Опубликовано:
- DevOps
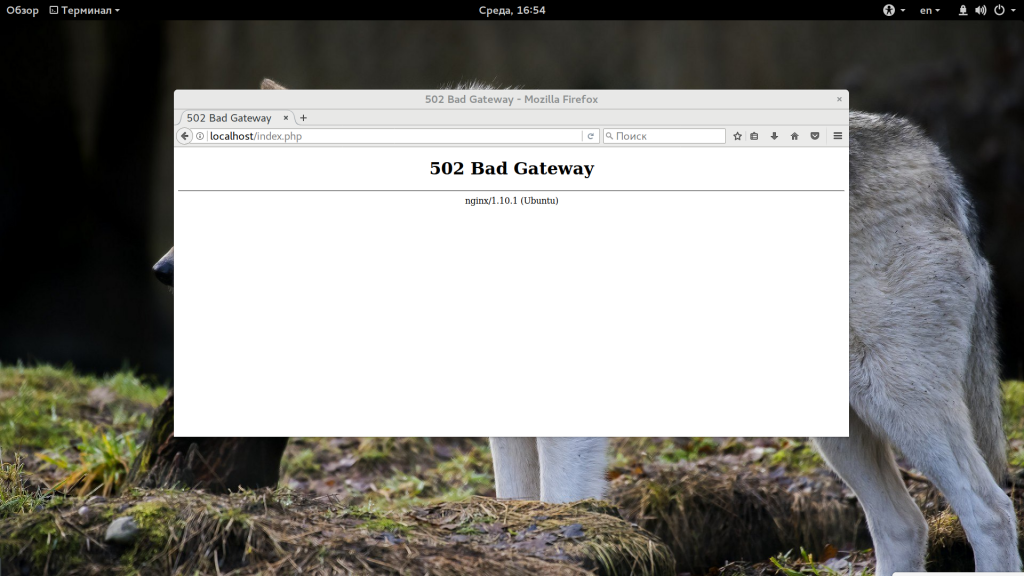
502 Bad Gateway обычно возникает, когда Nginx работает, как обратный прокси-сервер и не может подключиться к серверным службам. Это может быть связано со сбоем службы, сетевыми ошибками, проблемами конфигурации и т.д. Рассмотрим пять основных причин возникновения этой ошибки и то, как их исправить.
Поддерживать сервер сложно.
Вам приходится иметь дело со всеми обновлениями, исправлениями безопасности и случайными ошибками сервера (они же ошибки из ада).
Одной из таких распространённых ошибок на серверах Nginx является 502 Bad Gateway
.
Сообщение об ошибке загадочно.
Итак, многие веб-мастера засучивают рукава и смотрят error.log:
2017/04/04 08:34:43 [error] 949#949: *7 connect() failed (111: Connection refused) while connecting to upstream, client: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX, server: myserver.com, request: "GET /myurl-this/ HTTP/1.0", subrequest: "/redis-fetch", upstream: "redis://127.0.0.1:6379", host: "refserver.com", referrer: "http://referalsite.com/myurl-this/"Да, ещё больше непонятного…
Вы понимаете, что что-то напутано, потому что он сообщает failed
(сбой) и refused
(отказ).
Но что это означает?
Вот решение. Мы перечислили пять основных причин возникновения ошибки Nginx 502 Bad Gateway
и способы их решения.
Сбой серверной службы
Nginx зависит от серверных служб, таких как PHP-FPM, служб баз данных и серверов кэша для запуска веб-приложений.
Таким образом, если какой-либо из этих сервисов выйдет из строя или зависнет, Nginx не получит никаких данных, что приведёт к ошибке 502 Bad Gateway
.
Службы, которые, как мы видели, сбоили — это:
- PHP-FPM
- Apache
- Cache
- Database
Причины сбоя службы могут варьироваться от всплесков трафика и ограничений ресурсов до ошибок диска и DDoS-атак.
Если вы подозреваете, что серверная служба не отвечает или вышла из строя, попробуйте завершить все не отвечающие процессы и перезапустить службу.
Например, вот один из способов убить нефункционирующие процессы PHP-FPM и перезапустить службу.
$ kill -9 $(pgrep php-fpm)
$ /etc/init.d/php-fpm restart
* Restarting PHP FastCGI Process Manager php-fpm [ OK ]Внимание: Не запускайте эти команды, если не знаете, как они работают.
Если перезапуск службы не сработал, возможно, вам придётся попросить кого-нибудь более внимательно изучить состояние сервера.
Высокая нагрузка на сервер
Вторая наиболее распространённая причина ошибки Nginx 502 Bad Gateway
является высокая средняя загрузка серверов.
Всплески нагрузки приводят к тому, что службы не отвечают. Мы видели следующие причины скачков нагрузки:
- Внезапный всплеск посещаемости сайта (может быть сезонным или маркетинговым/рекламным).
- Заражение вредоносным программным обеспечением (вирусы/трояны/майнеры/сканеры и т.д.) на сервере.
- Рассылка спама в комментариях или использование других уязвимостей.
- Брут форс атаки на веб-приложения.
- Ошибки приложений, вызывающие утечку памяти или перегрузку ресурсов.
Для устранения проблем с высокой нагрузкой, сначала необходимо выяснить, какой ресурс используется (ввод/вывод, память, процессор или сеть).
Нужно узнать какая служба злоупотребляет этим ресурсом, и с этого момента узнаем, какой пользователь в этой службе владеет вредоносным сценарием или программным обеспечением.
Неправильная конфигурация сервиса
Сервер Nginx и серверные службы зависят от многих подсистем. Таких, как DNS resolver, процессы Apache, службы PHP, сервер базы данных и т.д. Если даже одна из этих служб имеет неправильную конфигурацию, эта служба не сможет ответить, и Nginx покажет ошибку 502 Bad Gateway
.
Проблемы с конфигурацией, с которой мы сталкивались:
- DNS resolver неправильно настроен в Nginx, что приводит к сбою поиска домена.
- Данные логина БД настроены неправильно после недавней миграции, восстановления или обновления.
- Синтаксическая ошибка настроек брандмауэра Apache (mod-security), вызывающая сбой Apache.
- Для приложений PHP установлены неправильные ограничения памяти или файлов.
- Ограничения пропускной способности (например, количество подключений на IP-адрес) установлены слишком строго, что приводит к сбою легальных посетителей.
- …и многое другое.
Не существует простого способа обнаружения ошибки конфигурации. Вам нужно просмотреть error.log и обратить внимание на то, что написано об ошибке.
Например, эта ошибка сообщает, что приложение PHP достигло максимально допустимого предела процессов (определяемого параметром pm.max_children).
WARNING: [mysite.com] server reached max_children setting (30), consider raising it
ERROR: unable to read what child say: Bad file descriptor (9)Если вы не знакомы с PHP или настройками веб-сервера, лучше всего обратиться к администратору сервера.
Порт сервиса заблокирован в брандмауэре
Брандмауэры/файрволлы — основа безопасности сервера. Но если их неправильно настроить, это может привести к блокировке запросов или сбою служб.
Например, на серверах Linux, на которых работает пакет автоматизации Plesk, Nginx работает на 80 порту, а Apache на 7080. Но брандмауэры/файрволлы по умолчанию блокируют необычные порты, и это приведёт к том, что Nginx не сможет подключиться к Apache.
Результат? Ошибка 502 Bad Gateway.
Такие проблемы часто возникают при включении новой службы (например, кэширующий сервис, Ruby, и т.д.) в бэкенде, во время миграции или после обновления сервера.
Чтобы исправить это, мы смотрим, на каком порту работает каждая служба с помощью следующей команды:
$ netstat -lpn
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 19785/nginx
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 19785/nginxИ если мы обнаруживаем, что какая-либо служба работает на нестандартных портах, мы либо изменим конфигурацию службы, чтобы изменить её на стандартный порт. Либо отредактируем конфигурацию брандмауэра, чтобы разрешить нестандартный порт.
Ошибки веб-приложений
Редким случаем ошибки 502 Bad Gateway
является ошибка приложения.
Если журнал ошибок веб сервера показывает пугающую ошибку, подобную этой, возможно, код приложения не совместим с версией сервера.
[notice] child pid 27831 exit signal Segmentation fault (11)Вам нужно будет проверить требования вашего приложения и настроить службы, чтобы они соответствовали требуемым версиям.
Итог
Ошибка 502 Bad Gateway в Nginx обычно возникает, когда Nginx работает как обратный прокси и не может подключиться к серверным службам. Это может быть связано со сбоями службы, сетевыми ошибками, проблемами конфигурации и т.д. Мы рассмотрели пять основных причин этой ошибки и способы её устранения.
A 502 Bad Gateway Nginx error is an HTTP status code that represents a server acting as a gateway or proxy server failing to receive a valid response from an upstream server. In the case of Nginx, a 502 bad gateway error occurs when the server cannot establish a connection with the upstream server or when the upstream server returns an invalid response.
This error is commonly seen when trying to access a website or web application that is hosted behind a reverse proxy or load balancer.
There are multiple variations of 502 Bad gateway Nginx Error you might find on different sites. For example:
- HTTP Error 502- Bad Gateway
- 502 Proxy Error
- 502 Bad Gateway
- 502 Service Temporarily Overloaded
- HTTP 502
- 502 Bad Gateway NGINX
- Error 502
Nginx is a well-known open-source web server that is highly popular for its performance, scalability, and flexibility. However, similar to other web servers, Nginx can face errors that hinder its ability to deliver content to clients. One such error is the 502 Bad Gateway Nginx error.
Encountering errors can be quite frustrating and confusing, especially if you are not technically proficient. You may come across several similar prominent errors, such as the white screen of death, and the error establishing database connection. But 502 bad gateway nginx error is a very popular one.
There can be multiple possible reasons for this error to happen and therefore different ways to troubleshoot it. In this post, we will tell you what 502 bad gateway Nginx really means, its possible causes and what are the best troubleshooting method you must follow.
Let us get started!
Read: 🚩 15 Methods to Fix 502 Bad Gateway Error on Your Website
What Causes a 502 Bad Gateway Nginx Error?
There can be several reasons why a 502 Bad Gateway error may occur in Nginx, but here are some of the most common ones listed down below:
Server Overload
When a backend server receives too many requests, it can become overloaded and fail to respond within the timeout period. This causes a 502 error as the upstream server cannot fulfill the client’s request. Proper server sizing, resource allocation, load balancing, and scaling strategies can prevent server overload.
Connectivity Issues
- Connectivity issues can cause a 502 Bad Gateway error in Nginx when there is a problem with the network connection between the reverse proxy server and the backend server.
- This can happen due to network congestion, misconfigured network settings, or hardware failures.
- When the reverse proxy server attempts to forward a request to the backend server but cannot establish a connection, it returns a 502 error to the client.
- The error occurs because the reverse proxy server acts as an intermediary between the client and the backend server and is unable to connect to the backend server to fulfill the client’s request.
- Troubleshooting network settings, checking firewall rules, and monitoring network traffic can help fix the issue.
DNS Issues
- DNS issues can cause a 502 Bad Gateway error in Nginx when the DNS resolution for the backend server fails.
- This can happen due to incorrect DNS configurations, DNS server failures, or DNS caching issues.
- When a client sends a request to the reverse proxy server, the reverse proxy server needs to resolve the domain name of the backend server to an IP address.
- If the DNS resolution fails, the reverse proxy server cannot forward the request to the backend server, resulting in a 502 error being returned to the client.
Read: 🚩 What is DNS?
Firewall Restrictions
- Firewall restrictions can cause a 502 Bad Gateway error in Nginx when a firewall blocks the connection between the reverse proxy server and the backend server.
- This can happen when the firewall is configured to restrict traffic to and from specific IP addresses or ports.
- When the reverse proxy server attempts to connect to the backend server, but the firewall blocks the connection, it returns a 502 error to the client.
- This occurs because the reverse proxy server acts as an intermediary between the client and the backend server and cannot establish a connection with the backend server to fulfill the client’s request.
- To fix firewall-related issues causing a 502 error, you may need to adjust firewall rules to allow traffic to flow between the reverse proxy and backend servers.
Software Bugs
- A 502 Bad Gateway error may occur due to a software bug or misconfiguration in the reverse proxy server or backend server.
- This error can happen because of coding errors or misconfigurations of server modules or applications.
- If the software or configuration of either server contains a bug, it may fail to handle requests or respond within the timeout period, resulting in a 502 error being returned to the client.
- To fix software-related issues causing a 502 error, you may need to examine the logs of both the reverse proxy and backend servers to identify any errors or warning messages.
PHP-FMP is Taking too long to respond
- PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) can cause a 502 Bad Gateway error in Nginx when it fails to respond within the timeout period or encounters a critical error.
- This error can happen due to insufficient resources, misconfiguration, or a bug in the PHP code.
- PHP-FPM is a popular way of running PHP applications in Nginx, where Nginx sends the request to PHP-FPM and it processes the PHP code and returns the result to Nginx, which then sends the response back to the client.
- To fix PHP-FPM-related issues, you may need to adjust the PHP-FPM configuration to increase the number of processes or threads or adjust the timeout settings.
- You may also need to examine the PHP code to identify and fix any bugs or performance issues.
- Additionally, monitoring the server logs and system resources can help identify any patterns or trends that could indicate a larger issue with PHP-FPM.
Read: 🚩 How to Fix HTTP 504 Gateway Timeout Error?
How to Fix a 502 Bad Gateway Nginx?
Here are some best solutions that you can follow to fix a 502 Bad Gateway Nginx error:
- Check the status of Nginx
- Check Backend Server Status
- Check the DNS configuration
- Check the Firewall Configuration
- Increase the Buffer Size
- Restart Nginx Server
- Check PHP-FPM status
Check the status of Nginx
The first thing you need to do is to check whether Nginx is running and responding to requests or not. To do that, run the following command given below:
systemctl status nginx
If the Nginx is running, you will get an output message something like this,
nginx.service - The nginx HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2022-10-11 10:25:41 UTC; 1 days ago
Docs: https://httpd.nginx.org/docs/2.4/
If the Nginx is not running, you will get an output message something like this,
nginx.service - The nginx HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead) since Fri 2022-10-11 10:25:41 UTC; 25s ago
Docs: https://httpd.nginx.org/docs/2.4/
Now, in case the Nginx is not running, you have to start it again by using the following command,
systemctl start nginx
Check Backend Server Status
- Log in to the reverse proxy server that is hosting Nginx.
- Open a terminal window and run the following command:
curl -I http://backend-server-ip-address/
• Replace “backend-server-ip-address” with the IP address of your backend server.
• Check the HTTP status code in the output of the command. If the backend server is running correctly, you should see a status code of 200 OK.
• If you receive a status code other than 200, it indicates that there may be an issue with the backend server. You can further investigate the issue by examining the logs of the backend server to identify any errors or warning messages.
Check the DNS configuration
If the DNS resolution fails, the reverse proxy server cannot forward the request to the backend server, resulting in a 502 Bad Gateway error being returned to the client. Therefore, it is important to verify that the DNS configuration for the backend server is correct.
To check the DNS configuration, you can perform the following steps:
- Log in to the reverse proxy server that is hosting Nginx.
- Open a terminal window and run the following command:
nslookup backend-server-domain-name
Replace “backend-server-domain-name” with the domain name of your backend server.
• Check the output of the command to verify that the correct IP address is returned for the backend server.
- If the output of the command indicates that the DNS resolution failed, there may be an issue with the DNS configuration. You can further investigate the issue by checking the DNS settings for the domain name of the backend server, or by contacting your DNS provider for assistance.
Check the Firewall Configuration
It is advised to check the firewall logs for an unusual block. Sometimes Firewalls also prevent or block sites. To overcome this issue, you need to temporarily disable your firewalls and check whether the issue persists or is resolved.
Increase the Buffer Size
Increasing the buffer size allows Nginx to store more data from the server’s response, ensuring that the response is complete and error-free. To increase the buffer size, you need to edit the Nginx configuration file and add the following directives.
proxy_buffer_size: Sets the size of each buffer. The default value is usually 4K. You can increase it to a higher value depending on your server’s requirements. For example, to set the buffer size to 16K, add the following line to your configuration file:
proxy_buffer_size 16k;
proxy_buffers: Sets the number of buffers to allocate. The default value is usually 8. You can increase it to a higher value depending on your server’s requirements. For example, to set the number of buffers to 32 and the buffer size to 16K, add the following line to your configuration file:
proxy_buffers 32 16k;
Note: It’s important to note that increasing the buffer size and number of buffers will increase memory usage on the server. So, you should experiment with different buffer sizes and buffer numbers to find the optimal setting for your server and application.
- After making changes to the Nginx configuration file, save the file and restart Nginx for the changes to take effect. You can do this by running the following command:
sudo service nginx restart
Restart Nginx Server
In some cases, just restarting the Nginx server may resolve the 502 bad gateway Nginx error. To do this,
You need to run a command in your terminal or shell. The exact command depends on the operating system and distribution you are using, but here are a few examples:
- Ubuntu and Debian:
sudo service nginx restart
- CentOS, Fedora, and RHEL:
sudo systemctl restart nginx
- macOS:
sudo nginx -s reload
These commands will gracefully restart the Nginx server, meaning that it will wait for any active connections to finish before shutting down and starting again.
Check PHP-FPM status
Sometimes, the 502 Bad Gateway Nginx error can also be triggered by PHP-FPM not running. Therefore, it is necessary to check the status of PHP-FPM to ensure it is running properly.
To check the running status, you can use the following command,
sudo service php-fpm status
If PHP-FPM is running, you should see a message stating that it is active.
However, in case PHP-FPM is not running, you can try restarting it using the following command:
sudo service php-fpm restart
This command will restart the PHP-FPM service, which can help resolve any issue that might be triggering a 502 bad gateway Nginx error.
Summary
A 502 Bad Gateway Nginx error is a common error that Nginx users may encounter. It is typically caused by connectivity issues, server overload, DNS issues, firewall restrictions, or software bugs.
However, following the steps outlined in this article, you can troubleshoot and resolve a 502 bad gateway nginx error.
If none of the above methods have worked for you, unfortunately, consider seeking assistance from Nginx forums or a highly experienced and qualified Nginx consultant.
If you have any tips or suggestions regarding the 502 Bad Gateway Nginx error that we may have missed in this post or if you would like to share your experience with the same, please let us know in the comment section below. We welcome your input.
Read: 🚩 How to fix HTTP 500 Internal Server Error in WordPress?
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I fix 502 Bad gateway nginx?
You can fix 502 Bad Gateway nginx error by following the below methods:
1. Check the status of Nginx
2. Check Backend Server Status
3. Check the DNS configuration
4. Check the Firewall Configuration
5. Increase the Buffer Size
6. Restart Nginx Server
7. Check PHP-FPM stat
How do I check my nginx status?
To check the nginx status, Run the following command given below:
systemctl status nginx
The Output will show whether the nginx is running or not.
What is a 502 Bad gateway error?
A 502 Bad Gateway Nginx error is an HTTP status code that represents a server acting as a gateway or proxy server failing to receive a valid response from an upstream server.
502 Bad Gateway is an error website visitors see relatively rarely. However, since it can prevent the users from interacting with the website or the hosted application, website owners should make rectifying this error their top priority.
This error typically occurs when a server acting as a gateway or proxy receives an invalid response from an upstream server. Since NGINX is a popular proxy server, users often see error messages like “502 Bad Gateway” and the active NGINX version.
The NGINX 502 Bad Gateway is a common issue website visitors encounter. There are several possible causes for this error and several solutions. This post will examine the most likely reasons and how site owners and developers can resolve the error.
Let’s start with a short introduction to the error.
Table of Content
- What Does the Error Code 502 Bad Gateway in NGINX Mean?
- What is PHP-FPM & How Does It Work?
- The Top Six Possibilities Behind 502 Bad Gateway in NGINX (And How to Fix Them)
- Reason # 1: NGINX is Not Running
- Examine the NGINX Status
- Examine the NGINX Configuration
- Check the Port Bindings
- Check for Conflicting Services
- Examine the NGINX Error Logs
- Examine The System Resources
- Reason # 2: PHP-FPM Isn’t Working
- Examine the NGINX and PHP-FPM Configurations
- Check the Status of PHP-FPM
- Restart NGINX and PHP-FPM
- Examine the Socket or Address and Port Settings
- Examine PHP-FPM Error Logs
- Examine the File Permissions
- Test Configurations With a Simple PHP Script
- Reason # 3: The PHP-FPM Timeout Has Expired
- Increase the Value of the Timeout
- Restart PHP-FPM Service
- Improve Your PHP Code
- Check for Resource Constraints
- Reason # 4: NGINX Requests Denied by the Firewall
- Examine the Firewall Rules
- Temporarily Disable the Firewall
- Examine the Firewall Logs
- Allow NGINX Through the Firewall
- Test Connectivity
- Reason # 5: A Domain Name is Not Permitted
- Check the server_name Directive
- Examine DNS Resolution
- Reason # 6: Bugs In Web Applications
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What Does the Error Code 502 Bad Gateway in NGINX Mean?
502 Bad Gateway indicates that the server you are trying to reach has encountered an error while communicating with another server. This occurs when one server serves as a proxy to receive data from other servers in the setup. The 502 error occurs when a server returns an error when attempting to connect to another server.
The exciting aspect of this discussion is the several ways to indicate that a 502 error has occurred. Here’re a few ways you’ll find this error being mentioned on various websites:
- 502 Bad Gateway NGINX
- HTTP 502
- HTTP Error 502 – Bad Gateway
- 502 Service Temporarily Overloaded
- Temporary Error (502)
- 502 Bad Gateway
- 502 Proxy Error
- Error 502
As with the 404 Not Found error, developers can customize the appearance of the 502 error page to match the current website design.
Before going into the probable reasons for the 502 Bad Gateway error in NGINX, let’s discuss PHP-FPM and its role in NGINX performance.
What is PHP-FPM & How Does It Work?
PHP applications deployed on a server use PHP-FPM (PHP-FastCGI Process Manager) as a tool for handling web requests. When combined with NGINX, PHP-FPM can make websites run faster and use fewer resources for responding to requests.
If you use PHP-FPM, PHP works as a separate service, and the web requests are handled through a TCP/IP port. NGINX only handles HTTP requests in this configuration, while PHP-FPM reads PHP code. This arrangement ensures a faster response by distributing the workload over two services.
Now that you have a good idea about the 502 Bad Gateway error in NGINX, let’s discuss why this error occurs.
The Top Six Possibilities Behind 502 Bad Gateway in NGINX (And How to Fix Them)
Here’re the six reasons users might encounter the 502 Bad Gateway error.
Reason # 1: NGINX is Not Running
If you receive a “502 Bad Gateway” error, first, you should check whether NGINX is up and running. Here’s how you can debug this problem:
Examine the NGINX Status
Start by confirming that NGINX is up and operating. For this, launch the terminal and enter the following command:
$ sudo service nginx status or systemctl status nginx
As you can see, this command will display the NGINX web server’s current status. If it isn’t running, you’ll see a message saying that NGINX isn’t running.
If that’s the case, you can try restarting it with the following command that restarts NGINX and attempts to bind it to the designated ports:
$ sudo service nginx restart
Examine the NGINX Configuration
An error in the NGINX configuration file can likely stop it from functioning correctly. To verify this, use the following command to verify the configuration syntax:
$ sudo nginx -t
This command checks the NGINX configuration file for syntax issues. If there are any errors, it will specify the exact problem.
You can rectify the mistakes by editing the configuration file (/etc/nginx/nginx.conf or /etc/nginx/conf.d/*). If the syntax is okay, you will see a similar message:
Check the Port Bindings
If NGINX is working correctly, you should next check that NGINX is bound to the adequately designated ports. NGINX listens on port 80 for HTTP and port 443 for HTTPS by default.
Open the NGINX configuration file (/etc/nginx/nginx.conf or /etc/nginx/conf.d/*) and look for the listen directives within the server blocks. Here you should check that the ports are correctly specified.
Check for Conflicting Services
If NGINX does not start because of port conflicts, the main reason is that another service may be already mapped to the same port. You can use the following command to identify any conflicting services:
$ sudo netstat -tuln | grep LISTEN
This command displays all the services currently listening on specific ports. Look for any services that use ports 80 or 443. If you discover any conflicts, you must stop or adjust those services to free up ports for NGINX.
Examine the NGINX Error Logs
When investigating the 502 error, the NGINX logs can help determine what went wrong with the reverse proxy server. Typically, error logs are stored at /var/log/nginx/error.log. We recommend examining these log files for any error messages that may point to the source of the problem.
Examine The System Resources
Verifying that your server has sufficient resources (CPU, RAM, and disc space) to support NGINX operations is always a good idea. Insufficient resources can prevent NGINX from booting up or cause it to crash. We recommend using system monitoring tools or command-line utilities such as htop to examine resource consumption.
Reason # 2: PHP-FPM Isn’t Working
If you’re getting a 502 Bad Gateway error because NGINX and PHP-FPM aren’t “cooperating”, you can troubleshoot the problem by doing the following:
Examine the NGINX and PHP-FPM Configurations
Start by checking that NGINX and PHP-FPM are both correctly configured and functioning.
Open the NGINX configuration file (/etc/nginx/nginx.conf or /etc/nginx/conf.d/*) and verify that the location block for PHP scripts is correctly set up. It should have directives like fastcgi_pass, which points to the PHP-FPM socket or address and port, and fastcgi_param parameters.
Similarly, review the PHP-FPM configuration file (/etc/php-fpm.conf or /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf) to ensure all settings are correctly set up.
Check the Status of PHP-FPM
Check to see if PHP-FPM is currently operational.
For this, launch the terminal or command prompt and type the following command:
$ sudo service php-fpm status
This command displays PHP-FPM’s current status. If it isn’t up, you’ll receive a message that PHP-FPM isn’t running.
Restart NGINX and PHP-FPM
If NGINX and PHP-FPM are running but not communicating correctly, you can try restarting both services.
To restart them, use the following commands:
$ sudo service nginx restart
$ sudo service php-fpm restart
Examine the Socket or Address and Port Settings
Check that the fastcgi_pass directive in the NGINX configuration file is correctly pointing to the PHP-FPM socket or IP and port.
Here’s what a properly formatted directive looks like:
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
If you use a TCP address and port, it should appear like this:
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
Check that the socket or address and port correspond to the PHP-FPM settings. After modifying the configuration, remember to restart both NGINX and PHP-FPM.
Examine PHP-FPM Error Logs
PHP-FPM logs provide essential insight into any PHP script execution issues. Typically, the log file is located in /var/log/php-fpm.log.
Examine the log file for error messages that may illuminate the problem. While you’re at it, we suggest checking NGINX’s error log (/var/log/nginx/error.log) for any relevant error messages.
Examine the File Permissions
An overlooked reason behind PHP-FPM and NGINX-related issues is misconfigured file permissions.
You should confirm that the PHP files and directories have the necessary permissions and ownership so that NGINX can access them and PHP-FPM can execute them.
Typically, PHP files should be readable by the NGINX user, and folders should have appropriate execution rights. Use the chown and chmod commands to change ownership and permissions, if necessary.
Test Configurations With a Simple PHP Script
Write a simple PHP script (we highly recommend printing info.php) to test NGINX and PHP-FPM operations. For this, we suggest the following:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Put this line in a file named info.php and save the file in the web root directory (for example, /var/www/html). Now, visit it using your browser (for example, http://your-domain.com/info.php).
If you can see the PHP information page, the NGINX, and PHP-FPM are working successfully together. If not, it could point to a problem with PHP-FPM settings or communication between NGINX and PHP-FPM.
Reason # 3: The PHP-FPM Timeout Has Expired
The error “The PHP-FPM timeout has expired” usually means that a PHP script executed by PHP-FPM took longer to complete than the timeout value mentioned in the config file.
When PHP-FPM receives a request to execute a PHP script, a worker process is launched to fulfill the request. PHP-FPM terminates the process and returns the timeout error if the script execution exceeds the timeout setting defined in the PHP-FPM configuration.
You can resolve this problem by taking the following steps:
Increase the Value of the Timeout
In the PHP-FPM configuration file (typically /etc/php-fpm.conf or /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf), change the request_terminate_timeout setting directive.
We suggest increasing the value of request_terminate_timeout to allow PHP scripts to run for extended periods.
For instance, in the following example, the timeout is set to 300 seconds (5 minutes):
request_terminate_timeout = 300s
We suggest adjusting the value to meet the needs of your application.
Restart PHP-FPM Service
If you change the PHP-FPM configuration file, you must restart the PHP-FPM service to implement the modifications.
The command may differ depending on your operating system and how PHP-FPM is installed. Here is an example of the restart commands:
$ sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
Improve Your PHP Code
If your PHP script takes too long to execute, you may need to optimize your code to improve its execution time frame. You should focus on finding and optimizing bottlenecks like database requests, intensive computations, or inefficient algorithms.
Check for Resource Constraints
Executing PHP scripts requires server resources. Time-out errors might also occur when a script gets stuck while waiting for the resources to continue execution.
As such, you should ensure that your server has sufficient resources to handle PHP script execution.
Reason # 4: NGINX Requests Denied by the Firewall
If you receive a “502 Bad Gateway” error in NGINX and think that the firewall is blocking requests, try the following ideas to troubleshoot the problem:
Examine the Firewall Rules
Start by checking the firewall rules to ensure it is not blocking inbound requests to NGINX.
Depending on your firewall solution ( iptables, UFW, or Firewalld), the rule syntax about port 80 for HTTP or port 443 for HTTPS might differ. You should check and allow inbound traffic to NGINX, and modify the rules accordingly.
Temporarily Disable the Firewall
As a first step in troubleshooting, temporarily disable the firewall and see if the 502 Bad Gateway error persists. This helps you narrow down the firewall as the source of the problem.
However, you should re-enable the firewall immediately to maintain security.
Examine the Firewall Logs
Check the firewall logs to see whether entries are linked to disallowed requests. In addition, firewall logs can give information about blocked traffic and the reasons for denials. The location of the firewall logs differs depending on the firewall solution. We suggest checking /var/log/iptables.log, /var/log/ufw.log, and /var/log/firewalld.log for the logs.
Allow NGINX Through the Firewall
We recommend allowing NGINX through the firewall to eliminate firewall-related causes of the NGINX 502 Bad Gateway error.
Start by configuring the necessary rules to allow NGINX through the firewall. Make changes to the firewall rules to allow inbound connections on the NGINX ports 80 and 443. The particular instructions or configuration procedures vary depending on the firewall solution.
Here are a couple of examples:
iptables
Use the following commands to whitelist ports 80 and 443 in iptables:
$ sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
$ sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT
UFW (Simplified Firewall)
Use the following commands to whitelist ports 80 and 443 in UFW:
$ sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
$ sudo ufw allow 443/tcp
Firewalld
Use the following commands to whitelist ports 80 and 443 in Firewalld:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=https --permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Test Connectivity
After modifying the firewall rules and validating the NGINX configuration, see if you can connect to NGINX.
Use programs such as Telnet or curl to verify connectivity locally and from remote systems. For example, to test NGINX’s response, use the following command:
# curl -I http://localhost/
If the connection is successful and the expected response is received, the firewall rules allow traffic to the NGINX reverse proxy server.
Reason # 5: A Domain Name is Not Permitted
If you get a “502 Bad Gateway” error message in NGINX with the message “A domain name is not permitted,” it usually means that NGINX received a request for a domain name not configured or allowed in the configuration file.
You can troubleshoot this problem by doing the following:
Check the server_name Directive
Start by checking the server_name directive to see if the domain name causing the problem is included in the directive block. The path should be: /etc/nginx/sites-available/domainname.conf
For example,
server_name example.com www.example.com;
If the domain name is missing or incorrect, add or change the server_name directive.
Examine DNS Resolution
Check that the domain name correctly resolves to the NGINX server’s IP address. You can do DNS lookups with tools like nslookup or dig to ensure the domain name resolves to the correct IP address. Here’s a sample lookup command:
# nslookup example.com
If the domain name does not resolve correctly, you may need to adjust your DNS configuration or contact your DNS provider.
Reason # 6: Bugs In Web Applications
Errors at the application level can (rarely) cause the 502 Bad Gateway error.
If your web server logs contain loading errors similar to the following, the application code may be incompatible with the server version and configuration.
[notice] child pid xxxxx exit signal Segmentation fault (11)
You must examine your application’s software needs and re-configure the services to meet the requirements.
Conclusion
The 502 Bad Gateway in NGINX error usually happens when NGINX runs as a reverse proxy and can’t connect to services on either side of the server setup. This error could occur because of a server crash, a network error, a problem with the NGINX setup, or domain-related issues.
Here at Redswitches, we offer The perfect platform for setting up NGINX as a Reverse Proxy server.
Optimizing a reverse proxy can make it run faster and handle calls more efficiently. Remember that the right configurations and optimizations may differ based on how you use the system and what you expect from the NGINX server. Redswitches is a one-stop solution for all of your website hosting needs.
FAQs
Q. What does the NGINX 502 Bad Gateway error indicate?
The 502 Bad Gateway error means an upstream server sent no or malformed response to the NGINX server in a reverse proxy server role. It usually happens when NGINX can’t connect to the backend server or when the backend server gives an invalid or unexpected response.
Q. Can too much traffic cause a 502 Bad Gateway?
Too much traffic can overwhelm the backend servers or the proxy infrastructure, causing the 502 Bad Gateway problem. In these situations, you may need to optimize your server resources, change timeouts, or use load balancers to handle the extra traffic.
Q. Can DNS problems result in a 502 Bad Gateway error?
Yes, a “502 Bad Gateway” error can be caused by trouble with DNS resolution. Ensure that the upstream server’s IP address can be found by resolving the domain name used in the NGINX setup.
Q. Can a PHP-FPM misconfiguration cause a 502 Bad Gateway error in NGINX?
A 502 Bad Gateway problem in NGINX can happen if PHP-FPM is set up incorrectly. To avoid these errors, ensure that NGINX is set up correctly to talk to PHP-FPM using the correct socket, address, and port. Check the PHP-FPM configuration file (php-fpm.conf or www.conf) to ensure it conforms to the proper NGINX configuration settings.
Начинающие веб-мастера и системные администраторы временами сталкиваются с ошибкой 502 bad gateway nginx. Nginx — это не просто один из лучших веб-серверов, в то же время, он проектировался как отличный прокси. Логически можно предположить, что эта ошибка возникает, когда что-то не так со шлюзом.
И необязательно чтобы вы использовали Nginx в качестве прокси для доступа к сети. Нет, для работы большинства сайтов требуется генерация динамического контента, например, на php. Поэтому Nginx часто выступает в прокси для Apache или php-fpm. В этой статье мы рассмотрим что означает 502 bad gateway Nginx, как исправить ее.
Как и следует из названия, эта ошибка значит, что Nginx попытался связаться со шлюзом и у него ничего не вышло. Например, запросы от пользователей принимает Nginx, поскольку он работает быстро и потребляет мало ресурсов, а за генерацию контента отвечает php-fpm. Если сервис php-fpm во время обработки запроса получил какую-либо ошибку и не вернул результата, или же он вообще отключен и Nginx не может получить к нему доступ мы получим такую ошибку.
Вот основные причины:
- Nginx используется в качестве прокси для Apache или php-fpm, но эти сервисы не запущены;
- Nginx используется качестве прокси для php-fpm, но параметры доступа к сокету неверно настроены;
- Неверно настроены значения размера буфера и таймаута для php-fpm в nginx.conf;
- Ошибки в конфигурации Nginx.
Как исправить ошибку 502 bad gateway Nginx
1. Анализ логов и перезапуск
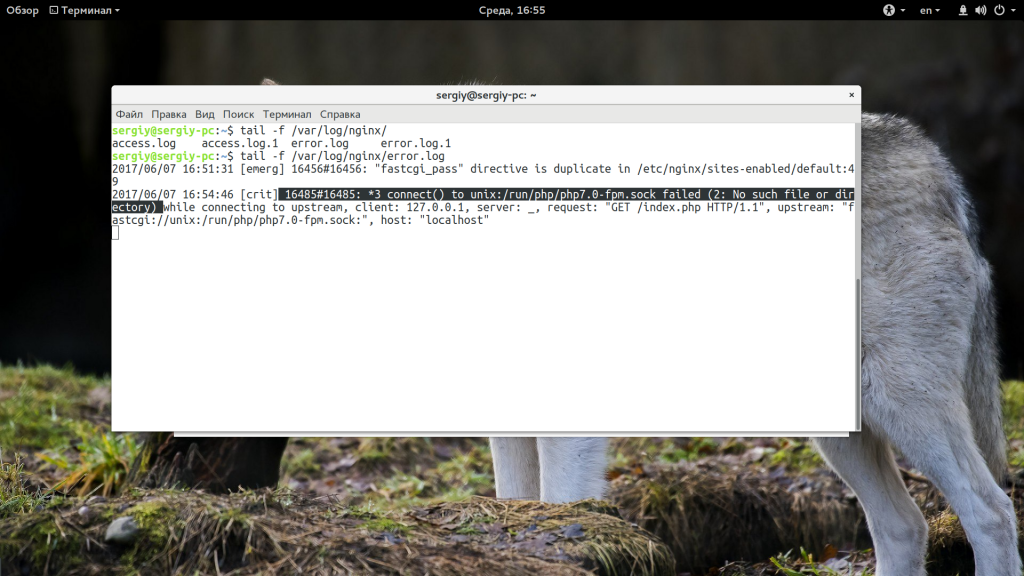
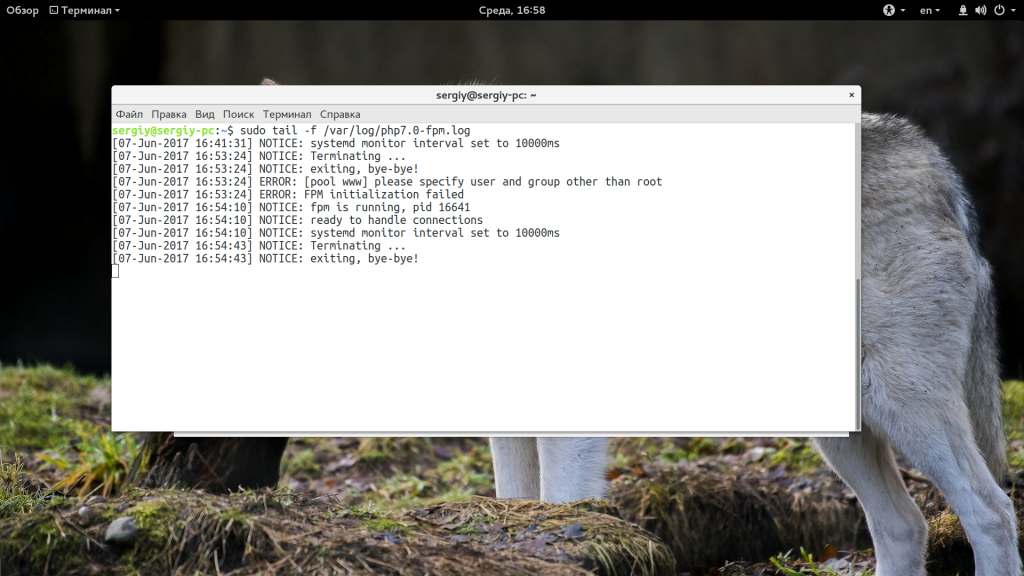
Чтобы исправить ошибку нужно выяснить что случилось со шлюзом. Лучший способ сделать это — посмотреть логи Nginx, там обязательно должно быть что-то написано и намного подробнее, чем в выводе браузера:
tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
Это уже должно дать вам некоторые подсказки что делать дальше. Еще в первую очередь не помешает проверить файл конфигурации Nginx на ошибки:
nginx -t
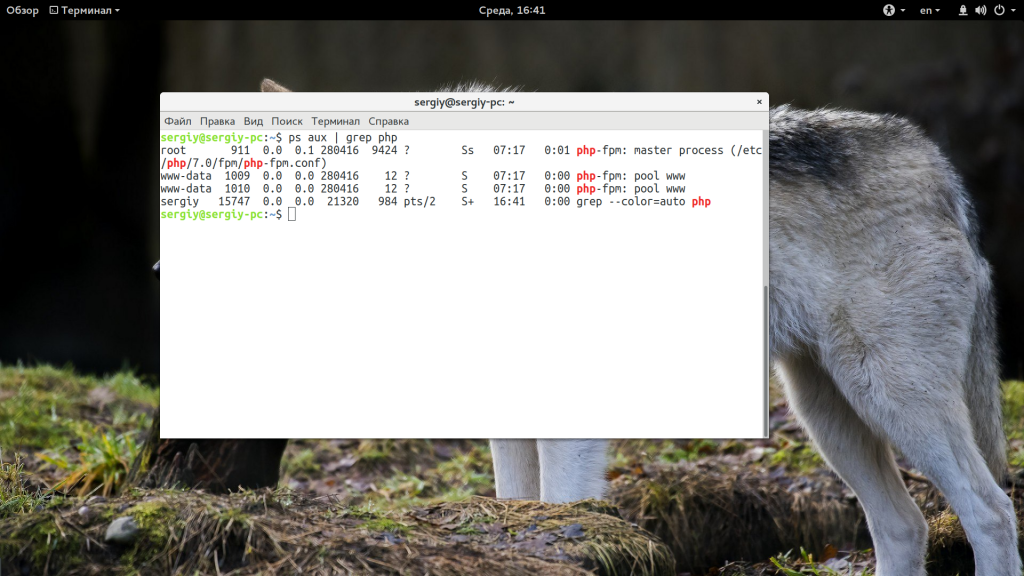
Допустим, у нас в качестве шлюза для генерации динамического содержимого используется php-fpm. Тогда нужно проверить запущен ли вообще этот сервис:
ps aux | grep php
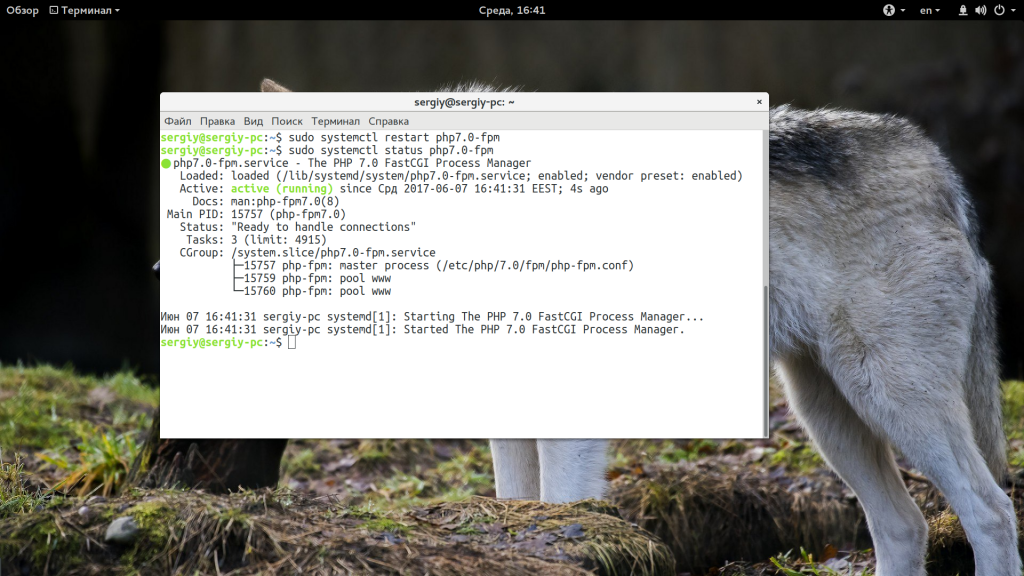
Если все процессы уже запущены, попробуйте перезапустить их с помощью systemd:
sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
Если процесс остановлен, то его нужно запустить:
sudo systemctl start php-fpm
Это самая распространенная причина, вызывающая ошибку 502 Bad Gateway и обычно после перезапуска сервиса все будет работать, вам осталось выяснить только почему он завершился. В этом вам может помочь просмотр лога php-fpm:
sudo tail -f /var/log/php7.0-fpm.log
Но если такой рецепт не помог, и ошибка 502 bad gateway nginx нужно идти дальше. Внимательно пересмотрите лог, возможно, там уже есть ответ.
2. Доступность php-fpm и владелец
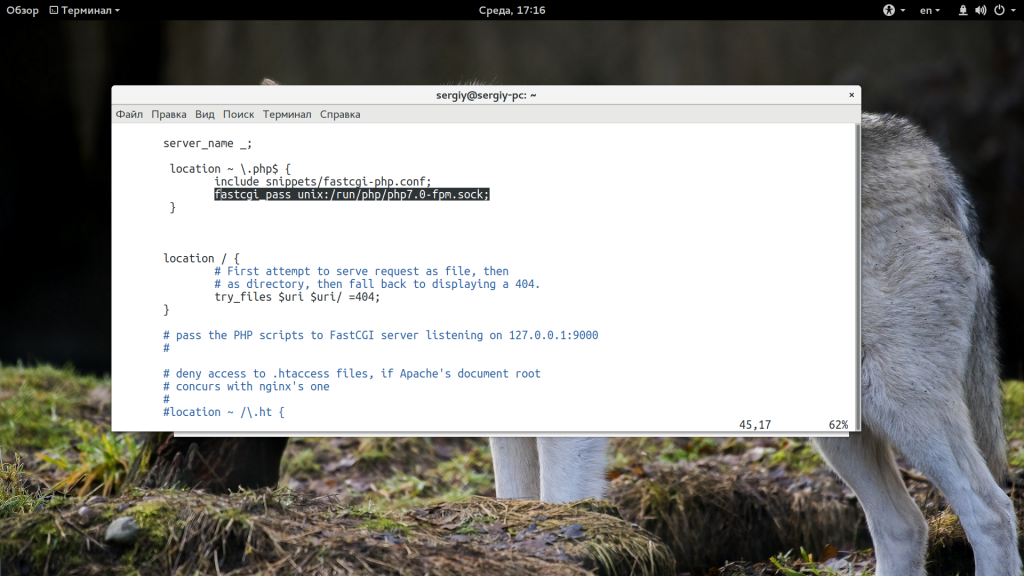
Также эта ошибка может возникать при проблемах доступа к файлу сокета php-fpm, например, когда этот файл называется по другому или для него выставлены неверные права. Сначала убедитесь, что в конфигурационном файле /etc/nginx/nginx.conf указан правильный адрес файла сокета php-fpm:
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php7.0-fpm.sock;
include fastcgi_params;
}
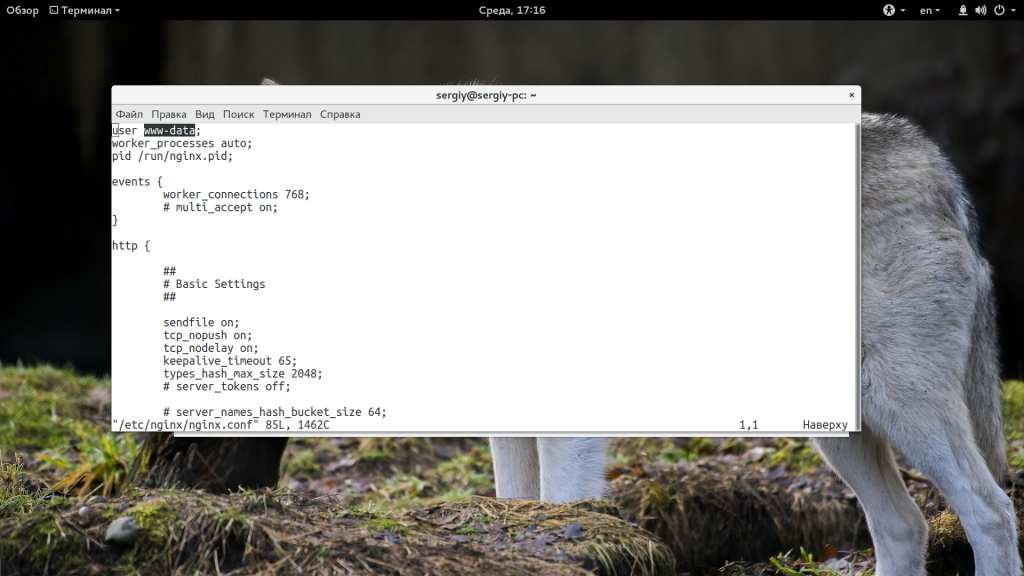
Файл /var/run/php7.0-fpm.sock должен действительно существовать в файловой системе. Дальше нужно убедиться, что у сокета правильный владелец, это должен быть тот же пользователь, от имени которого запускается Nginx, группа тоже должна соответствовать. Откройте файл /etc/php7.0/fpm/pool.d/www.conf и найдите строчки user и group. Они должны иметь такое же значение, как строчка user в конфиге nginx.conf:
listen = /var/run/php7.0-fpm.sock
listen.owner = www-data
listen.group = www-data
После того как выставите правильные параметры, перезапустите сервисы:
sudo service php5-fpm restart
$ sudo service nginx restart
3. Время отклика и размер буфера
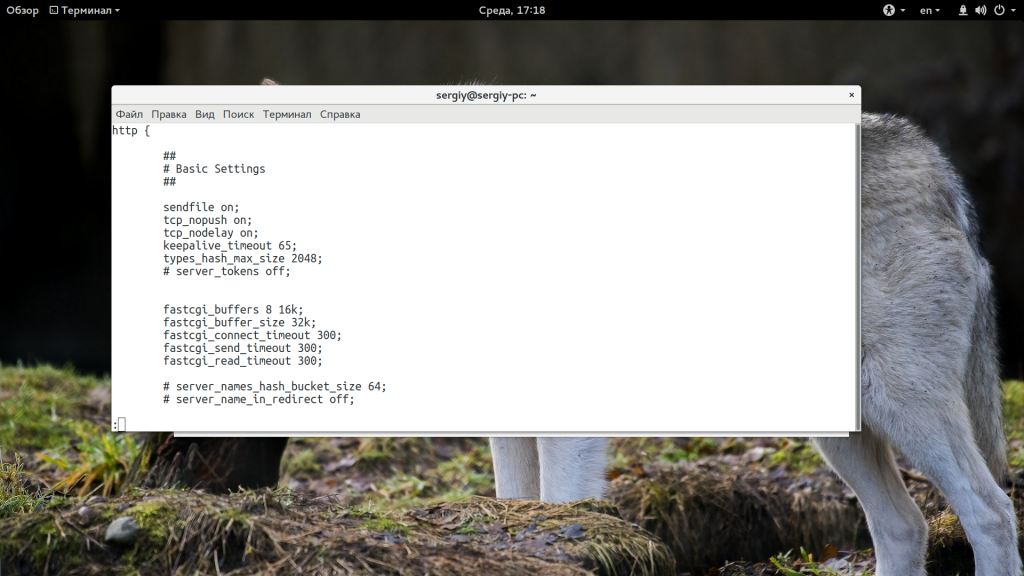
Возможно, размер буфера и время ожидания ответа от fastcgi настроены неверно и программа просто не успевает обработать большой запрос. Попробуйте увеличить такие параметры в /etc/nginx/nginx.conf. Если таких строк не существует, добавьте их в блок http, как здесь:
sudo vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
http {
...
fastcgi_buffers 8 16k;
fastcgi_buffer_size 32k;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
...
}
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели 502 bad gateway nginx что это значит и как исправить эту ошибку. Как видите, может быть достаточно много причин ее возникновения, но решить все достаточно просто если внимательно посмотреть логи и понять в чем там действительно проблема. Надеюсь, информация была полезной для вас.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Об авторе
Основатель и администратор сайта losst.ru, увлекаюсь открытым программным обеспечением и операционной системой Linux. В качестве основной ОС сейчас использую Ubuntu. Кроме Linux, интересуюсь всем, что связано с информационными технологиями и современной наукой.
Maintaining a server is hard.
You have to deal with all the upgrades, security patches and the occassional server errors (aka errors from hell).
One such common error in Nginx servers is “502 Bad Gateway“.
3 word error message – because Nginx doesn’t love you. That’s why.
The error message is cryptic.
So, many web masters roll up their sleeves and look at the error log:
2017/04/04 08:34:43 [error] 949#949: *7 connect() failed (111: Connection refused) while connecting to upstream, client: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX, server: myserver.com, request: "GET /myurl-this/ HTTP/1.0", subrequest: "/redis-fetch", upstream: "redis://127.0.0.1:6379", host: "refserver.com", referrer: "http://referalsite.com/myurl-this/"
Yeah, more gibberish.
You know something is messed up, because it says “failed” and “refused“.
But WHAT? You hardly have time to get a PhD in computer science.
Here’s help. We’ve listed the top 5 reasons for 502 Bad Gateway error, and how we fix them.
1. Backend service failed
Nginx depends on backend services like PHP-FPM, database services and cache servers to run web applications.
So, if any of these services crash or freeze, Nginx won’t get any data from them, resulting in “502 Bad gateway” error.
Some services that we’ve seen to fail are:
- PHP
- Apache
- Cache
- Database
The reasons for service failure can range from traffic spikes and resource limits to disk errors and DDoS attacks.
If you suspect a backend service is unresponsive or failed, you can try killing all unresponsive processes and restarting the service.
For instance, here’s one way we kill defunct PHP-FPM processes and restart services.
# kill -9 $(pgrep php-fpm)
# /etc/init.d/php-fpm restart
* Restarting PHP FastCGI Process Manager php-fpm [ OK ]
Warning : Do not use these commands if you are not sure how it works.
If the service restart didn’t work, you may need to get someone to take a closer look at the server health.
Our Nginx experts are online 24/7. Click here if you need help resolving your server error.
2. High server load
The second most common reason for “502 bad gateway” in Nginx is high load average in backend servers.
Load spikes cause services to not respond.
We’ve seen these reasons for load spikes:
- Sudden spike in website traffic (can be seasonal or marketing / promotional).
- Malware infection on the server.
- Comment spamming or other vulnerability exploits.
- Brute force attacks that’s designed to exploit web apps.
- Application bugs that cause memory leaks or resource hogging.
To troubleshoot a high load issue, first we figure out which resource is being abused (I/O, Memory, CPU or Net).
The we find out which service is abusing that resource, and from that point, find out which user in that service owns the abusive script or software.
Click here to know more about high load troubleshooting.
If your server is currently under high load, and you need urgent help, click here to contact our Emergency Server Support techs. We are online 24/7 and can help you in a few minutes.
3. Incorrect service configuration
Your Nginx server and the backend services relies on many sub-systems to work properly.
This includes DNS resolution, Apache processes, PHP services, DB server, etc.
If even one of these services have a wrong config entry, that service will fail to respond, and Nginx will show “502 bad gateway” error.
Some configuration issues that we’ve seen are:
- DNS resolver misconfigured in Nginx causing domain lookups to fail.
- DB login details set incorrectly after a recent migration, restore or upgrade.
- Apache firewall settings (mod_security) syntax error causing Apache to crash.
- Incorrect memory or file limits set for PHP applications.
- Capacity limits (like no: of connections per IP) set too restrictively causing legit visits to fail.
- ..and more
There is no easy way to find out a configuration error.
You really need to scan the error log and pay attention to what the error says.
For eg. this error here says the PHP application reached the maximum limit of processes (defined by pm.max_children setting) allowed.
WARNING: [mysite.com] server reached max_children setting (30), consider raising it
ERROR: unable to read what child say: Bad file descriptor (9)
If you are not familiar with PHP or web server settings, it is best to ask a server administrator.
If you need help fixing a similar error, click here to talk to our Nginx admins. We are online 24/7 and can attend your ticket within a few mins.
How Bobcares prevents configuration errors
As a quick aside, here’s how we prevent server errors related to config issues.
Configuration errors are generally caused by stale server settings that’s not adjusted for new traffic or site upgrades.
That is why Dedicated Server Admins audit our customer servers at least once a month.
During this audit, we detect possible performance bottlenecks, security loopholes and hardware issues.
This helps us to proactively resolve potential issues, rather than reacting to a downtime once an error has happened.
4. Service port blocked in firewall
Firewalls are the bedrock of server security. But if not setup right, these firewalls can cause legitimate requests to be blocked or services to fail.
For instance, in Linux servers that run Plesk automation suite, Nginx runs on port 80, and Apache runs on port 7080.
But firewalls by default block uncommon ports such as 7080, and it will result in Nginx unable to connect to Apache.
Result? 502 Bad Gateway error.
Such issues often happens when a new service is enabled (eg. caching server, Ruby, etc.) in the backend, or during a migration, or after a server upgrade.
To fix it, we look at what port each service runs on using a command like this:
# netstat -lpn
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 19785/nginx
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 19785/nginx
and if we find any service running in non-standard ports, we either change the service configuration to change it to a standard port, or edit firewall config to allow the non-standard port.
5. Web application bugs
A rare case for “502 Bad Gateway” error is application code error.
If your web server logs show a scary looing error like this, it is possible that our application code is incompatible with the server version.
[notice] child pid 27831 exit signal Segmentation fault (11)
You’ll need to inspect the software requirements of your application, and re-configure the services to match the required versions.
If you’re facing this issue right now, our Nginx experts can help you in a few minutes. Click here to open a support request. We are online 24/7.
In Summary
502 Bad Gateway in Nginx commonly occurs when Nginx runs as a reverse proxy, and is unable to connect to backend services. This can be due to service crashes, network errors, configuration issues, and more. Today we’ve seen the top 5 causes for this error, and how to fix it.