I am new to Python and I am facing problem in creating the Dataframe in the format of key and value i.e.
data = [{'key':'\[GlobalProgramSizeInThousands\]','value':'1000'},]
Here is my code:
columnsss = ['key','value'];
query = "select * from bparst_tags where tag_type = 1 ";
result = database.cursor(db.cursors.DictCursor);
result.execute(query);
result_set = result.fetchall();
data = "[";
for row in result_set:
`row["tag_expression"]`)
data += "{'value': %s , 'key': %s }," % ( `row["tag_expression"]`, `row["tag_name"]` )
data += "]" ;
df = DataFrame(data , columns=columnsss);
But when I pass the data in DataFrame it shows me
pandas.core.common.PandasError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!
while if I print the data and assign the same value to data variable then it works.
Syscall
19.4k10 gold badges37 silver badges53 bronze badges
asked Sep 1, 2014 at 10:47
1
You are providing a string representation of a dict to the DataFrame constructor, and not a dict itself. So this is the reason you get that error.
So if you want to use your code, you could do:
df = DataFrame(eval(data))
But better would be to not create the string in the first place, but directly putting it in a dict. Something roughly like:
data = []
for row in result_set:
data.append({'value': row["tag_expression"], 'key': row["tag_name"]})
But probably even this is not needed, as depending on what is exactly in your result_set you could probably:
- provide this directly to a DataFrame:
DataFrame(result_set) - or use the pandas
read_sql_queryfunction to do this for you (see docs on this)
answered Sep 1, 2014 at 11:24
jorisjoris
133k36 gold badges248 silver badges202 bronze badges
1
Just ran into the same error, but the above answer could not help me.
My code worked fine on my computer which was like this:
test_dict = {'x': '123', 'y': '456', 'z': '456'}
df=pd.DataFrame(test_dict.items(),columns=['col1','col2'])
However, it did not work on another platform. It gave me the same error as mentioned in the original question. I tried below code by simply adding the list() around the dictionary items, and it worked smoothly after:
df=pd.DataFrame(list(test_dict.items()),columns=['col1','col2'])
Hopefully, this answer can help whoever ran into a similar situation like me.
answered Mar 29, 2021 at 17:00
dayaoyaodayaoyao
1202 silver badges9 bronze badges
import json
# Opening JSON file
f = open('data.json')
# returns JSON object as
# a dictionary
data1 = json.load(f)
#converting it into dataframe
df = pd.read_json(data1, orient ='index')
answered Aug 1, 2022 at 4:56
1
Pandas module allows you to create and manipulate dataframe. You can create a pandas dataframe using the pandas.DataFrame() constructor. But many beginners may face errors like ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called! And it can be due to many factors. In this entire post, you will learn how to solve the issue of dataframe constructor not properly called error.
The main reason for getting this error is that you must be using the DataFrame() constructor in the wrong way. For example, you must be passing the data to the constructor of an invalid type.
Suppose I will pass the data of type string then I will get the constructor not properly called error.
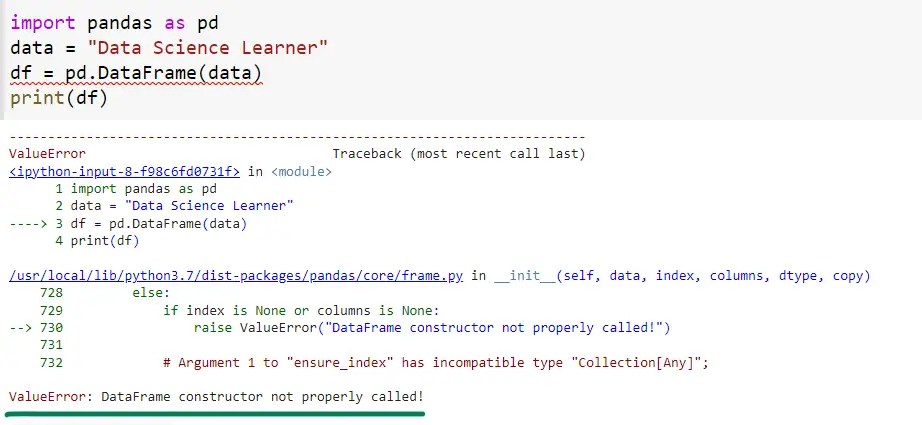
import pandas as pd
data = "Data Science Learner" #string value
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)Output
In the same way, If I will pass the integer or float will get the same error.
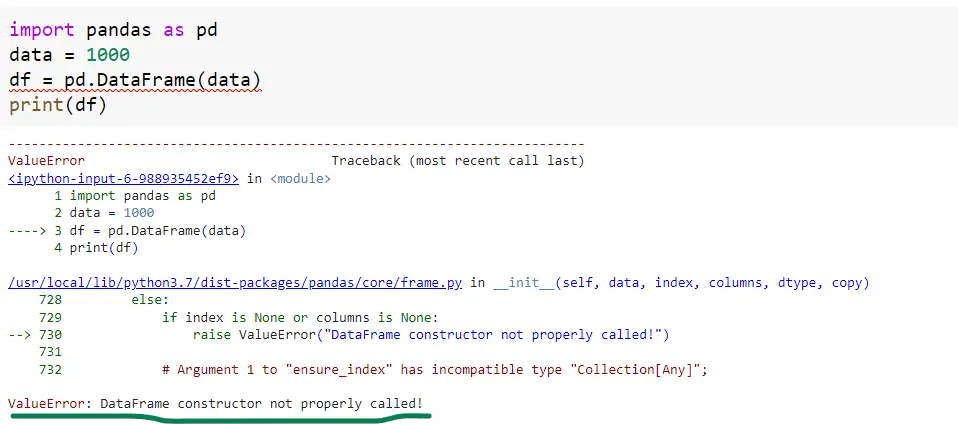
import pandas as pd
data = 1000 # integer value
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)Output
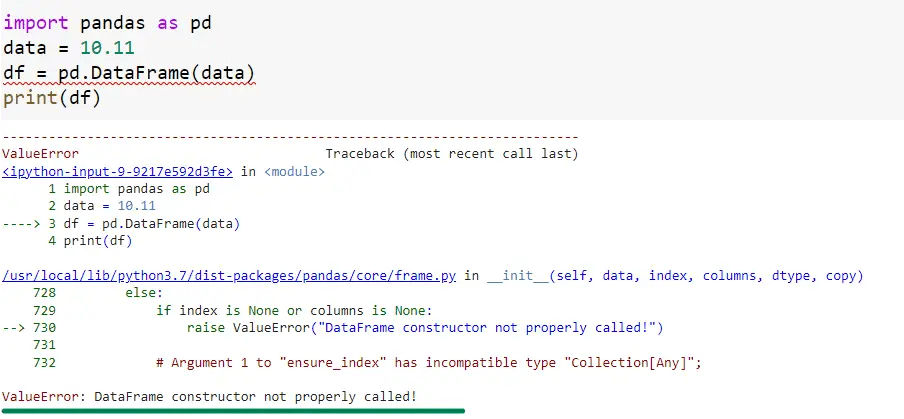
import pandas as pd
data = 10.11 # float value
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)Output
Solution for the dataframe constructor not properly called error
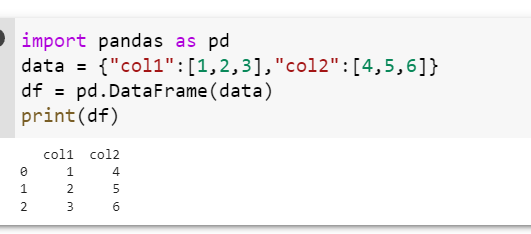
The solution for this type of error is that you have to pass the data to constructor pandas.DataFrame() in a proper way. For example you will pass the data to the constructor in the form key-value pairs like below. The number of elements for each of the column name should be the same otherwise it will lead to an error.
import pandas as pd
data = {"col1":[1,2,3],"col2":[4,5,6]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)Output
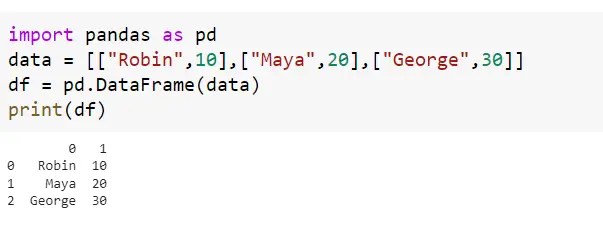
The other solution is to add the data to the pandas.DataFrame() as the list of lists. In this case, each list will act as a record or row of the dataframe.
You will not get the error when you will execute the below lines of code.
import pandas as pd
data = [["Robin",10],["Maya",20],["George",30]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)Output
Conclusion
If you are getting the error ValueError constructor not properly called! then the obvious case for getting is that you are not properly using the pandas.DataFrame() constructor. The above way of creating dataframe will solve this error.
I hope you have liked this tutorial and solved your query. In case you have any doubts then you can contact us for more help.
Join our list
Subscribe to our mailing list and get interesting stuff and updates to your email inbox.
We respect your privacy and take protecting it seriously
Thank you for signup. A Confirmation Email has been sent to your Email Address.
Something went wrong.

Contents
- Why Is the Dataframe Constructor Not Properly Called?
- – You Provided a String Representation to the Dataframe Constructor
- – You Misused the Input Types to Pandas Dataframe
- – You Used the Wrong Parameter to Pandas Dataframe
- – There Is a Mismatch Between Python and Azure-ML Libraries
- How To Fix Dataframe Constructor Not Called
- – Use a Dictionary for Pandas.dataframe
- – Provide the Right Input to the Dataframe
- – Use the Right Parameter for the DataFrame
- – Switch Python Version in Azure
- Useful Information About the Dataframe Error
- – What Is a Value Error?
- – How To Convert Json to a Dataframe?
- – How To Convert a List to a Dataframe?
- – How To Make Research About Python and Dataframe?
- – How Do You Create a Dataframe in Python?
- – How To Create a Dataframe From Another Dataframe in Pandas?
- Conclusion
The DataFrame Constructor is not called properly because: you provided a string representation to the pandas.DataFrame Constructor, you misused the input types to Pandas Dataframe, you used the wrong parameter to Pandas DataFrame, or there is a mismatch between Python and azure-ml libraries.
Let’s take a closer look at these possible reasons.
– You Provided a String Representation to the Dataframe Constructor
The DataFrame constructor requires that its input be an iterable, a dictionary, or another DataFrame. Failure to adhere to any of the requirements will lead to a ValueError. That’s because the string that you’ve provided can not work with pandas.DataFrame.
In the sample code below, we’ve violated the requirements for the pandas.DataFrame, so the code will result in a ValueError.
dataframe_test = DataFrame(index = idx, data=(myData))
– You Misused the Input Types to Pandas Dataframe
Pandas clearly define the input types that you must use, but it’s easy to think that it’ll do otherwise. Which raises the question: What if I supply a number instead of what Pandas require? Well, things won’t go as planned, and you’ll get the ValueError that the Constructor was not called properly.
For example, in the code below, we’ve supplied a number to Pandas. Therefore, any usage of the code will lead to a ValueError.
import pandas as p_d
p_d.DataFrame(5000)
Furthermore, in the example below, we used a string in the DataFrame, so we get the same ValueError.
data_frame = p_d.DataFrame(‘Email’)
– You Used the Wrong Parameter to Pandas Dataframe
When you are working with images in Pandas, you can see the ValueError about the Constructor. Meanwhile, if your code is a lot, it can be tough to know how to fix the error. We present an example in the next code.
In the code below, we’ve used the result of a calculation as the value of pandas.DataFrame. As a result, the code will result in an error.
def detect_Image(self):
img = self.aux4
(_, contours, _) = cv.findContours(img, cv.RETR_EXTERNAL,
cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
c = [cv.minEnclosingCircle(cnt) for cnt in contours]
print (‘Circles: ‘, len(c), ‘Type: ‘,
type(c))
for i in range(len(c)):
r = ci
a = pi * (r * r)
a = a * self.Scal
self.res = pd.dataframe(a)
print self.res
– There Is a Mismatch Between Python and Azure-ML Libraries
You can run into an error with pandas in a Python script when doing machine learning with Microsoft Azure. This error will happen if you are running Python 2.7.7 (sklearn v.0.15.1). As a result, it’ll return a non-zero exit code.
How To Fix Dataframe Constructor Not Called
You can fix the pandas.DataFrame not called by using a Dictionary for pandas.Dataframe, providing the right input to the DataFrame, using the right parameter for the DataFrame, or switching Python version in Azure.
In this section, we’ll be going more in-depth regarding the steps you can take to solve this error.
– Use a Dictionary for Pandas.dataframe
Using a dictionary for pandas.DataFrame will prevent the Constructor not called error. In Python, you use a convert string to dataframe Python code. This will allow you to use a dataframe in pandas.DataFrame. Another option is to create dataframe to use with Python Pandas.
In the example below, we’ve made corrections to the code. The corrections will prevent the ValueError.
import ast
myData = [“-35054”, “2018-09-15T09:09:23.340Z”, “2018-09-15T09:09:23.340Z”]
# convert string to a dict
dict = ast.literal_eval(myData)
# Use as input to the dataframe
df_test2 = DataFrame(index = idx, data=(dict))
– Provide the Right Input to the Dataframe
The right input to DataFrame will prevent the ValueError about the Constructor. In the code below, we modified a previous example. Only this time, the DataFrame has the correct input.
data_frame = p_d.DataFrame(columns=[‘Email’])
In PySpark, the right input will prevent valueerror: dataframe constructor not properly called! pyspark error. Also, this applies in Plotyl express, as it eliminates the valueerror dataframe constructor not properly called plotly express error. What’s more, in Scikit, you’ll get the following error code if you are using the wrong method to create a DataFrame:
in init raise valueerror dataframe constructor not properly called
– Use the Right Parameter for the DataFrame
Using the right parameter for the DataFrame will eliminate the error that will occur with DataFrame. Earlier in this article, we showed you an example of a code that does some image processing. However, the code resulted in an error stating that the Constructor was not called properly.
In the code below, we’ve made corrections that will prevent the error.
def detect_Image(self):
img = self.aux4
(_, contours, _) = cv.findContours(img, cv.RETR_EXTERNAL,
cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
c = [cv.minEnclosingCircle(cnt) for cnt in contours]
print(f”Circles: {len(circles)}, Type: {type(circles)}”)
areas_gen = (pi * (r * r) * self.Scal for _, radius in circles)
self.res = pd.dataframe({“Area”: areas_generated})
print(self.res)
From the code above, we’ve used a Python dictionary to eliminate the error. However, in some situations, you might use a list to solve this error. So you need to be wary of the error code that reads valueerror: if using all scalar values, you must pass an index, as this error means that you must use an index when using scalar values.
The following is an example of what we are talking about:
a = 2
b = 3
data_frame = pd.DataFrame({‘X’: x, ‘Y’: y}, index=[0])
However, the following line will produce a DataFrame error:
data_frame = pd.DataFrame({‘X’:y,’Y’:y}
– Switch Python Version in Azure
You get the Pandas error when you switch the python version in Azure. You can switch the Python version in an Execute Python Script module. All you have to do is select the Python Script, and a drop-down menu will appear on the right-hand side of the page. Choose another Python version.
Useful Information About the Dataframe Error
In this section, we’ll discuss additional relevant information that will help you understand why this error occurred in the first place. We’ll make it an interactive section, so we’ll pose some commonly-asked questions and we’ll give you the answers as well.
– What Is a Value Error?
A ValueError is an exception that Python raises when you supply an invalid value to a function. However, the value is a valid function. This definition best explains the reason why the DataFrame throws an error when you provide it with a string, because it expected a dictionary.
– How To Convert Json to a Dataframe?
You can convert JSON to DataFrame by using the read_json() function available in Pandas. However, when you are working with a nested JSON, you can use the json_normalize() function.
– How To Convert a List to a Dataframe?
You can convert a list to DataFrame by using a list with index and column names, using zip() function, creating from the multidimensional list, using a multidimensional list with column name, or using a list in the dictionary.
– How To Make Research About Python and Dataframe?
You can make further research about Python and DataFrame by checking the web for questions tagged Python. An example of such a site is StackOverflow. The research we are talking about should be about how to prevent the ValueError in DataFrame. When you do this, you’ll be in a better position to know what to check when this error occurs.
– How Do You Create a Dataframe in Python?
You can create a DataFrame in Python by importing Pandas into your code, creating the data as lists, creating a DataFrame using Pandas.DataFrame(), and printing the results.
The code below is the implementation of these steps.
import pandas as pd
# assign data
data = {‘Name’: [‘Frank’, ‘Michael’, ‘Maddison’, ‘Tony’], ‘Age’: [34, 25, 29, 28]}
# Create a DataFrame
data_frame = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Print the data
print(data_frame)
– How To Create a Dataframe From Another Dataframe in Pandas?
The DataFrame.assign() method allows you to create a new DataFrame from another DataFrame. It does this by assigning new columns to a DataFrame, so it returns a new object that contains the original columns added to the new ones.
Conclusion
This article explained how to fix the DataFrame error when using Pandas and related libraries. What’s more, we also answered some frequent questions about the error as a whole. The following are the main points that we discussed in this guide:
- A wrong input will cause a DataFrame ValueError.
- In Azure, mismatch in Python versions can cause a DataFrame ValueError.
- The Constructor in the DataFrame expects values like a dictionary or another DataFrame.
- The DataFrame.assign() method will create a DataFrame from another DataFrame.

- Author
- Recent Posts
Your Go-To Resource for Learn & Build: CSS,JavaScript,HTML,PHP,C++ and MYSQL. Meet The Team
You are here: Home / Basics / Solved: Dataframe Constructor Not Properly Called Error in Pandas
Pandas dataframes are used to manipulate tabular data in python. While data manipulation, we sometimes need to convert data from other python objects such as lists, strings, and tuples into a dataframe. During conversion, you might get into an exception with the message ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called! This article discusses the ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called! error, its causes, and the solutions.
Table of Contents
- What Is ValueError: Dataframe Constructor Not Properly Called! Error in Python?
- When Does the ValueError: DataFrame Constructor Not Properly Called Error Occur?
- When We Pass a String as the Input to the DataFrame() Function
- We Pass a String to the DataFrame() Function
- When We Pass a Scalar Value to the DataFrame() Function
- How to Solve ValueError: DataFrame Constructor Not Properly Called Exception in Python?
- Use the columns Parameter to Assign Column Names to the Dataframe
- Pass a List of Strings as Input to the DataFrame() Function
- Convert Strings Into Python Objects Before Passing Them to the DataFrame() Function
- Conclusion
What Is ValueError: Dataframe Constructor Not Properly Called! Error in Python?
As the message suggests the error “ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called! ” is a python ValueError exception. It means that the error occurs when we pass an incompatible value as input to the DataFrame() function. This may happen in the following cases.
- We pass a string as the input to the
DataFrame()function. - When we pass a string representation of a list instead of a list to the
DataFrame()function. - We pass a JSON string directly to the
DataFrame()function. - When we pass a string representation of a python dictionary instead of a dictionary to the
DataFrame()function. - We pass other scalar values such as integers or floating point numbers to the
DataFrame()function.
When Does the ValueError: DataFrame Constructor Not Properly Called Error Occur?
As introduced above the exception occurs in five cases. Let us discuss each of them one by one.
When We Pass a String as the Input to the DataFrame() Function
In most instances, ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called error occurs when we try to create an empty dataframe with a given column name. When we pass the column name directly to the DataFrame() function, the program runs into the ValueError exception. You can observe this in the following example.
import pandas as pd
columnName="Column1"
print("The column name is:")
print(columnName)
df=pd.DataFrame(columnName)
print("The dataframe is:")
print(df)Output:
The column name is:
Column1
ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!In this example, we tried to create an empty dataframe with the column name Column1. As we passed the column name directly to the DataFrame() function, the program runs into ValueError exception.
We Pass a String to the DataFrame() Function
We often create a dataframe from a list in python. You might think that you can also create a dataframe of characters in the string by passing the string to the DataFrame() function as an input argument. However, the program runs into the ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called! Exception.
You can observe this in the following example.
import pandas as pd
myStr="PFB"
print("The string is:")
print(myStr)
df=pd.DataFrame(myStr)
print("The dataframe is:")
print(df)Output:
The string is:
PFB
ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!In this example, we passed the string "PFB" to the DataFrame() function to create a dataframe. Due to this, the program runs into ValueError Exception.
When we pass a string representation of a list to the DataFrame() function, the program runs into ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called exception as shown below.
import pandas as pd
listStr='[1,22,333,4444,55555]'
print("The list string is:")
print(listStr)
df=pd.DataFrame(listStr)
print("The dataframe is:")
print(df)Output:
The list string is:
[1,22,333,4444,55555]
ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!In the above example, we passed a string "[1,22,333,4444,55555]" to the DataFrame() function. Due to this, the program runs into ValueError exception.
In a similar manner, when we pass a string representation of a dictionary to the DataFrame() function, the program runs into a ValueError exception as shown in the following example.
import pandas as pd
dictStr='{"Roll":1,"Maths":100, "Physics":80, "Chemistry": 90}'
print("The dictionary string is:")
print(dictStr)
df=pd.DataFrame(dictStr)
print("The dataframe is:")
print(df)Output:
The dictionary string is:
{"Roll":1,"Maths":100, "Physics":80, "Chemistry": 90}
ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!In some cases, we might also directly try to convert a JSON string into a pandas dataframe using the DataFrame() function. In these cases, the program will run into errors as shown below.
import pandas as pd
jsonStr='{"Roll":1,"Maths":100, "Physics":80, "Chemistry": 90}'
print("The json string is:")
print(jsonStr)
df=pd.DataFrame(jsonStr)
print("The dataframe is:")
print(df)Output:
The json string is:
{"Roll":1,"Maths":100, "Physics":80, "Chemistry": 90}
ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!When We Pass a Scalar Value to the DataFrame() Function
We can create a dataframe from an iterable object such as a list, tuple, set, or dictionary. However, when we pass an object of primitive data types such as integer or floating point number as input to the DataFrame() function, the program runs into the ValueError exception with the message ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!.
You can observe this in the following example.
import pandas as pd
myInt=1117
print("The integer is:")
print(myInt)
df=pd.DataFrame(myInt)
print("The dataframe is:")
print(df)Output:
The integer is:
1117
ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!In this example, we passed the integer 1117 to the DataFrame() function. Due to this, the program runs into ValueError exception.
How to Solve ValueError: DataFrame Constructor Not Properly Called Exception in Python?
In accordance with the reasons of the error, we can solve the ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called exception using various ways.
Use the columns Parameter to Assign Column Names to the Dataframe
The first way to solve the ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called exception in Python is to not pass a string directly to the DataFrame() constructor. If you are trying to create a dataframe with a given column name as a string, use the columns parameter in the constructor as shown below.
import pandas as pd
columnName="Column1"
print("The column name is:")
print(columnName)
df=pd.DataFrame(columns=[columnName])
print("The dataframe is:")
print(df)Output:
The column name is:
Column1
The dataframe is:
Empty DataFrame
Columns: [Column1]
Index: []In this example, we passed the string "Column1" to the columns parameter after putting it in a list. Due to this, the program executes successfully and we get an empty dataframe with the given column name.
Pass a List of Strings as Input to the DataFrame() Function
If you want to create a dataframe from the characters of the list. You can first convert the string to a list of characters. Then, you can pass the list as input to the DataFrame() constructor to avoid the ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called exception in Python. You can observe this in the following example.
import pandas as pd
myStr="PFB"
print("The string is:")
print(myStr)
df=pd.DataFrame(list(myStr))
print("The dataframe is:")
print(df)Output:
The string is:
PFB
The dataframe is:
0
0 P
1 F
2 BIn this example, we first created a list of characters using the string "PFB" and the list() function. Then, we passed the list of characters to the the DataFrame() function to create the output dataframe.
If you want to put the string as an element of the data frame, you can put the string in a list and then pass the list to the DataFrame() function as shown below.
import pandas as pd
myStr="PFB"
print("The string is:")
print(myStr)
df=pd.DataFrame([myStr])
print("The dataframe is:")
print(df)Output:
The string is:
PFB
The dataframe is:
0
0 PFBConvert Strings Into Python Objects Before Passing Them to the DataFrame() Function
If you want to convert a JSON string to a dataframe, first convert the json string to a python dictionary. Then, you can pass the dictionary to the DataFrame() function as shown below.
import pandas as pd
import json
jsonStr='{"Roll":1,"Maths":100, "Physics":80, "Chemistry": 90}'
print("The json string is:")
print(jsonStr)
myDict=json.loads(jsonStr)
df=pd.DataFrame([myDict])
print("The dataframe is:")
print(df)Output:
The json string is:
{"Roll":1,"Maths":100, "Physics":80, "Chemistry": 90}
The dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
0 1 100 80 90If you have a string representation of a list or dictionary and you want to convert it into a dataframe, first convert the string into a list or dictionary. For this, you can use the eval() method. The eval() method takes the string representation of the list or dictionary and converts them into a python list or dictionary respectively. After this, you can use the list to create a dataframe as shown below.
import pandas as pd
dictStr='{"Roll":1,"Maths":100, "Physics":80, "Chemistry": 90}'
print("The dictionary string is:")
print(dictStr)
myDict=eval(dictStr)
df=pd.DataFrame([myDict])
print("The dataframe is:")
print(df)Output:
The dictionary string is:
{"Roll":1,"Maths":100, "Physics":80, "Chemistry": 90}
The dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
0 1 100 80 90Conclusion
In this article, we discussed the ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called exception in Python. We also discussed the possible cause and solutions for this error. To learn more about python programming, you can read this article on how to overwrite a file in python. You might also like this article on CPython vs Python.
I hope you enjoyed reading this article. Stay tuned for more informative articles!
Happy Learning!
Recommended Python Training
Course: Python 3 For Beginners
Over 15 hours of video content with guided instruction for beginners. Learn how to create real world applications and master the basics.
Last updated on
In this tutorial, we’ll take a look at the Pandas error:
ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!
First, we’ll create examples of how to produce it.
Next, we’ll explain the reason and finally, we’ll see how to fix it.
ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called
Let’s try to create DataFrame by:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(0)
df = pd.DataFrame('a')
All of them result into error:
ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!
The same will happen if we try to create DataFrame from directly:
class k:
pass
a = k()
pd.DataFrame(a)
Reason
There are multiple reasons to get error like:
ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!
Pass single value
One reason is trying to pass single value and no index:
df = pd.DataFrame('a')
this results in:
ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!
Object to DataFrame
Sometimes we need to convert object as follows:
class k:
def __init__(self, name, ):
self.name = name
self.num = 0
a = k('test')
pd.DataFrame(a)
This is not possible and result in:
ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called!
Solution — single value
To solve error — ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called — when we pass a single value we need to use a list — add square brackets around the value. This will convert the input vector value:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(['a'])
The result is successfully created DataFrame:
| 0 | |
|---|---|
| 0 | a |
Solution — object to DataFrame
To convert object to DataFrame we can follow next steps:
class k:
def __init__(self, name, ):
self.name = name
self.num = 0
a = k('test')
To convert object «a» to DataFrame first convert it to JSON data by:
import json
print(json.dumps(a.__dict__))
the result is:
'{"name": "test", "num": 0}'
Next we convert the JSON string to dict:
json.loads(data)
result:
{'name': 'test', 'num': 0}
And finally we create DataFrame by:
pd.DataFrame.from_dict(json.loads(data), orient='index').T
the object is converted to Pandas DataFrame:
| name | num | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | test | 0 |
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed error: ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called! reasons and possible solutions.