|
Страница была создана 28.04.2022
Команда показывает статистику трафика и ошибок на определённом интерфейсе:
Switch#show interfaces имя_интерфейса
Пример вывода команды show interfaces, обратите внимание, на выделенный текст желтым цветом.
Switch#show interfaces gi0/1
GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Gigabit Ethernet, address is 001e.1478.b7b1 (bia 001e.1478.b7b1)
Description: SW-2
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit/sec, DLY 100 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s, media type is 10/100/1000BaseTX
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of «show interface» counters never
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 42164
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 781000 bits/sec, 122 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 183000 bits/sec, 65 packets/sec
75482 packets input, 104620499 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 6352 broadcasts (3951 multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
105684 input errors, 103301 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 3951 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
39937001 packets output, 2917338077 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 4 interface resets
10 unknown protocol drops
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
После того, как вы устранили вероятную ошибку, нужно сбросить счётчики, чтобы убедиться, что ошибок больше нет.
Switch#clear counters gi0/1
После сброса, повторно проверяем счетчики, как видим счетчики обнулились, в примере я выделил их жёлтым цветом.
Switch#show interfaces gi0/1
GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Gigabit Ethernet, address is 001e.1478.b7b1 (bia 001e.1478.b7b1)
Description: SW-2
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit/sec, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 1000Mb/s, media type is 10/100/1000BaseTX
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of «show interface» counters 00:00:08
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 1352000 bits/sec, 306 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 313000 bits/sec, 91 packets/sec
1274 packets input, 455165 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 199 broadcasts (118 multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 118 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
663 packets output, 312346 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 unknown protocol drops
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause outputv
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
В таблице показаны некоторые значение и описания к ним.
You can view the counters for a port on a Cisco switch using the
show interfaces command. E.g., if I want to check on whether
cyclic redundancy check (CRC) errors have been occurring on port fa0/16,
I can issue the command shown below:
Huron>show interfaces fa0/16
FastEthernet0/16 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Fast Ethernet, address is 0009.e897.d290 (bia 0009.e897.d290)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 10000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 19/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 10Mb/s, media type is 100BaseTX
input flow-control is unsupported output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input never, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 2d17h
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 24000 bits/sec, 40 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 756000 bits/sec, 64 packets/sec
46168 packets input, 4608074 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 1250 broadcasts (1161 multicast)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
121 input errors, 16 CRC, 105 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 1161 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
255151 packets output, 119141892 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 PAUSE output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Huron>
I can see that 16 CRC errors have occurred since the counters for this
port were last reset 2 days and 17 hours ago. I can tell the counters for
the port were reset that long ago from the line below that appears in
the output of the «show interface» command.
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 2d17h
I can reset the counters by entering
privileged EXEC mode by isssuing the enable command. I can
then clear the counters for just the one particular port by the command
clear counters port_designator. When you enter the
command you will be prompted to confirm that you wish the counters
on the interface to be reset. You can enter y to confirm that
you wish that action taken. E.g.:
Huron>enable
Password:
Huron#clear counters fa0/16
Clear "show interface" counters on this interface [confirm]y
Huron#show interface fa0/16
FastEthernet0/16 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Fast Ethernet, address is 0009.e897.d290 (bia 0009.e897.d290)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 10000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 10Mb/s, media type is 100BaseTX
input flow-control is unsupported output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input never, output 00:00:01, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 00:01:27
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts (0 multicast)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 0 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
80 packets output, 7161 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 PAUSE output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Huron#
In addition to resetting the error counters, the clear counters
command also resets the input and output counters.
Huron>show interfaces fa0/16 counters Port InOctets InUcastPkts InMcastPkts InBcastPkts Fa0/16 386867 1624 294 21 Port OutOctets OutUcastPkts OutMcastPkts OutBcastPkts Fa0/16 2527937 2352 671 39 Huron>enable Password: Huron#clear counters fa0/16 Clear "show interface" counters on this interface [confirm]y Huron#show interfaces fa0/16 counters Port InOctets InUcastPkts InMcastPkts InBcastPkts Fa0/16 0 0 0 0 Port OutOctets OutUcastPkts OutMcastPkts OutBcastPkts Fa0/16 192 0 3 0 Huron#
|
Страница была создана 28.04.2022
Команда показывает статистику трафика и ошибок на определённом интерфейсе:
Switch#show interfaces имя_интерфейса
Пример вывода команды show interfaces, обратите внимание, на выделенный текст желтым цветом.
Switch#show interfaces gi0/1
GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Gigabit Ethernet, address is 001e.1478.b7b1 (bia 001e.1478.b7b1)
Description: SW-2
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit/sec, DLY 100 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s, media type is 10/100/1000BaseTX
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of «show interface» counters never
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 42164
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 781000 bits/sec, 122 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 183000 bits/sec, 65 packets/sec
75482 packets input, 104620499 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 6352 broadcasts (3951 multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
105684 input errors, 103301 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 3951 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
39937001 packets output, 2917338077 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 4 interface resets
10 unknown protocol drops
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
После того, как вы устранили вероятную ошибку, нужно сбросить счётчики, чтобы убедиться, что ошибок больше нет.
Switch#clear counters gi0/1
После сброса, повторно проверяем счетчики, как видим счетчики обнулились, в примере я выделил их жёлтым цветом.
Switch#show interfaces gi0/1
GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Gigabit Ethernet, address is 001e.1478.b7b1 (bia 001e.1478.b7b1)
Description: SW-2
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit/sec, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 1000Mb/s, media type is 10/100/1000BaseTX
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of «show interface» counters 00:00:08
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 1352000 bits/sec, 306 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 313000 bits/sec, 91 packets/sec
1274 packets input, 455165 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 199 broadcasts (118 multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 118 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
663 packets output, 312346 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 unknown protocol drops
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause outputv
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
В таблице показаны некоторые значение и описания к ним.
- На главную
- Категории
- Сеть
- Сброс конфигурации порта Cisco (сброс порта cisco в default)
Часто бывает, что вам нужно сбросить порт свича или роутера после тестирования различных конфигураций к значениям по-умолчанию (сброс порта Cisco к дефолтному).
2016-08-08 08:34:05152

Чтобы не удалять построчно каждую строку конфигурации, можно применить простую команду сброса конфигурации порта к дефолтной (в привилегированном режиме) default:
#conf term
(config)#default interface fa0/0
Чтобы сбросить несколько портов к дефолтным настройкам, можно использовать команду range. Например, с первого порта по 24-й:
#conf term
(config)#default interface range fastEthernet 0/1-24
Все очень просто!

Ваш покорный слуга — компьютерщик широкого профиля: системный администратор, вебмастер, интернет-маркетолог и много чего кто. Вместе с Вами, если Вы конечно не против, разовьем из обычного блога крутой технический комплекс.
Лишь старые, занудные и бородатые администраторы до сих пор не признают веб-интерфейс, как способ конфигурирования устройств. Другое дело, что знать консольные команды, хотя бы для саморазвития — нужно. На примере управляемого Ethernet-коммутатора Raisecom ISCOM2128 мы приведем простейшие команды для диагностики.
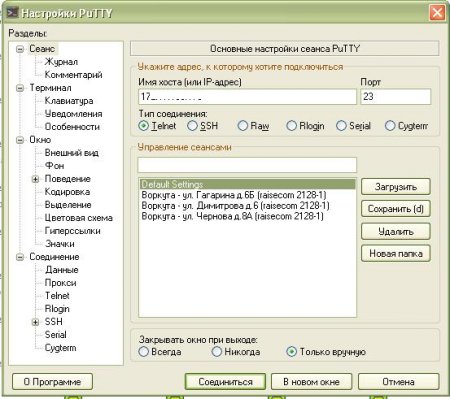
До недавнего времени (точнее до появления Powershell), комфортно работать в консоли можно было только на unix-like системах, тем более что установка на сервер CentOS 7 занимает менее часа. CentOS 7 — производная система от известного дистрибутива Red Hat Enterprise. Установка centos, в классическом её смысле, не обязательна — есть liveCD версии. Кстати, для удобства подключения через telnet к устройству можно использовать PuTTy, так как в нем можно удобно сортировать коммутаторы по адресу или по другим параметрам:
После авторизации и входа в режим настроек (команда enable) начинаем работать.
Содержание
- 1. Смотрим статус порта
- 2. Смотрим мак-адрес на порту
- 3. Смотрим статистику полученных/отправленных пакетов
- 4. Смотрим ошибки на порту
- 5. Что почитать?
1. Смотрим статус порта
sh interface port [номер порта]Результат:
sh interface port 2
R: Receive Direction
S: Send Direction
Status: Forwarding status
Port Admin Operate Speed/Duplex Flowctrl(R/S) Mac-learning Status up-sta up-sustained
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2 enable up(100M/full) auto off/off enable Forward Jan-01-2000 04:00:32 14y11m08d06h13m54s
iscom2128-1#
Расшифровка:
Operate — Статус порта
Speed / Duplex — скорость / режим передачи (full или half-duplex)
Flowctrl (R/S) — контроль потока (выключен)
Mac-learning — функция защиты атак по мак-адресу (подробнее здесь — http://www.tp-link.ua/article/?faqid=384)
Up-sustained — время, которое он активен.
2. Смотрим мак-адрес на порту
sh mac-address-table l2-address port [номер порта]Результат:
iscom2128-1#sh mac-address-table l2-address port 2
Aging time: 300 seconds
Mac Address Port Vlan Flags
--------------------------------------------------------
E427.7147.895D 2 1602 Static
9094.E4F3.AB57 2 1602 Static
iscom2128-1#
Расшифровка:
Mac Address — Маки, которые «светятся» на этом порту
Port — порт коммутатора
Vlan — Виртуальная локальная сеть, которая привязана к порту.
3. Смотрим статистику полученных/отправленных пакетов
show interface port [номер порта] statistics dynamic Результат:
#show interface port 2 statistics dynamic
Dynamic statistics period: 2 seconds
Port 2
------------------------------------------------
Input Normal Statistics:
InOctets: 2,943,231,389
InUcastPkts: 28,213,316
InMulticastPkts: 33,173
InBroadcastPkts: 63,099
Output Normal Statistics:
OutOctets: 858,223,315,985
OutUcastPkts: 47,829,671
OutMulticastPkts: 588,341,260
OutBroadcastPkts: 622,454
Bit Statistics:
Ingress Bits: 23,545,851,112
Egress Bits: 6,865,786,527,880
Speed during 2 seconds Statistics:
Ingress Speed(bps): 0
Egress Speed(bps): 1,972,216
Speed Rate during 2 seconds Statistics:
Ingress Speed Rate: <1%
Egress Speed Rate: 1%
Please press <Ctrl+C> to stop.
Dynamic statistics period: 2 seconds
Расшифровка:
In/out Octets: — общее количество входящих/исходящих октетов на интерфейс (1 октет — 1 байт)
In/out UcastPkts — входящие/исходящие юникастовые пакеты
In/out MulticastPkts — входящие/исходящие мультикастовые пакеты
In/out BroadcastPkts — входящие/исходящие броадкастовые пакеты
Ingress Bits — входящий трафик (со стороны абонента — исходящий)
Egress Bits — исходящий трафик (со стороны абонента — входящий)
Ingress Speed Rate — уровень входящей скорости (со стороны абонента — исходящая)
Egress Speed Rate — уровень исходящей скорости (со стороны абонента — входящая)
4. Смотрим ошибки на порту
show interface port [номер порта] statistics Результат:
Input Normal Statistics:
InOctets: 698,171,799
InUcastPkts: 6,770,736
InMulticastPkts: 14,711
InBroadcastPkts: 550
Input Error Statistics:
DropEvents(Pkts): 0
CRCAlignErrors(Pkts): 0
UndersizePkts: 0
OversizePkts: 0
Fragments(Pkts): 0
Jabbers(Pkts): 0
Collisions(Pkts): 0
Discards(Pkts): 23
Output Normal Statistics:
OutOctets: 267,191,770,641
OutUcastPkts: 7,057,340
OutMulticastPkts: 194,853,568
OutBroadcastPkts: 422,719
Output Error Statistics:
OutputError(Pkts): 0
OutputDiscard(Pkts): 0
Abort(Pkts): 0
Differred(Pkts): 0
LateCollisions(Pkts): 0
NoCarrier(Pkts): 0
LostCarrier(Pkts): 0
MacTransmitError(Pkts): 0
Bit Statistics:
Ingress Bits: 5,585,374,392
Egress Bits: 2,137,534,165,128Расшифровка по ошибкам
По пакетам расшифровка выше. Ошибки не отслеживаются в реальном времени (только статика)
Drop Events (Pkts): Фактическое число потерянных кадров из-за превышения максимального числа кадров
CRC Align Errors( Pkts): Количество ошибок «выравнивания» — (кадры, которые не заканчиваются четным числом октетов и имеют неверную контрольную сумму CRC), полученных на порт. Это могут быть проблемы с NIC (сетевая карта, грубо говоря), с портом на коммутаторе или с кабелем. Также из-за несоответствия дуплексных режимов. При первом подключении кабеля к порту могут возникнуть некоторые из этих ошибок. Кроме того, если к порту подключен концентратор, ошибки могут вызвать конфликты между другими устройствами концентратора.
Undersize Pkts: Такие ошибки возникают при получение фрейма размером 61-64 байта. Фрейм передается дальше, на работу не влияет
Oversize Pkts: Они возникают при получении пакета размером более 1518 байт и правильной контрольной суммой
Fragments (Pkts): Это количество принятых кадров длиной менее 64 байт (без преамбулы и начального ограничителя кадра, но включая байты FCS — контрольной суммы) и содержащих ошибки FCS или ошибки выравнивания
Jabbers (Pkts): Возникает при получении пакета размером более 1518 байт и имеющего ошибки в контрольной сумме
Collisions (Pkts): Коллизии возникают, когда две станции одновременно пытаются передать кадр данных по общей сред
Discards (Pkts): Отброшенные пакеты, поскольку их коммутация не требовалась. Это может быть нормальным, если концентратор подключен к порту и два устройства на данном концентраторе обмениваются данными. Число исходящих пакетов, которые выбраны для отбрасывания несмотря на отсутствие ошибок. Одна из возможных причин отбрасывания таких пакетов — освобождение буферного пространства.
5. Что почитать?
FTTx — http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fiber_to_the_x
SNMP — http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/SNMP
Port Security — http://xgu.ru/wiki/Port_security
Страница была создана 28.04.2022
Команда показывает статистику трафика и ошибок на определённом интерфейсе:
Switch#show interfaces имя_интерфейса
Пример вывода команды show interfaces, обратите внимание, на выделенный текст желтым цветом.
Switch#show interfaces gi0/1
GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Gigabit Ethernet, address is 001e.1478.b7b1 (bia 001e.1478.b7b1)
Description: SW-2
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit/sec, DLY 100 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s, media type is 10/100/1000BaseTX
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of «show interface» counters never
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 42164
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 781000 bits/sec, 122 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 183000 bits/sec, 65 packets/sec
75482 packets input, 104620499 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 6352 broadcasts (3951 multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
105684 input errors, 103301 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 3951 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
39937001 packets output, 2917338077 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 4 interface resets
10 unknown protocol drops
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
После того, как вы устранили вероятную ошибку, нужно сбросить счётчики, чтобы убедиться, что ошибок больше нет.
Switch#clear counters gi0/1
После сброса, повторно проверяем счетчики, как видим счетчики обнулились, в примере я выделил их жёлтым цветом.
Switch#show interfaces gi0/1
GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Gigabit Ethernet, address is 001e.1478.b7b1 (bia 001e.1478.b7b1)
Description: SW-2
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit/sec, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 1000Mb/s, media type is 10/100/1000BaseTX
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of «show interface» counters 00:00:08
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 1352000 bits/sec, 306 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 313000 bits/sec, 91 packets/sec
1274 packets input, 455165 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 199 broadcasts (118 multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 118 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
663 packets output, 312346 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 unknown protocol drops
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause outputv
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
В таблице показаны некоторые значение и описания к ним.
Introduction
This document describes the errdisabled state, how to recover from it, and provides examples of errdisable recovery. This document uses the terms errdisable and error disable interchangeably. Customers often contact Cisco Technical Support when they notice that one or more of their switch ports have become error disabled, which means that the ports have a status of errdisabled. These customers want to know why the error disablement happened and how they can restore the ports to normal.
Note: The port status of err-disabled displays in the output of the show interfaces interface_number status command.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
To create the examples in this document, you need two Cisco Catalyst 4500/6500 Series Switches (or the equivalent) in a lab environment with cleared configurations. The switches must run Cisco IOS® Software and each switch must have two Fast Ethernet ports that are capable of EtherChannel and PortFast.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
Platforms That Use Errdisable
The errdisable feature is supported on these Catalyst switches:
-
Catalyst switches that run Cisco IOS Software:
-
2900XL / 3500XL
-
2940 / 2950 / 2960 / 2970
-
3550 / 3560 / 3560-E / 3750 / 3750-E
- 3650 / 3850
-
4500 / 4503 / 4506 / 4507 / 4510 / 4500-X
-
6500 / 6503 / 6504 / 6506 / 6509
- 9200 / 9300 / 9400 / 9500
-
The way in which errdisable is implemented varies between software platforms. This document specifically focuses on errdisable for switches that run Cisco IOS Software.
Errdisable
Function of Errdisable
If the configuration shows a port to be enabled, but software on the switch detects an error situation on the port, the software shuts down that port. In other words, the port is automatically disabled by the switch operating system software because of an error condition that is encountered on the port.
When a port is error disabled, it is effectively shut down and no traffic is sent or received on that port. The port LED is set to the color orange and, when you issue the show interfaces command, the port status shows err-disabled. Here is an example of what an error-disabled port looks like from the command-line interface (CLI) of the switch:
cat6knative#show interfaces gigabitethernet 4/1 status Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type Gi4/1 err-disabled 100 full 1000 1000BaseSX
Or, if the interface has been disabled because of an error condition, you can see messages that are similar to these in both the console and the syslog:
%SPANTREE-SP-2-BLOCK_BPDUGUARD: Received BPDU on port GigabitEthernet4/1 with BPDU Guard enabled. Disabling port. %PM-SP-4-ERR_DISABLE: bpduguard error detected on Gi4/1, putting Gi4/1 in err-disable state
This example message displays when a host port receives the bridge protocol data unit (BPDU). The actual message depends on the reason for the error condition.
The error disable function serves two purposes:
-
It lets the administrator know when and where there is a port problem.
-
It eliminates the possibility that this port can cause other ports on the module (or the entire module) to fail.
Such a failure can occur when a bad port monopolizes buffers or port error messages monopolize interprocess communications on the card, which can ultimately cause serious network issues. The error disable feature helps prevent these situations.
Causes of Errdisable
This feature was first implemented in order to handle special collision situations in which the switch detected excessive or late collisions on a port. Excessive collisions occur when a frame is dropped because the switch encounters 16 collisions in a row. Late collisions occur because every device on the wire did not recognize that the wire was in use. Possible causes of these types of errors include:
-
A cable that is out of specification (either too long, the wrong type, or defective)
-
A bad network interface card (NIC) card (with physical problems or driver problems)
-
A port duplex misconfiguration
A port duplex misconfiguration is a common cause of the errors because of failures to negotiate the speed and duplex properly between two directly connected devices (for example, a NIC that connects to a switch). Only half-duplex connections can ever have collisions in a LAN. Because of the carrier sense multiple access (CSMA) nature of Ethernet, collisions are normal for half duplex, as long as the collisions do not exceed a small percentage of traffic.
There are various reasons for the interface to go into errdisable. The reason can be:
-
Duplex mismatch
-
Port channel misconfiguration
-
BPDU guard violation
-
UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD) condition
-
Late-collision detection
-
Link-flap detection
-
Security violation
-
Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP) flap
-
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) guard
-
DHCP snooping rate-limit
-
Incorrect GBIC / Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) module or cable
-
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) inspection
-
Inline power
Note: Error-disable detection is enabled for all of these reasons by default. In order to disable error-disable detection, use the no errdisable detect cause command. The show errdisable detect command displays the error-disable detection status.
Determine If Ports Are in the Errdisabled State
You can determine if your port has been error disabled if you issue the show interfaces command.
Here is an example of an active port:
cat6knative#show interfaces gigabitethernet 4/1 status
!--- Refer to show interfaces status for more information on the command.
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
Gi4/1 Connected 100 full 1000 1000BaseSX
Here is an example of the same port in the error disabled state:
cat6knative#show interfaces gigabitethernet 4/1 status
!--- Refer to show interfaces status for more information on the command.
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
Gi4/1 err-disabled 100 full 1000 1000BaseSX
Note: When a port is error disabled, the LED on the front panel that is associated with the port is set to the color orange.
Determine the Reason for the Errdisabled State (Console Messages, Syslog, and the show errdisable recovery Command)
When the switch puts a port in the error-disabled state, the switch sends a message to the console that describes why it disabled the port. The example in this section provides two sample messages that show the reason for port disablement:
-
One disablement is because of the PortFast BPDU guard feature.
-
The other disablement is because of an EtherChannel configuration problem.
Note: You can also see these messages in the syslog if you issue the show log command.
Here are the sample messages:
%SPANTREE-SP-2-BLOCK_BPDUGUARD: Received BPDU on port GigabitEthernet4/1 with BPDU Guard enabled. Disabling port. %PM-SP-4-ERR_DISABLE: bpduguard error detected on Gi4/1, putting Gi4/1 in err-disable state %SPANTREE-2-CHNMISCFG: STP loop - channel 11/1-2 is disabled in vlan 1
If you have enabled errdisable recovery, you can determine the reason for the errdisable status if you issue the show errdisable recovery command. Here is an example:
cat6knative#show errdisable recovery ErrDisable Reason Timer Status ----------------- -------------- udld Enabled bpduguard Enabled security-violatio Enabled channel-misconfig Enabled pagp-flap Enabled dtp-flap Enabled link-flap Enabled l2ptguard Enabled psecure-violation Enabled gbic-invalid Enabled dhcp-rate-limit Enabled mac-limit Enabled unicast-flood Enabled arp-inspection Enabled Timer interval: 300 seconds Interfaces that will be enabled at the next timeout: Interface Errdisable reason Time left(sec) --------- --------------------- -------------- Fa2/4 bpduguard 273
Recover a Port from Errdisabled State
This section provides examples of how you can encounter an error-disabled port and how to fix it, as well as a brief discussion of a few additional reasons that a port can become error disabled. In order to recover a port from the errdisable state, first identify and correct the root problem, and then reenable the port. If you reenable the port before you fix the root problem, the ports just become error disabled again.
Correct the Root Problem
After you discover why the ports were disabled, fix the root problem. The fix depends on what triggered the problem. There are numerous things that can trigger the shutdown. This section discusses some of the most noticeable and common causes:
-
EtherChannel misconfiguration
In order for EtherChannel to work, the ports that are involved must have consistent configurations. The ports must have the same VLAN, the same trunk mode, the same speed, the same duplex, and so on. Most of the configuration differences within a switch are caught and reported when you create the channel. If one switch is configured for EtherChannel and the other switch is not configured for EtherChannel, the spanning tree process can shut down the channeled ports on the side that is configured for EtherChannel. The on mode of EtherChannel does not send PAgP packets to negotiate with the other side before channeling; it just assumes that the other side is channeling. In addition, this example does not turn on EtherChannel for the other switch, but leaves these ports as individual, unchanneled ports. If you leave the other switch in this state for a minute or so, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the switch where the EtherChannel is turned on thinks that there is a loop. This puts the channeling ports in the errdisabled state.
In this example, a loop was detected and the ports were disabled. The output of the show etherchannel summary command shows that the Number of channel-groups in use is 0. When you look at one of the ports that are involved, you can see that the status is err-disabled:
%SPANTREE-2-CHNL_MISCFG: Detected loop due to etherchannel misconfiguration of Gi4/1 cat6knative#show etherchannel summary !--- Refer to show etherchannel for more information on the command. Flags: D - down P - in port-channel I - stand-alone s - suspended H - Hot-standby (LACP only) R - Layer3 S - Layer2 U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator u - unsuitable for bundling Number of channel-groups in use: 0 Number of aggregators: 0 Group Port-channel Protocol Ports ------+-------------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------The EtherChannel was torn down because the ports were placed in errdisable on this switch.
cat6knative#show interfaces gigabitethernet 4/1 status Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type Gi4/1 err-disabled 100 full 1000 1000BaseSX
In order to determine what the problem was, look at the error message. The message indicates that the EtherChannel encountered a spanning tree loop. As this section explains, this problem can occur when one device (the switch, in this case) has EtherChannel turned on manually with use of the on mode (as opposed to desirable) and the other connected device (the other switch, in this case) does not have EtherChannel turned on at all. One way to fix the situation is to set the channel mode to desirable on both sides of the connection, and then reenable the ports. Then, each side forms a channel only if both sides agree to channel. If they do not agree to channel, both sides continue to function as normal ports.
cat6knative(config-terminal)#interface gigabitethernet 4/1 cat6knative(config-if)#channel-group 3 mode desirable non-silent
-
Duplex mismatch
Duplex mismatches are common because of failures to autonegotiate speed and duplex properly. Unlike a half duplex device, which must wait until there are no other devices that transmit on the same LAN segment, a full-duplex device transmits whenever the device has something to send, regardless of other devices. If this transmission occurs while the half-duplex device transmits, the half-duplex device considers this either a collision (during the slot time) or a late collision (after the slot time). Because the full-duplex side never expects collisions, this side never realizes that it must retransmit that dropped packet. A low percentage rate of collisions is normal with half duplex, but is not normal with full duplex. A switch port that receives many late collisions usually indicates a duplex mismatch problem. Be sure that the ports on both sides of the cable are set to the same speed and duplex. The show interfaces interface_number command tells you the speed and duplex for Catalyst switch ports. Later versions of Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) can warn you about a duplex mismatch before the port is put in the error-disabled state.
In addition, there are settings on a NIC, such as autopolarity features, that can cause the problem. If you are in doubt, turn these settings off. If you have multiple NICs from a vendor and the NICs all appear to have the same problem, check the manufacturer website for the release notes and be sure that you have the latest drivers.
Other causes of late collisions include:
-
A bad NIC (with physical problems, not just configuration problems)
-
A bad cable
-
A cable segment that is too long
-
-
BPDU port guard
A port that uses PortFast must only connect to an end station (such as a workstation or server) and not to devices that generate spanning tree BPDUs, such as switches, or bridges and routers that bridge. If the switch receives a spanning tree BPDU on a port that has spanning tree PortFast and spanning tree BPDU guard enabled, the switch puts the port in errdisabled mode in order to guard against potential loops. PortFast assumes that a port on a switch cannot generate a physical loop. Therefore, PortFast skips the initial spanning tree checks for that port, which avoids the timeout of end stations at bootup. The network administrator must carefully implement PortFast. On ports that have PortFast enabled, BPDU guard helps ensure that the LAN stays loop-free.
This example shows how to turn on this feature. This example was chosen because creation of an error-disable situation is easy in this case:
cat6knative(config-if)#spanning-tree bpduguard enable !--- Refer to spanning-tree bpduguard for more information on the command.In this example, a Catalyst 6509 switch is connected to another switch (a 6509). The 6500 sends BPDUs every 2 seconds (with use of the default spanning tree settings). When you enable PortFast on the 6509 switch port, the BPDU guard feature watches for BPDUs that come in on this port. When a BPDU comes into the port, which means that a device that is not an end device is detected on that port, the BPDU guard feature error disables the port in order to avoid the possibility of a spanning tree loop.
cat6knative(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast enable !--- Refer to spanning-tree portfast (interface configuration mode) !--- for more information on the command. Warning: Spantree port fast start can only be enabled on ports connected to a single host. Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc. to a fast start port can cause temporary spanning tree loops. %PM-SP-4-ERR_DISABLE: bpduguard error detected on Gi4/1, putting Gi4/1 in err-disable state.In this message, the switch indicates that it received a BPDU on a PortFast-enabled port, and so the switch shuts down port Gi4/1.
cat6knative#show interfaces gigabitethernet 4/1 status Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type Gi4/1 err-disabled 100 full 1000 1000BaseSX
You need to turn off the PortFast feature because this port is a port with an improper connection. The connection is improper because PortFast is enabled, and the switch connects to another switch. Remember that PortFast is only for use on ports that connect to end stations.
cat6knative(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast disable
-
UDLD
The UDLD protocol allows devices that are connected through fiber-optic or copper Ethernet cables (for example, Category 5 cabling) to monitor the physical configuration of the cables and detect when a unidirectional link exists. When a unidirectional link is detected, UDLD shuts down the affected port and alerts the user. Unidirectional links can cause a variety of problems, which include spanning-tree topology loops.
Note: UDLD exchanges protocol packets between the neighboring devices. Both devices on the link must support UDLD and have UDLD enabled on the respective ports. If you have UDLD enabled on only one port of a link, it can also leave the end configured with UDLD to go to errdisable state.
Each switch port that is configured for UDLD sends UDLD protocol packets that contain the port device (or port ID) and the neighbor device (or port IDs) that are seen by UDLD on that port. The neighboring ports must see their own device or port ID (echo) in the packets that are received from the other side. If the port does not see its own device or port ID in the incoming UDLD packets for a specific duration of time, the link is considered unidirectional. Therefore, the respective port is disabled and a message that is similar to this is printed on the console:
PM-SP-4-ERR_DISABLE: udld error detected on Gi4/1, putting Gi4/1 in err-disable state.
For more information on UDLD operation, configuration, and commands, refer to the document Configuring UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD).
-
Link-flap error
Link flap means that the interface continually goes up and down. The interface is put into the errdisabled state if it flaps more than five times in 10 seconds. The common cause of link flap is a Layer 1 issue such as a bad cable, duplex mismatch, or bad Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) card. Look at the console messages or the messages that were sent to the syslog server that state the reason for the port shutdown.
%PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: link-flap error detected on Gi4/1, putting Gi4/1 in err-disable state
Issue this command in order to view the flap values:
cat6knative#show errdisable flap-values !--- Refer to show errdisable flap-values for more information on the command. ErrDisable Reason Flaps Time (sec) ----------------- ------ ---------- pagp-flap 3 30 dtp-flap 3 30 link-flap 5 10 -
Loopback error
A loopback error occurs when the keepalive packet is looped back to the port that sent the keepalive. The switch sends keepalives out all the interfaces by default. A device can loop the packets back to the source interface, which usually occurs because there is a logical loop in the network that the spanning tree has not blocked. The source interface receives the keepalive packet that it sent out, and the switch disables the interface (errdisable). This message occurs because the keepalive packet is looped back to the port that sent the keepalive:
%PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: loopback error detected on Gi4/1, putting Gi4/1 in err-disable state
Keepalives are sent on all interfaces by default in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1EA-based software. In Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2SE-based software and later, keepalives are not sent by default on fiber and uplink interfaces. For more information, refer to Cisco bug ID CSCea46385
(registered customers only) .
The suggested workaround is to disable keepalives and upgrade to Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2SE or later.
-
Port security violation
You can use port security with dynamically learned and static MAC addresses in order to restrict the ingress traffic of a port. In order to restrict the traffic, you can limit the MAC addresses that are allowed to send traffic into the port. In order to configure the switch port to error disable if there is a security violation, issue this command:
cat6knative(config-if)#switchport port-security violation shutdown
A security violation occurs in either of these two situations:
-
When the maximum number of secure MAC addresses is reached on a secure port and the source MAC address of the ingress traffic differs from any of the identified secure MAC addresses
In this case, port security applies the configured violation mode.
-
If traffic with a secure MAC address that is configured or learned on one secure port attempts to access another secure port in the same VLAN
In this case, port security applies the shutdown violation mode.
-
-
L2pt Guard
When the Layer 2 PDUs enter the tunnel or access port on the inbound edge switch, the switch overwrites the customer PDU-destination MAC address with a well-known Cisco proprietary multicast address (01-00-0c-cd-cd-d0). If 802.1Q tunneling is enabled, packets are also double-tagged. The outer tag is the customer metro tag and the inner tag is the customer VLAN tag. The core switches ignore the inner tags and forward the packet to all trunk ports in the same metro VLAN. The edge switches on the outbound side restore the proper Layer 2 protocol and MAC address information and forward the packets to all tunnel or access ports in the same metro VLAN. Therefore, the Layer 2 PDUs are kept intact and delivered across the service-provider infrastructure to the other side of the customer network.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/7 l2protocol-tunnel {cdp | vtp | stp}The interface goes to errdisabled state. If an encapsulated PDU (with the proprietary destination MAC address) is received from a tunnel port or access port with Layer 2 tunneling enabled, the tunnel port is shut down to prevent loops. The port also shuts down when a configured shutdown threshold for the protocol is reached. You can manually reenable the port (issue a shutdown, no shutdown command sequence) or if errdisable recovery is enabled, the operation is retried after a specified time interval.
To recover the interface from errdisable state, reenable the port with the command errdisable recovery cause l2ptguard. This command is used to configure the recovery mechanism from a Layer 2 maximum rate error so that the interface can be brought out of the disabled state and allowed to try again. You can also set the time interval. Errdisable recovery is disabled by default; when enabled, the default time interval is 300 seconds.
-
Incorrect SFP cable
Ports go into errdisable state with the %PHY-4-SFP_NOT_SUPPORTED error message when you connect Catalyst 3560 and Catalyst 3750 Switches and use an SFP Interconnect Cable.
The Cisco Catalyst 3560 SFP Interconnect Cable (CAB-SFP-50CM=) provides for a low-cost, point-to-point, Gigabit Ethernet connection between Catalyst 3560 Series Switches. The 50-centimeter (cm) cable is an alternative to the SFP transceivers to interconnect Catalyst 3560 Series Switches through their SFP ports over a short distance. All Cisco Catalyst 3560 Series Switches support the SFP Interconnect Cable.
When a Catalyst 3560 Switch is connected to a Catalyst 3750 or any other type of Catalyst switch model, you cannot use the CAB-SFP-50CM= cable. You can connect both switches with a copper cable with SFP (GLC-T) on both devices instead of a CAB-SFP-50CM= cable.
-
802.1X Security Violation
DOT1X-SP-5-SECURITY_VIOLATION: Security violation on interface GigabitEthernet4/8, New MAC address 0080.ad00.c2e4 is seen on the interface in Single host mode %PM-SP-4-ERR_DISABLE: security-violation error detected on Gi4/8, putting Gi4/8 in err-disable state
This message indicates that the port on the specified interface is configured in single-host mode. Any new host that is detected on the interface is treated as a security violation. The port has been error disabled.
Ensure that only one host is connected to the port. If you need to connect to an IP phone and a host behind it, configure Multidomain Authentication Mode on that switchport.
The Multidomain authentication (MDA) mode allows an IP phone and a single host behind the IP phone to authenticate independently, with 802.1X, MAC authentication bypass (MAB), or (for the host only) web-based authentication. In this application, Multidomain refers to two domains — data and voice — and only two MAC addresses are allowed per port. The switch can place the host in the data VLAN and the IP phone in the voice VLAN, though they appear to be on the same switch port. The data VLAN assignment can be obtained from the vendor-specific attributes (VSAs) received from the AAA server within authentication.
For more information, refer to the Multidomain Authentication Mode section of Configuring 802.1X Port-Based Authentication.
Reenable the Errdisabled Ports
After you fix the root problem, the ports are still disabled if you have not configured errdisable recovery on the switch. In this case, you must reenable the ports manually. Issue the shutdown command and then the no shutdown interface mode command on the associated interface in order to manually reenable the ports.
The errdisable recovery command allows you to choose the type of errors that automatically reenable the ports after a specified amount of time. The show errdisable recovery command shows the default error-disable recovery state for all the possible conditions.
cat6knative#show errdisable recovery ErrDisable Reason Timer Status ----------------- -------------- udld Disabled bpduguard Disabled security-violatio Disabled channel-misconfig Disabled pagp-flap Disabled dtp-flap Disabled link-flap Disabled l2ptguard Disabled psecure-violation Disabled gbic-invalid Disabled dhcp-rate-limit Disabled mac-limit Disabled unicast-flood Disabled arp-inspection Disabled Timer interval: 300 seconds Interfaces that will be enabled at the next timeout:
Note: The default timeout interval is 300 seconds and, by default, the timeout feature is disabled.
In order to turn on errdisable recovery and choose the errdisable conditions, issue this command:
cat6knative#errdisable recovery cause ?
all Enable timer to recover from all causes
arp-inspection Enable timer to recover from arp inspection error disable
state
bpduguard Enable timer to recover from BPDU Guard error disable
state
channel-misconfig Enable timer to recover from channel misconfig disable
state
dhcp-rate-limit Enable timer to recover from dhcp-rate-limit error
disable state
dtp-flap Enable timer to recover from dtp-flap error disable state
gbic-invalid Enable timer to recover from invalid GBIC error disable
state
l2ptguard Enable timer to recover from l2protocol-tunnel error
disable state
link-flap Enable timer to recover from link-flap error disable
state
mac-limit Enable timer to recover from mac limit disable state
pagp-flap Enable timer to recover from pagp-flap error disable
state
psecure-violation Enable timer to recover from psecure violation disable
state
security-violation Enable timer to recover from 802.1x violation disable
state
udld Enable timer to recover from udld error disable state
unicast-flood Enable timer to recover from unicast flood disable state
This example shows how to enable the BPDU guard errdisable recovery condition:
cat6knative(Config)#errdisable recovery cause bpduguard
A nice feature of this command is that, if you enable errdisable recovery, the command lists general reasons that the ports have been put into the error-disable state. In this example, notice that the BPDU guard feature was the reason for the shutdown of port 2/4:
cat6knative#show errdisable recovery ErrDisable Reason Timer Status ----------------- -------------- udld Disabled bpduguard Enabled security-violatio Disabled channel-misconfig Disabled pagp-flap Disabled dtp-flap Disabled link-flap Disabled l2ptguard Disabled psecure-violation Disabled gbic-invalid Disabled dhcp-rate-limit Disabled mac-limit Disabled unicast-flood Disabled arp-inspection Disabled Timer interval: 300 seconds Interfaces that will be enabled at the next timeout: Interface Errdisable reason Time left(sec) --------- --------------------- -------------- Fa2/4 bpduguard 290
If any one of the errdisable recovery conditions is enabled, the ports with this condition are reenabled after 300 seconds. You can also change this default of 300 seconds if you issue this command:
cat6knative(Config)#errdisable recovery interval timer_interval_in_seconds
This example changes the errdisable recovery interval from 300 to 400 seconds:
cat6knative(Config)#errdisable recovery interval 400
Verify
-
show version—Displays the version of the software that is used on the switch.
-
show interfaces interface interface_number status—Shows the current status of the switch port.
-
show errdisable detect—Displays the current settings of the errdisable timeout feature and, if any of the ports are currently error disabled, the reason that they are error disabled.
Troubleshoot
-
show interfaces status err-disabled—Shows which local ports are involved in the errdisabled state.
-
show etherchannel summary—Shows the current status of the EtherChannel.
-
show errdisable recovery—Shows the time period after which the interfaces are enabled for errdisable conditions.
-
show errdisable detect—Shows the reason for the errdisable status.
For more information on how to troubleshoot switchport issues, refer to Troubleshooting Switch Port and Interface Problems.
Related Information
- Interface Is in errdisable Status Troubleshooting Hardware and Common Issues on Catalyst 6500/6000 Series Switches Running Cisco IOS System Software
- Spanning Tree PortFast BPDU Guard Enhancement
- Understanding EtherChannel Inconsistency Detection
- Troubleshooting Switch Port and Interface Problems
- LAN Product Support
- LAN Switching Technology Support
- Technical Support — Cisco Systems
Introduction
This document describes the errdisabled state, how to recover from it, and provides examples of errdisable recovery. This document uses the terms errdisable and error disable interchangeably. Customers often contact Cisco Technical Support when they notice that one or more of their switch ports have become error disabled, which means that the ports have a status of errdisabled. These customers want to know why the error disablement happened and how they can restore the ports to normal.
Note: The port status of err-disabled displays in the output of the show interfaces interface_number status command.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
To create the examples in this document, you need two Cisco Catalyst 4500/6500 Series Switches (or the equivalent) in a lab environment with cleared configurations. The switches must run Cisco IOS® Software and each switch must have two Fast Ethernet ports that are capable of EtherChannel and PortFast.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
Platforms That Use Errdisable
The errdisable feature is supported on these Catalyst switches:
-
Catalyst switches that run Cisco IOS Software:
-
2900XL / 3500XL
-
2940 / 2950 / 2960 / 2970
-
3550 / 3560 / 3560-E / 3750 / 3750-E
- 3650 / 3850
-
4500 / 4503 / 4506 / 4507 / 4510 / 4500-X
-
6500 / 6503 / 6504 / 6506 / 6509
- 9200 / 9300 / 9400 / 9500
-
The way in which errdisable is implemented varies between software platforms. This document specifically focuses on errdisable for switches that run Cisco IOS Software.
Errdisable
Function of Errdisable
If the configuration shows a port to be enabled, but software on the switch detects an error situation on the port, the software shuts down that port. In other words, the port is automatically disabled by the switch operating system software because of an error condition that is encountered on the port.
When a port is error disabled, it is effectively shut down and no traffic is sent or received on that port. The port LED is set to the color orange and, when you issue the show interfaces command, the port status shows err-disabled. Here is an example of what an error-disabled port looks like from the command-line interface (CLI) of the switch:
cat6knative#show interfaces gigabitethernet 4/1 status Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type Gi4/1 err-disabled 100 full 1000 1000BaseSX
Or, if the interface has been disabled because of an error condition, you can see messages that are similar to these in both the console and the syslog:
%SPANTREE-SP-2-BLOCK_BPDUGUARD: Received BPDU on port GigabitEthernet4/1 with BPDU Guard enabled. Disabling port. %PM-SP-4-ERR_DISABLE: bpduguard error detected on Gi4/1, putting Gi4/1 in err-disable state
This example message displays when a host port receives the bridge protocol data unit (BPDU). The actual message depends on the reason for the error condition.
The error disable function serves two purposes:
-
It lets the administrator know when and where there is a port problem.
-
It eliminates the possibility that this port can cause other ports on the module (or the entire module) to fail.
Such a failure can occur when a bad port monopolizes buffers or port error messages monopolize interprocess communications on the card, which can ultimately cause serious network issues. The error disable feature helps prevent these situations.
Causes of Errdisable
This feature was first implemented in order to handle special collision situations in which the switch detected excessive or late collisions on a port. Excessive collisions occur when a frame is dropped because the switch encounters 16 collisions in a row. Late collisions occur because every device on the wire did not recognize that the wire was in use. Possible causes of these types of errors include:
-
A cable that is out of specification (either too long, the wrong type, or defective)
-
A bad network interface card (NIC) card (with physical problems or driver problems)
-
A port duplex misconfiguration
A port duplex misconfiguration is a common cause of the errors because of failures to negotiate the speed and duplex properly between two directly connected devices (for example, a NIC that connects to a switch). Only half-duplex connections can ever have collisions in a LAN. Because of the carrier sense multiple access (CSMA) nature of Ethernet, collisions are normal for half duplex, as long as the collisions do not exceed a small percentage of traffic.
There are various reasons for the interface to go into errdisable. The reason can be:
-
Duplex mismatch
-
Port channel misconfiguration
-
BPDU guard violation
-
UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD) condition
-
Late-collision detection
-
Link-flap detection
-
Security violation
-
Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP) flap
-
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) guard
-
DHCP snooping rate-limit
-
Incorrect GBIC / Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) module or cable
-
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) inspection
-
Inline power
Note: Error-disable detection is enabled for all of these reasons by default. In order to disable error-disable detection, use the no errdisable detect cause command. The show errdisable detect command displays the error-disable detection status.
Determine If Ports Are in the Errdisabled State
You can determine if your port has been error disabled if you issue the show interfaces command.
Here is an example of an active port:
cat6knative#show interfaces gigabitethernet 4/1 status
!--- Refer to show interfaces status for more information on the command.
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
Gi4/1 Connected 100 full 1000 1000BaseSX
Here is an example of the same port in the error disabled state:
cat6knative#show interfaces gigabitethernet 4/1 status
!--- Refer to show interfaces status for more information on the command.
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
Gi4/1 err-disabled 100 full 1000 1000BaseSX
Note: When a port is error disabled, the LED on the front panel that is associated with the port is set to the color orange.
Determine the Reason for the Errdisabled State (Console Messages, Syslog, and the show errdisable recovery Command)
When the switch puts a port in the error-disabled state, the switch sends a message to the console that describes why it disabled the port. The example in this section provides two sample messages that show the reason for port disablement:
-
One disablement is because of the PortFast BPDU guard feature.
-
The other disablement is because of an EtherChannel configuration problem.
Note: You can also see these messages in the syslog if you issue the show log command.
Here are the sample messages:
%SPANTREE-SP-2-BLOCK_BPDUGUARD: Received BPDU on port GigabitEthernet4/1 with BPDU Guard enabled. Disabling port. %PM-SP-4-ERR_DISABLE: bpduguard error detected on Gi4/1, putting Gi4/1 in err-disable state %SPANTREE-2-CHNMISCFG: STP loop - channel 11/1-2 is disabled in vlan 1
If you have enabled errdisable recovery, you can determine the reason for the errdisable status if you issue the show errdisable recovery command. Here is an example:
cat6knative#show errdisable recovery ErrDisable Reason Timer Status ----------------- -------------- udld Enabled bpduguard Enabled security-violatio Enabled channel-misconfig Enabled pagp-flap Enabled dtp-flap Enabled link-flap Enabled l2ptguard Enabled psecure-violation Enabled gbic-invalid Enabled dhcp-rate-limit Enabled mac-limit Enabled unicast-flood Enabled arp-inspection Enabled Timer interval: 300 seconds Interfaces that will be enabled at the next timeout: Interface Errdisable reason Time left(sec) --------- --------------------- -------------- Fa2/4 bpduguard 273
Recover a Port from Errdisabled State
This section provides examples of how you can encounter an error-disabled port and how to fix it, as well as a brief discussion of a few additional reasons that a port can become error disabled. In order to recover a port from the errdisable state, first identify and correct the root problem, and then reenable the port. If you reenable the port before you fix the root problem, the ports just become error disabled again.
Correct the Root Problem
After you discover why the ports were disabled, fix the root problem. The fix depends on what triggered the problem. There are numerous things that can trigger the shutdown. This section discusses some of the most noticeable and common causes:
-
EtherChannel misconfiguration
In order for EtherChannel to work, the ports that are involved must have consistent configurations. The ports must have the same VLAN, the same trunk mode, the same speed, the same duplex, and so on. Most of the configuration differences within a switch are caught and reported when you create the channel. If one switch is configured for EtherChannel and the other switch is not configured for EtherChannel, the spanning tree process can shut down the channeled ports on the side that is configured for EtherChannel. The on mode of EtherChannel does not send PAgP packets to negotiate with the other side before channeling; it just assumes that the other side is channeling. In addition, this example does not turn on EtherChannel for the other switch, but leaves these ports as individual, unchanneled ports. If you leave the other switch in this state for a minute or so, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the switch where the EtherChannel is turned on thinks that there is a loop. This puts the channeling ports in the errdisabled state.
In this example, a loop was detected and the ports were disabled. The output of the show etherchannel summary command shows that the Number of channel-groups in use is 0. When you look at one of the ports that are involved, you can see that the status is err-disabled:
%SPANTREE-2-CHNL_MISCFG: Detected loop due to etherchannel misconfiguration of Gi4/1 cat6knative#show etherchannel summary !--- Refer to show etherchannel for more information on the command. Flags: D - down P - in port-channel I - stand-alone s - suspended H - Hot-standby (LACP only) R - Layer3 S - Layer2 U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator u - unsuitable for bundling Number of channel-groups in use: 0 Number of aggregators: 0 Group Port-channel Protocol Ports ------+-------------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------The EtherChannel was torn down because the ports were placed in errdisable on this switch.
cat6knative#show interfaces gigabitethernet 4/1 status Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type Gi4/1 err-disabled 100 full 1000 1000BaseSX
In order to determine what the problem was, look at the error message. The message indicates that the EtherChannel encountered a spanning tree loop. As this section explains, this problem can occur when one device (the switch, in this case) has EtherChannel turned on manually with use of the on mode (as opposed to desirable) and the other connected device (the other switch, in this case) does not have EtherChannel turned on at all. One way to fix the situation is to set the channel mode to desirable on both sides of the connection, and then reenable the ports. Then, each side forms a channel only if both sides agree to channel. If they do not agree to channel, both sides continue to function as normal ports.
cat6knative(config-terminal)#interface gigabitethernet 4/1 cat6knative(config-if)#channel-group 3 mode desirable non-silent
-
Duplex mismatch
Duplex mismatches are common because of failures to autonegotiate speed and duplex properly. Unlike a half duplex device, which must wait until there are no other devices that transmit on the same LAN segment, a full-duplex device transmits whenever the device has something to send, regardless of other devices. If this transmission occurs while the half-duplex device transmits, the half-duplex device considers this either a collision (during the slot time) or a late collision (after the slot time). Because the full-duplex side never expects collisions, this side never realizes that it must retransmit that dropped packet. A low percentage rate of collisions is normal with half duplex, but is not normal with full duplex. A switch port that receives many late collisions usually indicates a duplex mismatch problem. Be sure that the ports on both sides of the cable are set to the same speed and duplex. The show interfaces interface_number command tells you the speed and duplex for Catalyst switch ports. Later versions of Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) can warn you about a duplex mismatch before the port is put in the error-disabled state.
In addition, there are settings on a NIC, such as autopolarity features, that can cause the problem. If you are in doubt, turn these settings off. If you have multiple NICs from a vendor and the NICs all appear to have the same problem, check the manufacturer website for the release notes and be sure that you have the latest drivers.
Other causes of late collisions include:
-
A bad NIC (with physical problems, not just configuration problems)
-
A bad cable
-
A cable segment that is too long
-
-
BPDU port guard
A port that uses PortFast must only connect to an end station (such as a workstation or server) and not to devices that generate spanning tree BPDUs, such as switches, or bridges and routers that bridge. If the switch receives a spanning tree BPDU on a port that has spanning tree PortFast and spanning tree BPDU guard enabled, the switch puts the port in errdisabled mode in order to guard against potential loops. PortFast assumes that a port on a switch cannot generate a physical loop. Therefore, PortFast skips the initial spanning tree checks for that port, which avoids the timeout of end stations at bootup. The network administrator must carefully implement PortFast. On ports that have PortFast enabled, BPDU guard helps ensure that the LAN stays loop-free.
This example shows how to turn on this feature. This example was chosen because creation of an error-disable situation is easy in this case:
cat6knative(config-if)#spanning-tree bpduguard enable !--- Refer to spanning-tree bpduguard for more information on the command.In this example, a Catalyst 6509 switch is connected to another switch (a 6509). The 6500 sends BPDUs every 2 seconds (with use of the default spanning tree settings). When you enable PortFast on the 6509 switch port, the BPDU guard feature watches for BPDUs that come in on this port. When a BPDU comes into the port, which means that a device that is not an end device is detected on that port, the BPDU guard feature error disables the port in order to avoid the possibility of a spanning tree loop.
cat6knative(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast enable !--- Refer to spanning-tree portfast (interface configuration mode) !--- for more information on the command. Warning: Spantree port fast start can only be enabled on ports connected to a single host. Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc. to a fast start port can cause temporary spanning tree loops. %PM-SP-4-ERR_DISABLE: bpduguard error detected on Gi4/1, putting Gi4/1 in err-disable state.In this message, the switch indicates that it received a BPDU on a PortFast-enabled port, and so the switch shuts down port Gi4/1.
cat6knative#show interfaces gigabitethernet 4/1 status Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type Gi4/1 err-disabled 100 full 1000 1000BaseSX
You need to turn off the PortFast feature because this port is a port with an improper connection. The connection is improper because PortFast is enabled, and the switch connects to another switch. Remember that PortFast is only for use on ports that connect to end stations.
cat6knative(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast disable
-
UDLD
The UDLD protocol allows devices that are connected through fiber-optic or copper Ethernet cables (for example, Category 5 cabling) to monitor the physical configuration of the cables and detect when a unidirectional link exists. When a unidirectional link is detected, UDLD shuts down the affected port and alerts the user. Unidirectional links can cause a variety of problems, which include spanning-tree topology loops.
Note: UDLD exchanges protocol packets between the neighboring devices. Both devices on the link must support UDLD and have UDLD enabled on the respective ports. If you have UDLD enabled on only one port of a link, it can also leave the end configured with UDLD to go to errdisable state.
Each switch port that is configured for UDLD sends UDLD protocol packets that contain the port device (or port ID) and the neighbor device (or port IDs) that are seen by UDLD on that port. The neighboring ports must see their own device or port ID (echo) in the packets that are received from the other side. If the port does not see its own device or port ID in the incoming UDLD packets for a specific duration of time, the link is considered unidirectional. Therefore, the respective port is disabled and a message that is similar to this is printed on the console:
PM-SP-4-ERR_DISABLE: udld error detected on Gi4/1, putting Gi4/1 in err-disable state.
For more information on UDLD operation, configuration, and commands, refer to the document Configuring UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD).
-
Link-flap error
Link flap means that the interface continually goes up and down. The interface is put into the errdisabled state if it flaps more than five times in 10 seconds. The common cause of link flap is a Layer 1 issue such as a bad cable, duplex mismatch, or bad Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) card. Look at the console messages or the messages that were sent to the syslog server that state the reason for the port shutdown.
%PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: link-flap error detected on Gi4/1, putting Gi4/1 in err-disable state
Issue this command in order to view the flap values:
cat6knative#show errdisable flap-values !--- Refer to show errdisable flap-values for more information on the command. ErrDisable Reason Flaps Time (sec) ----------------- ------ ---------- pagp-flap 3 30 dtp-flap 3 30 link-flap 5 10 -
Loopback error
A loopback error occurs when the keepalive packet is looped back to the port that sent the keepalive. The switch sends keepalives out all the interfaces by default. A device can loop the packets back to the source interface, which usually occurs because there is a logical loop in the network that the spanning tree has not blocked. The source interface receives the keepalive packet that it sent out, and the switch disables the interface (errdisable). This message occurs because the keepalive packet is looped back to the port that sent the keepalive:
%PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: loopback error detected on Gi4/1, putting Gi4/1 in err-disable state
Keepalives are sent on all interfaces by default in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1EA-based software. In Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2SE-based software and later, keepalives are not sent by default on fiber and uplink interfaces. For more information, refer to Cisco bug ID CSCea46385
(registered customers only) .
The suggested workaround is to disable keepalives and upgrade to Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2SE or later.
-
Port security violation
You can use port security with dynamically learned and static MAC addresses in order to restrict the ingress traffic of a port. In order to restrict the traffic, you can limit the MAC addresses that are allowed to send traffic into the port. In order to configure the switch port to error disable if there is a security violation, issue this command:
cat6knative(config-if)#switchport port-security violation shutdown
A security violation occurs in either of these two situations:
-
When the maximum number of secure MAC addresses is reached on a secure port and the source MAC address of the ingress traffic differs from any of the identified secure MAC addresses
In this case, port security applies the configured violation mode.
-
If traffic with a secure MAC address that is configured or learned on one secure port attempts to access another secure port in the same VLAN
In this case, port security applies the shutdown violation mode.
-
-
L2pt Guard
When the Layer 2 PDUs enter the tunnel or access port on the inbound edge switch, the switch overwrites the customer PDU-destination MAC address with a well-known Cisco proprietary multicast address (01-00-0c-cd-cd-d0). If 802.1Q tunneling is enabled, packets are also double-tagged. The outer tag is the customer metro tag and the inner tag is the customer VLAN tag. The core switches ignore the inner tags and forward the packet to all trunk ports in the same metro VLAN. The edge switches on the outbound side restore the proper Layer 2 protocol and MAC address information and forward the packets to all tunnel or access ports in the same metro VLAN. Therefore, the Layer 2 PDUs are kept intact and delivered across the service-provider infrastructure to the other side of the customer network.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/7 l2protocol-tunnel {cdp | vtp | stp}The interface goes to errdisabled state. If an encapsulated PDU (with the proprietary destination MAC address) is received from a tunnel port or access port with Layer 2 tunneling enabled, the tunnel port is shut down to prevent loops. The port also shuts down when a configured shutdown threshold for the protocol is reached. You can manually reenable the port (issue a shutdown, no shutdown command sequence) or if errdisable recovery is enabled, the operation is retried after a specified time interval.
To recover the interface from errdisable state, reenable the port with the command errdisable recovery cause l2ptguard. This command is used to configure the recovery mechanism from a Layer 2 maximum rate error so that the interface can be brought out of the disabled state and allowed to try again. You can also set the time interval. Errdisable recovery is disabled by default; when enabled, the default time interval is 300 seconds.
-
Incorrect SFP cable
Ports go into errdisable state with the %PHY-4-SFP_NOT_SUPPORTED error message when you connect Catalyst 3560 and Catalyst 3750 Switches and use an SFP Interconnect Cable.
The Cisco Catalyst 3560 SFP Interconnect Cable (CAB-SFP-50CM=) provides for a low-cost, point-to-point, Gigabit Ethernet connection between Catalyst 3560 Series Switches. The 50-centimeter (cm) cable is an alternative to the SFP transceivers to interconnect Catalyst 3560 Series Switches through their SFP ports over a short distance. All Cisco Catalyst 3560 Series Switches support the SFP Interconnect Cable.
When a Catalyst 3560 Switch is connected to a Catalyst 3750 or any other type of Catalyst switch model, you cannot use the CAB-SFP-50CM= cable. You can connect both switches with a copper cable with SFP (GLC-T) on both devices instead of a CAB-SFP-50CM= cable.
-
802.1X Security Violation
DOT1X-SP-5-SECURITY_VIOLATION: Security violation on interface GigabitEthernet4/8, New MAC address 0080.ad00.c2e4 is seen on the interface in Single host mode %PM-SP-4-ERR_DISABLE: security-violation error detected on Gi4/8, putting Gi4/8 in err-disable state
This message indicates that the port on the specified interface is configured in single-host mode. Any new host that is detected on the interface is treated as a security violation. The port has been error disabled.
Ensure that only one host is connected to the port. If you need to connect to an IP phone and a host behind it, configure Multidomain Authentication Mode on that switchport.
The Multidomain authentication (MDA) mode allows an IP phone and a single host behind the IP phone to authenticate independently, with 802.1X, MAC authentication bypass (MAB), or (for the host only) web-based authentication. In this application, Multidomain refers to two domains — data and voice — and only two MAC addresses are allowed per port. The switch can place the host in the data VLAN and the IP phone in the voice VLAN, though they appear to be on the same switch port. The data VLAN assignment can be obtained from the vendor-specific attributes (VSAs) received from the AAA server within authentication.
For more information, refer to the Multidomain Authentication Mode section of Configuring 802.1X Port-Based Authentication.
Reenable the Errdisabled Ports
After you fix the root problem, the ports are still disabled if you have not configured errdisable recovery on the switch. In this case, you must reenable the ports manually. Issue the shutdown command and then the no shutdown interface mode command on the associated interface in order to manually reenable the ports.
The errdisable recovery command allows you to choose the type of errors that automatically reenable the ports after a specified amount of time. The show errdisable recovery command shows the default error-disable recovery state for all the possible conditions.
cat6knative#show errdisable recovery ErrDisable Reason Timer Status ----------------- -------------- udld Disabled bpduguard Disabled security-violatio Disabled channel-misconfig Disabled pagp-flap Disabled dtp-flap Disabled link-flap Disabled l2ptguard Disabled psecure-violation Disabled gbic-invalid Disabled dhcp-rate-limit Disabled mac-limit Disabled unicast-flood Disabled arp-inspection Disabled Timer interval: 300 seconds Interfaces that will be enabled at the next timeout:
Note: The default timeout interval is 300 seconds and, by default, the timeout feature is disabled.
In order to turn on errdisable recovery and choose the errdisable conditions, issue this command:
cat6knative#errdisable recovery cause ?
all Enable timer to recover from all causes
arp-inspection Enable timer to recover from arp inspection error disable
state
bpduguard Enable timer to recover from BPDU Guard error disable
state
channel-misconfig Enable timer to recover from channel misconfig disable
state
dhcp-rate-limit Enable timer to recover from dhcp-rate-limit error
disable state
dtp-flap Enable timer to recover from dtp-flap error disable state
gbic-invalid Enable timer to recover from invalid GBIC error disable
state
l2ptguard Enable timer to recover from l2protocol-tunnel error
disable state
link-flap Enable timer to recover from link-flap error disable
state
mac-limit Enable timer to recover from mac limit disable state
pagp-flap Enable timer to recover from pagp-flap error disable
state
psecure-violation Enable timer to recover from psecure violation disable
state
security-violation Enable timer to recover from 802.1x violation disable
state
udld Enable timer to recover from udld error disable state
unicast-flood Enable timer to recover from unicast flood disable state
This example shows how to enable the BPDU guard errdisable recovery condition:
cat6knative(Config)#errdisable recovery cause bpduguard
A nice feature of this command is that, if you enable errdisable recovery, the command lists general reasons that the ports have been put into the error-disable state. In this example, notice that the BPDU guard feature was the reason for the shutdown of port 2/4:
cat6knative#show errdisable recovery ErrDisable Reason Timer Status ----------------- -------------- udld Disabled bpduguard Enabled security-violatio Disabled channel-misconfig Disabled pagp-flap Disabled dtp-flap Disabled link-flap Disabled l2ptguard Disabled psecure-violation Disabled gbic-invalid Disabled dhcp-rate-limit Disabled mac-limit Disabled unicast-flood Disabled arp-inspection Disabled Timer interval: 300 seconds Interfaces that will be enabled at the next timeout: Interface Errdisable reason Time left(sec) --------- --------------------- -------------- Fa2/4 bpduguard 290
If any one of the errdisable recovery conditions is enabled, the ports with this condition are reenabled after 300 seconds. You can also change this default of 300 seconds if you issue this command:
cat6knative(Config)#errdisable recovery interval timer_interval_in_seconds
This example changes the errdisable recovery interval from 300 to 400 seconds:
cat6knative(Config)#errdisable recovery interval 400
Verify
-
show version—Displays the version of the software that is used on the switch.
-
show interfaces interface interface_number status—Shows the current status of the switch port.
-
show errdisable detect—Displays the current settings of the errdisable timeout feature and, if any of the ports are currently error disabled, the reason that they are error disabled.
Troubleshoot
-
show interfaces status err-disabled—Shows which local ports are involved in the errdisabled state.
-
show etherchannel summary—Shows the current status of the EtherChannel.
-
show errdisable recovery—Shows the time period after which the interfaces are enabled for errdisable conditions.
-
show errdisable detect—Shows the reason for the errdisable status.
For more information on how to troubleshoot switchport issues, refer to Troubleshooting Switch Port and Interface Problems.
Related Information
- Interface Is in errdisable Status Troubleshooting Hardware and Common Issues on Catalyst 6500/6000 Series Switches Running Cisco IOS System Software
- Spanning Tree PortFast BPDU Guard Enhancement
- Understanding EtherChannel Inconsistency Detection
- Troubleshooting Switch Port and Interface Problems
- LAN Product Support
- LAN Switching Technology Support
- Technical Support — Cisco Systems
Страница была создана 28.04.2022
Команда показывает статистику трафика и ошибок на определённом интерфейсе:
Switch#show interfaces имя_интерфейса
Пример вывода команды show interfaces, обратите внимание, на выделенный текст желтым цветом.
Switch#show interfaces gi0/1
GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Gigabit Ethernet, address is 001e.1478.b7b1 (bia 001e.1478.b7b1)
Description: SW-2
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit/sec, DLY 100 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s, media type is 10/100/1000BaseTX
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of «show interface» counters never
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 42164
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 781000 bits/sec, 122 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 183000 bits/sec, 65 packets/sec
75482 packets input, 104620499 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 6352 broadcasts (3951 multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
105684 input errors, 103301 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 3951 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
39937001 packets output, 2917338077 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 4 interface resets
10 unknown protocol drops
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
После того, как вы устранили вероятную ошибку, нужно сбросить счётчики, чтобы убедиться, что ошибок больше нет.
Switch#clear counters gi0/1
После сброса, повторно проверяем счетчики, как видим счетчики обнулились, в примере я выделил их жёлтым цветом.
Switch#show interfaces gi0/1
GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Gigabit Ethernet, address is 001e.1478.b7b1 (bia 001e.1478.b7b1)
Description: SW-2
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit/sec, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 1000Mb/s, media type is 10/100/1000BaseTX
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of «show interface» counters 00:00:08
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 1352000 bits/sec, 306 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 313000 bits/sec, 91 packets/sec
1274 packets input, 455165 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 199 broadcasts (118 multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 118 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
663 packets output, 312346 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 unknown protocol drops
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause outputv
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
В таблице показаны некоторые значение и описания к ним.
|
You can view the counters for a port on a Cisco switch using the
show interfaces command. E.g., if I want to check on whether
cyclic redundancy check (CRC) errors have been occurring on port fa0/16,
I can issue the command shown below:
Huron>show interfaces fa0/16
FastEthernet0/16 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Fast Ethernet, address is 0009.e897.d290 (bia 0009.e897.d290)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 10000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 19/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 10Mb/s, media type is 100BaseTX
input flow-control is unsupported output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input never, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 2d17h
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 24000 bits/sec, 40 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 756000 bits/sec, 64 packets/sec
46168 packets input, 4608074 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 1250 broadcasts (1161 multicast)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
121 input errors, 16 CRC, 105 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 1161 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
255151 packets output, 119141892 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 PAUSE output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Huron>
I can see that 16 CRC errors have occurred since the counters for this
port were last reset 2 days and 17 hours ago. I can tell the counters for
the port were reset that long ago from the line below that appears in
the output of the «show interface» command.
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 2d17h
I can reset the counters by entering
privileged EXEC mode by isssuing the enable command. I can
then clear the counters for just the one particular port by the command
clear counters port_designator. When you enter the
command you will be prompted to confirm that you wish the counters
on the interface to be reset. You can enter y to confirm that
you wish that action taken. E.g.:
Huron>enable
Password:
Huron#clear counters fa0/16
Clear "show interface" counters on this interface [confirm]y
Huron#show interface fa0/16
FastEthernet0/16 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Fast Ethernet, address is 0009.e897.d290 (bia 0009.e897.d290)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 10000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 10Mb/s, media type is 100BaseTX
input flow-control is unsupported output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input never, output 00:00:01, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 00:01:27
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts (0 multicast)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 0 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
80 packets output, 7161 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 PAUSE output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Huron#
In addition to resetting the error counters, the clear counters
command also resets the input and output counters.
Huron>show interfaces fa0/16 counters Port InOctets InUcastPkts InMcastPkts InBcastPkts Fa0/16 386867 1624 294 21 Port OutOctets OutUcastPkts OutMcastPkts OutBcastPkts Fa0/16 2527937 2352 671 39 Huron>enable Password: Huron#clear counters fa0/16 Clear "show interface" counters on this interface [confirm]y Huron#show interfaces fa0/16 counters Port InOctets InUcastPkts InMcastPkts InBcastPkts Fa0/16 0 0 0 0 Port OutOctets OutUcastPkts OutMcastPkts OutBcastPkts Fa0/16 192 0 3 0 Huron#

The error disabled feature is supported on most Catalyst switches running the Cisco IOS software. Including all the following models:
- Catalyst 2940 / 2950 / 2960 / 2960S
- Catalyst 3550 / 3560 / 3560-E / 3750 / 3750-E
- Catalyst 4000 / 4500 / 4507R
- Catalyst 6000 / 6500
The Errdisable error disable feature was designed to inform the administrator when there is a port problem or error. The reasons a catalyst switch can go into Errdisable mode and shutdown a port are many and include:
-
Duplex Mismatch
-
Loopback Error
- Link Flapping (up/down)
- Port Security Violation
- Unicast Flodding
- UDLD Failure
- Broadcast Storms
- BPDU Guard
When a port is in error-disabled state, it is effectively shut down and no traffic is sent or received on that port. The port LED is set to the orange color and, when you issue the show interfaces command, the port status shows as Errdisabled.
Following is an example of what an error-disabled port looks like:
2960G# show interface gigabit0/7
GigabitEthernet0/7 is down, line protocol is down (err-disabled)
Hardware is Gigabit Ethernet, address is 001b.54aa.c107 (bia 001b.54aa.c107)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec,
reliability 234/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Auto-duplex, Auto-speed, media type is 10/100/1000BaseTX
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 18w5d, output 18w5d, output hang never
Last clearing of «show interface» counters never
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
1011 packets input, 862666 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 157 broadcasts (0 multicast)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
3021 input errors, 2 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 144 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
402154 packets output, 86290866 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 1 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 PAUSE output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
To recover a port that is in an Errdisable state, manual intervention is required, and the administrator must access the switch and configure the specific port with ‘shutdown‘ followed by the ‘no shutdown‘ command. This command sequence will enable the port again, however, if the problem persists expect to find the port in Errdisable state again soon.
Understanding and Configuring Errdisable AutoRecovery
As outlined above, there are a number of reasons a port can enter the Errdisable state. One common reason is the Port Security error, also used in our example below.
Of all the errors, Port Security is more a feature rather than an error. Port Security allows the restriction of MAC Addresses on an interface configured as a layer 2 port. This effectively prevents others connecting unwanted hubs or switches on the network. Port Security allows us to specify a single MAC Address to be connected to a specific port, thus restricting access to a specific computer.
In the case of a violation, Port Security will automatically disable the port. This is the behaviour of the default port security policy when enabling Port Security. Following is a configuration example of port security:
2960G(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/48
2960G(config-if)# switchport access vlan 2
2960G(config-if)# switchport mode access
2960G(config-if)# switchport port-security
2960G(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
Once a host is connected to the port, we can get more information on its port-security status and actions that will be taken when a violation occurs:
2960G# show port-security interface GigabitEthernet 0/48
Port Security : Enabled
Port Status : Secure-up
Violation Mode : Shutdown
Aging Time : 0 mins
Aging Type : Absolute
SecureStatic Address Aging : Disabled
Maximum MAC Addresses : 1
Total MAC Addresses : 1
Configured MAC Addresses : 0
Sticky MAC Addresses : 0
Last Source Address:Vlan : 001b.54aa.c107
Security Violation Count : 0
Note that the Violation Mode is set to Shutdown. This means that when a violation is detected, the switch will place gigabitethernet 0/48 in the err-disable shutdown state as shown below:
%PORT_SECURITY-2-PSECURE_VIOLATION: Security violation occurred, caused by MAC address 0031.f6ac.03f5 on port GigabitEthernet0/48
While it’s almost always necessary to know when a port security violation occurs there are some circumstances where autorecovery is a desirable feature, especially durng accidental violations.
The following commands enable the autorecovery feature 30 seconds after a port security violation:
2960G(config)# errdisable recovery cause psecure-violation
2960G(config)# errdisable recovery interval 30
Determine the Reason for the Errdisabled State
To view the Errdisabled reasons, and see for which reason the autorecovery feature has been enabled, use the show Errdisable recovery command:
2960G# show errdisable recovery
ErrDisable Reason Timer Status
—————— —————
udld Disabled
bpduguard Disabled
security-violatio Disabled
channel-misconfig Disabled
vmps Disabled
pagp-flap Disabled
dtp-flap Disabled
link-flap Disabled
secure-violation Enabled
sfp-config-mismat Disabled
gbic-invalid Disabled
dhcp-rate-limit Disabled
unicast-flood Disabled
storm-control Disabled
loopback Disabled
Timer interval: 30 seconds
Interfaces that will be enabled at the next timeout.
We have now confirmed that autorecovery is enabled for port-security violations. If it is required to enable the Errdisable autorecovery feature for all supported reasons, use the following command:
2960G(config)# errdisable recovery cause all
To test our configuration we forced a port security violation, causing the switch to place the offending port in the shutdown state. Notice we’ve enabled autorecovery for all Errdisable reasons and the time left to enable the interfaces placed in shutdown state by the port security violation:
2960G# show errdisable recovery
ErrDisable Reason Timer Status
—————— —————
udld Enabled
bpduguard Enabled
security-violatio Enabled
channel-misconfig Enabled
vmps Enabled
pagp-flap Enabled
dtp-flap Enabled
link-flap Enabled
psecure-violation Enabled
sfp-config-mismat Enabled
gbic-invalid Enabled
dhcp-rate-limit Enabled
unicast-flood Enabled
storm-control Enabled
loopback Enabled
Timer interval: 30 seconds
Interfaces that will be enabled at the next timeout:
Interface Errdisable reason Time left(sec)
——— —————— —————
Gi0/48 security-violation 17
Seventeen seconds later, the switch automatically recovered from the port security violation and re-enabled the interface:
%PM-4-ERR_RECOVER: Attempting to recover from secure-violation err-disable state on gigabitethernet0/48
18w4d: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthernet0/48, changed state to up
18w4d: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/48, changed state to up
Disabling The Errdisable Feature
There are cases where it might be necessary to disable the Errdisable mechanism for specific supported features in order to overcome constant interface shutdowns and auto recoveries. While the Catalyst IOS does not allow disabling all features we can still fine-tune the mechanism and selectively disable a few.
To view the Errdisable reasons monitored by the switch, use the show Errdisable detect command:
2960G# show errdisable detect
ErrDisable Reason Detection Mode
----------------- --------- ----
bpduguard Enabled port
channel-misconfig Enabled port
community-limit Enabled port
dhcp-rate-limit Enabled port
dtp-flap Enabled port
gbic-invalid Enabled portinline-power Enabled port
invalid-policy Enabled port
link-flap Enabled port
loopback Enabled port
lsgroup Enabled port
mac-limit Enabled port
pagp-flap Enabled portport-mode-failure Enabled port
secure-violation Enabled port/vlan
security-violation Enabled portsfp-config-mismatch Enabled port
small-frame Enabled port
storm-control Enabled port
udld Enabled port
vmps Enabled port
As shown, the command lists all supported Errdisable reasons. For our example, let’s assume we want to disable the inline-power Errdisable feature.
To achieve this, we simply use the following command:
2960G(config)# errdisable recovery cause all
And verify that Errdisable has been disabled for the feature:
2960G# show errdisable detectErrDisable Reason Detection Mode
----------------- --------- ----
bpduguard Enabled port
channel-misconfig Enabled port
community-limit Enabled port
dhcp-rate-limit Enabled port
dtp-flap Enabled port
gbic-invalid Enabled portinline-power Disabled port
invalid-policy Enabled port
link-flap Enabled port
loopback Enabled port
lsgroup Enabled port
mac-limit Enabled port
pagp-flap Enabled portport-mode-failure Enabled port
psecure-violation Enabled port/vlan
security-violation Enabled portsfp-config-mismatch Enabled port
small-frame Enabled port
storm-control Enabled port
udld Enabled port
vmps Enabled port
Overall, the Errdisable feature is an extremely useful tool if configured and monitored correctly. Take the necessary time to play around with the supported options of your Cisco Catalyst switch and fine-tune it to suit your network needs.
Back to Cisco Switches Section
clear l – clear z
clear lisp eid
To clear the ASA EID table, use the clear lisp eid command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear lisp eid
[
ip_address
]
Syntax Description
|
ip_address |
Removes the specified IP address from the EID table. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
9.5(2) |
We introduced this command. |
Usage Guidelines
The ASA maintains an EID table that correlates the EID and the site ID. The clear
lisp
eid
command clears EID entries in the table.
About LISP Inspection for Cluster Flow Mobility
The ASA inspects LISP traffic for location changes and then uses this information for seamless clustering operation. With
LISP integration, the ASA cluster members can inspect LISP traffic passing between the first hop router and the ETR or ITR,
and can then change the flow owner to be at the new site.
Cluster flow mobility includes several inter-related configurations:
-
(Optional) Limit inspected EIDs based on the host or server IP address—The first hop router might send EID-notify messages
for hosts or networks the ASA cluster is not involved with, so you can limit the EIDs to only those servers or networks relevant
to your cluster. For example, if the cluster is only involved with 2 sites, but LISP is running on 3 sites, you should only
include EIDs for the 2 sites involved with the cluster. See the policy-map
type
inspect
lisp , allowed-eid,
and validate-key commands. -
LISP traffic inspection—The ASA inspects LISP traffic for the EID-notify message sent between the first hop router and the
ITR or ETR. The ASA maintains an EID table that correlates the EID and the site ID. For example, you should inspect LISP traffic
with a source IP address of the first hop router and a destination address of the ITR or ETR. See the inspect
lisp command. -
Service Policy to enable flow mobility on specified traffic—You should enable flow mobility on business-critical traffic.
For example, you can limit flow mobility to only HTTPS traffic, and/or to traffic to specific servers. See the cluster
flow-mobility
lisp command. -
Site IDs—The ASA uses the site ID for each cluster unit to determine the new owner. See the site-id
command. -
Cluster-level configuration to enable flow mobility—You must also enable flow mobility at the cluster level. This on/off
toggle lets you easily enable or disable flow mobility for a particular class of traffic or applications. See the flow-mobility
lisp command.
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
allowed-eids |
Limits inspected EIDs based on IP address. |
|
clear cluster info flow-mobility counters |
Clears the flow mobility counters. |
|
clear lisp eid |
Removes EIDs from the ASA EID table. |
|
cluster flow-mobility lisp |
Enables flow mobility for the service policy. |
|
flow-mobility lisp |
Enables flow mobility for the cluster. |
|
inspect lisp |
Inspects LISP traffic. |
|
policy-map type inspect lisp |
Customizes the LISP inspection. |
|
site-id |
Sets the site ID for a cluster chassis. |
|
show asp table classify domain inspect-lisp |
Shows the ASP table for LISP inspection. |
|
show cluster info flow-mobility counters |
Shows flow mobility counters. |
|
show conn |
Shows traffic subject to LISP flow-mobility. |
|
show lisp eid |
Shows the ASA EID table. |
|
show service-policy |
Shows the service policy. |
|
validate-key |
Enters the pre-shared key to validate LISP messages. |
clear local-host (Deprecated)
To reinitalize per-client run-time states such as connection limits and embryonic limits, use
the clear
local-host command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear local-host
[
ip_address
]
[
all
]
[
zone
[
zone_name
]
]
Syntax Description
|
all |
(Optional) Clears all connections, including to-the-box traffic. Without the all keyword, only through-the-box traffic is cleared. |
|
ip_address |
(Optional) Specifies the local host IP address. |
|
zone [zone_name |
(Optional) Specifies zone connections. |
Command Default
Clears all through-the-box run-time states.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
|
9.3(2) |
The zone keyword was added. |
|
9.16(1) |
This command was deprecated. Use the clear conn address command |
Usage Guidelines
When you make security policy changes to the configuration, all new
connections use the new security policy. Existing connections continue to use the policy that was configured at the time of
the connection establishment. To ensure that all connections use the new policy, you need to disconnect the current connections
so they can reconnect using the new policy using the clear local-host command. You can alternatively use the clear conn command for more granular connection clearing, or the clear xlate command for connections that use dynamic NAT.
The clear local-host command releases the hosts from the host license limit. You can see the number of hosts that are counted toward the license
limit by entering the show local-host command.
Examples
The following example clears the run-time state and assocaited connections for the host 10.1.1.15:
ciscoasa# clear local-host 10.1.1.15
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear conn |
Terminates connections in any state. |
|
clear xlate |
Clears a dynamic NAT session, and any connections using NAT. |
|
show local-host |
Displays the network states of local hosts. |
clear logging asdm
To clear the ASDM logging buffer, use the clear logging asdm command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear logging asdm
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
|
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was changed from the clear pdm logging command to the clear asdm log command. |
Usage Guidelines
ASDM system log messages are stored in a separate buffer from the ASA system log messages. Clearing the ASDM logging buffer
only clears the ASDM system log messages; it does not clear the ASA system log messages. To view the ASDM system log messages,
use the show asdm log command.
Examples
The following example clears the ASDM logging buffer:
ciscoasa(config)# clear logging asdm
ciscoasa(config)#
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show |
Displays the contents of the ASDM logging buffer. |
clear logging buffer
To clear the log buffer, use the clear logging buffer command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear logging buffer
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
This example shows how to clear the contents of the log buffer:
ciscoasa
#
clear logging buffer
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
logging buffered |
Configures the log buffer. |
|
show logging |
Displays logging information. |
clear logging counter
To clear the logged counters and statistics, use the clear logging counter command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear logging counter
{
all
|
console
|
monitor
|
buffer
|
trap
|
asdm
|
mail
}
Syntax Description
|
counter |
Clears the counters and statistics for the specified logging destination. Specify all to clear statistics for all logging destinations. Optionally, you can specify the destination that you want to clear the |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
9.14(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
The show logging command provides statistics of messages logged for each logging category configured on the ASA. In order to clear these statistics/counters,
use the clear logging counter command.
Examples
This example shows how to clear the counters of the logged messages:
ciscoasa
#
clear logging counter all
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show logging |
Displays logging information. |
clear logging queue bufferwrap
To clear the saved log buffers (ASDM, internal, FTP, and flash), use the clear logging queue bufferwrap command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear logging queue bufferwrap
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.2(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example shows how to clear the contents of the saved log buffers:
ciscoasa
#
clear logging queue bufferwrap
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
logging buffered |
Configures the log buffer. |
|
show logging |
Displays logging information. |
clear mac-address-table
To clear dynamic MAC address table entries, use the clear mac-address-table command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear mac-address-table
[
interface_name
]
Syntax Description
|
interface_name |
(Optional) Clears the MAC address table entries for the selected interface. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
— |
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example clears the dynamic MAC address table entries:
ciscoasa# clear mac-address-table
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
arp |
Adds a static ARP entry. |
|
firewall transparent |
Sets the firewall mode to transparent. |
|
mac-address-table aging-time |
Sets the timeout for dynamic MAC address entries. |
|
mac-learn |
Disables MAC address learning. |
|
show mac-address-table |
Shows MAC address table entries. |
clear memory appcache-threshold
To clear the hit count of memory appcache-threshold, use the clear memory appcache-threshold command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear memory appcache-threshold
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behaviors or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
— |
|
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
9.10(1) |
This command was introduced. |
Usage Guidelines
Whenever the application cache threshold is hit, the counter increments by 1. The clear memory appcache-threshold command clears the hit count of memory application cache threshold and resets to 0.
Examples
The following example clears the hit count of memory appcache-threshold:
ciscoasa# clear memory appcache-threshold
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
memory appcache-threshold enable |
Enable memory appcache-threshold to restrict application cache allocations after reaching certain memory threshold |
|
show memory appcache-threshold |
Show the status and hit count of memory appcache-threshold |
clear memory delayed-free-poisoner
To clear the delayed free-memory poisoner tool queue and statistics, use the clear memory delayed-free-poisoner command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear memory delayed-free-poisoner
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behaviors or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
— |
|
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear memory delayed-free-poisoner command returns all memory held in the delayed free-memory poisoner tool queue to the system without validation and clears the related statistical counters.
Examples
The following example clears the delayed free-memory poisoner tool queue and statistics:
ciscoasa# clear memory delayed-free-poisoner
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
memory delayed-free-poisoner enable |
Enables the delayed free-memory poisoner tool. |
|
memory delayed-free-poisoner validate |
Forces validation of the delayed free-memory poisoner tool queue. |
|
show memory delayed-free-poisoner |
Displays a summary of the delayed free-memory poisoner tool queue usage. |
clear memory profile
To clear the memory buffers held by the memory profiling function, use the clear memory profile command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear memory profile
[
peak
]
Syntax Description
|
peak |
(Optional) Clears the contents of the peak memory buffer. |
Command Default
Clears the current “in use” profile buffer by default.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
— |
|
|
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear memory profile command releases the memory buffers held by the profiling function, and therefore requires that profiling stop before it
is cleared.
Examples
The following example clears the memory buffers held by the profiling function:
ciscoasa# clear memory profile
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
memory profile enable |
Enables the monitoring of memory usage (memory profiling). |
|
memory profile text |
Configures a text range of memory to profile. |
|
show memory profile |
Displays information about the memory usage (profiling) of the ASA. |
clear mfib counters
To clear MFIB router packet counters, use the clear mfib counters command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear mfib counters
[
group
[
source
]
]
Syntax Description
|
group |
(Optional) IP address of the multicast group. |
|
source |
(Optional) IP address of the multicast route source. This is a unicast IP address in four-part dotted-decimal notation. |
Command Default
When this command is used with no arguments, route counters for all routes are cleared.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example clears all MFIB router packet counters:
ciscoasa# clear mfib counters
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show |
Displays MFIB route and packet count data. |
clear module
To clear information about the SSM on the ASAs, information about the SSC on the ASA 5505, information about the SSP installed
on the ASA 5585-X, information about the IPS SSP installed on the ASA 5585-X, information about the ASA Services Module, and
system information, use the clear module command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear module
[
mod_id
|
slot
]
[
all
|
[
details
|
recover
|
log
[
console
]
]
]
Syntax Description
|
all |
(Default) Clears all SSM information. |
||
|
console |
(Optional) Clears console log information for the module. |
||
|
details |
(Optional) Clears additional information, including remote management configuration for SSMs (for example, ASA-SSM-x |
||
|
log |
(Optional) Clears log information for the module. |
||
|
mod_id |
Clears the module name used for software modules, such as IPS. |
||
|
recover |
(Optional) For SSMs, clears the settings for the hw-module module recover command.
(Optional) For an IPS module installed on the ASA 5512-X, 5515-X, 5525-X, 5545-X, or 5555-X, clears the settings for the sw-module module mod_id recover configure image image_location |
||
|
slot |
Clears the module slot number, which can be 0 or 1. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
— |
|
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
|
8.2(1) |
Support for the SSC was added. |
|
8.2(5) |
Support for the ASA 5585-X and the IPS SSP on the ASA 5585-X was added. |
|
8.4(2) |
Support for a dual SSP installation was added. |
|
8.5(1) |
Support for the ASASM was added. |
|
8.6(1) |
Support for the ASA 5512-X, 5515-X, 5525-X, 5545-X, and 5555-X was added. |
Usage Guidelines
This command clears information about the SSC, SSM, ASASM, IPS SSP, and device and built-in interfaces.
Examples
The following example clears the recovery settings for an SSM:
ciscoasa# clear module 1 recover
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
hw-module |
Recovers an SSM by loading a recovery image from a TFTP server. |
|
hw-module |
Shuts down an SSM and performs a hardware reset. |
|
hw-module |
Reloads the SSM software. |
|
hw-module |
Shuts down the SSM software in preparation for being powered off without losing configuration data. |
|
show |
Shows SSM information. |
clear nac-policy
To reset NAC policy usage statistics, use the clear nac-policy command in global configuration mode.
clear nac-policy
[
nac-policy-name
]
Syntax Description
|
nac-policy-name |
(Optional) Name of the NAC policy for which to reset usage statistics. |
Command Default
If you do not specify a name, the CLI resets the usage statistics for all NAC policies.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Global configuration |
|
|
— |
— |
|
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.0(2) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example resets the usage statistics for the NAC policy named framework1:
ciscoasa
(config)#
clear nac-policy framework1
The following example resets all NAC policy usage statistics:
ciscoasa
(config)#
clear nac-policy
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show |
Displays NAC policy usage statistics on the ASA. |
|
show |
Displays the number of IPsec, WebVPN, and NAC sessions. |
|
show |
Displays information about VPN sessions, including NAC results. |
clear nat counters
To clear NAT policy counters, use the
clear
nat
counters
command in global configuration mode.
clear nat counters
[
src_ifc
[
src_ip
[
src_mask
]
]
[
dst_ifc
[
dst_ip
[
dst_mask
]
]
]
]
Syntax Description
|
dst_ifc |
(Optional) Specifies destination interface to filter. |
|
dst_ip |
(Optional) Specifies destination IP address to filter. |
|
dst_mask |
(Optional) Specifies mask for destination IP address. |
|
src_ifc |
(Optional) Specifies source interface to filter. |
|
src_ip |
(Optional) Specifies source IP address to filter. |
|
src_mask |
(Optional) Specifies mask for source IP address. |
Command Default
This command has no default settings.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Global configuration |
|
|
|
|
|
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(4) |
This command was added. |
Examples
This example shows how to clear the NAT policy counters:
ciscoasa(config)# clear nat counters
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
nat |
Identifies addresses on one interface that are translated to mapped addresses on another interface. |
|
|
Enables or disables NAT configuration requirements. |
|
|
Displays the protocol stack counters. |
clear nve
To clear NVE source interface statistics, use the clear nve command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear nve 1
Syntax Description
|
1 |
Specifies the NVE instance, which is always 1. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
9.4(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
This command clears the parameters, status and statistics of a NVE interface, status of its carrier interface, IP address
of the carrier interface, VNIs that use this NVE as the VXLAN VTEP, and peer VTEP IP addresses associated with this NVE interface.
Examples
The following example clears the NVE interface statistics:
ciscoasa# clear nve 1
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show nve |
Shows the parameters, status and statistics of a NVE interface, status of its carrier interface (source interface), IP address |
clear object
To clear the hit counts of network-service objects, use the clear
object command in privileged EXEC mode..
clear object
[
id
object_name
|
network-service
]
Syntax Description
|
id |
(Optional) Clear the counter of the specified |
|
network-service |
(Optional.) Clear the counters of all network-service objects. This |
Command Default
Without parameters, all objects hit counts are cleared.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
9.17(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example clears the hit counts of all objects.
ciscoasa# clear object
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show |
Shows network-service objects and their hit |
clear object-group
To clear the hit counts of objects in a network object group, use the clear
object-group command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear object-group
[
object_group_name
]
Syntax Description
|
object_group_name |
The name of the object group whose counters should be cleared. If you do not specify a name, counters for all object groups are cleared. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.3(1) |
This command was added. |
|
9.17(1) |
This command was extended to work with network-service objects. |
Examples
The following example shows how to clear the network object hit count for the network object group named “Anet”:
ciscoasa# clear object-group Anet
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show object-group |
Shows object group information and hit counts. |
clear ospf
To clear OSPF process information, use the clear ospf command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear ospf
[
pid
]
{
process
counters
}
Syntax Description
|
counters |
Clears the OSPF counters. |
|
pid |
(Optional) Internally used identification parameter for an OSPF routing process; valid values are from 1 to 65535. |
|
process |
Restarts the OSPF routing process. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
|
9.0(1) |
Support for multiple context mode was added. |
Usage Guidelines
This command does not remove any part of the configuration. Use the no form of the configuration commands to clear specific commands from the configuration or use the clear configure router ospf command to remove all global OSPF commands from the configuration.
 Note |
The clear configure router ospf command does not clear OSPF commands entered in interface configuration mode. |
Examples
The following example shows how to clear the OSPF neighbor counters:
ciscoasa# clear ospf counters
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear |
Clears all global router commands from the running configuration. |
clear path-monitoring
To clear path monitoring settings on the interface, use the clear path-monitoring command.
clear path-monitoring
[
interface
name
]
Syntax Description
|
Interface |
Removes the path-monitoring settings configured on the specified interface. |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
9.18(1) |
This command was introduced. |
Examples
The following example clears the path monitoring settings on the outside1 interface:
> clear path-montoring outside1
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show path-monitoring |
Shows path-monitoring metric information. |
clear pclu
To clear PC logical update statistics, use the clear pclu command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear pclu
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example clears PC information:
ciscoasa# clear pclu
clear phone-proxy secure-phones
To clear the secure phone entries in the phone proxy database, use the clear phone-proxy secure-phones command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear phone-proxy secure-phones
[
mac_address
|
noconfirm
]
Syntax Description
|
mac_address |
Removes the IP phone from the phone proxy database with the specified MAC address. |
|
noconfirm |
Removes all the secure phone entries in the phone proxy database without prompting for confirmation. If you do not specify |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.2(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
Because secure phones always request a CTL file upon bootup, the phone proxy creates a database that marks the phone as secure.
The entries in the secure phone database are removed after a specified configured timeout (via the timeout secure-phones command). Alternatively, you can use the clear phone-proxy secure-phones command to clear the phone proxy database without waiting for the configured timeout.
Examples
The following example clears secure entries in the phone proxy database:
ciscoasa# clear phone-proxy secure-phones 001c.587a.4000
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
timeout secure-phones |
Configures the idle timeout after which the secure phone entry is removed from the phone proxy database. |
clear pim counters
To clear the PIM traffic counters, use the clear pim counters command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear pim counters
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
This command only clears the traffic counters. To clear the PIM topology table, use the clear pim topology command.
Examples
The following example clears the PIM traffic counters:
ciscoasa# clear pim counters
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear |
Forces MRIB synchronization through reset. |
|
clear |
Clears the PIM topology table. |
|
show |
Displays the PIM traffic counters. |
clear pim group-map
To delete group-to-rendezvous point (RP) mapping entries from the RP mapping cache, use the clear pim group-map command.
clear pim group-map
[
rp-address
]
Syntax Description
|
rp-address |
Rendezvous point mapping address. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
9.5(2) |
This command was introduced. |
Examples
The following example deletes group-RP mapping entries at the 23.23.23.2 RP address:
ciscoasa(config)# sh pim group-map
Group Range Proto Client Groups RP address Info
224.0.1.39/32* DM static 0 0.0.0.0
224.0.1.40/32* DM static 0 0.0.0.0
224.0.0.0/24* L-Localstatic 1 0.0.0.0
232.0.0.0/8* SSM config 0 0.0.0.0
224.0.0.0/4* SM config 0 9.9.9.9 RPF: ,0.0.0.0
224.0.0.0/4 SM BSR 0 23.23.23.2 RPF: Gi0/3,23.23.23.2
ciscoasa(config)# clear pim group-map 23.23.23.2
ciscoasa(config)# sh pim group-map
Group Range Proto Client Groups RP address Info
224.0.1.39/32* DM static 0 0.0.0.0
224.0.1.40/32* DM static 0 0.0.0.0
224.0.0.0/24* L-Localstatic 1 0.0.0.0
232.0.0.0/8* SSM config 0 0.0.0.0
224.0.0.0/4* SM config 0 9.9.9.9 RPF: ,0.0.0.0
224.0.0.0/4 SM static 0 0.0.0.0 RPF: ,0.0.0.0Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear pim counters |
Clears PIM counters and statistics. |
|
clear pim topology |
Clears the PIM topology table. |
|
clear pim counters |
Clears PIM traffic counters. |
clear pim reset
To force MRIB synchronization through reset, use the clear pim reset command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear pim reset
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
All information from the topology table is cleared, and the MRIB connection is reset. This command can be used to synchronize
states between the PIM topology table and the MRIB database.
Examples
The following example clears the topology table and resets the MRIB connection:
ciscoasa# clear pim reset
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear |
Clears PIM counters and statistics. |
|
clear |
Clears the PIM topology table. |
|
clear |
Clears PIM traffic counters. |
clear pim topology
To clear the PIM topology table, use the clear pim topology command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear pim topology
[
group
]
Syntax Description
|
group |
(Optional) Specifies the multicast group address or name to be deleted from the topology table. |
Command Default
Without the optional group argument, all entries are cleared from the topology table.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
This command clears existing PIM routes from the PIM topology table. Information obtained from the MRIB table, such as IGMP
local membership, is retained. If a multicast group is specified, only those group entries are cleared.
Examples
The following example clears the PIM topology table:
ciscoasa# clear pim topology
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear pim counters |
Clears PIM counters and statistics. |
|
clear pim reset |
Forces MRIB synchronization through reset. |
|
clear pim counters |
Clears PIM traffic counters. |
clear priority-queue statistics
To clear the priority-queue statistics counters for an interface or for all configured interfaces, use the clear priority-queue statistics command in either global configuration or privileged EXEC mode.
clear priority-queue statistics
[
interface-name
]
Syntax Description
|
interface-name |
(Optional) Specifies the name of the interface for which you want to show the best-effort and low-latency queue details. |
Command Default
If you omit the interface name, this command clears the priority-queue statistics for all configured interfaces.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
Global configuration |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example shows the use of the clear priority-queue statistics command in privileged EXEC mode to remove the priority queue statistics for the interface named “test”:
ciscoasa# clear priority-queue statistics test
ciscoasa#
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear configure priority queue |
Removes the priority-queue configuration from the named interface. |
|
priority-queue |
Configures priority queueing on an interface. |
|
show priority-queue statistics |
Shows the priority queue statistics for a specified interface or for all interfaces. |
|
show running-config priority-queue |
Shows the current priority-queue configuration on the named interface. |
clear process
To clear statistics for specified processes running on the ASA, use the clear process command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear process
[
cpu-hog
|
internals
]
Syntax Description
|
cpu-hog |
Clears CPU hogging statistics. |
|
internals |
Clears process internal statistics. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example shows how to clear CPU hogging statistics:
ciscoasa# clear process cpu-hog
ciscoasa#
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
cpu hog granular-detection |
Triggers real-time CPU hog detection information. |
|
show processes |
Displays a list of the processes that are running on the ASA. |
clear resource usage
To clear resource usage statistics, use the clear resource usage command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear resource usage
[
context
context_name
|
all
|
summary
|
system
]
[
resource
{
[
rate
]
resource_name
|
all
}
]
Syntax Description
|
context context_name |
(Multiple mode only) Specifies the context name for which you want to clear statistics. Specify all (the default) for all contexts. |
|
resource [rate ] resource_name |
Clears the usage of a specific resource. Specify all (the default) for all resources. Specify rate to clear the rate of usage of a resource. Resources that are measured by rate include conns , inspects , and syslogs . You must specify the rate keyword with these resource types. The conns resource is also measured as concurrent connections; only use the rate keyword to view the connections per second. Resources include the following types:
|
|
summary |
(Multiple mode only) Clears the combined context statistics. |
|
system |
(Multiple mode only) Clears the system-wide (global) usage statistics. |
Command Default
For multiple context mode, the default context is all , which clears resource usage for every context. For single mode, the context name is ignored and all resource statistics
are cleared.
The default resource name is all , which clears all resource types.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
— |
|
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.2(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example clears all resource usage statistics for all contexts, but not the system-wide usage statistics:
ciscoasa# clear resource usage
The following example clears the system-wide usage statistics:
ciscoasa# clear resource usage system
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
context |
Adds a security context. |
|
show resource types |
Shows a list of resource types. |
|
show resource usage |
Shows the resource usage of the ASA. |
clear route
To remove dynamically learned routes from the routing table, use the clear
route command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear route
[
management-only
]
[
ip_address
[
ip_mask
]]
Syntax Description
|
ip_address[ ip_mask] |
Specifies the destination IP address and, optionally, subnet mask of the route to be |
|
management-only |
Clears the IPv4 management routing table. If you omit this keyword, the route is removed |
Command Default
All dynamically learned routes are removed from the data interface routing table.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
9.2(1) |
This command was added. |
|
9.5(1) |
The management-only keyword was added. |
|
9.17(1) |
Starting with version 9.17, for units that are part of a high availability group or |
Usage Guidelines
Use the clear
route command to recover any missing routes. Whenever this command is
executed, all routes from global RIB are deleted. All routes (dynamic or static) are pushed to
global RIB by the respective modules (protocols).
On the other hand, when the best route is installed on the global RIB, the same is
redistributed to peers and NP table. This process runs sequentially on multiple threads. The
time taken to complete a cycle depends on the number of routes on the global RIB.
Thus, if you are using the clear
route command consecutively, ensure to follow a minimum time interval of 30
seconds and a maximum time interval of 120 seconds. If this command is executed multiple times
without following the recommended time interval, there is a chance of the distributed routes
getting deleted, resulting in losing the routes from the RIB.
Examples
The following example shows how to remove all dynamically learned routes:
ciscoasa# clear route
The following example shows how to remove dynamically learned routes for a specific address.
ciscoasa# clear route 10.118.86.3
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show route |
Displays route information. |
|
show running-config route |
Displays configured routes. |
clear service-policy
To clear operational data or statistics (if any) for enabled policies, use the clear service-policy
command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear service-policy
[
global
|
interface
intf
]
[
user-statistics
]
Syntax Description
|
global |
(Optional) Clears the statistics of the global service policy. |
|
interface intf |
(Optional) Clears the service policy statistics of a specific interface. |
|
user-statistics |
(Optional) Clears the global counters for user statistics but does not clear the per-user statistics. Per-user or per-user-group
When the accounting keyword for the user-statistics command is specified, all global counters for sent packets, received packets, and sent dropped packets are cleared. When For the ASA to collect these user statistics, you must configure a policy map to collect user statistics. See the user-statistics command in this guide. |
Command Default
By default, this command clears all the statistics for all enabled service policies.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
Some inspection engines let you selectively clear statistics. See the clear service-policy inspect commands.
Examples
The following example shows how to clear service policy statistics for the outside interface.
ciscoasa# clear service-policy interface outside
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear service-policy inspect gtp |
Clears service policy statistics for the GTP inspection engine. |
|
clear service-policy inspect radius-accounting |
Clears service policy statistics for the RADIUS accounting inspection engine. |
|
show service-policy |
Displays the service policy. |
|
show running-config service-policy |
Displays the service policies configured in the running configuration. |
|
clear configure service-policy |
Clears service policy configurations. |
|
service-policy |
Configures service policies. |
clear service-policy inspect gtp
To clear GTP inspection statistics, use the
clear
service-policy
inspect
gtp
command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear service-policy inspect gtp
{
pdp-context
{
all
|
apn
ap_name
|
imsi
IMSI_value
|
ms-addr
IP_address
|
tid
tunnel_ID
|
version
version_num
}
|
requests
[
name
|
map
name
|
version
version_num
]
|
statistics
[
gsn
IP_address
|
IP_address
]
}
Syntax Description
|
|
Clears Packet Data Protocol (PDP) or bearer context information. You can specify the contexts to clear using the following
|
|
|
Clears GTP requests. You can optionally limit the requests to clear using the following parameters:
|
|
|
Clears GTP statistics for the
You can clear the statistics for a specific endpoint by specifying the endpoint’s address on the |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
|
9.5(1) |
The following changes were made:
|
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to clear statistics from GTP inspection. Use the
show
version of this command to view the statistics.
Examples
The following example clears GTP statistics:
ciscoasa# clear service-policy inspect gtp statistics
Related Commands
|
Commands |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Enables GTP inspection. |
|
|
Displays GTP statistics. |
clear service-policy inspect m3ua
To clear M3UA inspection statistics, use the clear service-policy inspect m3ua command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear service-policy inspect m3ua
{
drops
|
endpoint
[
ip_address
]
|
session
[
[
assocID
hex_number
]
}
Syntax Description
|
drops |
Clears M3UA drop statistics. |
|
endpoint [ip_address ] |
Clears M3UA endpoint statistics. You can optionally include the IP address of an endpoint to clear only the statistics for |
|
session [assocID hex_number ] |
Clears all M3UA sessions, which are tracked if you enable strict application server process (ASP) state validation. If you want to clear a specific section, add the assocID keyword with the hexadecimal session number. Use the show service-policy inspect m3ua session command to see the current sessions and their association IDs. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
9.6(2) |
This command was added. |
|
9.7(1) |
The session keyword was added. |
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to clear statistics or sessions from M3UA inspection. Use the show version of this command to view the statistics and sessions.
Examples
The following example clears M3UA endpoint statistics:
ciscoasa# clear service-policy inspect m3ua endpoint
The following example clears a specific M3UA session:
ciscoasa(config)# show service-policy inspect m3ua session
1 in use, 1 most used
Flags: d - double exchange , s - single exchange
AssocID: c0bbe629 in Down state, idle:0:00:06, timeout:0:30:00, s
ciscoasa(config)# clear service-policy inspect m3ua session assocID c0bbe629
Related Commands
|
Commands |
Description |
|---|---|
|
inspect |
Enables M3UA inspection. |
|
show |
Displays the M3UA statistics. |
|
strict-asp-state |
Enables strict M3UA ASP state validation. |
clear service-policy inspect radius-accounting
To clear RADIUS accounting users, use the clear service-policy inspect radius-accounting command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear service-policy inspect radius-accounting users
{
all
|
ip_address
|
policy_map
}
Syntax Description
|
all |
Clears all users. |
|
ip_address |
Clears a user with this IP address. |
|
policy_map |
Clears users associated with this policy map. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.2(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example clears all RADIUS accounting users:
ciscoasa# clear service-policy inspect radius-accounting users all
clear session
To delete the contents of a configuration session or to reset its access flag, use the clear session command in global configuration mode.
clear session
session_name
{
access
|
configuration
}
Syntax Description
|
session_name |
The name of an existing configuration session. Use the show configuration session command for a list of current sessions. |
|
access |
Clears the access flag. The flag indicates that a session is being edited. Clear this flag only if you know the edit session |
|
configuration |
Clears the configuration changes made within the session without deleting the session. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Global configuration |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
9.3(2) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
Use this command in conjunction with the configure session command, which creates isolated sessions for editing ACLs and their objects.
The primary use of this command is to reset the access flag. When you open a session, the flag marks it as being edited. If
you then break your connection to the ASA without cleanly exiting the session, the flag stays set, and this can prevent you
from opening the session again. If you are certain no one is actually editing the session, you can reset the flag to regain
access.
You can also use this command to empty the session of changes without deleting the session. If you decide you no longer need
a session you created, and you do not want to commit the changes defined in the session, use the clear configuration session command to delete the session and the changes it contains.
Examples
The following example resets the access flag on my-session:
ciscoasa(config)# clear session my-session access
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear |
Deletes a configuration session and its contents. |
|
configure |
Creates or opens a session. |
|
show |
Shows the changes made in each current session. |
clear shared license
To reset shared license statistics, shared license client statistics, and shared license backup server statistics to zero,
use the clear shared license command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear shared license
[
all
|
backup
|
client
[
hostname
]
]
Syntax Description
|
all |
(Optional) Clears all statistics. This is the default setting. |
|
backup |
(Optional) Clears statistics for the backup server. |
|
client |
(Optional) Clears statistics for all participants. |
|
hostname |
(Optional) Clears statistics for a particular participant. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.2(1) |
This command was added. |
|
9.0(1) |
Support for multiple context mode was added. |
Usage Guidelines
The shared license counters include statistical data as well as error data.
Examples
The following example shows how to reset all shared license counters:
ciscoasa# clear shared license all
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
activation-key |
Enters a license activation key. |
|
clear |
Clears the shared licensing server configuration. |
|
license-server |
Identifies the shared licensing server IP address and shared secret for a participant. |
|
license-server |
Identifies the shared licensing backup server for a participant. |
|
license-server |
Identifies the backup server IP address and serial number for the main shared licensing server. |
|
license-server |
Enables a unit to be the shared licensing backup server. |
|
license-server |
Enables a unit to be the shared licensing server. |
|
license-server |
Sets the port on which the server listens for SSL connections from participants. |
|
license-server |
Sets the refresh interval provided to participants to set how often they should communicate with the server. |
|
license-server secret |
Sets the shared secret on the shared licensing server. |
|
show |
Shows the current licenses installed. |
|
show |
Shows the shared licensing server configuration. |
|
show |
Shows shared license statistics. |
|
show |
Shows license information about VPN sessions. |
clear shun
To disable all the shuns that are currently enabled and clear the shun statistics, use the clear shun command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear shun
[
statistics
]
Syntax Description
|
statistics |
(Optional) Clears the interface counters only. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example shows how to disable all the shuns that are currently enabled and clear the shun statistics:
ciscoasa(config)# clear shun
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
shun |
Enables a dynamic response to an attacking host by preventing new connections and disallowing packets from any existing connection. |
|
show shun |
Displays the shun information. |
clear snmp-server statistics
To clear SNMP server statistics (SNMP packet input and output counters), use the clear snmp-server statistics command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear snmp-server statistics
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example shows how to clear SNMP server statistics:
ciscoasa
#
clear snmp-server statistics
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear configure snmp-server |
Clears the SNMP server configuration. |
|
show snmp-server statistics |
Displays SNMP server configuration information. |
clear ssl
To clear SSL information for debugging purposes, use the clear ssl command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear ssl
{
cache
[
all
|
errors
|
mib
|
objects
}
Syntax Description
|
all |
Clears all sessions and statistics in SSL session cache. |
|
cache |
Clears expired sessions in SSL session cache. |
|
errors |
Clears ssl errors. |
|
mib |
Clears SSL MIB statistics. |
|
objects |
Clears SSL object statistics. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.4(1) |
This command was added. |
|
9.5(2) |
Support for multiple context mode was added. |
Usage Guidelines
DTLS cache is never cleared because it would impact Secure Client functionality.
Examples
The following example shows clearing ssl cache and clearing all sessions and statistics in SSL session cache.
ciscoasa# clear ssl cache
SSL session cache cleared: 2
No SSL VPNLB session cache
No SSLDEV session cache
DLTS caches are not cleared
ciscoasa# clear ssl cache all
Clearing all sessions and statistics
SSL session cache cleared: 5
No SSL VPNLB session cache
No SSLDEV session cache
DLTS caches are not clearedclear startup-config errors
To clear configuration error messages from memory, use the clear startup-config errors command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear startup-config errors
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
— |
|
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
To view configuration errors generated when the ASA loaded the startup configuration, use the show startup-config errors command.
Examples
The following example clears all configuration errors from memory:
ciscoasa# clear startup-config errors
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show startup-config errors |
Shows configuration errors generated when the ASA loaded the startup configuration. |
clear sunrpc-server active
To clear the pinholes opened by Sun RPC application inspection, use the clear sunrpc-server active command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear sunrpc-server active
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
Use the clear sunrpc-server active command to clear the pinholes opened by Sun RPC application inspection that allow service traffic, such as NFS or NIS, to
pass through the ASA.
Examples
The following example shows how to clear the SunRPC services table:
ciscoasa# clear
sunrpc-server
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear configure sunrpc-server |
Clears the Sun remote processor call services from the ASA. |
|
inspect sunrpc |
Enables or disables Sun RPC application inspection and configures the port used. |
|
show running-config sunrpc-server |
Displays information about the SunRPC services configuration. |
|
show sunrpc-server active |
Displays information about active Sun RPC services. |
clear terminal
To clear the terminal settings for the current CLI session and use the defaults, use the clear terminal command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear terminal
{
interactive
|
pager
[
[
lines
]
number
]
}
Syntax Description
|
interactive |
Clears the interactive help setting (when you enter ? at the CLI). The default is enabled. |
|
pager [[lines ] number |
Clears the setting for the number of lines in a page before the —more— prompt appears. The default is 24. |
Command Default
The default terminal behavior is:
-
interactive —Enabled
-
pager —24 lines
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example shows how to clear the pager setting:
ciscoasa# clear
terminal pager
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
terminal pager |
Sets the number of lines on a page before the “—More—” prompt appears. |
|
terminal interactive |
Enables or disables help when you enter ? at the CLI. |
clear threat-detection rate
To clear statistics when you enable basic threat detection using the threat-detection basic-threat command, use the clear threat detection rate command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear threat-detection rate
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.0(2) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example clears the rate statistics:
ciscoasa# clear threat-detection rate
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show running-config all threat-detection |
Shows the threat detection configuration, including the default rate settings if you did not configure them individually. |
|
show threat-detection rate |
Shows basic threat detection statistics. |
|
threat-detection basic-threat |
Enables basic threat detection. |
|
threat-detection rate |
Sets the threat detection rate limits per event type. |
|
threat-detection scanning-threat |
Enables scanning threat detection. |
clear threat-detection scanning-threat
To clear the attackers and targets after you enable scanning threat detection with the threat-detection scanning-threat command, use the clear threat-detection scanning-threat command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear threat-detection scanning-threat
[
attacker
[
ip_address
[
mask
]
]
|
target
[
ip_address
[
mask
]
]
Syntax Description
|
attacker |
(Optional) Clears only attackers. |
|
ip_address |
(Optional) Clears a specific IP address. |
|
mask |
(Optional) Sets the subnet mask. |
|
target |
(Optional) Clears only targets. |
Command Default
If you do not specify an IP address, all hosts are released.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.0(2) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
To view current attackers and targets, use the show threat-detection scanning-threat command.
Examples
The following example shows targets and attackers with the show threat-detection scanning-threat command, and then clears all targets:
ciscoasa# show threat-detection scanning-threat
Latest Target Host & Subnet List:
192.168.1.0
192.168.1.249
Latest Attacker Host & Subnet List:
192.168.10.234
192.168.10.0
192.168.10.2
192.168.10.3
192.168.10.4
192.168.10.5
192.168.10.6
192.168.10.7
192.168.10.8
192.168.10.9
ciscoasa# clear threat-detection scanning-threat target
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show threat-detection shun |
Shows currently shunned hosts. |
|
show threat-detection statistics host |
Shows the host statistics. |
|
show threat-detection statistics protocol |
Shows the protocol statistics. |
|
show threat-detection statistics top |
Shows the top 10 statistics. |
|
threat-detection scanning-threat |
Enables scanning threat detection. |
clear threat-detection shun
To release the currently shunned hosts after you enable scanning threat detection with the threat-detection scanning-threat command and automatically shunning attacking hosts, use the clear threat-detection shun command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear threat-detection shun
[
ip_address
[
mask
]
]
Syntax Description
|
ip_address |
(Optional) Releases a specific IP address from being shunned. |
|
mask |
(Optional) Sets the subnet mask for the shunned host IP address. |
Command Default
If you do not specify an IP address, all hosts are released.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.0(2) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
To view currently shunned hosts, use the show threat-detection shun command.
Examples
The following example views currently shunned hosts with the show threat-detection shun command, and then releases host 10.1.1.6 from being shunned:
ciscoasa# show threat-detection shun
Shunned Host List:
10.1.1.6
198.1.6.7
ciscoasa# clear threat-detection shun 10.1.1.6 255.255.255.255
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show threat-detection shun |
Shows currently shunned hosts. |
|
show threat-detection statistics host |
Shows the host statistics. |
|
show threat-detection statistics protocol |
Shows the protocol statistics. |
|
show threat-detection statistics top |
Shows the top 10 statistics. |
|
threat-detection scanning-threat |
Enables scanning threat detection. |
clear threat-detection statistics
To clear the statistics after you enable TCP Intercept statistics with the threat-detection statistics tcp-intercept command, use the clear threat-detection scanning-threat command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear threat-detection statistics
[
tcp-intercept
]
Syntax Description
|
tcp-intercept |
(Optional) Clears TCP Intercept statistics. |
Command Default
Clears TCP Intercept statistics.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.0(4) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
To view TCP Intercept statistics, enter the show threat-detection statistics top command.
Examples
The following example shows TCP Intercept statistics with the show threat-detection statistics top tcp-intercept command, and then clears all statistics:
ciscoasa# show threat-detection statistics top tcp-intercept
Top 10 Protected Servers under Attack (sorted by average rate)
Monitoring Window Size: 30 mins Sampling Interval: 30 secs
<Rank> <Server IP:Port> <Interface> <Ave Rate> <Cur Rate> <Total> <Source IP (Last Attack Time)>
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 192.168.1.2:5000 inside 1249 9503 2249245 <various> Last: 10.0.0.3 (0 secs ago)
2 192.168.1.3:5000 inside 10 10 6080 10.0.0.200 (0 secs ago)
3 192.168.1.4:5000 inside 2 6 560 10.0.0.200 (59 secs ago)
4 192.168.1.5:5000 inside 1 5 560 10.0.0.200 (59 secs ago)
5 192.168.1.6:5000 inside 1 4 560 10.0.0.200 (59 secs ago)
6 192.168.1.7:5000 inside 0 3 560 10.0.0.200 (59 secs ago)
7 192.168.1.8:5000 inside 0 2 560 10.0.0.200 (59 secs ago)
8 192.168.1.9:5000 inside 0 1 560 10.0.0.200 (59 secs ago)
9 192.168.1.10:5000 inside 0 0 550 10.0.0.200 (2 mins ago)
10 192.168.1.11:5000 inside 0 0 550 10.0.0.200 (5 mins ago)
ciscoasa# clear threat-detection statistics
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show threat-detection statistics top |
Shows the top 10 statistics. |
|
threat-detection statistics |
Enables threat detection statistics. |
clear traffic
To reset the counters for transmit and receive activity, use the clear traffic command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear traffic
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear traffic command resets the counters for transmit and receive activity that is displayed with the show traffic command. The counters indicate the number of packets and bytes moving through each interface since the last clear traffic
command was entered or since the ASA came online. And the number of seconds indicate the duration the ASA has been online
since the last reboot.
Examples
The following example shows the clear traffic command:
ciscoasa# clear
traffic
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show traffic |
Displays the counters for transmit and receive activity. |
clear uauth
To delete all the cached authentication and authorization information for a user or for all users, use the clear uauth command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear uauth
[
username
]
Syntax Description
|
username |
(Optional) Specifies the user authentication information to remove by username. |
Command Default
Omitting the username
argument deletes the authentication and authorization information for all users.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
— |
— |
|
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear uauth command deletes the AAA authorization and authentication caches for one user or for all users, which forces the user or users
to reauthenticate the next time that they create a connection.
This command is used with the timeout command.
Each user host IP address has an authorization cache attached to it. If the user attempts to access a service that has been
cached from the correct host, the ASA considers it preauthorized and immediately proxies the connection. Once you are authorized
to access a website, for example, the authorization server is not contacted for each image as it is loaded (assuming the images
come from the same IP address). This process significantly increases performance and reduces the load on the authorization
server.
The cache allows up to 16 address and service pairs for each user host.
 Note |
When you enable Xauth, an entry is added to the uauth table (as shown by the show uauth command) for the IP address that is assigned to the client. However, when using Xauth with the Easy VPN Remote feature in |
Use the timeout uauth command to specify how long the cache should be kept after the user connections become idle. Use the clear uauth command to delete all the authorization caches for all the users, which will cause them to have to reauthenticate the next
time that they create a connection.
Examples
The following example shows how to cause the user to reauthenticate:
ciscoasa(config)# clear uauth user
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
aaa authentication |
Enables, disables, or views LOCAL, TACACS+ or RADIUS user authentication (on a server designated by the aaa-server command). |
|
aaa authorization |
Enables, disables, or views TACACS+ or RADIUS user authorization (on a server designated by the aaa-server command). |
|
show uauth |
Displays current user authentication and authorization information. |
|
timeout |
Sets the maximum idle time duration. |
clear uc-ime
To clear the counters used to display statistics about the Cisco Intercompany Media Engine proxy, use the clear uc-ime command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear uc-ime
[
[
mapping-service-sessions
|
signaling-sessions
|
fallback-notification
]
statistics
]
Syntax Description
|
fallback-notification |
(Optional) Clears the counters for fallback notification statistics. |
|
mapping-service-sessions |
(Optional) Clears the counters for mapping-service-session statistics. |
|
signaling-sessions |
(Optional) Clears the counters for signaling-session statistics. |
|
statistics |
(Optional) The keyword to configure which counters to clear for the Cisco Intercompany Media Engine proxy. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.3(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example clears the counters which are used to display signaling-sessions statistics:
ciscoasa# clear configure signaling-sessions statistics
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear configure uc-ime |
Clears the running configuration for the Cisco Intercompany Media Engine proxy on the ASA. |
|
show running-config uc-ime |
Shows the running configuration of the Cisco Intercompany Media Engine proxy. |
|
show uc-ime |
Displays statistical or detailed information about fallback notifications, mapping-service sessions, and signaling sessions. |
|
uc-imc |
Creates the Cisco Intercompany Media Engine proxy instance on the ASA. |
clear url-block block statistics
To clear the block buffer usage counters, use the clear url-block block statistics command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear url-block block statistics
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear url-block block statistics command clears the block buffer usage counters, except for the Current number of packets held (global) counter.
Examples
The following example clears the URL block statistics and displays the status of the counters after they have been cleared:
ciscoasa# clear url-block block statistics
ciscoasa# show url-block block statistics
URL Pending Packet Buffer Stats with max block 0
-----------------------------------------------------
Cumulative number of packets held: | 0
Maximum number of packets held (per URL): | 0
Current number of packets held (global): | 38
Packets dropped due to
| exceeding url-block buffer limit: | 0
| HTTP server retransmission: | 0
Number of packets released back to client: | 0
Related Commands
|
Commands |
Description |
|---|---|
|
filter url |
Directs traffic to a URL filtering server. |
|
show url-block |
Displays information about the URL cache, which is used for buffering URLs while waiting for responses from an N2H2 or Websense |
|
url-block |
Manages the URL buffers used for web server responses. |
|
url-cache |
Enables URL caching while pending responses from an N2H2 or Websense server and sets the size of the cache. |
|
url-server |
Identifies an N2H2 or Websense server for use with the filter command. |
clear url-cache statistics
To remove url-cache command statements from the configuration, use the clear url-cache command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear url-cache statistics
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear url-cache command removes URL cache statistics from the configuration.
Using the URL cache does not update the Websense accounting logs for Websense protocol Version 1. If you are using Websense
protocol Version 1, let Websense run to accumulate logs so you can view the Websense accounting information. After you get
a usage profile that meets your security needs, enter the url-cache command to increase throughput. Accounting logs are updated for Websense protocol Version 4 and for N2H2 URL filtering while
using the url-cache command.
Examples
The following example clears the URL cache statistics:
ciscoasa# clear url-cache statistics
Related Commands
|
Commands |
Description |
|---|---|
|
filter url |
Directs traffic to a URL filtering server. |
|
show url-cache statistics |
Displays information about the URL cache, which is used for buffering URLs while waiting for responses from an N2H2 or Websense |
|
url-block |
Manages the URL buffers used for web server responses while waiting for a filtering decision from the filtering server. |
|
url-cache |
Enables URL caching while pending responses from an N2H2 or Websense server and sets the size of the cache. |
|
url-server |
Identifies an N2H2 or Websense server for use with the filter command. |
clear url-server
To clear URL filtering server statistics, use the clear url-server command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear url-server statistics
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear url-server command removes URL filtering server statistics from the configuration.
Examples
The following example clears the URL server statistics:
ciscoasa# clear url-server statistics
Related Commands
|
Commands |
Description |
|---|---|
|
filter url |
Directs traffic to a URL filtering server. |
|
show url-server |
Displays information about the URL cache, which is used for buffering URLs while waiting for responses from an N2H2 or Websense |
|
url-block |
Manages the URL buffers used for web server responses while waiting for a filtering decision from the filtering server. |
|
url-cache |
Enables URL caching while pending responses from an N2H2 or Websense server and sets the size of the cache. |
|
url-server |
Identifies an N2H2 or Websense server for use with the filter command. |
clear user-identity active-user-database
To set the status of specified users to logged out for the Identity Firewall, use the clear user-identity active-user-database command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear user-identity active-user-database
[
user
[
domain_nickname
]
use_rname
]
|
user-group
[
domain_nickname\
]
user_group_name
]
Syntax Description
|
domain_nickname \user_group_name |
Specifies a user group for which to clear statistics.
The group_name |
|
domain_nickname |
Specifies a user for which to clear statistics.
The user_name |
|
user |
Specifies to clear statistics for users. |
|
user-group |
Specifies to clear statistics for user groups. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.4(2) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
This command sets the status of the specified user, all users belong to the specified user group, or all users to logged out.
When you specify the user-group keyword, the status of all users belong to the specified user group are set to logged out. When you do not specify the domain_nickname
argument with the user-group keyword, users in the groups with user_group_name in default domain are given the logged out status.
When you specify the user keyword, the status of the specified user is set to logged out. When you do not specify the domain_nickname
argument with the user keyword, the user with user_name in default domain receives a logged out status.
When you do not specify either the user or user-group keywords, all users have their status set to logged out.
Examples
The following example sets the status of all users in user group users1 in the SAMPLE domain to logged out:
ciscoasa# clear user-identity active-user-database user-group SAMPLEusers1Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear |
Clears the configuration for the Identity Firewall feature. |
|
show |
Displays the active users for the Identify Firewall. |
clear user-identity ad-agent statistics
To clear the AD Agent statistics for the Identity Firewall, use the clear user-identity ad-agent statistics command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear user-identity ad-agent statistics
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.4(2) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
The ASA maintains the following information about the primary and secondary AD Agents:
-
Status of the AD Agents
-
Status of the domains
-
Statistics for the AD Agents
Use the clear user-identity ad-agent statistics command to clear the statistics data of AD Agents.
Examples
The following example clears the AD Agent statistics for the Identity Firewall:
ciscoasa# clear user-identity ad-agent statistics
ciscoasa# show user-identity ad-agent statistics
Primary AD Agent Total Last Activity
------------------------- ---------- ------------------------
Input packets: 0 N/A
Output packets: 0 N/A
Send updates: 0 N/A
Recv updates: 0 N/A
Keepalive failed: 0 N/A
Send update failed: 0 N/A
Query failed: 0 N/A
Secondary AD Agent Total Last Activity
------------------------- ---------- ------------------------
Input packets: 0 N/A
Output packets: 0 N/A
Send updates: 0 N/A
Recv updates: 0 N/A
Keepalive failed: 0 N/A
Send update failed: 0 N/A
Query failed: 0 N/A
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear configure user-identity |
Clears the configuration for the Identity Firewall feature. |
|
show user-identity ad-agent [statistics ] |
Displays statistical information about the AD Agent for the Identity Firewall. |
clear user-identity statistics
To clear the counters used to display statistics about the Identity Firewall, use the clear user-identity statistics command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear user-identity statistics
[
user
[
domain_nickname
]
use_rname
]
|
user-group
[
domain_nickname\
]
user_group-name
]
Syntax Description
|
domain_nickname \user_group_name |
Specifies a user group for which to clear statistics.
The group_name |
|
domain_nickname |
Specifies a user for which to clear statistics.
The user_name |
|
user |
Specifies to clear statistics for users. |
|
user-group |
Specifies to clear statistics for user groups. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.4(2) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
When domain_nickname is not specified before user_group_name , the ASA removes the Identity Firewall statistics for the group with user_group_name in the default domain.
When domain_nickname is not specified before user_name , the ASA removes the Identity Firewall statistics for the user with user_name in the default domain.
Examples
The following example clears the counters which are used to display statistics for a user group:
ciscoasa# clear user-identity statistics user-group SAMPLEusers1
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear configure user-identity |
Clears the configuration for the Identity Firewall feature. |
|
show user-identity statistics |
Displays statistics for a user or user group for the Identify Firewall. |
clear user-identity user-not-found
To clear the ASA local user-not-found database for the Identity Firewall, use the clear user-identity user-not-found command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear user-identity user-not-found
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.4(2) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
The ASA maintains a local user-not-found database of the IP addresses not found in Microsoft Active Directory. The ASA keeps
only the last 1024 packets (contiguous packets from the same source IP address are treated as one packet) of the user-not-found
list and not the entire list in the database.
User the clear user-identity user-not-found command to clear the local database on the ASA.
 Tip |
Use the show user-identity user-not-found command to display the IP addresses of the users who are not found in Microsoft Active Directory. |
Examples
The following example clears the local user-not-found database for the Identity Firewall:
ciscoasa# show user-identity user-not-found
172.13.1.2
171.1.45.5
169.1.1.2
172.13.12
ciscoasa# clear user-identity user-not-found
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear configure user-identity |
Clears the configuration for the Identity Firewall feature. |
|
show user-identity user-not-found |
Displays the IP addresses of the Active Directory users not found in the ASA user-not-found database. |
clear user-identity user no-policy-activated
To clear the local records on the ASA of users who are not activated for the Identity Firewall, use the clear user-identity user no-policy-activated command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear user-identity user no-policy-activated
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.4(2) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
Use the clear user-identity user no-policy-activated to clear the local records of users not activated by any security policy, meaning the user is not part of an activated user
group or not referenced in an access list or service policy configuration.
The clear user-identity user no-policy-activated command also clears the IP addresses of users who are active but not activated.
When you create a user group for the Identity Firewall, it must be activated, meaning the group is an import user group (defined
as a user group in an access list or service policy configuration) or a local user group (defined in an object-group user).
Examples
The following example clears the local records on the ASA for users who are not activated:
ciscoasa# clear user-identity user no-policy-activated
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear |
Clears the configuration for the Identity Firewall feature. |
|
show |
Displays the list of activated user groups for the Identity Firewall. |
clear vpn cluster stats internal
To clear the internal counters for VPN clustering, use this command in global configuration or privileged EXEC mode.
clear vpn cluster stats internal
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Global configuration |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
9.9(1) |
Command added. |
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show vpn cluster stats internal |
Clear all VPN cluster counters. |
clear vpn-sessiondb statistics
To clear information about VPN sessions, including all statistics or specific sessions or protocols, use the clear vpn-sessiondb statistics command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear vpn-sessiondb
{
all
|
anyconnect
|
failover
|
email-proxy
|
global
|
index
index_number
|
ipaddress
IPaddr
|
l2l
|
name
username
|
protocol
protocol
|
ra-ikev1-ipsec
|
ra-ikev2-ipsec
|
tunnel-group
name
|
vpn-lb
|
webvpn
}
Syntax Description
|
all |
Clears statistics for all sessions. |
|
anyconnect |
Clears statistics for AnyConnect VPN client sessions. |
|
failover |
Clears statistics for failover IPsec sessions. |
|
email-proxy |
(Deprecated) Clears statistics for e-mail proxy sessions. |
|
global |
Clears statistics for global session data. |
|
index indexnumber |
Clears statistics of a single session by index number. The output of the show vpn-sessiondb detail command displays index |
|
ipaddress IPaddr |
Clears statistics for sessions of the IP address that you specify. |
|
l2l |
Clears stastistics for VPN LAN-to-LAN sessions. |
|
protocol protocol |
Clears statistics for the following protocols:
|
|
ra-ikev1-ipsec |
Clears statistics for IPsec IKEv1 and L2TP sessions. |
|
ra-ikev2-ipsec |
Clears statistics for IPsec IKEv2 sessions. |
|
tunnel-group groupname |
Clears statistics for sessions for the tunnel group (connection profile) that you specify. |
|
vpn-lb |
Clears statistics for VPN load balancing management sessions. |
|
webvpn |
Clears statistics for clientless SSL VPN sessions. |
Command Default
There is no default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
— |
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.4(1) |
This command was added. |
|
9.0(1) |
Support for multiple context mode was added. |
|
9.3(2) |
The ra-ikev2-ipsec keyword was added. |
|
9.8(1) |
The email-proxy option was deprecated. |
|
9.0(1) |
The OSPFv3 session type and multiple context mode was added. |
clear wccp
To reset WCCP information, use the clear wccp command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear wccp
[
web-cache
|
service_number
]
Syntax Description
|
web-cache |
Specifies the web-cache service. |
|
service-number |
A dynamic service identifier, which means the service definition is dictated by the cache. The dynamic service number can |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.2(1) |
This command was added. |
Examples
The following example shows how to reset the WCCP information for the web-cache service:
ciscoasa# clear wccp web-cache
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
show |
Displays the WCCP configuration. |
|
wccp |
Enables support of WCCP redirection. |
clear webvpn sso-server statistics
To reset the statistics from the WebVPN Single Sign-On (SSO) server, use the clear webvpn sso-server statistics command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear webvpn sso-server statistics
servername
Syntax Description
|
servername |
Specifies the name of the SSO server to be reset. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the mode in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
— |
— |
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
8.0(2) |
This command was added. |
|
9.0(1) |
Support for multiple context mode was added. |
Usage Guidelines
This command does not reset the «pending requests» statistic.
Examples
The following example displays crypto accelerator statistics:
ciscoasa # clear webvpn sso-server statistics
ciscoasa # Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
clear crypto accelerator statistics |
Clears the global and accelerator-specific statistics in the crypto accelerator MIB. |
|
clear crypto protocol statistics |
Clears the protocol-specific statistics in the crypto accelerator MIB. |
|
show crypto accelerator statistics |
Displays the global and accelerator-specific statistics in the crypto accelerator MIB. |
|
show crypto protocol statistics |
Displays the protocol-specific statistics from the crypto accelerator MIB. |
clear xlate
To clear current dynamic translation and connection information, use the
clear
xlate
command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear xlate
[
global
ip1
[
— ip2
]
[
netmask
mask
]
]
[
local
ip1
[
— ip2
]
[
netmask
mask
]
]
[
gport
port1
[
— port2
]
]
[
interface
if_name
]
[
state
state
]
Syntax Description
|
|
(Optional) Clears the active translations by global IP address or range of addresses. |
|
|
(Optional) Clears the active translations by the global port or range of ports. |
|
|
(Optional) Displays the active translations by interface. |
|
|
(Optional) Clears the active translations by local IP address or range of addresses. |
|
|
(Optional) Clears the active translations by local port or range of ports. |
|
|
(Optional) Specifies the network mask to qualify the global or local IP addresses. |
|
|
(Optional) Clears the active translations by state. You can enter one or more of the following states:
When specifying more than one state, separate the states with a space. |
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
The following table shows the modes in which you can enter the command:
|
Command Mode |
Firewall Mode |
Security Context |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Routed |
Transparent |
Single |
Multiple |
||
|
Context |
System |
||||
|
Privileged EXEC |
|
|
|
|
|
Command History
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
7.0(1) |
This command was added. |
Usage Guidelines
The
clear
xlate
command clears the contents of the translation slots (“xlate” refers to the translation slot). Translation slots can persist
after key changes have been made. Always use the clear xlate command after adding, changing, or removing the global or nat
commands in your configuration.
An xlate describes a NAT or PAT session. These sessions can be viewed with the
show
xlate
command with the
detail
option. There are two types of xlates: static and dynamic.
A static xlate is a persistent xlate that is created using the
static
command. The
clear
xlate
command does not clear for a host in a static entry. Static xlates can only be removed by removing the
static
command from the configuration; the
clear
xlate
command does not remove the static translation rule. If you remove a static command from the configuration, preexisting connections
that use the static rule can still forward traffic. Use the
clear
local-host
or
clear
conn
command to deactivate these connections.
A dynamic xlate is an xlate that is created on demand with traffic processing (through the
nat
or
global
command). The
clear
xlate
command removes dynamic xlates and their associated connections. You can also use the
clear
local-host
or
clear
conn
command to clear the xlate and associated connections. If you remove a
nat
or a
global
command from the configuration, the dynamic xlate and associated connections may remain active. Use the
clear
xlate
command to remove these connections.
Examples
The following example shows how to clear the current translation and connection slot information:
ciscoasa# clear xlate global
Related Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Clears local host network information. |
|
|
Clears cached user authentication and authorization information. |
|
|
Displays all active connections. |
|
|
Displays the local host network information. |
|
|
Displays the current translation information. |
Часть 1 Часть 2
Содержание
Самые распространенные команды по устранению неполадок портов и интерфейсов для CatOS и Cisco IOS
Основные сведения о выходных данных счетчиков портов и интерфейсов для CatOS и Cisco IOS
Команды Show Port для CatOS и Show Interfaces для Cisco IOS
Команды Show Mac для CatOS и Show Interfaces Counters для Cisco IOS
Команды Show Counters для CatOS и Show Counters Interface для Cisco IOS
Команда Show Controller Ethernet-Controller для Cisco IOS
Команда Show Top для CatOS
Распространенные сообщения о системных ошибках
Сообщения об ошибках в модулях WS-X6348
%PAGP-5-PORTTO / FROMSTP и %ETHC-5-PORTTO / FROMSTP
%SPANTREE-3-PORTDEL_FAILNOTFOUND
%SYS-4-PORT_GBICBADEEPROM: / %SYS-4-PORT_GBICNOTSUPP
Команда отклонена: [интерфейс] не является коммутационным портом
Основные сведения о выходных данных счетчиков портов и интерфейсов для CatOS и Cisco IOS
На большинстве коммутаторов имеется механизм отслеживания пакетов и ошибок, происходящих в интерфейсах и портах. Распространенные команды, используемые для нахождения сведений этого типа, описываются в разделе Самые распространенные команды по устранению неполадок портов и интерфейсов для CatOS и Cisco IOS данного документа.
Примечание: На различных платформах и выпусках счетчики могут быть реализованы по-разному. Хотя значения счетчиков весьма точны, однако конструктивно они не являются очень точными. Для сбора точных статистических данных о трафике предлагается использовать анализатор сетевых пакетов для мониторинга нужных входящих и исходящих интерфейсов.
Чрезмерное количество ошибок обычно указывает на проблему. В полудуплексном режиме нормальной является регистрация некоторого количества ошибок соединения в счетчиках FCS, выравнивания, пакетов с недопустимо малой длиной и конфликтов. Обычно один процент ошибок по отношению ко всему трафику является приемлемым для полудуплексных соединений. Если количество ошибок по отношению к входящим пакетам превысило два или три процента, может стать заметным спад производительности.
В полудуплексных средах коммутатор и подключенное устройство могут одновременно обнаружить канал и начать передачу, что приводит к конфликту. Конфликты могут вызвать появление пакетов с недопустимо малой длиной, последовательности FCS и ошибки выравнивания, так как кадр не полностью копируется в канал, что приводит к фрагментации кадра.
В дуплексном режиме значение счетчиков ошибок последовательности FCS, контрольной суммы CRC, выравнивания и пакетов с недопустимо малой длиной должно быть минимальным. Если соединение работает в режиме полного дуплекса, счетчик конфликтов неактивен. Если показания счетчиков ошибок последовательности FCS, контрольной суммы CRC, выравнивания или пакетов с недопустимо малой длиной увеличиваются, проверьте соответствие дуплексных режимов. Для определения дуплексного режима вы можете обратиться в компанию выполняющую регулярное обслуживание сетевых устройств и компьютеров вашей организации. Несоответствие дуплексных режимов возникает, когда коммутатор работает в дуплексном режиме, а подключенное устройство — в полудуплексном, или наоборот. Следствиями несоответствия дуплексных режимов являются чрезвычайно медленная передача, периодические сбои подключения и потеря связи. Другие возможные причины ошибок канала передачи данных в полнодуплексном режиме — дефекты кабелей, неисправные порты коммутатора, программные или аппаратные неполадки сетевой платы. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Распространенные проблемы портов и интерфейсов данного документа.
Команды Show Port для CatOS и Show Interfaces для Cisco IOS
Команда show port {mod/port} используется в ОС CatOS в модуле Supervisor. Альтернатива этой команды — команда show port counters {mod/port}, которая отображает только счетчики ошибок портов. Описание выходных данных счетчиков ошибок см. в таблице 1.
Switch> (enable) sh port counters 3/1 Port Align-Err FCS-Err Xmit-Err Rcv-Err UnderSize ----- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- --------- 3/1 0 0 0 0 0 Port Single-Col Multi-Coll Late-Coll Excess-Col Carri-Sen Runts Giants ----- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- --------- --------- --------- 3/1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Команда show interfaces card-type {slot/port} — эквивалентная команда для Cisco IOS в модуле Supervisor. Альтернативой данной команды (для коммутаторов серии Catalyst 6000, 4000, 3550, 2970 2950/2955 и 3750) является команда show interfaces card-type {slot/port} counters errors , которая отображает счетчики ошибок интерфейсов.
Примечание: Для коммутаторов серии 2900/3500XL используйте только команду show interfaces card-type {slot/port} с командной show controllers Ethernet-controller .
Router#sh interfaces fastEthernet 6/1 FastEthernet6/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected) Hardware is C6k 100Mb 802.3, address is 0009.11f3.8848 (bia 0009.11f3.8848) MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Full-duplex, 100Mb/s input flow-control is off, output flow-control is off ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:14, output 00:00:36, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/2000/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue :0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Команда show interfaces выдает на экран выходные данные до описанной здесь точки (по порядку):
-
up, line protocol is up (connected) — Первое «up» относится к состоянию физического уровня интерфейса. Сообщение «line protocol up» показывает состояние уровня канала передачи данных для данного интерфейса и означает, что интерфейс может отправлять и принимать запросы keepalive.
-
MTU – максимальный размер передаваемого блока данных (MTU) составляет 1500 байт для Ethernet по умолчанию (максимальный размер блока данных кадра).
-
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s (полнодуплексный, 100 Мбит/с) — текущая скорость и режим дуплексирования для данного интерфейса. Но это не позволяет узнать, использовалось ли для этого автоматическое согласование.
-
Последние входные, выходные данные — число часов, минут и секунд с момента последнего успешного приема или передачи интерфейсом пакета. Полезно знать время отказа заблокированного интерфейса.
-
Последнее обнуление счетчиков «show interface» — время последнего применения команды clear counters после последней перезагрузки коммутатора. Команда clear counters используется для сброса статистики интерфейса.
Примечание: Переменные, которые могут повлиять на маршрутизацию (например, на загрузку и надежность), не очищаются вместе со счетчиками.
-
Очередь входа — число пакетов в очереди входа. Size/max/drops = текущее число кадров в очереди/максимальное число кадров в очереди (до начала потерь кадров)/фактическое число потерянных кадров из-за превышения максимального числа кадров. Сбросы используется для подсчета выборочного отбрасывания пакетов на коммутаторах серии Catalyst 6000 с ОС Cisco IOS. (Счетчик сбросов может использоваться, но его показания не увеличиваются на коммутаторах серии Catalyst 4000 с Cisco IOS.) Выборочное отбрасывание пакетов — механизм быстрого отбрасывания пакетов с низким приоритетом в случае перегрузки ЦПУ, чтобы сохранить некоторые вычислительные ресурсы для пакетов с высоким приоритетом.
-
Общее число выходных сбросов – количество пакетов, сброшенных из-за заполнения очереди выхода. Типичной причиной этого может быть коммутация трафика из канала с высокой пропускной способностью в канал с меньшей пропускной способностью, либо коммутация трафика из нескольких входных каналов в один выходной канал. Например, если большой объем пульсирующего трафика поступает в гигабитный интерфейс и переключается на интерфейс 100 Мбит/с, это может вызвать увеличение отбрасывания исходящего трафика на интерфейсе 100 Мбит/с. Это происходит потому, что очередь выхода на указанном интерфейсе переполняется избыточным трафиком из-за несоответствия скорости входящей и исходящей полосы пропускания.
-
Очередь выхода — число пакетов в очереди выхода. Size/max означает текущее число кадров в очереди/максимальное количество кадров, которое может находиться в очереди до заполнения, после чего начинается отбрасывание кадров.
-
Пятиминутная скорость ввода/вывода – средняя скорость ввода и вывода, которая наблюдалась интерфейсом за последние пять минут. Чтобы получить более точные показания за счет указания более короткого периода времени (например, для улучшения обнаружения всплесков трафика), выполните команду интерфейса load-interval <секунды>.
В остальной части выходных данных команды show interfaces отображаются показания счетчиков ошибок, которые аналогичны или эквивалентны показаниям счетчиков ошибок в CatOS.
Команда show interfaces card-type {slot/port} counters errors эквивалентна команде Cisco IOS для отображения счетчиков портов для CatOS. Описание выходных данных счетчиков ошибок см. в таблице 1.
Router#sh interfaces fastEthernet 6/1 counters errors
Port Align-Err FCS-Err Xmit-Err Rcv-Err UnderSize OutDiscards Fa6/1
0 0 0 0 0 0
Port Single-Col Multi-Col Late-Col Excess-Col Carri-Sen Runts Giants Fa6/1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Таблица 1.
Сведения о счетчиках ошибок CatOS содержатся в выходных данных команды show port или show port counters для коммутаторов серии Cisco Catalyst 6000, 5000 и 4000. Сведения о счетчиках ошибок Cisco IOS содержатся в выходных данных команды show interfaces или show interfaces card-type x/y counters errors для коммутаторов серии Catalyst 6000 и 4000
|
Счетчики (в алфавитном порядке) |
Описание и распространенные причины увеличения значений счетчиков ошибок |
|---|---|
|
Align-Err |
Описание: CatOS sh port и Cisco IOS sh interfaces counters errors. Количество ошибок выравнивания определяется числом полученных кадров, которые не заканчиваются четным числом октетов и имеют неверную контрольную сумму CRC. Распространенные причины: они обычно являются результатом несоответствия дуплексных режимов или физической проблемы (такой как прокладка кабелей, неисправный порт или сетевая плата). При первом подключении кабеля к порту могут возникнуть некоторые из этих ошибок. Кроме того, если к порту подключен концентратор, ошибки могут вызвать конфликты между другими устройствами концентратора. Исключения для платформы: ошибки выравнивания не подсчитываются в Catalyst 4000 Series Supervisor I (WS-X4012) или Supervisor II (WS-X4013). |
|
Перекрестные помехи |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Счетчик CatOS, указывающий на истечение срока таймера передачи сбойных пакетов. Сбойный пакет — это кадр длиной свыше 1518 октетов (без кадрирующих битов, но с октетами FCS), который не заканчивается четным числом октетов (ошибка выравнивания) или содержит серьезную ошибку FCS). |
|
Carri-Sen |
Описание: CatOS sh port и Cisco IOS sh interfaces counters errors. Значение счетчика Carri-Sen (контроль несущей) увеличивается каждый раз, когда контроллер Ethernet собирается отослать данные по полудуплексному соединению. Контроллер обнаруживает провод и перед передачей проверяет, не занят ли он. Распространенные причины: это нормально для полудуплексного сегмента Ethernet. |
|
конфликты |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Число конфликтов, произошедших до того, как интерфейс успешно передал кадр носителю. Распространенные причины: это нормальное явление для полудуплексных интерфейсов, но не для полнодуплексных интерфейсов. Быстрый рост числа конфликтов указывает на высокую загрузку соединения или возможное несоответствие дуплексных режимов с присоединенным устройством. |
|
CRC |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Значение данного счетчика увеличивается, когда контрольная сумма CRC, сгенерированная исходящей станцией ЛВС или устройством на дальнем конце, не соответствует контрольной сумме, рассчитанной по принятым данным. Распространенные причины: обычно это означает проблемы с шумами или передачей в интерфейсе ЛВС или самой ЛВС. Большое значение счетчика CRC обычно является результатом конфликтов, но может указывать на физическую неполадку (такую как проводка кабелей, неправильный интерфейс или неисправная сетевая плата) или несоответствие дуплексных режимов. |
|
deferred |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Число кадров, успешно переданных после ожидания освобождения носителя. Распространенные причины: они обычно наблюдаются в полудуплексных средах, в которых несущая уже используется при попытке передачи кадра. |
|
pause input |
Описание: Cisco IOS show interfaces счетчик. Приращение значения счетчика «pause input» означает, что подключенное устройство запрашивает приостановку трафика, когда его буфер приема почти заполнен. Распространенные причины: приращение показаний этого счетчика служит в информационных целях, так как коммутатор принимает данный кадр. Передача пакетов с запросом приостановки прекращается, когда подключенное устройство способно принимать трафик. |
|
input packetswith dribble condition |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Битовая ошибка указывает, что кадр слишком длинный. Распространенные причины: приращение показаний счетчика ошибок в кадрах служит в информационных целях, так как коммутатор принимает данный кадр. |
|
Excess-Col |
Описание: CatOS sh port и Cisco IOS sh interfaces counters errors. Количество кадров, для которых передача через отдельный интерфейс завершилась с ошибкой из-за чрезмерного числа конфликтов. Избыточный конфликт возникает, когда для некоторого пакета конфликт регистрируется 16 раз подряд. Затем пакет отбрасывается. Распространенные причины: чрезмерное количество конфликтов обычно обозначает, что нагрузку на данный сегмент необходимо разделить между несколькими сегментами, но может также указывать на несоответствие дуплексных режимов с присоединенным устройством. На интерфейсах, сконфигурированных в качестве полнодуплексных, конфликты наблюдаться не должны. |
|
FCS-Err |
Описание: CatOS sh port и Cisco IOS sh interfaces counters errors. Число кадров допустимого размера с ошибками контрольной последовательности кадров (FCS), но без ошибок кадрирования. Распространенные причины: обычно это указывает на физическую проблему (такую как прокладка кабелей, неисправный порт или сетевая плата), однако также может означать несоответствие дуплексных режимов. |
|
кадр |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Число неправильно принятых пакетов с ошибками контрольной суммы CRC и нецелым числом октетов (ошибка выравнивания). Распространенные причины: обычно это вызвано конфликтами или физической проблемой (например, проводкой кабелей, неисправным портом или сетевой платой), а также может указывать на несоответствие дуплексных режимов. |
|
Кадры с недопустимо большой длиной |
Описание: CatOS sh port и Cisco IOS sh interfaces и sh interfaces counters errors. Полученные кадры, размеры которых превышают максимально допускаемые стандартом IEEE 802.3 (1518 байт для сетей Ethernet без поддержки jumbo-кадров) и обладают неверной последовательностью FCS. Распространенные причины: во многих случаях это следствие поврежденной сетевой интерфейсной платы. Попробуйте найти проблемное устройство и удалить его из сети. Исключения для платформ: коммутаторы серии Catalyst Cat4000 с Cisco IOS версии, предшествующей 12.1(19)EW, показания счетчика кадров с недопустимо большой величиной увеличиваются в случае кадра размером > 1518 байтов. После версии 12.1(19)EW кадры giant в выходных данных команды show interfaces учитываются только в случае приема кадра размером > 1518 байтов с неверной последовательностью FCS. |
|
ignored |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Количество полученных пакетов, проигнорированных интерфейсом из-за недостатка места во внутренних буферах оборудования интерфейса. Распространенные причины: широковещательный шторм и всплески помех могут вызвать рост показаний данного счетчика. |
|
Ошибки ввода |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Распространенные причины: в счетчике учитываются ошибки кадров, кадры с недопустимо маленькой или недопустимо большой величиной, кадры, отброшенные из-за переполнения буфера, несоответствия значения контрольной суммы CRC или перегрузки, а также проигнорированные пакеты. Другие ошибки, относящиеся к входным данным, также могут увеличивать количество ошибок ввода; некоторые датаграммы могут содержать несколько ошибок. Поэтому эта сумма может не совпадать с суммой перечисленных ошибок ввода. Также см. раздел Ошибки ввода в интерфейсе уровня 3, подключенном к порту коммутатора уровня 2. |
|
Late-Col |
Описание: CatOS sh port и Cisco IOS sh interfaces и sh interfaces counters errors. Количество обнаруженных конфликтов в определенном интерфейсе на последних этапах процесса передачи. Для порта со скоростью 10 Мбит/с это позднее, чем время передачи 512 битов для пакета. В системе со скоростью передачи данных 10 Мбит/с 512 битовых интервалов соответствуют 51,2 микросекунды. Распространенные причины: это ошибка, в частности, может указывать на несоответствие дуплексных режимов. В сценарии с несоответствием дуплексных режимов на стороне с полудуплексным режимом наблюдается поздний конфликт. Во время передачи со стороны с полудуплексным режимом на стороне с дуплексным режимом выполняется одновременная передача без ожидания своей очереди, что приводит к возникновению позднего конфликта. Поздние конфликты также могут указывать на слишком большую длину кабеля или сегмента Ethernet. На интерфейсах, сконфигурированных в качестве полнодуплексных, конфликты наблюдаться не должны. |
|
lost carrier |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Число потерь несущей во время передачи. Распространенные причины: проверьте исправность кабеля. Проверьте физическое соединение на обеих сторонах. |
|
Multi-Col |
Описание: CatOS sh port и Cisco IOS sh interfaces counters errors. Число множественных конфликтов произошедших до того, как порт успешно передал кадр носителю. Распространенные причины: это нормальное явление для полудуплексных интерфейсов, но не для полнодуплексных интерфейсов. Быстрый рост числа конфликтов указывает на высокую загрузку соединения или возможное несоответствие дуплексных режимов с присоединенным устройством. |
|
no buffer |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Число принятых пакетов, которые отвергнуты из-за отсутствия буферного пространства. Распространенные причины: сравните со счетчиком пропущенных пакетов. Часто такие ошибки вызываются широковещательными штормами. |
|
Отсутствует несущая |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Сколько раз несущая отсутствовала во время передачи. Распространенные причины: проверьте исправность кабеля. Проверьте физическое соединение на обеих сторонах. |
|
Out-Discard |
Описание: количество исходящих пакетов, которые выбраны для отбрасывания несмотря на отсутствие ошибок Распространенные причины: одна возможная причина отбрасывания таких пакетов — освобождение буферного пространства. |
|
output buffer failuresoutput buffers swapped out |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Число буферов с ошибками и число выгруженных буферов. Распространенные причины: порт размещает пакеты в буфере Tx, когда скорость поступающего в порт трафика высока и порт не может обработать такой объем трафика. Порт начинает пропускать пакеты в случае заполнения буфера Tx, при этом увеличиваются значения счетчиков недогрузок и сбоев выходных буферов. Увеличение значений счетчиков сбоев выходных буферов может означать, что порты работают с минимальными настройками скорости и/или дуплексного режима, или через порт проходит слишком большой объем трафика. Например, рассмотрите сценарий, в котором гигабайтный многоадресный поток пересылается 24 портам с пропускной способностью 100 Мбит/с. Если выходной интерфейс перегружен, обычно наблюдаются сбои выходного буфера, число которых растет вместе с числом выходящих отброшенных пакетов (Out-Discards). Сведения об устранении неполадок см. в разделе Отложенные кадры (Out-Lost или Out-Discard) данного документа. |
|
output errors |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Сумма всех ошибок, препятствовавших целевой передаче датаграмм от заданного интерфейса. |
|
overrun (переполнение) |
Описание: сколько раз аппаратному оборудованию приемника не удалось поместить принятые данные в аппаратный буфер. Распространенные причины: входящая скорость трафика превысила способность приемника к обработке данных. |
|
packets input/output |
Описание: Cisco IOS sh interfaces счетчик. Общее количество безошибочных пакетов, полученных и переданных на данном интерфейсе. Мониторинг приращений показаний этих счетчиков полезен при проверке правильного прохождения трафика через интерфейс. Счетчик байтов включает эти данные и инкапсуляцию MAC-адресов в безошибочные пакеты, принятые и переданные системой. |
|
Rcv-Err |
Описание: CatOS show port или show port counters и Cisco IOS (только для коммутаторов серии Catalyst 6000) «sh interfaces counters error». Распространенные причины: см. исключения для платформ. Исключения для платформ: коммутаторы серии Catalyst 5000 rcv-err = сбои буферов приема. Например, кадры недопустимо маленькой или недопустимо большой величины или ошибки последовательности FCS (FCS-Err) не приводят к увеличению значения счетчика rcv-err. Значение счетчика rcv-err для 5K увеличивается только в случае избыточного трафика. В отличие от коммутаторов серии Catalyst 5000 на коммутаторах серии Catalyst 4000 значение rcv-err равно сумме всех ошибок приема, т.е. значение счетчика rcv-err увеличивается в случае регистрации таких ошибок, как прием интерфейсом кадров с недопустимо маленькой или недопустимо большой величиной или ошибки последовательности FCS. |
|
Кадры с недопустимо маленькой величиной |
Описание: CatOS sh port и Cisco IOS sh interfaces и sh interfaces counters errors. Принятые кадры с размером меньше минимального размера кадра IEEE 802.3 (64 байта для Ethernet) и неверной контрольной суммой CRC. Распространенные причины: это может быть вызвано несоответствием дуплексных режимов и физическими проблемами, такими как неисправный кабель, порт или сетевая плата на присоединенном устройстве. Исключения для платформ: на коммутаторах серии Catalyst 4000 с Cisco IOS версии, предшествующей версии 12.1(19)EW, кадры с недопустимо маленькой величиной — это кадры размера undersize. Undersize = кадр < 64 байтов. Значение счетчика кадров с недопустимо маленькой величиной увеличивается при получении кадра размером менее 64 байтов. После версии 12.1(19)EW кадр с недопустимо маленькой величиной = фрагмент. Фрагмент — это кадр < 64 байта с неверной контрольной суммой CRC. В результате значение счетчика кадров с недопустимо маленькой величиной увеличивается в show interfacesвместе со счетчиком фрагментов в show interfaces counters errors при получении кадра < 64 байтов с неверной контрольной суммой CRC. |
|
Single-Col |
Описание: CatOS sh port и Cisco IOS sh interfaces counters errors. Число конфликтов, произошедших до того, как интерфейс успешно передал кадр носителю. Распространенные причины: это нормальное явление для полудуплексных интерфейсов, но не для полнодуплексных интерфейсов. Быстрый рост числа конфликтов указывает на высокую загрузку соединения или возможное несоответствие дуплексных режимов с присоединенным устройством. |
|
underruns |
Описание: сколько раз скорость передатчика превышала возможности коммутатора. Распространенные причины: это может происходить в случае высокой пропускной способности, когда через интерфейс проходит большой объем пульсирующего трафика от многих других интерфейсов одновременно. В случае недогрузки возможен сброс интерфейса. |
|
Undersize |
Описание: CatOS sh port и Cisco IOS sh interfaces counters errors. Полученные фреймы с размером меньше минимального размера фрейма в стандарте IEEE 802.3, равного 64 байтам (без битов кадрирования, но с октетами FCS), но хорошо сформированных во всем остальном. Распространенные причины: проверьте устройство, отправляющее такие кадры. |
|
Xmit-Err |
Описание: CatOS sh port и Cisco IOS sh interfaces counters errors. Это указывает на заполнение внутреннего буфера отправки (Tx). Распространенные причины: часто ошибки Xmit-Err возникают из-за передачи трафика из канала с высокой пропускной способностью в канал с меньшей пропускной способностью или трафика из нескольких входящих каналов в один исходящий. Например, если большой объем пульсирующего трафика поступает в гигабитный интерфейс и переключается на интерфейс на 100 Мбит/с, на 100-мегабитном интерфейсе это может вызывать приращение значения счетчика Xmit-Err. Это происходит потому, что выходной буфер заданного интерфейса переполняется избыточным трафиком из-за несоответствия скорости входящей и исходящей полосы пропускания. |
Команды Show Mac для CatOS и Show Interfaces Counters для Cisco IOS
Команда show mac {mod/port} полезна при использовании CatOS в модуле Supervisor для отслеживания входящего и исходящего трафика данного порта в соответствии с показаниями счетчиков приема (Rcv) и передачи (Xmit) для трафика одноадресной, многоадресной и широковещательной рассылки. Эти выходные данные получены от Catalyst 6000, использующего CatOS:
Console> (enable) sh mac 3/1 Port Rcv-Unicast Rcv-Multicast Rcv-Broadcast-------- -------------------- -------------------- --------------------3/1 177 256272 3694Port Xmit-Unicast Xmit-Multicast Xmit-Broadcast-------- -------------------- -------------------- --------------------3/1 30 680377 153Port Rcv-Octet Xmit-Octet-------- -------------------- --------------------3/1 22303565 48381168 MACDely-Exced MTU-Exced In-Discard Out-Discard-------- ---------- ---------- ---------- -----------3/1 0 0 233043 17Port Last-Time-Cleared----- --------------------------3/1 Sun Jun 1 2003, 12:22:47
В данной команде также используются следующие счетчики ошибок: Dely-Exced, MTU-Exced, In-Discard и Out-Discard.
-
Dely-Exced — количество кадров, отклоненных данным портом из-за чрезмерной задержки передачи данных через коммутатор. Показания данного счетчика растут только при очень интенсивном использовании порта.
-
MTU Exceed — это показатель того, что одно из устройств на данном порту или сегменте передает объем данных больше, чем разрешено размером кадра (1518 байт для сети Ethernet без поддержки jumbo-кадров).
-
In-Discard – результат обработки допустимых входящих кадров, которые были отброшены, поскольку их коммутация не требовалась. Это может быть нормальным, если концентратор подключен к порту и два устройства на данном концентраторе обмениваются данными. Порт коммутатора продолжает видеть данные, но не переключает его (так как в таблице CAM отображается MAC-адрес обоих устройств, связанных с одним и тем же портом). Поэтому трафик отбрасывается. Значение данного счетчика также увеличивается в случае порта, настроенного в качестве магистрали, если данная магистраль блокирует некоторые сети VLAN, или в случае порта, который является единственным членом некоторой сети VLAN.
-
Out-Discard (Число отбрасываемых исходящих пакетов) – число исходящих пакетов, которые выбраны для отбрасывания несмотря на отсутствие ошибок. Одна из возможных причин отбрасывания таких пакетов — освобождение буферного пространства.
-
In-Lost — на коммутаторах серии Catalyst 4000; этот счетчик представляет собой сумму всех пакетов с ошибками, полученных данным портом. С другой стороны на коммутаторах серии Catalyst 5000 счетчик In-Lost отслеживает сумму всех сбоев буферов приема.
-
Out-Lost — на коммутаторах серии Catalyst 4000 и 5000 учитываются исходящие кадры, которые были потеряны до пересылки (из-за недостатка буферного пространства). Обычно это вызывается перегрузкой порта.
Команда show interfaces card-type {slot/port} counters используется при выполнении Cisco IOS в модуле Supervisor.
Команда show counters [mod/port] предоставляет еще более подробную статистику для портов и интерфейсов. Эта команда доступна для CatOS, а эквивалентная ей команда show counters interface card-type {slot/port} была введена в Cisco IOS версии 12.1(13)E только для коммутаторов серии Catalyst 6000. Эти команды отображают 32- и 64-разрядные счетчики ошибок для каждого порта или интерфейса. Дополнительные сведения см. в документации по командам CatOS show counters.
Команда Show Controller Ethernet-Controller для Cisco IOS
На коммутаторах серии Catalyst 3750, 3550, 2970, 2950/2955, 2940 и 2900/3500XL используйте команду «show controller ethernet-controller» для отображения выходных данных счетчика трафика и счетчика ошибок, которые аналогичны выходным данным команд sh port, sh interface, sh mac и show counters для коммутаторов серии Catalyst 6000, 5000 и 4000.
|
Счетчик |
Описание |
Возможные причины |
|---|---|---|
|
Переданные кадры |
||
|
Отброшенные кадры |
Общее количество кадров, попытка передачи которых прекращена из-за недостатка ресурсов. В это общее количество входят кадры всех типов назначения. |
Отбрасывание кадров вызвано чрезмерной нагрузкой трафиком данного интерфейса. Если в этом поле наблюдается рост числа пакетов, уменьшите нагрузку на данный интерфейс. |
|
Устаревшие кадры |
Число кадров, передача которых через коммутатор заняла более двух секунд. По этой причине они были отброшены коммутатором. Это случается только в условиях экстремально высокой нагрузки. |
Отбрасывание кадров вызвано чрезмерной нагрузкой трафиком данного коммутатора. Если в этом поле наблюдается рост числа пакетов, уменьшите нагрузку на данный коммутатор. Может потребоваться изменение топологии сети, чтобы снизить нагрузку трафиком данного коммутатора. |
|
Deferred frames (отложенные кадры) |
Общее число кадров, первая попытка передачи которых была отложена из-за трафика в сетевом носителе. В это общее число входят только кадры, которые в последствии передаются без ошибок и конфликтов. |
Отбрасывание кадров вызвано чрезмерной нагрузкой трафика, направленного к данному коммутатору. Если в этом поле наблюдается рост числа пакетов, уменьшите нагрузку на данный коммутатор. Может потребоваться изменение топологии сети, чтобы снизить нагрузку трафика на данный коммутатор. |
|
Collision frames (кадры с конфликтами) |
В счетчиках кадров с конфликтами содержится число пакетов, одна попытка передачи которых была неудачной, а следующая — успешной. Это означает, что в случае увеличения значения счетчика кадров с конфликтами на 2, коммутатор дважды неудачно пытался передать пакет, но третья попытка была успешной. |
Отбрасывание кадров вызвано чрезмерной нагрузкой трафиком данного интерфейса. Если в этих полях наблюдается рост числа пакетов, уменьшите нагрузку на данный интерфейс. |
|
Excessive collisions (частые конфликты) |
Значение счетчика частых конфликтов возрастает после возникновения 16 последовательных поздних конфликтов. Через 16 попыток отправки пакета, он отбрасывается, а значение счетчика возрастает. |
Увеличение значения этого счетчика указывает на проблему с проводкой, чрезмерно загруженную сеть или несоответствие дуплексных режимов. Чрезмерная загрузка сети может быть вызвана совместным использованием сети Ethernet слишком большим числом устройств. |
|
Late collisions (поздние конфликты) |
Поздний конфликт возникает, когда два устройства передают одновременно, но конфликт не обнаруживается ни одной из сторон соединения. Причина этого заключается в том, что время передачи сигнала с одного конца сети к другому превышает время, необходимое, чтобы поместить целый пакет в сеть. Два устройства, вызвавшие поздний конфликт, никогда не видят пакет, отправляемый другим устройством, пока он не будет полностью помещен в сеть. Поздние конфликты обнаруживаются передатчиком только после истечения первого временного интервала для передачи 64 байтов. Это связано с тем, что конфликты обнаруживаются только при передаче пакетов длиннее 64 байтов. |
Поздние конфликты являются следствием неправильной прокладки кабелей или несовместимого числа концентраторов в сети. Неисправные сетевые платы также могут вызывать поздние конфликты. |
|
Хорошие кадры (1 конфликт) |
Общее число кадров, которые испытали только один конфликт, а затем были успешно переданы. |
Конфликты в полудуплексной среде — обычное ожидаемое поведение. |
|
Хорошие кадры (> 1 конфликта) |
Общее число кадров, которые испытали от 2 до 15 конфликтов включительно, а затем были успешно переданы. |
Конфликты в полудуплексной среде — обычное ожидаемое поведение. По мере приближения к верхнему пределу данного счетчика для таких кадров возрастает риск превышения 15 конфликтов и причисления к частым конфликтам. |
|
Отброшенные кадры сети VLAN |
Число кадров, отброшенных интерфейсом из-за задания бита CFI. |
Биту Canonical Format Indicator (CFI) в TCI кадра 802.1q задается значение 0 для канонического формата кадра Ethernet. Если биту CFI задано значение 1, это указывает на наличие поля сведений о маршрутизации (RIF) или неканонического кадра Token Ring, который отброшен. |
|
Received Frames (принятые кадры) |
||
|
No bandwidth frames (кадры с недостатком пропускной способности) |
Только 2900/3500XL. Количество раз, которое порт принимал пакеты из сети, но у коммутатора не было ресурсов для его принятия. Это случается только в условиях высокой нагрузки, но может произойти и в случае всплесков трафика на нескольких портах. Таким образом, небольшое число в поле «No bandwidth frames» – не повод для беспокойства. (Оно должно оставаться намного меньше одного процента принятых кадров.) |
Отбрасывание кадров вызвано чрезмерной нагрузкой трафиком данного интерфейса. Если в этом поле наблюдается рост числа пакетов, уменьшите нагрузку на данный интерфейс. |
|
No buffers frames (кадры без буфера) |
Только 2900/3500XL. Количество раз, которое порт принимал пакеты из сети, но у коммутатора не было ресурсов для его принятия. Это случается только в условиях высокой нагрузки, но может произойти и в случае всплесков трафика на нескольких портах. Таким образом, небольшое число в поле «No buffers frames» – не повод для беспокойства. (Оно должно оставаться намного меньше одного процента принятых кадров.) |
Отбрасывание кадров вызвано чрезмерной нагрузкой трафиком данного интерфейса. Если в этом поле наблюдается рост числа пакетов, уменьшите нагрузку на данный интерфейс. |
|
No dest, unicast (одноадресные пакеты без назначения) |
Это число одноадресных пакетов, которые не были пересланы данным портом другим портам. |
Ниже дается краткое описание случаев, когда значение счетчиков «No dest» (unicast, multicast и broadcast) может возрастать.
|
|
No dest, multicast (многоадресные пакеты без назначения) |
Это число многоадресных пакетов, которые не были пересланы данным портом другим портам. |
|
|
No dest,broadcast (широковещательные пакеты без назначения) |
Это число широковещательных пакетов, которые не были пересланы данным портом другим портам. |
|
|
Alignment errors (ошибки выравнивания) |
Ошибки выравнивания определяются числом полученных кадров, которые не заканчиваются четным количеством октетов и имеют неверную контрольную сумму CRC. |
Ошибки выравнивания вызываются неполным копированием кадра в канал, что приводит к фрагментированным кадрам. Ошибки выравнивания являются результатом конфликтов при несоответствии дуплексных режимов, неисправном оборудовании (сетевой плате, кабеле или порте), или подключенное устройство генерирует кадры, не завершающиеся октетом, или с неверной последовательностью FCS. |
|
FCS errors (ошибки FCS) |
Число ошибок последовательности FCS соответствует числу кадров, принятых с неверной контрольной суммой (CRC) в кадре Ethernet. Такие кадры отбрасываются и не передаются на другие порты. |
Ошибки FCS являются результатом конфликтов в случае несоответствия дуплексных режимов, неисправного оборудования (сетевая плата, кабель или порт) или кадров с неверной последовательностью FCS, формируемых подключенным устройством. |
|
Undersize frames (неполномерные кадры) |
Это общее число принятых пакетов с длиной менее 64 октетов (без битов кадрирования, но с октетами FCS) и допустимым значением FCS. |
Это указывает на поврежденный кадр, сформированный подключенным устройством. Убедитесь, что подключенное устройство функционирует правильно. |
|
Oversize frames (кадры избыточного размера) |
Число принятых портом из сети пакетов с длиной более 1514 байтов. |
Это может указывать на сбой оборудования либо проблемы конфигурации режима магистрального соединения для dot1q или ISL. |
|
Collision fragments (фрагменты с конфликтами) |
Общее число кадров с длиной менее 64 октетов (без битов кадрирования, но с октетами FCS) и неверным значением FCS. |
Увеличение значения этого счетчика указывает на то, что порты настроены на полудуплексный режим. Установите в настройках дуплексный режим. |
|
Overrun frames (кадры с переполнением) |
Количество раз, которое оборудованию приемника не удалось поместить принятые данные в аппаратный буфер. |
Входящая скорость трафика превысила способность приемника к обработке данных. |
|
VLAN filtered frames (кадры, отфильтрованные по сети VLAN) |
Общее число кадров, отфильтрованных по типу содержащейся в них информации о сети VLAN. |
Порт можно настроить на фильтрацию кадров с тегами 802.1Q. При получении кадра с тегом 802.1Q он фильтруется, а значение счетчика увеличивается. |
|
Source routed frames (кадры с маршрутом источника) |
Общее число полученных кадров, которые были отброшены из-за задания бита маршрута источника в адресе источника собственного кадра. |
Этот тип маршрутизации источников определен только для Token Ring и FDDI. Спецификация IEEE Ethernet запрещает задание этого бита в кадрах Ethernet. Поэтому коммутатор отбрасывает такие кадры. |
|
Valid oversize frames (допустимые кадры избыточного размера) |
Общее число полученных кадров с длиной, превышающей значение параметра System MTU, но с правильными значениями FCS. |
В данном случае собирается статистика о кадрах с длиной превышающей настроенное значение параметра System MTU, размер которых можно увеличить с 1518 байтов до размера, разрешенного для инкапсуляции Q-in-Q или MPLS. |
|
Symbol error frames (кадры с ошибками символа) |
В Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Base-X) используется кодирование 8B/10B для преобразования 8-битных данных из MAC-подуровня (уровень 2) в 10-битный символ для отправки по проводу. Когда порт получает символ, он извлекает 8-битные данные из данного символа (10 битов). |
Символьная ошибка означает, что интерфейс обнаружил прием неопределенного (недопустимого) символа. Небольшое число символьных ошибок можно игнорировать. Большое число символьных ошибок может указывать на неисправность устройства, кабеля или оборудования. |
|
Invalid frames, too large (недопустимые кадры, слишком большие) |
Кадры с недопустимо большой величиной или полученные кадры с неверной последовательностью FCS, размер которых превышает размер максимального кадра в IEEE 802.3 (1518 байт для сетей Ethernet без поддержки jumbo-кадров). |
В большинстве случаев это является следствием поврежденной сетевой интерфейсной платы. Попробуйте найти проблемное устройство и удалить его из сети. |
|
Invalid frames, too small (недопустимые кадры, слишком маленькие) |
Кадры с недопустимо маленькой величиной или кадры, размером менее 64 байта (с битами FCS, но без заголовка кадра) и недопустимым значением FCS или ошибкой выравнивания. |
Это может произойти из-за несоответствия дуплексных режимов и физических проблем, таких как неисправный кабель, порт или сетевая плата на подключенном устройстве. |
Команда Show Top для CatOS
Команда show top позволяет собирать и анализировать данные о каждом физическом порте коммутатора. Данная команда для каждого физического порта отображает следующие данные:
-
уровень загрузки порта (Uti %)
-
число входящих и исходящих байтов (Bytes)
-
число входящих и исходящих пакетов (Pkts)
-
число входящих и исходящих пакетов широковещательной рассылки (Bcst)
-
число входящих и исходящих пакетов многоадресной рассылки (Mcst)
-
число ошибок (Error)
-
число ошибок переполнения буфера (Overflow)
Примечание: При вычислении уровня загрузки порта данная команда объединяет строки Tx и Rx в один счетчик, а также определяет пропускную способность в дуплексном режиме при вычислении процента загруженности. Например, порт Gigabit Ethernet работает в дуплексном режиме с пропускной способностью 2000 Мбит/с.
Число ошибок (in Errors) представляет сумму всех пакетов с ошибками, полученных данным портом.
Переполнение буфера означает, что порт принимает больше трафика, чем может быть сохранено в его буфере. Это может быть вызвано пульсирующим трафиком, а также переполнением буферов. Предлагаемое действие — уменьшить скорость передачи исходного устройства.
Также см. значения счетчиков «In-Lost» и «Out-Lost» в выходных данных команды show mac .
Распространенные сообщения о системных ошибках
В Cisco IOS иногда используется различный формат для системных сообщений. Для сравнения можно проверить системные сообщения CatOS и Cisco IOS. Описание выпусков используемого программного обеспечения см. в руководстве Сообщения и процедуры восстановления. Например, можно прочитать документ Сообщения и процедуры восстановления для ПО CatOS версии 7.6 и сравнить его с содержимым документа Сообщения и процедуры восстановления для выпусков Cisco IOS 12.1 E.
Сообщения об ошибках в модулях WS-X6348
Просмотите следующие сообщения об ошибках.
-
Coil Pinnacle Header Checksum (контрольная сумма заголовка Coil/Pinnacle)
-
Ошибка состояния компьютера Coil Mdtif
-
Ошибка контрольной суммы пакета Coil Mdtif.
-
Ошибка «Coil Pb Rx Underflow»
-
Ошибка четности Coil Pb Rx
Можно проверить наличие в сообщениях системного журнала одной из описанных ниже ошибок.
%SYS-5-SYS_LCPERR5:Module 9: Coil Pinnacle Header Checksum Error - Port #37
При появлении этого типа сообщений или в случае сбоя группы портов 10/100 в модулях WS-X6348 см. в следующих документах дальнейшие советы по устранению неполадок в зависимости от используемой операционной системы.
%PAGP-5-PORTTO / FROMSTP и %ETHC-5-PORTTO / FROMSTP
В CatOS используйте команду show logging buffer для просмотра сохраненных сообщений журнала. Для Cisco IOS используйте команду show logging .
Протокол PAgP выполняет согласование каналов EtherChannel между коммутаторами. Если устройство присоединяется или покидает порт моста, на консоли отображается информационное сообщение. В большинстве случае появление этого сообщение совершенно нормально, однако при появлении таких сообщений на портах, которые по каким-то причинам не участвуют в переброске, требуется дополнительное изучение. Для изучения консольных сообщений всегда можно обратиться в IT-аутсорсинговую компанию, которая специализируется на обслуживании сетевого оборудования.
В программном обеспечении CatOS версии 7.x или выше «PAGP-5» изменено на «ETHC-5», чтобы сделать данное сообщение более понятным.
Это сообщение характерно для коммутаторов серии Catalyst 4000, 5000 и 6000 с ПО CatOS. Для коммутаторов с ПО Cisco IOS нет сообщений об ошибках, эквивалентных данному.
%SPANTREE-3-PORTDEL_FAILNOTFOUND
Это сообщение не указывает на проблему с коммутатором. Оно обычно возникает вместе с сообщениями %PAGP-5-PORTFROMSTP.
Протокол PAgP выполняет согласование каналов EtherChannel между коммутаторами. Если устройство присоединяется или покидает порт моста, на консоли отображается информационное сообщение. В большинстве случае появление этого сообщение совершенно нормально и не требует, каких-либо действий вроде аудита IT-инфраструктуры, однако при появлении таких сообщений на портах, которые по каким-то причинам не участвуют в переброске, требуется дополнительное изучение.
Это сообщение характерно для коммутаторов серии Catalyst 4000, 5000 и 6000 с ПО CatOS. Для коммутаторов с ПО Cisco IOS нет сообщений об ошибках, эквивалентных данному.
%SYS-4-PORT_GBICBADEEPROM: / %SYS-4-PORT_GBICNOTSUPP
Наиболее распространенная причина появления этого сообщения заключается в установке несертифицированного стороннего (не Cisco) конвертера GBIC в модуль Gigabit Ethernet. У такого конвертера GBIC нет памяти Cisco SEEPROM, что приводит к созданию сообщения об ошибке.
GBIC-модули WS-G5484, WS-G5486 и WS-G5487, используемые с WS-X6408-GBIC, также могут вызвать появление таких сообщений об ошибках, однако реальных проблем с данными платами и GBIC-модулями нет, а для программного обеспечения есть обновленное исправление.
Команда отклонена: [интерфейс] не является коммутационным портом
В коммутаторах, поддерживающих и интерфейсы L3, и коммутационные порты L2, сообщение Команда отклонена: [интерфейс] не является коммутационным портом отображается при попытке ввода команды, относящейся к уровню2, для порта, который настроен в качестве интерфейса уровня 3.
Чтобы преобразовать данный интерфейс из режима уровня 3 в режим уровня 2, выполните команду настройки интерфейса switchport. После применения этой команды настройте для данного порта требуемые свойства уровня 2.
Часть 4