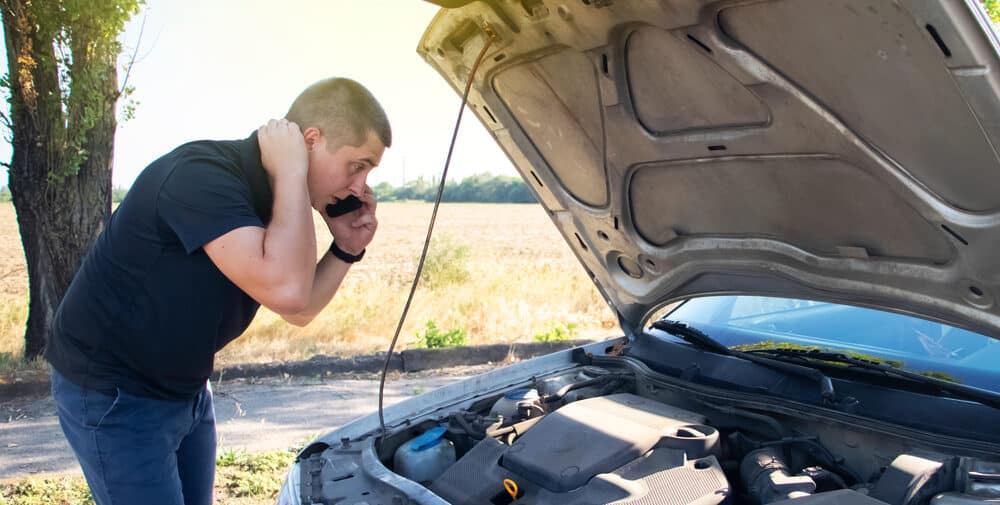
Как-то раз пришел в машину, сел, повернул ключ иии… стартер маслает, бенза полный бак, а машина не заводится…даже не схватывает. Как в жиге копейке когда-то было. Ни с того ни с сего, просто не заводится и все.
Почесал репу, вышел, поднял капот, посмотрел внимательно я на него, он на меня, еще раз почесал репу, снова сел за руль, повернул ключ… и она с полтыка завелась… Ну ок, молодец, подумал я и поехал на работу. С работы вечером выходил настороженно, но машина снова завелась с полтыка.
Через пару дней все повторилось, машина просто отказалась заводиться, причем на сей раз на горячую спустя минут 5 после того, как я ее заглушил. Продолжались мои попытки ее завести минут 15, а с учетом того, что стоял я в этот момент ровно под знаком остановка запрещена, чувства были не самые приятные. Приготовился уже звонить знакомому эвакуаторщику, но она, ска, завелась тут же))
Ладно, приехал домой, вставил шнурок и немного одурел. По блокам двигателя, абс, панели приборов, иммобилайзеру и т.д. одна и та же ошибка
01314 — Engine Control Module
004 — No Signal/Communication – Intermittent
И по АКПП немного другая, но смысл тот же
49408 — No Communication with Engine Control Module (SAE ECM/PCM)
U0100 — 000 — — Intermittent
С большими глазами полез в интернет, и почти сразу нарвался вот на эту тему на аудиклабе, где у человека на a6 было все тоже самое. В итоге у него пришли там к тому, что слетела прошивка блока управления двигателем, ему его перепрошили и все пока у него хорошо…
Скажем прямо, я немного пода%уел… Во думаю попал…
Следующие пару дней проходили по такому сценарию: приехал, ушел, возвращаюсь и минут по 10 прыгаю возле нее и пытаюсь завести. Если уже 1 раз завел, то если не уходить, заводится хоть 100 раз подряд. Как только уходишь от машины, снова не заводится.
Почитал еще драйв, аудиклаб, забугорные форумы, все везде сводится к одному «умерли мозги», «менять блок управления двигателем» «шить флеш память», «ищи ЭБУ» и тому подобное…
И тут я вспомнил, как когда-то из-за банальных проблем с расходомером на опеле мне тоже чуть мозги в машине не поменяли, и решил просто пораскинуть уже своими мозгами логически. Раз машина даже не схватывает, а через 5 минут все ок, значит что-то с электроникой. Может иммобилайзер чето бунтует.
Поменял батарейку в ключе (в audi a4 b7 батарейка в выкидном ключе 2032), но проблема не ушла.
Кстати, советую делать это – менять батарейку в ключе — при открытой машине, т.к. при извлечении батарейки ключ отвязывается от машины, и его потом надо вставить в замок зажигания, включить это зажигание и подержать пару секунд любую кнопку, а то можно, как в моем случае при закисшем замке водительской двери, еще полчаса разрабатывать личинку замка с помощью спец жидкости для замков. Свои плюсы тоже есть, теперь работает механическое отпирание водительской двери)))
Так и катался еще неделю, матерясь по нескольку раз в день и читая форумы, морально готовясь к замене мозгов. Своих))
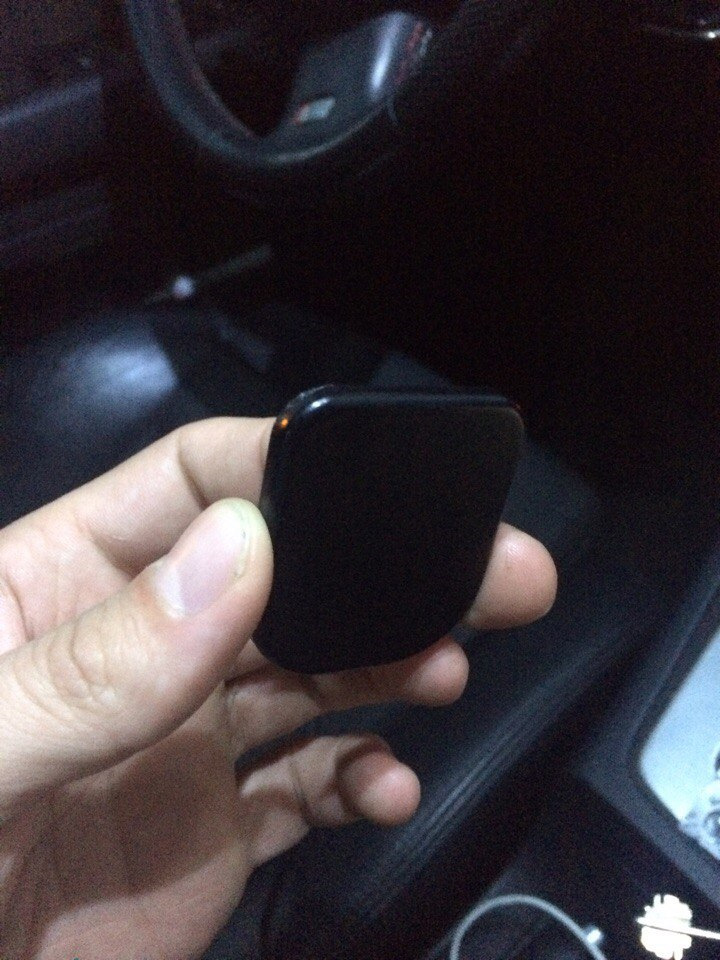
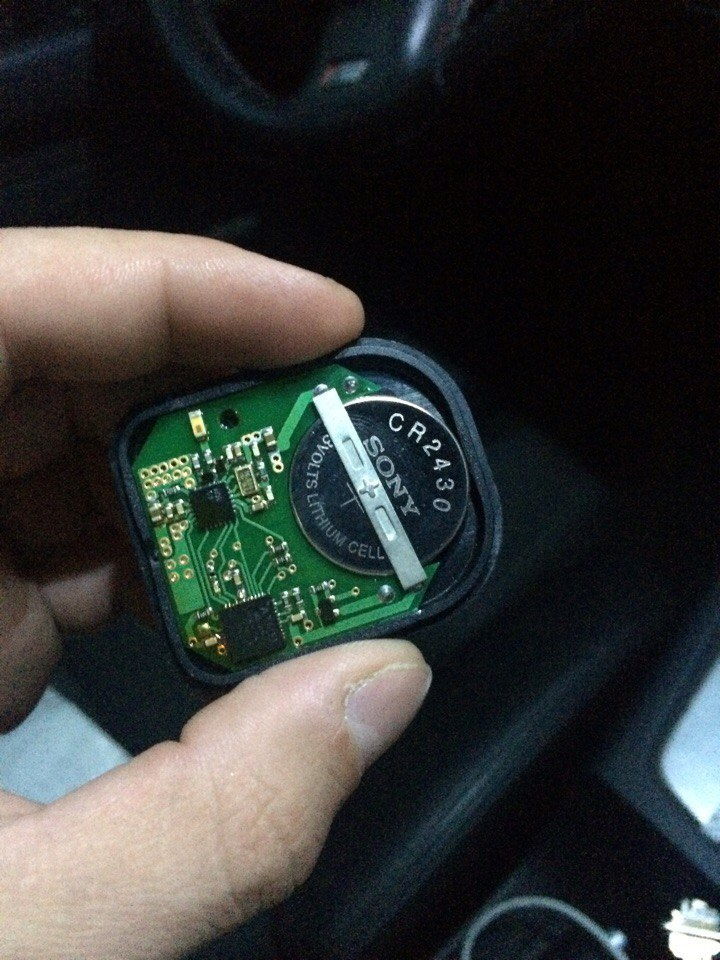
И вот в очередной день, убирая на выходных в машине, нахожу под сидением вот эту штуковину…
Твою ж то маму, подумал я… метка…
Попробовал сразу завести машину-не заводится. Разобрал метку, постучал батарейкой об деревяшку, и о чудо, машина завелась. В итоге поехал в магаз, купил батарейку CR2430, и вот уже как неделю машина заводится с полтыка. Ошибок нет. Все ОК.
Я так понимаю, наличие метки свидетельствует о том, что где-то под торпедой установлена какая-то сигналка, как ее там найти инересно, вот это вопрос, потому что были мысли замутить автозапуск, может кто в минске разбирается и может подсказать куда копать и где блоки искать.
Ну и в завершение, форумы — это зло)

From Ross-Tech Wiki
Jump to:navigation, search
01314 — Engine Control Module
01314 — Engine Control Module: No Communications
Possible Causes
- CAN-Databus Wiring/Connectors from/to Engine Control Module faulty
- Fault(s) stored in Engine Control Module
- Engine Control Module recently flashed or re-mapped
Possible Solutions
- Check CAN-Databus Wiring/Connectors from/to Engine Control Module
- Check Measuring Value Blocks (MVB)
- Usually Measuring Value Blocks (MVB) 125+ show the current Communication Status
Special Notes
- When found in the (1K) chassis with 2.5L gas engine using a MAF (G70) sensor, check the T121/62 (Red/Black) traced power wire to the ECM. If power is missing or a voltage drop is present that wire may be damaged anywhere between 6″ and 18″ from the connector itself. This will result in no communication in addition to a no-start.
- Based on 2.5L Jetta feedback over the years a majority look like this example however some are damaged further away per this example: with the close-up and distant views.
01314 — Engine Control Module: Check DTC Memory
Possible Causes
- Fault(s) stored in Engine Control Module
Possible Solutions
- Check Engine Control Module for Fault Codes
Special Notes
- Engine Control Module stored a Code which influences other Control Modules Functionality.
- To clear this Fault Code you will need to correct the Problem in the Engine Control Module first.
Need a replacement ECM? We sell preprogrammed “plug and play” engine computers (ECMs, TCMs, and PCMs) for all makes and models! We only sell OEM parts that are GUARANTEED to work with your vehicle.
Order today and it’ll ship within 48 hours: find the right ECM for your vehicle now »
Modern vehicles have extremely smart engines. Your car or truck’s central computer (depending on your vehicle) can be called an Engine Control Unit (ECU), Engine Control Module (ECM), Powertrain Control Module (PCM), or Transmission Control Module (TCM). This computer module is constantly monitoring your vehicle and its engine for any signs of trouble. Issues that your car’s computer monitors for are coded in order to let technicians and mechanics know what the general or specific issue is. These are also what trigger your check engine light to illuminate.
Below is a list of common error codes that can be triggered by your ECM / ECU, PCM, or TCM:
What does error code P0301 mean?
A P0301 error code indicates that cylinder 1 has misfired. The sufficient burning of fuel is necessary for proper engine function as combustion is what supplies the energy to power the engine. A misfire occurs when an insufficient amount of fuel is burning in a cylinder. When P0301 occurs it should be fixed immediately as long term driving with engine misfires could cause substantial and costly damage to your engine. The cause of P0301 is often worn out spark plugs, spark plug wires, or a faulty ignition coil.
P0302
A P0302 error code indicates that cylinder 2 has misfired. The sufficient burning of fuel is necessary for proper engine function as combustion is what supplies the energy to power the engine. Just like with P0301, a misfire occurs when an insufficient amount of fuel is burning in the cylinder. When P0302 occurs it should be fixed immediately as long term driving with engine misfires could cause substantial and costly damage to your engine. The cause of P0302 is often worn out spark plugs, spark plug wires, or a faulty ignition coil.
P0303
A P0303 error code indicates that cylinder 3 has misfired. The sufficient burning of fuel is necessary for proper engine function as combustion is what supplies the energy to power the engine. Just like with codes P0301 and P0302, a misfire occurs when an insufficient amount of fuel is burning in the cylinder. When P0303 occurs it should be fixed immediately as long term driving with engine misfires could cause substantial and costly damage to your engine. The cause of P303 is often worn out spark plugs, spark plug wires, or a faulty ignition coil.
P0304
A P0304 error code indicates that cylinder 4 has misfired. The sufficient burning of fuel is necessary for proper engine function as combustion is what supplies the energy to power the engine. Just like with codes P0301, P0302, and P0303, a misfire occurs when an insufficient amount of fuel is burning in the cylinder. When P0304 occurs it should be fixed immediately as long term driving with engine misfires could cause substantial and costly damage to your engine. The cause of P304 is often worn out spark plugs, spark plug wires, or a faulty ignition coil.
P0305
A P0305 error code indicates that cylinder 5 has misfired. The sufficient burning of fuel is necessary for proper engine function as combustion is what supplies the energy to power the engine. Just like with codes P0301, P0302, P0303, and P0304, a misfire occurs when an insufficient amount of fuel is burning in the cylinder. When P0305 occurs it should be fixed immediately as long term driving with engine misfires could cause substantial and costly damage to your engine. The cause of P305 is often worn out spark plugs, spark plug wires, or a faulty ignition coil.
P0306
A P0306 error code indicates that cylinder 6 has misfired. The sufficient burning of fuel is necessary for proper engine function as combustion is what supplies the energy to power the engine. Just like with codes P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, and P0305, a misfire occurs when an insufficient amount of fuel is burning in the cylinder. When P0306 occurs it should be fixed immediately as long term driving with engine misfires could cause substantial and costly damage to your engine. The cause of P0306 is often worn out spark plugs, spark plug wires, or a faulty ignition coil.
P0201
Error code P0201 occurs when the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) or ECM (Engine Control Module) detects a cylinder 1 injection circuit malfunction. In other words, this error code is triggered when these modules determine a low or high voltage drop or resistance at the injector 1. This code is a generic trouble code, meaning it applies to all vehicles equipped with OBD-II, or vehicles made in 1996 to present. Symptoms include poor acceleration and lack of power, engine running rough, engine dies or may not start at all, or excessive fuel consumption. Causes include, defective cylinder 1 injector, plugged or dirt in fuel injector, corroded fuel injector, connections or wiring, poor electrical connections in the connector or harness, open or short wiring harness, or a damaged PCM.
P0202
Error code P0202 occurs when the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) or ECM (Engine Control Module) detects a cylinder 2 injection circuit malfunction. In other words, this error code is triggered when these modules determine a low or high voltage drop or resistance at the injector 2. This code is a generic trouble code, meaning it applies to all vehicles equipped with OBD-II, or vehicles made in 1996 to present. Symptoms include poor acceleration and lack of power, engine running rough, engine dies or may not start at all, or excessive fuel consumption. Causes include, defective cylinder 2 injector, plugged or dirt in fuel injector, corroded fuel injector, connections or wiring, poor electrical connections in the connector or harness, open or short wiring harness, or a damaged PCM.
P0203
Error code P0203 occurs when the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) or ECM (Engine Control Module) detects a cylinder 3 injection circuit malfunction. In other words, this error code is triggered when these modules determine a low or high voltage drop or resistance at the injector 3. This code is a generic trouble code, meaning it applies to all vehicles equipped with OBD-II, or vehicles made in 1996 to present. Symptoms include poor acceleration and lack of power, engine running rough, engine dies or may not start at all, or excessive fuel consumption. Causes include, defective cylinder 3 injector, plugged or dirt in fuel injector, corroded fuel injector, connections or wiring, poor electrical connections in the connector or harness, open or short wiring harness, or a damaged PCM.
P0204
Error code P0204 occurs when the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) or ECM (Engine Control Module) detects a cylinder 4 injection circuit malfunction. In other words, this error code is triggered when these modules determine a low or high voltage drop or resistance at the injector 4. This code is a generic trouble code, meaning it applies to all vehicles equipped with OBD-II, or vehicles made in 1996 to present. Symptoms include poor acceleration and lack of power, engine running rough, engine dies or may not start at all, or excessive fuel consumption. Causes include, defective cylinder 4 injector, plugged or dirt in fuel injector, corroded fuel injector, connections or wiring, poor electrical connections in the connector or harness, open or short wiring harness, or a damaged PCM.
P0205
Error code P0205 occurs when the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) or ECM (Engine Control Module) detects a cylinder 5 injection circuit malfunction. In other words, this error code is triggered when these modules determine a low or high voltage drop or resistance at the injector 5. This code is a generic trouble code, meaning it applies to all vehicles equipped with OBD-II, or vehicles made in 1996 to present. Symptoms include poor acceleration and lack of power, engine running rough, engine dies or may not start at all, or excessive fuel consumption. Causes include, defective cylinder 5 injector, plugged or dirt in fuel injector, corroded fuel injector, connections or wiring, poor electrical connections in the connector or harness, open or short wiring harness, or a damaged PCM.
P0206
Error code P0206 occurs when the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) or ECM (Engine Control Module) detects a cylinder 6 injection circuit malfunction. In other words, this error code is triggered when these modules determine a low or high voltage drop or resistance at the injector 6. This code is a generic trouble code, meaning it applies to all vehicles equipped with OBD-II, or vehicles made in 1996 to present. Symptoms include poor acceleration and lack of power, engine running rough, engine dies or may not start at all, or excessive fuel consumption. Causes include, defective cylinder 6 injector, plugged or dirt in fuel injector, corroded fuel injector, connections or wiring, poor electrical connections in the connector or harness, open or short wiring harness, or a damaged PCM.
P0601
The P0601 error code occurs when a memory check sum error is detected with the internal control module. This code is a generic trouble code, meaning it applies to all vehicles equipped with OBD-II system, or vehicles made since 1996 up to present. The two most common causes of the P0601 error code are that the ECM (or ECU) is failing or has failed or that the ECM/ECU is receiving low voltage.
P0400
The P0400 error code is defined as an Exhaut Gas Recirculation Flow Malfunction. Modern vehicles are equipped with an EGR (Exhaust Gas Re-Circulation) system which is used to reduce the combustion temperature, thus reducing NOx gas formation, a harmful gas produced by car engines. When this error code occurs, it means that the EGR flow monitoring criteria have not been met due to restriction in the EGR passages, usually caused by carbon buildup, the EGR Valve is defective, lack of proper vacuum or electrical signal to the EGR valve, excessive Vacuum flow to EGR valve, malfunctioning EGR Vacuum supply solenoid, or lack of proper EGR system feedback to the computer.
P0401
Similar to a P0400 error code, a P0401 error code occurs when there is an issue with the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR). Normally, the EGR recirculates small amounts of exhaust back into the combustion chambers of the engine in order to decrease the combustion temperature, thereby reducing the formation of smog-producing nitrogen oxides. Error code P0401 means that there is insufficient recirculation flow.
P0402
In contrast to the P0401 error code, the P0402 error occurs when excess recirculation flow through the EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) is detected. The EGR recirculates small amounts of exhaust back into the combustion chambers of the engine in roder to decrease combustion temperature and and reduce the formation of smog-producing nitrogen oxides. Excess flow disrupts this reduction process.
P0487
Error code P0487 indicates that the Exhaust Gas Recirculation Throttle Control Circuit A is open. This means that the vehicle’s computer was not able to register the right amount of air pressure in manifold because of a malfunction. This error code is a generic code that typically applies to diesel engines built since 2004, including but not limited to Dodge, Ford, GM, Mercedes Benz, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Suzuki, and Volkswagen vehicles.
P0488
Error code P0488 indicates that there is an issue with the rate of flow of the EGR system, meaning there is a problem with Exhaust Gas Recirculation Throttle Control Circuit “A” Range/Performance. Code P0488 means that the powertrain control module (PCM) has detected a discrepancy between the actual position of the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve and the desired throttle position.
P0403
Similar to a P0400, P0401, and P0402 error code, a P0403 error code occurs when there is an issue with the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR). Normally, the EGR recirculates small amounts of exhaust back into the combustion chambers of the engine in order to decrease the combustion temperature, thereby reducing the formation of smog-producing nitrogen oxides. Error code P0403 means that the PCM is not seeing the proper EGR Vacuum Solenoid voltage readings when it allows or denies vacuum to open or close the EGR valve.
P0404
Similar to the P0400, P0401, P0402, and P0403 error codes, a P0404 error code occurs when there is an issue with the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR). Normally, the EGR recirculates small amounts of exhaust back into the combustion chambers of the engine in order to decrease the combustion temperature, thereby reducing the formation of smog-producing nitrogen oxides. Error code P0404 means that the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) has been told that the valve is performing in a way that is outside of its specified parameters. More specifically, the PCM has been told that the valve is closed when it should be open, or vice-versa.
P0405
Similar to the P0400, P0401, P0402, P0403, and P0404 error codes, a P0405 error code occurs when there is an issue with the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR). Normally, the EGR recirculates small amounts of exhaust back into the combustion chambers of the engine in order to decrease the combustion temperature, thereby reducing the formation of smog-producing nitrogen oxides. Code P0405 means that the EGR Valve Position Sensor is giving low voltage readings that are usually below the .5 – 1.0 voltage range.
P0489
Similar to error codes P0487 and P0488, code P0489 indicates that the Exhaust Gas Recirculation “A” Control Circuit is Low. Meaning, the EGR “A” control circuit is sending is reporting a low voltage flow caused by defective wiring or clogged EGR passages. This code is a generic trouble code, meaning it applies to all vehicle makes/models equipped with OBD-II system, especially those made since 1996 up to present.
P0480
The P0480 error code means that there is a cooling fan 1 control circuit malfunction. The cooling fan’s function is just like it sounds–to keep the engine cool while your vehicle is not in motion (as you drive your car enough air passes through the radiator to keep it cool). If the temperature reaches more than 223˚ F (the value depends on make, model or engine of the vehicle), the PCM automatically command the cooling fan relay to turn on its fan by supplying the ground to the relay. If this does not occur properly, you will receive a P0480 error code.
P0601
Error code P0601 indicates that there is a memory check sum error detected in the internal control module. This refers to a fault in the internal control memory of the PCM and is found when the PCM performs a self-check.
P0207
Error code P0207 means that the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) detected a fault in the injector or the wiring to the injector. It monitors the injector and when the injector is activated, the PCM expects to see the voltage pulled “”low”” or close to zero. When the injector is switched off, the your PCM expects to see a voltage that is close to battery voltage or “”high”” and also monitors resistance in the circuit. If it doesn’t see the expected voltage, or if resistance is low or high, it will set this code.
P0208
Similar to code P0207, error code P0208 occurs when the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) detects a fault in the injector or the wiring to the injector. It continuously monitors the injector and when the injector is activated, the PCM expects to see the voltage pulled “”low”” or close to zero. If this is not the case, then this error code is activated.
P0307
On vehicles with more than six cylinders, a P0307 error code indicates that cycliner 7 has misfired. The sufficient burning of fuel is necessary for proper engine function as combustion is what supplies the energy to power the engine. Just like with codes P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, and P0306, a misfire occurs when an insufficient amount of fuel is burning in the cylinder. When P0307 (or any of the other cylinder error code) occurs it should be fixed immediately as long term driving with engine misfires could cause substantial and costly damage to your engine. The cause of P0306 is often worn out spark plugs, spark plug wires, or a faulty ignition coil.
P0308
On vehicles with eight or more cylinders, a P0308 error code indicates that cycliner 8 has misfired. The sufficient burning of fuel is necessary for proper engine function as combustion is what supplies the energy to power the engine. Just like with codes P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, P0306, and P0307, a misfire occurs when an insufficient amount of fuel is burning in the cylinder. When P0308 (or any of the other cylinder error codes) occurs it should be fixed immediately as long term driving with engine misfires could cause substantial and costly damage to your engine. The cause of P0306 is often worn out spark plugs, spark plug wires, or a faulty ignition coil.
P0508
When the idle air control system circuit is too low, error code P0508 is activated. This is because when the circuit is too low it is seen as an inconsistency in the engine’s RPM idle. If your engine’s RPM idle is too high or too low, the PCM will try to correct the RPM problem. But if it unable to solve the problem, then P0508 will occur.
P0509
Error code P0509 is another generic trouble code which means it applies to all vehicles made since 1996 up to present and equipped with OBD-II system. In contrast to error code P0508, P0509 indicates that the Idle Air Control Circuit is high, meaning, like P0508, the vehicle’s computer has picked up an inconsistency regarding the engine’s RPM when it’s in idle, which is commonly caused by shortages or leaks.
P0622
When the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) detects a problem with or the absence of the PWM (Pulse Width Modulated) signal that turns the alternator field winding in the generator on and off. The PWM signal is how the PCM monitors the load placed on the engine by various electrical consumers such as the A/C system, power windows, and others, and if that process is somehow interrupted or malfunctioning, error code P0622 is activated.
P1765
Error code P1765 occurs when the key is on or the engine running and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) either detects that the transmission control voltage status with the solenoid off was 0v (should be 12v) or was 12v with the solenoid on. This is most likely caused by a faulty transmission control relay, because the transmission control relay harness is open or shorted, or the transmission control relay circuit has a poor electrical connection.
P1388
Your vehicle has a system called the Comprehensive Component Monitor (CCM), which monitors the variable camshaft timing. If the camshaft timing exceeds a maximum calibrated value or remains in a retarded position, then the CCM will activate error code P1388.
P1495
Error code p1495 means that there is a problem with your vehicle’s leak detection pump. Your car is smart and has an Evaporative Emission System designed to prevent fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. The leak detection pump is a part of this emission system and if your car’s computer detects an issue with it, P1495 is activated. This code only applies to specific vehicle makes, such as Chrysler, Dodge, and Jeep.
P1494
Similar to error code P1495, error code P1494 indicates that there is an issue with the Evaporative Emission System. In this case, the Powertrain Control Module detects an issue with the EVAP leak detection pump pressure switch condition. This code is manufacturing specific, applying only to Chrysler, Dodge, and Jeep models.
P1491
Error code P1491 is a manufacturer specific code, mostly utilized by Honda, Acura and Isuzu. It indicates that there is insufficient lift in the Exhaust Gas Recirculation valve. The Exhaust Gas Recirculation system circulates exhaust gases back into the engine in order to cool the combustion process and reduce the amount of nitrogen oxides being released into the air. Your car turns the EGR valve solenoid on and off rapidly in order to control it during operation. P1491 is activated when your car detects a problem with this valve function.
P0505
Error code P0505 indicates a problem with your vehicle’s Idle Air Control System (IAC). The Idle Control System is what controls the idle speed of your car’s engine. The IAC component, specifically, is what controls and allows a certain amount of metered air to the throttle plate, which also controls the idle speed. If the Powertrain Control Module (your car’s computer) detects any irregularities with the IAC’s circuits, you will get this error code.
P0463
The P0463 error code is activated when your vehicle’s Powertrain Control Module (PCM) detects inaccurate fuel level readings from the fuel level sensor, which is what let’s the PCM know how much fuel is in your tank. Specifically, this error code is activated when the fuel level sensor is indicating a higher level of fuel than is actually in your tank.
P0462
The P0462 error code is activated when your vehicle’s Powertrain Control Module (PCM) detects inaccurate fuel level readings from the fuel level sensor, which is what lets the PCM know how much fuel is in your tank. Specifically, this error code is activated when the fuel level sensor is indicating a lower level of fuel than is actually in your tank.
P0460
The P0460 error code is a generic code indicating a general Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Malfunction. This code is activated when there is a discrepancy detected between the fuel gauge and the actual fuel level of the tank.
P0443
Error code P0443 is activated when your vehicle’s Engine Control Module or Powertrain Control Module (ECM or PCM) detects a malfunction within the purge control valve or a short in the purge valve circuit, which is a critical component of your vehicle’s Evaporative Control System (EVAP). The EVAP regulates and controls your car’s emissions.
P0141
Error code P0141 indicates a malfunctioning heater circuit sensor, specifically sensor 2. Your engine has oxygen sensors that contain heaters in order to get them up to operating temperature quickly so that they can start providing information to your vehicle’s Powertrain Control Module as quickly as possible. Code P0141 occurs when the powertrain control module detects a short in the circuit or excessive resistance in the heater circuit.
P0135
Error code P0141 indicates a malfunctioning heater circuit sensor, specifically sensor 1. Your engine has oxygen sensors that contain heaters in order to get them up to operating temperature quickly so that they can start providing information to your vehicle’s Powertrain Control Module as quickly as possible. Code P0135 occurs when the Powertrain Control Module tests the upstream heated oxygen sensor’s heater circuit on Bank 1 and detects a short in the circuit or excessive resistance in the heater circuit.
P0133
Error code P0133 occurs when the Engine Control Module detects a slow response in oxygen sensor 1. Specifically, P0133 indicates that the air/fuel ratio in the engine is not being automatically adjusted by the oxygen sensor signal or the Engine Control Module in the correct way, or is not being adjusted as expected when the engine warms up or under normal engine use.
P0121
Your Throttle Position Sensor “A” and “B” circuits have an expected output voltage range, and error code P0121 occurs when your Engine Control Module (ECM) recognizes that your “A” circuit’s expected output voltage has either gone above or below the sensor’s expected range when compared to “B” Circuit. This is a serious problem because when code P0121 is triggered, your ECM will go into failsafe mode. This can result in your car limiting speed or acceleration.
P0122
Similar to error code P0121, error code P0122 indicates an issue with your engine’s Throttle Position Sensor (TPS). Specifically, this error code means that the PCM or ECM has determined that the TPS circuit A output voltage is lower than its expected range.
P0123
Similar to error code P0121 and P0122, error code P0123 indicates an issue with your engine’s Throttle Position Sensor (TPS). Specifically, this error code means that the PCM or ECM has determined that the TPS circuit A output voltage is higher than its expected range.
P0230
Error code P0230 means that your engine is experiencing a malfunctioning Fuel Pump Primary Circuit. Your vehicle’s PCM or ECM controls the fuel pump through electrical relay, and a P0230 code indicates that the circuit is experiencing a problem when it is commanded to turn on or off. This code is usually set when there’s an incorrect voltage detected by the PCM or ECM.
P0340
Error code P0340 indicates that you have a camshaft position sensor circuit malfunction. The camshaft position sensor is located in the internal combustion engine and monitors the position and rotational speed of the camshaft. When code P0340 is activated it means the ignition spark and fuel injector timing has failed.
P1282 Error code P1282 is activated when there is an issue with your engine’s fuel pump relay control circuit.
Specifically, it means that your car’s PCM or ECM has detected a shorted or open condition in the fuel pump relay control circuit when the key is on and the fuel pump is commanded to turn on.
P0751
The P0751 error code means that your engine’s shift solenoid “”A”” is not working properly or is stuck off. Specifically, this code is activated when the gear required by the ECM does not match the actual gear when vehicle is driven. This is most often caused by foreign material obstructing the mechanical function of the solenoid or the flow of the fluid through the transmission valve body.
P0351 – P0358
Error codes P0351 – P0358 all indicate a problem with the ignition coil circuit. The last digit of each of these codes refers to the cylinder that is experiencing the issue with its ignition coil circuit. The ignition system converts battery voltage into the high voltage used to ignite the cylinder air/fuel mixture, and modern engines use a coil pack that sits directly on top of the spark plug to convert the low primary circuit voltage to high secondary voltage needed to fire the spark plugs. The most common symptom of a malfunctioning ignition coil circuit is a cylinder misfire.
P0441
Error code P0441 indicates an issue with the Evaporate Emission Control System (EVAP) purge valve. The purge valve is the part of the EVAP that draws the fuel vapors into the engine intake manifold, preventing them from escaping into the atmosphere and where they are then used as part of the air-fuel mixture needed for combustion within the cylinders of the engine. When error code P0441 is activated, it means that the purge valve is not correctly regulating the fuel vapors. This can lead to a rough or erratic idle.
P0442
The P0442 error code also has to do with the Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP). This code is activated when an error is detected during an EVAP leak test. During the leak test, the ECM closes the vent control valve and purge valve to create a vacuum. If the EVAP system does not maintain the pressure, the ECM recognizes an evaporative emission control leak. This can lead to decreased fuel economy and the smell of gas.
P0455
Like the P0442 code, the P0455 error code indicates a leak in the Evaporative Emission Control System. The difference is, a P0455 code means that, when the ECM performs a leak test, it finds that there is a very large leak. This usually means that there is a loose, broken, or missing gas cap.
P0753
Error Code P0753 is defined as an error with the Shift Solenoid A Electrical/1-2 Shift Solenoid Circuit Electrical. What this means is that the PCM or ECM has detected irregular electrical activity in the transmission shift solenoid A, which is usually caused by a faulty shift solenoid. Common symptoms include failure to shift into or out of gear, transmission control module in Limp-in mode, harsh shifting, slippage or overheating of transmission, and decreased fuel efficiency.
P0131
Error code P0131 indicates that there is a problem in the wiring, such as corrosion, breaks or separation in the oxygen bank 1 sensor 1. The oxygen Sensor could be non-functioning, or there could be a bad connection to the ECM. It is also possible that the power source is not supplying enough voltage to the sensor. The oxygen Sensor is positioned in the exhaust system to monitor oxygen levels in the exhaust gases that exit the engine and if its sensors are malfunctioning it can mean big problems for your vehicle.
P0132
Error code P0132 indicates that the oxygen bank 1 sensor 1 has lagged or taken too long to switch from high to low (working) voltage for too long. The oxygen Sensor is positioned in the exhaust system to monitor oxygen levels in the exhaust gases that exit the engine. Issues with the oxygen sensors lead to combustion and cylinder problems. This is a big problem for drivers because malfunctioning cylinders lead to a spike in fuel consumption. A vehicle with a cylinder in a bad condition also emits harmful gasses such as the hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides that pollute the environment.
P0137
Error code P0137 means there is a problem with the second oxygen sensor installed on a car or truck. The second oxygen sensor is usually after the catalytic convert and tests the oxygen level after the exhaust gases have moved through the converter. When the sensor’s voltage level stays below the standard expected level for longer than 120 minutes, it will send a trigger signal which the car’s computer then interprets as a potential repair issue.
P0138
Error code P0138 means there is a problem with the second oxygen sensor installed on a car or truck. The second oxygen sensor is usually after the catalytic convert and tests the oxygen level after the exhaust gases have moved through the converter. When the sensor’s voltage level stays above the standard expected level for longer than 120 minutes, it will send a trigger signal which the car’s computer then interprets as a potential repair issue.
P0743
Inside your transmission is a Torque Converter Clutch (TCC), whose job it is to maintain a 1 to 1 RPM ratio between the Transmission Input Shaft and the Torque Converter’s rotational speed. This way, loss of power that may occur with the fluid and/or hydraulic lock that usually happens in the conventional Torque Converter is eliminated. Error code P0743 indicates that the PCM is reading higher than 200RPM difference between the rotational speed Torque Converter and the Transmission Input Shaft.
P2107
Error code P2107 means your engine is overheating and should be shut off as soon as possible. Engine coolants come with a sensor which sends a signal voltage to the PCM or ECM, letting the computer know of the temperature. If this temperature is excessively higher than the specified temperature for the vehicle, then error code P2107 is activated.
P1389
Error code P1389 is specific Chrysler, Jeep, and Dodge models. It indicates the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) is not detecting any electrical voltage at the ASD (Automative Shutdown) relay power circuit.
P0106
P0106 is defined as “Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Circuit Range/Performance Problem”, and is set when the PCM (Power Train Control Module) detects a signal voltage from the MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) sensor that is abnormal with regard to the current engine load or throttle position, or a signal voltage that does not show a valid relationship with the MAP sensor. This is typically caused by an intake/exhaust leak, wiring problem, or MAP sensor or BARO sensor malfunction.
P0107
P0107 is the error code for a problem with the MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) circuit sensor having too low voltage input to the Engine Control Module (ECM). This means the voltage input to the ECM is .5 volt or lower. This means that it is not in the correct lower range for proper engine operation.
P0108
P0108 is the error code for a problem with the MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) circuit sensor having too high voltage input to the Engine Control Module (ECM). This means that the voltage input to the ECU is too high and that it is not in the correct range for proper engine operation to work with inputs from the Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAF) and Throttle Position Switch (TPS).
P1297
Error code 1297 indicates that the Engine Control Module (ECM) detects no change in Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor voltage. Too small difference is seen between Barometric Pressure with ignition ON (Engine Running). Probably causes of this include a faulty Manifold, Absolute Pressure (MAP), a sensor restricted MAP, a MAP sensor harness is open or shorted, a MAP sensor circuit has a poor electrical connection, or a faulty Engine Control Module (ECM).
P0118
The P0118 error code indicates an issue with the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor. The ECT is a thermistor (an electrical resistor whose resistance is greatly reduced by heating) and is located in a coolant passage in the cylinder head. Its primary job is to monitor the rise and fall of engine coolant temperature. When the engine has been running for more than a few minutes and the ECT is reading a less than freezing temperature, the PCM thinks there is a circuit fault and activates the P0118 code.
Недавно стал обладателем такой ошибки. По описанию из Vida, причин, которые могут вызывать ее достаточно много.
Описание из Vida:
ECM-434C Система топливного бака, утечка. Небольшая утечка, B5254T2
Возможные причины:
Утечка величиной 0,5 — 1,0 мм или меньше в топливном баке, трубе топливной заливной горловины, крышке заливной горловины топливного бака, угольном фильтре системы выделения паров топлива, клапане системы выделения паров топлива или в шлангах между этими компонентами.
Первым делом конечно посмотрю визуально, может и правда где-то убегает бензин, хотя запаха бензина ни разу не было.
Еще на ум приходит — проверить крышку топливного бака…
Может у кого-то уже был положительный опыт борьбы с этой ошибкой?
16.01.13
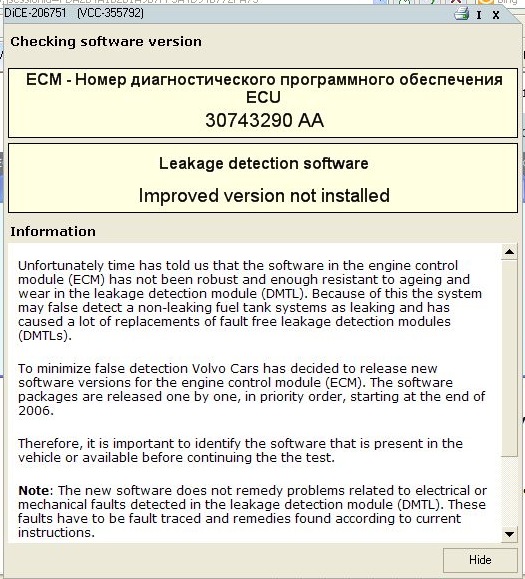
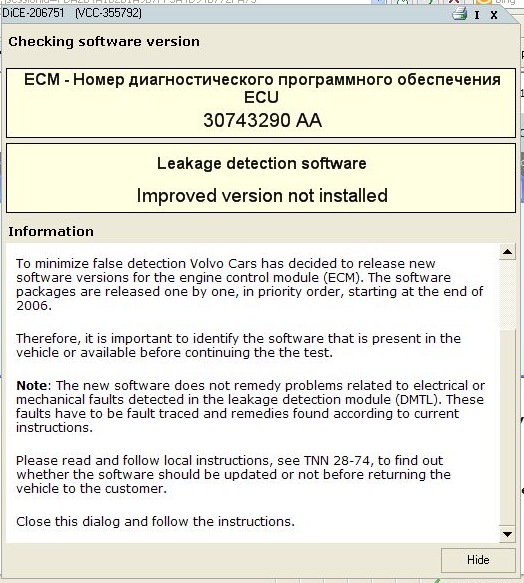
Попробовал провести экспресс-тест системы утечек, однако, был вежливо послан Vida к дилеру за свежей прошивкой модуля ECM.
Кроме того, попробовал перевернуть прокладку на крышке топливного бака. Вроде прилегать стала лучше. Конечно не по «фен-шую», но вполне неплохо держит.
Ошибка неделю не появлялась. Теперь опять высветилась…
Буду смотреть всю топливную…
01.02.2013
Посмотрел топливную, в части системы контроля утечек. Визуально все хорошо. Только в одном месте вроде хомута не было. Поставил. Скинул ошибку. Пока больше не появлялась.
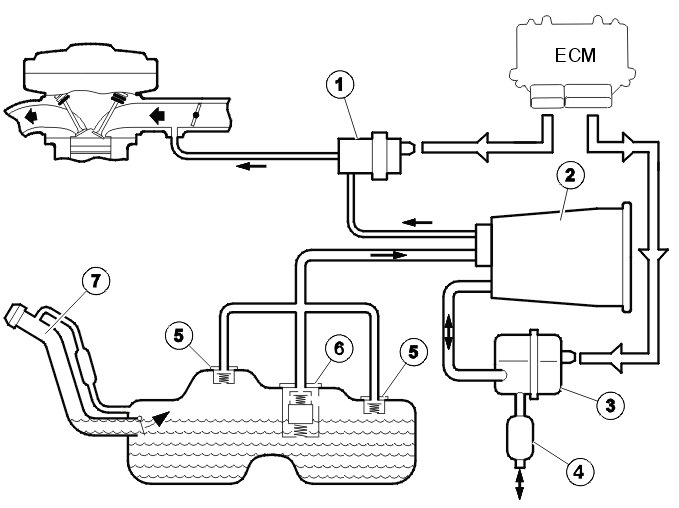
Виден фильтрующий элемент и насос контроля утечек, а также металлический хомут, который я поставил
Виден в глубине фильтр воздуха поступающего на насос контроля утечек топлива
А вот и сам бачок адсорбера паров топлива.
15.02.2013
Недавно опять загорелась лампочка Check Engine. Хотел было ее в очередной раз скинуть через пару дней, а она возьми и потухни сама на следующий день.
Тут-то ко мне и закралась мысль, что ноги здесь растут из устаревшей прошивки ECM, которая еще не умеет вносить коррекционную поправку на старение насоса контроля утечек топлива… Вот и выдает ошибки направо и налево…
Нужно будет прошиваться…
28.03.2013
Стал замечать, что загорается CE действительно, когда в баке остается менее 85% объема топливного бака.
Проверил вариант с переливом топлива. Т.е., когда на заправке Мы просим заправщика налить «до полного», а он рад стараться и льет под самую горловину. В этом случае топливо может попасть в бачок адсорбера и тем самым выдать ошибку.
Чтобы исключить эту возможность, 2 заправки заправлял сам до 2-ой отсечки заправочного пистолета. Однако ошибка появилась опять.
Кроме того, чаще всего ошибка ЕСМ-434с пропадает с повышением температуры выше +15. И когда топлива становится менее 50%.
Тут у меня только одна мысль, что это связано с увеличением выделения паров топлива с повышением окружающей температуры. Теперь надо понять с каким конкретно элементом системы контроля утечки топлива связано это явление.
У меня под подозрением сейчас клапан EVAP, т.к. он запирает и открывает забор паров топлива из бачка адсорбера.
Также под подозрением фильтр поступающего воздуха (см. рис.). Возможно он подзабился грязью. Надо попробовать до него добраться.
Поиски продолжаются…
29.04.2013
Похоже нашел вариант, как обхитрить систему. Попробовал заправить топливо только на 80% объема бака. Ошибка так и не появилась. Отъездил весь бак!
Буду продолжать наблюдения.
Диагностика подтеканий, оригинальная версия (2005-)
Все газы, испаряющиеся из топлива в топливном баке, должны направляться в угольный фильтр системы выделения паров топлива и там содержаться, с тем чтобы их можно было направить в двигатель для сгорания. Для того чтобы обнаружить утечки, вызывающие испарение газов в атмосферу, выполняется диагностика система топливного бака на наличие утечек. Система топливного бака состоит из следующих компонентов:
— топливный бак
— Продувочный клапан (1)
— Угольный фильтр EVAP (2)
— блок диагностики утечек (3)
— воздухоочиститель (4)
— Переливной клапан (5)
— Клапан канала ограничения поплавка (6)
— труба топливной заливной горловины (7)
— все линии между указанными выше компонентами.
В системе топливного бака имеется блок диагностики утечек для выявления любых утечек. Блок диагностики утечек поднимает давление в системе топливного бака при выключенном зажигании, если соблюдены условия для диагностики. Модуль управления может обнаруживать нарушения в функционировании блока диагностики утечек и утечку величиной 0,5 мм или больше. Небольшая утечка; утечка больше, чем 0,5 мм, но меньше, чем 1,0 мм. Большая утечка: утечка больше, чем 1,0 мм.
Блок диагностики утечек состоит из насоса и клапана, который управляет потоком воздуха в блоке. Система топливного бака проверяет на наличие утечек путем измерения потребления электроэнергии насосом. Потребление насосом электроэнергии соответствует определенному давлению в системе топливного бака. Во время диагностики проверяется скорость, с которой может увеличиваться давление, принимая во внимание количество топлива в баке. Чем быстрее повышается давление, тем лучше загерметизирована система топливного бака.
Условия для диагностики
Диагностика начинается тогда, когда соблюдены все следующие условия:
— Для следующих компонентов и функций не должно быть зарегистрировано кода неисправности:
— силовой каскад для насоса в блоке диагностики утечек
— силовой каскад для клапана в блоке диагностики утечек
— силовой каскад для продувочного клапана системы выделения паров топлива клапан системы выделения паров топлива
— датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости двигателя
— сигнал скорости.
— Двигатель выключен до тех пор, пока температура охлаждающей жидкости двигателя не упадет до температуры на несколько градусов выше наружной температуры, затем двигатель работает не менее 10 минут.
— Зажигание выкл.
— Скорость автомобиля 0 км/ч.
— Температура охлаждающей жидкости двигателя -5 °С или выше.
— Максимальная высота 2500 метров над уровнем моря.
— Наружная температура от -5 до +35 °С.
— Объем топлива в баке меньше, чем 85 %. Модуль управления двигателя (ECM) игнорирует эти параметры, если регистрируется код неисправности для датчика уровня топлива и объем топлива невозможно определить.
— Напряжение аккумулятора 11,0-14,5 В. Напряжение должно быть стабильным.
— Продувочный клапан системы выделения паров топлива закрыт.
— Низкий объем в угольном фильтре.
Крышка заливной горловины топливного бака, проверка
Исключением из указанных выше условий является случай, когда автомобиль был дозаправлен. Модуль управления двигателя (ECM) начинает проверку крышки заливной горловины топливного бака после дозаправки. Это — упрощенная версия проверки блока диагностики утечек для больших утечек. Крышка заливной горловины топливного бака контролируется во время движения автомобиля. Это позволяет модулю управления проверять, установлена ли крышка на место. Если крышка отсутствует, в модуле управления двигателя (ECM) регистрируется код неисправности, а в модуле снабжения водителя информацией (DIM) появляется текстовое сообщение.
Фазы диагностики
Диагностика делится на следующие фазы и выполняется последовательно, когда все условия для выполнения диагностики соблюдены.
— Опорная фаза
— Функциональная проверка
— Диагностика подтеканий
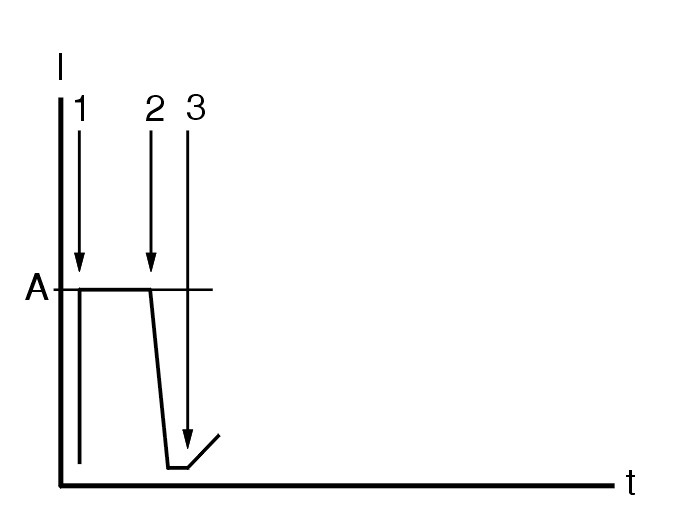
Опорная фаза (1-2)
Опорная фаза (1-2)
Иллюстрация представляет собой схему исправной системы топливного бака.
Перед началом диагностики утечек модуль управления выполняет опорную фазу для утечки. Во время опорной фазы (1-2) для утечки величиной 0,5 мм насос в блоке диагностики утечек закачивает воздух снаружи через 0,5 мм отверстие и обратно выкачивает его наружу. Одновременно измеряется потребление электроэнергии (А) насосом и величина регистрируется в модуле управления Зарегистрированное значение (А) потребления электроэнергии насосом соответствует утечке 0,5 мм. Затем это значение используется модулем управления двигателя (ECM) для определения состояния утечки системы топливного бака.
Функциональная проверка (1-3)
Если значение потребления электроэнергии насосом слишком высокое или низкое во время опорной фазы (1-2), или если диапазон изменений значения слишком большой во время опорной фазы (1-2), диагностика отменяется и начинается снова в следующий раз, когда имеются условия для диагностики. Код неисправности регистрируется, если диагностика отменяется несколько раз подряд из-за чрезмерного колебания потребления электроэнергии насосом.
После опорной фазы в блоке диагностики утечек активируется клапан (2) и управляет потоком воздуха, идущим к топливному баку, чтобы повысить давление системы топливного бака. Это изменение потока воздуха вызовет кратковременное снижение потребления электроэнергии насосом, прежде чем произойдет повышение давления в системе топливного бака (3). Код неисправности регистрируется, если значение потребления электроэнергии насосом уменьшается слишком быстро, медленно или не уменьшается совсем.
Диагностика утечек, большая утечка (утечка больше, чем 1,0 мм)
Диагностика «больших утечек» выполняется каждый раз, когда имеются условия для выполнения диагностики. Блок диагностики утечек повышает давление системы топливного бака, измеряет потребление электроэнергии насосом (4) и сравнивает его с расчетным ожидаемым значением (В). Регистрируется код неисправности для большой утечки, если измеренное значение не достигает расчетного желаемого значения за определенное время (время определяется атмосферным давлением и уровнем топлива в баке).
Диагностика утечки, небольшая утечка (утечка больше, чем 0,5 мм, но меньше, чем 1,0 мм)
Диагностика небольших утечек выполняется каждый второй раз, когда имеются условия для выполнения диагностики. Диагностика больших утечек всегда производится перед диагностикой небольших утечек. Блок диагностики утечек продолжает повышать давление системы топливного бака (5-6). Через определенное время (это время зависит от уровня топлива в баке) модуль управления двигателя (ECM) проверяет эту систему топливного бака на наличие утечек. Основой для определения являются:
— время
— измеренное опорное потребление тока насосом (А)
— измеренное потребление электроэнергии насосом во время выполнения оценки
— форма и характеристика кривой тока во время повышения давления.
Код неисправности регистрируется, если обнаружена небольшая утечка.
Если моя писанина была Вам полезна, то ткните Нравится.
Спасибо.
These days, it’s impossible to maintain your car without a good understanding of its computer systems. Gone are the days of adjusting your timing belt or setting your own fuel-to-air ratio. Nowadays, those functions are controlled by three computers:
- Engine control module (ECM)
- Powertrain control module (PCM)
- Transmission control module (TCM).
Today, we’re going to take a look at the most common signs of ECM failure. These ECM failure symptoms can be your first warning of serious engine trouble, so it’s important not to take them lightly.
What Is an ECM and What Does It Do?
Your ECM is responsible for making constant, on-the-fly adjustments to your engine. This includes managing the fuel-to-air ratio and engine timing, which are its primary functions. It also shares vital data with the PCM and the TCM, which control the shifting, anti-lock brakes, and traction control systems.
Managing all of these functions is a lot of work. In order to have the information it needs to do the job effectively, your ECM relies on information from dozens of sensors. For this reason, ECM failure symptoms actually lead to a broken sensor or faulty wire, rather than failure of the ECM itself.
The Most Common ECM Failure Symptoms
1. Your ‘Check Engine’ Light Is On
Your car’s check engine light is a sort of catch-all that many people ignore. This is understandable. Oftentimes, it ends up meaning nothing more than that some oxygen sensor or tire pressure sensor is on the fritz. But sometimes, it means that there’s a problem with your ECM.
Now, a check engine light by itself is no reason to worry. But if it’s happening along with one or more of these other symptoms, you may have a problem with your ECM
2. Your Car Won’t Start
Your engine is never as finicky about fuel-to-air ratio as it is when it’s first starting up. If your ECM is setting the ratio incorrectly, this is the first time you’ll notice. Hiccups during startup, or having to turn the key half a dozen times to get the engine to turn over, are a sure sign of engine trouble, and a possible sign that your ECM is to blame
3. Your Engine Stutters or Misfires
A rich fuel-to-air ratio can cause your engine to misfire, while a lean ratio can cause stuttering when it periodically fails to ignite. Similar problems can be caused directly by an improperly-adjusted engine timing. Either way, it’s possible that your ECM is causing the problem.
4. Sudden Drop in Fuel Economy
Another way that your fuel-to-air ratio and engine timing affect your car’s performance is in the realm of fuel economy. Now, this isn’t typically a problem that happens slowly over time. If you’ve watched your gas mileage slip downwards over the course of a few years, you may want to see a mechanic about the problem, but it’s not your ECM.
That said, if you’ve seen your mileage plummet over the course of a couple of weeks, your ECM or an attached sensor is the likely culprit.
5. Sudden Loss of Acceleration
Your ECM works in tandem with the TCM to make proper adjustments for acceleration. While the TCM handles shifting, your ECM adjusts the throttle accordingly, leading to the relatively smooth, effortless shifting you expect from an automatic transmission.
When the ECM isn’t adjusting the throttle properly, shifting can feel herky-jerky, as if you’re in the car with a first-time driver learning to work a stick shift.
6. Your Engine Shuts Off for No Reason
This is another symptom of an improper fuel-to-air ratio. Generally, it happens while your vehicle is idling, because the engine is running relatively slowly and doesn’t have a lot of momentum to keep it running if there’s a brief hiccup. If your car is stalling while you’re at idle, you should have it looked at before the problem gets any worse.
7. Rough or Irregular Shifting
This problem is related to the loss of acceleration, but it happens when your ECM is sending bad data to your TCM. In this case, your TCM isn’t getting the information it needs to shift at appropriate times. As a result, shifting can feel rough and clunky or can happen at inappropriate times, causing the engine to rev up or bog down.
How Do I Diagnose My ECM?
The least invasive way to diagnose your ECM is to connect an onboard diagnostic (OBD or OBD II) tool to the diagnostic port. From there, you can scan to see if your engine computers have produced any error codes. There are many of these codes, and your diagnostic tool’s manual should have information on what they mean.
We’ve written about some of these codes in the past. Here are a few of the most common:
- The P0600 Code: This code means that there’s a problem with one of the sensors connected to your ECM. Alternatively, it may just indicate a wiring error.
- The P0700 Code: This code means that there’s an error with your TCM. This is a different computer than the ECM, but it can cause some similar symptoms.
- The P0606 Code: This code is produced when there’s a problem with your vehicle’s PCM. Once again, this is only somewhat related to your ECM, but a lot of the symptoms are the same.
What If Your ECM Really Has Failed?
These ECM failure symptoms don’t necessarily mean that it’s time to panic. Oftentimes, the cause of the problem is an affordable sensor or a faulty wire. The only way to know for sure is to perform a thorough diagnosis. Some of the articles we’ve linked provide helpful advice on checking for the most common problems.
If worse comes to worst and you have to replace or repair your PCM, you don’t have to go it alone. Contact us today on our website, or call our knowledgeable technicians at 888-848-0144. We specialize in replacing automotive computers and we can make the process quick and painless.
52 632
Что означает код U0100?
Ошибка U0100 — «потеря связи с блоком управления двигателя ECM/PCM».
Блок управления
двигателем (ECM) — это компьютер, отвечающий за управление двигателем. Блок
управления двигателем взаимодействует с другими блоками управления автомобилем
по шине обмена данными. Эта шина называется сетью контроллеров (CAN) и
позволяет всем модулям взаимодействовать друг с другом.
Есть две шины CAN: CAN
High и CAN low. CAN High — имеет высокую скорость передачи
данных 500 Кбит/сек. CAN low — с низкой скоростью передачи данных с 125k
бит/сек. Физически это экранированная
витая пара. На конце каждого канала данных находится согласующий резистор.
Блоки управления
обмениваются данными по шине CAN между собой. Код ошибки U0100 означает, что
PCM не может отправлять или принимать сигналы связи по шине CAN.
Симптомы ошибки U0100
- Горит
индикатор «Check Engine» - Автомобиль
не заводится.
Частые причины ошибки U0100
Код DTC U0100
вызван, как правило, одним из следующих факторов:
- Неисправный
ECM - Проблема
с проводкой модуля управления - Проблема
с шиной CAN
Как диагностировать и устранять ошибку U0100
Предварительная проверка
Просодическое
появление ошибки U0100 может быть вызвано разрядом или неисправностью
аккумулятора. Очистите ошибку и проверьте, вернется ли код. Если это
произойдет, то следующий шаг — визуальный осмотр проводки. Опытный специалист
может визуально выявить, обрыв проводов или отсутствие контакта. Если источник
проблемы найден, то неисправность должна быть устранена, а код ошибки удален.
Если ничего не обнаружено, необходимо проверить бюллетени технического
обслуживания (TSB). TSB — это рекомендуемые производителем транспортного
средства процедуры диагностики и ремонта. Поиск соответствующего бюллетеня
может значительно сократить время диагностики.
Проверьте аккумулятор
Прежде чем
приступить к диагностике, необходимо убедиться, что батарея полностью заряжена.
Для функционирования блока управления двигателем необходим соответствующий
источник питания. При необходимости зарядите или замените батарею.
Проверьте наличие других кодов неисправностей
Если связанные
коды ошибок сохранены для нескольких различных блоков вероятно, проблема
связана не только с блоком управления двигателем, но и с CAN шиной. В этом
случае диагностике перейдет к проверке CAN шины. Шина должна быть проверена на
отсутствие короткого замыкание на землю и по питанию. Проверка целостности CAN
шины производится через диагностический порт с помощью цифрового мультиметра
(DMM). Подключив мультиметр к контактам CAN High и CAN Low диагностического
порта можно обнаружить обрывы, замыкания и высокое сопротивление в шине CAN.
На каждом конце
шины CAN имеется два терминирующих резистора. Если один из них выйдет из строя,
шина будет продолжать работать. Однако, если они оба выйдут из строя, шина
отключится. Целостность резисторов проверяется путем измерения их
сопротивления. Для этого к диагностическому порту подключается цифрового
мультиметра (установлен на измерение сопротивления цепи). Нормальное показание составляет
около 60 Ом.
Проверьте PCM
Для диагностики
работоспособности блока управления двигателем используется диагностический
сканер ODB II. Сканер подключается к диагностическому порту
автомобиля. После подключения к автомобилю сканер становится еще одним модулем
в сети и обменивается данными по сети.
Если ECM не
реагирует на действия сканера, то необходимо выяснить причины. Проводка блока управления (ECM) должна быть полностью
проверена перед тем, как утверждать, что блок неисправен. Для проверки
целостности проводки и блока управления используется цифровой мультиметр (DMM).
Если в цепи обнаружен обрыв или короткое замыкание, необходимо устранить неисправность.
Тогда проблема может быть исправлена.
Если все признаки
указывают на неисправность ECM, то перед заменой блока управления двигателем необходимо
проверить его программное обеспечение. В некоторых случаях при обновлении
прошивки блока управления он будет работать корректно. Если это не дает никаких
результатов, то блок управления необходимо заменить.
Примечание к ошибке U0100
Диагностика
ошибки U0100 осуществляется при включенном зажигании, необходимом напряжении в
бортовой сети автомобиля и правильной конфигурации других ключевых блоков.
The engine control module (ECM) is known by many other names, including the engine control unit (ECU). Whatever it is called, it has the same function. This vital component sends messages to the motor to ensure proper operation.
When the engine control module (ECM) starts to fail, it leads to many performance issues. I look at the bad ECM symptoms, its location, and the estimated replacement cost. Let’s take a quick look at the signs.
Symptoms Of A Bad Engine Control Module (ECM)
The most common symptom of a bad engine control module is a check engine light on the dashboard. You may also notice engine performance issues, like a misfiring or a stalling engine. If your car won’t start at all, that’s another strong sign your ECM is bad.
Here is a more detailed list of the signs of a bad or failing engine control module (ECM) to look for:
1. Check Engine Light
All modern vehicles come equipped with a Check Engine Light to let you know when something is wrong. While this light can illuminate as a result of a long list of troubles, having a bad ECM is one of them.
If a sensor, circuit or other electrical component of the ECM has gone bad, it will turn on the Check Engine Light. The only way to diagnose the cause is with an OBDII trouble code scanner.
2. Engine Misfiring/Stalling
As the ECM starts to fail, the wrong messages get sent to the engine, creating an imbalance. A faulty computer leads to misfiring. In extreme cases, the car might even stall while sitting at a traffic light.
However, these symptoms will be erratic. One day, the car might run fine and the next day, it could be challenging to control. There’s no pattern to the severity or frequency of symptoms when the ECM is going out.
3. Performance Issues
All engine performance issues can be linked back to a possible defective ECM. When this module goes bad, it can create an imbalance in the fuel-air ratio or the timing settings of the engine.
What you are left with is a decrease in performance, especially when you attempt to push the gas pedal down or you are towing up a hill. If you are noticing less acceleration or a reduction in power, it could be the ECM.
4. Decreased Fuel Economy
A defective ECM makes it difficult for the engine to properly regulate fuel intake. For this reason, your motor might start burning more fuel when the engine control module is going bad.
If you keep an eye on the fuel economy, you might notice the trouble early. However, spending more time at the gas pump should be a sure-fire sign that something is wrong.
5. Car Won’t Start
When the ECM fails completely, your car might not start any longer. With no engine management, the motor simply doesn’t know what to do.
You might hear it attempt to crank, but it can’t start without the right amount of air and fuel being injected. However, having a car that won’t start doesn’t automatically mean you have a bad ECM. It could also be a dead car battery, trouble with the ignition system, or a fault in the fuel system.
Engine Control Module (ECM) Location
The location of the engine control module depends on the vehicle you are driving. However, it’s almost always easy to access.
You might find the ECM in the engine compartment. However, some vehicles have it under the dashboard, under the driver’s seat or behind the glove compartment. Check your vehicle’s service manual to find the precise location.
The Function of the Engine Control Module
The ECM is also known as the engine control unit. It is by far one of the most essential components found in modern vehicles. It serves as the primary computer for the engine’s performance and drivability.
The ECM takes data from the various sensors on the vehicle and calculates what the engine needs to do. It analyzes aspects such as fuel delivery, engine spark, and air ratios.
Because all of the operations of the vehicle are controlled by the ECM, it can cause a lot of problems when it malfunctions. In extreme cases, the vehicle can become impossible to drive.
RELATED: 5 Symptoms of a Bad Engine Control Unit (ECU)
The average engine control module replacement cost is between $500 and $1000 on most car models. The ECM itself will cost about $450 to $900. That leaves $50 to $100 in labor expenses.
If you choose to change the ECM yourself, you aren’t going to save a lot of money, because the main cost is for the engine control module itself. The cost for the ECM also varies based on what type of vehicle you drive. If you have a small, compact car, you will pay a lot less than the driver of the large luxury SUV.
Before you have the ECM replaced, the shop will want to diagnose it first. This is an additional expense that could cost as little as $100 or as much as $300. You can save money if you have a code scanner on hand by checking the trouble codes on your own. However, you might need to do a little research online to figure out what the trouble codes mean.
If you want to save money, you might be tempted to purchase a used ECM. While this is tempting, it’s simply not the best solution. For one, the used ECM doesn’t usually have a warranty, so it could fail at any moment. Additionally, it will still need to be reprogrammed, which adds to the expense.
In a few cases, the shop might be able to reprogram or reconfigure your existing ECM. When this happens, the cost is much lower, since you won’t need to purchase a new engine control module.
Some engine control modules need to be programmed by the car manufacturer when replaced because of the immobilizer. You need to check this with the dealer before you try to switch it.
Categories:
Electric, Engine
Так как возможно существует взаимосвязь, начну издалека: недавно привёз с eBay новый раскладной ключ, взамен обычного старого. В начале недели, получив посылку, нарезал полотно у мастера и переставил метку с родного ключа. Всё отлично, так ездил до четверга включительно. Сегодня утром, машина не завелась.
На приборной панели остаётся гореть значок «Check engine». Бензонасос шумит, стартер не крутит, но слышно как срабатывает втягивающее реле.
Подключив VAG-COM, сразу запустил опрос систем двигателя.
Выявилась ошибка, что-то вроде того, что иммобилайзер блокирует двигатель (номер не сохранил). Сбросил ошибку, «Check engine» с приборной пропал. Попытка завести двигатель, результата не дала. Значок «Check engine» вернулся обратно.
Запустил комплексный опрос систем, итог следующий:
Address 03: ABS Brakes Labels: 1C0-907-37x-ABS.lbl
Part No: 1C0 907 379 C
Component: ABS FRONT MK60 0103
Coding: 0001025
Shop #: WSC 01317 785 002001 Fault Found:
01314 — Engine Control Module
004 — No Signal/Communication — Intermittent
——————————————————————————-
Address 19: CAN Gateway Labels: 6N0-909-901-19.lbl
Part No: 6N0 909 901
Component: Gateway K<->CAN 0001
Coding: 00006
Shop #: WSC 013171 Fault Found:
01314 — Engine Control Module
49-10 — No Communications — Intermittent
Диагностическая программа указывает на ошибку Блока Управления Двигателя.
Сайт ross-tech.com, подсказывает следующие ответы по поводу данной ошибки:
01314 — Engine Control Module
01314 — Engine Control Module: No Communications
Possible Causes
CAN-Databus Wiring/Connectors from/to Engine Control Module faulty
Fault(s) stored in Engine Control Module
Engine Control Module recently flashed or re-mapped
Possible Solutions
Check CAN-Databus Wiring/Connectors from/to Engine Control Module
Check Measuring Value Blocks (MVB)
Usually Measuring Value Blocks (MVB) 125+ show the current Communication Status
Возможно кто-то сталкивался с подобным?
P.S. Пробывал переводить сигнализацию в режим Valet. Без изменений.