There are in fact multiples things you need to know about indentation in Python:
Python really cares about indention.
In a lot of other languages the indention is not necessary but improves readability. In Python indentation replaces the keyword begin / end or { } and is therefore necessary.
This is verified before the execution of the code, therefore even if the code with the indentation error is never reached, it won’t work.
There are different indention errors and you reading them helps a lot:
1. «IndentationError: expected an indented block»
They are two main reasons why you could have such an error:
— You have a «:» without an indented block behind.
Here are two examples:
Example 1, no indented block:
Input:
if 3 != 4:
print("usual")
else:
Output:
File "<stdin>", line 4
^
IndentationError: expected an indented block
The output states that you need to have an indented block on line 4, after the else: statement
Example 2, unindented block:
Input:
if 3 != 4:
print("usual")
Output
File "<stdin>", line 2
print("usual")
^
IndentationError: expected an indented block
The output states that you need to have an indented block line 2, after the if 3 != 4: statement
— You are using Python2.x and have a mix of tabs and spaces:
Input
def foo():
if 1:
print 1
Please note that before if, there is a tab, and before print there is 8 spaces.
Output:
File "<stdin>", line 3
print 1
^
IndentationError: expected an indented block
It’s quite hard to understand what is happening here, it seems that there is an indent block… But as I said, I’ve used tabs and spaces, and you should never do that.
- You can get some info here.
- Remove all tabs and replaces them by four spaces.
- And configure your editor to do that automatically.
2. «IndentationError: unexpected indent»
It is important to indent blocks, but only blocks that should be indent.
So basically this error says:
— You have an indented block without a «:» before it.
Example:
Input:
a = 3
a += 3
Output:
File "<stdin>", line 2
a += 3
^
IndentationError: unexpected indent
The output states that he wasn’t expecting an indent block line 2, then you should remove it.
3. «TabError: inconsistent use of tabs and spaces in indentation» (python3.x only)
- You can get some info here.
- But basically it’s, you are using tabs and spaces in your code.
- You don’t want that.
- Remove all tabs and replaces them by four spaces.
- And configure your editor to do that automatically.
Eventually, to come back on your problem:
Just look at the line number of the error, and fix it using the previous information.
There are in fact multiples things you need to know about indentation in Python:
Python really cares about indention.
In a lot of other languages the indention is not necessary but improves readability. In Python indentation replaces the keyword begin / end or { } and is therefore necessary.
This is verified before the execution of the code, therefore even if the code with the indentation error is never reached, it won’t work.
There are different indention errors and you reading them helps a lot:
1. «IndentationError: expected an indented block»
They are two main reasons why you could have such an error:
— You have a «:» without an indented block behind.
Here are two examples:
Example 1, no indented block:
Input:
if 3 != 4:
print("usual")
else:
Output:
File "<stdin>", line 4
^
IndentationError: expected an indented block
The output states that you need to have an indented block on line 4, after the else: statement
Example 2, unindented block:
Input:
if 3 != 4:
print("usual")
Output
File "<stdin>", line 2
print("usual")
^
IndentationError: expected an indented block
The output states that you need to have an indented block line 2, after the if 3 != 4: statement
— You are using Python2.x and have a mix of tabs and spaces:
Input
def foo():
if 1:
print 1
Please note that before if, there is a tab, and before print there is 8 spaces.
Output:
File "<stdin>", line 3
print 1
^
IndentationError: expected an indented block
It’s quite hard to understand what is happening here, it seems that there is an indent block… But as I said, I’ve used tabs and spaces, and you should never do that.
- You can get some info here.
- Remove all tabs and replaces them by four spaces.
- And configure your editor to do that automatically.
2. «IndentationError: unexpected indent»
It is important to indent blocks, but only blocks that should be indent.
So basically this error says:
— You have an indented block without a «:» before it.
Example:
Input:
a = 3
a += 3
Output:
File "<stdin>", line 2
a += 3
^
IndentationError: unexpected indent
The output states that he wasn’t expecting an indent block line 2, then you should remove it.
3. «TabError: inconsistent use of tabs and spaces in indentation» (python3.x only)
- You can get some info here.
- But basically it’s, you are using tabs and spaces in your code.
- You don’t want that.
- Remove all tabs and replaces them by four spaces.
- And configure your editor to do that automatically.
Eventually, to come back on your problem:
Just look at the line number of the error, and fix it using the previous information.
IndentationError: expected an indented block
IndentationError: expected an indented blockAs the error implies, this occurs after statements that require indenting, such as after if statements, for loops and try except exception handling.
Unlike many programming languages that use braces, Python requires indents to determine which code block belongs to a statement. More simply, after detecting the : character in your script, Python will look for an indent.
This lesson will quickly examine a few reasons when this error can occur and how to fix it.
Imagine you are looking at sales figures for Company A, which sells software packages. You want to write a script for determining which employees are meeting a certain sales threshold.
Using enumerate, we can iterate through employees and use the index as an ID for each employee. We can then print off a message showing if that employee hit the sales target or not.
The script below shows how we can execute this process:
company_employee_sales = [58, 39, 52]
for employee_id, employee_sales in enumerate(company_employee_sales):
print(f'Employee {employee_id + 1}:')
if employee_sales > 50:
print('Hit sales target!\n')
else:
print('Room for improvement.\n')Out:
File "<ipython-input-7-8f5233f8cf0e>", line 4
print(f'Employee {employee_id + 1}:')
^
IndentationError: expected an indented blockAlthough we’ve made the if else loop correctly, the for statement is causing an indentation error. This error is happening because we’ve provided a list for Python to iterate through in our for loop, but it doesn’t know which logic it needs to apply while looping.
The straightforward fix is to add an indent at the line indicated in the error:
company_employee_sales = [58, 39, 52]
for employee_id, employee_sales in enumerate(company_employee_sales):
print(f'Employee {employee_id + 1}:')
if employee_sales > 50:
print('Hit sales target!\n')
else:
print('Room for improvement.\n')Out:
Employee 1:
Employee 2:
Employee 3:
Hit sales target!Now that Python has the correct structure, it will check the sales figure for each employee individually and consider if the number is greater than 50 or not. It will then print the corresponding message and move on to the next employee.
When working on larger scripts, you’ll often anticipate many if elif branches ahead of time by creating a branch and commenting on some logic you plan on filling in later.
Here’s an example using our sales analysis script that we used previously:
company_employee_sales = [58, 39, 52]
for employee_id, employee_sales in enumerate(company_employee_sales):
print(f'Employee {employee_id + 1}:')
if employee_sales > 50:
# add functionality here to display that the employee hit their target
else:
print('Room for improvement.')Out:
File "<ipython-input-9-d1e1fb64bfe8>", line 7
else:
^
IndentationError: expected an indented blockIn this case, Python throws the error because it’s looking for a code block after the if statement, i.e., what your program should do if the statement is true. The code seems to be structured correctly, but the program will fail to run until the actual code is placed after the if.
Having a statement like this without anything following it is known as an empty suite. A quick fix for this is to use the pass keyword:
company_employee_sales = [58, 39, 52]
for employee_id, employee_sales in enumerate(company_employee_sales):
print(f'Employee {employee_id + 1}:')
if employee_sales > 50:
# add functionality here to display that the employee hit their target
pass
else:
print('Room for improvement.')Out:
Employee 1:
Employee 2:
Room for improvement.
Employee 3:In this situation, the pass keyword allows Python to skip when the if is true. This command bypasses the indentation error, allowing us to work on other areas until we are ready to come back and write the functionality that displays a message.
To keep code well-documented, we can use docstrings at the start of a function, class, or method to quickly say what the code does. This description is to make life easier for yourself and others when reviewing the code later.
To write a docstring, you use two sets of triple apostrophes (»’) or quotes («»»), which makes multi-line comments in Python possible.
The example below shows how we can use a docstring to describe a function to contain the if-else loop we’ve been using in our sales analysis script.
def analyze_sales(sales_figure):
'''function used for taking sales figures as an input and outputting a message related to the target'''
if sales_figure > 50:
message = 'Hit sales target!\n'
else:
message = 'Room for improvement.\n'
return message
company_employee_sales = [58, 39, 52]
for employee_id, employee_sales in enumerate(company_employee_sales):
print(f'Employee {employee_id + 1}:')
print(analyze_sales(employee_sales))Out:
File "<ipython-input-13-e17405f37406>", line 2
'''function used for taking sales figures as an input and outputting a message related to the target'''
^
IndentationError: expected an indented blockThis script crashed because Python is looking for indentation at the start of the function. To fix this, we can add an indent to the docstring. Shown below is this solution in action:
def analyze_sales(sales_figure):
'''function used for taking sales figures as an input and outputting a message related to the target'''
if sales_figure > 50:
message = 'Hit sales target!\n'
else:
message = 'Room for improvement.\n'
return message
company_employee_sales = [58, 39, 52]
for employee_id, employee_sales in enumerate(company_employee_sales):
print(f'Employee {employee_id + 1}:')
print(analyze_sales(employee_sales))Out:
Employee 1:
Hit sales target!
Employee 2:
Room for improvement.
Employee 3:
Hit sales target!Note that in this example, using a regular comment (#) to mark the docstring would prevent the indentation error without the need to add an indent. Avoid doing this, though, as it’s best practice to keep docstrings within two sets of triple apostrophes/quotes.
This error occurs when Python is looking for an indented block of code after certain types of statements. The indented block tells Python that the code within the block is relevant to the statement. This s}tructure is fundamental to the Python programming language, so it’s no surprise incorrectly indenting things can make scripts malfunction! Luckily, this is an easy fix, and in most cases, all you need to do is quickly add an indent in the correct place, and you’ll be good to go.
Error handling is one of the best features of Python. With known error Exceptions, you can reduce the bugs in your program. As Python operates on indentation blocks for deducing the inside block for any statement, you may encounter IndentationError: Expected An Indented Block Error.
IndentationError: Expected An Indented Block Error is a known error in python which is thrown when an indented block is missing from the statement. IndentationError states that there is an error related to the Indentation of general statements in your code. In Python, general statement blocks expect an indentation in child statements. If you fail to provide these indentations, Indentation Error will arise.
In this tutorial, we will be discussing a new type of error, i.e., IndentationError: expected an indented block. We all know c, c++, and java when we write any loop, conditional statements, or function code inside the brackets. But in python, it is actually part of this programming language.
What is meant by Indentation?
The meaning of Indentation in python is the space from margin to the beginning of characters in a line. Where in other programming languages, indentation is just for the sake of the readability purpose. But in python, indentation is necessary.
In most popular programming languages like c, c++, and java, spaces or indentation are just used to make the code look good and be easier to read. But In Python, it is actually part of this programming language. Because python is the sensitive language for indentation, many beginners face confusion or problems in the starting as Putting in extra space or leaving one out where it is needed will surely generate an error message. Some causes of indentation error are:
- When we forget to indent the statements within a compound statement
- When we forget to indent the statements of a user-defined function.
The error message IndentationError: expected an indented block would seem to indicate that you have a spaces error or indentation error.
Examples of IndentationError: Expected an indented block
Here are some examples through which you will know about the Indentation error: expected an indented block.
1. IndentationError: Expected an indented block in IF condition statements
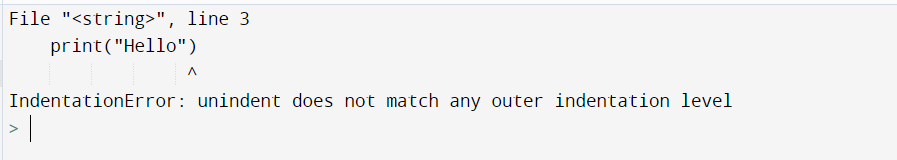
In this example, we will be using the if condition for writing the code and seeing the particular error. We have taken two variables, ‘a’ and ‘b,’ with some integer value. Then, applied if condition and no indented the if block. Let us look at the example for understanding the concept in detail.
a=10
b=20
if b>a:
print("b is greater than a")
Output:
Explanation:
- Firstly, we have taken two variables, ‘a’ and ‘b,’ and assigned the values 10 and 20 in them.
- Then, we have applied if condition.
- And at last, without giving the indentation block of if statement we have printed b is greater than a.
- Hence, we have seen the output as IndentationError: expected an indented block.
2. If-else condition for seeing the error as expected an indented block
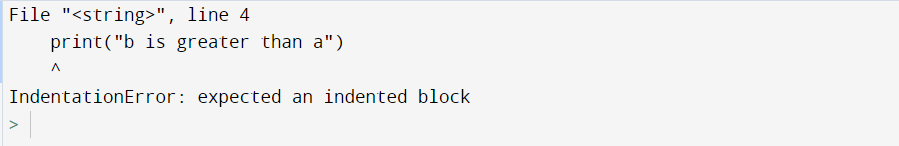
In this example, we will be using the if-else condition for writing the code and seeing the particular error. We have taken two variables, ‘a’ and ‘b,’ with some integer value. Then, applied the if-else condition and indented the if block but not the else block. So let’s see which error occurs. Let us look at the example for understanding the concept in detail.
a=10
b=20
if b>a:
print("b is greater than a")
else:
print("b is smaller than a")
Output:
Explanation:
- Firstly, we have taken two variables, ‘a’ and ‘b,’ and assigned the values 10 and 20 in them.
- Then, we have applied the if-else condition.
- In the if condition, we have applied the tab space but not in the else condition.
- And at last, without giving the indentation block of else statement, we have tried to print b is smaller than a.
- Hence, we have seen the output as IndentationError: expected an indented block.
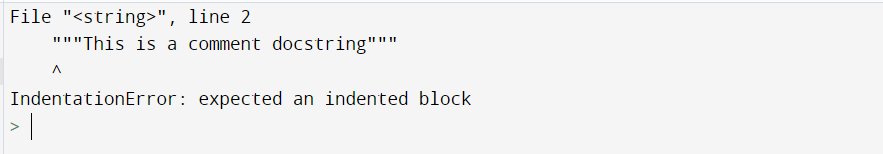
3. Indentation Error: expected an indented block in Docstring Indentation
In this example, we will be showing that the error can also come up if the programmer forgets to indent a docstring. Docstrings must be in the same line with the rest of the code in a function. The Docstring processing tools will strip an amount of indentation from the second and further lines of the docstring, equal to the minimum indentation of all unblank lines after the first line. Let us look at the example for understanding the concept in detail.
def pythonpool():
"""This is a comment docstring"""
print("Hello")
#fixing this error as
#def pythonpool():
# """This is a comment docstring"""
# print("Hello")
Output:
4. Indentation Error: expected an indented block in Tabbed Indentation
In this example, we will see the indentation error in the tabbed indentation. As you can see in the code, while writing “This is a comment docstring,” we have passed the tab space for an indent, and in print () there is less indent. so this will produce a tabbed indentation. Let us look at the example for understanding the concept in detail.
def pythonpool():
"""This is a comment docstring"""
print("Hello")
Output:
5. Indentation Error: expected an indented block in empty class/function

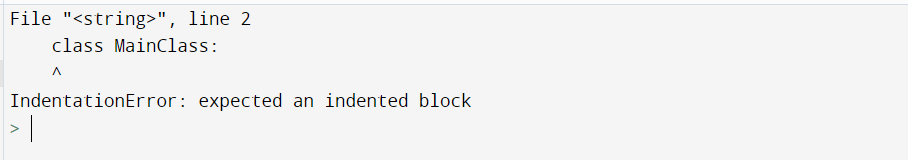
In this example, we will see the error in an empty class. We have declared two classes with the name as EmptyClass and MainClass. But in Class EmptyClass, we didn’t pass (statement) any indent, so it generated the error. Let us look at the example for understanding the concept in detail.
#error code
class EmptyClass:
class MainClass:
pass
#solution code
class EmptyClass:
pass
class MainClass:
pass
Output:
Where Indentation is required?
The indentation is required in the python block. Whenever you encounter a colon(:) is a line break, and you need to indent your block. Python uses white space to distinguish code blocks. You are allowed to use spaces and tabs to create a python block. When several statements in python use the same indentation, they are considered as a block. Basically, Indentation is required to create a python block or write the loop, conditional statements, and user-defined function you require indentation.
How to solve the IndentationError: expected an indented block
To solve this error, here are some key points which you should remember while writing the program or code:
- In your code, give the indent with only the tab spaces, equal to every loop, conditional, and user-defined function.
- Otherwise, in your code, give the indent with only the spaces equal to every loop, conditional, and user-defined function.
Examples of solved IndentationError: expected an indented block
Here are some examples through which you will know how to solve the error Indentation error: expected an indented block.
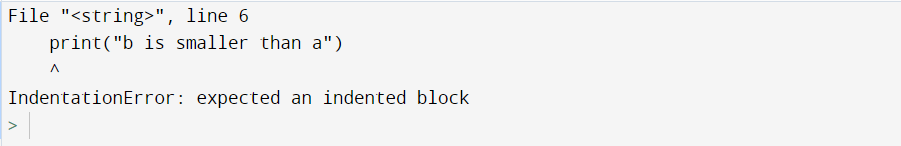
1. If-else conditional statement indentation
In this example, we will be using the if-else condition for writing the code and seeing the particular output. We have taken two variables, ‘a’ and ‘b,’ with some integer value. After this, I applied the if-else condition with a proper indentation in both conditions and printed the output. Let us look at the example for understanding the concept in detail.
a=10
b=20
if b>a:
print("b is greater than a")
else:
print("b is smaller than a")
Output:
Explanation:
- Firstly, we have taken two variables, ‘a’ and ‘b,’ and assigned the values 10 and 20 in them.
- Then, we have applied the if-else condition.
- While applying the if-else condition, we have given the proper indentation of a tab in both the condition of if and as well as of else condition.
- And printed the output after checking the condition.
- Hence, we have seen the output without any IndentationError: expected an indented block error.
2. For loop statement indentation
In this example, we have applied for loop and printed the output while giving the proper indentation for the loop block. Let us look at the example for understanding the concept in detail.
for i in range(1,10):
print(i)
Output:
Explanation:
- In this example, we have applied for loop.
- The for loop is starting from 1 and going till 10.
- And with proper indent, we have printed the value of i.
- Hence, you can see the correct output without any error.
How to fix indentation in some code editors
1. Sublime text
For setting the indentation in sublime text editor you need to perform the following steps:
To set the Indentaion to tabs
- Go to view option.
- Choose Indentation.
- Convert Indentation to tabs.
And go to the sub-menu and look for the ‘Indent Using Spaces’ option and uncheck it.
2. VS code
For setting the indentation in VS code text editor you need to perform the following steps:
- Go to the File menu.
- Choose preferences.
- Choose settings.
- Type tabsize in the search bar.
- Then, uncheck the checkbox of Detect Indentation.
- Change the tab size to 2 or 4 according to your choice.
3. Pycharm
For setting the indentation in Pycharm text editor you need to perform the following steps:
- Go to the File menu.
- Choose settings.
- Then, Choose the editor.
- Choose code style.
- Choose Python.
- And choose tabs and indents.
- Suppose it is set to 0. please set it to 4. which is recommended by PEP8.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have learned the concept of IndentationError: expected an indented block. We have seen what Indentation is, what indentation error is, how indentation error is solved, why it is required to solve the indentation error. We have also explained the examples of showing the IndentationError: expected an indented block and the examples of showing the solution of the given error. All the examples are explained in detail with the help of examples.
However, if you have any doubts or questions, do let me know in the comment section below. I will try to help you as soon as possible.
Other Typical Python Errors
- How to Solve TypeError: ‘int’ object is not Subscriptable
- 4 Quick Solutions To EOL While Scanning String Literal Error
- Invalid literal for int() with base 10 | Error and Resolution
- NumPy.ndarray object is Not Callable: Error and Resolution
- How to Solve “unhashable type: list” Error in Python
FAQs
1. What does expected an indented block mean in Python?
Excepted an indented block error in python, we must have at least one line of code while writing the function, conditional statements, and loops. We can also say that a conditional must have at least one line of code to run if the condition is true.
2. How to follow pep8 format to avoid getting IndentationError?
PEP8 formats says to you should follow 4 spaces indentation to avoid getting error.
3. Explain why this error is mostly generated in code editors like sublime.
This error is mostly generated in sublime as it does not follows PEP8 format, i.e., 4 spaces indentation. Sublime text editor follows tabs as indentation, so there are most chances to get the indentation error.
Отступы в Python строгие. Очень важно соблюдать их в коде.
Если неправильно организовать отступы, пробелы или табуляции в программе, то вернется ошибка IndentationError: expected an intended block.
В этом руководстве рассмотрим, что это за ошибка и когда она появляется. Разберем пример и посмотрим, как решить эту проблему.
Языки программирования, такие как C и JavaScript, не требуют отступов. В них для структуризации кода используются фигурные скобы. В Python этих скобок нет.
Структура программы создается с помощью отступов. Без них интерпретатор не сможет корректно распознавать разные блоки кода. Возьмем такой код в качестве примера:
def find_average(grades):
average = sum(grades) / len(grades)
print(average)
return average
Откуда Python знает, какой код является частью функции find_average(), а какой — основной программы? Вот почему так важны отступы.
Каждый раз, когда вы забываете поставить пробелы или символы табуляции, Python напоминает об этом с помощью ошибки отступа.
Пример возникновения ошибки отступа
Напишем программу, которая извлекает все бублики из списка с едой в меню. Они после этого будут добавлены в отдельный список.
Для начала создадим список всей еды:
lunch_menu = ["Бублик с сыром", "Сэндвич с сыром", "Cэндвич с огурцом", "Бублик с лососем"]
Меню содержит два сэндвича и два бублика. Теперь напишем функцию, которая создает новый список бубликов на основе содержимого списка lunch_menu:
def get_bagels(menu):
bagels = []
for m in menu:
if "Бублик" in m:
bagels.append(m)
return bagels
get_bagels() принимает один аргумент — список меню, по которому она пройдется в поиске нужных элементов. Она проверяет, содержит ли элемент слово «Бублик», и в случае положительного ответа добавит его в новый список.
Наконец, функцию нужно вызвать и вывести результат:
bagels = get_bagels(lunch_menu)
print(bagels)
Этот код вызывает функцию get_bagels() и выводит список бубликов в консоль. Запустим код и посмотрим на результат:
File "test.py", line 4
bagels = []
^
IndentationError: expected an indented block
Ошибка отступа.
Решение ошибки IndentationError
Ошибка отступа сообщает, что отступ был установлен неправильно. Его нужно добавить на 4 строке. Посмотрим на код:
def get_bagels(menu):
bagels = []
Значение переменной bagels должно присваиваться внутри функции, но этого не происходит, что и приводит к ошибке. Для решения проблемы нужно добавить отступ:
def get_bagels(menu):
bagels = []
Теперь запустим код:
['Бублик с сыром', 'Бублик с лососем']Код нашел все бублики и добавил их в новый список. После этого вывел его в консоль.
Вывод
Ошибка IndentationError: expected an indented block возникает, если забыть добавить отступ в коде. Для исправления нужно проверить все отступы, которые должны присутствовать.