This is a list of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response status codes. Status codes are issued by a server in response to a client’s request made to the server. It includes codes from IETF Request for Comments (RFCs), other specifications, and some additional codes used in some common applications of the HTTP. The first digit of the status code specifies one of five standard classes of responses. The optional message phrases shown are typical, but any human-readable alternative may be provided, or none at all.
Unless otherwise stated, the status code is part of the HTTP standard (RFC 9110).
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains the official registry of HTTP status codes.[1]
All HTTP response status codes are separated into five classes or categories. The first digit of the status code defines the class of response, while the last two digits do not have any classifying or categorization role. There are five classes defined by the standard:
- 1xx informational response – the request was received, continuing process
- 2xx successful – the request was successfully received, understood, and accepted
- 3xx redirection – further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request
- 4xx client error – the request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled
- 5xx server error – the server failed to fulfil an apparently valid request
1xx informational response
An informational response indicates that the request was received and understood. It is issued on a provisional basis while request processing continues. It alerts the client to wait for a final response. The message consists only of the status line and optional header fields, and is terminated by an empty line. As the HTTP/1.0 standard did not define any 1xx status codes, servers must not[note 1] send a 1xx response to an HTTP/1.0 compliant client except under experimental conditions.
- 100 Continue
- The server has received the request headers and the client should proceed to send the request body (in the case of a request for which a body needs to be sent; for example, a POST request). Sending a large request body to a server after a request has been rejected for inappropriate headers would be inefficient. To have a server check the request’s headers, a client must send
Expect: 100-continueas a header in its initial request and receive a100 Continuestatus code in response before sending the body. If the client receives an error code such as 403 (Forbidden) or 405 (Method Not Allowed) then it should not send the request’s body. The response417 Expectation Failedindicates that the request should be repeated without theExpectheader as it indicates that the server does not support expectations (this is the case, for example, of HTTP/1.0 servers).[2] - 101 Switching Protocols
- The requester has asked the server to switch protocols and the server has agreed to do so.
- 102 Processing (WebDAV; RFC 2518)
- A WebDAV request may contain many sub-requests involving file operations, requiring a long time to complete the request. This code indicates that the server has received and is processing the request, but no response is available yet.[3] This prevents the client from timing out and assuming the request was lost. The status code is deprecated.[4]
- 103 Early Hints (RFC 8297)
- Used to return some response headers before final HTTP message.[5]
2xx success
This class of status codes indicates the action requested by the client was received, understood, and accepted.[1]
- 200 OK
- Standard response for successful HTTP requests. The actual response will depend on the request method used. In a GET request, the response will contain an entity corresponding to the requested resource. In a POST request, the response will contain an entity describing or containing the result of the action.
- 201 Created
- The request has been fulfilled, resulting in the creation of a new resource.[6]
- 202 Accepted
- The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. The request might or might not be eventually acted upon, and may be disallowed when processing occurs.
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information (since HTTP/1.1)
- The server is a transforming proxy (e.g. a Web accelerator) that received a 200 OK from its origin, but is returning a modified version of the origin’s response.[7][8]
- 204 No Content
- The server successfully processed the request, and is not returning any content.
- 205 Reset Content
- The server successfully processed the request, asks that the requester reset its document view, and is not returning any content.
- 206 Partial Content
- The server is delivering only part of the resource (byte serving) due to a range header sent by the client. The range header is used by HTTP clients to enable resuming of interrupted downloads, or split a download into multiple simultaneous streams.
- 207 Multi-Status (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The message body that follows is by default an XML message and can contain a number of separate response codes, depending on how many sub-requests were made.[9]
- 208 Already Reported (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The members of a DAV binding have already been enumerated in a preceding part of the (multistatus) response, and are not being included again.
- 226 IM Used (RFC 3229)
- The server has fulfilled a request for the resource, and the response is a representation of the result of one or more instance-manipulations applied to the current instance.[10]
3xx redirection
This class of status code indicates the client must take additional action to complete the request. Many of these status codes are used in URL redirection.[1]
A user agent may carry out the additional action with no user interaction only if the method used in the second request is GET or HEAD. A user agent may automatically redirect a request. A user agent should detect and intervene to prevent cyclical redirects.[11]
- 300 Multiple Choices
- Indicates multiple options for the resource from which the client may choose (via agent-driven content negotiation). For example, this code could be used to present multiple video format options, to list files with different filename extensions, or to suggest word-sense disambiguation.
- 301 Moved Permanently
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI.
- 302 Found (Previously «Moved temporarily»)
- Tells the client to look at (browse to) another URL. The HTTP/1.0 specification (RFC 1945) required the client to perform a temporary redirect with the same method (the original describing phrase was «Moved Temporarily»),[12] but popular browsers implemented 302 redirects by changing the method to GET. Therefore, HTTP/1.1 added status codes 303 and 307 to distinguish between the two behaviours.[11]
- 303 See Other (since HTTP/1.1)
- The response to the request can be found under another URI using the GET method. When received in response to a POST (or PUT/DELETE), the client should presume that the server has received the data and should issue a new GET request to the given URI.
- 304 Not Modified
- Indicates that the resource has not been modified since the version specified by the request headers If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match. In such case, there is no need to retransmit the resource since the client still has a previously-downloaded copy.
- 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1)
- The requested resource is available only through a proxy, the address for which is provided in the response. For security reasons, many HTTP clients (such as Mozilla Firefox and Internet Explorer) do not obey this status code.
- 306 Switch Proxy
- No longer used. Originally meant «Subsequent requests should use the specified proxy.»
- 307 Temporary Redirect (since HTTP/1.1)
- In this case, the request should be repeated with another URI; however, future requests should still use the original URI. In contrast to how 302 was historically implemented, the request method is not allowed to be changed when reissuing the original request. For example, a POST request should be repeated using another POST request.
- 308 Permanent Redirect
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI. 308 parallel the behaviour of 301, but does not allow the HTTP method to change. So, for example, submitting a form to a permanently redirected resource may continue smoothly.
4xx client errors
This class of status code is intended for situations in which the error seems to have been caused by the client. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. These status codes are applicable to any request method. User agents should display any included entity to the user.
- 400 Bad Request
- The server cannot or will not process the request due to an apparent client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, size too large, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
- 401 Unauthorized
- Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is required and has failed or has not yet been provided. The response must include a WWW-Authenticate header field containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. See Basic access authentication and Digest access authentication. 401 semantically means «unauthorised», the user does not have valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
- Some sites incorrectly issue HTTP 401 when an IP address is banned from the website (usually the website domain) and that specific address is refused permission to access a website.[citation needed]
- 402 Payment Required
- Reserved for future use. The original intention was that this code might be used as part of some form of digital cash or micropayment scheme, as proposed, for example, by GNU Taler,[14] but that has not yet happened, and this code is not widely used. Google Developers API uses this status if a particular developer has exceeded the daily limit on requests.[15] Sipgate uses this code if an account does not have sufficient funds to start a call.[16] Shopify uses this code when the store has not paid their fees and is temporarily disabled.[17] Stripe uses this code for failed payments where parameters were correct, for example blocked fraudulent payments.[18]
- 403 Forbidden
- The request contained valid data and was understood by the server, but the server is refusing action. This may be due to the user not having the necessary permissions for a resource or needing an account of some sort, or attempting a prohibited action (e.g. creating a duplicate record where only one is allowed). This code is also typically used if the request provided authentication by answering the WWW-Authenticate header field challenge, but the server did not accept that authentication. The request should not be repeated.
- 404 Not Found
- The requested resource could not be found but may be available in the future. Subsequent requests by the client are permissible.
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- A request method is not supported for the requested resource; for example, a GET request on a form that requires data to be presented via POST, or a PUT request on a read-only resource.
- 406 Not Acceptable
- The requested resource is capable of generating only content not acceptable according to the Accept headers sent in the request. See Content negotiation.
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
- The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy.
- 408 Request Timeout
- The server timed out waiting for the request. According to HTTP specifications: «The client did not produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time.»
- 409 Conflict
- Indicates that the request could not be processed because of conflict in the current state of the resource, such as an edit conflict between multiple simultaneous updates.
- 410 Gone
- Indicates that the resource requested was previously in use but is no longer available and will not be available again. This should be used when a resource has been intentionally removed and the resource should be purged. Upon receiving a 410 status code, the client should not request the resource in the future. Clients such as search engines should remove the resource from their indices. Most use cases do not require clients and search engines to purge the resource, and a «404 Not Found» may be used instead.
- 411 Length Required
- The request did not specify the length of its content, which is required by the requested resource.
- 412 Precondition Failed
- The server does not meet one of the preconditions that the requester put on the request header fields.
- 413 Payload Too Large
- The request is larger than the server is willing or able to process. Previously called «Request Entity Too Large» in RFC 2616.[19]
- 414 URI Too Long
- The URI provided was too long for the server to process. Often the result of too much data being encoded as a query-string of a GET request, in which case it should be converted to a POST request. Called «Request-URI Too Long» previously in RFC 2616.[20]
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
- The request entity has a media type which the server or resource does not support. For example, the client uploads an image as image/svg+xml, but the server requires that images use a different format.
- 416 Range Not Satisfiable
- The client has asked for a portion of the file (byte serving), but the server cannot supply that portion. For example, if the client asked for a part of the file that lies beyond the end of the file. Called «Requested Range Not Satisfiable» previously RFC 2616.[21]
- 417 Expectation Failed
- The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field.[22]
- 418 I’m a teapot (RFC 2324, RFC 7168)
- This code was defined in 1998 as one of the traditional IETF April Fools’ jokes, in RFC 2324, Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol, and is not expected to be implemented by actual HTTP servers. The RFC specifies this code should be returned by teapots requested to brew coffee.[23] This HTTP status is used as an Easter egg in some websites, such as Google.com’s «I’m a teapot» easter egg.[24][25][26] Sometimes, this status code is also used as a response to a blocked request, instead of the more appropriate 403 Forbidden.[27][28]
- 421 Misdirected Request
- The request was directed at a server that is not able to produce a response (for example because of connection reuse).
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
- The request was well-formed but was unable to be followed due to semantic errors.[9]
- 423 Locked (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The resource that is being accessed is locked.[9]
- 424 Failed Dependency (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The request failed because it depended on another request and that request failed (e.g., a PROPPATCH).[9]
- 425 Too Early (RFC 8470)
- Indicates that the server is unwilling to risk processing a request that might be replayed.
- 426 Upgrade Required
- The client should switch to a different protocol such as TLS/1.3, given in the Upgrade header field.
- 428 Precondition Required (RFC 6585)
- The origin server requires the request to be conditional. Intended to prevent the ‘lost update’ problem, where a client GETs a resource’s state, modifies it, and PUTs it back to the server, when meanwhile a third party has modified the state on the server, leading to a conflict.[29]
- 429 Too Many Requests (RFC 6585)
- The user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time. Intended for use with rate-limiting schemes.[29]
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large (RFC 6585)
- The server is unwilling to process the request because either an individual header field, or all the header fields collectively, are too large.[29]
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons (RFC 7725)
- A server operator has received a legal demand to deny access to a resource or to a set of resources that includes the requested resource.[30] The code 451 was chosen as a reference to the novel Fahrenheit 451 (see the Acknowledgements in the RFC).
5xx server errors
The server failed to fulfil a request.
Response status codes beginning with the digit «5» indicate cases in which the server is aware that it has encountered an error or is otherwise incapable of performing the request. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and indicate whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. Likewise, user agents should display any included entity to the user. These response codes are applicable to any request method.
- 500 Internal Server Error
- A generic error message, given when an unexpected condition was encountered and no more specific message is suitable.
- 501 Not Implemented
- The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfil the request. Usually this implies future availability (e.g., a new feature of a web-service API).
- 502 Bad Gateway
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable
- The server cannot handle the request (because it is overloaded or down for maintenance). Generally, this is a temporary state.[31]
- 504 Gateway Timeout
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
- The server does not support the HTTP version used in the request.
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates (RFC 2295)
- Transparent content negotiation for the request results in a circular reference.[32]
- 507 Insufficient Storage (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The server is unable to store the representation needed to complete the request.[9]
- 508 Loop Detected (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The server detected an infinite loop while processing the request (sent instead of 208 Already Reported).
- 510 Not Extended (RFC 2774)
- Further extensions to the request are required for the server to fulfil it.[33]
- 511 Network Authentication Required (RFC 6585)
- The client needs to authenticate to gain network access. Intended for use by intercepting proxies used to control access to the network (e.g., «captive portals» used to require agreement to Terms of Service before granting full Internet access via a Wi-Fi hotspot).[29]
Unofficial codes
The following codes are not specified by any standard.
- 218 This is fine (Apache HTTP Server)
- Used by Apache servers. A catch-all error condition allowing the passage of message bodies through the server when the
ProxyErrorOverridesetting is enabled. It is displayed in this situation instead of a 4xx or 5xx error message.[34] - 419 Page Expired (Laravel Framework)
- Used by the Laravel Framework when a CSRF Token is missing or expired.[citation needed]
- 420 Method Failure (Spring Framework)
- A deprecated response used by the Spring Framework when a method has failed.[35]
- 420 Enhance Your Calm (Twitter)
- Returned by version 1 of the Twitter Search and Trends API when the client is being rate limited; versions 1.1 and later use the 429 Too Many Requests response code instead.[36] The phrase «Enhance your calm» comes from the 1993 movie Demolition Man, and its association with this number is likely a reference to cannabis.[citation needed]
- 430 Request Header Fields Too Large (Shopify)
- Used by Shopify, instead of the 429 Too Many Requests response code, when too many URLs are requested within a certain time frame.[37]
- 450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft)
- The Microsoft extension code indicated when Windows Parental Controls are turned on and are blocking access to the requested webpage.[38]
- 498 Invalid Token (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 498 indicates an expired or otherwise invalid token.[39]
- 499 Token Required (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 499 indicates that a token is required but was not submitted.[39]
- 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded (Apache Web Server/cPanel)
- The server has exceeded the bandwidth specified by the server administrator; this is often used by shared hosting providers to limit the bandwidth of customers.[40]
- 529 Site is overloaded
- Used by Qualys in the SSLLabs server testing API to signal that the site can’t process the request.[41]
- 530 Site is frozen
- Used by the Pantheon Systems web platform to indicate a site that has been frozen due to inactivity.[42]
- 598 (Informal convention) Network read timeout error
- Used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network read timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.[43]
- 599 Network Connect Timeout Error
- An error used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network connect timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.
Internet Information Services
Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) web server expands the 4xx error space to signal errors with the client’s request.
- 440 Login Time-out
- The client’s session has expired and must log in again.[44]
- 449 Retry With
- The server cannot honour the request because the user has not provided the required information.[45]
- 451 Redirect
- Used in Exchange ActiveSync when either a more efficient server is available or the server cannot access the users’ mailbox.[46] The client is expected to re-run the HTTP AutoDiscover operation to find a more appropriate server.[47]
IIS sometimes uses additional decimal sub-codes for more specific information,[48] however these sub-codes only appear in the response payload and in documentation, not in the place of an actual HTTP status code.
nginx
The nginx web server software expands the 4xx error space to signal issues with the client’s request.[49][50]
- 444 No Response
- Used internally[51] to instruct the server to return no information to the client and close the connection immediately.
- 494 Request header too large
- Client sent too large request or too long header line.
- 495 SSL Certificate Error
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has provided an invalid client certificate.
- 496 SSL Certificate Required
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when a client certificate is required but not provided.
- 497 HTTP Request Sent to HTTPS Port
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has made a HTTP request to a port listening for HTTPS requests.
- 499 Client Closed Request
- Used when the client has closed the request before the server could send a response.
Cloudflare
Cloudflare’s reverse proxy service expands the 5xx series of errors space to signal issues with the origin server.[52]
- 520 Web Server Returned an Unknown Error
- The origin server returned an empty, unknown, or unexpected response to Cloudflare.[53]
- 521 Web Server Is Down
- The origin server refused connections from Cloudflare. Security solutions at the origin may be blocking legitimate connections from certain Cloudflare IP addresses.
- 522 Connection Timed Out
- Cloudflare timed out contacting the origin server.
- 523 Origin Is Unreachable
- Cloudflare could not reach the origin server; for example, if the DNS records for the origin server are incorrect or missing.
- 524 A Timeout Occurred
- Cloudflare was able to complete a TCP connection to the origin server, but did not receive a timely HTTP response.
- 525 SSL Handshake Failed
- Cloudflare could not negotiate a SSL/TLS handshake with the origin server.
- 526 Invalid SSL Certificate
- Cloudflare could not validate the SSL certificate on the origin web server. Also used by Cloud Foundry’s gorouter.
- 527 Railgun Error
- Error 527 indicates an interrupted connection between Cloudflare and the origin server’s Railgun server.[54]
- 530
- Error 530 is returned along with a 1xxx error.[55]
AWS Elastic Load Balancing
Amazon Web Services’ Elastic Load Balancing adds a few custom return codes to signal issues either with the client request or with the origin server.[56]
- 460
- Client closed the connection with the load balancer before the idle timeout period elapsed. Typically when client timeout is sooner than the Elastic Load Balancer’s timeout.[56]
- 463
- The load balancer received an X-Forwarded-For request header with more than 30 IP addresses.[56]
- 464
- Incompatible protocol versions between Client and Origin server.[56]
- 561 Unauthorized
- An error around authentication returned by a server registered with a load balancer. You configured a listener rule to authenticate users, but the identity provider (IdP) returned an error code when authenticating the user.[56]
Caching warning codes (obsoleted)
The following caching related warning codes were specified under RFC 7234. Unlike the other status codes above, these were not sent as the response status in the HTTP protocol, but as part of the «Warning» HTTP header.[57][58]
Since this «Warning» header is often neither sent by servers nor acknowledged by clients, this header and its codes were obsoleted by the HTTP Working Group in 2022 with RFC 9111.[59]
- 110 Response is Stale
- The response provided by a cache is stale (the content’s age exceeds a maximum age set by a Cache-Control header or heuristically chosen lifetime).
- 111 Revalidation Failed
- The cache was unable to validate the response, due to an inability to reach the origin server.
- 112 Disconnected Operation
- The cache is intentionally disconnected from the rest of the network.
- 113 Heuristic Expiration
- The cache heuristically chose a freshness lifetime greater than 24 hours and the response’s age is greater than 24 hours.
- 199 Miscellaneous Warning
- Arbitrary, non-specific warning. The warning text may be logged or presented to the user.
- 214 Transformation Applied
- Added by a proxy if it applies any transformation to the representation, such as changing the content encoding, media type or the like.
- 299 Miscellaneous Persistent Warning
- Same as 199, but indicating a persistent warning.
See also
- Custom error pages
- List of FTP server return codes
- List of HTTP header fields
- List of SMTP server return codes
- Common Log Format
Explanatory notes
- ^ Emphasised words and phrases such as must and should represent interpretation guidelines as given by RFC 2119
References
- ^ a b c «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry». Iana.org. Archived from the original on December 11, 2011. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ Fielding, Roy T. «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 10.1.1 «Expect»«.
- ^ Goland, Yaronn; Whitehead, Jim; Faizi, Asad; Carter, Steve R.; Jensen, Del (February 1999). HTTP Extensions for Distributed Authoring – WEBDAV. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2518. RFC 2518. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «102 Processing — HTTP MDN». 102 status code is deprecated
- ^ Oku, Kazuho (December 2017). An HTTP Status Code for Indicating Hints. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8297. RFC 8297. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ Stewart, Mark; djna. «Create request with POST, which response codes 200 or 201 and content». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.3.4».
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 7.7».
- ^ a b c d e Dusseault, Lisa, ed. (June 2007). HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV). IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4918. RFC 4918. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Delta encoding in HTTP. IETF. January 2002. doi:10.17487/RFC3229. RFC 3229. Retrieved February 25, 2011.
- ^ a b «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.4 «Redirection 3xx»«.
- ^ Berners-Lee, Tim; Fielding, Roy T.; Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk (May 1996). Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.0. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1945. RFC 1945. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «The GNU Taler tutorial for PHP Web shop developers 0.4.0». docs.taler.net. Archived from the original on November 8, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2017.
- ^ «Google API Standard Error Responses». 2016. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ «Sipgate API Documentation». Archived from the original on July 10, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ «Shopify Documentation». Archived from the original on July 25, 2018. Retrieved July 25, 2018.
- ^ «Stripe API Reference – Errors». stripe.com. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 413». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 414». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 416». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ TheDeadLike. «HTTP/1.1 Status Codes 400 and 417, cannot choose which». serverFault. Archived from the original on October 10, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Larry Masinter (April 1, 1998). Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol (HTCPCP/1.0). doi:10.17487/RFC2324. RFC 2324.
Any attempt to brew coffee with a teapot should result in the error code «418 I’m a teapot». The resulting entity body MAY be short and stout.
- ^ I’m a teapot
- ^ Barry Schwartz (August 26, 2014). «New Google Easter Egg For SEO Geeks: Server Status 418, I’m A Teapot». Search Engine Land. Archived from the original on November 15, 2015. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ «Google’s Teapot». Retrieved October 23, 2017.[dead link]
- ^ «Enable extra web security on a website». DreamHost. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ «I Went to a Russian Website and All I Got Was This Lousy Teapot». PCMag. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Nottingham, M.; Fielding, R. (April 2012). «RFC 6585 – Additional HTTP Status Codes». Request for Comments. Internet Engineering Task Force. Archived from the original on May 4, 2012. Retrieved May 1, 2012.
- ^ Bray, T. (February 2016). «An HTTP Status Code to Report Legal Obstacles». ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ alex. «What is the correct HTTP status code to send when a site is down for maintenance?». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Holtman, Koen; Mutz, Andrew H. (March 1998). Transparent Content Negotiation in HTTP. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2295. RFC 2295. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk; Leach, Paul; Lawrence, Scott (February 2000). An HTTP Extension Framework. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2774. RFC 2774. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «218 This is fine — HTTP status code explained». HTTP.dev. Retrieved July 25, 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Enum HttpStatus». Spring Framework. org.springframework.http. Archived from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «Twitter Error Codes & Responses». Twitter. 2014. Archived from the original on September 27, 2017. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Status Codes and SEO: what you need to know». ContentKing. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ «Screenshot of error page». Archived from the original (bmp) on May 11, 2013. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ a b «Using token-based authentication». ArcGIS Server SOAP SDK. Archived from the original on September 26, 2014. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Error Codes and Quick Fixes». Docs.cpanel.net. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved October 15, 2015.
- ^ «SSL Labs API v3 Documentation». github.com.
- ^ «Platform Considerations | Pantheon Docs». pantheon.io. Archived from the original on January 6, 2017. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ^ «HTTP status codes — ascii-code.com». www.ascii-code.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2017. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^
«Error message when you try to log on to Exchange 2007 by using Outlook Web Access: «440 Login Time-out»«. Microsoft. 2010. Retrieved November 13, 2013. - ^ «2.2.6 449 Retry With Status Code». Microsoft. 2009. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved October 26, 2009.
- ^ «MS-ASCMD, Section 3.1.5.2.2». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 26, 2015. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «Ms-oxdisco». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «The HTTP status codes in IIS 7.0». Microsoft. July 14, 2009. Archived from the original on April 9, 2009. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
- ^ «ngx_http_request.h». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on September 19, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «ngx_http_special_response.c». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «return» directive Archived March 1, 2018, at the Wayback Machine (http_rewrite module) documentation.
- ^ «Troubleshooting: Error Pages». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Error 520: web server returns an unknown error». Cloudflare.
- ^ «527 Error: Railgun Listener to origin error». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on October 13, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ «Error 530». Cloudflare. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e «Troubleshoot Your Application Load Balancers – Elastic Load Balancing». docs.aws.amazon.com. Retrieved May 17, 2023.
- ^ «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Caching». datatracker.ietf.org. Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- ^ «Warning — HTTP | MDN». developer.mozilla.org. Retrieved August 15, 2021. Some text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.5 Generic (CC BY-SA 2.5) license.
- ^ «RFC 9111: HTTP Caching, Section 5.5 «Warning»«. June 2022.
External links
- «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15 «Status Codes»«.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry at the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
- HTTP status codes at http-statuscode.com
- MDN status code reference at mozilla.org
Составили подробный классификатор кодов состояния HTTP. Добавляйте в закладки, чтобы был под рукой, когда понадобится.
Что такое код ответа HTTP
Когда посетитель переходит по ссылке на сайт или вбивает её в поисковую строку вручную, отправляется запрос на сервер. Сервер обрабатывает этот запрос и выдаёт ответ — трехзначный цифровой код HTTP от 100 до 510. По коду ответа можно понять реакцию сервера на запрос.
Первая цифра в ответе обозначает класс состояния, другие две — причину, по которой мог появиться такой ответ.
Как проверить код состояния страницы
Проверить коды ответа сервера можно вручную с помощью браузера и в панелях веб‑мастеров: Яндекс.Вебмастер и Google Search Console.
В браузере
Для примера возьмём Google Chrome.
-
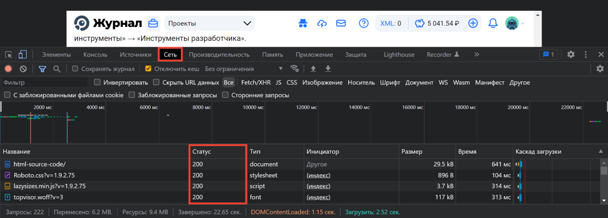
Откройте панель разработчика в браузере клавишей F12, комбинацией клавиш Ctrl + Shift + I или в меню браузера → «Дополнительные инструменты» → «Инструменты разработчика». Подробнее об этом рассказывали в статье «Как открыть исходный код страницы».
-
Переключитесь на вкладку «Сеть» в Инструментах разработчика и обновите страницу:
В Яндекс.Вебмастере
Откройте инструмент «Проверка ответа сервера» в Вебмастере. Введите URL в специальное поле и нажмите кнопку «Проверить»:
Как добавить сайт в Яндекс.Вебмастер и другие сервисы Яндекса
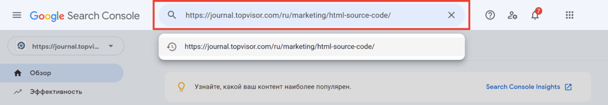
В Google Search Console
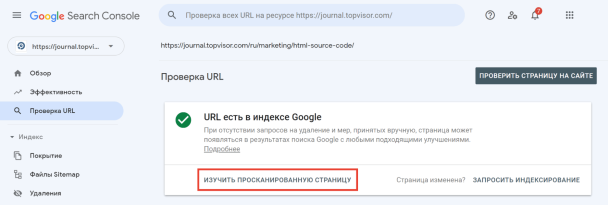
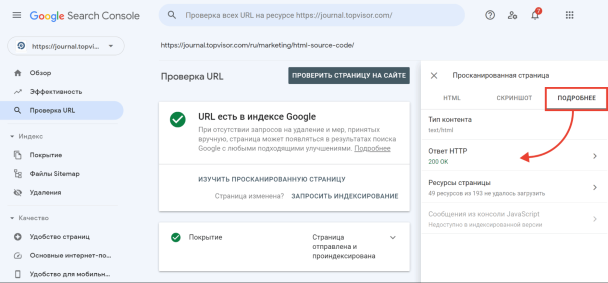
Чтобы посмотреть код ответа сервера в GSC, перейдите в инструмент проверки URL — он находится в самом верху панели:
Введите ссылку на страницу, которую хотите проверить, и нажмите Enter. В результатах проверки нажмите на «Изучить просканированную страницу» в блоке «URL есть в индексе Google».
А затем в открывшемся окне перейдите на вкладку «Подробнее»:
Теперь расскажем подробнее про все классы кодов состояния HTTP.
1* класс кодов (информационные сообщения)
Это системный класс кодов, который только информирует о процессе передачи запроса. Такие ответы не являются ошибкой, хотя и могут отображаться в браузере как Error Code.
100 Continue
Этот ответ сообщает, что полученные сведения о запросе устраивают сервер и клиент может продолжать отправлять данные. Такой ответ может требоваться клиенту, если на сервер отправляется большой объём данных.
101 Switching Protocols
Сервер одобрил переключение типа протокола, которое запросил пользователь, и в настоящий момент выполняет действие.
102 Processing
Запрос принят — он находится в обработке, и на это понадобится чуть больше времени.
103 Checkpoint
Контрольная точка — используется в запросах для возобновления после прерывания запросов POST или PUT.
POST отправляет данные на сервер, PUT создает новый ресурс или заменяет существующий данными, представленными в теле запроса.
Разница между ними в том, что PUT работает без изменений: повторное его применение даёт такой же результат, что и в первый раз, а вот повторный вызов одного и того же метода POST часто меняет данные.
Пример — оформленный несколько раз интернет‑заказ. Такое часто происходит как раз по причине неоднократного использования запроса PUT.
105 Name Not Resolved
Не удается преобразовать DNS‑адрес сервера — это означает ошибку в службе DNS. Эта служба преобразует IP‑адреса в знакомые нам доменные имена.
2* класс кодов (успешно обработанные запросы)
Эти коды информируют об успешности принятия и обработки запроса. Также сервер может передать заголовки или тело сообщений.
200 ОК
Все хорошо — HTTP‑запрос успешно обработан (не ошибка).
201 Created
Создано — транзакция успешна, сформирован новый ресурс или документ.
202 Accepted
Принято — запрос принят, но ещё не обработан.
203 Non‑Authoritative Information
Информация не авторитетна — запрос успешно обработан, но передаваемая информация была взята не из первичного источника (данные могут быть устаревшими).
204 No Content
Нет содержимого — запрос успешно обработан, однако в ответе только заголовки без контента сообщения. Не нужно обновлять содержимое документа, но можно применить к нему полученные метаданные.
205 Reset Content
Сбросить содержимое. Запрос успешно обработан — но нужно сбросить введенные данные. Страницу можно не обновлять.
206 Partial Content
Частичное содержимое. Сервер успешно обработал часть GET‑запроса, а другую часть вернул.
GET — метод для чтения данных с сайта. Он говорит серверу, что клиент хочет прочитать какой‑то документ.
Представим интернет‑магазин и страницы каталога. Фильтры, которые выбирает пользователь, передаются благодаря методу GET. GET‑запрос работает с получением данных, а POST‑запрос нужен для отправки данных.
При работе с подобными ответами следует уделить внимание кэшированию.
207 Multi‑Status
Успешно выполнено несколько операций — сервер передал результаты выполнения нескольких независимых операций. Они появятся в виде XML‑документа с объектом multistatus.
226 IM Used
Успешно обработан IM‑заголовок (специальный заголовок, который отправляется клиентом и используется для передачи состояния HTTP).
3* класс кодов (перенаправление на другой адрес)
Эти коды информируют, что для достижения успешной операции нужно будет сделать другой запрос, возможно, по другому URL.
300 Multiple Choices
Множественный выбор — сервер выдает список нескольких возможных вариантов перенаправления (максимум — 5). Можно выбрать один из них.
301 Moved Permanently
Окончательно перемещено — страница перемещена на другой URL, который указан в поле Location.
302 Found/Moved
Временно перемещено — страница временно перенесена на другой URL, который указан в поле Location.
303 See Other
Ищите другую страницу — страница не найдена по данному URL, поэтому смотрите страницу по другому URL, используя метод GET.
304 Not Modified
Модификаций не было — с момента последнего визита клиента изменений не было.
305 Use Proxy
Используйте прокси — запрос к нужному ресурсу можно сделать только через прокси‑сервер, URL которого указан в поле Location заголовка.
306 Unused
Зарезервировано. Код в настоящий момент не используется.
307 Temporary Redirect
Временное перенаправление — запрашиваемый ресурс временно доступен по другому URL.
Этот код имеет ту же семантику, что код ответа 302 Found, за исключением того, что агент пользователя не должен изменять используемый метод HTTP: если в первом запросе использовался POST, то во втором запросе также должен использоваться POST.
308 Resume Incomplete
Перемещено полностью (навсегда) — запрашиваемая страница была перенесена на новый URL, указанный в поле Location заголовка. Метод запроса (GET/POST) менять не разрешается.
4* класс кодов (ошибки на стороне клиента)
Эти коды указывают на ошибки со стороны клиентов.
400 Bad Request
Неверный запрос — запрос клиента не может быть обработан, так как есть синтаксическая ошибка (возможно, опечатка).
401 Unauthorized
Не пройдена авторизация — запрос ещё в обработке, но доступа нет, так как пользователь не авторизован.
Для доступа к запрашиваемому ресурсу клиент должен представиться, послав запрос, включив при этом в заголовок сообщения поле Authorization.
402 Payment Required
Требуется оплата — зарезервировано для использования в будущем. Код предусмотрен для платных пользовательских сервисов, а не для хостинговых компаний.
403 Forbidden
Запрещено — запрос принят, но не будет обработан, так как у клиента недостаточно прав. Может возникнуть, когда пользователь хочет открыть системные файлы (robots, htaccess) или не прошёл авторизацию.
404 Not Found
Не найдено — запрашиваемая страница не обнаружена. Сервер принял запрос, но не нашёл ресурса по указанному URL (возможно, была ошибка в URL или страница была перемещена).
405 Method Not Allowed
Метод не разрешён — запрос был сделан методом, который не поддерживается данным ресурсом. Сервер должен предложить доступные методы решения в заголовке Allow.
406 Not Acceptable
Некорректный запрос — неподдерживаемый поисковиком формат запроса (поисковый робот не поддерживает кодировку или язык).
407 Proxy Authentication Required
Нужно пройти аутентификацию прокси — ответ аналогичен коду 401, только нужно аутентифицировать прокси‑сервер.
408 Request Timeout
Тайм‑аут запроса — запрос клиента занял слишком много времени. На каждом сайте существует свое время тайм‑аута — проверьте интернет‑соединение и просто обновите страницу.
409 Conflict
Конфликт (что‑то пошло не так) — запрос не может быть выполнен из‑за конфликтного обращения к ресурсу (несовместимость двух запросов).
410 Gone
Недоступно — ресурс раньше был размещён по указанному URL, но сейчас удалён и недоступен (серверу неизвестно месторасположение).
411 Length Required
Добавьте длины — сервер отклоняет отправляемый запрос, так как длина заголовка не определена, и он не находит значение Content‑Length.
Нужно исправить заголовки на сервере, и в следующий раз робот сможет проиндексировать страницу.
412 Precondition Failed
Предварительное условие не выполнено — стоит проверить правильность HTTP‑заголовков данного запроса.
413 Request Entity Too Large
Превышен размер запроса — перелимит максимального размера запроса, принимаемого сервером. Браузеры поддерживают запросы от 2 до 8 килобайт.
414 Request‑URI Too Long
Превышена длина запроса — сервер не может обработать запрос из‑за длинного URL. Такая ошибка может возникнуть, например, когда клиент пытается передать чересчур длинные параметры через метод GET, а не POST.
415 Unsupported Media Type
Формат не поддерживается — сервер не может принять запрос, так как данные подгружаются в некорректном формате, и сервер разрывает соединение.
416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
Диапазон не поддерживается — ошибка возникает в случаях, когда в самом HTTP‑заголовке прописывается некорректный байтовый диапазон.
Корректного диапазона в необходимом документе может просто не быть, или есть опечатка в синтаксисе.
417 Expectation Failed
Ожидания не оправдались — прокси некорректно идентифицировал содержимое поля «Expect: 100‑Continue».
418 I’m a teapot
Первоапрельская шутка разработчиков в 1998 году. В расшифровке звучит как «я не приготовлю вам кофе, потому что я чайник». Не используется в работе.
422 Unprocessable Entity
Объект не обработан — сервер принял запрос, но в нём есть логическая ошибка. Стоит посмотреть в сторону семантики сайта.
423 Locked
Закрыто — ресурс заблокирован для выбранного HTTP‑метода. Можно перезагрузить роутер и компьютер. А также использовать только статистический IP.
424 Failed Dependency
Неуспешная зависимость — сервер не может обработать запрос, так как один из зависимых ресурсов заблокирован.
Выполнение запроса напрямую зависит от успешности выполнения другой операции, и если она не будет успешно завершена, то вся обработка запроса будет прервана.
425 Unordered Collection
Неверный порядок в коллекции — ошибка возникает, если клиент указал номер элемента в неупорядоченном списке или запросил несколько элементов в порядке, отличном от серверного.
426 Upgrade Required
Нужно обновление — в заголовке ответа нужно корректно сформировать поля Upgrade и Connection.
Этот ответ возникает, когда серверу требуется обновление до SSL‑протокола, но клиент не имеет его поддержки.
428 Precondition Required
Нужно предварительное условие — сервер просит внести в запрос информацию о предварительных условиях обработки данных, чтобы выдавать корректную информацию по итогу.
429 Too Many Requests
Слишком много запросов — отправлено слишком много запросов за короткое время. Это может указывать, например, на попытку DDoS‑атаки, для защиты от которой запросы блокируются.
431 Request Header Fields Too Large
Превышена длина заголовков — сервер может и не отвечать этим кодом, вместо этого он может просто сбросить соединение.
Исправляется это с помощью сокращения заголовков и повторной отправки запроса.
434 Requested Host Unavailable
Адрес запрашиваемой страницы недоступен.
444 No Response
Нет ответа — код отображается в лог‑файлах, чтобы подтвердить, что сервер никак не отреагировал на запрос пользователя и прервал соединение. Возвращается только сервером nginx.
Nginx — программное обеспечение с открытым исходным кодом. Его используют для создания веб‑серверов, а также в качестве почтового или обратного прокси‑сервера. Nginx решает проблему падения производительности из‑за роста трафика.
449 Retry With
Повторите попытку — ошибка говорит о необходимости скорректировать запрос и повторить его снова. Причиной становятся неверно указанные параметры (возможно, недостаточно данных).
450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls
Заблокировано родительским контролем — говорит о том, что с компьютера попытались зайти на заблокированный ресурс. Избежать этой ошибки можно изменением параметров системы родительского контроля.
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
Недоступно по юридическим причинам — доступ к ресурсу закрыт, например, по требованию органов государственной власти или по требованию правообладателя в случае нарушения авторских прав.
456 Unrecoverable Error
Неустранимая ошибка — при обработке запроса возникла ошибка, которая вызывает некорректируемые сбои в таблицах баз данных.
499 Client Closed Request
Запрос закрыт клиентом — нестандартный код, используемый nginx в ситуациях, когда клиент закрыл соединение, пока nginx обрабатывал запрос.
5* класс кодов (ошибки на стороне сервера)
Эти коды указывают на ошибки со стороны серверов.
При использовании всех методов, кроме HEAD, сервер должен вернуть в теле сообщения гипертекстовое пояснение для пользователя. И его можно использовать в работе.
500 Internal Server Error
Внутренняя ошибка сервера — сервер столкнулся с неким условием, из‑за которого не может выполнить запрос.
Проверяйте, корректно ли указаны директивы в системных файлах (особенно htaccess) и нет ли ошибки прав доступа к файлам. Обратите внимание на ошибки внутри скриптов и их медленную работу.
501 Not Implemented
Не выполнено — код отдается, когда сам сервер не может идентифицировать метод запроса.
Сами вы эту ошибку не исправите. Устранить её может только сервер.
502 Bad Gateway
Ошибка шлюза — появляется, когда сервер, выступая в роли шлюза или прокси‑сервера, получил ответное сообщение от вышестоящего сервера о несоответствии протоколов.
Актуально исключительно для прокси и шлюзовых конфигураций.
503 Service Unavailable
Временно не доступен — сервер временно не имеет возможности обрабатывать запросы по техническим причинам (обслуживание, перегрузка и прочее).
В поле Retry‑After заголовка сервер укажет время, через которое можно повторить запрос.
504 Gateway Timeout
Тайм‑аут шлюза — сервер, выступая в роли шлюза или прокси‑сервера, не получил ответа от вышестоящего сервера в нужное время.
Исправить эту ошибку самостоятельно не получится. Здесь дело в прокси, часто — в веб‑сервере.
Первым делом просто обновите веб‑страницу. Если это не помогло, нужно почистить DNS‑кэш. Для этого нажмите горячие клавиши Windows+R и введите команду cmd (Control+пробел). В открывшемся окне укажите команду ipconfig / flushdns и подтвердите её нажатием Enter.
505 HTTP Version Not Supported
Сервер не поддерживает версию протокола — отсутствует поддержка текущей версии HTTP‑протокола. Нужно обеспечить клиента и сервер одинаковой версией.
506 Variant Also Negotiates
Неуспешные переговоры — с такой ошибкой сталкиваются, если сервер изначально настроен неправильно. По причине ошибочной конфигурации выбранный вариант указывает сам на себя, из‑за чего процесс и прерывается.
507 Insufficient Storage
Не хватает места для хранения — серверу недостаточно места в хранилище. Нужно либо расчистить место, либо увеличить доступное пространство.
508 Loop Detected
Обнаружен цикл — ошибка означает провал запроса и выполняемой операции в целом.
509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded
Превышена пропускная способность — используется при чрезмерном потреблении трафика. Владельцу площадки следует обратиться к своему хостинг‑провайдеру.
510 Not Extended
Не продлён — ошибка говорит, что на сервере отсутствует нужное для клиента расширение. Чтобы исправить проблему, надо убрать часть неподдерживаемого расширения из запроса или добавить поддержку на сервер.
511 Network Authentication Required
Требуется аутентификация — ошибка генерируется сервером‑посредником, к примеру, сервером интернет‑провайдера, если нужно ввести пароль для получения доступа к сети через платную точку доступа.
Эффективное устранение кодов ошибок HTTP представляет собой серьезную задачу, поскольку требует понимания причин их возникновения и навыков поиска и устранения неисправностей. Коды ошибок, представленные трехзначными числами (например, 404, 500), означают наличие проблем с обработкой запроса клиента или сервера. Выявление конкретной ошибки и ее первопричины требует знания протокола HTTP, конфигурации сервера и поведения приложения.
Как исправить ошибку сервера?
Во-первых, необходимо определить точный код ошибки HTTP, возвращаемой сервером (например, 404, 500), а затем проследовать действиям ниже.
Проверка журналов сервера: Проанализируйте журналы сервера, чтобы получить представление о времени возникновения ошибки и ее источнике. В веб-сервере Apache мы можем проверить журнал с помощью следующей команды:
cat /var/log/apache2/error.log
Для просмотра журнала доступа Nginx можно воспользоваться командой cat, less или tail. С помощью приведенной ниже команды проверьте журнал событий:
tail -n 50 /var/log/apache2/error.log
Проверка конфигурации сервера: Проверьте конфигурацию виртуальных хостов и файлы .htaccess на предмет возможных ошибок в конфигурации. Как уже описывали выше, можно воспользоваться утилитами cat или nano:
nano /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
Вторая команда – это конфигурация виртуального хоста, которую мы должны проверить на корректность работы. Для сервера Nginx мы будем использовать команды:
nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Очистите cookies и кэш-память: Убедитесь, что после применения изменений на сайте вы очищаете браузер от временного хранящейся информации.
Расположение этого пункта может отличаться в зависимости от браузера, но обычно его можно найти в разделе Настройки или Конфигурация далее перейти в подраздел Конфиденциальность и безопасность и найти вкладку Очистить данные просмотра или Очистить историю.
Если эти базовые меры не помогли, можно попытаться сделать следующее:
- Проверить соединение с базой данных: Проверить настройки подключения к базе данных и доступность, если приложение использует базу данных;
- Отладка кода приложения: Проверить код приложения на предмет возможных проблем, вызывающих ошибку;
- Проверить сетевые подключения: Проверить настройки сети и брандмауэра, которые могут блокировать доступ клиентов;
- Использовать онлайн-ресурсы: Использовать форумы разработчиков и онлайн-ресурсы для обмена опытом и решениями;
- Внедрить исправления: Применить найденные исправления для устранения кодов ошибок HTTP.
Устранение ошибок HTTP требует систематического и методичного подхода, особенно для сложных веб-приложений. Поддержание в актуальном состоянии серверного и прикладного программного обеспечения, а также соблюдение лучших практик веб-разработки помогут предотвратить появление ошибок HTTP в будущем. Давайте рассмотрим тип распространенного кода ошибки более подробно!
400 Bad Request
Это означает, что сервер получает неверный синтаксис в HTTP-запросе со стороны клиента, который может возникать из-за:
- Неправильной настройка программного обеспечения или наличие ошибки в приложении браузера;
- Ошибка человека, связанная с невнимательностью, в результате которой URL-запрос не соответствует правилам настройки;
- Повреждение cookies в результате какого-либо воздействия на хранилище браузера.
401 Unauthorized Error
Это означает, что сервер не может предоставить доступ пользователю на сайт из-за нелегитимного запроса. Такое может произойти из-за неправильного ввода учетных данных и нарушения идентификации, авторизации системы. Следовательно, для получения доступа и просмотра защищенного ресурса пользователю необходимо ввести учетные данные. Для решения этой проблемы можно попросить администратора веб-сервера проверить .htpasswd и ввести учетные данные для корректной работы с сайтом:
find ./ -name .htpasswd
Используя этот путь, вы можете открыть файл в текстовом редакторе nano, используя соответствующий синтаксис nano, а затем путь для открытия вашего файла!
403 Forbidden
В этом случае мы сталкиваемся с запрещающими правилами на веб-сервере для соединений из нашей сети или машины. Для решения возникшей проблемы проверьте основную причину. Возможно, права доступа к файлам не установлены пользователем на сервере, посмотрим на типичную конфигурацию в этом случае. У нас есть пользователь www-data для управления сервером, мы пытаемся получить доступ к файлу .php или .html, значит добавляем правило для чтения файла:
chmod 644 /etc/site-for-test/index.html
В другой ситуации в файл .htaccess могут быть добавлены свои специфические запрещающие правила на сервере, определить их расположение можно через рабочий каталог, обычно они используются, как правила переопределения. Найти можно через команду, приведенную ниже:
find ./ -name .htaccess
Но есть и другая причина этой ошибки – если на веб-сервере нет листинга индексных файлов или каталогов, то сервер выдает сообщение об отказе. Если вы хотите включить листинг сайта, зайдите в конфигурацию и измените соответствующий параметр:
nano /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
Это поможет в решении ошибки!
404 Not Found
Страница не найдена на сервере. Когда вы столкнулись с данной проблемой, необходимо задать себе несколько вопросов:
- Какой процесс был при возникновении этой ошибки?
- Указан ли правильный путь к корневому каталогу?
- Существуют ли в системе необходимые файлы?
И остальные детали, в которых крыться некорректная настройка веб-сервера или некорректном запросе URL:
nano /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
500 Internal Server Eroor
Это означает, что сервер получает запрос, но не может его обработать из-за неизвестной проблемы на стороне веб-сервера. Обычно возникает при наличии двух или более проблем. Может происходить по разным сценариям, например: неправильно настроен системный файл .htaccess, .htpasswd и другие параметры, или отсутствует HTML-файл для формирования ответа клиенту, проверьте журнал сервера, как мы показывали в базовом руководстве выше!
502 Bad Gateway и 504 Gateway Timeout
Шлюз или прокси-сервер не получает должного ответа от внутреннего сервера. Если для передачи трафика используется прокси, то проверьте:
- Работоспособность бэкэнда и ответы, а также проверьте его конфигурацию;
- Проверьте конфигурацию на стороне прокси-сервера и возможность взаимодействия по-другому порту, возможно, используемый вами порт занят другим программным обеспечением;
- Проверьте состояние сетевого соединения и конфигурацию системы, отправив данные через утилиту netcat и протестируйте передачу данных;
- Если в вашем web-приложении используются сокеты, необходимо проверить их расположение, наличие доступа и разрешения.
503 Service Unavailable
Эта проблема означает, что сервер не может обработать все запросы от клиентов. Если ваша машина не обслуживается, то увеличьте ресурсы процессора, оперативной памяти и проверьте одновременно доступ пользователей, потоков и процессов в конфигурации сервера! Так же ошибка может свидетельствовать о некорректной настройке балансировщика—нагрузки, для проверки его корректной настройки. Перейдите в /etc/nginx/nginx.conf и удостоверьтесь в формате и корректности записей.
HTTP status code
This article mainly introduces the status codes that are often encountered in the operation and maintenance process, and simulates them through the popular Nginx in the industry.
2XX status code
The 2XX type status code indicates that an HTTP request is successful, the most typical is 200
# 200 status code
# This is the status code we most want to see, which means that an HTTP request has received a correct response, so I will not do simulation testing here.
3XX status code
# 3XX type status codes mainly indicate the HTTP request URL redirection behavior, the most common 3XX status codes are 301,302,304
301
Test case
# URL: Permanent redirection, implemented in Nginx through the rewrite instruction combined with the permanent tag.
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
rewrite ^(.*)$ /index.html permanent;
location / {
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
curl 127.0.0.1 -I
# TTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
302
Test case
# URL: Temporary redirection, implemented in Nginx through the rewrite instruction combined with the redirect tag
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
rewrite ^(.*)$ /index.html redirect;
location / {
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
curl 127.0.0.1 -I
# HTTP/1.1 302 Moved Temporarily
301 VS 302
# 301 and 302 status codes are URL redirection. Among them 301 permanent redirection, 302 temporary redirection. Whether it is permanent or temporary, there is no sensory difference between the two to the user. They all jumped to connection B when accessing connection A, and saw that the address on the browser also changed from A to B. In that case, why do 301 and 302 exist at the same time?
# The main difference between them is the search engine. Search engines need to establish indexing rules and weights. If connection A is set to be permanently redirected to connection B, the search engine can determine that the address of A has changed permanently, and will treat B as the only valid target address . At this time, the search engine will bring the address-related information to the new address, and at the same time completely discard the original address in the search engine index database. However, search engines have no such behavior for 302.
304
Test case
# Client-side caching, completed by the expires command in Nginx
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|html)$ {
expires 1d;
}
}
# When the client browser is accessed for the first time, as long as the accessed resource is not expired during the second access, the status code is 304, indicating that the response resource from the previous request was used
4XX status code
# 4XX type status codes mainly indicate client errors. The HTTP request header initiated by the client is incomplete, the user name used by the client, the password is wrong, etc. Will be marked as client-side errors. Common 4XX status codes are 400, 401, 403, etc.
400
# When the WEB server encounters an incomplete HTTP request header, it will return a 400 status code. Excessive request header information or cookie information is usually the cause of incomplete request headers. How large is the request header?
# This value is determined by the configuration of the WEB server. In WEB servers such as Nginx, the configuration field that determines this value is large_client_header_buffers. We simulated the 400 status code by adjusting this field.
Test case
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
# This command is valid in both the HTTP section and the SERVER section of NGINX.
# If the experiment is found to be ineffective in the SERVER section, you can set it in the HTTP section.
large_client_header_buffers 1 1k;
location / {
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
# Test
# Set a cookie far more than 1K
curl --cookie "user=sidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisidisisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisidisisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisidisisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisidisisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidissidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisidisidisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisisissisisisisisisisisisisisisisiisissiissisisisiissi" 127.0.0.1 -I
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Server: nginx/1.18.0
Date: Mon, 04 May 2019 11:05:55 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 233
Connection: close
401
# Permission verification error. It requires user name and password authentication, but the client fails the authentication. To simulate this status code in Nginx, Nginx must be adjusted to an authentication mode.
Test case
Generate authorized user name and password
htpasswd -c /etc/passwd.db youmen
# Nginx authorization configuration
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
location / {
auth_basic "secret";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/passwd.db;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
# Test
# test.com Bind in the local hosts file, then open the browser and enter the correct user name and password to access
403
# There is no permission to access, the file permission is too small or the setting does not allow access to a certain IP address, etc., a 403 status code will appear
Test case
# Set file permissions to the smallest
# ll /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3700 3⽉ 6 04:26 /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
# chmod 0 /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
# ll /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
---------- 1 root root 3700 3⽉ 6 04:26 /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
# Nginx configuration file
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
location / {
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
curl http://127.0.0.1/index.html -I
# HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
404
# File does not exist, when we access a file that does not exist, this error will appear
# Restore the 403 status code to configure the owner group, and enter the URL at will
curl http://127.0.0.1/youmen -I
# HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
499
#499 This status code is not a standard status code defined in the http protocol, but a status code defined by Nginx itself. When the client actively disconnects, Nginx will return a 499 status code. According to the definition of this status code, as long as the client is actively disconnected before Nginx returns the result, this status code should be reproduced.
Test case
# Create a PHP script and place the script in the root directory of Nginx to simulate a long time response
cat sleep.php
<?php
sleep(80);
echo "ok"
?>
# Open PHP-FPM service
systemctl start php-fpm
# Test Nginx configuration file
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|html)$ {
expires 1d;
}
location / {
# Make sure that the SCRIPT_FILENAME configuration exists in fastcgi.conf. Make sure to save it in the following 5XX cases.
in
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi.conf;
# PHP-FPM The 9000 port is enabled by default. If you have made a personalized configuration, please adjust it manually.
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
}
}
# Test
# Don't wait for the program to end normally, CTRL + C to exit directly
curl http://127.0.0.1/sleep.php -I
^C
# View access.log at the same time in CURL simulation test
tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log
127.0.0.1 - - [13/May/2019:23:24:33 -0400] "HEAD /sleep.php HTTP/1.1" 499 0
"-" "curl/7.29.0"
5XX status code
# 5XX type status codes mainly indicate server-side errors, don’t worry about client-side problems at this time
500
Generally there are the following situations
Test case
# Change the sleep.php in the root directory of Nginx at will to make its PHP syntax problematic.
# cat sleep.php
<?php
echo "aa"
sleep(80);
echo "ok"
?>
# Test Nginx configuration file
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|html)$ {
expires 1d;
}
location / {
# Make sure that the SCRIPT_FILENAME configuration exists in fastcgi.conf. Make sure to save it in the following 5XX cases.
In
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi.conf;
# PHP-FPM The 9000 port is enabled by default. If you have made a personalized configuration, please adjust it manually.
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
}
}
curl http://127.0.0.1/sleep.php -I
# HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server Error
# 1. Web script errors, such as php syntax errors, lua syntax errors, etc.
# 2. When the amount of access is large, too many files cannot be opened due to system resource limitations.
# General analysis ideas:
# View nginx error log, view php error log
# If it is too many open files, modify the worker_rlimit_nofile parameter of nginx,
# Use ulimit to view the system open file limit, modify /etc/security/limits.conf
# If it is a script problem, you need to fix the script error and optimize the code
# Various optimizations are done well, but too many open files still appear,
# Then we must consider doing load balancing and spread the traffic to different servers
Summary of the cause of the error:
1. Hard disk space is full
Use df -k to check whether the hard disk space is full. Clearing the hard disk space can solve the 500 error. If the access log is turned on in nginx, it is best to turn off the access log when it is not needed. The access log will take up a lot of hard disk space.
2. nginx configuration file error
This does not mean a syntax error. If there is a syntax error in the nginx configuration file, it will prompt when it is started. When configuring rewrite, 500 errors will occur if some rules are not handled properly. Please check your rewrite rules carefully. If some variables in the configuration file are set improperly, a 500 error will also occur, such as referencing a variable with no value.
3. If the above problems do not exist, it may be that the simulated concurrent number is too much, and you need to adjust the number of concurrency settings in nginx.conf
3. System open file limit
The solution is:
vim /etc/security/limits.conf
soft nofile 65535
hard nofile 65535
# Open /etc/nginx/nginx.conf again
# Add a line under worker_processes
vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
systemctl reload nginx
kill -9 `ps -ef | grep php | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}'`
/usr/bin/spawn-fcgi -a 127.0.0.1 -p 9000 -C 100 -u www-data -f /usr/bin/php-cgi
killall -HUP nginx
# Look at the fault of nginx after restarting
After restarting, look at the error log of nginx, and there is no 500 error reported.
It may be a database problem. I did not find any problems in the nginx log php log, and finally found that the database could not be accessed. The problem was solved after correction.
502
# 502 Bad Geteway. There are many reasons for the Nginx 502 error, mainly due to problems with the back-end server in the proxy mode. These errors are generally not a problem of Nginx itself, and the cause must be found from the backend. If this reproduces a situation where the back-end PHP-FPM process hangs, a 502 error will occur
simulation
# First shut down the PHP-FPM process on the backend.
# systemctl stop php-fpm
# Simulation test
curl http://127.0.0.1/sleep.php -I
# HTTP/1.1 502 Bad Gateway
It means that the requested php-fpm has been executed, but the execution is not completed for some reason, which eventually leads to the termination of the php-fpm process. There are many reasons for the error. Generally, it is not Nginx itself. Find the cause from the backend, such as PHP hanging;
For PHP, the common cause of 502 is that the script execution time exceeds the Timeout setting time, or the setting is too large, causing PHP to be unable to release for a long time, and no worker process comes out to receive requests;
Appropriately increase PHP execution time, first clear 502, optimization will take more time;
There are two types of control php execution time,
1> In php.ini max_execution (Earse Q smoked)_timeout
2> It may also be related to the performance of the php execution program, the website has a large amount of visits, and the number of php-cgi processes is too small. For this situation, you only need to increase the number of php-cgi processes and set the max_children in php-fpm.conf Increase the value appropriately. This data is set according to the configuration of your VPS or independent server. Generally, a php-cgi process occupies 20M of memory, so you can calculate the appropriate amount by yourself.
503
Service temporarily unavailable
Due to the maintenance or overload of the temporary server, the server is currently unable to process the request. This state is temporary and will be restored after a period of time;
Mostly because the website has too much traffic, causing too many traffic requests, Nginx does not forward to the backend, or the Upstream address and port problems, first check the CPU, memory, and the load is extremely high. If you do not check the configuration;
Upgrade the space to a better configuration, or check the website system program to make it better;
If a single IP concurrency is set too small, it will cause a 503 error.
504
# 504 Gateway Time-out. As the name suggests, it is overtime. When the execution time of PHP-FPM is longer than the reading time of Nginx, the 504 status code will appear.
# Just set the time in the script in the example above to exceed the maximum timeout time of php-fpm
The server acts as a gateway or proxy, but did not receive a request from the upstream server in time. That is, the client’s request did not reach the gateway, and the request did not reach the executable php-fpm;
# 1>May be related to the Nginx.conf configuration, Nginx connection timeout;
# 2>When the PHP-FPM execution time exceeds the read timeout time of Nginx;
summary
1XX # A status code that represents a temporary response and requires the requester to continue the operation
200 # Indicates that an HTTP request received a correct response
301 # Permanent redirect
302 # Temporary redirect
401 # Authorization required
403 # Access denied, no permission
404 # The page cannot be found, the server cannot find the requested page
410 # If the requested resource has been permanently deleted, the server will return this response
500 # Server internal error
О чем речь? Коды ошибок HTTP указывают на конкретные причины проблем, с которыми сталкивается сервер в попытке обработать клиентские запросы.
На что обратить внимание? Рассказать подробно про каждый вид ошибки будет сложно, так как их довольно много. Однако чаще всего встречается не такое большое количество, как правило, это всем знакомые ошибки 404, 502, 504 и т.д.
В статье рассказывается:
- Суть кодов ошибок HTTP
- Коды 3xx (перенаправление)
- Коды ошибок HTTP на стороне клиента
- Серверные коды ошибок HTTP
- Способы устранения некоторых кодов ошибок HTTP
- Способы проверки кодов ошибок HTTP
- Часто задаваемые вопросы о кодах ошибок HTTP
-
Пройди тест и узнай, какая сфера тебе подходит:
айти, дизайн или маркетинг.Бесплатно от Geekbrains
HTTP-статус является сообщением, которое сервер отправляет клиенту в ответ на его запрос. Например, когда пользователь переходит по ссылке или вводит запрос в веб-браузер. Коды показывают, был ли выполнен конкретный запрос клиента. Сведения в коде влияют на то, как поисковый робот или браузер будет обрабатывать содержимое страницы.
Стандартизированный код состояния состоит из трех цифр. Некоторые коды ошибок HTTP часто встречались пользователям сети, другие — нет. В целом никаких трудностей в интерпретации стандартизированных кодов состояния не возникнет даже у людей, далеких от программирования.
Обозначим ключевые термины:
- Клиент — это программное или аппаратное обеспечение, имеющее подключение к интернету и запрашивающее некоторую функцию или данные у сервера.
- Сервер — это компьютер, на котором хранятся данные. Он выполняет ряд служебных функций для других компьютеров сети, принимает клиентские запросы и отвечает на них.
Существует 5 категорий серверных ответов. Класс состояния можно определить по первой цифре.
- 5** — серверные ошибки. Причина технической ошибки со стороны сервера указывается в коротком текстовом описании после кода. Например, ошибка 500 — это внутренние сбои, реже — высокая нагрузка на сервер.
- 4** — клиентские ошибки.
- 3** — перенаправления на другой адрес (не ошибка).
- 2** — успешный запрос (не ошибка).
- 1** — информационные сообщения, передача данных (не ошибка).
Топ-30 самых востребованных и высокооплачиваемых профессий 2023
Поможет разобраться в актуальной ситуации на рынке труда
Подборка 50+ бесплатных нейросетей для упрощения работы и увеличения заработка
Только проверенные нейросети с доступом из России и свободным использованием
ТОП-100 площадок для поиска работы от GeekBrains
Список проверенных ресурсов реальных вакансий с доходом от 210 000 ₽
Уже скачали 22610
Полный список кодов состояния приведен в спецификации протокола.
Не будем останавливаться на HTTP-ответах 1** и 2**. Рассмотрим подробнее другие стандартизированные коды ошибок состояния HTTP.
Коды 3xx (перенаправление)
Эти стандартизированные коды нужны для того, чтобы сообщить пользователю, какое действие следует выполнить для успешного осуществления запроса. Коды 3xx предназначены для перенаправления клиента. Это не коды ошибок HTTP сервера. Однако знание того, как интерпретируются различные HTTP-статусы, поможет пользователям и веб-мастерам эффективно использовать программное обеспечение.
| Код | Значение | Характеристика |
| 300 | Несколько возможных ответов | Код ответа 300 Multiple Choices означает, что по запрашиваемому адресу есть несколько представлений. Клиент может выбрать один из вариантов, выданных сервером. Для правильной индексации страницы пользователю следует исправить название ресурса или заголовки. |
| 301 | Ресурс перемещен на новый URL | Клиент получает HTTP-код 301 Moved Permanently. Ранее проиндексированный URL окончательно перемещен на новый URL, указанный в заголовке Location. Робот проиндексирует новую страницу. |
| 302 | Перемещен временно | Клиент получает HTTP-код 302 Found. На данный момент ресурс временно доступен на другом адресе. Страница остается в индексе. В ответе указывается новый адрес запрашиваемого URL. |
| 303 | Смотри другой адрес | HTTP-статус 303 See Other указывает, что запрошенная страница находится по другому адресу по запросу GET. Если нужно, чтобы страница отображалась в поиске, нужен код ответа 200. |
| 304 | Ресурс не модифицирован | HTTP-код 304 Not Modified используется для кэширования и означает, что страница не изменялась с момента крайнего обращения робота. Это ускоряет индексирование и экономит трафик. |
| 305 | Нужно использовать прокси | HTTP-код 305 Use Proxy означает, что запрошенный ресурс доступен через прокси-сервер. Данные сервера указаны в ответе. |
| 307 | Временное перемещение | Клиент получает HTTP-код 307 Temporary Redirect, который означает, что запрашиваемая страница временно переехала на новый адрес. Данные прописаны в Location. |
| 308 | Ресурс перенесен навсегда | HTTP-код 308 Permanent Redirect означает, что ресурс находится на другом URL-адресе. Данные прописаны в Location. Робот индексирует страницу перенаправления в случае, если она доступна. |
Коды ошибок HTTP на стороне клиента
- 400 Bad Request
Запрос неправильный. Ошибка возникает в случае, если браузер клиента отправляет некорректный запрос серверу. Это может быть синтаксическая ошибка. Например, в запросе отсутствовали символы завершения строки.
- 401 Unauthorized
Этот код ошибки HTTP клиента сообщает, что на ресурс можно войти, используя действительный ID пользователя и пароль. Отказ в доступе также возникает, если пользователь неправильно ввел данные для авторизации (логин и пароль).
Проблема решится, когда пользователь авторизуется.
- 402 Payment Required
Это нестандартный HTTP-статус. Он означает, что запрос не может быть выполнен, пока пользователь не произведет оплату. Код используется в платных пользовательских сервисах, а не в хостинговых провайдерах.
- 403 Forbidden
Запрет доступа к запрашиваемой странице. Он связан с тем, что у пользователя нет прав. Доступ может быть ограничен для определенных IP или в случае, если неавторизованный клиент пытается открыть файлы в системной папке. Этот код встречается, если сервер обнаружил вредоносные данные.
Скачать
файл
- 404 Not Found
Это один из самых распространенных кодов ошибки HTTP клиента. Сервер дает ответ, что страница не найдена по данному URL. Например, страница перенесена на другой адрес. Не стоит путать код 404 с ошибкой «Сервер не найден». В данном случае клиент в состоянии общаться с сервером, но данных по его запросу нет.
- 405 Method Not Allowed
Сервер сообщает, что используемый метод не может применяться на данном ресурсе. Он предложит доступные методы в заголовке Allow.
- 406 Not Acceptable
Этот код ошибки указывает, что запрашиваемый контент не может быть распознан из-за кодировки, метода сжатия и других причин.
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
Доступ будет открыт, если пройти авторизацию через сервер-посредник (прокси-сервер). Это аналог кода 401.
- 408 Request Timeout
Сервер хочет отключить соединение, так как обработка запроса пользователя вышла за рамки установленного времени. У каждого ресурса есть свое время ожидания. Пользователю первым делом необходимо проверить интернет-соединение и обновить страницу.
- 409 Conflict
Запрос пользователя вызывает конфликт с текущим состоянием сервера или несовместим с другим запросом.
- 410 Gone
Это ответ сервера в случае, если запрашиваемый контент больше недоступен или удален.
- 411 Length Required
Сервер отказывается обрабатывать запрос, так как не указан Content‑Length заголовка. Необходимо указать заголовки на сервере, чтобы этот код ошибки состояния HTTP больше не возникал.
- 412 Precondition Failed
Клиент указал в запросах условие, которое нельзя выполнить. В одном или нескольких HTTP‑заголовках было указано значение false.
- 413 Request Entity Too Large
Размер запроса превышает лимит, объявленный сервером. Сервер может закрыть соединение. Веб-браузеры поддерживают запрос от 2 до 8 килобайт.
- 414 Request‑URI Too Long
У веб-сервера есть ограничение длины для интерпретации, а запрашиваемый URL длиннее установленных рамок. Чтобы избежать возникновения этого кода ошибки HTTP запросов, следует использовать метод GET, а не POST.
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
Запрос клиента не может быть обработан сервером. Такое случается, если загружаются данные неподходящего формата. В таком случае сервер просто отклоняет запрос.
- 416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
Недопустимое значение байтов диапазона в HTTP-заголовке. Сервер не может обработать запрос. Причина может быть в опечатке клиента.
- 417 Expectation Failed
Сервер отклонил запрос пользователя, так как в поле Expect введено некорректное значение.
- 418 I’m a teapot
Это первоапрельская шутка разработчиков, появившаяся в 1998 году. Сервер не может сварить вам кофе, потому что он чайник. На деле этот код не применяется.
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
Сервер видит запрос клиента. Синтаксис верный, но обработка невозможна из-за наличия логической ошибки. Нужно обратить внимание на семантическое ядро сайта.
Только до 25.09
Скачай подборку материалов, чтобы гарантированно найти работу в IT за 14 дней
Список документов:
ТОП-100 площадок для поиска работы от GeekBrains
20 профессий 2023 года, с доходом от 150 000 рублей
Чек-лист «Как успешно пройти собеседование»
Чтобы получить файл, укажите e-mail:
Введите e-mail, чтобы получить доступ к документам
Подтвердите, что вы не робот,
указав номер телефона:
Введите телефон, чтобы получить доступ к документам
Уже скачали 52300
- 423 Locked
Страница, которую запрашивает пользователь, заблокирована от применения указанного метода. Возможен следующий вариант решения проблемы: перезагрузка роутера и компьютера и использование статистического IP.
- 424 Failed Dependency
Успешное выполнение данного запроса зависит от исхода других операций. Если одна из них завершится неуспешно, то и остальные тоже. В случае, если условия не будут соблюдены, соединение разорвется.
- 425 Unordered Collection
Этот код ошибки HTTP возникает, если клиент отправил запрос, указывающий позицию в неупорядоченной коллекции. Также причиной данного кода ответа может быть использование порядка элементов, отличающегося от серверного.

Читайте также
- 426 Upgrade Required
Ошибка говорит о том, что необходимо обновить протокол. Указываются точные расширения протокола, которыми должен обслуживаться ресурс.
Эта ошибка возникает, когда сервер запрашивает соединение, которое не поддерживается клиентом.
- 428 Precondition Required
Этот код статуса означает, что сервер требует, чтобы запрос был условным. Это значит, что он должен соответствовать условиям правильной отправки данных на сервер. Так он сможет выдать корректные данные.
- 429 Too Many Requests
Этот код ошибок HTTP возникает, когда превышен лимит отправляемых пользователем запросов за короткий промежуток времени. Это делается, прежде всего, из соображений безопасности.
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large
Невозможна обработка запроса пользователя, так как отправлен заголовок слишком большой длины. Возможно также отсутствие ответа кодом со стороны сервера. В таком случае соединение будет разорвано.
Решение проблемы: сокращение длины заголовков и отправка повторного запроса.
- 434 Requested Host Unavailable
Сведения о данном HTTP-коде не найдены.
- 444 No Response
Это код ошибки HTTP со стороны клиента в веб-сервере Nginx. Он сообщает, что соединение закрыто без отправки данных клиенту. Нельзя использовать данный метод в текущей процедуре обработки события.
Nginx — это мощный веб-сервер. Чаще всего его используют в качестве сервера-посредника и обратного сервера. Nginx расходует минимум ресурсов и держит большое количество одновременных соединений.
- 449 Retry With
Ошибка говорит о том, что полученных данных недостаточно для обработки запроса сервером. Рекомендуется внести корректировки в запрос и повторить его.
- 450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls
Эту ошибку увидят дети, которые пытаются войти на заблокированный ресурс. Избежать появления данного кода ответа можно, если изменить параметры родительского контроля.
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
Клиент видит данный код ошибки HTTP в случае, если доступ к сайту закрыт по юридическим причинам. Это могут быть государственные санкции, цензура, требование правообладателя о нарушении авторских прав.
- 456 Unrecoverable Error
При обработке запроса пользователя появляются непоправимые ошибки в базе данных.
- 499 Client Closed Request
Эту ошибку веб-сервер Nginx выдает в случае, если клиент закрыл соединение во время его обработки. Сервер не может отправить назад заголовок HTTP.
Серверные коды ошибок HTTP
Эти ошибки не относятся к пользовательским. Они возникают со стороны сервера, когда он не может обработать запрос клиента или осуществить запрашиваемое действие.
- 500 Internal Server Error
Код ошибки HTTP сервера появляется, когда он встречает ситуацию, обработка которой ему не знакома. Также возможен вариант, что данный запрос не поддерживается сервером и его обработка невозможна. В таких ситуациях сервер тоже отправляет HTTP-статус 500.
- 501 Not Implemented
Ошибка 501 сообщает, что метод запроса сервером не поддерживается и его невозможно корректно обработать.
В ряде случаев в теле ошибки может быть указано: «Отправьте запрос позднее. Возможно, необходимая функция будет доступна».
- 502 Bad Getaway
Такая ошибка отправляется в случае недействительного ответа от вышестоящего сервера. Основная причина — несогласованные протоколы сервера и посредника.
- 503 Service Unavailable
Сервер временно не доступен. Он не может обработать запрос клиента по следующим причинам:
- Перегрузка сервера из-за обращения большого количества пользователей и нехватки ресурсов для обработки всех запросов.
- Техническое обслуживание сервера, которое приводит к временной блокировке его работы.
Клиенту рекомендуется отправить запрос позднее.
- 504 Gateway Timeout
Это код ошибки HTTP сервера является аналогом статуса 408. Сервер действует как шлюз и не получил ответ от вышестоящего сервера в обозначенное в настройках время.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
Этот код аналогичен 426. Он сообщает, что сервер не поддерживает версию протокола HTTP, который используется клиентом. Это случается, если используется устаревший формат HTTP-протокола. Решением проблемы будет установка одной версии.
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates
Этот код говорит о проблемах в настройках сервера. Программисту сначала нужно обнаружить суть проблемы, а в дальнейшем выбрать наиболее эффективное решение.
- 507 Insufficient Storage
Код ошибки HTTP сервера 507 сообщает о том, что не хватает места для обработки пользовательских запросов. Решение: необходимо освободить пространство на сервере или расширить его. В этом случае не возникнет трудностей с обработкой запросов клиента.
- 508 Loop Detected
Данный код сервер отправляет в случае, если обнаружена цикличность запросов клиента. Это приводит к закрытию операции.
- 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded
Это сообщение о том, что превышен лимит потребляемого трафика. Ошибка актуальна в случае, если установлено ограничение.
- 510 Not Extended
У сервера отсутствует расширение, которое пользователь запрашивает. Список доступных расширений прописывается в теле ошибки.
- 511 Network Authentication Required
511 код ошибки HTTP сервера означает, что пользователю необходимо авторизоваться. Данные для аутентификации необходимы при PPPoE-подключении.
Способы устранения некоторых кодов ошибок HTTP
Рассмотрим, что рекомендуется делать для устранения ошибок протокола HTTP:
- Если внесены изменения после тестирования программного обеспечения, нужно обновить веб-браузер.
- Проанализируйте журнал сервера для понимания процессов обработки запросов. У веб-серверов Apache и Nginx имеются файлы access.log и error.log. В них содержатся необходимые сведения.
- Обратите внимание: описание кодов ошибок HTTP— это часть стандарта. Он осуществляется приложением, которое обслуживает запросы клиента. Получается, что код ответа сервера во многом определяется тем, как программное обеспечение обрабатывает ту или иную ошибку.
Итак, рассмотрим самые распространенные ошибки со стороны клиента или сервера.
Ошибка 400 Bad Request
Среди основных причин, которые приводят к возникновению ошибки 400:
- Большое количество файлов cookies и данных в кэше. Решением проблемы будет очистка кэша веб-браузера и файлов cookies.
- Неисправности в браузере.
- Неправильный HTTP-запрос из-за клиентской ошибки, например, при использовании curl.
Ошибка 401 Unauthorized
Код ошибки HTTP запроса 401 сообщает, что клиенту нужно войти на сайт, используя действительный ID пользователя и пароль.
Эта ошибка появляется, когда клиент пытается получить доступ к просмотру ресурса, защищенного HTTP-авторизацией. Код ошибки будет появляться до тех пор, пока клиент не введет действительный логин и пароль. Он внесен в файл .htpasswd.
Ошибка 403 Forbidden
Этот код состояния сообщает клиенту, что сервер не может выполнить запрос из-за того, что имеется запрет на доступ к требуемым файлам или страницам.
В основном код ошибки 403 появляется, если у клиента нет прав на чтение файла, который он запрашивает.
Рассмотрим, каким образом можно устранить ошибку 403 на следующем примере:
- клиент осуществляет попытку открыть индексный файл (http://example.com/index.html);
- рабочий веб-браузер принадлежит пользователю www-data;
- индексный файл расположен в /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html.
Итак, когда клиент видит код ошибки 403, первым делом нужно проверить, есть ли у пользователя www-data право доступа.
Другая распространенная причина появления кода ошибки 403 — намеренное использование файла .htaccess для того, чтобы установить запрет определенным IP-адресам на доступ к ресурсам. Поэтому в случае получения такого кода ошибки нужно проверить настройки файла .htaccess.
Сервер может отправлять ошибку 403 и в случае, если клиент пытается открыть каталог, у которого нет индексного файла и отключен листинг. Например, клиент пытается открыть каталог http://example.com/emptydir/. При этом в emptydir отсутствует индексный файл. Рекомендуется включить листинг каталога в настройках сервера.
Ошибка 404 Not Found
Код ошибки HTTP 404 сообщает, что сервер не находит данные по запросу клиента.
Причин возникновения HTTP-статуса 404 может быть много. Рассмотрим основные факторы, которые приводят к данной ошибке, а также возможные варианты решения проблемы:
- Первым делом проверьте правильность написания ссылки, которая отправляет клиента на сервер.
- Часто случается, что клиент вводит неправильный URL.
- Есть вероятность, что запрашиваемый файл отсутствует в указанном месте на сервере (перемещен или удален).
- Проверьте, верно ли указано расположение корневой директории (document root) в конфигурации сервера.
- Ошибку 404 может вызвать и то, что у пользователя, которому принадлежит рабочий процесс, нет необходимых прав для открытия каталога, где находится необходимый файл. Для этого требуются соответствующие права доступа.
- Проверьте, поддерживает ли сервер символические ссылки.
Ошибка 500 Internal Server Error
Код ошибки HTTP сервера 500 говорит о том, что есть внутренние неизвестные причины, которые не позволяют выполнить запрос пользователя. Случается, что сервер отправляет этот код в ситуациях, когда больше подходят другие коды 5xx.
Основные причины ошибки 500: неправильные права доступа на папки и файлы, вызывающие невозможность запуска скрипта. Также неправильная инструкция в файле .htaccess или неподдерживаемые директивы приводят к данному HTTP-статусу в ответ на запрос клиента.
Ошибка 502 Bad Gateway
Код ошибки 502 является результатом запроса, при котором был получен недопустимый ответ от сервера.
В случае, если это обратный прокси-сервер (выравниватель нагрузки) необходимо проверить:
- backend сервера;
- верно ли настроен обратный прокси и правильный ли backend в настройках;
- настройки сетевого соединения между серверами backend и обратным прокси-сервером. Также нужно проверить порты и отсутствует ли блокировка брандмауэром;
- есть ли разрешения у сокетов и корректно ли они расположены.
Ошибка 503 Service Unavailable
Код ошибки 503 сообщает, что сервер временно недоступен. Это может быть связано с перегрузкой или техническим обслуживанием.
Технические работы проводятся в случае нехватки ресурсов, плановой разгрузки сервера, а также при его настройке для отработки большого количества входящих запросов.
Ошибка 504 Gateway Timeout
Код состояния 504 говорит о том, что сервер не получает ответ от севера-посредника (шлюз, прокси-сервер) в рамках установленного времени. Сбои в шлюзах влияют на работу основного сервера.

Читайте также
Основные причины появления кода ошибки HTTP сервера 504:
- проблемы с сетью, слабое интернет-соединение между шлюзом и основным сервером;
- перегрузка сервера-шлюза, который из-за большой нагрузки не может быстро выполнить работу;
- в настройках сервера указан короткий период ожидания ответа от сервера-посредника.
Способы проверки кодов ошибок HTTP
Проверить коды ошибки состояния HTTP можно, используя специализированные сервисы или через опции браузера. В браузере Google Chrome код ответа можно посмотреть в графе Status в разделе Network. Для этого нужно сделать следующее:
- откройте в веб-браузере нужную вам страницу;
- нажмите клавишу F12 для того, чтобы открыть дополнительное окно с консолью.
Другой способ посмотреть код ответа — это специализированные сервисы, такие как bertal, 2ip, cy-pr, wwhois, 4seo.
Принцип их работы рассмотрим на примере mainspy:
- Зайдите на сайт сервиса.
- Введите URL для проверки. Можно один или несколько.
- Запустите проверку.
В течение нескольких секунд на экране отобразится отчет, в котором напротив каждого URL будет стоять код ответа сервера.
Аналитика кодов ответа доступна не только роботам. Человек также может интерпретировать полученные от сервера данные и быстро определить, где ошибка и каким образом ее можно устранить.
Часто задаваемые вопросы о кодах ошибок HTTP
Что сообщают коды ошибок?
Коды ошибок HTTP — это трехзначный код, отправляемый сервером в ответ на запрос клиента. Его используют поисковые роботы, а поясняющие слова после кода ориентированы на пользователей сети.
Что нужно делать с кодами ошибок HTTP?
Нужно обязательно обновить веб-браузер в случае внесения изменений на сервере.
Проверьте системную информацию на сервере для того, чтобы понять, как происходит обработка запросов клиента. Веб-серверы Apache или Nginx создают файлы + access.log + и + error.log +. Их можно сканировать и получить необходимые сведения.
О чем говорит ошибка 404?
Страница, которую запрашивает пользователь, не найдена. Запрос принят, но по URL нет необходимого ресурса. Он может быть перемещен или удален.
Таким образом, HTTP-статус кратко сообщает суть ответа сервера. Это может быть успешное выполнение запроса пользователя или уведомление о наличии определенных трудностей. Знание основных кодов ошибок HTTP со стороны сервера или со стороны клиента, а также способов устранения проблем поможет пользователям оперативно решить возникающие трудности в работе с веб-серверами или приложениями.