I was able to clone a copy of this repo over HTTPS authenticated. I’ve made some commits and want to push back out to the GitHub server. Using Cygwin on Windows 7 x64.
C:\cygwin\home\XPherior\Code\lunch_call>git push
Password:
error: The requested URL returned error: 403 while accessing https://MichaelDrog
alis@github.com/derekerdmann/lunch_call.git/info/refs
fatal: HTTP request failed
Also set it up with verbose mode. I’m still pretty baffled.
C:\cygwin\home\XPherior\Code\lunch_call>set GIT_CURL_VERBOSE=1
C:\cygwin\home\XPherior\Code\lunch_call>git push
Password:
* Couldn't find host github.com in the _netrc file; using defaults
* About to connect() to github.com port 443 (#0)
* Trying 207.97.227.239... * 0x23cb740 is at send pipe head!
* Connected to github.com (207.97.227.239) port 443 (#0)
* successfully set certificate verify locations:
* CAfile: C:\Program Files (x86)\Git/bin/curl-ca-bundle.crt
CApath: none
* SSL connection using AES256-SHA
* Server certificate:
* subject: 2.5.4.15=Private Organization; 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.60.2.1.3=US; 1.
3.6.1.4.1.311.60.2.1.2=California; serialNumber=C3268102; C=US; ST=California; L
=San Francisco; O=GitHub, Inc.; CN=github.com
* start date: 2011-05-27 00:00:00 GMT
* expire date: 2013-07-29 12:00:00 GMT
* subjectAltName: github.com matched
* issuer: C=US; O=DigiCert Inc; OU=www.digicert.com; CN=DigiCert High Ass
urance EV CA-1
* SSL certificate verify ok.
> GET /derekerdmann/lunch_call.git/info/refs?service=git-receive-pack HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: git/1.7.4.3282.g844cb
Host: github.com
Accept: */*
Pragma: no-cache
< HTTP/1.1 401 Authorization Required
< Server: nginx/1.0.4
< Date: Thu, 15 Sep 2011 22:44:41 GMT
< Content-Type: text/plain
< Connection: keep-alive
< Content-Length: 55
< WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm="GitHub"
<
* Ignoring the response-body
* Expire cleared
* Connection #0 to host github.com left intact
* Issue another request to this URL: 'https://MichaelDrogalis@github.com/dereker
dmann/lunch_call.git/info/refs?service=git-receive-pack'
* Couldn't find host github.com in the _netrc file; using defaults
* Re-using existing connection! (#0) with host github.com
* Connected to github.com (207.97.227.239) port 443 (#0)
* 0x23cb740 is at send pipe head!
* Server auth using Basic with user 'MichaelDrogalis'
> GET /derekerdmann/lunch_call.git/info/refs?service=git-receive-pack HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Basic XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
User-Agent: git/1.7.4.3282.g844cb
Host: github.com
Accept: */*
Pragma: no-cache
< HTTP/1.1 401 Authorization Required
< Server: nginx/1.0.4
< Date: Thu, 15 Sep 2011 22:44:41 GMT
< Content-Type: text/plain
< Connection: keep-alive
< Content-Length: 55
* Authentication problem. Ignoring this.
< WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm="GitHub"
* The requested URL returned error: 401
* Closing connection #0
* Couldn't find host github.com in the _netrc file; using defaults
* About to connect() to github.com port 443 (#0)
* Trying 207.97.227.239... * 0x23cb740 is at send pipe head!
* Connected to github.com (207.97.227.239) port 443 (#0)
* successfully set certificate verify locations:
* CAfile: C:\Program Files (x86)\Git/bin/curl-ca-bundle.crt
CApath: none
* SSL re-using session ID
* SSL connection using AES256-SHA
* old SSL session ID is stale, removing
* Server certificate:
* subject: 2.5.4.15=Private Organization; 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.60.2.1.3=US; 1.
3.6.1.4.1.311.60.2.1.2=California; serialNumber=C3268102; C=US; ST=California; L
=San Francisco; O=GitHub, Inc.; CN=github.com
* start date: 2011-05-27 00:00:00 GMT
* expire date: 2013-07-29 12:00:00 GMT
* subjectAltName: github.com matched
* issuer: C=US; O=DigiCert Inc; OU=www.digicert.com; CN=DigiCert High Ass
urance EV CA-1
* SSL certificate verify ok.
* Server auth using Basic with user 'MichaelDrogalis'
> GET /derekerdmann/lunch_call.git/info/refs HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Basic xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
User-Agent: git/1.7.4.3282.g844cb
Host: github.com
Accept: */*
Pragma: no-cache
* The requested URL returned error: 403
* Expire cleared
* Closing connection #0
error: The requested URL returned error: 403 while accessing https://MichaelDrog
alis@github.com/derekerdmann/lunch_call.git/info/refs
fatal: HTTP request failed
These are the versions of git and curl that I have:
C:\Users\XPherior>git --version
git version 1.7.4.msysgit.0
C:\Users\XPherior>curl --version
curl 7.21.7 (amd64-pc-win32) libcurl/7.21.7 OpenSSL/0.9.8r zlib/1.2.5
Protocols: dict file ftp ftps gopher http https imap imaps ldap pop3 pop3s rtsp
smtp smtps telnet tftp
Features: AsynchDNS GSS-Negotiate Largefile NTLM SSL SSPI libz
asked Sep 15, 2011 at 22:45
13
I just got the same problem and just figured out what’s cause.
Github seems only supports ssh way to read&write the repo, although https way also displayed ‘Read&Write’.
So you need to change your repo config on your PC to ssh way:
- Edit
.git/configfile under your repo directory. - Find
url=entry under section[remote "origin"]. - Change it from:
url=https://MichaelDrogalis@github.com/derekerdmann/lunch_call.git
to:
url=ssh://git@github.com/derekerdmann/lunch_call.git
That is, change all the texts before@symbol tossh://git - Save
configfile and quit. now you could usegit push origin masterto sync your repo on GitHub.
zeFree
2,1292 gold badges31 silver badges39 bronze badges
answered Oct 14, 2011 at 18:26
XiaoXiao
12.3k2 gold badges29 silver badges36 bronze badges
18
To definitely be able to login using https protocol, you should first set your authentication credential to the git Remote URI:
git remote set-url origin https://yourusername@github.com/user/repo.git
Then you’ll be asked for a password when trying to git push.
In fact, this is on the http authentication format. You could set a password too:
https://youruser:password@github.com/user/repo.git
You should be aware that if you do this, your github password will be stored in plaintext in your .git directory, which is obviously undesirable.
answered Jul 6, 2012 at 19:41
Thiago MacedoThiago Macedo
6,1971 gold badge21 silver badges22 bronze badges
20
One small addition to Sean’s answer.
Instead of editing .git/config file manually, you can use git remote set-url command.
In your case it should be:
git remote set-url origin ssh://git@github.com/derekerdmann/lunch_call.git
I find it easier and cleaner, than messing around with dot-files.
- help.github.com: Changing a remote’s URL
answered Jun 4, 2012 at 22:29
fetshfetsh
1,9491 gold badge16 silver badges17 bronze badges
1
Edit .git/config file under your repo directory
Find url= entry under section [remote "origin"]
Change it from url=https://github.com/rootux/my-repo.git to
https://USERNAME@github.com/rootux/my-repo.git
where USERNAME is your github user name
answered Nov 7, 2012 at 9:39
Gal BrachaGal Bracha
19.1k11 gold badges72 silver badges86 bronze badges
3
The other answers that suggest switching to SSH sort of miss the point. HTTPS is supported, but you must log in with you GITHUB password, not your SSH passphrase (which was what was giving me the same exact error).
I was having the same problem, but making sure to use my actual GitHub password at the terminal password prompt fixed the solution with no alteration to the config, or resorting to SSH.
The reason it is important to note this, is many public institutions (such as my school) will block SSH, but allow HTTPS (which is the only reason I started cloning over HTTPS in the first place).
Hope that helps anyone else having the same issue…
answered Jan 17, 2012 at 17:27
BMBBMB
1,59813 silver badges10 bronze badges
4
If you are using windows, sometimes this may happen because Windows stores credentials for outer repo (in our case github) in its own storage. And credentials that saved there can be different from those you need right now.
So to avoid this problem, just find github in this storage and delete saved credentials. After this, while pushing git will request your credentials and will allow you to push.
answered Apr 18, 2018 at 7:34
Andrew GansAndrew Gans
7006 silver badges9 bronze badges
2
Same error and resolution on Mac OS X.
Everything was working fine till I created a new account on GitHub and tried to push
$ git push -u origin master
And got the error:
remote: Permission to NEWUSER/NEWREPO.git denied to OLDUSER. fatal: unable to access ‘https://github.com/NEWUSER/NEWREPO.git/’: The requested URL returned error: 403
It should have fixed by setting the user.name either for global or current repo
$ git config –-global user.name NEWUSER
$ git config user.name NEWUSER
But it didn’t.
I got it fixed by deleting the OLDUSER associated with GitHub from Keychain Access app under Passwords section. Then the push command went successful.
$ git push -u origin master
reference
Laurel
5,98514 gold badges31 silver badges58 bronze badges
answered Nov 10, 2014 at 11:36
zeeawanzeeawan
6,6872 gold badges50 silver badges56 bronze badges
2
This works for me -:
git remote set-url origin https://username@github.com/user/repo.git
Hope it helps
Jeff Hammond
5,3743 gold badges28 silver badges46 bronze badges
answered Sep 27, 2015 at 21:41
2
I think @deepwaters got the answer correct for older versions. The HTTPS URL needs to have the username. I had git 1.7.0.4 and git push origin master wouldn’t even ask for a password till I added it.
answered Jun 27, 2012 at 14:44
nisahnisah
2,4783 gold badges22 silver badges20 bronze badges
0
answered Jun 20, 2012 at 19:03
gsfgsf
1,78816 silver badges11 bronze badges
1
A 403 code is «Forbidden». The server saw your request and refused it. Do you have permission to push to that repository?
answered Sep 16, 2011 at 0:32
Nick VeysNick Veys
23.5k4 gold badges47 silver badges64 bronze badges
3
A lot of answers here, but this is what solved my problem.
Since July 2020 you must use Token authentication to access GitHub if you are using HTTPS.
So you must generate an access token in your profile settings page and use it as your password. Check the boxes necessary to write to the repository.
Now add your username to the repo with this command:
git remote set-url origin https://yourusername@github.com/user/repo.git
When you try to push, it will ask for your password. Enter your newly generated token.
If you are still having trouble pushing, use the web interface to fork it as a personal repo to isolate any permission problem. You’ll be able to focus to solve the auth problem.
answered Jul 29, 2021 at 23:58
nevesneves
33.4k27 gold badges162 silver badges192 bronze badges
Figured it out. I cloned over HTTPS. Setting up my public SSH keys, cloning over SSH, and pushing over SSH fixed it.
answered Sep 16, 2011 at 3:29
MikeMike
19.3k11 gold badges56 silver badges73 bronze badges
3
Do this for a temporary fix
git push -u https://username:password@github.com/username/repo_name.git master
answered Sep 19, 2018 at 15:41
prashantitisprashantitis
1,7973 gold badges23 silver badges52 bronze badges
0
I faced the same error and the cause was stupid — I did not have privileges to commit to selected repository. I did not know that I have to
- fork selected project first
- clone repository locally
- commit my changes locally
- push changes to my github clone
- request pull request to upstream
as described in https://help.github.com/categories/63/articles
answered Mar 2, 2014 at 14:54
Leos LiterakLeos Literak
8,83519 gold badges81 silver badges157 bronze badges
2
I actually had a very simple fix to this. All i did was edit the git config file differently after cloning the repository. The remote origin url is what you need to edit in your default config file. It should look like seen below
[core]
repositoryformatversion = 0
filemode = true
bare = false
logallrefupdates = true
[remote "origin"]
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*
url = https://*username*@github.com/*username*/*repository*.git
[branch "master"]
remote = origin
merge = refs/heads/master
answered Oct 13, 2015 at 23:00
AkahAkah
1,38914 silver badges19 bronze badges
3
- Click on your repository
- On the right hand side, click on «Settings»
- On the left hand side option panel, click on «Collaborators»
- Add the person name you know in GitHub
- Click «Add Collaborators»
After this our «Push to Git» worked fine.
Teepeemm
4,3315 gold badges35 silver badges58 bronze badges
answered Mar 13, 2015 at 13:38
KrishnaKrishna
911 silver badge1 bronze badge
0
change it from
url=https://MichaelDrogalis@github.com/derekerdmann/lunch_call.git
to
url=ssh://git@github.com/derekerdmann/lunch_call.git
It works!
Do not forget the «git» before the «@».
Juan Sosa
5,2621 gold badge35 silver badges41 bronze badges
answered Oct 18, 2012 at 1:07
JimmyDongJimmyDong
1531 silver badge7 bronze badges
1
answered Dec 6, 2012 at 18:37
SMSMSMSM
1,5093 gold badges19 silver badges34 bronze badges
0
For those having permission denied 403 error while using ssh(according to Xiao) or http urls
try these commands
>git config --global --unset-all credential.helper
>git config --unset-all credential.helper
with administrator rights
>git config --system --unset-all credential.helper
answered Jan 12, 2017 at 18:17
Moosa BalochMoosa Baloch
1,1751 gold badge13 silver badges26 bronze badges
1
None of the above answers worked for my enterprise GitHub account. Follow these steps for pushing via ssh key generation way.
Create a repo by visiting your git account.
Generate ssh key:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "your_email@example.com"
Copy the contents of the file ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub to your SSH keys in your GitHub account settings.
Test SSH key:
ssh -T git@github.com
clone the repo:
git clone git://github.com/username/your-repository
Now cd to your git clone folder and do:
git remote set-url origin git@github.com:username/your-repository.git
Now try editing a file (try the README) and then do:
git add -A
git commit -am "my update msg"
git push -u origin master
Update: new git version seems to recommend not to have any file while new repo is created. Hence make aa blank repo.
answered Feb 13, 2018 at 7:02
CKMCKM
1,9112 gold badges23 silver badges30 bronze badges
1
Below is the solution
For Windows you can find the keys here:
control panel > user accounts > credential manager > Windows credentials > Generic credentials
Next, remove the Github keys.
In mac
1-In Finder, search for the Keychain Access app.
2In Keychain Access, search for github.com.
3-Find the «internet password» entry for github.com.
4-Edit or delete the entry accordingly.
answered Apr 13, 2020 at 9:27
Kapil SoniKapil Soni
1,0032 gold badges15 silver badges37 bronze badges
0
What worked for me:
My repo was a fork and still linked to the the parents repo.
git remote -v
Will tell you if it is your repo or not.
git remote set-url origin https://github.com/USERNAME/OTHERREPOSITORY.git
Allows you to reconfigure it to your repo and then allow you to push.
Andrew Lygin
6,0971 gold badge32 silver badges37 bronze badges
answered Aug 26, 2016 at 17:13
Tim SiwulaTim Siwula
96011 silver badges15 bronze badges
0
if you get 403 error with github,
sure to check all checkboxs when create token:
https://github.com/settings/tokens
i think github token generate page has design flaw.
answered Mar 1, 2022 at 3:18
sailfish009sailfish009
2,5611 gold badge24 silver badges31 bronze badges
For anyone curious, my mac machine vs lucid vm ran git 1.7.6 vs 1.7.0.4, and the exact same repo was pushable from my mac (newer git) but not the VM
Same curl version. Perhaps some older git versions don’t support https pushes?
answered Mar 5, 2012 at 23:49
patconpatcon
1,6771 gold badge12 silver badges9 bronze badges
2
Add the user name as part of the URL and This error happens because the git command is hitting http instead of https. So set the url
git remote set-url origin https://<username>@github.com/Path_to_repo.git
After which you will be prompted for password:
Tunaki
133k46 gold badges342 silver badges424 bronze badges
answered Mar 5, 2016 at 15:01
venkat samvenkat sam
1581 silver badge12 bronze badges
Try below command using administrator permission. This command solved my issue. Hope it will resolve your problem.
git config --system --unset-all credential.helper
answered Apr 25, 2020 at 18:03
FaisalFaisal
4,6013 gold badges40 silver badges49 bronze badges
1
I faced similar issue and most of the answer did not work in my case, i was getting permission denied 403 forbidden error. Following steps helped me to resolve the issue:
Install git CLI by below command if you have brew installed:
brew install gh
Reference to install git CLI https://github.com/cli/cli#installation
then run
gh auth login
it will ask you following questions, answer like this,
What account do you want to log into? GitHub.com
? What is your preferred protocol for Git operations? HTTPS
? Authenticate Git with your GitHub credentials? Yes
? How would you like to authenticate GitHub CLI? Login with a web browser
It will generate code for you, enter generated to code your browser for authentication.
! First copy your one-time code: 14*B-E2*7
Press Enter to open github.com in your browser...
✓ Authentication complete.
By following above steps you will be able to push code to your repository.
answered Feb 6 at 17:42
NicoNico
1,7882 gold badges23 silver badges41 bronze badges
I figured out my own variation of this problem.
The issue was not changing the protocol from https to ssl, but instead,
setting the Github global username and email! (I was trying to push to a
private repository.
git config --global user.email "your_github_email_@email.com"
git config --global user.name "Your full name"
answered Feb 17, 2014 at 21:08
Lucas Ou-YangLucas Ou-Yang
5,50513 gold badges44 silver badges62 bronze badges
1
Github has page dedicated to troubleshooting this error:
https://help.github.com/articles/https-cloning-errors
In my case it turned out that using a new version of git (1.8.5.2) solved this problem.
answered Sep 27, 2014 at 13:23
AndyLAndyL
14.3k14 gold badges43 silver badges70 bronze badges
Здравствуйте.
—
1) Вы пытаетесь загрузить с другого аккаунта, выйти из него я не знаю как, но зато, при установке git на ваш компьютер, создаётся файл .githistory, обычно пихается в пользовательскую папку, как и данные по composer. (for Windows) — для других систем не узнавал.
2) Если вы нашли .githistory — и используете другой аккаунт, удалите его. Возможно другие файлы со словом git так же стоит удалить.
3) Убедитесь, что вы после удаления истории сделали новую регистрацию:
$ git config --global user.name 'login'
$ git config --global user.email 'mail@yourmail.ru'
4) Когда создаёте репозиторий на GitHub , клонируйте его на свой компьютер.
Чтобы убедится, что вы открыли консоль [Git Bash] в нужном месте, просто сделайте команду$ git status
Если репозиторий и директория верны, он красным подсветит файлы, которые нужно добавить.
Если он пишет, что такой директории не существует, значит перейдите в вашу папку.$ cd your_folder — ещё раз проверьте статус.
Если git увидел ваш склонированный репозиторий, значит делайте запрос:$ git add .
или$ git add --all
Почему я не начал с $ git init ?
Если вы склонировали, то папка .git там уже есть.
Закидывайте к этой папке и файлу README.md ваши файлы, и делайте $ git add .
Только теперь можно делать коммиты$ git commit -m "your commit"
высветились все файлы? Тогда пропускаете $ git remote add origin.... — потому что ветка уже создана, при создании репозитория на сайте.
Теперь мы загружаем:$ git push -u origin master
Если не ошибаюсь, дописать записанное можно через команду:$ git pull
—-
Самое главное, это сменить пользователя на того, у которого есть права, иначе вам не поможет удаление программы и установка новой. Есть команда, которая чистит кеш истории$ git credential-cache exit
Но она почему-то в последнее время бесполезная и нерабочая, так что ищите способ очистить кеш.
Что касается ключей и ssh — их можно и не создавать, но как показывает практика, не только git , но и composer не дадут вам работать.
Успехов вам, надеюсь помог.
—
P.S. данный метод мне помог, если вы видите содержимое файла README.md смотрите в settings что у вас за ошибка, устраните её, и обновите браузер. Возможно, ещё придётся выбрать тему, или указать описание, так же смотрите, где у вас галочки стоят, они тоже могут вызвать головную боль.
Решение ошибки remote: Permission to user/repo denied to user/other-repo. fatal: unable to access user/repo: The requested URL returned error: 403
Дата: 27.03.2017
В данном уроке рассмотрим варианты решения данной оишбки:
remote: Permission to user/repo denied to user/other-repo.
fatal: unable to access user/repo: The requested URL returned error: 403
Возникает она чаще всего у новичков при попытке выполнить команду:
$ git push
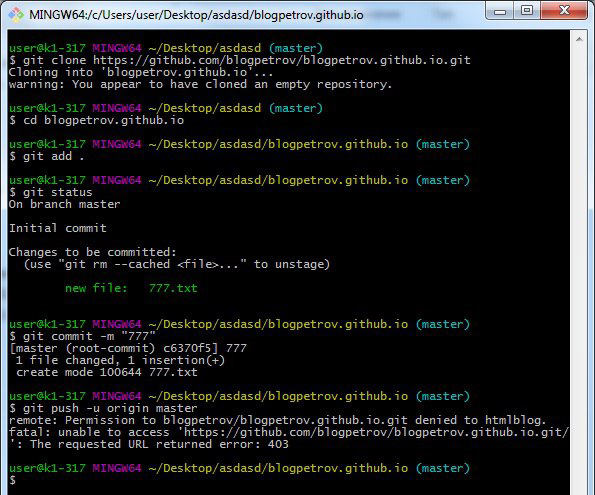
Пример ошибки на скриншоте ниже.
Данная ошибка возникает довольно часто при работе с Git в терминале Windows. Суть ошибка довольно таки простая, но почему-то в интернете постоянно создаются темы с вопросом на данную тему и нет внятного ответа на русском языке.
Ошибка говорит нам о том, что мы пытаемся отправить данные в чужой репозиторий. И о том, что текущий пользователь Git не имеет прав для отправки данных в указанный в команде репозиторий.
Существует два способа решить данную ошибку:
Вариант 1. Дать текущему пользователю права для работы с репозиторием
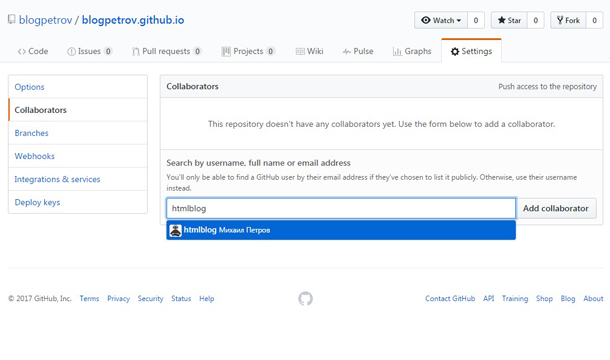
Данный способ подойдет, если вы являетесь владельцем обеих учетных записей указанных в ошибке. Необходимо зайти на GitHub под именем того пользователя, в чей репозиторий вы не можете отправить данные. В настройках репозитория указать необходимого соавтора. Ему на почту отправится приглашение, которое необходимо подтвердить, перейдя по ссылке в письме.
После этого вы сможете работать с репозиторием как со своим и ошибка больше не появится.
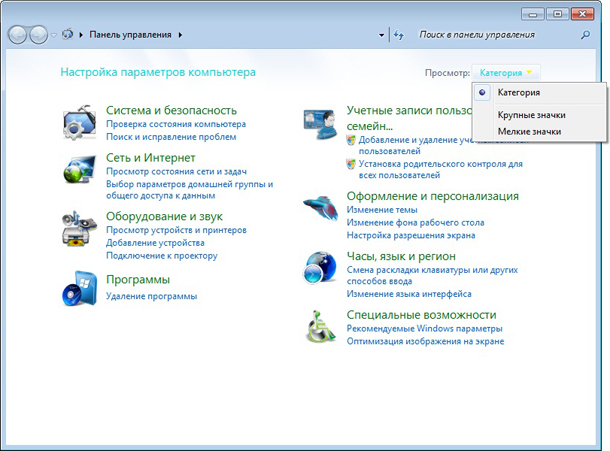
Вариант 2. Назначить в системе текущим пользователем Git ту учетную запись, в которую не можете отправить данные
Для этого необходимо перейти в Панель управления Windows. Выбрать отображение в виде категорий.
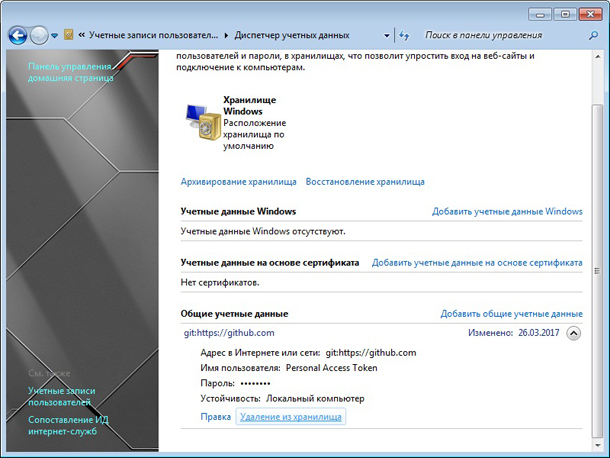
Перейти в раздел “Учетные записи пользователей и семейная безопасность”. Далее в раздел “Диспетчер учетных данных”. В самом низу будет блок “Общие учетные данные”. Нажмите в нем ссылку “Удаление из хранилища”.
После этого при попытке выполнить команду:
$ git push -u origin master
Терминал запросит у вас пароль от учетной записи на Github в чей репозиторий вы пытаетесь отправить данные.
После ввода пароля система установит данного пользователя как основного и будет использовать его в дальнейшем при работе с Git.
Надеюсь данный пост поможет вам решить ошибку, с которой я разбирался почти сутки.
git
github
Не забудьте сказать спасибо. Поставьте лайк!
This article discusses a problem that may occur when you try to push to a remote GitHub repository using HTTPS from an A2 Hosting server.
- Problem
- Cause
- Resolution
- Method #1: Use SSH
- Method #2: Modify the HTTPS URL
Problem
When you try to push changes to a GitHub repository from an A2 Hosting server using an HTTPS URL, you receive the following error message:
error: The requested URL returned error: 403 Forbidden while accessing https://github.com/github-username/github-repository-name.git/info/refs
Cause
There are a few possible causes for this problem:
- You typed an incorrect password. Make sure you are using the correct GitHub password for the account.
- The Git client on the A2 Hosting server requires a modified HTTPS URL to work correctly. If this is the cause, the password prompt does not even appear when you try to do a push operation.
Resolution
If you are sure you are using the correct GitHub password, there are two ways to resolve the “403 Forbidden” problem:
Method #1: Use SSH
Instead of using HTTPS URLs to push changes to GitHub, you can use SSH instead. For information about how to do this, please visit https://help.github.com/articles/changing-a-remote-s-url.
Method #2: Modify the HTTPS URL
Some A2 Hosting managed servers have an old version of the Git client installed. To push changes to GitHub using this older client version, you must include your GitHub username in the HTTPS URL.
To do this, follow these steps:
- Log in to your A2 Hosting account using SSH.
- At the command prompt, change to the directory where the Git repository is located.
- Type the following command:
git config -l | grep url
You should see output that resembles the following:
remote.origin.url=https://github.com/github-username/github-repository-name.git
-
You need to add your GitHub username to the github.com portion of the URL. To do this, type the following command, replacing the values in red with your own account information:
git remote set-url origin "https://github-username@github.com/github-username/github-repository-name.git"
-
To verify the new remote URL setting, type the following command:
git config -l | grep url
Now when you try to push changes to the GitHub repository, you are prompted for a password, and the push operation should succeed.
Git push error 403 generally means that the user doesn’t have the write permissions to the repository. This can happen if the user doesn’t have the required permissions to write to the repository or if the repository is read-only.
To fix this error, the user needs to be given the required permissions to write to the repository or the repository needs to be made writable.
Contents
- 1 How do I fix error 403 in git?
- 2 How do I fix the requested URL returned error 403 on GitHub?
- 3 What does the error code 403 mean?
- 4 What is the git push command?
- 5 How do I push a project to GitHub?
- 6 How do I push code to GitHub?
- 7 How do you fix 403 Forbidden access to this resource on the server is denied?
How do I fix error 403 in git?
There are a few ways that you can fix the error 403 in git. The first thing you can do is to try to reset the git repository. This can be done by running the following command:
git reset –hard
If this doesn’t work, you can try to force push the repository. This can be done by running the following command:
git push -f
If neither of these commands work, you can try to delete the repository and create it again. This can be done by running the following command:
git clone –bare [email protected]:username/reponame.git
How do I fix the requested URL returned error 403 on GitHub?
If you’re seeing the “403: The requested URL returned error 403” message on GitHub, it means that you don’t have the right permissions to access the requested resource. This could be because you don’t have the correct permissions to view the repository, or because the repository is private.
If you believe you should have the correct permissions to view the repository, you can contact the repository owner for help. If the repository is private, you’ll need to be invited to become a member in order to access it.
What does the error code 403 mean?
The HTTP 403 Forbidden error code means that the web server is refusing to serve the requested page, or perhaps more likely, that the visitor does not have the necessary permissions to view the page.
403 errors can be caused by a variety of issues, including permissions, file permissions, and even the user’s browser security settings.
If you’re seeing a 403 error on your website, the first thing to check is whether you have the correct permissions set up for the page you’re trying to access. If you don’t have the correct permissions, you’ll need to correct them in order to fix the problem.
If you’re sure that you have the correct permissions and you’re still seeing 403 errors, it’s possible that there’s a problem with your server’s security settings. In this case, you’ll need to contact your web hosting provider for assistance.
Finally, it’s also possible that your browser is blocking access to the page for security reasons. To fix this, you’ll need to adjust your browser’s security settings.
What is the git push command?
The git push command is used to push commits and branches from your local repository to a remote repository. This can be used to share your work with others, or to collaborate on a project with others.
When you push commits to a remote repository, Git will automatically push all of the commits that are upstream of the commit that you pushed. This can be useful when you want to share your work with others, or when you want to keep your history clean.
You can also push branches to a remote repository. This can be useful when you want to collaborate with others on a project. When you push a branch to a remote repository, Git will automatically merge the branch with the remote branch.
How do I push a project to GitHub?
GitHub is a web-based hosting service for software development projects that use the Git revision control system. GitHub offers both paid and free plans for users.
In order to use GitHub, you must first create a GitHub account. Once you have created an account, you can create a new repository. A repository is simply a storage location for your project’s files.
To create a new repository, log in to your GitHub account and click the New Repository button.
Enter a name for your repository and choose whether to make it public or private.
If you choose to make your repository public, anyone will be able to view and clone it. If you choose to make your repository private, only those with whom you share the repository’s URL will be able to view it.
Click the Create repository button.
GitHub will create your repository and provide you with a URL for it.
The next step is to add your project’s files to the repository.
To do this, you will need to clone the repository to your computer.
Cloning a repository will create a copy of it on your computer. This copy will be linked to the original repository on GitHub.
To clone a repository, open your terminal and run the following command:
git clone URL
Where URL is the URL of the repository you want to clone.
For example, if you want to clone the repository for this tutorial, run the following command:
git clone https://github.com/tutorial-repo/tutorial.git
This will create a directory called tutorial on your computer, which will contain a copy of the repository’s files.
Now that you have cloned the repository, you can add your project’s files to it.
To do this, you will need to create a new directory in the repository for your project’s files.
For example, if you are working on a project called my-project, you would create a new directory called my-project in the repository.
Then, you would copy your project’s files into the my-project directory.
Once you have added your project’s files, you can commit them to the repository.
Committing your files will save them to the repository and create a new Git commit.
To commit your files, open your terminal and run the following command:
git commit -m “message”
Where message is the commit message you want to use.
For example, if you want to commit the files in the my-project directory, run the following command:
git commit -m “added my-project files”
This will create a new Git commit that contains the files from the my-project directory.
You can also push your commits to the original repository on GitHub.
To do this, open your terminal and run the following command:
git push
Where URL is the URL of the repository you want to push your commits to.
For example, if you want to push your commits to the repository for this tutorial, run the following command:
git push https://github.com/tutorial-repo/tutorial.git
This will push your commits to the repository on GitHub.
Now that you have added your project’s files and committed them to the repository, you can open them in a Git GUI client.
A Git GUI client is a graphical interface for working with Git repositories.
There are many different GUI clients available, such as SourceTree, GitX, and Tort
How do I push code to GitHub?
GitHub is a code hosting platform that enables developers to share and collaborate on code. It makes it easy for developers to push their code to a remote repository and to collaborate on code with others. In this article, we will show you how to push code to a GitHub repository.
To push code to a GitHub repository, you first need to create a repository on GitHub. You can create a new repository by clicking on the ‘Create a new repository’ button on the GitHub homepage.
Next, you need to install the GitHub desktop client. The GitHub desktop client is a tool that enables you to easily manage your GitHub repositories. You can download the GitHub desktop client from the GitHub website.
Once you have installed the GitHub desktop client, you need to log in to your GitHub account. Once you have logged in, you will be presented with the ‘GitHub Desktop’ window.
The ‘GitHub Desktop’ window has two main sections – the ‘Local Repositories’ section and the ‘Remote Repositories’ section. The ‘Local Repositories’ section displays the repositories that are stored on your computer. The ‘Remote Repositories’ section displays the repositories that are stored on GitHub.
To push code to a GitHub repository, you first need to clone the repository to your computer. You can clone a repository by clicking on the ‘Clone or download’ button and then selecting ‘Clone with Git’.
Next, you need to navigate to the folder on your computer where you want to store the cloned repository. You can do this by clicking on the ‘Change…’ button and selecting the desired folder.
Once you have selected the folder, you need to click on the ‘Clone’ button. This will clone the repository to your computer.
Once the repository has been cloned, you need to open it in the GitHub desktop client. To do this, navigate to the folder where the repository was cloned and double-click on the ‘GitHub’ folder. This will open the ‘GitHub’ window.
The ‘GitHub’ window has two main sections – the ‘Local Repositories’ section and the ‘Remote Repositories’ section. The ‘Local Repositories’ section displays the local repositories that are stored on your computer. The ‘Remote Repositories’ section displays the remote repositories that are stored on GitHub.
To push code to a GitHub repository, you first need to add the repository to the ‘Remote Repositories’ section. To do this, click on the ‘Add Repository’ button and select ‘GitHub’.
Next, you need to enter the URL of the repository. The URL of the repository is the address of the repository on GitHub. You can find the URL of the repository by clicking on the ‘Clone or download’ button and then selecting ‘Copy to clipboard’.
Once you have entered the URL of the repository, you need to click on the ‘Add’ button. The repository will be added to the ‘Remote Repositories’ section.
Next, you need to select the branch of the repository that you want to push code to. You can do this by clicking on the ‘Branch’ drop-down list and selecting the desired branch.
Once you have selected the branch, you need to click on the ‘Sync’ button. This will synchronize the local and remote repositories.
Next, you need to checkout the code from the repository. You can do this by clicking on the ‘Checkout’ button. This will checkout the code from the repository and store it in the ‘Local Repositories’ section.
How do you fix 403 Forbidden access to this resource on the server is denied?
403 Forbidden access to this resource on the server is denied. This is usually caused by incorrect permissions on the file or directory.
To fix this, you need to ensure that the correct permissions are set on the file or directory. You can do this by using the chmod command.
For example, if you want to give everyone read access to a file, you would use the following command:
chmod a+r myfile.txt
If you want to give everyone write access to a file, you would use the following command:
chmod a+w myfile.txt
If you want to give only certain users read and write access to a file, you would use the following command:
chmod u+rwx myfile.txt