate a “Divide by zero” error.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub SimDivError() On Error Goto eh ' This will create a division by zero error Error 11 Exit Sub eh: Debug.Print Err.Number, Err.Description End Sub
This statement is included in VBA for backward compatibility. You should use Err.Raise instead.
A Simple Error Handling Strategy
With all the different options you may be confused about how to use error handling in VBA. In this section, I’m going to show you how to implement a simple error handling strategy that you can use in all your applications.
The Basic Implementation
This is a simple overview of our strategy
- Place the On Error GoTo Label line at the start of our topmost sub.
- Place the error handling Label at the end of our topmost sub.
- If an expected error occurs then handle it and continue.
- If the application cannot continue then use Err.Raise to jump to the error handling label.
- If an unexpected error occurs the code will automatically jump to the error handling label.
The following image shows an overview of how this looks
The following code shows a simple implementation of this strategy:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Const ERROR_NO_ACCOUNTS As Long = vbObjectError + 514 Sub BuildReport() On Error Goto eh ' If error in ReadAccounts then jump to error ReadAccounts ' Do something with the code Done: Exit Sub eh: ' All errors will jump to here MsgBox Err.Source & ": The following error occured " & Err.Description End Sub Sub ReadAccounts() ' EXPECTED ERROR - Can be handled by the code ' Application can handle A1 being zero If Sheet1.Range("A1") = 0 Then Sheet1.Range("A1") = 1 End If ' EXPECTED ERROR - cannot be handled by the code ' Application cannot continue if no accounts workbook If Dir("C:\Docs\Account.xlsx") = "" Then Err.Raise ERROR_NO_ACCOUNTS, "UsingErr" _ , "There are no accounts present for this month." End If ' UNEXPECTED ERROR - cannot be handled by the code ' If cell B3 contains text we will get a type mismatch error Dim total As Long total = Sheet1.Range("B3") ' continue on and read accounts End Sub
This is a nice way of implementing error handling because
- We don’t need to add error handling code to every sub.
- If an error occurs then VBA exits the application gracefully.
A Complete Error Handling Strategy
The above strategy has one major drawback. It doesn’t provide any information about the error. It is better than having no strategy as it prevents the application crashing. But that is the only real benefit.
VBA doesn’t fill Err.Source with anything useful so we have to do this ourselves.
In this section, I am going to introduce a more complete error strategy. I have written two subs that perform all the heavy lifting so all you have to do is add them to your project.
The purpose of this strategy is to provide you with the Stack* and line number when an error exists.
*The Stack is the list of sub/functions that were currently in use when the error occurred.
This is our strategy
- Place error handling in all the subs.
- When an error occurs, the error handler adds details to the error and raises it again.
- When the error reaches the topmost sub it is displayed.
We are simply “bubbling” the error to the top. The following diagram shows a simple visual of what happens when an error occurs in Sub3
The only messy part to this is formatting the strings correctly. I have written two subs that handle this, so it is taken care of for you.
There are the two helper subs, RaiseError and DisplayError. You can download the library below:
An Example of using this strategy
Here is a simple coding example that uses these subs. In this strategy, we don’t place any code in the topmost sub. We only call subs from it.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub Topmost() On Error Goto EH Level1 Done: Exit Sub EH: DisplayError Err.source, Err.Description, "Module1.Topmost", Erl End Sub Sub Level1() On Error Goto EH Level2 Done: Exit Sub EH: RaiseError Err.Number, Err.source, "Module1.Level1", Err.Description, Erl End Sub Sub Level2() On Error Goto EH ' Error here Dim a As Long a = "7 / 0" Done: Exit Sub EH: RaiseError Err.Number, Err.source, "Module1.Level2", Err.Description, Erl End Sub
The result looks like this:
If your project has line numbers the result will include the line number of the error:
Error Handling in a Nutshell
- Error Handling is used to handle errors that occur when your application is running.
- You write specific code to handle expected errors. You use the VBA error handling statement On Error GoTo [label] to send VBA to a label when an unexpected error occurs.
- You can get details of the error from Err.Description.
- You can create your own error using Err.Raise.
- Using one On Error statement in the top most sub will catch all errors in subs that are called from here.
- If you want to record the name of the Sub with the error, you can update the error and rethrow it.
- You can use a log to record information about the application as it is running.
What’s Next?
Free VBA Tutorial If you are new to VBA or you want to sharpen your existing VBA skills then why not try out the The Ultimate VBA Tutorial.
Related Training: Get full access to the Excel VBA training webinars and all the tutorials.
(NOTE: Planning to build or manage a VBA Application? Learn how to build 10 Excel VBA applications from scratch.)
In this Article
- VBA Errors Cheat Sheet
- Errors
- VBA Error Handling
- VBA On Error Statement
- On Error GoTo 0
- On Error Resume Next
- Err.Number, Err.Clear, and Catching Errors
- On Error GoTo Line
- VBA IsError
- If Error VBA
- VBA Error Types
- Runtime Errors
- Syntax Errors
- Compile Errors
- Debug > Compile
- OverFlow Error
- Other VBA Error Terms
- VBA Catch Error
- VBA Ignore Error
- VBA Throw Error / Err.Raise
- VBA Error Trapping
- VBA Error Message
- VBA Error Handling in a Loop
- VBA Error Handling in Access
VBA Errors Cheat Sheet
Errors
On Error – Stop code and display error
On Error Goto 0
On Error – Skip error and continue running
On Error Resume Next
On Error – Go to a line of code [Label]
On Error Goto [Label]
Clears (Resets) Error
On Error GoTo –1
Show Error number
MsgBox Err.Number
Show Description of error
MsgBox Err.Description
Function to generate own error
Err.Raise
See more VBA “Cheat Sheets” and free PDF Downloads
VBA Error Handling
VBA Error Handling refers to the process of anticipating, detecting, and resolving VBA Runtime Errors. The VBA Error Handling process occurs when writing code, before any errors actually occur.
VBA Runtime Errors are errors that occur during code execution. Examples of runtime errors include:
- Referencing a non-existent workbook, worksheet, or other object (Run-time Error 1004)
- Invalid data ex. referencing an Excel cell containing an error (Type Mismatch – Run-time Error 13)
- Attempting to divide by zero
VBA On Error Statement
Most VBA error handling is done with the On Error Statement. The On Error statement tells VBA what to do if it encounters an error. There are three On Error Statements:
- On Error GoTo 0
- On Error Resume Next
- On Error GoTo Line
On Error GoTo 0
On Error GoTo 0 is VBA’s default setting. You can restore this default setting by adding the following line of code:
On Error GoTo 0When an error occurs with On Error GoTo 0, VBA will stop executing code and display its standard error message box.
Often you will add an On Error GoTo 0 after adding On Error Resume Next error handling (next section):
Sub ErrorGoTo0()
On Error Resume Next
ActiveSheet.Shapes("Start_Button").Delete
On Error GoTo 0
'Run More Code
End SubOn Error Resume Next
On Error Resume Next tells VBA to skip any lines of code containing errors and proceed to the next line.
On Error Resume NextNote: On Error Resume Next does not fix an error, or otherwise resolve it. It simply tells VBA to proceed as if the line of code containing the error did not exist. Improper use of On Error Resume Next can result in unintended consequences.
A great time to use On Error Resume Next is when working with objects that may or may not exist. For example, you want to write some code that will delete a shape, but if you run the code when the shape is already deleted, VBA will throw an error. Instead you can use On Error Resume Next to tell VBA to delete the shape if it exists.
On Error Resume Next
ActiveSheet.Shapes("Start_Button").Delete
On Error GoTo 0Notice we added On Error GoTo 0 after the line of code containing the potential error. This resets the error handling.
In the next section we’ll show you how to test if an error occurred using Err.Number, giving you more advanced error handling options.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Err.Number, Err.Clear, and Catching Errors
Instead of simply skipping over a line containing an error, we can catch the error by using On Error Resume Next and Err.Number.
Err.Number returns an error number corresponding with the type of error detected. If there is no error, Err.Number = 0.
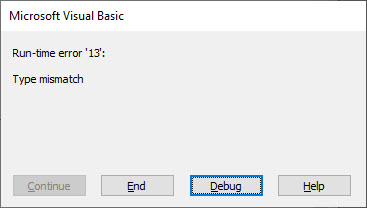
For example, this procedure will return “11” because the error that occurs is Run-time error ’11’.
Sub ErrorNumber_ex()
On Error Resume Next
ActiveCell.Value = 2 / 0
MsgBox Err.Number
End SubError Handling with Err.Number
The true power of Err.Number lies in the ability to detect if an error occurred (Err.Number <> 0). In the example below, we’ve created a function that will test if a sheet exists by using Err.Number.
Sub TestWS()
MsgBox DoesWSExist("test")
End Sub
Function DoesWSExist(wsName As String) As Boolean
Dim ws As Worksheet
On Error Resume Next
Set ws = Sheets(wsName)
'If Error WS Does not exist
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
DoesWSExist = False
Else
DoesWSExist = True
End If
On Error GoTo -1
End FunctionNote: We’ve added a On Error GoTo -1 to the end which resets Err.Number to 0 (see two sections down).
With On Error Resume Next and Err.Number, you can replicate the “Try” & “Catch” functionality of other programming languages.
On Error GoTo Line
On Error GoTo Line tells VBA to “go to” a labeled line of code when an error is encountered. You declare the Go To statement like this (where errHandler is the line label to go to):
On Error GoTo errHandlerand create a line label like this:
errHandler:Note: This is the same label that you’d use with a regular VBA GoTo Statement.
Below we will demonstrate using On Error GoTo Line to Exit a procedure.
On Error Exit Sub
You can use On Error GoTo Line to exit a sub when an error occurs.
You can do this by placing the error handler line label at the end of your procedure:
Sub ErrGoToEnd()
On Error GoTo endProc
'Some Code
endProc:
End Subor by using the Exit Sub command:
Sub ErrGoToEnd()
On Error GoTo endProc
'Some Code
GoTo skipExit
endProc:
Exit Sub
skipExit:
'Some More Code
End SubErr.Clear, On Error GoTo -1, and Resetting Err.Number
After an error is handled, you should generally clear the error to prevent future issues with error handling.
After an error occurs, both Err.Clear and On Error GoTo -1 can be used to reset Err.Number to 0. But there is one very important difference: Err.Clear does not reset the actual error itself, it only resets the Err.Number.
What does that mean? Using Err.Clear, you will not be able to change the error handling setting. To see the difference, test out this code and replace On Error GoTo -1 with Err.Clear:
Sub ErrExamples()
On Error GoTo errHandler:
'"Application-defined" error
Error (13)
Exit Sub
errHandler:
' Clear Error
On Error GoTo -1
On Error GoTo errHandler2:
'"Type mismatch" error
Error (1034)
Exit Sub
errHandler2:
Debug.Print Err.Description
End SubTypically, I recommend always using On Error GoTo -1, unless you have a good reason to use Err.Clear instead.
VBA On Error MsgBox
You might also want to display a Message Box on error. This example will display different message boxes depending on where the error occurs:
Sub ErrorMessageEx()
Dim errMsg As String
On Error GoTo errHandler
'Stage 1
errMsg = "An error occured during the Copy & Paste stage."
'Err.Raise (11)
'Stage 2
errMsg = "An error occured during the Data Validation stage."
'Err.Raise (11)
'Stage 3
errMsg = "An error occured during the P&L-Building and Copy-Over stage."
Err.Raise (11)
'Stage 4
errMsg = "An error occured while attempting to log the Import on the Setup Page"
'Err.Raise (11)
GoTo endProc
errHandler:
MsgBox errMsg
endProc:
End SubHere you would replace Err.Raise(11) with your actual code.
VBA IsError
Another way to handle errors is to test for them with the VBA ISERROR Function. The ISERROR Function tests an expression for errors, returning TRUE or FALSE if an error occurs.
Sub IsErrorEx()
MsgBox IsError(Range("a7").Value)
End SubVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
If Error VBA
You can also handle errors in VBA with the Excel IFERROR Function. The IFERROR Function must be accessed by using the WorksheetFunction Class:
Sub IfErrorEx()
Dim n As Long
n = WorksheetFunction.IfError(Range("a10").Value, 0)
MsgBox n
End SubThis will output the value of Range A10, if the value is an error, it will output 0 instead.
VBA Error Types
Runtime Errors
As stated above:
VBA Runtime Errors are errors that occur during code execution. Examples of runtime errors include:
- Referencing a non-existent workbook, worksheet, or other object
- Invalid data ex. referencing an Excel cell containing an error
- Attempting to divide by zero
You can “error handle” runtime errors using the methods discussed above.
Syntax Errors
VBA Syntax Errors are errors with code writing. Examples of syntax errors include:
- Mispelling
- Missing or incorrect punctuation
The VBA Editor identifies many syntax errors with red highlighting:
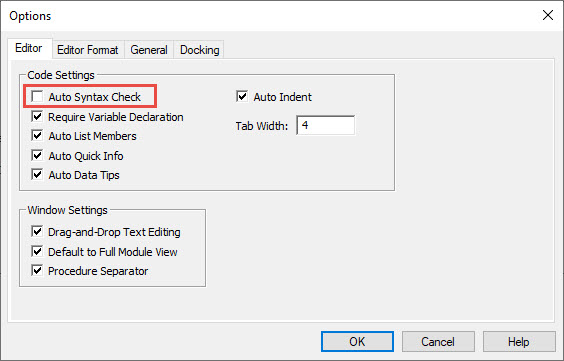
The VBA Editor also has an option to “Auto Syntax Check”:
When this is checked, the VBA Editor will generate a message box alerting you syntax errors after you enter a line of code:
I personally find this extremely annoying and disable the feature.
Compile Errors
Before attempting to run a procedure, VBA will “compile” the procedure. Compiling transforms the program from source code (that you can see) into executable form (you can’t see).
VBA Compile Errors are errors that prevent the code from compiling.
A good example of a compile error is a missing variable declaration:
Other examples include:
- For without Next
- Select without End Select
- If without End If
- Calling a procedure that does not exist
Syntax Errors (previous section) are a subset of Compile Errors.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Debug > Compile
Compile errors will appear when you attempt to run a Procedure. But ideally, you would identify compile errors prior to attempting to run the procedure.
You can do this by compiling the project ahead of time. To do so, go to Debug > Compile VBA Project.
The compiler will “go to” the first error. Once you fix that error, compile the project again. Repeat until all errors are fixed.
You can tell that all errors are fixed because Compile VBA Project will be grayed out:
OverFlow Error
The VBA OverFlow Error occurs when you attempt to put a value into a variable that is too large. For example, Integer Variables can only contain values between -32,768 to 32,768. If you enter a larger value, you’ll receive an Overflow error:
Instead, you should use the Long Variable to store the larger number.
Other VBA Error Terms
VBA Catch Error
Unlike other programming languages, In VBA there is no Catch Statement. However, you can replicate a Catch Statement by using On Error Resume Next and If Err.Number <> 0 Then. This is covered above in Error Handling with Err.Number.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
VBA Ignore Error
To ignore errors in VBA, simply use the On Error Resume Next statement:
On Error Resume NextHowever, as mentioned above, you should be careful using this statement as it doesn’t fix an error, it just simply ignores the line of code containing the error.
VBA Throw Error / Err.Raise
To through an error in VBA, you use the Err.Raise method.
This line of code will raise Run-time error ’13’: Type mismatch:
Err.Raise (13)VBA Error Trapping
VBA Error Trapping is just another term for VBA Error Handling.
VBA Error Message
A VBA Error Message looks like this:
When you click ‘Debug’, you’ll see the line of code that is throwing the error:
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
VBA Error Handling in a Loop
The best way to error handle within a Loop is by using On Error Resume Next along with Err.Number to detect if an error has occurred (Remember to use Err.Clear to clear the error after each occurrence).
The example below will divide two numbers (Column A by Column B) and output the result into Column C. If there’s an error, the result will be 0.
Sub test()
Dim cell As Range
On Error Resume Next
For Each cell In Range("a1:a10")
'Set Cell Value
cell.Offset(0, 2).Value = cell.Value / cell.Offset(0, 1).Value
'If Cell.Value is Error then Default to 0
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
cell.Offset(0, 2).Value = 0
Err.Clear
End If
Next
End SubVBA Error Handling in Access
All of the above examples work exactly the same in Access VBA as in Excel VBA.
Function DelRecord(frm As Form)
'this function is used to delete a record in a table from a form
On Error GoTo ending
With frm
If .NewRecord Then
.Undo
Exit Function
End If
End With
With frm.RecordsetClone
.Bookmark = frm.Bookmark
.Delete
frm.Requery
End With
Exit Function
ending:
End
End Function
Error handling refers to the way runtime errors are handled. Error handling in VBA is done using the On Error statement and the Err object. Runtime errors can be generated by attempting to execute error-causing code or they can be raised explicitly using the Err.Raise method. There are a number of built-in types of runtime errors, and custom errors can be defined as well. Each type of runtime error has a unique number which can be used to determine at runtime which type of error has occurred and respond accordingly.
On Error
The On Error statement is used to control what happens when a runtime error occurs. The On Error statement sets or removes the current error handling scope. When a runtime error occurs in VBA the error trap is triggered and if an On Error statement has been set, VBA will respond according to which type of On Error statement was used.
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| On Error Resume Next | Skips lines of code that cause errors. Use with caution. |
| On Error GoTo Line | When an error occurs execution will jump to a specified label or line number. |
| On Error GoTo 0 | Clears the current error and disables error handling. |
| On Error GoTo -1 | Clears the current error and resets the error trap. |
| Resume | When used after the On Error GoTo statement, Resume will continue execution from the line of code that caused the error. |
| Resume Next | When used after the On Error GoTo statement, Resume Next will continue execution from the line of code directly after the line that caused the error. |
| Resume Line | When used after the On Error GoTo statement, Resume Line will jump to a specified label or line number and continue execution. |
On Error Resume Next
Public Sub Example()
On Error Resume Next
Err.Raise 1004
Debug.Print "Error was skipped"
End SubOn Error GoTo Line
Public Sub Example()
On Error GoTo HandleError
Err.Raise 1004
Exit Sub
HandleError:
Debug.Print "Error Handled"
End SubNote: It is not recommended to use line numbers.
Public Sub Example()
10
20 On Error GoTo 80
30
40 Err.Raise 1004
50
60 Exit Sub
70
80 Debug.Print "Error Handled"
90
End SubOn Error GoTo…Resume
Public Sub Example()
Dim N As Long
N = 0
On Error GoTo HandleError
'Divide by zero error will be fixed by error handler
Debug.Print 1 / N
Debug.Print "Error Handled."
Exit Sub
HandleError:
If Err.Number = 11 Then
Debug.Print "Handling 'Division by zero' Error..."
N = 1
Resume
Else
Err.Raise Err.Number
End If
End SubOn Error GoTo…Resume Next
Public Sub Example()
On Error GoTo HandleError
Err.Raise 1004
Debug.Print "Error Handled. Resuming Next..."
Exit Sub
HandleError:
Debug.Print "Handling Error..."
Resume Next
End SubOn Error GoTo…Resume Line
Public Sub Example()
On Error GoTo HandleError
Err.Raise 1004
Continue:
Debug.Print "Resuming..."
Exit Sub
HandleError:
Debug.Print "Error Handled"
Resume Continue
End SubNote: It is not recommended to use line numbers.
Public Sub Example()
10
20 On Error GoTo 100
30
40 Err.Raise 1004
50
60 Debug.Print "Resuming..."
70
80 Exit Sub
90
100 Debug.Print "Error Handled"
110 Resume 60
120
End SubOn Error GoTo 0
Public Sub Example()
On Error Resume Next
Err.Raise 1004 'Error will be skipped
On Error GoTo 0
Err.Raise 1004 'Error will be raised
End SubOn Error GoTo -1
Public Sub Example()
On Error GoTo HandleError1
Err.Raise 1004
Exit Sub
HandleError1:
Debug.Print "HandleError1"
On Error GoTo -1
On Error GoTo HandleError2
Err.Raise 1004
Exit Sub
HandleError2:
Debug.Print "HandleError2"
Exit Sub
End SubThe Err Object
The Err Object is used to access information about a runtime error that has occurred. When a runtime error occurs, the Err object’s properties are filled with information about the error. The Err object can also be used to raise errors explicitly.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Clear | Clears properties of the Err object. Does NOT reset error trap or clear error handling scope. |
| Description | A text description of the error. |
| HelpContext | The context ID for a topic in a help file. |
| HelpFile | The path to help file. |
| LastDllError | Returns a system error code produced by a call to a dynamic-link library (DLL). Read-only. Always returns zero on Mac. |
| Number | The error number, 0 through 65535. |
| Raise | Raises a specified runtime error. |
| Source | The name of the object or application that originated the error. |
The Err Object is a Singleton
The Err object has a single default global instance and cannot be instantiated. The Err object can be accessed anywhere in VBA just by typing Err.
Public Sub Example()
Err.Raise 1004 'No need to instantiate Err object
End SubPublic Sub Example()
Dim E As ErrObject
Set E = New ErrObject 'Causes error
End SubProperties
The Err object’s properties are filled with data when a runtime error occurs. The Number property is especially important because it can be used to dynamically respond to different types of errors. If no runtime error has occurred, the Number property will be 0. Therefore, to determine if an error has occurred in a particular line, the Number property can be checked to see if it is 0 or not.
Public Sub Example()
On Error Resume Next
Err.Raise 1004
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
With Err
Debug.Print "Number: " & .Number
Debug.Print "Description: " & .Description
Debug.Print "Source: " & .Source
Debug.Print "HelpFile: " & .HelpFile
Debug.Print "HelpContext: " & .HelpContext
Debug.Print "LastDllError: " & .LastDllError
End With
Err.Raise Err.Number
Else
Debug.Print "No Error"
End If
End SubClearing The Err Object
The Err object can be reset in a few different ways. The Err object is reset when Err.Clear is called, a Resume or Resume Next statement is executed for the error, or another On Error statement is executed. Exiting an error-causing procedure does not reset the Err object.
Note: Exiting an error-causing procedure does not reset the Err object.
Public Sub Example()
Call ErrorCausingProcedure1
Debug.Print Err.Number 'Prints 1004
Call ErrorCausingProcedure2
Debug.Print Err.Number 'Prints 0
Call ErrorCausingProcedure3
Debug.Print Err.Number 'Prints 0
Call ErrorCausingProcedure4
Debug.Print Err.Number 'Prints 0
End Sub
Public Sub ErrorCausingProcedure1()
'Exiting procedure doe NOT reset the Err object
On Error Resume Next
Err.Raise 1004
End Sub
Public Sub ErrorCausingProcedure2()
'Calling Err.Clear resets the Err object
On Error Resume Next
Err.Raise 1004
Err.Clear
End Sub
Public Sub ErrorCausingProcedure3()
'Resume Next resets the Err object
On Error GoTo HandleError
Err.Raise 1004
Exit Sub
HandleError:
Resume Next
End Sub
Public Sub ErrorCausingProcedure4()
'On Error statement resets the Err object
On Error Resume Next
Err.Raise 1004
On Error GoTo 0
End SubCalling Err.Clear only clears the Err object. Err.Clear does not reset the error handling trap or end the error handling scope. On Error GoTo -1 will clear the Err object and reset error trapping, allowing another error to be raised. On Error GoTo 0 will clear the Err object and clear the error handling scope.
Public Sub Example()
On Error Resume Next
'Error is skipped
Err.Raise 1004
'Prints 1004
Debug.Print Err.Number
'Err object is reset
Err.Clear
'Prints 0
Debug.Print Err.Number
'Error is skipped because error handling scope was not reset
Err.Raise 1004
'Prints 1004
Debug.Print Err.Number
'Clears Err object and error handling scope
On Error GoTo 0
'Prints 0
Debug.Print Err.Number
'Raises a runtime error
Err.Raise 1004
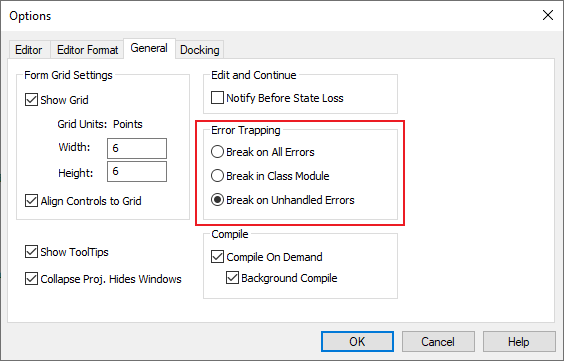
End SubError Trapping Options
Error Trapping options can be selected which can override error handling code in VBA. To change error trapping options navigate to Tools → Options → General in the Visual Basic Editor.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Break on All Errors | Will enter break mode when any error is encountered regardless of error handling code. |
| Break in Class Module | Will enter break mode and show errors inside class modules. |
| Break on Unhandled Errors | This is the default setting. Will enter break mode when an error is encountered and it is not handled by code. |
CVErr Function
The CVErr function can be used to return an error from a function. CVErr returns a value of type Variant with subtype Error. Only variables of type Variant can be assigned a value using the CVErr function. CVErr can take any error number as an argument. CVErr can be used to return a cell error from a user-defined function that is intended for use in spreadsheets.
Option Explicit
Public Function ReturnValueError() As Variant
'Shows #VALUE Error in cell
ReturnValueError = CVErr(xlErrValue)
End Function| xlErr Constant | Cell Error |
|---|---|
| xlErrBlocked | #BLOCKED! |
| xlErrCalc | #CALC! |
| xlErrConnect | #CONNECT! |
| xlErrDiv0 | #DIV/0! |
| xlErrField | #FIELD! |
| xlErrGettingData | #GETTING_DATA |
| xlErrNA | #N/A |
| xlErrName | #NAME? |
| xlErrNull | #NULL! |
| xlErrNum | #NUM! |
| xlErrRef | #REF! |
| xlErrSpill | #SPILL! |
| xlErrUnknown | #UNKNOWN! |
| xlErrValue | #VALUE! |
IsError Function
The IsError function returns True if the argument expression evaluates to an error. IsError can be used to test if a cell value contains an error or a user-defined function returns an error. To return an error from a function use the CVErr function.
Option Explicit
Public Sub Example()
If IsError(Range("A1").Value) Then
Debug.Print "Range A1 contains an error."
End If
Dim E As Variant
E = ReturnError()
If IsError(E) Then
Debug.Print "E is Error: " & CStr(E)
End If
End Sub
Public Function ReturnError() As Variant
ReturnError = CVErr(xlErrValue)
End FunctionError Function
The Error/Error$ function is used to return the description text of an error. The Error function can be used to return a specific error description based on an error number or it can return the description text of the last error to occur.
Specific Error Description
Pass the optional ErrorNumber argument to the Error function to return a specific error description. Although the Error function can take a number between -2147483648 and 65535, it should be intended for use with the range 0 through 65535. If the error number is outside the valid range an Overflow runtime error will occur. If the error number is within the valid range but is not defined, the message «Application-defined or object-defined error» will be returned.
Public Sub Example()
Debug.Print Error(5) 'Prints: Invalid procedure call or argument
End SubMost Recent Error Description
Call the Error function with no ErrorNumber argument to return the description text for the last error to occur. If no error has occurred, a zero-length string will be returned. The Err.Description property can be used to get the text description of the most recent runtime error instead of using the Error function.
Public Sub Example()
On Error Resume Next
Err.Raise 5
Debug.Print Error() 'Prints: Invalid procedure call or argument
End SubRaising Errors
Use the Err.Raise method to raise a runtime error. Errors should be raised when an unacceptable state has been reached in a program. Existing VBA error numbers can be used to raise errors or custom error numbers can be created.
Raising Existing Errors
An appropriate VBA error number can be selected which describes the error.
Public Function RandomLong(MinValue As Long, MaxValue As Long) As Long
If MinValue > MaxValue Then
Err.Raise 5
End If
Randomize
RandomLong = Int((MaxValue - MinValue + 1) * Rnd + MinValue)
End FunctionUser-Defined Errors
To raise a user-defined error, create an error number by using the vbObjectError constant and adding a number between 513 and 65535. The range 0 through 512 is reserved for system errors. The vbObjectError constant has the value -2147221504 so user-defined errors will be negative. To derive the positive portion of a user-defined error simply subtract the vbObjectError constant from the error number.
Public Sub Example()
On Error GoTo HandleError
Err.Raise Number:=vbObjectError + 513, Description:="Custom Error"
Exit Sub
HandleError:
Debug.Print Err.Number - vbObjectError, Err.Description 'Prints: 513 Custom Error
Resume Next
End SubError Statement
The Error statement raises a runtime error for a given error number. The Error statement is included for backward compatibility with older versions of VBA and Err.Raise should be used instead for new code.
Public Sub Example()
'Backward compatible
Error 5
'Use this for new code
Err.Raise 5
End SubError Numbers
Runtime errors each have a number used to identify what type of error it is. Error numbers can be used with the Err.Raise method, the Error statement, and the Error function. When a runtime error occurs, the Err.Number property will be set to the number associated with the type of error. Any positive error number not listed in the table below returns «Application-defined or object-defined error».
| Error Number | Error Text |
|---|---|
| 3 | Return without GoSub |
| 5 | Invalid procedure call or argument |
| 6 | Overflow |
| 7 | Out of memory |
| 9 | Subscript out of range |
| 10 | This array is fixed or temporarily locked |
| 11 | Division by zero |
| 13 | Type mismatch |
| 14 | Out of string space |
| 16 | Expression too complex |
| 17 | Can’t perform requested operation |
| 18 | User interrupt occurred |
| 20 | Resume without error |
| 28 | Out of stack space |
| 35 | Sub or Function not defined |
| 47 | Too many DLL application clients |
| 48 | Error in loading DLL |
| 49 | Bad DLL calling convention |
| 51 | Internal error |
| 52 | Bad file name or number |
| 53 | File not found |
| 54 | Bad file mode |
| 55 | File already open |
| 57 | Device I/O error |
| 58 | File already exists |
| 59 | Bad record length |
| 61 | Disk full |
| 62 | Input past end of file |
| 63 | Bad record number |
| 67 | Too many files |
| 68 | Device unavailable |
| 70 | Permission denied |
| 71 | Disk not ready |
| 74 | Can’t rename with different drive |
| 75 | Path/File access error |
| 76 | Path not found |
| 91 | Object variable or With block variable not set |
| 92 | For loop not initialized |
| 93 | Invalid pattern string |
| 94 | Invalid use of Null |
| 96 | Unable to sink events of object because the object is already firing events to the maximum number of event receivers that it supports |
| 97 | Can not call friend function on object which is not an instance of defining class |
| 98 | A property or method call cannot include a reference to a private object, either as an argument or as a return value |
| 321 (1 — 2) | Invalid file format |
| 322 | Can’t create necessary temporary file |
| 325 | Invalid format in resource file |
| 380 (1 — 2) | Invalid property value |
| 381 | Invalid property array index |
| 382 | Set not supported at runtime |
| 383 | Set not supported (read-only property) |
| 385 | Need property array index |
| 387 | Set not permitted |
| 393 | Get not supported at runtime |
| 394 | Get not supported (write-only property) |
| 422 | Property not found |
| 423 | Property or method not found |
| 424 | Object required |
| 429 | ActiveX component can’t create object |
| 430 | Class does not support Automation or does not support expected interface |
| 432 | File name or class name not found during Automation operation |
| 438 | Object doesn’t support this property or method |
| 440 | Automation error |
| 442 | Connection to type library or object library for remote process has been lost. Press OK for dialog to remove reference. |
| 443 | Automation object does not have a default value |
| 445 | Object doesn’t support this action |
| 446 | Object doesn’t support named arguments |
| 447 | Object doesn’t support current locale setting |
| 448 | Named argument not found |
| 449 | Argument not optional |
| 450 | Wrong number of arguments or invalid property assignment |
| 451 | Property let procedure not defined and property get procedure did not return an object |
| 452 | Invalid ordinal |
| 453 | Specified DLL function not found |
| 454 | Code resource not found |
| 455 | Code resource lock error |
| 457 | This key is already associated with an element of this collection |
| 458 | Variable uses an Automation type not supported in Visual Basic |
| 459 | Object or class does not support the set of events |
| 460 (1 — 2) | Invalid clipboard format |
| 461 | Method or data member not found |
| 462 | The remote server machine does not exist or is unavailable |
| 463 | Class not registered on local machine |
| 481 (1 — 2) | Invalid picture |
| 482 (1 — 2) | Printer error |
| 735 | Can’t save file to TEMP |
| 744 | Search text not found |
| 746 | Replacements too long |
| 1004 | Application-defined or object-defined error |
| 31001 | Application-defined or object-defined error. *Out of memory |
| 31004 | Application-defined or object-defined error. *No object |
| 31018 | Application-defined or object-defined error. *Class is not set |
| 31027 | Application-defined or object-defined error. *Unable to activate object |
| 31032 | Application-defined or object-defined error. *Unable to create embedded object |
| 31036 | Application-defined or object-defined error. *Error saving to file |
| 31037 | Application-defined or object-defined error. *Error loading from file |
In a VBA code, there may be some errors like syntax errors, compilation errors, or runtime errors so we need to handle these errors. Suppose there is a code of 200 lines and the code has an error it’s very difficult to find an error in the code of 200 lines so it’s better to handle the error where we are expecting some error in our code. There are many errors handling methods in VBA which we will discuss in this article but before that, we will discuss types of error.
VBA Errors
Syntax Error
This error will occur if any syntax is not correctly written in the code then VBA will display an error message.
Examples of Syntax Error
Compilation Error
When there is a statement where there is an error in more than one line of its statement then VBA will display an error message. In the following example, a for loop is written without Next which is a compilation error
Runtime Error
A code that is written perfectly but an error occurs at the time of execution. For example, if a file address is attached to the code which doesn’t exist or when a number is divided by zero a case runtime error occurs.
Logical Error
The compiler can not highlight the logical errors but it will give a wrong output. The code will run without any error but the output will come wrong. In case of a large number of codes, it is difficult to identify the logical errors we need to press “F8” it will run the code one line at a time and we can identify the mistakes for which we are getting the wrong output. The following code is written to the difference between two numbers where we are getting the summation of two numbers.
Here, we can identify our logical error that instead of “-” we have written “+”
Expected Vs Unexpected Errors
- Expected Errors: Where we are expecting to get an error, there we write our own code to handle the error.
- Unexpected Errors: Where we don’t need to write our own code we have VBA error handling statements to handle the errors
Types of Error Handling Statements
On Error
It is used to handle errors that occur during run time.
- On Error GoTo 0: This statement will show an error message that a number or a variable is divided by zero.
- On Error Resume Next: It tells VBA if it gets a run time error then don’t show the error message simply resume to the next statement.
- On Error GoTo [label]: If it gets an error then it will go to the specific statement which we will mention in the “label” part.
The Err Object
When an error occurs an err object is created with help of that we can get the type of error and error number.
The Er1 Function
It is used to get the line number of the error.
Err.Raise
We can create our own errors with the help of this method.
Syntax: Err. Raise [Number of the error],[Source of the error], [Description of the error]
From 1-512, number of errors is reserved by VBA. So, we can use anything from 513 to 65535.
Err.Clear
It is used to clear the number and type of the error from the Err.Object.
Error Function
It is used to print the description of the error from its number.
Last Updated :
16 Nov, 2022
Like Article
Save Article