In python, lists are mutable as the elements of a list can be modified. But if you try to modify a value whose index is greater than or equal to the length of the list then you will encounter an Indexerror: list assignment index out of range.
Python Indexerror: list assignment index out of range Example
If ‘fruits’ is a list, fruits=[‘Apple’,’ Banana’,’ Guava’]and you try to modify fruits[5] then you will get an index error since the length of fruits list=3 which is less than index asked to modify for which is 5.
Python3
fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
print("Type is", type(fruits))
fruits[5] = 'Mango'
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/example.py", line 3, in <module>
fruits[5]='Mango'
IndexError: list assignment index out of range
So, as you can see in the above example, we get an error when we try to modify an index that is not present in the list of fruits.
Python Indexerror: list assignment index out of range Solution
Method 1: Using insert() function
The insert(index, element) function takes two arguments, index and element, and adds a new element at the specified index.
Let’s see how you can add Mango to the list of fruits on index 1.
Python3
fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
print("Original list:", fruits)
fruits.insert(1, "Mango")
print("Modified list:", fruits)
Output:
Original list: ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
Modified list: ['Apple', 'Mango', 'Banana', 'Guava']
It is necessary to specify the index in the insert(index, element) function, otherwise, you will an error that the insert(index, element) function needed two arguments.
Method 2: Using append()
The append(element) function takes one argument element and adds a new element at the end of the list.
Let’s see how you can add Mango to the end of the list using the append(element) function.
Python3
fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
print("Original list:", fruits)
fruits.append("Mango")
print("Modified list:", fruits)
Output:
Original list: ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
Modified list: ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava', 'Mango']
Python IndexError FAQ
Q: What is an IndexError in Python?
A: An IndexError is a common error that occurs when you try to access an element in a list, tuple, or other sequence using an index that is out of range. It means that the index you provided is either negative or greater than or equal to the length of the sequence.
Q: How can I fix an IndexError in Python?
A: To fix an IndexError, you can take the following steps:
- Check the index value: Make sure the index you’re using is within the valid range for the sequence. Remember that indexing starts from 0, so the first element is at index 0, the second at index 1, and so on.
- Verify the sequence length: Ensure that the sequence you’re working with has enough elements. If the sequence is empty, trying to access any index will result in an IndexError.
- Review loop conditions: If the IndexError occurs within a loop, check the loop conditions to ensure they are correctly set. Make sure the loop is not running more times than expected or trying to access an element beyond the sequence’s length.
- Use try-except: Wrap the code block that might raise an IndexError within a try-except block. This allows you to catch the exception and handle it gracefully, preventing your program from crashing.
Last Updated :
30 Jun, 2023
Like Article
Save Article
The reason for the error is that you’re trying, as the error message says, to access a portion of the list that is currently out of range.
For instance, assume you’re creating a list of 10 people, and you try to specify who the 11th person on that list is going to be. On your paper-pad, it might be easy to just make room for another person, but runtime objects, like the list in python, isn’t that forgiving.
Your list starts out empty because of this:
a = []
then you add 2 elements to it, with this code:
a.append(3)
a.append(7)
this makes the size of the list just big enough to hold 2 elements, the two you added, which has an index of 0 and 1 (python lists are 0-based).
In your code, further down, you then specify the contents of element j which starts at 2, and your code blows up immediately because you’re trying to say «for a list of 2 elements, please store the following value as the 3rd element».
Again, lists like the one in Python usually aren’t that forgiving.
Instead, you’re going to have to do one of two things:
- In some cases, you want to store into an existing element, or add a new element, depending on whether the index you specify is available or not
- In other cases, you always want to add a new element
In your case, you want to do nbr. 2, which means you want to rewrite this line of code:
a[j]=a[j-2]+(j+2)*(j+3)/2
to this:
a.append(a[j-2]+(j+2)*(j+3)/2)
This will append a new element to the end of the list, which is OK, instead of trying to assign a new value to element N+1, where N is the current length of the list, which isn’t OK.
Ad
At Career Karma, our mission is to empower users to make confident decisions by providing a trustworthy and free directory of bootcamps and career resources. We believe in transparency and want to ensure that our users are aware of how we generate revenue to support our platform.
Career Karma recieves compensation from our bootcamp partners who are thoroughly vetted before being featured on our website. This commission is reinvested into growing the community to provide coaching at zero cost to their members.
It is important to note that our partnership agreements have no influence on our reviews, recommendations, or the rankings of the programs and services we feature. We remain committed to delivering objective and unbiased information to our users.
In our bootcamp directory, reviews are purely user-generated, based on the experiences and feedback shared by individuals who have attended the bootcamps. We believe that user-generated reviews offer valuable insights and diverse perspectives, helping our users make informed decisions about their educational and career journeys.
Find the right bootcamp for you
X
By continuing you agree to our
Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and you consent to
receive offers and opportunities from Career Karma by telephone, text message, and email.

IndexError: list assignment index out of range
List elements can be modified and assigned new value by accessing the index of that element. But if you try to assign a value to a list index that is out of the list’s range, there will be an error. You will encounter an IndexError list assignment index out of range. Suppose the list has 4 elements and you are trying to assign a value into the 6th position, this error will be raised.
Example:
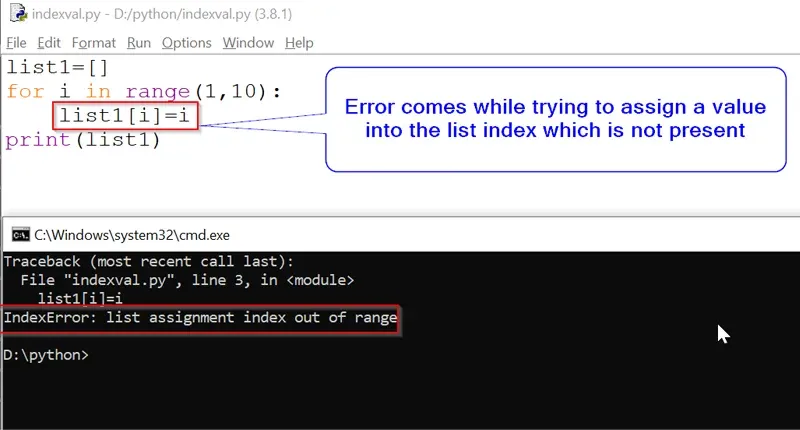
list1=[]
for i in range(1,10):
list1[i]=i
print(list1)Output:
IndexError: list assignment index out of rangeIn the above example we have initialized a “list1“ which is an empty list and we are trying to assign a value at list1[1] which is not present, this is the reason python compiler is throwing “IndexError: list assignment index out of range”.
We can solve this error by using the following methods.
Using append()
We can use append() function to assign a value to “list1“, append() will generate a new element automatically which will add at the end of the list.
Correct Code:
list1=[]
for i in range(1,10):
list1.append(i)
print(list1)Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]In the above example we can see that “list1” is empty and instead of assigning a value to list, we append the list with new value using append() function.
Using insert()
By using insert() function we can insert a new element directly at i’th position to the list.
Example:
list1=[]
for i in range(1,10):
list1.insert(i,i)
print(list1)Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]In the above example we can see that “list1” is an empty list and instead of assigning a value to list, we have inserted a new value to the list using insert() function.
Example with While loop
num = []
i = 1
while(i <= 10):
num[i] = I
i=i+1
print(num)Output:
IndexError: list assignment index out of rangeCorrect example:
num = []
i = 1
while(i <= 10):
num.append(i)
i=i+1
print(num)Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]Conclusion:
Always check the indices before assigning values into them. To assign values at the end of the list, use the append() method. To add an element at a specific position, use the insert() method.
The IndexError: List Assignment Index Out of Range error occurs when you assign a value to an index that is beyond the valid range of indices in the list. As Python uses zero-based indexing, when you try to access an element at an index less than 0 or greater than or equal to the list’s length, you trigger this error.
It’s not as complicated as it sounds. Think of it this way: you have a row of ten mailboxes, numbered from 0 to 9. These mailboxes represent the list in Python. Now, if you try to put a letter into mailbox number 10, which doesn’t exist, you’ll face a problem. Similarly, if you try to put a letter into any negative number mailbox, you’ll face the same issue because those mailboxes don’t exist either.
The IndexError: List Assignment Index Out of Range error in Python is like trying to put a letter into a mailbox that doesn’t exist in our row of mailboxes. Just as you can’t access a non-existent mailbox, you can’t assign a value to an index in a list that doesn’t exist.
Let’s take a look at example code that raises this error and some strategies to prevent it from occurring in the first place.
Example of “IndexError: List Assignment Index Out of Range”
Remember, assigning a value at an index that is negative or out of bounds of the valid range of indices of the list raises the error.
Example:
my_list = [10, 20, 30]
my_list[4] = 6 # Assigning to an out-of-range index
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File"C:\Users\name\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\check.py", line 3, in <module>
My_list[4] = 6 #Assigning to an out of range index
IndexError: list assignment index out of range
How to resolve “IndexError: List Assignment Index Out of Range”
You can use methods such as append() or insert() to insert a new element into the list.
How to use the append() method
Use the append() method to add elements to extend the list properly and avoid out-of-range assignments.
Example:
my_list = [10, 20, 30]
my_list.append(98) # Add a new element at the end of the list
print(my_list)
Output:
[10, 20, 30, 98]
How to use the insert() method
Use the insert() method to insert elements at a specific position instead of direct assignment to avoid out-of-range assignments.
Example:
my_list = [10, 20, 30]
my_list.insert(3,987) #Inserting element at index 3
print(my_list)
Output:
[10, 20, 30, 987]
Now one big advantage of using insert() is even if you specify an index position which is way out of range it won’t give any error and it will just append the element at the end of the list.
Example:
my_list = [10, 20, 30]
my_list.insert(300000,987) #Inserting at an out-of-range index
print(my_list)
Output:
[10, 20, 30, 87]
Track, Analyze and Manage Errors With Rollbar
Managing errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates error monitoring and triaging, making fixing Python errors easier than ever. Try it today!