Появление сообщения об ошибке 401 Unauthorized Error («отказ в доступе») при открытии страницы сайта означает неверную авторизацию или аутентификацию пользователя на стороне сервера при обращении к определенному url-адресу. Чаще всего она возникает при ошибочном вводе имени и/или пароля посетителем ресурса при входе в свой аккаунт. Другой причиной являются неправильные настройки, допущенные при администрировании web-ресурса. Данная ошибка отображается в браузере в виде отдельной страницы с соответствующим описанием. Некоторые разработчики интернет-ресурсов, в особенности крупных порталов, вводят собственную дополнительную кодировку данного сбоя:
- 401 Unauthorized;
- Authorization Required;
- HTTP Error 401 – Ошибка авторизации.
Попробуем разобраться с наиболее распространенными причинами возникновения данной ошибки кода HTTP-соединения и обсудим способы их решения.
Причины появления ошибки сервера 401 и способы ее устранения на стороне пользователя
При доступе к некоторым сайтам (или отдельным страницам этих сайтов), посетитель должен пройти определенные этапы получения прав:
- Идентификация – получение вашей учетной записи («identity») по username/login или email.
- Аутентификация («authentic») – проверка того, что вы знаете пароль от этой учетной записи.
- Авторизация – проверка вашей роли (статуса) в системе и решение о предоставлении доступа к запрошенной странице или ресурсу на определенных условиях.
Большинство пользователей сохраняют свои данные по умолчанию в истории браузеров, что позволяет быстро идентифицироваться на наиболее часто посещаемых страницах и синхронизировать настройки между устройствами. Данный способ удобен для серфинга в интернете, но может привести к проблемам с безопасностью доступа к конфиденциальной информации. При наличии большого количества авторизованных регистрационных данных к различным сайтам используйте надежный мастер-пароль, который закрывает доступ к сохраненной в браузере информации.
Наиболее распространенной причиной появления ошибки с кодом 401 для рядового пользователя является ввод неверных данных при посещении определенного ресурса. В этом и других случаях нужно попробовать сделать следующее:
- Проверьте в адресной строке правильность написания URL. Особенно это касается перехода на подстраницы сайта, требующие авторизации. Введите правильный адрес. Если переход на страницу осуществлялся после входа в аккаунт, разлогинитесь, вернитесь на главную страницу и произведите повторный вход с правильными учетными данными.
- При осуществлении входа с сохраненными данными пользователя и появлении ошибки сервера 401 проверьте их корректность в соответствующих настройках данного браузера. Возможно, авторизационные данные были вами изменены в другом браузере. Также можно очистить кэш, удалить cookies и повторить попытку входа. При удалении истории браузера или очистке кэша потребуется ручное введение логина и пароля для получения доступа. Если вы не помните пароль, пройдите процедуру восстановления, следуя инструкциям.
- Если вы считаете, что вводите правильные регистрационные данные, но не можете получить доступ к сайту, обратитесь к администратору ресурса. В этом случае лучше всего сделать скриншот проблемной страницы.
- Иногда блокировка происходит на стороне провайдера, что тоже приводит к отказу в доступе и появлению сообщения с кодировкой 401. Для проверки можно попробовать авторизоваться на том же ресурсе с альтернативного ip-адреса (например, используя VPN). При подтверждении блокировки трафика свяжитесь с провайдером и следуйте его инструкциям.
Некоторые крупные интернет-ресурсы с большим количеством подписчиков используют дополнительные настройки для обеспечения безопасности доступа. К примеру, ваш аккаунт может быть заблокирован при многократных попытках неудачной авторизации. Слишком частые попытки законнектиться могут быть восприняты как действия бота. В этом случае вы увидите соответствующее сообщение, но можете быть просто переадресованы на страницу с кодом 401. Свяжитесь с администратором сайта и решите проблему.
Иногда простая перезагрузка проблемной страницы, выход из текущей сессии или использование другого веб-браузера полностью решают проблему с 401 ошибкой авторизации.
Устранение ошибки 401 администратором веб-ресурса
Для владельцев сайтов, столкнувшихся с появлением ошибки отказа доступа 401, решить ее порою намного сложнее, чем обычному посетителю ресурса. Есть несколько рекомендаций, которые помогут в этом:
- Обращение в службу поддержки хостинга сайта. Как и в случае возникновения проблем с провайдером, лучше всего подробно описать последовательность действий, приведших к появлению ошибки 401, приложить скриншот.
- При отсутствии проблем на стороне хостинг-провайдера можно внести следующие изменения в настройки сайта с помощью строки Disallow:/адрес проблемной страницы. Запретить индексацию страницам с ошибкой в «rоbоts.txt», после чего добавить в файл «.htассеss» строку такого типа:
Redirect 301 /oldpage.html http://site.com/newpage.html.
Где в поле /oldpage.html прописывается адрес проблемной страницы, а в http://site.com/newpage.html адрес страницы авторизации.
Таким образом вы перенаправите пользователей со всех страниц, которые выдают ошибку 401, на страницу начальной авторизации.
- Если после выполнения предыдущих рекомендаций пользователи при попытках авторизации все равно видят ошибку 401, то найдите на сервере файл «php.ini» и увеличьте время жизни сессии, изменив значения следующих параметров: «session.gc_maxlifetime» и «session.cookie_lifetime» на 1440 и 0 соответственно.
- Разработчики веб-ресурсов могут использовать более сложные методы авторизации и аутентификации доступа для создания дополнительной защиты по протоколу HTTP. Если устранить сбой простыми методами администрирования не удается, следует обратиться к специалистам, создававшим сайт, для внесения соответствующих изменений в код.
Хотя ошибка 401 и является проблемой на стороне клиента, ошибка пользователя на стороне сервера может привести к ложному требованию входа в систему. К примеру, сетевой администратор разрешит аутентификацию входа в систему всем пользователям, даже если это не требуется. В таком случае сообщение о несанкционированном доступе будет отображаться для всех, кто посещает сайт. Баг устраняется внесением соответствующих изменений в настройки.
Дополнительная информация об ошибке с кодом 401
Веб-серверы под управлением Microsoft IIS могут предоставить дополнительные данные об ошибке 401 Unauthorized в виде второго ряда цифр:
- 401, 1 – войти не удалось;
- 401, 2 – ошибка входа в систему из-за конфигурации сервера;
- 401, 3 – несанкционированный доступ из-за ACL на ресурс;
- 401, 501 – доступ запрещен: слишком много запросов с одного и того же клиентского IP; ограничение динамического IP-адреса – достигнут предел одновременных запросов и т.д.
Более подробную информацию об ошибке сервера 401 при использовании обычной проверки подлинности для подключения к веб-узлу, который размещен в службе MS IIS, смотрите здесь.
Следующие сообщения также являются ошибками на стороне клиента и относятся к 401 ошибке:
- 400 Bad Request;
- 403 Forbidden;
- 404 Not Found;
- 408 Request Timeout.
Как видим, появление ошибки авторизации 401 Unauthorized не является критичным для рядового посетителя сайта и чаще всего устраняется самыми простыми способами. В более сложной ситуации оказываются администраторы и владельцы интернет-ресурсов, но и они в 100% случаев разберутся с данным багом путем изменения настроек или корректировки html-кода с привлечением разработчика сайта.
Это руководство поможет вам устранить неполадки, возникающие при использовании функции «Войти с аккаунтом Google» для входа в сторонние приложения и сервисы. Сторонними считаются сервисы и приложения, созданные не компанией Google, а третьими лицами – другими разработчиками и организациями.
Некоторые сообщения об ошибках связаны с неполадками, устранение которых не входит в обязанности Google. Например, приложение или сервис, которым вы хотите воспользоваться, не соответствует требованиям безопасности Google. Код ошибки поможет определить, почему не получается войти в аккаунт. Затем вы сможете устранить проблему самостоятельно или обратиться напрямую к разработчику для ее решения.
Примечание. Благодаря функции «Войти с аккаунтом Google» пользователям доступно множество преимуществ, например усиленная защита аккаунта. Подробнее о том, как функция «Войти с аккаунтом Google» может улучшить работу в интернете…
Как войти в аккаунт Google
- Чтобы использовать функцию «Войти с аккаунтом Google», необходимо войти в аккаунт Google.
- Если с этим возникла проблема, следуйте инструкциям в статье Не удается войти в аккаунт Google.
Что делать, если не получается войти в аккаунт
Важно. Функция «Войти с аккаунтом Google» позволяет входить в сторонние сервисы или приложения, но не объединяет ваши аккаунты в них с аккаунтом Google.
Если вы столкнулись с неполадкой при использовании функции «Войти с аккаунтом Google», сначала определите, с каким аккаунтом связана эта проблема.
Аккаунт заблокирован или отключен
При использовании функции «Войти с аккаунтом Google» вы можете увидеть сообщение о том, что ваш аккаунт отключен или заблокирован. Сначала выясните, отключен ли ваш аккаунт Google. Если нет, это может означать, что третье лицо отключило ваш аккаунт на своем сайте.
- Чтобы узнать, отключен ли ваш аккаунт Google:
- Попробуйте войти в свой аккаунт Google. Если он отключен, при попытке входа вы увидите сообщение «Аккаунт отключен».
- Проверьте доступ к другим сервисам Google. Например, если вы можете войти в Gmail, используя аккаунт Google, значит он не отключен.
- Если вы указали в этом аккаунте Google дополнительный адрес электронной почты, проверьте, не пришло ли на этот адрес уведомление об отключении.
- Если ваш аккаунт Google отключен:
- Войдите в приложение или сервис другим способом.
- Уточните у третьего лица, можно ли войти в аккаунт другим способом, например с помощью адреса электронной почты и пароля.
- Узнайте, как восстановить доступ к аккаунту.
- Войдите в приложение или сервис другим способом.
- Если ваш аккаунт заблокирован третьим лицом, свяжитесь с разработчиком напрямую.
Аккаунт удален
Что происходит, когда удаляется аккаунт Google:
- Удаляются и данные, необходимые для использования функции «Войти с аккаунтом Google». Это значит, что вы больше не сможете использовать кнопку «Войти с помощью Google» для входа через удаленный аккаунт.
- Удаление аккаунта Google не обязательно означает, что вы потеряете доступ к стороннему аккаунту. Попробуйте войти в приложение или сервис другим способом (например, указав имя пользователя и пароль) или свяжитесь с разработчиком напрямую.
Что происходит, когда удаляется сторонний аккаунт:
- Третьи лица не оповещают Google об удалении аккаунта, даже если вы создали его с помощью функции «Войти с аккаунтом Google». Возможно, вы всё ещё будете видеть в вашем аккаунте Google информацию о том, что приложение или сервис связаны с вашим аккаунтом.
- Чтобы узнать, как третье лицо обрабатывает ваши данные, ознакомьтесь с его условиями использования услуг.
- Некоторые третьи стороны просто отключают аккаунты.
- Другие полностью удаляют ваши данные из своего сервиса.
- Если данные были удалены, вам нужно создать новый аккаунт в приложении или сервисе. Вы по-прежнему сможете использовать функцию «Войти с аккаунтом Google», но для этого может потребоваться другой аккаунт Google.
Не удается использовать функцию «Войти с аккаунтом Google» с существующим сторонним аккаунтом
Возможно, при попытке использовать функцию «Войти с аккаунтом Google» для входа в ранее созданный аккаунт приложения или сервиса вы увидите сообщение об ошибке.
Сторонние сервисы используют функцию «Войти с аккаунтом Google» по-разному. Некоторые из них не поддерживают несколько способов входа в один и тот же аккаунт. Если вы столкнулись с этой проблемой, свяжитесь с разработчиком напрямую.
Коды ошибок и устранение неполадок
Если вы вошли в аккаунт Google, но у вас все равно не получается воспользоваться функцией «Войти с аккаунтом Google», возможно, вы увидите сообщение с кодом ошибки. Вы можете использовать его, чтобы определить причину неполадки и найти решение проблемы.
| Код ошибки | Сообщение об ошибке |
|---|---|
| 400 invalid_request | Доступ заблокирован: приложение отправило недопустимый запрос. |
| 401 invalid_client | Источник не зарегистрирован. |
| 401 deleted_client | Клиент OAuth был удален. |
| 403 invalid_account | Сообщения об ошибке могут быть разными. |
| 403 access_denied | Сообщения об ошибке могут быть разными. |
|
403 disallowed_useragent |
Невозможно выполнить вход, поскольку это приложение не отвечает правилам Google в отношении встроенных компонентов WebView. Если у приложения есть сайт, попробуйте войти в аккаунт в браузере. |
|
403 org_internal |
Это приложение доступно только пользователям из владеющей им организации. |
|
403 restricted_client |
Это приложение пока не может выполнять запросы OAuth. Чтобы исправить это, настройте окно запроса доступа OAuth в Google Cloud Console. |
| 400 admin_policy_enforced | |
|
400 policy_enforced |
Попытку входа в аккаунт Google заблокировала Дополнительная защита. Эта функция безопасности закрывает доступ к вашим данным большинству сторонних приложений и сервисов, чтобы обеспечить защиту аккаунта. |
|
400 origin_mismatch 400 redirect_uri_mismatch |
Невозможно выполнить вход в приложение, поскольку оно не отвечает правилам OAuth 2.0 Google. |
400 invalid_request
Если вы видите ошибку 400 invalid_request или сообщение «Доступ заблокирован: приложение отправило недопустимый запрос», значит в приложении используется запрещенный Google способ авторизации.
С Google вы можете безопасно входить на сторонние сайты и в приложения, а также предоставлять им доступ к своим данным. Для дополнительной защиты Google блокирует приложения, которые могут подвергнуть ваш аккаунт опасности.
Совет. Узнайте, как функция «Войти с аккаунтом Google» помогает безопасно делиться данными.
Что делать, если появилась эта ошибка
Эту проблему может решить только сторонний разработчик. Чтобы сообщить об ошибке, свяжитесь с ним напрямую.
Ошибки 401
Ошибка с кодом 401 обычно означает, что разработчик неправильно зарегистрировал приложение в Google.
Чтобы обезопасить ваш аккаунт, Google разрешает разработчикам добавлять функцию «Войти с аккаунтом Google» только в приложения, прошедшие регистрацию. Ваши данные не передаются разработчикам незарегистрированных приложений. Вот как могут выглядеть сообщения об ошибке:
- 401 invalid_client. Приложение не соответствует описанию в форме регистрации, или разработчик приложения предоставил Google неполную информацию.
- 401 deleted_client. Регистрация приложения или сервиса недействительна.
Что делать, если появилась эта ошибка
Эту проблему может решить только сторонний разработчик. Чтобы сообщить об ошибке, свяжитесь с ним напрямую.
403 invalid_account
Если при попытке входа вы видите ошибку 403 invalid_account, возможно, ваш аккаунт Google отключен.
Что делать, если появилась эта ошибка
Проверьте, отключен ли ваш аккаунт Google.
Если да, узнайте, как восстановить доступ к аккаунту.
403 access_denied
Ошибка 403 access_denied означает, что ваш аккаунт Google не может использовать либо приложение или сервис, либо функцию «Войти с аккаунтом Google». На это может быть несколько причин:
- Приложение находится в тестовом режиме, и разработчик не дал вам права на вход в качестве тестового пользователя.
- Вы не можете пользоваться функцией «Войти с аккаунтом Google» из-за типа аккаунта Google, в который вы вошли.
- Например, в аккаунте ребенка нельзя использовать функцию «Войти с аккаунтом Google» без разрешения родителя или законного представителя.
Что делать, если появилась эта ошибка
- Войдите в приложение с аккаунта другого типа.
- Если вы считаете, что у вашего аккаунта должен быть доступ, свяжитесь с разработчиком напрямую.
403 disallowed_useragent
Ошибка 403 disallowed_useragent означает, что приложение использует встроенные компоненты WebView. Некоторые разработчики используют WebView, чтобы показывать веб-контент в приложении. Встроенные компоненты WebView представляют угрозу вашей безопасности, поскольку с их помощью третьи лица могут отслеживать и изменять ваши взаимодействия с Google.
Чтобы защитить ваш аккаунт, с 30 сентября 2021 года Google больше не разрешает использовать встроенные компоненты WebView.
Что делать, если появилась эта ошибка
Эту проблему может решить только сторонний разработчик. Чтобы сообщить об ошибке, свяжитесь с ним напрямую.
Если у приложения есть сайт, попробуйте войти в аккаунт в браузере.
403 org_internal
Если вы видите ошибку 403 org_internal, значит приложение доступно только пользователям из владеющей им организации. Например, организация может открыть доступ к приложению или сервису только аккаунтам с адресами электронной почты, заканчивающимися на @example.com.
Что делать, если появилась эта ошибка
Если вы состоите в организации, войдите с рабочего аккаунта.
403 restricted_client
Ошибка 403 restricted_client означает, что функция «Войти с аккаунтом Google» недоступна в стороннем приложении, поскольку оно не соблюдает определенные требования Google по безопасности, необходимые для защиты вашего аккаунта.
Что делать, если появилась эта ошибка
Эту проблему может решить только сторонний разработчик. Чтобы сообщить об ошибке, свяжитесь с ним напрямую.
400 admin_policy_enforced
Ошибка 400 admin_policy_enforced означает, что использовать функцию «Войти с аккаунтом Google» запретил администратор. Эта ошибка может появиться, если вы пытаетесь войти с рабочего аккаунта или аккаунта другой организации. Иногда администратор блокирует только определенные приложения.
Что делать, если появилась эта ошибка
Если вы считаете, что у вас должен быть доступ к приложению, свяжитесь с администратором Google Workspace в своей организации.
400 policy_enforced
Вы можете увидеть ошибку 400 policy_enforced, если ваш аккаунт Google участвует в программе Дополнительной защиты. В целях безопасности эта функция блокирует доступ большинства сторонних приложений или сервисов к данным вашего аккаунта Google.
Что делать, если появилась эта ошибка
Для исправления этой ошибки вам необходимо отключить Дополнительную защиту, а значит, вы потеряете доступ к преимуществам этой программы.
400 origin_mismatch или 400 redirect_uri_mismatch
Ошибки 400 origin_mismatch и 400 redirect_uri_mismatch могут означать следующее:
- Разработчик неправильно настроил приложение или сервис.
- Способ, которым приложение пыталось получить доступ к вашим данным, нарушает наши правила.
В целях безопасности разработчик может добавить функцию «Войти с аккаунтом Google» в свое приложение только после того, как зарегистрирует его. Приложение также должно соответствовать нашим правилам и стандартам безопасности. В противном случае функция «Войти с аккаунтом Google» будет недоступна, пока разработчик не устранит проблему.
Что делать, если появилась эта ошибка
Эту проблему может решить только сторонний разработчик. Чтобы сообщить об ошибке, свяжитесь с ним напрямую.
Как устранить прочие неполадки в стороннем приложении или сервисе
Иногда приложения и сервисы недоступны несмотря на то, что на их сайт можно войти с аккаунтом Google. Большинство причин, по которым это происходит, не зависят от нас, так как Google не оказывает услуги, предлагаемые третьими сторонами. Мы только помогаем подтверждать вашу личность на сайте или в приложении.
Вот некоторые из проблем, с которыми вы можете столкнуться в приложении или сервисе:
- Вы купили фильм в стороннем сервисе, но не можете его посмотреть.
- Вам не удается купить товар на стороннем сайте.
- Вы не можете продлить подписку на стороннем сайте.
Если у вас возникли подобные проблемы, свяжитесь с разработчиком напрямую.
Как связаться с разработчиком стороннего приложения или сервиса
Чтобы найти контактную информацию стороннего разработчика:
- Откройте приложение или сервис.
- Нажмите Войти с аккаунтом Google.
- Возможно, чтобы перейти на экран входа с аккаунтом Google, вам придется выйти из приложения или сервиса.
- Чтобы узнать адрес электронной почты разработчика, в верхней части следующего экрана нажмите на название приложения или сайта. В некоторых случаях адрес электронной почты разработчика может быть недоступен.
Как защитить взломанный аккаунт
- Если вы считаете, что кто-то взломал ваш аккаунт Google, следуйте инструкциям в статье Как защитить взломанный аккаунт Google.
- Злоумышленники могут использовать взломанный аккаунт Google для входа в сторонние приложения или сервисы. Чтобы усилить защиту аккаунта, включите двухэтапную аутентификацию.
- Воспользуйтесь программой защиты связанных аккаунтов. Она обнаруживает подозрительные события и отправляет оповещения о безопасности совместимым сторонним приложениям и сервисам, связанным с вашим аккаунтом Google.
- Если вы считаете, что кто-то взломал ваш сторонний аккаунт, свяжитесь с разработчиком напрямую.
This page describes how different
HTTP status codes,
network errors, and DNS errors affect Google Search. We cover the top 20 status codes that
Googlebot
encountered on the web, and the most prominent network and DNS errors. More exotic status
codes, such as
418 (I'm a teapot),
aren’t covered. All issues mentioned on this page generate a corresponding error or warning in
Search Console’s
Page Indexing report.
HTTP status codes
HTTP status codes are generated by the server that’s hosting the site when it responds to a
request made by a client, for example a browser or a crawler. Every HTTP status code has a
different meaning, but often the outcome of the request is the same. For example, there are
multiple status codes that signal redirection, but their outcome is the same.
Search Console generates error messages for status codes in the 4xx–5xx range,
and for failed redirections (3xx). If the server responded with a
2xx status code, the content received in the response may be considered for
indexing.
The following table contains the most encountered HTTP status codes by Googlebot and an
explanation how Google handles each status code.
| HTTP status codes | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Google considers the content for indexing. If the content suggests an error, for example
|
|||||||||||
|
Googlebot follows up to 10 redirect hops. If the crawler doesn’t receive content within
In case of robots.txt, Googlebot follows at least five redirect hops as defined by
Any content Googlebot received from the redirecting URL is ignored, and the final target
|
|||||||||||
|
Google’s indexing pipeline doesn’t consider URLs that return a
Any content Googlebot received from URLs that return a
|
|||||||||||
|
If the robots.txt file returns a server error status code for more than 30 days, Google
Any content Googlebot received from URLs that return a
|
soft 404 errors
A soft 404 error is when a URL that returns a page telling the user that the page does
not exist and also a
200 (success)
status code. In some cases, it might be a page with no main content or empty page.
Such pages may be generated for various reasons by your website’s web server or content
management system, or the user’s browser. For example:
- A missing server-side include file.
- A broken connection to the database.
- An empty internal search result page.
- An unloaded or otherwise missing JavaScript file.
It’s a bad user experience to return a 200 (success) status code, but then
display or suggest an error message or some kind of error on the page. Users may think the
page is a live working page, but then are presented with some kind of error. Such pages are
excluded from Search.
When Google’s algorithms detect that the page is actually an error page based on its content,
Search Console will show a soft 404 error in the site’s
Page Indexing report.
Fix soft 404 errors
Depending on the state of the page and the desired outcome, you can solve soft 404
errors in multiple ways:
- The page and content are no longer available.
- The page or content is now somewhere else.
- The page and content still exist.
Try to determine which solution would be the best for your users.
The page and content are no longer available
If you removed the page and there’s no replacement page on your site with similar content,
return a
404 (not found) or 410 (gone)
response (status) code for the page. These status codes indicate to search engines that the
page doesn’t exist and the content should not be indexed.
If you have access to your server’s configuration files, you can make these error pages useful
to users by customizing them. A good custom 404 page helps people find the
information they’re looking for, and also provides other helpful content that encourages
people to explore your site further. Here are some tips for designing a useful custom
404 page:
-
Tell visitors clearly that the page they’re looking for can’t be found. Use language that is
friendly and inviting. -
Make sure your
404page has the same look and feel (including navigation) as
the rest of your site. -
Consider adding links to your most popular articles or posts, as well as a link to your
site’s home page. - Think about providing a way for users to report a broken link.
Custom 404 pages are created solely for users. Since these pages are useless from
a search engine’s perspective, make sure the server returns a 404 HTTP status
code to prevent having the pages indexed.
The page or content is now somewhere else
If your page has moved or has a clear replacement on your site, return a
301 (permanent redirect)
to redirect the user. This will not interrupt their browsing experience and it’s also a great
way to tell search engines about the new location of the page. Use the
URL Inspection tool
to verify whether your URL is actually returning the correct code.
The page and content still exist
If an otherwise good page was flagged with a soft 404 error, it’s likely it
didn’t load properly for Googlebot, it was missing critical resources, or it displayed a
prominent error message during rendering. Use the
URL Inspection tool
to examine the rendered content and the returned HTTP code. If the rendered page is blank,
nearly blank, or the content has an error message, it could be that your page references many
resources that can’t be loaded (images, scripts, and other non-textual elements), which can be
interpreted as a soft 404.
Reasons that resources can’t be loaded include blocked resources (blocked by
robots.txt), having too many
resources on a page, various server errors, or slow loading or very large resources.
Network and DNS errors
Network and DNS errors have quick, negative effects on a URL’s presence in Google Search.
Googlebot treats network timeouts, connection reset, and DNS errors similarly to
5xx server errors. In case of network errors, crawling immediately starts
slowing down, as a network error is a sign that the server may not be able to handle the
serving load. Since Googlebot couldn’t reach the server hosting the site, Google also hasn’t
received any content from the server. The lack of content means that Google can’t index the
crawled URLs, and already indexed URLs that are unreachable will be removed from Google’s
index within days. Search Console may generate errors for each respective error.
Debug network errors
These errors happen before Google starts crawling a URL or while Google is crawling the URL.
Since the errors may occur before the server can respond and so there’s no status code that
can hint at issues, diagnosing these errors can be more challenging. To debug timeout and
connection reset errors:
-
Look at your firewall settings and logs. There may be an overly-broad
blocking rule set. Make sure that
Googlebot IP addresses
are not blocked by any firewall rule. -
Look at the network traffic. Use tools like
tcpdump and
Wireshark to capture and analyze
TCP packets, and look for anomalies that point to a specific network component or server
module. - If you can’t find anything suspicious, contact your hosting company.
The error may be in any server component that handles network traffic. For example, overloaded
network interfaces may drop packets leading to timeouts (inability to establish a connection)
and reset connections (RST packet sent because a port was mistakenly closed).
Debug DNS errors
DNS errors are most commonly caused by misconfiguration, but they may be also caused by a
firewall rule that’s blocking Googlebot DNS queries. To debug DNS errors, do the following:
-
Inspect your firewall rules. Make sure that
none of Google’s IPs
are blocked by any firewall rule, and that bothUDPandTCP
requests are allowed. -
Look at your DNS records. Double check that your
Aand
CNAMErecords are pointing to the right IP addresses and hostname,
respectively. For example:dig +nocmd example.com a +noall +answer
dig +nocmd www.example.com cname +noall +answer
-
Check that all your name servers are pointing to the correct IP addresses of your
site. For example:dig +nocmd example.com ns +noall +answerexample.com. 86400 IN NS a.iana-servers.net. example.com. 86400 IN NS b.iana-servers.net.dig +nocmd @a.iana-servers.net example.com +noall +answerexample.com. 86400 IN A 93.184.216.34dig +nocmd @b.iana-servers.net example.com +noall +answer... -
If you’ve made changes to your DNS configuration within the last 72 hours,
you may need to wait for your changes to propagate across the global DNS network. To speed up propagation, you can
flush Google’s Public DNS cache. -
If you’re running your own DNS server, make sure it’s healthy and that it’s
not overloaded.
Trying to access a site and being met with an error page is at best inconvenient, whether that site is yours or someone else’s. As with many HTTP response codes, part of what makes a 401 error so frustrating is the lack of information it offers for diagnosing and resolving the issue.
The 401 error can happen with any browser, so it’s a pretty common issue people face. In most cases, this problem is relatively simple and straightforward to fix.
In this post, we’ll explain what 401 error messages are and why they happen. Then, we’ll walk you through five methods you can use to fix them.
Let’s get started!
What is the 401 Error Code?
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) defines the error 401 Unauthorized as:
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The server generating a 401 response MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource.
An Introduction to the 401 Error Code
HTTP 400 status codes are encountered when there is a problem making a request. A 401 error, in particular, happens when your browser denies you access to the page you’re trying to visit.
As a result, instead of loading the web page, the browser will load an error message. 401 errors can happen within any browser so the message appearing may differ.
For example, in Chrome or Edge, you’ll likely see a paper icon along with a simple message telling you that the page in question isn’t working. It will include the phrase “HTTP Error 401” at the bottom, and instruct you to contact the site’s owner if the problem persists:
At other times and in other browsers, you might get a slightly less friendly warning that’s just a blank page with a “401 Authorization Required” message:
Other variations include:
- “HTTP 401 Error – Unauthorized”
- “401 Unauthorized”
- “Access Denied”
These errors occur on websites that require a login in order to access them. In most cases, it means that something is either wrong with the credentials or with the browser’s ability to read them as valid.
This is similar to HTTP 403 Forbidden Error, in that access isn’t permitted to the user. However, unlike with the 403 error, the 401 error message indicates that the authentication process failed.
The code is sent via the WWW-Authenticate header, which is responsible for identifying the authentication method used for granting access to a web page or resource.
| Error Code | HTTP 401 Unauthorized Error |
| Error Type | Commonly a client-side error |
| Error Variations | 401 Authorization Required 401 Unauthorized HTTP 401 Error – Unauthorized Access Denied |
| Error Causes | Outdated Browser Cache and Cookies Plugin Incompatibility Incorrect URL or Outdated Link |
The HTTP 401 error is all too common 🤦♀️ — and this guide will give you everything you need to fix it the next time you see that message showing up ✅Click to Tweet
What Causes a 401 Error?
If you encounter an error code in the 400s, you know you’re dealing with a client-side (or browser-side) issue. While the problem may be happening within your browser, however, it doesn’t necessarily always mean that’s the culprit, which we’ll explain in more detail later.
401 errors occur on restricted resources, such as password-protected pages of your WordPress site. So it’s safe to assume that the cause of the problem has something to do with the authentication credentials.
Outdated Browser Cache and Cookies
One of the most common reasons you might experience a 401 error is that your browser’s cache and cookies are out of date, preventing the authorization from successfully going through. If your browser isn’t using the valid authentication credentials (or any at all), the server will reject the request.
Plugin Incompatibility
At other times, this error is caused by a plugin incompatibility or error. For example, a firewall or security plugin can mistake your login attempt as malicious activity, and return a 401 error to protect the page.
Incorrect URL or Outdated Link
It’s also possible that the source of the problem can be attributed to a minor mistake. Common culprits in this category include an incorrectly-typed URL or an outdated link.
How to Fix the 401 Error?
Now that we’ve gone through a bit of background on the 401 error, it’s time to discuss how you can resolve it.
Let’s take a look at five methods you can use:
1. Look for Errors in the URL
We’ll start off with the easiest potential fix: making sure you used the correct URL. This may sound simple, but 401 errors can sometimes appear if the URL wasn’t correctly entered in.
Another possibility is that the link you used to visit the page in question points to the wrong URL. For example, it might be outdated, or leading to a page that no longer exists (and no redirects are in place).
Therefore, it’s worth double-checking the URL you used. If you typed it in yourself, verify that you spelled everything correctly. If you clicked on a link, confirm that it’s pointing to the page you’re trying to access (or try to visit that page directly through the website).
2. Clear Your Browser’s Cache
Your browser’s cache is designed to improve your online experience, by reducing page loading times. Unfortunately, sometimes it can also cause unwanted interruptions.
As we mentioned earlier, one of the common causes of the 401 error is outdated or incorrect cache data or cookies. Therefore, if you don’t notice any issues with the page’s URL, the next step is to clear your browser’s cache.
This will clean out any invalid information that’s locally stored in your browser, which could be interrupting the authentication process. Similarly, your browser’s cookies might contain authentication data that simply needs to be refreshed.
If you’re a Google Chrome user, you can do this by clicking on the menu icon in the top-right corner of the browser, and then going to Settings. Under the Privacy and security section, click on Clear browsing data:
A new window will open. Under the Basic tab, make sure all three boxes are selected, and then select Clear data:
This process will look a little different in other browsers. For example, in Mozilla Firefox, you would click on the library icon in the top-right corner of the browser, followed by History > Clear Recent History:
In the panel that opens next, select Everything in the drop-down menu at the top, make sure “Cache” is selected, and then click on the Clear Now button:
If you’re using a different browser, please refer to this guide for clearing the cache
3. Flush Your DNS
Another method you can try to resolve the 401 error is flushing your Domain Name Server (DNS). While this is a rarer issue, it can be a possible cause, so it’s worth giving it a try if the first two solutions don’t work.
To do this in Windows, click on the Start button and type cmd into the search bar. Hit Enter, and the Command Prompt will open. Copy and paste the command ipconfig/flushdns, and then hit Enter again:
On a Mac, you can do this by going to Finder > Applications > Utilities > Terminal:
Input the command line sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder and press Enter. Then, you can try refreshing the page you were trying to visit, to see if the 401 error has been resolved.
4. Deactivate Your WordPress Plugins
The problem causing your 401 error might not be due to your browser. If you’re having trouble accessing your WordPress site, it’s also possible that one or more plugins are to blame.
Some plugins, especially security-focused plugins, are configured to show a 401 error when they suspect suspicious login activity that might indicate an attack. Others might just be suffering from compatibility issues. Therefore, it’s a good idea to deactivate all of your WordPress plugins and see if that resolves the issue.
You can deactivate your plugins all at the same time in your dashboard, by going to Plugins > Installed Plugins. Check the box at the top to select all of them. Then under the Bulk Actions drop-down menu, select Deactivate and click on the Apply button:
After that, try reloading the page that returned the 401 error to see if this has resolved the issue. If it has, you can manually activate each plugin one at a time, in order to determine which one is causing the problem.
Then you can remove that plugin, replace it with a new one, or contact its developer for assistance.
5. Check the WWW-Authenticate Header Response
At this point, if the issue hasn’t been fixed, it may be caused by a server-side problem. This means our last fix will be a bit more involved.
As we saw earlier, the 401 response is sent through the WWW-Authenticate header, which appears as “WWW-Authenticate: <type> realm=<realm>”. It includes ‘challenges’, or strings of data that indicate what type of authentication is required in order for access to be granted.
In a nutshell, you’ll want to check and see if the header response was sent, and more specifically, what authentication scheme was used. At the very least, this can help narrow down the cause of the problem, and bring you one step closer to a solution.
To do this, go to the web page that’s displaying the 401 error, and access the developer console in Chrome. You can right-click on the page and select Inspect, or use Ctrl+Shift+J.
Next, click on the Network tab and reload the page. This will generate a list of resources. Select the Status header to sort the table and locate the 401 status code:
Select that entry, and then click on the Headers tab. Under Response Headers, locate the WWW-Authenticate header:
The information that is present in the response header, particularly the authentication schemes, can give you more information about what’s happening and point you towards a solution. It can help you understand what type of authentication the server is expecting.
For example, in the above example, we can see that the authentication scheme is “Basic”. This means the authentication request should only require an ID and password. For more detailed information and instructions on how to use this information, we recommend referring to the HTTP Authentication Scheme Registry.
HTTP 401 errors, begone! 🧙♂️ 5 ways to stop those pesky messages (no magic required) ✨Click to Tweet
Summary
When your browser and server have trouble communicating or authenticating requests, you’re sometimes forced to deal with errors such as the 401 error. While this problem is irritating, the message is usually temporary and fixable.
Here are five methods you can use to fix the 401 error:
- Look for errors in the URL.
- Clear your browser’s cache.
- Flush your DNS.
- Deactivate your WordPress plugins.
- Check the WWW-Authenticate header response.
What is a 401 error?
The proper 401 Error meaning is an HTTP status code that indicates the request lacks valid authentication credentials for the requested resource. It means that the server knows about the client but the client doesn’t have sufficient permissions to access the resource and is not authorized to do so without proper authentication.
If you are a web developer, admin, or regular user, knowing the importance of the 401 Error is crucial because it helps you diagnose and troubleshoot issues related to authentication and access control.
For example, if you are an administrator, it will help you implement effective security measures. Meanwhile, for regular users, it will be beneficial for them to understand the reason behind denied access to certain resources.
401 Error variations
Here are some of the 401 error variations which indicate the same:
- HTTP Error 401
- Access denied
- 401 Unauthorized Error
- 401 Authorization Required
- 401 Unauthorized
Understanding HTTP Status codes
If you are a non-techie and don’t know exactly what are HTTP status codes, they can be understood as a set of standardized three-digit numbers used by web servers to communicate the outcome of a client’s request.
This means they provide you with the status or information about the success redirection, type of errors, and other states of the request-response cycle.
These status codes play a crucial role in web communication as they provide important feedback, indicating whether a request was successful or encountered any problems. With the assistance of these codes, one can readily take appropriate actions based on the response received from the server.
Now, when discussing the 4xx series status codes, such as 401 errors, they are typically classified as client error codes. This series indicates that the client’s request has failed or is invalid due to certain reasons. These error codes generally represent the issues or errors caused by the client’s request or a lack of proper authentication.
Some examples of 4xx Series error codes
As we have already discussed, the 4xx series is called client-side errors which includes some of the popular error codes that you might have familiar with.
- 400 (Bad Request Error)
- 403 (Forbidden)
- 404 (Not Found)
Now, let us focus on 401 Error. This error is specifically used when the client is unable to provide valid authentication credentials to access a resource. Its main purpose is to show the client that the requested resources require valid credentials to proceed further.
What causes 401 Error?
Some of the most common scenarios when you might face a 401 Error message:
- Missing or invalid credentials: If you are unable to provide authentic credentials due to any reasons or provide incurred or expired credentials, a 401 error will be triggered.
- Unauthorized access attempt: When you try to access a resource that requires authentication, but the provided credentials do not grant sufficient permission, a 401 Error will be returned.
- Revoked or Expired tokens: If you use an expired or outdated authentication token, the server may respond with a 401 error.
- Corrupt or outdated Browser cache and cookies: If you ever see a 401 error, it’s usually because your browser’s cache and cookies are outdated or corrupted. This can cause trouble with authorization. If your browser doesn’t have the correct authentication credentials (or any at all), the server won’t accept your request. Just remember to keep your browser’s cache and cookies up to date to avoid running into these kinds of errors.
- Incorrect or Outdated URL: Sometimes, in a rush, you might mistakenly enter the wrong URL or encounter a situation where the URL has been changed. This can trigger a 401 error as a result.
- Plugin conflicts: Sometimes, a 401 error can happen because of a plugin issue. For example, if you are using a firewall or security plugin that might mistakenly think your login attempt is suspicious and block access with a 401 error to keep the page safe.
How a 401 Error affect the user experience?
The 401 Error code can have various impacts on the user experience. It typically results in the user being denied access to the requested resource or receiving an error page instead. The error message associated with the 401 Error should provide guidance on how to resolve the issue or provide appropriate instructions.
Now that you have obtained a solid understanding of the 401 unauthorized error and its background, let’s delve into the methods to resolve and fix this issue.
- Ensure the URL is correct
- Check Authentic credentials
- Clear your browser cache and cookies
- Flush Your DNS cache
- Disable WordPress Plugins
- Check out your website’s .htaccess file
- Check the WWW-Authenticate header
1. Ensure the URL is correct
One of the most common mistakes that many users make is typing an incorrect URL in the browser’s address bar. Therefore, it’s important to take a moment and carefully enter the correct URL, ensuring that there are no misspelled or outdated entries.
If you happen to enter a wrong, outdated, or misspelled URL, you might encounter an “Error code 401” message. But there’s no need to worry! This error simply indicates that the URL you were trying to access doesn’t exist, resulting in a “401 unauthorized access” response from the server.
Let us understand it with an example, Suppose you have bookmarked a page or saved its address in your browsers, but things can change over time. The page’s address might have been updated or even deleted.
To investigate it further, you can try going to the website’s homepage and looking for a link to the page that is causing the “Unauthorized 401” error. If the page opens correctly through that link, make sure to compare the URL of the page with the one that initially gave you the error.
2. Ensure correct Authentication credentials
Sometimes, you might come across the frustrating 401 Error code when you’re trying to access a locked resource, such as a password-protected page. It basically means that your authentication credentials are not valid, and as a result, you’re denied access to the page you’re trying to open.
Here’s what you can do to tackle this issue. Take your time to double-check if you are logged in with the correct login credentials such as the user ID and password or not.
If you’re confident that you’ve entered the details correctly, you might want to consider changing your password. This could help ensure that you have the right credentials to access the resource without any hiccups.
However, in case you are unable to access your password-protected website, Check out our complete guide on “How To Easily Reset WordPress & Start Over?“.
3. Clear your browser cache and cookies
Without a doubt, browser cache and cookies are intended to enhance your online experience by speeding up website loading. However, there are occasions when they can also be the culprit behind triggering errors.
Specifically, corrupted or outdated cache files and cookies can result in unexpected interruptions or browsing issues. To resolve this, the best course of action is to completely clear your browser’s cache and cookies.
If you are using Chrome browser, follow the steps given below:
Read: 🚩 Browser Market Share & Usage Statistics
Step 1: Depending on your browser, Go to the settings menu.
In Google Chrome, for example, you can find the settings menu by clicking on the three vertical dots located in the upper right corner of the window.
Step 2: To proceed, select “More tools” and then click on “Clear browsing data”.
Step 3: A pop-up window will be displayed, and you can choose all three options located under the “Basic” section as depicted in the picture below. These options consist of “Browsing history,” “Cookies and other site data,” and “Cached images and files.
Step 4: Click on “Clear data” to initiate the process.
By doing so, any corrupt or invalid information stored locally in your browser will be completely erased. This ensures that if it was causing the authentication issue, it won’t occur again.
4. Flush your DNS Cache
Similar to your browser cache and cookies, the DNS cache is also stored locally on your computer. Although it is uncommon for a DNS cache to trigger a 401 error, it is worth giving it a try as a troubleshooting step.
For Windows 10 and Windows 11 users:
Step 1: Open the Run command by pressing the Windows key and R. Alternatively, you can search for it in the Start menu.
Step 2: Type “cmd” and hit Enter to open the Command Prompt.
Step 3: Once the Command Prompt window is open, type “ipconfig/release” to release your current IP address.
Step 4: Next, type “ipconfig/flushdns” to release the DNS cache.
Step 5: Type “ipconfig /renew” to obtain a new IP address.
Step 6: Type “netsh int ip set dns” and hit Enter to reset your IP settings.
Step 7: Finally, type “netsh winsock reset” to restore the Winsock Catalog.
Step 8: After completing these steps, restart your computer to ensure the changes take effect.
For MacOS users:
Step 1: First of all, open the system preference options on your Mac. If you have Gas Mask installed, it can make searching for system-related tasks easier.
Step 2: Next, navigate to the Ethernet tab and click on the advanced options.
Step 3: Under the TCP/IP tab, you will find the option to release a DHCP lease. Clicking on this option will allow you to clear out the local DNS on your Mac.
Step 4: Go to Utilities > Terminal and enter the command to clear the local DNS cache.
Step 5: The command for flushing the local DNS cache is “dscacheutil -flushcache”.
Step 6: Once you have entered the command, there will be no separate success or failure message that pops up. However, in most cases, the cache will be cleared without any major issues.
5. Disable WordPress Plugins
It is important to note that the cause of the 401 error may not always lie with your browser, but rather with your WordPress plugins. If you are experiencing difficulties accessing your WordPress site, it is possible that certain plugin(s) are responsible for this issue.
Especially, security plugins have a reputation for causing these types of problems. These plugins are designed to block access and return a 401 error message if they detect any suspicious activity.
Another possibility is that there may be compatibility issues with certain plugins. Some plugins can conflict with your website and trigger such issues. In such cases, the best course of action is to disable all the installed WordPress plugins and check if this resolves the issue.
Step 1: Log in to your WordPress admin dashboard
Step 2: Navigate to the “Plugins” menu option on the left-hand side of the dashboard.
Step 3: A list of installed plugins will be displayed. Take note of the currently active plugins or make a list if needed.
Step 4: Select all the plugins by ticking the checkboxes next to their names or use the “Bulk Actions” dropdown menu to select all.
Step 5: From the “Bulk Actions” dropdown menu, choose “Deactivate” and click the “Apply” button. This will deactivate all the selected plugins simultaneously.
Step 6: Once the deactivation process is complete, try accessing your website and check if the 401 error is resolved.
If the error is no longer occurring, it indicates that one or more of the plugins were causing the issue. You can then proceed with identifying the conflicting or incompatible plugins by reactivating them one by one and testing the website after each activation until the error reappears. This way, you can pinpoint the specific plugin causing the conflict.
If you find the defective plugin, consider either updating it to a newer version or reaching out to the plugin developer for support. Alternatively, you may need to find an alternative plugin that serves a similar purpose but does not cause conflicts.
6. Check out your website’s .htaccess file
You might be surprised to learn, especially if you are not aware of it, that the hosting panel is not the only place where you can set a password for your website. Another method is by configuring the code in the .htaccess file.
If you have previously set a password through the .htaccess file but have either forgotten about it or it was added through a plugin, it’s essential to check or examine your website’s .htaccess file to determine if it is causing the issue.
Let us see how you can proceed.
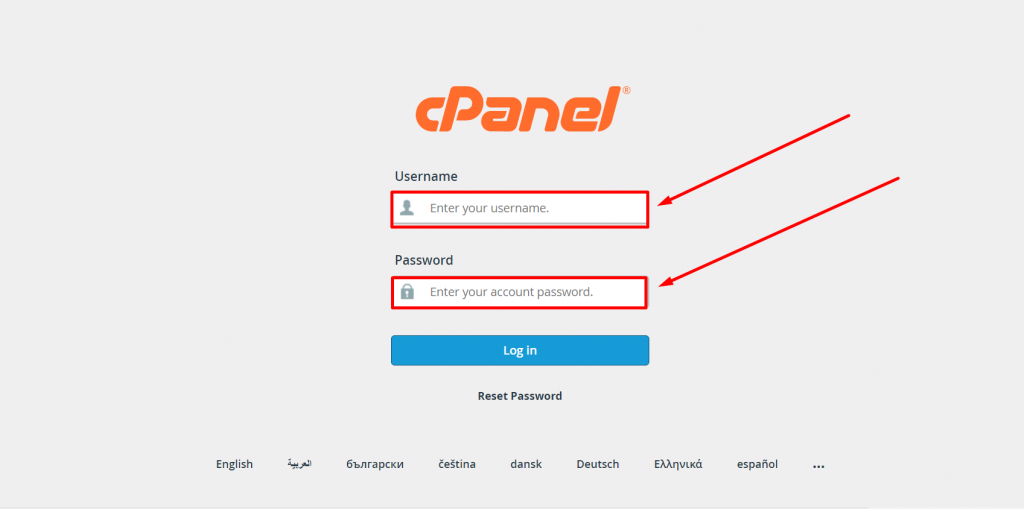
If your web hosting provider offers you cPanel accessibility, it will become easy for you to locate WordPress .htaccess files without using an FTP client.
1. To do this, first, you need to login into your cPanel as shown below:
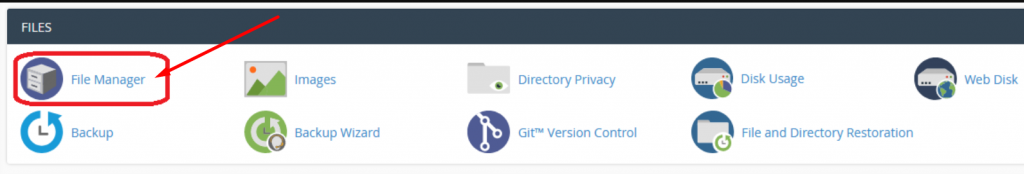
2. Lookout for the Files section and click on the File Manager option as shown.
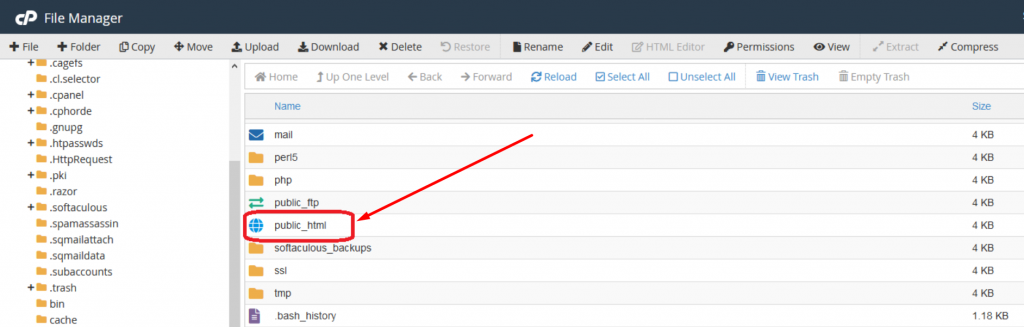
3. Now you will be able to see a list of all the core files displayed on your screen. Select and click on the public_html folder to open.
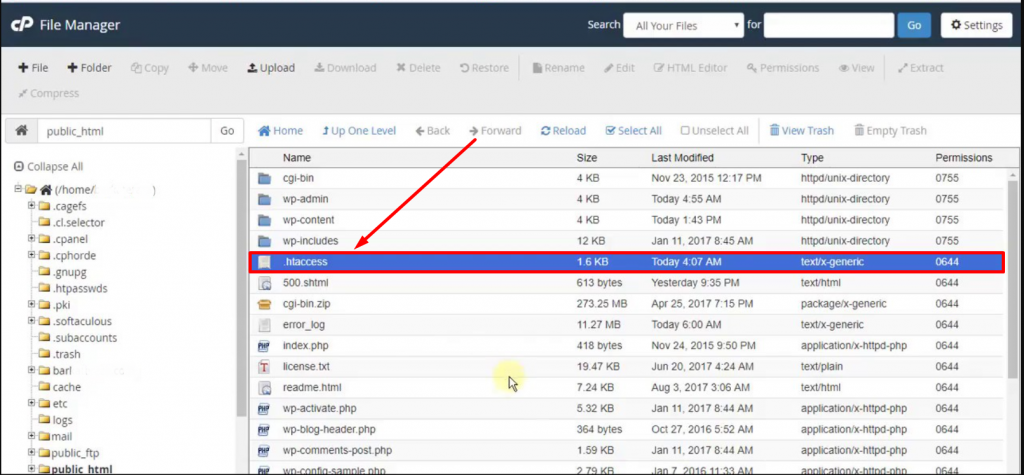
4. Now if you have an existing .htacess file available, it will reflect in the public_html or htdocs folder, if not then either it is hidden or doesn’t exist yet.
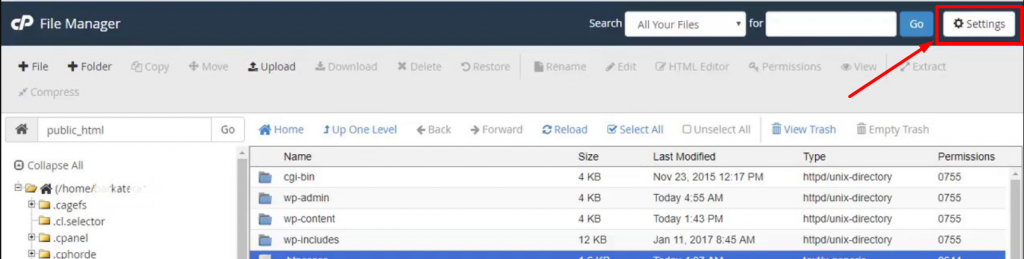
However, if your WordPress .htaccess file is hidden, you can unhide it by simply going to the Settings section located at the top right corner of the “files manager window” as shown in the image below:
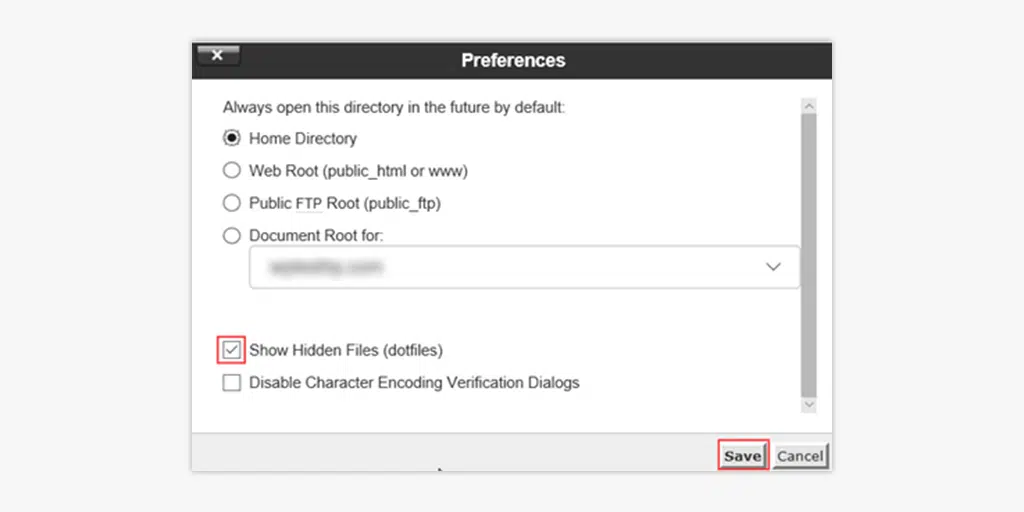
A preferences window will pop out as shown in the picture below:
Now simply, check the ” Show Hidden Files (dotfiles)” box and click on Save. All the hidden files will start reflecting on your file manager window.
Read: 🚩 WordPress .htaccess File: How to Create And Edit it?
Now when you right-click on the .htaccess file and select the edit option, Its content should look similar to this:
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Permission required"
AuthUserFile ../../.htpasswd
require valid-user
The login credentials for the protection are stored in a file called “.htpasswd.” This file contains the encrypted password and the associated username.
If you no longer require the protection, you can remove the corresponding code from the .htaccess file and save the changes to confirm.
If the above troubleshooting methods don’t work, this means the issue is from the server side.
The “WWW-Authenticate” header is an HTTP response header that is used to indicate the type of authentication required for accessing a resource on a web server. When a server sends a “401 Unauthorized” status code, it includes the “WWW-Authenticate” header to specify the authentication scheme that the client needs to use in order to access the requested resource.
This header provides information to the client about the authentication method that should be used, such as Basic Authentication or Digest Authentication. It typically includes a challenge, which is a value that the client needs to include in subsequent requests to authenticate itself.
To check the “WWW-Authenticate” header, you can follow these steps:
Step 1: Open your web browser and navigate to the desired web page that generates a 401 error code.
Step 2: Right-click anywhere on the page and select “Inspect” or “Inspect Element” from the context menu. This will open the browser’s developer tools.
Step 3: In the developer tools, navigate to the “Network” tab.
Step 4: Refresh the page by pressing the “F5” key or clicking the refresh button in the browser.
Step 5: Look for the request corresponding to the resource you want to check in the list of network requests. It should have a “401 Unauthorized” status code.
Step 6: Click on the request to view its details.
Step 7: In the headers section, locate the “WWW-Authenticate” header. This header will provide information about the authentication scheme required for accessing the resource.
Step 8: The value of the “WWW-Authenticate” header will indicate the authentication method to be used, such as “Basic”, “Digest”, or others.
You can also refer to HTTP Authentication Scheme Registry for more information about page authentication methods.
Comparison: 401 vs 403 Error
The 401 Error differentiates itself by focusing specifically on the lack of valid authentication credentials. It indicates that the client needs to provide proper authentication to gain access to the resource, while the 400 and 403 errors highlight other issues, such as invalid requests or insufficient permissions.
Here is a comparison table between a 401 error and a 403 error:
| Error Code | Error Name | Meaning or authentication information |
|---|---|---|
| 401 | Unauthorized | Indicates the need for authentication. |
| The client lacks valid credentials |
| Error Code | Error Name | Meaning of authentication information. |
|---|---|---|
| 403 | Forbidden | Indicates that the client is authenticated, but lacks the necessary permissions to access the requested resource |
In summary, a 401 error signifies the need for authentication, while a 403 error indicates that the client is authenticated but lacks the necessary permissions to access the requested resource.
Real-world Examples of 401 Errors
Examples from popular websites or web applications
- Social media platform: If a user attempts to access a private profile or restricted content without logging in or providing valid credentials, a 401 Error may be returned.
- Cause: The user attempts to view a private post without logging in or providing valid credentials.
- Resolution: The platform returns a 401 Error and prompts the user to log in or create an account to gain access to the restricted content.
- Online banking: When a client tries to access account information or perform financial transactions without proper authentication, a 401 Error can occur.
- Cause: The user tries to access account details or perform financial transactions without providing the correct authentication credentials.
- Resolution: The banking system returns a 401 Error and directs the user to enter valid login credentials to access their account securely.
By analyzing real-world examples of 401 Errors, it becomes evident that these errors occur when accessing sensitive or restricted resources, emphasizing the importance of proper authentication and authorization.
Conclusion
A “401 Error” is triggered when the client lacks or is unable to provide valid authentication credentials to access a password-protected resource. Additionally, you may have noticed that this error is primarily caused by the client side, making it easily fixable. However, it can also be triggered from the server side, although this is rare.
So, in this post, we have compiled some of the best 7 troubleshooting methods that you can try to fix 401 errors.
- Ensure the URL is correct
- Check Authentic credentials
- Clear your browser cache and cookies
- Flush Your DNS cache
- Disable WordPress Plugins
- Check out your website’s .htaccess file
- Check the WWW-Authenticate header
We hope the methods mentioned above will help you fix the 401 error and resolve your issues. If you have any queries or would like to suggest any additional methods, please let us know in the comment section below.
Save your time, money, and resources, and give your website mammoth growth with WPOven’s best wordpress vps hosting.
- 24X7 WordPress Expert support
- Cloudflare integration
- High-end Security
- Datacentres around the world, etc.
You can have all these features and much more in a single plan with unlimited Free migrations, unlimited staging, and a 14-day risk-free guarantee, Signup Now!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I fix a 401 error?
You can fix a 401 error by following these methods:
1. Ensure the URL is correct
2. Check Authentic credentials
3. Clear your browser cache and cookies
4. Flush Your DNS cache
5. Disable WordPress Plugins
6. Check out your website’s .htaccess file
7. Check the WWW-Authenticate header
What is the reason for 401 unauthorized error?
The reason for the 401 unauthorized error are:
1. Missing or invalid credentials
2. Unauthorized access attempt
3. Revoked or Expired tokens
4. Corrupt or outdated Browser cache and cookies
5. Incorrect or Outdated URL
6. Plugin conflicts
What is an example of a 401 error?
An example of a 401 error is If a user attempts to access a private profile or restricted content on a social media platform without logging in or providing valid credentials, a 401 Error may be returned.













![How to Fix "401 Unauthorized Access" Error? [7 Methods] 3 HTTP Error 401](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/1-3.png.webp)
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 7 Clear browsing data in Chrome](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/7.png)
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 8 Clearing data in Google Chrome](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/8.png)
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 13 Opening Command Prompt in Windows](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/6.png)
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 14 Using Ipconfig command on CMD](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/ipconfig-release.png)
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 15 ipconfig renew](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/ipconfig-renew.png)
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 16 netsh winsock reset](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/netsh-winsock-reset.png)
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 17 Renew DHCP in MacOS](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/renew-DHCP-lease.png)
![How to Fix "401 Unauthorized Access" Error? [7 Methods] 4 Deactivate WordPress Plugins](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/4-3.png.webp)
![How to Fix "401 Unauthorized Access" Error? [7 Methods] 5 Network tab in browser's developers tools](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/2-2.png.webp)
![How to Fix "401 Unauthorized Access" Error? [7 Methods] 6 Authentication scheme Information in header section](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/3-2.png.webp)