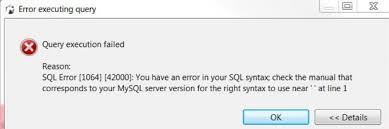
Не пойму где накосячил, мб кто увидит?
mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY my_password;
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'IDENTIFIED BY my_password' at line 1
UP:
Попробовал ввести без пароля, но получилось вот
mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'root'@'%';
ERROR 1410 (42000): You are not allowed to create a user with GRANTИнтересно как так, если я сижу за этим юзером
UPP
Вот чтобы меня за дурака не держали, я взял копипастом команду пользователя из комментариев, которая у него сработала.
mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'my_password';
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'IDENTIFIED BY 'my_password'' at line 1Следом вот заменил имя пользователя
mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'admin'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'my_password';
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'IDENTIFIED BY 'my_password'' at line 1Люди добрые, отакая от фигня. Что это может быть, подскажите пожалуйста.
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON students_db.* TO ‘students_db_user’@’localhost’ IDENTEFIED BY ‘password’;
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near ‘IDENTEFIED BY ‘password» at line 1
задан 5 мар 2018 в 11:08
1
Пример как нужно содавать пользователя и давать ему права, можете по примеру построить свой
CREATE USER 'monty'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'some_pass';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'monty'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION;
ответ дан 5 мар 2018 в 11:59
Question: I have been using IDENTIFIED BY ‘password’ along with GRANT statement for years in many MySQL versions. However, the same failed in MySQL version 8.0.26 on my new CentOS Stream release 8. Below is the complete error message. What could be the issue? – Tushar.
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON qdb.* TO 'quser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'qcuser123'; ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near IDENTIFIED BY 'quser123' at line 1
Error while using GRANT with IDENTIFIED by password
Tushar, the use of IDENTIFIED BY password with GRANT statement has been deprecated since MySQL version 5.7.6. It means you need to use IDENTIFIED by password with CREATE USER or ALTER USER and apply GRANT PRIVILEGES as shown below:
CREATE USER and assign a password.
mysql> CREATE USER 'quser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'qc123'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.12 sec)
Add privileges using GRANT:
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON qdb.* TO 'quser'@'localhost'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
Why this change in the latest MySQL?
The change makes sense for the below reasons:
- Using
IDENTIFIED BYpassword with GRANT privileges will set any password specified as the new password for the account. Assume if there is an account that already exists with a different password, executing GRANT privileges along with IDENTIFIED BY password will overwrite the existing password. So removing IDENTIFIED from GRANT means, the account remains with the password that was set during creation. - As of MySQL version 5.7.2, if an account already exists, IDENTIFIED by ‘password’ is prohibited and it should be used only during account creation ie., with
CREATE USERorALTER USER. - GRANT may create a user account if it does not exist.
- If
NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER enabled- If an account specified in the GRANT statement does not exist, then GRANT will fail to create an account unless the non-empty password is specified via IDENTIFIED BY or via IDENTIFIED WITH.
- If
NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER disabled- If an account specified in the GRANT statement does not exist, then GRANT creates the account. This can be insecure if no password is specified via IDENTIFIED BY.
- If
Finally, GRANT with IDENTIFIED BY password has been deprecated and the user account needs to be created using CREATE USER or ALTER USER.
via StackOverflow.
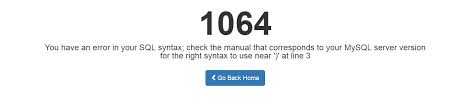
So, you’re creating a custom SQL query to perform a task in the database. After putting the code together and running it in PHPmyAdmin it responds with a 1064 error. It may look similar to this:
The 1064 error displays any time you have an issue with your SQL syntax, and is often due to using reserved words, missing data in the database, or mistyped/obsolete commands. So follow along and learn more about what the 1064 error is, some likely causes, and general troubleshooting steps.
Note: Since syntax errors can be hard to locate in long queries, the following online tools can often save time by checking your code and locating issues:
- PiliApp MySQL Syntax Check
- EverSQL SQL Query Syntax Check & Validator
Causes for the 1064 error
- Reserved Words
- Missing Data
- Mistyped Commands
- Obsolete Commands
This may seem cryptic since it is a general error pointing to a syntax issue in the SQL Query statement. Since the 1064 error can have multiple causes, we will go over the most common things that will result in this error and show you how to fix them. Follow along so you can get your SQL queries updated and running successfully.
Using Reserved Words
Every version of MySQL has its own list of reserved words. These are words that are used for specific purposes or to perform specific functions within the MySQL engine. If you attempt to use one of these reserved words, you will receive the 1064 error. For example, below is a short SQL query that uses a reserved word as a table name.
CREATE TABLE alter (first_day DATE, last_day DATE);
How to fix it:
Just because the word alter is reserved does not mean it cannot be used, it just has special requirements to use it as the MySQL engine is trying to call the functionality for the alter command. To fix the issue, you will want to surround the word with backticks, this is usually the button just to the left of the “1” button on the keyboard. The code block below shows how the code will need to look in order to run properly.
CREATE TABLE `alter` (first_day DATE, last_day DATE);
Missing Data
Sometimes data can be missing from the database. This causes issues when the data is required for a query to complete. For example, if a database is built requiring an ID number for every student, it is reasonable to assume a query will be built to pull a student record by that ID number. Such a query would look like this:
SELECT * from students WHERE studentID = $id
If the $id is never properly filled in the code, the query would look like this to the server:
SELECT * from students WHERE studentID =
Since there is nothing there, the MySQL engine gets confused and complains via a 1064 error.
How to fix it:
Hopefully, your application will have some sort of interface that will allow you to bring up the particular record and add the missing data. This is tricky because if the missing data is the unique identifier, it will likely need that information to bring it up, thus resulting in the same error. You can also go into the database (typically within phpMyAdmin) where you can select the particular row from the appropriate table and manually add the data.
Mistyping of Commands
One of the most common causes for the 1064 error is when a SQL statement uses a mistyped command. This is very easy to do and is easily missed when troubleshooting at first. Our example shows an UPDATE command that is accidentally misspelled.
UDPATE table1 SET id = 0;
How to fix it:
Be sure to check your commands prior to running them and ensure they are all spelled correctly.
Below is the syntax for the correct query statement.
UPDATE table1 SET id = 0;
Obsolete Commands
Some commands that were deprecated (slated for removal but still allowed for a period of time) eventually go obsolete. This means that the command is no longer valid in the SQL statement. One of the more common commands is the ‘TYPE‘ command. This has been deprecated since MySQL 4.1 but was finally removed as of version 5.1, where it now gives a syntax error. The ‘TYPE‘ command has been replaced with the ‘ENGINE‘ command. Below is an example of the old version:
CREATE TABLE t (i INT) TYPE = INNODB;
This should be replaced with the new command as below:
CREATE TABLE t (i INT) ENGINE = INNODB;
For developers or sysadmins experienced with the command line, get high availability and root access for your application, service, and websites with Cloud VPS Hosting.
Error 1064 Summary
As you can see there is more than one cause for the 1064 error within MySQL code. Now, you know how to correct the issues with your SQL Syntax, so your query can run successfully. This list will be updated as more specific instances are reported.
So, you’re creating a custom SQL query to perform a task in the database. After putting the code together and running it in PHPmyAdmin it responds with a 1064 error. It may look similar to this:
The 1064 error displays any time you have an issue with your SQL syntax, and is often due to using reserved words, missing data in the database, or mistyped/obsolete commands. So follow along and learn more about what the 1064 error is, some likely causes, and general troubleshooting steps.
Note: Since syntax errors can be hard to locate in long queries, the following online tools can often save time by checking your code and locating issues:
- PiliApp MySQL Syntax Check
- EverSQL SQL Query Syntax Check & Validator
Causes for the 1064 error
- Reserved Words
- Missing Data
- Mistyped Commands
- Obsolete Commands
This may seem cryptic since it is a general error pointing to a syntax issue in the SQL Query statement. Since the 1064 error can have multiple causes, we will go over the most common things that will result in this error and show you how to fix them. Follow along so you can get your SQL queries updated and running successfully.
Using Reserved Words
Every version of MySQL has its own list of reserved words. These are words that are used for specific purposes or to perform specific functions within the MySQL engine. If you attempt to use one of these reserved words, you will receive the 1064 error. For example, below is a short SQL query that uses a reserved word as a table name.
CREATE TABLE alter (first_day DATE, last_day DATE);
How to fix it:
Just because the word alter is reserved does not mean it cannot be used, it just has special requirements to use it as the MySQL engine is trying to call the functionality for the alter command. To fix the issue, you will want to surround the word with backticks, this is usually the button just to the left of the “1” button on the keyboard. The code block below shows how the code will need to look in order to run properly.
CREATE TABLE `alter` (first_day DATE, last_day DATE);
Missing Data
Sometimes data can be missing from the database. This causes issues when the data is required for a query to complete. For example, if a database is built requiring an ID number for every student, it is reasonable to assume a query will be built to pull a student record by that ID number. Such a query would look like this:
SELECT * from students WHERE studentID = $id
If the $id is never properly filled in the code, the query would look like this to the server:
SELECT * from students WHERE studentID =
Since there is nothing there, the MySQL engine gets confused and complains via a 1064 error.
How to fix it:
Hopefully, your application will have some sort of interface that will allow you to bring up the particular record and add the missing data. This is tricky because if the missing data is the unique identifier, it will likely need that information to bring it up, thus resulting in the same error. You can also go into the database (typically within phpMyAdmin) where you can select the particular row from the appropriate table and manually add the data.
Mistyping of Commands
One of the most common causes for the 1064 error is when a SQL statement uses a mistyped command. This is very easy to do and is easily missed when troubleshooting at first. Our example shows an UPDATE command that is accidentally misspelled.
UDPATE table1 SET id = 0;
How to fix it:
Be sure to check your commands prior to running them and ensure they are all spelled correctly.
Below is the syntax for the correct query statement.
UPDATE table1 SET id = 0;
Obsolete Commands
Some commands that were deprecated (slated for removal but still allowed for a period of time) eventually go obsolete. This means that the command is no longer valid in the SQL statement. One of the more common commands is the ‘TYPE‘ command. This has been deprecated since MySQL 4.1 but was finally removed as of version 5.1, where it now gives a syntax error. The ‘TYPE‘ command has been replaced with the ‘ENGINE‘ command. Below is an example of the old version:
CREATE TABLE t (i INT) TYPE = INNODB;
This should be replaced with the new command as below:
CREATE TABLE t (i INT) ENGINE = INNODB;
For developers or sysadmins experienced with the command line, get High-Availability and Root Access for your application, service, and websites with Cloud VPS Hosting.
Error 1064 Summary
As you can see there is more than one cause for the 1064 error within MySQL code. Now, you know how to correct the issues with your SQL Syntax, so your query can run successfully. This list will be updated as more specific instances are reported.
Just my 2 cents on the subject. I was having the exact same issue with trying to connect from MySQL Workbench. I’m running a bitnami-mysql virtual machine to set up a local sandbox for development.
Bitnami’s tutorial said to run the ‘Grant All Privileges’ command:
/opt/bitnami/mysql/bin/mysql -u root -p -e "grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by 'PASSWORD' with grant option";
This was clearly not working, I finally got it to work using Mike Lischke’s answer.
What I think happened was that the root@% user had the wrong credentials associated to it. So if you’ve tried to modify the user’s privileges and with no luck try:
- Dropping the user.
- Create the user again.
- Make sure you have the correct binding on your MySQL config file.
In my case I’ve commented the line out since it’s just for a sandbox environment.
1. Dropping the user.
From Mysql Console:
List Users (helpful to see all your users):
select user, host from mysql.user;
Drop Desired User:
drop user '{{ username }}'@'%';
2. Create the user again.
Create User and Grant Permissions:
CREATE USER '{{ username }}'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '{{ password }}';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO '{{ username }}'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION;
Run this command:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
3. Make sure you have the correct binding on your MySQL config file.
Locate your MySQL config file (additional notes at the end). If you want to have MySQL listen for connections on more than one network find the following line on the config file:
bind-address=127.0.0.1
and comment it using a ‘#’:
#bind-address=127.0.0.1
For production environments you might want to use limit the network access (additional notes at the end).
Then restart your MySQL service.
Hope this helps someone having the same issue!
Binding: If you want to know more about this I suggest looking at the following
solution How to bind MySQL server to more than one IP address. It
basically says you can leave MySQL open and limit connections by using
a firewall, or natively if you have MySQL version 8.0.13 and above.
MySQL Config File The file could have different locations depending on your
Linux distribution and installation. On my system it was located at
'/etc/my.cnf'. Here are other suggested locations:
- /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d
- /etc/mysql/my.cnf
You can also search for the config locations as shown in this website:
How to find locations of MySQL config files.
Не пойму где накосячил, мб кто увидит?
mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY my_password;
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'IDENTIFIED BY my_password' at line 1
UP:
Попробовал ввести без пароля, но получилось вот
mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'root'@'%';
ERROR 1410 (42000): You are not allowed to create a user with GRANTИнтересно как так, если я сижу за этим юзером
UPP
Вот чтобы меня за дурака не держали, я взял копипастом команду пользователя из комментариев, которая у него сработала.
mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'my_password';
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'IDENTIFIED BY 'my_password'' at line 1Следом вот заменил имя пользователя
mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'admin'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'my_password';
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'IDENTIFIED BY 'my_password'' at line 1If you’ve been using WordPress for a while, you may have decided to get into more advanced database management. This often involves using the MySQL command line, which can, in turn, lead to confusing problems such as MySQL 1064 errors.
Fortunately, while resolving this error can be confusing at first due to its many potential causes, its solutions tend to be relatively simple. Once you determine the reason behind the database error you’re seeing, you should be able to fix it fairly quickly.
In this post, we’ll cover the various possible causes of the MySQL 1064 error. Then we’ll share solutions for each common situation, to help you get your database and your site back up and running.
Let’s get started!
Why the MySQL 1064 Error Occurs
The MySQL 1064 error is a syntax error. This means the reason there’s a problem is because MySQL doesn’t understand what you’re asking it to do. However, there are many different situations that can lead to this type of miscommunication between you and your database.
The simplest cause is that you’ve made a mistake while typing in a command and MySQL can’t understand your request. Alternatively, you may be attempting to use outdated or even obsolete commands that can’t be read.
In other cases, you may have attempted to include a ‘reserved word’ in one of your commands. Reserved words are terms that can only be used in specific contexts in MySQL. If you attempt to use them in other ways, you’ll be faced with an error.
It’s also possible that there is some data missing from your database. When you make a request via MySQL which references data that isn’t where it’s supposed to be, you’ll also see the 1064 error. Finally, transferring your WordPress database to another server can also lead to the same issue.
As you can see, there are many potential causes for this problem, which can make it tricky to resolve. Unless you’re in the process of moving your database or taking some other action that points to a specific cause, you’ll likely need to try a few different solutions before you land on the right one. Fortunately, none of them are too difficult to execute, as we’ll see next.
Oh no, you’re getting the MySQL 1064 Error…😭 Don’t despair! Here are 5 proven solutions to get it fixed immediately 🙏Click to Tweet
How to Fix the MySQL 1064 Error (5 Methods)
If you already have an idea of what’s causing your MySQL 1064 error, you can simply skip down to the resolution for your specific situation. However, if you’re not sure why the error has occurred, the simplest strategy is to try the easiest solution first.
In that case, we’d suggest testing out the five most likely fixes in the following order.
1. Correct Mistyped Commands
The good thing about MySQL typos is that they’re the simplest explanation for syntax issues such as the 1064 error. Unfortunately, they can also be the most tedious to correct. Generally speaking, your best option is to manually proofread your code and look for any mistakes you may have made.
We suggest using the MySQL Manual as a reference while you do so, double-checking anything you’re not sure about. As you might imagine, this can get pretty time-consuming, especially if you’ve been working in the MySQL command line for a while or if you’re new to this task.
An alternative to manually checking your work is to employ a tool such as EverSQL:
With this solution, you can simply input your MySQL to check for errors automatically. However, keep in mind that these platforms aren’t always perfect and you may still want to validate the results yourself.
2. Replace Obsolete Commands
As platforms grow and change, some commands that were useful in the past are replaced by more efficient ones. MySQL is no exception. If you’re working on your database following a recent update or have referenced an outdated source during your work, it’s possible that one or more of your commands are no longer valid.
You can check to see whether this is the case using the MySQL Reference Manual. You’ll find mentions of commands that have been made obsolete by each MySQL version in the relevant sections:
Once you’ve determined which command is likely causing the problem, you can simply use the ‘find and replace’ function to remove the obsolete command and add in the new version. For example, if you were using storage_engine and find that it no longer works, you could simply replace all instances with the new default_storage_engine command.
3. Designate Reserved Words
In MySQL, using a reserved word out of context will result in a syntax error, as it will be interpreted as incorrect. However, you can still use reserved words however you please by containing them within backticks, like this: `select`
Each version of MySQL has its own reserved words, which you can read up on in the MySQL Reference Manual. A quick find and replace should enable you to resolve this issue if you think it may be causing your 1064 error.
4. Add Missing Data
If your latest MySQL query attempts to reference information in a database and can’t find it, you’re obviously going to run into problems. In the event that none of the preceding solutions resolves your MySQL 1064 error, it may be time to go looking for missing data.
Unfortunately, this is another solution that can be quite tedious and has to be done by hand. The best thing you can do in this situation is to work backward, starting with your most recent query. Check each database it references, and make sure all the correct information is present. Then move on to the next most recent query, until you come to the one that’s missing some data.
5. Use Compatibility Mode to Transfer WordPress Databases
This final 1064 error solution isn’t as straightforward as the others on our list. However, if you’re migrating your WordPress site to a new host or otherwise moving it to a different server, you’ll need to take extra steps to avoid causing problems with your database.
The simplest solution is to use a migration plugin that includes a compatibility mode, such as WP Migrate DB:
This will enable an auto-detection feature that will make sure your latest site backup and database are compatible with multiple versions of MySQL. You can access the compatibility mode setting by navigating to Tools > Migrate DB > Advanced Options:
Check the box next to Compatible with older versions of MySQL before starting your site migration. This way, you should be able to avoid any issues during the process.
Summary
Database errors can throw a wrench in your plans, and may even compromise your website’s stability. Knowing how to resolve issues such as the MySQL 1064 error can help you react quickly, and minimize downtime on your site.
There are five methods you can try to fix the MySQL 1064 error when you encounter it, depending on its most likely cause:
- Correct mistyped commands.
- Replace obsolete commands.
- Designate reserved words.
- Add missing data.
- Transfer WordPress databases in compatibility mode.
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Get started with a free trial of our Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
Sqlstate 42000 Is a general code that come together with other number. Most often comes with the code 1064 and is related with SQL syntax error. This kind of error has been seen reported mostly on MySQL but also on other type of databases. This happen because your command is not a valid one within the “Structured Query Language” or SQL. Syntax errors are just like grammar errors in linguistics. In the following article we will try to explain the MySQL error 1064 but not only. Also we will show other error codes that comes together with Sqlstate[42000].
Full view of my sql error code 1064:
SQLSTATE[42000]: Syntax error or access violation: 1064 You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL (or any other like MariaDb) server version for the right syntax to use near (And here is the part of the code where the error comes)
sqlstate 42000 – mysql error 1064 – you have an error in your sql syntax
Other error codes related with Sqlstate 42000:
- 1 – syntax error or access violation 1055
- 2 – syntax error or access violation 1071 specified key was too long
- 3 – syntax error or access violation 1066 not unique table/alias
- 4 – syntax error or access violation 1068 multiple primary key defined
Understand and FIX MySQL error 1064 – sqlstate 42000
SQL 1064 means that MySQL can’t understand your command!
This type of error first need to be understood and after that you can fix it. The common causes of this error are:
- Upgrading MySQL or any other database to another version
- Using Wrong syntax that is not supported on your current version
- Error in applying the back tick symbol or while creating a database without them can also create an error
- Due to using reserved words
- Particular data missing while executing a query
- Mistyped/obsolete commands
If you see words like “near” or “at line”, you need to check for problems in those lines of the code before the command ends.
How do I Fix SQL Error Code 1064?
- Read the message on the error:
So in general the error tells you where the parser encountered the syntax error. MySQL also suggest how to fix it. Check the example below …..
- Check the text of your command!
In some cases the PHP commands has wrong lines. Create SQL commands using programing language can be the good example of this. So you will need to check and fix those commands. Use echo, console.log(), or its equivalent to show the entire command so you can see it.
- Mistyping of commands
The error can occur also when you misspell a command (e.g. instead of UPDATE you write UDPATE). This can occur often since are so easy to miss. To prevent this, make sure that you review your command for any typing error before running it. There are a lot of online syntax checkers that can help to debug your queries.
- Check for reserved words
Reserved words are words that vary from one MySQL version to another. Every version has its list of keywords that are reserved. They are used to perform specific functions in the MySQL engine. If you read the error and identified that occurred on an object identifier, check that it isn’t a reserved word (and, if it is, be sure that it’s properly quoted). “If an identifier contains special characters or is a reserved word, you must quote it whenever you refer to it.” You can find a full list of the reserved words specific for each MySQL version and their usage requirements at MySQL.com.
- Obsolete commands – another reason
Another possible reason for the sqlstate 42000 MySQL error 1064 is when you use outdated commands. As Platforms grow and change, some commands that were useful in the past are replaced by more efficient ones. A number of commands and keywords have been deprecated. This mean that they are due for removal, but still allowed for a short period of time before they turn obsolete. On cases that you have an older backup of a MySQL database that you want to import, a quick solution is to just search and replace “TYPE=InnoDB” with “ENGINE=InnoDB”.
- Particular data is missing while executing a query
If the relevant data missing from the database which is required for the query, you’re obviously going to run into problems. Using phpMyAdmin or MySQL Workbench you can enter the missing data. Interface of the application allow you to add the missing data manually to an appropriate row of the table.
You have an error in your sql syntax
“You have an error in your sql syntax” – Example 1
The error code generated jointly with the statement “syntax error or access violation”, “You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL (or any other like MariaDB) server version for the right syntax to use near” and after that the part of SQL code where the issue is. So in simple way, the error view is showing you also where is the error. For example we have the error:
“Check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'from, to, name, subject, message) VALUES ('[email protected]l.com', '[email protected],com' at line 1”
So how to understand this?
from is a keyword in SQL. You may not use it as a column name without quoting it. In MySQL, things like column names are quoted using back ticks, i.e. `from`. Or you can just rename the column.
Another example of “You have an error in your sql syntax” sqlstate 42000 – Example 2
Error:
check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '' at line 1 [ SELECT COUNT(*) as count,region, MONTHNAME(date) asmonth FROM tempur_stores.stats WHERE date > DATE_ADD(DATE(NOW()), INTERVAL -1 WEEK) AND date < DATE(NOW()) GROUP BY region, MONTH(date ]
On the query:
$stmt = DB::query(Database::SELECT, 'SELECT COUNT(*) as `count`,`region`, MONTHNAME(`date`) as`month` FROM tempur_stores.stats WHERE `date` > DATE_ADD(DATE(NOW()), INTERVAL -1 WEEK) AND `date` < DATE(NOW()) GROUP BY `region`, MONTH(`date`');
The above query is missing a closing parenthesis in the query:
$stmt = DB::query(Database::SELECT, 'SELECT COUNT(*) as `count`,`region`, MONTHNAME(`date`) as`month`
FROM tempur_stores.stats
WHERE `date` > DATE_ADD(DATE(NOW()), INTERVAL -1 WEEK)
AND `date` < DATE(NOW())
GROUP BY `region`, MONTH(`date`');
---------- ^ right there
Just put a parenthesis ) before that apostrophe and it should work.
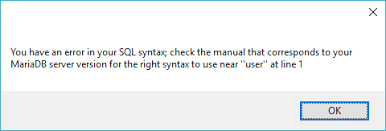
MariaDB error 1064 – Example 3
An example with MariaDB version issue. Trying to do example of tagging and when:
$id = Questions::create([ 'body' => request('title'), 'skillset_id' => request('skillsetId'), 'tags' => ['red', 'blue'] ])->id;
Getting error:
You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MariaDB server version for the right syntax to use near ‘>’$.”en”‘ = ? and `type` is null limit 1’ at line 1 (SQL: select * from `tags` where `name`->’$.”en”‘ = red and `type` is null limit 1)
Reason is that is using MariaDB and JSON columns are only supported by MySQL. Convert to MySQL to resolve the issue.
MariaDB error 1064
Fix error 1064 mysql 42000 while creating a database – Example 4
MySQL error 1064 can be appearing also while you are creating database using hyphen in the name like Test-Db. This can be solved by using back tick around the database name properly or remove the hyphen in the database name.
Example:
mysql> create database Test-DB;
You will get error:
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that Corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '-DB' at line 1
Solution:
mysql> create database ` Test-DB `;
So adding back tick around the database name will solve the issue.
Transfer WordPress MySQL database to another server
Exporting WordPress database to another server can also be cause the 1064 error. Can be resolved by choosing the compatibility mode and changing the database version to the current version you’re using. Please select the compatibility mode under the advanced tab when performing a backup and after that click the auto-detect file character set when restoring the MySQL database.
Read Also –
- Location of SQL Server Error Log File
- How to fix SQL Server Error 18456
- How to Restore Master Database
Conclusions:
The reason behind the error it’s related closely to the end of error message. We would need to see the SQL query to understand completely the issue you’re facing. So this is the reason that we can’t completely fix the MySQL error 1064 but we exposed some examples for you. You will need to review the documentation for the version of MySQL that you are having this error appear with and your syntax to fix the problem. There are multiple reasons for its cause. We suggest you perform the sqlstate 42000 error fixes if only has experience on MySQL database.
Дата: 25.11.2013
Автор: Василий Лукьянчиков , vl (at) sqlinfo (dot) ru
Статья ориентирована на новичков. В ней объясняется, что означает ошибка сервера MySQL №1064, рассматриваются типичные ситуации и причины возникновения этой ошибки, а также даются рекомендации по исправлению.
Рассмотрим простейший пример.
SELECT mid, time, title, artist, download, view_count, rating, vote_num FROM dle_mservice WHERE category = ‘1’ AND approve = ‘1’ ORDER BY time DESC LIMIT -10,10;
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near ‘-10,10’ at line 1
Сервер MySQL сообщает, что в первой строке нашего SQL запроса имеется синтаксическая ошибка, и в одинарных кавычках цитирует часть запроса с того места где начинается ошибка. Это очень полезное свойство, так как позволяет сразу определить место, которое сервер счел ошибочным. В данном случае это ‘-10,10’, ошибка возникает из-за того, что параметр LIMIT не может быть отрицательным числом.
Однако, бывает и так, что цитируемый кусок запроса не содержит синтаксической ошибки. Это означает, что данная часть запроса находится не на своем месте из-за чего весь запрос становится синтаксически неверным. Например, отсутствует разделитель между двумя запросами, пропущен кусок запроса, невидимый символ в дампе и т.д. Неудобством таких ситуаций является то, что сообщение об ошибке не содержит исходный запрос.
Действия по исправлению зависят от контекста возникновения ошибки. Таковых всего 3:
1. Запрос в редакторе.
Самый простейший случай — вы пишите свой запрос в редакторе. Если причина не опечатка, то:
- Смотреть в документации синтаксис команды для вашей версии сервера MySQL.
Обратите внимание: речь идет о версии сервера MySQL, а не клиента (phpmyadmin, workbench и т.д.). Версию сервера можно узнать выполнив команду select version();
- В MySQL допускается использование ключевых слов в качестве имен столбцов/таблиц, но при этом их необходимо заключать в обратные кавычки (там где буква ё на клавиатуре).
Пример:select order from test;
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near ‘order from test’ at line 1
MariaDB [test]> select `order` from test;
+——-+
| order |
+——-+
| NULL |
+——-+ - По умолчанию ; разделяет команды. Если же нужно выполнить набор из нескольких инструкций как одну команду (например, при создании процедур, фунуций, триггеров), то в зависимости от используемого клиента может потребоваться переопределить разделитель с помощью DELIMITER, иначе интерпретация команды остановится на первой ; и будет ошибка синтаксиса. Пример:
delimiter //
create procedure test()
begin
set @a=1;
select @a;
end//Обратите внимание: DELIMITER это команда консольного клиента mysql, необходимость его использования зависит от того как вы передаете команду серверу. Например,:
- mysql_query() выполняет содержимое как одну команду, добавление delimiter приведет к error 1064 с цитатой, начинающейся со слова delimiter
- phpmyadmin удаляет слово delimiter из-за чего возникает error 1064 с цитатой, начинающейся с переопределенного разделителя
- в MysqlQueryBrowser напротив необходимо использовать delimiter.
2. Перенос базы на другой сервер.
У вас есть дамп (т.е. файл с расширением .sql) и при попытке его импортировать вы получаете ошибку 1064. Причины:
-
В различных версиях набор ключевых слов и синтаксис может немного отличаться. Наиболее распространенный случай: команда create table, в которой ключевое слово type было заменено на engine. Например, если вы получаете ошибку:
You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near ‘TYPE=MyISAM CHARACTER SET `utf8`’ at line 29
Это означает, что вы переносите базу в пятую версию сервера MySQL, в котором ключевое слово TYPE не поддерживается и его нужно заменить на ENGINE.
Редко бываю случаи, когда перенос идет на старый (~3.23) сервер, который кодировки не поддерживает. Тогда ошибка будет иметь вид:
#1064 — You have an error in your SQL syntax near ‘DEFAULT CHARACTER SET cp1251 COLLATE cp1251_general_ci’ at line 1
Такое может произойти, если вы переносите базу с хостинга на локальный комп, где стоит древняя версия MySQL. Лучшим решением в данном случае будет не править дамп, а обновить MySQL.
-
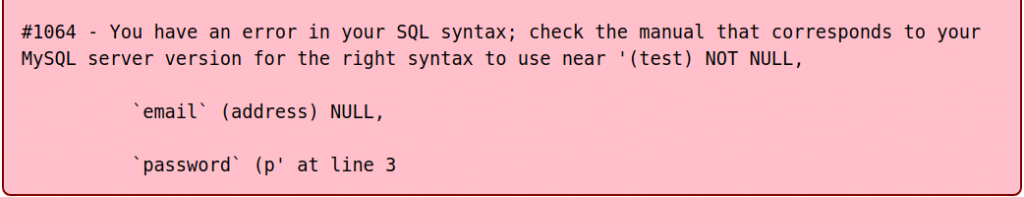
Часто проблемы вызваны тем, что дамп делается неродными средствами MySQL (например, phpmyadmin) из-за чего в нем могут быть BOM-маркер, собственный синтаксис комментариев, завершения команды и т.д. Кроме того при использовании того же phpmyadmin возможна ситуация при которой из-за ограничения апача на размер передаваемого файла команда будет обрезана, что приведет к ошибке 1064.
Например, если вы получаете ошибку:#1064 — You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near ‘
CREATE TABLE `jos_banner` (
`bid` int(11) NOT NULL auto_increment,
`ci‘ at line 1Значит ваш дамп содержит BOM-маркер. Это три байта в начале файла, помогающие программе определить что данный файл сохранен в кодировке UTF-8. Проблема в том, что MySQL пытается интерпретировать их как команду из-за чего возникает ошибка синтаксиса. Нужно открыть дамп в текстовом редакторе (например, Notepad++) и сохранить без BOM.
Для избежания подобных проблем при создании дампа и его импорте лучше пользоваться родными средствами MySQL, см http://sqlinfo.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?id=583
3. Некорректная работа сайта.
Если во время работы сайта появляются ошибки синтаксиса, то, как правило, причина в установке вами сомнительных модулей к вашей cms. Лучшее решение — отказаться от их использования. Еще лучше предварительно проверять их работу на резервной копии.
Пример. Движок dle 7.2, поставили модуль ,вроде бы все Ок, но:
MySQL Error!
————————
The Error returned was:
You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near ‘AND approve=’1‘ AND date < ‘2008-10-04 04:34:25‘ LIMIT 5’ at line 1
Error Number:
1064
SELECT id, title, date, category, alt_name, flag FROM dle_post WHERE MATCH (title, short_story, full_story, xfields, title) AGAINST (‘Приобретение и оплата скрипта ‘) AND id != AND approve=‘1’ AND date < ‘2008-10-04 04:34:25’ LIMIT 5
В данном примере мы видим, что причина ошибки в отсутствии значения после «id != «
Обратите внимание: из процитированного сервером MySQL куска запроса причина ошибки не ясна. Если ваша CMS не показывает весь запрос целиком, то нужно в скриптах найти место где выполняется данный запрос и вывести его на экран командой echo.
Кусок кода, который отвечает за данный запрос это
$db->query («SELECT id, title, date, category, alt_name, flag FROM « . PREFIX . «_post WHERE MATCH (title, short_story, full_story, xfields, title) AGAINST (‘$body’) AND id != «.$row[‘id’].» AND approve=’1′».$where_date.» LIMIT «.$config[‘related_number’]);
Далее можно искать откуда взялась переменная $row и почему в ней нет элемента ‘id’ и вносить исправления, но лучше отказаться от использования такого модуля (неизвестно сколько сюрпризов он еще принесет).
P.S. Если после прочтения статьи ваш вопрос с MySQL Error 1064 остался нерешенным, то задавайте его на форуме SQLinfo
Дата публикации: 25.11.2013
© Все права на данную статью принадлежат порталу SQLInfo.ru. Перепечатка в интернет-изданиях разрешается только с указанием автора и прямой ссылки на оригинальную статью. Перепечатка в бумажных изданиях допускается только с разрешения редакции.
Oops!! Stuck with MySQL Error code 1064 SQL State 42000? We can help you in fixing it.
The SQL State Error 42000 occurs mainly due to the SQL syntax error or due to the outdated JDBC MySQL driver.
At Bobcares, we often get requests to fix MySQL errors, as a part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s see how our Support Engineers fix MySQL errors for our customers.
Why MySQL Error code 1064 SQL State 42000 occurs?
The MySQL Error code mainly occurs due to the SQL Syntax error. It happens when MySQL is unable to validate the commands.
The Syntax Error occurs due to many factors like mistyping the commands, deprecated or missing data from the database.
In some cases, the error occurs when the JDBC driver initializes the connection.
How we fix the MySQL Error code 1064?
Recently, one of our customers approached us saying that he is getting MySQL Error code 1064 SQL State 42000. On checking, we found an error in the SQL syntax.
Now, let’s see the main causes for this Error 1064 SQL State 42000 and how our Support Engineers fix them.
1. Using Reserved Words
The reserved words perform some specific functions within the MySQL engine.
Sometimes we receive the error while using the reserved words, The error occurs when the MySQL is not meeting the exact requirements for using the particular keyword.
Create Table alter (first name, last name);The alter is a reserved word. To fix the error 1064 with the reserved word we specify the alter word within backticks.
Create Table 'alter' (first name, last name);2. Outdated JDBC driver
When the JDBC driver initializes the connection, it sends several commands to the MySQL server. At that time we may receive the MySQL Error code SQL State 42000.
The problem is that the commands were deprecated for some time which results in the error.
We fix the error by upgrading the JDBC MySQL driver to the latest version.
3. Mistyping and Missing of Data
The 1064 error occurs when the data is not found in the database or mistyping the commands.
In case, if the data is missing from the database, we manually add the data to the database. Also, we make sure that all the commands are spelled correctly.
[Need any assistance with SQL State 42000 Error codes? – We’ll help you]
Conclusion
In short, today we discussed in detail on MySQL Error code 1064 and saw how our Support Engineers find the fix for this error.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
I used to run a one-liner for creating a new database and adding a new user to it, with a custom password. It looked like this:
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ohdear_ci.*
TO 'ohdear_ci'@'localhost'
IDENTIFIED BY 'ohdear_secret';
In MySQL 8 however, you’ll receive this error message.
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'IDENTIFIED BY 'ohdear_secret'' at line 1
The reason appears to be that MySQL dropped support for this short-hand version and now requires the slightly longer version instead.
mysql> CREATE USER 'ohdear_ci'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'ohdear_secret'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec) mysql> GRANT ALL ON ohdear_ci.* TO 'ohdear_ci'@'localhost'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.15 sec)
If you have scripting in place that uses the short, one-liner version, be aware those might need changing if you move to MySQL 8.