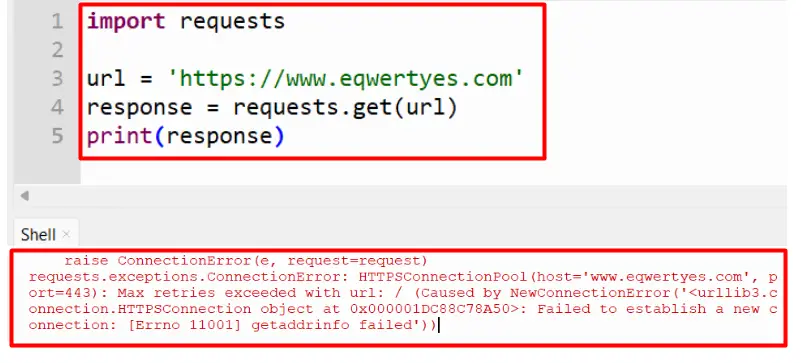
I’m trying to get the content of App Store > Business:
import requests
from lxml import html
page = requests.get("https://itunes.apple.com/in/genre/ios-business/id6000?mt=8")
tree = html.fromstring(page.text)
flist = []
plist = []
for i in range(0, 100):
app = tree.xpath("//div[@class='column first']/ul/li/a/@href")
ap = app[0]
page1 = requests.get(ap)
When I try the range with (0,2) it works, but when I put the range in 100s it shows this error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/preetham/Desktop/eg.py", line 17, in <module>
page1 = requests.get(ap)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/requests/api.py", line 55, in get
return request('get', url, **kwargs)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/requests/api.py", line 44, in request
return session.request(method=method, url=url, **kwargs)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/requests/sessions.py", line 383, in request
resp = self.send(prep, **send_kwargs)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/requests/sessions.py", line 486, in send
r = adapter.send(request, **kwargs)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/requests/adapters.py", line 378, in send
raise ConnectionError(e)
requests.exceptions.ConnectionError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='itunes.apple.com', port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: /in/app/adobe-reader/id469337564?mt=8 (Caused by <class 'socket.gaierror'>: [Errno -2] Name or service not known)
The “Max retries exceeded with url” error thrown sometimes by the requests library in Python falls under two classes of errors: requests.exceptions.ConnectionError (most common) and requests.exceptions.SSLError. In this article, we will discuss the causes of the error, how to reproduce it, and, importantly, how to solve the error.
The error occurs when the requests library cannot successfully send requests to the issued site. This happens because of different reasons. Here are the common ones. of them:
- Wrong URL – A typo maybe (go to Solution 1),
- Failure to verify SSL certificate (Solution 2),
- Using requests with no or unstable internet connection (Solution 3), and
- Sending too many requests or server too busy (Solution 4)
Wrong URL – A typo?
There is a chance that the URL you requested was incorrect. It could be distorted because of a typo. For example, suppose we want to send a get request to “https://www.example.com” (which is a valid URL), but instead, we issued the URL: “https://www.example.cojkm” (we used .cojkm in the domain extension instead of .com).
|
import requests url = ‘https://www.example.cojkm’ response = requests.get(url) print(response) |
Output:
requests.exceptions.ConnectionError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='www.example.cojkm', port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: / (Caused by NewConnectionError('<urllib3.connection.VerifiedHTTPSConnection object at 0x7fd5b5d33100>: Failed to establish a new connection: [Errno 111] Connection refused'))
Failure to verify the SSL certificate
The requests library, by default, implements SSL certificate verification to ensure you are making a secure connection. If the certificates can’t be verified, you end up with an error like this:
requests.exceptions.SSLError: [Errno 1] _ssl.c:503: error:14090086:SSL routines:SSL3_GET_SERVER_CERTIFICATE:certificate verify failed
Using requests with no or unstable internet connection
The requests package sends and receives data via the web; therefore, the internet connection should be available and stable. If you have no or unstable internet, requests will throw an error like this:
Error: requests.exceptions.ConnectionError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host=’www.example.com’, port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: / (Caused by NewConnectionError(‘<urllib3.connection.VerifiedHTTPSConnection object at 0x7f7f5fadb100>: Failed to establish a new connection: [Errno -3] Temporary failure in name resolution’))
Sending too many requests/ server overload
Some websites blocks connections when so many requests are made so fast. Another problem related to this is when the server is overloaded – managing a large number of connections at the same time. In this case, requests.get() throws an error like this:
requests.exceptions.ConnectionError: HTTPConnectionPool(host='www.srgfesrsergserg.com', port=80): Max retries exceeded with url: / (Caused by NewConnectionError('<urllib3.connection.HTTPConnection object at 0x0000008EC69AAA90>: Failed to establish a new connection: [Errno 11001] getaddrinfo failed'))
Solutions to requests Max Retries Exceeded With Url Error
In this section, we will cover some solutions to solve the “Max Retries Exceeded With Url” Error caused by the above reasons.
Solution 1: Double check URL
Ensure that you have a correct and valid URL. Consider a valid URL mentioned earlier: “https://www.example.com“. “Max retries exceeded with url” error mostly when incorrect edits are done around www and top-level domain name (e.g., .com).
Another error arises when the scheme/protocol (https) is incorrectly edited: requests.exceptions.InvalidSchema. If the second-level domain (in our case, “example”) is wrongly edited, we will be directed to a different website altogether, and if the site does not exist, we get a 404 response.
Other wrong URLS that leads to “Max retries exceeded with url” is “wwt.example.com” and “https://www.example.com “(a white space after .com).
Solution 2: Solving SSLError
As mentioned, the error is caused by an untrusted SSL certificate. The quickest fix is to set the attribute verify=False on requests.get(). This tells requests to send a request without verifying the SSL certificate.
|
requests.get(‘https://example.com’, verify=False) |
Please be aware that the certificate won’t be verified; therefore, your application will be exposed to security threats like man-in-the-middle attacks. It is best to avoid this method for scripts used at the production level.
Solution 3: Solving the “Max retries exceeded with url” error related to an unstable connection
This solution fits cases when you have intermittent connection outages. In these cases, we want requests to be able to carry out many tries on requests before throwing an error. For this case, we can use two solutions:
- Issue timeout argument in requests.get(), or
- Retry connections on connections-related errors
Solution 3a: Issue timeout argument in requests.get()
If the server is overloaded, we can use a timeout to wait longer for a response. This will increase the chance of a request finishing successfully.
|
import requests url = ‘https://www.example.com’ response = requests.get(url, timeout=7) print(response) |
The code above will wait 7 seconds for the requests package to connect to the site and read the source.
Alternatively, you can pass a timeout as a 2-element tuple where the first element is connection timeout (time to establish a connection to the server) and the second value is read timeout (time allowed for the client to read data from the server)
|
requests.get(‘https://api.github.com’, timeout=(3, 7)) |
When the above line is used, a connection must be established within 3 seconds, and data read within 7 seconds; otherwise, requests raise Timeout Error.
Solution 3b: Retry connections on connections-related errors
The requests use the Retry utility in urllib3 (urllib3.util.Retry) to retry connections. We will use the following code to send requests (explained after).
|
import requests from requests.adapters import HTTPAdapter, Retry import time def send_request(url, n_retries=4, backoff_factor=0.9, status_codes=[504, 503, 502, 500, 429]): sess = requests.Session() retries = Retry(connect=n_retries, backoff_factor=backoff_factor, status_forcelist=status_codes) sess.mount(«https://», HTTPAdapter(max_retries=retries)) sess.mount(«http://», HTTPAdapter(max_retries=retries)) response = sess.get(url) return response |
We have used the following parameters on urllib3.util.Retry class:
- connect – the number of connection-related tries. By default, send_request() will make 4 tries plus 1 (an original request which happens immediately).
- backoff_factor – determines delays between retries. The sleeping time is computed with the formula {backoff_factor} * (2 ^ ({retry_number} – 1)). We will work on an example for this argument when calling the function.
- status_forcelist – retry for all connections that resulted in 504, 503, 502, 400, and 429 status codes only (Read more about status codes in https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_HTTP_status_codes)
Let’s now call our function and time the execution.
|
# start the timer start_time = time.time() # send a request to GitHub API url = «https://api.github.com/users» response = send_request(url) # print the status code print(response.status_code) # end timer end_time = time.time() # compute the run time print(«Run time: «, end_time—start_time) |
Output:
200 Run time: 0.8597214221954346
The connection was completed successfully (status 200) taking 0.86 of a second to finish. To see the implementation of backoff, let’s try to send a request to a server that does not exist, catch an exception when it occurs and compute execution time.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
try: # start execution timer start_time = time.time() url = «http://localhost/6000» # call send_request() method to send a request to the url # this will never be successful because there is no server running # on port 6000. response = send_request(url) print(response.status_code) except Exception as e: # Catch any exception — execution will end here because # requests can’t connect to http://localhost/6000 print(«Error Name: «, e.__class__.__name__) print(«Error Message: «, e) finally: # Pick end time end_time = time.time() # Calculate the time taken to execute. print(«Run time: «, end_time—start_time) |
Output:
Error Name: ConnectionError
Error Message: HTTPConnectionPool(host='localhost', port=80): Max retries exceeded with url: /6000 (Caused by NewConnectionError('<urllib3.connection.HTTPConnection object at 0x7f06a5862a00>: Failed to establish a new connection: [Errno 111] Connection refused'))
Run time: 12.61784315109253
After 4 retries (plus 1 original request) with a backoff_factor=0.9, the execution time was 12.6 seconds. Let’s use the formula we saw earlier to compute sleeping time.
sleeping_time = {backoff_factor} * (2 ^ ({retry_number} – 1))
There are 5 requests in total
- First request (which is made immediately) – 0 seconds sleeping,
- First retry ( which is also sent immediately after the failure of the first request) – 0 seconds sleeping,
- Second retry -> 0.9*(2^(2-1)) = 0.9*2 = 1.8 seconds of sleeping,
- Third retry -> 0.9*(2^(3-1)) = 0.9*4 = 3.6 seconds of sleeping time, and,
- Fourth retry -> 0.9*(2^(4-1)) = 0.9*8 = 7.2 seconds.
That is a total of 12.6 seconds of sleeping time implemented by urllib3.util.Retry. The actual execution time is 12.61784315109253 seconds. The 0.01784315109253 difference, which is not accounted for, is attributable to the DNC and general computer power latency.
Solution 4: Using headers when sending requests
Some websites blocks web crawlers. They notice that a bot is sending requests based on headers passed. For example, let’s run this code and turn on the verbose to see what happened behind the hoods.
|
import http.client # turn verbose on http.client.HTTPConnection.debuglevel = 1 import requests url = ‘https://www.example.com’ response = requests.get(url) |
Output (truncated):
send: b'GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: www.example.com\r\nUser-Agent: python-requests/2.28.1\r\nAccept-Encoding: gzip, deflate\r\nAccept: */*\r\nConnection: keep-alive\r\n\r\n' reply: 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n'
In that log, you can see that User-Agent is python-requests v2.28.1 and not a real browser. With such identification, you might get blocked and get the “Max retries exceeded with url” error. To avoid this, we need to pass our actual browser as a user-agent. You can go to the following link to get some headers: http://myhttpheader.com/. In that link, my user-agent is “Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:91.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/91.0”. Let’s now use that user agent instead.
|
import http.client # Turn verbose on. http.client.HTTPConnection.debuglevel = 1 import requests headers = {‘User-Agent’:‘Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:91.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/91.0’} url = ‘https://www.example.com’ response = requests.get(url, timeout=5, headers=headers) |
Output (truncated)
send: b'GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: www.example.com\r\nUser-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:91.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/91.0\r\nAccept-Encoding: gzip, deflate\r\nAccept: */*\r\nConnection: keep-alive\r\n\r\n' reply: 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n'
Conclusion
The “Max retries exceeded with url” error is caused by an invalid URL, server overloading, failed SSL verification, unstable internet connection, and an attempt to send many requests to a server. In this article, we discussed solutions for all these problems using examples.
The key is always to understand the kind of error you have and then pick the appropriate solution.
“ConnectionError: Max retries exceeded with url” is a common error in Python related to a connection error. The below explanations can help you know more about the cause of this error and solutions.
How does the error “Max retries exceeded with URL” happen?
“Max retries exceeded with URL” is a common error related to a connection error. You will encounter this situation while making requests using the requests library.
This error indicates that the request could not be completed successfully. There can be no more connections since the server is overloaded. You need to verify that you can connect to the device causing the problems. There are five common cases:
- The host is not listening on the port given
- There are too many open HTTPconnections.
- There is not enough RAM on the computer.
- Another option is that the target website has blacklisted the IP as a result of the frequent requests.
- The requested URL is incorrect.
In general, the detailed error message should resemble the following output. The word “requests.exceptions.ConnectionError” normally appears at the beginning of an error message, informing us that something went wrong when the request was attempting to connect. There are hence no general solutions because it depends on your error message.
The exception “requests.exceptions.SSLError” can occasionally appear, which is obviously an SSL-related problem. The error comes with a longer message text, potentially something like this: Unable to establish a new connection: Connection rejected or [Errno -2] Unknown name or service are also errors. These messages allow us to further identify and address the problem.
[Errno 61] Connection refused
Example
import requests
response = requests.get("https://eu.httpbin.org/")
print(response.status_code)
The fact that the website eu.httpbin.org is not a secure HTTPS connection, and port 443 is of HTTPS, while port 80 is instead an HTTP one. One possible reason why this would happen is if the connection was attempted to port 443, but the host was not listening to it. In this case, consider listening on port 80 instead.
import requests
response = requests.get("http://eu.httpbin.org/")
print(response.status_code)
[Errno -2] Name or service not known
Example
import requests
from lxml import html
page = requests.get("https://learnshareit.com")
tree = html.fromstring(page.text)
Your connection is being denied by the LearnshareIT server at this time (you had sent too many requests from the same IP address in a short period of time). The error log can be understood as “The connection could not be established as the intended machine actively rejected it. To fix this, please read the two approaches below.
Method 1: Let enough time between queries to the server
You must let enough time for queries to the server, which may be done using Python’s sleep() (time in sec) function (remember to import sleep)
import time
page = ''
while page == '':
try:
page = requests.get("https://learnshareit.com")
break
except:
print("Error.Waiting 6s")
time.sleep(6)
print("Now try reconnecting")
continue
Method 2: Disable SSL verification
Another way to fix this problem is to disable SSL verification. You should also use try catch exceptions like 1st method to make sure not to send too many requests:
import requests
page = requests.get("https://learnshareit.com", verify=False)
Summary
The error ConnectionError: Max retries exceeded with url occurs when too many failed requests have been made. To help with this situation, make sure you are connecting to the correct URL and remember to leave a sleep time for your requests before continuing to retry.
Maybe you are interested in similar errors:
- RuntimeError: dictionary changed size during iteration
- TypeError: int() argument must be a string, a bytes-like object or a number, not ‘list’
- JSONDecodeError: Expecting value: line 1 column 1 (char 0)
- UnicodeEncodeError: ‘ascii’ codec can’t encode character in position
- SyntaxError: Missing parentheses in call to ‘print’ in Python
- DataFrame constructor not properly called!
I’m Edward Anderson. My current job is as a programmer. I’m majoring in information technology and 5 years of programming expertise. Python, C, C++, Javascript, Java, HTML, CSS, and R are my strong suits. Let me know if you have any questions about these programming languages.
Name of the university: HCMUT
Major: CS
Programming Languages: Python, C, C++, Javascript, Java, HTML, CSS, R
The «requests.exceptions.ConnectionError: Max retries exceeded with url» error in Python is raised when the requests library is unable to establish a connection to the requested URL, and has exhausted the maximum number of retries it is set to perform. This error can be caused by a variety of reasons, including network timeouts, DNS resolution issues, or a general inability to reach the server. In this article, we will discuss several methods for resolving this error and successfully establishing a connection to the desired URL.
Method 1: Increase Retry Limit
If you are encountering the requests.exceptions.ConnectionError with the message «Max retries exceeded with url» error in Python, it means that the request you are trying to make has failed due to a connection error. This error can occur due to various reasons such as network issues, server downtime, or a slow internet connection.
One of the ways to fix this error is to increase the retry limit. This means that if the request fails due to a connection error, the program will retry the request a certain number of times before giving up. Here is how you can increase the retry limit in Python using the requests library:
import requests
from requests.adapters import HTTPAdapter
from requests.packages.urllib3.util.retry import Retry
retries = Retry(total=5, backoff_factor=0.1, status_forcelist=[ 500, 502, 503, 504 ])
session = requests.Session()
session.mount('http://', HTTPAdapter(max_retries=retries))
response = session.get('https://www.example.com')In the above code, we first import the necessary libraries. Then we define the number of retries we want to make using the Retry object. In this example, we have set the total retries to 5, with a backoff factor of 0.1 seconds between retries, and a list of status codes that should trigger a retry.
Next, we create a session object using the requests.Session() method. This allows us to reuse the same TCP connection for multiple requests, which can improve performance.
Finally, we mount the HTTPAdapter with the retries to the session object using the session.mount() method. This ensures that the retries are applied to all requests made using the session object.
We then make the request using the session.get() method, which will retry the request up to the specified number of times if it fails due to a connection error.
By increasing the retry limit, you can improve the reliability of your Python code and avoid the requests.exceptions.ConnectionError error.
Method 2: Use a Proxy Server
If you are facing the requests.exceptions.ConnectionError error with the message «Max retries exceeded with url» while using Python requests library, it indicates that the requests library was unable to establish a connection with the given URL. One of the ways to fix this error is by using a proxy server.
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your computer and the internet. By using a proxy server, you can route your requests through a different IP address, which can help you bypass any network restrictions or firewalls that may be causing the ConnectionError.
Here are the steps to fix the ConnectionError using a proxy server:
Step 1: Install the requests library
If you have not already installed the requests library, you can install it using the following command:
Step 2: Import the requests library
Import the requests library using the following command:
Step 3: Set up the proxy server
You can set up a proxy server by passing the proxy server URL as a parameter to the requests.get() method. Here is an example code snippet:
proxies = {
'http': 'http://localhost:8080',
'https': 'https://localhost:8080',
}
response = requests.get('https://www.example.com', proxies=proxies)In the above code, we have defined a dictionary proxies that contains the URL of the proxy server. We have also passed this dictionary as a parameter to the requests.get() method.
Step 4: Verify the response
After making the request, you can verify the response by checking the status code of the response. Here is an example code snippet:
if response.status_code == 200:
print('Request successful')
else:
print('Request failed with status code: ', response.status_code)In the above code, we have checked if the status code of the response is 200, which indicates that the request was successful.
Step 5: Handle exceptions
If the request fails even after using a proxy server, you can handle the exception using a try-except block. Here is an example code snippet:
try:
response = requests.get('https://www.example.com', proxies=proxies)
response.raise_for_status()
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as err:
print('HTTP error occurred: ', err)
except Exception as err:
print('Other error occurred: ', err)In the above code, we have used a try-except block to catch any HTTP errors or other exceptions that may occur during the request.
That’s it! By following these steps, you can fix the requests.exceptions.ConnectionError error with the message «Max retries exceeded with url» using a proxy server.
Method 3: Handle Network Exceptions
When working with Python requests library, you may encounter the requests.exceptions.ConnectionError error message with the Max retries exceeded with url description. This error occurs when the request to the URL fails due to network issues such as DNS resolution failures, connection timeouts, or HTTP errors. To handle this error, you can use the requests library’s built-in exception handling mechanism. Here’s how to do it in a few simple steps:
- Import the
requestslibrary.
- Wrap the request code in a
try-exceptblock to catch theConnectionErrorexception.
try:
response = requests.get(url)
# process the response
except requests.exceptions.ConnectionError as e:
print("ConnectionError:", e)- Use the
max_retriesparameter to set the maximum number of retries for the request.
from requests.adapters import HTTPAdapter
from requests.packages.urllib3.util.retry import Retry
retry_strategy = Retry(
total=3,
backoff_factor=1,
status_forcelist=[ 500, 502, 503, 504 ],
method_whitelist=["HEAD", "GET", "OPTIONS"]
)
adapter = HTTPAdapter(max_retries=retry_strategy)
http = requests.Session()
http.mount("https://", adapter)
http.mount("http://", adapter)
try:
response = http.get(url)
# process the response
except requests.exceptions.ConnectionError as e:
print("ConnectionError:", e)- Use the
timeoutparameter to set a timeout for the request.
try:
response = requests.get(url, timeout=5)
# process the response
except requests.exceptions.ConnectionError as e:
print("ConnectionError:", e)- Use the
verifyparameter to disable SSL verification if necessary.
try:
response = requests.get(url, verify=False)
# process the response
except requests.exceptions.ConnectionError as e:
print("ConnectionError:", e)By using these techniques, you can handle the requests.exceptions.ConnectionError error and ensure that your Python code can handle network exceptions effectively.
Method 4: Check URL and Network Connectivity
If you are encountering the error «requests.exceptions.ConnectionError: Max retries exceeded with url» in Python, it means that the program is unable to connect to the specified URL due to network connectivity issues. One way to solve this problem is to check the URL and network connectivity using the following steps:
Step 1: Import the requests module
The first step is to import the requests module in your Python code. The requests module allows you to send HTTP requests using Python.
Step 2: Define the URL
Next, define the URL that you want to connect to. In this example, we will use the Google homepage URL.
url = "https://www.google.com"Step 3: Check the network connectivity
Before sending a request to the URL, check the network connectivity using the following code:
import socket
try:
socket.create_connection(("www.google.com", 80))
print("Network connection is active")
except OSError:
print("Network connection is down")This code creates a connection to the Google homepage on port 80 (HTTP) using the socket module. If the connection is successful, it means that the network connectivity is active. If the connection fails, it means that the network connectivity is down.
Step 4: Send a request to the URL
If the network connectivity is active, you can send a request to the URL using the following code:
try:
response = requests.get(url)
print(response.content)
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print("Error: ", e)This code sends a GET request to the Google homepage URL using the requests module. If the request is successful, it prints the content of the response. If the request fails, it prints the error message.
Method 5: Use a Different HTTP Library
If you are facing the error requests.exceptions.ConnectionError: Max retries exceeded with url while using the Python Requests library, it may be due to the fact that the library is unable to establish a connection to the server.
One way to fix this issue is to use a different HTTP library. Here are some examples of how you can do this:
The urllib library is a built-in Python library that can be used to send HTTP requests. Here is an example of how you can use it to send a GET request:
import urllib.request
response = urllib.request.urlopen('http://example.com/')
html = response.read()
print(html)The httplib library is another built-in Python library that can be used to send HTTP requests. Here is an example of how you can use it to send a GET request:
import httplib
conn = httplib.HTTPConnection("www.python.org")
conn.request("GET", "/")
r1 = conn.getresponse()
print(r1.status, r1.reason)
data1 = r1.read()
print(data1)
conn.close()The http.client library is a newer version of the httplib library and can also be used to send HTTP requests. Here is an example of how you can use it to send a GET request:
import http.client
conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection("www.python.org")
conn.request("GET", "/")
r1 = conn.getresponse()
print(r1.status, r1.reason)
data1 = r1.read()
print(data1)
conn.close()The urllib3 library is a third-party library that can be used to send HTTP requests. Here is an example of how you can use it to send a GET request:
import urllib3
http = urllib3.PoolManager()
response = http.request('GET', 'http://example.com/')
print(response.data)There are multiple errors that appear while programming in Python such as SyntaxError, Valueerror, IndexError, etc. One such error is “ConnectionError” which arises in Python while working with the “request” module. To rectify this particular error, various solutions are used in Python.
In this Python post, we will explain the reason and solutions for “ConnectionError: Max retries exceeded with URL” using suitable examples. This post will explore the following content for a profound understanding of the concept:
- Reason: Unable to Establish a Connection to a Specified URL
- Solution 1:Check the URL
- Solution 2: Use a Retry Object
- Solution 3: Use Try-Except
- Solution 4: Use a Stable Internet Connection
Reason: Unable to Establish a Connection to a Specified URL
The stated error occurs when a Python script cannot establish a connection to a specified URL after a certain number of retries. The error message states “failed to establish a connection” because of exceeding the maximum number of retries in a program. The stated error may also occur because of network connectivity issues, down servers, or incorrect URLs.
The above snippet shows that the “ConnectionError” has been returned in the output.
Solution 1: Check the URL
To resolve this error you need to make sure that the URL you are trying to connect to is correct and reachable. We can check this specified URL by accessing it in a web browser. If the specified URL is incorrect, then you must correct it. In such a case, correcting the specified URL will resolve the stated error.
Code:
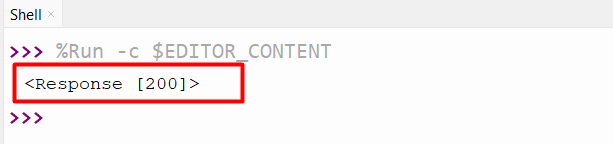
import requests url = 'https://www.itslinuxfoss.com' response = requests.get(url) print(response)
The “requests” module “requests.get()” function is used to make the connection to the specified URL.
Output:
The above output confirmed that the connection has been established.
Solution 2: Use a Retry Object
We can also resolve the “Connection Error” by increasing the number of retries in the Python script. The retry object method will give more chances to establish a connection to a specified URL.
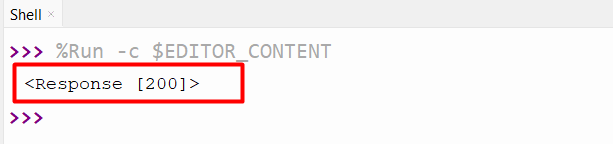
Code:
import requests
from requests.adapters import HTTPAdapter
specified_url = "https://www.itslinuxfoss.com"
session = requests.Session()
retry = HTTPAdapter(max_retries=5)
session.mount("http://", retry)
session.mount("https://", retry)
response = session.get(specified_url)
print(response)
The “request” module’s function “HTTPAdapter()” accepts the “max_retries” parameter to increase the number of retries.
Output:
The connection has been built successfully.
Solution 3: Use Try-Except
The error can also be fixed and handled using the “Try-Except” block. This method helps us to continue running our script even if it encounters the “ConnectionError: Max retries exceeded with url” error.
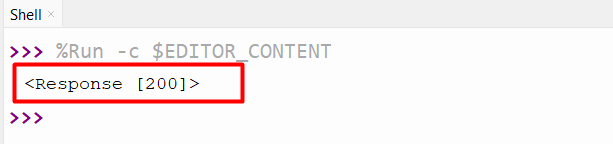
Code:
import requests
specified_url = "https://www.itslinuxfoss.com"
try:
response = requests.get(specified_url)
response.raise_for_status()
print(response)
except requests.exceptions.RequestException:
print("Request failed")
The “try” block executes the code and makes the connection to the URL. But if the connection is not established then the “except” block will run.
Output:
The above output proved that the connection has been established successfully.
Solution 4: Use a Stable Internet Connection
Connectivity issues can also cause this error in Python, so we can rectify this error by using a stable internet connection.
Conclusion
To resolve the ConnectionError error, various solutions are used in Python, such as checking the URL, using a retry object, using a Try-Except block, and maintaining a Stable internet connection. The URL must be double-checked because if the URL is not reachable then the “ConnectionError” appears in the script. The increasing number of retries in Python script and using a try-except block will increase the chances of a successful connection. This guide presented various solutions on how to resolve the error named“ConnectionError: Max retries exceeded with url” in Python.