I have created a small web site, where I am showing some data, which I get from an API (JSON data type). In my console I am getting these two errors:
1) GET http://fonts.gstatic.com/s/opensans/v10/u-WUoqrET9fUeobQW7jkRRJtnKITppOI_IvcXXDNrsc.woff2 404 (Not Found)
error 1) is in my code pointing to this line of code:
<script src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js"></script>
2) GET http://localhost/[object%20Event] 404 (Not Found)
and error 2) is in my code pointing on this line of code:
function getData(url){
return $.ajax({
type: 'GET',
dataType: 'json',
url: url
});
}
Any idea what these errors mean? These particular errors have no effect on the site; the site is still working and showing all data.
gitsitgo
6,6093 gold badges33 silver badges45 bronze badges
asked Apr 15, 2015 at 18:47
5
The 404 code means that the server was unable to locate the files you were looking for via GET request.
You might try adding the text/javascript type to your tags, as the examples for google maps api do.
ie:
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js"></script>As far as the second problem you encountered, it looks like the url you passed into the getData() function was invalid.
answered Apr 15, 2015 at 18:54
5
ajax is asynchronous request means that you cant return it when it is in progress so if you want return any thing from ajax you must call it’s events like success and error.so your code must like below:
function getData(url){
$.ajax({
type: 'GET',
dataType: 'json',
url: url,
success: function(data){
return data;
},
error: function(data){
console.log(data.responseText);
}
});
}
answered Jan 3, 2021 at 18:21
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In computer network communications, the HTTP 404, 404 not found, 404, 404 error, page not found, or file not found error message is a hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) standard response code, to indicate that the browser was able to communicate with a given server, but the server could not find what was requested. The error may also be used when a server does not wish to disclose whether it has the requested information.[1]
The website hosting server will typically generate a «404 Not Found» web page when a user attempts to follow a broken or dead link; hence the 404 error is one of the most recognizable errors encountered on the World Wide Web.
Overview
When communicating via HTTP, a server is required to respond to a request, such as a web browser request for a web page, with a numeric response code and an optional, mandatory, or disallowed (based upon the status code) message. In code 404, the first digit indicates a client error, such as a mistyped Uniform Resource Locator (URL). The following two digits indicate the specific error encountered. HTTP’s use of three-digit codes is similar to the use of such codes in earlier protocols such as FTP and NNTP. At the HTTP level, a 404 response code is followed by a human-readable «reason phrase». The HTTP specification suggests the phrase «Not Found»[1] and many web servers by default issue an HTML page that includes both the 404 code and the «Not Found» phrase.
A 404 error is often returned when pages have been moved or deleted. In the first case, it is better to employ URL mapping or URL redirection by returning a 301 Moved Permanently response, which can be configured in most server configuration files, or through URL rewriting; in the second case, a 410 Gone should be returned. Because these two options require special server configuration, most websites do not make use of them.
404 errors should not be confused with DNS errors, which appear when the given URL refers to a server name that does not exist. A 404 error indicates that the server itself was found, but that the server was not able to retrieve the requested page.
History
The origin of the 404 error code dates back to the early days of the World Wide Web. In 1992, Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the Web, and his team at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, created the first web server software, called CERN httpd.[2] This software used a simple file system to store and retrieve web pages, and it assigned a three-digit number to each type of request and response. The number 404 was chosen to indicate that the requested file was not found on the server.[3]
The term «404 Not Found» was coined by Berners-Lee himself, who explained in a 1998 interview that he wanted to make the error message «slightly apologetic».[4][3] He also said that he considered using «400 Bad Request» instead, but decided that it was too vague and technical.[4][3]
The first documented case of a 404 error appearing on a web page was in 1993, when a user tried to access a page about the Mosaic web browser on the NCSA website. The page had been moved to a different location, but the link had not been updated.[2] The user reported the error to the NCSA team, who fixed the link and added a humorous message to their 404 page: «We’re sorry, but the document you requested is not here. Maybe you should try someplace else.»[3]
Since then, 404 errors have become one of the most common and recognizable errors on the Web. Many websites have customized their 404 pages with creative designs, messages, or features to entertain or assist their visitors. For example, Google’s 404 page features a broken robot and a link to its homepage,[5] while GitHub’s 404 page shows a random image of a parallax star field and a link to its status page.[6] Some websites have also used their 404 pages to showcase their brand personality, humor, or social causes. For instance, Lego’s 404 page shows an image of a Lego character searching for a missing brick,[7] while Amazon’s 404 page displays the image of a dog with a message about conservation.[8]
Soft 404 errors
Some websites report a «not found» error by returning a standard web page with a «200 OK» response code, falsely reporting that the page loaded properly; this is known as a soft 404. The term «soft 404» was introduced in 2004 by Ziv Bar-Yossef et al.[9]
Soft 404s are problematic for automated methods of discovering whether a link is broken. Some search engines, like Yahoo and Google, use automated processes to detect soft 404s.[10] Soft 404s can occur as a result of configuration errors when using certain HTTP server software, for example with the Apache software, when an Error Document 404 (specified in a .htaccess file) is specified as an absolute path (e.g. http://example.com/error.html) rather than a relative path (/error.html).[11] This can also be done on purpose to force some browsers (like Internet Explorer) to display a customized 404 error message rather than replacing what is served with a browser-specific «friendly» error message (in Internet Explorer, this behavior is triggered when a 404 is served and the received HTML is shorter than a certain length, and can be manually disabled by the user).
There are also «soft 3XX» errors where content is returned with a status 200 but comes from a redirected page, such as when missing pages are redirected to the domain root/home page.
Proxy servers
Some proxy servers generate a 404 error when a 500-range error code would be more correct. If the proxy server is unable to satisfy a request for a page because of a problem with the remote host (such as hostname resolution failures or refused TCP connections), this should be described as a 5xx Internal Server Error, but might deliver a 404 instead. This can confuse programs that expect and act on specific responses, as they can no longer easily distinguish between an absent web server and a missing web page on a web server that is present.
Intentional 404s
In July 2004, the UK telecom provider BT Group deployed the Cleanfeed content blocking system, which returns a 404 error to any request for content identified as potentially illegal by the Internet Watch Foundation.[12] Other ISPs return a HTTP 403 «forbidden» error in the same circumstances.[13] The practice of employing fake 404 errors as a means to conceal censorship has also been reported in Thailand[14] and Tunisia.[15] In Tunisia, where censorship was severe before the 2011 revolution, people became aware of the nature of the fake 404 errors and created an imaginary character named «Ammar 404» who represents «the invisible censor».[16]
Microsoft Internet Server 404 substatus error codes
The webserver software developed by Microsoft, Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS), returns a set of substatus codes with its 404 responses. The substatus codes take the form of decimal numbers appended to the 404 status code. The substatus codes are not officially recognized by IANA and are not returned by non-Microsoft servers.
Substatus codes
Microsoft’s IIS 7.0, IIS 7.5, and IIS 8.0 servers define the following HTTP substatus codes to indicate a more specific cause of a 404 error:
- 404.0 – Not found.
- 404.1 – Site Not Found.
- 404.2 – ISAPI or CGI restriction.
- 404.3 – MIME type restriction.
- 404.4 – No handler configured.
- 404.5 – Denied by request filtering configuration.
- 404.6 – Verb denied.
- 404.7 – File extension denied.
- 404.8 – Hidden namespace.
- 404.9 – File attribute hidden.
- 404.10 – Request header too long.
- 404.11 – Request contains double escape sequence.
- 404.12 – Request contains high-bit characters.
- 404.13 – Content length too large.
- 404.14 – Request URL too long.
- 404.15 – Query string too long.
- 404.16 – DAV request sent to the static file handler.
- 404.17 – Dynamic content mapped to the static file handler via a wildcard MIME mapping.
- 404.18 – Query string sequence denied.
- 404.19 – Denied by filtering rule.
- 404.20 – Too Many URL Segments.
Custom error pages
Web servers can typically be configured to display a customised 404 error page, including a more natural description, the parent site’s branding, and sometimes a site map, a search form or 404-page widget. The protocol level phrase, which is hidden from the user, is rarely customized. Internet Explorer, however, will not display custom pages unless they are larger than 512 bytes, opting instead to display a «friendly» error page.[17] Google Chrome included similar functionality, where the 404 is replaced with alternative suggestions generated by Google algorithms, if the page is under 512 bytes in size.[18] Another problem is that if the page does not provide a favicon, and a separate custom 404-page exists, extra traffic and longer loading times will be generated on every page view.[19][20]
Many organizations use 404 error pages as an opportunity to inject humor into what may otherwise be a serious website. For example, Metro UK shows a polar bear on a skateboard, and the web development agency Left Logic has a simple drawing program.[21] During the 2015 UK general election campaign the main political parties all used their 404 pages to either take aim at political opponents or show relevant policies to potential supporters.[22] In Europe, the NotFound project, created by multiple European organizations including Missing Children Europe and Child Focus, encourages site operators to add a snippet of code to serve customized 404 error pages[23] which provide data about missing children.[24]
While many websites send additional information in a 404 error message—such as a link to the homepage of a website or a search box—some also endeavor to find the correct web page the user wanted. Extensions are available for some content management systems (CMSs) to do this.[25]
Tracking 404 errors
A number of tools exist that crawl through a website to find pages that return 404 status codes. These tools can be helpful in finding links that exist within a particular website. The limitation of these tools is that they only find links within one particular website, and ignore 404s resulting from links on other websites. As a result, these tools miss out on 83% of the 404s on websites.[26] One way around this is to find 404 errors by analyzing external links.[27]
One of the most effective ways to discover 404 errors is by using Google Search Console, Google Analytics or crawling software.
Another common method is tracking traffic to 404 pages using log file analysis.[28] This can be useful to understand more about what 404s users reached on the site. Another method of tracking traffic to 404 pages is using JavaScript-based traffic tracking tools.[29]
Causes
There are many possible causes for a page not to exist. Some of the common ones are:[30][31][32]
- The page was deleted by the owner or administrator of the website.
- The page was moved to a different location or renamed without updating the links that point to it.
- The page was never created in the first place or is still under construction.
- The page is temporarily unavailable due to maintenance or technical issues.
- The page is blocked by the user’s network or firewall settings.
- The page is restricted by the website’s privacy or security policies.
- The page contains illegal or harmful content that was removed by the authorities or the website itself.
Solutions
If a user encounters a page that doesn’t exist, there are some steps they can take to try to find the information they are looking for or to report the problem.[30][31][32]
- Check the URL of the page. Sometimes, a simple typo or spelling mistake can cause a page not to load. Make sure the correct address is entered and try again.
- Refresh the page. Sometimes, a temporary glitch or network issue can prevent a page from loading. Try reloading the page by pressing F5 or clicking on the refresh button on the browser.
- Go back to the previous page. Sometimes, a link might be broken or outdated. Try going back to the page where the link was found and see if there is an updated or alternative link to the same information.
- Use a search engine. Sometimes, a page might be indexed by a search engine even if it doesn’t exist anymore. Try searching for keywords related to the topic of the page and see if other sources of information can be found.
- Contact the website owner or administrator. Sometimes, a page might be removed or moved without notice. Try contacting the person or organization responsible for the website and ask them about the status of the page. Their contact information can usually be found on their homepage or in their footer section.
- Report the error. Sometimes, a page might not exist due to an error on the website’s part. Try reporting the error to the website owner or administrator so they can fix it as soon as possible. Their feedback form or email address can usually be found on their homepage or in their footer section.
See also
- Blue screen of death
- Funky caching
- Link rot
- List of HTTP status codes
References
- ^ a b Fielding, R.; Reschke, J. (June 2014). Fielding, R; Reschke, J (eds.). «RFC 7231, HTTP/1.1 Semantics and Content, Section 6.5.4 404 Not Found». ietf.org. doi:10.17487/RFC7231. S2CID 14399078. Retrieved 13 December 2018.
- ^ a b «404 page design: best practices and awesome examples». www.justinmind.com. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b c d «What is a 404 error and what should I do if I get one? » Internet » Windows » Tech Ease». Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b What is the world wide web? — Twila Camp, retrieved 19 May 2023
- ^ «Google 404 Error Page». Google.
- ^ «Github 404 Error Page». Github.
- ^ «LEGO 404 Error Page». Lego.
- ^ «Amazon’s 404 error page». Amazon.
- ^ Ziv Bar-Yossef; Andrei Z. Broder; Ravi Kumar; Andrew Tompkins (2004). «Sic transit gloria telae». Proceedings of the 13th international conference on World Wide Web. pp. 328–337. doi:10.1145/988672.988716. ISBN 978-1581138443. S2CID 587547.
- ^ «Why is your crawler asking for strange URLs that have never existed on my site?». Yahoo Ysearch Help page. Archived from the original on 15 July 2014. Retrieved 4 September 2013.
- ^ «Farewell to soft 404s». Google Official Blog. Retrieved 20 September 2008.
- ^ «LINX Public Affairs » Cleanfeed: the facts». Publicaffairs.linx.net. 10 September 2004. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 6 March 2011.
- ^ «DEMON – Error 403». Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- ^ Sambandaraksa, Don (18 February 2009). «The old fake ‘404 Not Found’ routine — Dead link». Bangkok Post. Retrieved 12 September 2010.
- ^ Noman, Helmi (12 September 2008). «Tunisian journalist sues government agency for blocking Facebook, claims damage for the use of 404 error message instead of 403». Open Net Initiative. Retrieved 21 November 2010.
- ^ «Anti-censorship movement in Tunisia: creativity, courage and hope!». Global Voices Advocacy. 27 May 2010. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ «Friendly HTTP Error Pages». msdn.com. 18 August 2010. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- ^ «Issue 1695: Chrome needs option to turn off «Friendly 404″ displays». bugs.chromium.org. Retrieved 25 December 2021.
- ^ Heng, Christopher (7 September 2008). «What is Favicon.ico and How to Create a Favicon Icon for Your Website». The Site Wizard. Retrieved 23 February 2011.
- ^ «The Dastardly «favicon.ico not found» Error». Internet Folks. 3 August 1999.
- ^ «From skateboarding bears to missing children: The power of the 404 Not Found error page». Metro. 6 June 2011. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ «The political Page 404 war». BBC Newsbeat. 27 April 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2018.
- ^ «Notfound.org». notfound. Archived from the original on 2 September 2014.
- ^ «Missing children messages go on 404 error pages». BBC News. 27 September 2012. Retrieved 20 September 2014.
- ^ Swenson, Sahala (19 August 2008). «Make your 404 pages more useful». Official Google Webmaster Central Blog. Google, Inc. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ «Sources Leading To 404s». SpringTrax. Retrieved 11 February 2013.
- ^ Cushing, Anne (2 April 2013). «A Data-Centric Approach To Identifying 404 Pages Worth Saving». Search Engine Land. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ^ «Tracking and Preventing 404 Errors». 404errorpages.com. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ^ «Understand 404 Errors». SpringTrax.com. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ^ a b Edgar, Matthew (11 April 2023). «How To Fix 404 Errors On Your Website». Matthew Edgar. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b Frickey, Dean (18 November 2008). «A More Useful 404». A List Apart. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b «What ‘Error 404’ means and how to fix it». IONOS Digital Guide. 31 January 2023. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
External links
- A More Useful 404
- 404 Not Found of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content specification, at the Internet Engineering Task Force
- ErrorDocument Directive – instructions on custom error pages for the Apache 2.0 web server
- 404: Not Found – an award-winning song about the error code
Ошибка 404, либо Error 404 Not Found — ошибка, которая появляется, если браузеру не удалось обнаружить на сервере указанный URL.
Сообщение об ошибке 404
Что означает ответ 404
Error 404 Not Found отображается по-разному: «HTTP 404 не найден», «Ошибка 404 Not Found», «404 Страница не найдена». Смысл надписи всегда остаётся тем же: страница отсутствует либо просто не работает. Not Found в переводе означает «не найдено».
Ошибка 404 — классический код ответа по протоколу HTTP. Он свидетельствует, что связь с сервером установлена, но данных по заданному запросу на сервере нет.
Однако если просто ввести в поисковую строку произвольный набор символов, то браузер не покажет ошибку 404 Not Found — появится сообщение, что установить соединение с конкретным сервером невозможно.
Разберёмся в техническом формировании ответа Error 404 Not Found.
Техническая сторона вопроса. При связи по HTTP браузер запрашивает указанный URL и ждёт цифрового ответа. То есть любой запрос пользователя направляется на сервер размещения искомого сайта. Когда браузеру удаётся связаться с сервером, он получает кодированный ответ. Если запрос корректный и страница найдена, отправляется ответ с кодом 200 OK, что соответствует благополучной загрузке. При отсутствии страницы отправляется ответ об ошибке.
Что значит код «404». В ответе 404 первая четвёрка указывает на то, что запрос был чрезмерно длительным или в самом адресе была ошибка. Ноль предполагает синтаксическую неточность. Завершающая цифра кода отображает конкретную причину ошибки — «4» означает отсутствие данной ссылки.
Какие ещё ошибки бывают. Ошибку 404 не нужно путать с другими ответами, которые указывают на невозможность связи с сервером. Например, ошибка 403 сообщает, что доступ к URL ограничен, а ответ «Сервер не найден» свидетельствует, что браузер не смог обнаружить место размещения сайта.
Google на 404 странице сообщает о возможных причинах ошибки
Причины ошибки
Причины, по которым HTTP возвращает ответ 404 Not Found:
- Неверный адрес. К примеру, при ручном наборе пользователь допустил опечатку в адресе либо ссылка ведёт на несуществующую страницу. При этом домен должен быть написан верно. Если пользователь ошибется в названии домена, страница вообще не загрузится (без показа ошибки).
- Битая ссылка. Это нерабочий URL, который никуда не ведёт. Данный вариант иногда возникает при внутренней перелинковке. К примеру, раньше страница существовала, а потом её удалили и забыли убрать ссылку.
- Удалённая страница. Когда пользователь попытается перейти на удалённую с сервера страницу, он также увидит ошибку 404. Ссылка для перехода может сохраниться в браузерных закладках или на сторонних ресурсах.
- Неправильный редирект на страницу с изменённым адресом. Допустим, в процессе редизайна URL изменили, но оставили без внимания связанные ссылки.
- Неполадки на сервере. Это самый редкий вариант.
В большинстве ситуаций ошибка 404 отображается, когда не удаётся обнаружить нужную страницу на доступном сервере.
Причины отсутствия страницы на сайте бывают разными
Возможные последствия для сайта
Нужно ли считать 404 ошибку опасной для сайтов? Кажется, что нет ничего плохого в том, что пользователь не смог открыть одну веб-страницу. Однако если такая ситуация будет повторяться регулярно, это чревато оттоком аудитории. Одни пользователи решат, что сайт вовсе не существует. Другие подумают, что лучше не заходить на сайт, который работает с ошибками. Третьи будут игнорировать ресурс, на котором не смогли получить обещанную информацию.
Поисковые системы относятся к Not Found более лояльно. Например, Google отмечает, что 404 страницы не влияют на рейтинг. Но если при индексации роботы будут находить все больше ошибочных страниц, вряд ли это приведёт к более высокому ранжированию.
Если вы хотите улучшить взаимодействие с посетителями, важно найти и исправить все ошибки 404 на сайте.
Как выявить ошибку
На небольшом ресурсе легко проверить работоспособность ссылок вручную. Но если на сайте сотни и тысячи страниц, без дополнительного софта не обойтись. Есть немало сервисов и программ, позволяющих находить битые ссылки. Рассмотрим некоторые из них.
Search Console Google
Консоль поиска Google позволяет находить страницы с ошибкой 404 за несколько кликов:
- Войдите в учётную запись Google и перейдите в Search Console.
- Откройте раздел «Ошибки сканирования» → «Диагностика».
- Кликните на «Not Found».
Чтобы получить список страниц с ошибками, подтвердите права на ресурс — добавьте проверочную запись TXT в записи DNS регистратора домена. Такая запись не повлияет на работу сайта. Подробнее о процедуре подтверждения, читайте в справке Google.
Для использования Search Console Google нужно подтвердить свои права на сайт
Яндекс Вебмастер
Сервис для вебмастеров от Яндекса поможет быстро найти все ошибки 404:
- Откройте Вебмастер после авторизации в Яндекс-аккаунте.
- Выберите «Индексирование» → «Доступные для поиска страницы» → «Исключённые страницы».
- В выданном списке выберите фильтр «Ошибка HTTP: 404».
Чтобы использовать Яндекс.Вебмастер, также нужно подтвердить право владения сайтом — добавить метатег в HTML-код главной страницы.
Для входа в Вебмастер авторизуйтесь в Яндексе
Screaming Frog
Для начала загрузите и установите программу на компьютер. После запуска добавьте URL проверяемого сайта и начните поиск проблем. Неработающие ссылки можно искать даже в бесплатной версии.
Инструмент SEO-паук в Screaming Frog помогает найти технические неисправности сайта
SiteAnalyzer
Эта бесплатная десктопная программа позволяет обнаружить технические погрешности на сайте. SiteAnalyzer быстро отыщет нерабочие и несуществующие ссылки.
SiteAnalyzer бесплатно найдёт неработающие URL
Как исправить ошибку Not Found
Выбор конкретного решения зависит от причины ошибки:
- Ссылка ведёт в никуда из-за неверного URL. Для решения проблемы замените ошибочную ссылку на правильный адрес, чтобы сервер отдавал код 200 OK.
- Битая ссылка. Подобная ситуация не редкость при внутренней перелинковке страниц. К примеру, ссылка есть, а саму страницу давно удалили. Решений два: удалить ссылку или заменить её на другую.
Удалять и менять ссылки вручную удобно только на небольших сайтах. Исправление ошибок на крупных порталах лучше автоматизировать. Например, с помощью специальных плагинов для внутренней перелинковки (Terms Description, Dagon Design Sitemap Generator) и для автоматического формирования адресов страниц (Cyr-To-Lat).
Чтобы ошибки 404 появлялись как можно реже, достаточно соблюдать простые рекомендации:
- Не присваивайте сложные адреса основным разделам сайта. Это снизит число ошибок, связанных с опечатками в URL.
- Не меняйте адреса страниц слишком часто. Это неудобно для пользователей и вводит в заблуждение поисковых роботов.
- Размещайте сайт на надёжном сервере. Это предотвратит ошибки, возникающие из-за неработоспособности сервера.
Мы разобрались, как найти и исправить ошибки Not Found внутри сайта. Но неработающая ссылка может быть расположена и на стороннем ресурсе. Допустим, когда-то на другом сайте разместили рекламную публикацию со ссылкой на определённую страницу. Спустя какое-то время страницу удалили. В этом случае появится ошибка 404. Устранить её можно, связавшись с администрацией ссылающегося сайта. Если же удалить/исправить ссылку нельзя, постарайтесь использовать ошибку с выгодой.
Как сделать страницу 404 полезной
Грамотно оформленная страница с ошибкой Error 404 Not Found — действенный инструмент конвертации посетителей. Ограничений по использованию страницы с ошибкой 404 нет. При этом практически все CMS позволяют настраивать дизайн этой страницы.
Что публиковать на странице 404:
- меню с кликабельными ссылками;
- ссылку на главную страницу;
- анонс последних публикаций;
- контакты для обратной связи.
При оформлении страницы-ошибки желательно опираться на рекомендации поисковиков:
- Яндекс настоятельно рекомендует, чтобы страница контрастировала с основным содержанием сайта — иные цвета, другие графические приёмы либо их отсутствие. Необходимо чётко и понятно объяснить пользователю, что запрошенной страницы не существует и предложить другое решение.
- Google советует придерживаться единого стиля оформления. Но также рекомендует понятно рассказать об ошибке и предложить полезные материалы.
Главное — по возможности отказаться от стандартной страницы 404. Подумайте, как привлечь внимание пользователя. Расскажите ему об отсутствии искомой страницы и предложите взамен что-то полезное или интересное.
Примеры оформления страниц 404
Designzillas
Мультяшная страница креативной студии привлекает внимание и её хочется досмотреть до конца. Если прокрутить страницу, можно увидеть, как из яйца вылупится дракон. При этом на странице есть ссылки на все основные разделы сайта.
Меню на сайте Designzillas есть и на 404 странице
Domenart Studio
Веб-студия «Домен АРТ» использует красочную страницу 404, оформленную в единой стилистике ресурса. Заблудившимся пользователям предлагают попробовать ещё раз ввести адрес или перейти в нужный раздел.
Контакты, поиск, меню — и всё это на 404 странице Domenart Studio
E-co
«Эко Пауэр», дистрибьютор производителя источников питания, демонстрирует короткое замыкание как символ ошибки. Посетителям предлагают перейти на главную.
Ошибка 404 «Эко Пауэр» выглядит как страница входа
Дом со всем
Компания «Дом со всем», занимающаяся бурением скважин, разместила на странице 404 свои контакты и перечень услуг. Со страницы можно перейти в любой раздел сайта или заказать обратный звонок. С таким наполнением посетителю не нужно искать дополнительную информацию где-то ещё.
Компания «Дом со всем» предлагает заказать обратный звонок
Kualo
Страница 404 на веб-хостинге Kualo может заставить пользователя забыть, зачем он сюда пришёл. Увлекательная игра притягивает внимание. В конце игры посетителю предлагают посмотреть сайт хостинга.
На странице Kualo можно просто поиграть и заработать скидки
Рано или поздно с ошибкой 404 сталкивается большинство сайтов. При регулярной проверке можно своевременно исправить неработающие ссылки, чтобы в ответ пользователи получали код 200 OK. Но для крупного ресурса лучше настроить оригинальную страницу, которая будет отображаться при появлении ошибки Not Found и подскажет посетителям, что делать дальше.
Главные мысли

Aug 15, 2022 8:03:00 AM |
404 Not Found Error: What It Is and How to Fix It
An in-depth explanation of what a 404 Not Found Error response code is, including tips to help you resolve this error in your own application.
The 404 Not Found Error is an HTTP response status code, which indicates that the requested resource could not be found. Like most HTTP response codes, the cause of a 404 Not Found Error can be challenging to track down and resolve.
This article will explore the 404 Not Found Error by examining what might cause this error. Later on, we’ll provide a few tips to diagnose and debug your application’s 404 error.
With that, let’s get started!
Server- or Client-Side?
All HTTP response status codes in the 4xx category are client error responses. These types of messages contrast with errors in the 5xx category, such as the 502 Bad Gateway Error, which are server error responses.
That said, the appearance of a HTTP 404 error doesn’t always mean the issue is client-related (web browser or device used to access the application). Sometimes, the root of the problem is server-side. Remember, the server is still the network object producing the 404 Not Found Error.
We’ll explore some of the scenarios (and potential solutions) where the error results from the server and/or client issues in the following sections.
Start With a Thorough Application Backup
Make a backup of your application, database, etc. before trying to fix or change the system. Even better, if you have the capability, create a complete copy of the application onto a secondary staging server that isn’t available to the public. This will give you a clean testing ground to test all potential fixes without threatening your live application.
After you’ve done that, it’s time to start diagnosing and fixing your 404 error.
Diagnosing a 404 Not Found Error
A HTTP 404 error happens when a resource is unavailable. The client (web browser) received a message from the server (remote computer) that the specific resource (web page/URL) is unavailable.
Here are a few scenarios where this could happen:
- The client sent a proper request to the server, and the server successfully received that request, and the server could not find a valid resource at that particular location. This is typically due to an invalid URL specified by the client. This represents the majority of 404 Not Found Errors.
- Some web applications «fake» 404 Not Found Errors when requesting an invalid resource. The server returns a standard 200 OK response code, which means the resource loaded as expected, however, the server displayed a custom «404 page.” Such fake errors are typically referred to as soft 404 errors.
The provided URL could have been valid in the past, but the server has failed to provide a server-side redirect.
Troubleshooting on the Client-Side
The best way to start troubleshooting a 404 Not Found Error is to look for potential issues on the client side. Here are a few tips to try on the browser or device that’s giving you problems.
Check the Requested URL
The most common cause of a 404 Not Found Error is inputting an incorrect URL. Domain names (e.g., airbrake.io) are case-insensitive, meaning that this mixed case link to AirBrAKe.IO works just as well as the standard, lowercase version of airbrake.io. However, path, query, or fragment portions that appear after the domain name are often case-sensitive unless the application/server configuration pre-processes all URLs as lowercase before execution.
For example, while airbrake.io can be upper, lower, or mixed case, a link to airbrake.io/ERROR-MONITORING/ (with BLOG in uppercase) is invalid, resulting in our good friend the 404 Not Found Error.
Of course, the lowercase version to https://www.airbrake.io/error-monitoring works just fine, as expected.
As you can see, a minor typo in part of the URL can easily result in an unexpected 404 Not Found Error.
Clear Relevant Cookies
As you may already be aware, HTTP cookies are tiny pieces of data stored on your local device. Websites and applications use these cookies to «remember» information about this particular browser and/or device.
Most modern web apps take advantage of cookies to store user and browser-specific data. By doing so, the app can identify the client and allow future visits to be faster and easier.
However, cookies can store just about any information. In many cases, web applications or services — such as ad networks — will use data retrieved from local cookies to redirect or handle incoming requests. An invalid or corrupted cookie can «confuse» the server as you try to access a resource that no longer exists. .
In most cases, you only need to concern yourself with cookies relevant to the website or application causing the problem. Cookies are stored based on the web application’s domain name, so you can explicitly remove only those cookies that match the website domain (e.g., airbrake.io).
However, if you are unfamiliar with manually removing certain cookies, it’s much easier and safer to clear all cookies at once.
Clearing cookies can be accomplished in different ways, depending on the browser you’re using:
- Google Chrome
- Internet Explorer
- Microsoft Edge
- Mozilla Firefox
- Safari
Log Out and Log In
If your application has some form of user authentication, the last client-side step to try is to log out and then log back in.
If you’ve recently cleared the browser cookies, this should usually log you out automatically the next time you try to load the page.
The application may have a problem with your previous session in some situations. As with other data, the session token (or session string) is stored locally on your device in the cookies and is transferred by the client to the server during every request. If the server doesn’t recognize the session token sent by the client or something has gone wrong with the server that indicates that particular token is invalid, you may get a 404 error.
For most web applications, logging out and logging back in will force the local session token to be recreated.
Debugging Common Platforms
If you’re running common software packages on the server that is responding with the 404 Not Found Error, you may want to start by looking into the stability and functionality of those platforms first.
The most common content management systems — like WordPress, Joomla!, and Drupal — are all typically well-tested out of the box. Still, once you start modifying the underlying extensions or PHP code, it’s easy to cause an unforeseen issue that results in a HTTP 404 error.
Here are a few tips to help you troubleshoot some of these popular software platforms:
Rollback Recent Upgrades
If you recently updated the content management system itself before the 404 Not Found Error appeared, consider rolling back to the previous version you had installed when things were working fine.
Similarly, any extensions or modules you may have recently upgraded can cause server-side issues, so reverting to previous versions of those may also help.
For assistance with this task, simply Google «downgrade [PLATFORM_NAME]» and follow along. In some cases, however, certain CMSs don’t provide a version downgrade capability. This is typically the case for the more popular platforms.
Uninstall New Extensions, Modules, or Plugins
The purpose of new extensions, modules, or plugins (they all mean the same thing) is to improve the capabilities and features of the platform beyond what it’s capable of out of the box.
Keep in mind that some extensions can take complete control of the system. Once they do, they can make virtually any changes to the PHP code, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or database. As such, it may be wise to uninstall any recently added extensions if you’re experiencing a 404 error.
Check for Unexpected Database Changes
If you uninstall an extension, it may not completely remove all changes made by the extension. This is particularly true for many WordPress extensions, which are given carte blanche within the application. This can include full access rights to the database.
These extensions can modify database records that don’t «belong» to the extension itself but are created and managed by other extensions (or even the base CMS itself). In those scenarios, the extension may not know how to revert alterations to database records, so it will ignore such things when uninstalled.
If you’re convinced an extension is the likely culprit for the 404 Not Found Error, open the database and manually look through tables and records that were likely modified by the extension.
Troubleshooting on the Server-Side
If you aren’t running a CMS application, here are some additional tips to help you troubleshoot your server.
Check Your Web Server Configuration
Most modern web servers provide one or more configuration files that allow you to adjust server behavior based on various circumstances easily.
For example, the server may be configured to reject requests to specific directories or URLs, resulting in a 404 Not Found Error.
Configuration options for each different type of web server can vary dramatically. We’ll list a few popular web servers you can look through:
- Apache
- Nginx
- IIS
- Node.js
- Apache Tomcat
Look Through the Logs
Nearly every web application will keep some form of server-side logs. Application logs are typically the history of what the application did, including requested pages, connected servers, database results, etc.
Server logs are related to the actual hardware running the application. These logs will often provide details about the health and status of all connected services or the server itself.
Google «logs [PLATFORM_NAME]» if you’re using a CMS, or «logs [PROGRAMMING_LANGUAGE]» and «logs [OPERATING_SYSTEM]» to get more information on finding the logs in question.
Validate Application Links
There are several tools you can use to ensure your application is not producing any 404 Not Found Errors.
For starters, you should register your site with the Google Search Console (if you haven’t done so already). This tool gives you insight into what Google’s web crawler bots have found while traversing your site.
Any issues will be displayed here for all your registered applications and can be an easy (and automatic) way to find invalid links or other site problems.
Need to check a particular resource or URL? Use the W3C Link Checker tool to check links for 404 errors.
Debug Your Application Code or Scripts
If all else fails, it may be that a problem in some custom code within your application is causing the issue. Try to diagnose where the issue may come from by manually debugging your application and parsing through application and server logs.
Ideally, make a copy of the entire application to a local development machine and perform a step-by-step debug process. This will allow you to recreate and view when and how the 404 error occurred.
You know the page: you click on a link, but instead of getting the site you want, an error pops up indicating that the requested page is not available. Something along the lines of ‘404 Not Found’. A 404 error is the standardized HTTP status code. The message is sent from the webserver of an online presence, to the web browser (usually the client) that sent the HTTP request. The browser then displays this error code.
Contents
- How does a ‘404 error’ come about?
- How to fix the error ‘404 Not Found’
- HTTP 404 errors can damage a website’s ranking and reputation
- Identifing 404 errors on your own website
- Creating a 404 error page
- Why should you personalize your 404 error page?
How does a ‘404 error’ come about?
The typical trigger for an error 404 message is when website content has been removed or moved to another URL. There are also other reasons why an error message could appear. These include:
- The URL or its content (such as files or images) was either deleted or moved (without adjusting any internal links accordingly)
- The URL was written incorrectly (during the creation process or a redesign), linked incorrectly, or typed into the browser incorrectly
- The server responsible for the website is not running or the connection is broken
- The requested domain name can’t be converted to an IP by the domain name system (DNS)
- The entered domain name doesn’t exist (anymore)
Dead links are often left for long periods of time since operators have no idea that the linked content has been deleted or moved. Many websites still appear in the search engine results pages (SERPs) even though they aren’t available online anymore (or at least not at the specified URL). Other linked websites such as blogs, news portals, etc. are often not informed that the site has been removed or can now be found under a new URL. Many website operators don’t check their external links regularly and therefore a functioning link could easily become a dead one.
$1 Domain Names
Register great TLDs for less than $1 for the first year.
Why wait? Grab your favorite domain name today!
Matching email
SSL certificate
24/7/365 support
How to fix the error ‘404 Not Found’
A 404 error is rarely a reason to celebrate. At the end of the day, the website’s visitors have not found the content that they were looking for. However the appearance of a 404 page does not necessarily mean that the desired information is not available at all. In many cases, the solution to the original error is easily found and the visitor can be quickly directed to the web page that they were originally looking for. So how exactly can you go about achieving a 404 error fix? Our advice would be to try out these potential solutions (in the order that they are listed):
- Reload the page: It might be that the error 404 has appeared for the simple reason that the page did not load properly. This can be checked quite easily by clicking on the ‘Refresh’ button in your browser or also by pressing the F5 button.
- Check the URL: Regardless of whether you have entered the URL address manually or been directed via a link, could be that a mistake has been made. For this reason you should check the specified path of the website. It could be that either you, or the person who entered the link, has mistyped something. Apart from spelling mistakes, it could also be that forward slashes have been left out or misplaced. But bear in mind that this can only really be checked with ‘clean’ URLs, as they contain unreadable words instead of incomprehensible abbreviations, letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Go back through the directory levels: For example, if a URL of the following structure example.com/Directory1/Directory2/Directory3 causes a 404 error page, then you can always go back to the previous directory level (in this example: example.com/Directory1/Directory2) in order to check whether the desired page is linked there. All you need to do is clear the last directory in the URL. The link for the page you are looking for should be visible on the previous page. If it is not to be found on that page then you can also go back to the previous page and look for the correct link there. But if it so happens that this method is also successful and you eventually end up back on the homepage, then move onto the next tip.
- Use the website’s search function: Many websites offer a search function as part of their homepage. By entering one or several keywords, it can help you find the specific page that you are looking for.
- Use a search engine: You also have the possibility of using the website of your choice to find a website. As long as the desired site exists, you should be able to find it by entering the website domain and/or a keyword transcription of the subject matter.
- Delete the browser cache and cookies: Ifyou can access the website from another device, and the HTTP 404 error only seems to appear on a certain computer, then the problem could lie with your browser. Therefore you should delete the browser cache as well as all cookies for this site, and this may then finally allow you to access the page.
- Contact the website: If none of the abovementioned tips have been successful then the only remaining option may be to get in touch with the person/people responsible for the website. Contact information can usually be found in the website’s masthead or else on a specific ‘Contact Us’ page. The operators of the website should be able to provide information as to whether the page you are looking for actually exists. It might be the case that the page in question has been moved to a new URL, and in this scenario you will be doing the website operator a big favor. They can then carry out a 404 error fix by introducing a domain redirect, which will automatically direct users from the old web page to the current one.
HTTP 404 errors can damage a website’s ranking and reputation
Search engines, such as Google and Bing, will have a negative impression of a site if it has many 404 errors. Once the crawlers have established that many requests are being met with 404 codes, it presumes the site isn’t very well maintained. Dead links affect a site’s ranking and Google can decrease its placement in the SERPs or even stop indexing it if there are too many 404 error pages occurring. This may result in a considerable decrease in visitor numbers for the website.
The visitor loses trust in the site if it’s full of broken links or if the landing page (the page that is accessed from the search engine results) is dead. If the site is experiencing this problem regularly, many users won’t take the trouble to continue to search since they aren’t even sure if the desired content is still available.
Identifing 404 errors on your own website
It’s important for website operators to prevent HTTP 404 pages. This applies to internal 404 error pages on their own website as well as external 404 error pages on other sites. There are numerous free tools available to help you find these broken links more easily. Three of the best and most well-known are:
- Google Search Console (formerly known as ‘Google Webmaster Tools’): if you already have a Google account and have registered your website there, you should make use of the Google Search Console option. Any 404 errors found by the Google crawler are displayed in the web tool and can also be marked as corrected here too. Additional functions enable you to find errors in robots.txt files and use crawling statistics to work out how often your site has been crawled by Google crawlers.
- Dead Link Checker: one of the simplest and fastest tools for finding both internally and externally linked 404 pages is the Dead Link Checker. With this web app you simply enter the URL of the site you want to inspect and then start the check. Here you have the choice of checking a single web page or a whole site. The app lists all the tracked error pages with status codes and URL.
- W3C Link Checker: this online tool from World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is particularly detailed when it comes to testing individual website pages, so the process takes longer to verify links than with other websites. The W3C Link Checker works just like the Dead Link Checker: you enter the URL and let the tool do the rest. It’s also possible to add further details
Creating a 404 error page
Some content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Joomla and Drupal automatically generate a 404 error page when a website’s URL can’t be found. The HTTP 404 page is just a simple standard error message, but most of them can be personalized using special CMS extensions.
If your CMS doesn’t give you the option of creating or changing your 404 page, or if your website is solely based on HTML, PHP, etc., it will prove a bit more complicated. You can create an error page as follows:
- Create an error page (‘404.html‘ or ‘404.php‘) in the root directory (if there isn’t an existing one already).
- Open the .htaccess file (or create one if needed) in the root directory, enter this in ‘ErrorDocument 404 /404.html‘ and save the change. The error page will be generated with this code.
- To see if it’s worked, try to access an unavailable webpage and hopefully the error 404 message should appear in the browser.
Why should you personalize your 404 error page?
Having a standard 404 error page is better than having none at all, although a customized page is more preferred for several reasons. On the one hand, you can be sure that visitors receive an accurate HTTP status code: for example, if the requested content is no longer present on the site, this should be conveyed with the ‘410 Gone‘ message. The visitor then knows that this content has been permanently deleted.
On the other hand, you can provide a specially-designed error page containing related links (i.e. links to your homepage or subpages where the content overlaps that which the visitor originally requested). You could even add a search function for your website. By taking these extra measures and providing incentives, you might be able to prevent visitors from leaving your site straight after seeing the 404 code.
With a creative 404 message you may even find that visitors are more forgiving. Naturally they will be disappointed at not finding content they were promised, but an original or funny 404 page could make up for it. If done properly, error pages do have some potential.
Make sure that the design of the error message matches the style of your website and you already have the foundation for a good 404 error page. If you let visitors know in a funny and light-hearted way that your content isn’t available, you’ll hopefully get a smile out of them and they won’t hold a grudge. For inspiration, check out our article on cool and creative 404 pages.
Related articles

HTTP status codes and their meaning
404, 302, 503 – short number combinations with great significance. Users encounter server status reports time and time again and if you know how to interpret them you can act accordingly. Knowledge of HTTP codes is even more relevant for website owners. With the right know-how you can vastly improve user experience on your homepage, which will have an effect on the search engine ranking.
HTTP status codes and their meaning

Modern web development: the basics
The trends driving web development are moving away from static web presences and heading increasingly in the direction of interactive content. Even though languages like HTML and CSS still rule the roost, a growing number of developers prefer the server-side programming language, PHP, for dynamic websites. Client-side script languages like JavaScript make it possible for a site to react to user…
Modern web development: the basics

How are websites accessed?
In order to access a web page in a browser, you just have to enter the URL into the address bar in your web browser and the requested website will pop up on your screen. This seems simple enough, but the process that’s taking place in the background is a highly complex one. Learn about what happens when you access a website – from the URL translation to the relevant IP address via data transfer,…
How are websites accessed?
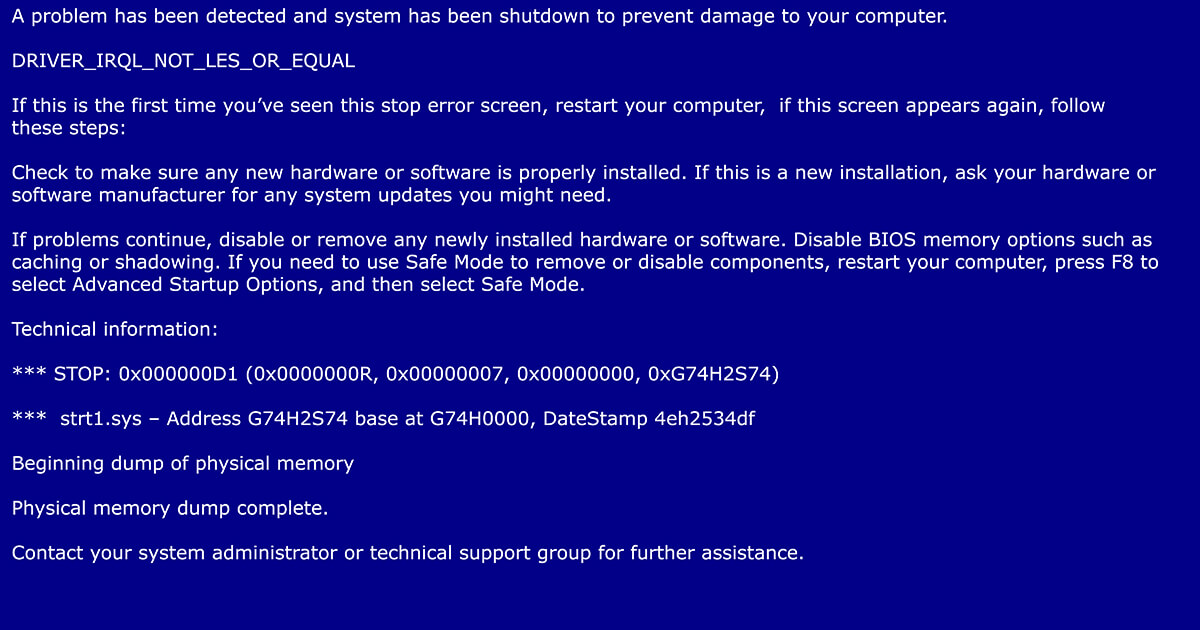
How to fix a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)
The infamous blue screen of death usually shows up without any warning. It’s an important indicator of internal problems with hardware, software, or drivers. If Windows can no longer be run as a result of such a problem, then the forced shutdown takes place in the form of a blue screen containing an error message. This may cause unsaved files and documents to be lost. The most important thing with…
How to fix a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)

HTTP 400: Bad Request explained
Internet users are often confronted with error messages. HTTP status codes can be especially annoying, and even more so if you don’t understand what they mean. The message ‘HTTP 400 – Bad Request’ is a mystery for many internet users, but luckily it can be solved in most cases. We explain what the error message means and how to fix the error.
HTTP 400: Bad Request explained

What are 301 Redirects?
301 redirects are a part of everyday life in the world of online marketing, SEO and web development. Permanent redirection is used to avoid 404 errors that occur when a website’s address has been changed. In this article, we’ll explain how redirects work, why they are needed and how you can set up a 301 redirect using htaccess. Keep on reading to find out more.
What are 301 Redirects?