Answer recommended by PHP
Collective
DEV environment
This always works for me:
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors occurred in the same file. Also, these settings can be overridden by PHP. In these cases the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini (or php-fpm.conf) with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
php_flag display_errors 1
PROD environment
Note that above recommendation is only suitable for the DEV environment. On a live site it must be
display_errors = off
log_errors = on
And then you’ll be able to see all errors in the error log. See Where to find PHP error log
AJAX calls
In case of AJAX call, on a DEV server, open DevTools (F12), then Network tab.
Then initiate the request which result you want to see, and it will appear in the Network tab. Click on it and then the Response tab. There you will see the exact output.
While on a live server just check the error log all the same.
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 11:25
Fancy JohnFancy John
38.2k3 gold badges27 silver badges27 bronze badges
16
You can’t catch parse errors in the same file where error output is enabled at runtime, because it parses the file before actually executing anything (and since it encounters an error during this, it won’t execute anything). You’ll need to change the actual server configuration so that display_errors is on and the approriate error_reporting level is used. If you don’t have access to php.ini, you may be able to use .htaccess or similar, depending on the server.
This question may provide additional info.
answered Jun 27, 2009 at 19:14
Michael MadsenMichael Madsen
54.3k8 gold badges72 silver badges83 bronze badges
0
Inside your php.ini:
display_errors = on
Then restart your web server.
j0k
22.6k28 gold badges79 silver badges90 bronze badges
answered Jan 8, 2013 at 9:27
user1803477user1803477
1,6251 gold badge10 silver badges4 bronze badges
5
To display all errors you need to:
1. Have these lines in the PHP script you’re calling from the browser (typically index.php):
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
2.(a) Make sure that this script has no syntax errors
—or—
2.(b) Set display_errors = On in your php.ini
Otherwise, it can’t even run those 2 lines!
You can check for syntax errors in your script by running (at the command line):
php -l index.php
If you include the script from another PHP script then it will display syntax errors in the included script. For example:
index.php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
// Any syntax errors here will result in a blank screen in the browser
include 'my_script.php';
my_script.php
adjfkj // This syntax error will be displayed in the browser
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 9:52
andreandre
1,8611 gold badge16 silver badges8 bronze badges
2
Some web hosting providers allow you to change PHP parameters in the .htaccess file.
You can add the following line:
php_value display_errors 1
I had the same issue as yours and this solution fixed it.
answered May 18, 2013 at 15:01
KalhuaKalhua
5594 silver badges2 bronze badges
1
Warning: the below answer is factually incorrect. Nothing has been changed in error handling, uncaught exceptions are displayed just like other errors. Suggested approach must be used with caution, because it outputs errors unconditionally, despite the display_error setting and may pose a threat by revealing the sensitive information to an outsider on a live site.
You might find all of the settings for «error reporting» or «display errors» do not appear to work in PHP 7. That is because error handling has changed. Try this instead:
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Error $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
Or, to catch exceptions and errors in one go (this is not backward compatible with PHP 5):
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Throwable $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
answered Mar 28, 2016 at 19:26
Frank ForteFrank Forte
2,03120 silver badges19 bronze badges
9
This will work:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
?>
answered May 5, 2014 at 13:23
Mahendra JellaMahendra Jella
5,4501 gold badge33 silver badges38 bronze badges
1
Use:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
This is the best way to write it, but a syntax error gives blank output, so use the console to check for syntax errors. The best way to debug PHP code is to use the console; run the following:
php -l phpfilename.php
answered May 4, 2016 at 19:14
Abhijit JagtapAbhijit Jagtap
2,7402 gold badges29 silver badges43 bronze badges
0
Set this in your index.php file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
answered Sep 26, 2017 at 12:32
Sumit GuptaSumit Gupta
5674 silver badges12 bronze badges
0
Create a file called php.ini in the folder where your PHP file resides.
Inside php.ini add the following code (I am giving an simple error showing code):
display_errors = on
display_startup_errors = on
answered Mar 31, 2015 at 18:38
NavyaKumarNavyaKumar
5875 silver badges3 bronze badges
In order to display a parse error, instead of setting display_errors in php.ini you can use a trick: use include.
Here are three pieces of code:
File: tst1.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
When running this file directly, it will show nothing, given display_errors is set to 0 in php.ini.
Now, try this:
File: tst2.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
include ("tst3.php");
File: tst3.php
<?php
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
Now run tst2.php which sets the error reporting, and then include tst3. You will see:
Parse error: syntax error, unexpected end of file, expecting variable (T_VARIABLE) or ${ (T_DOLLAR_OPEN_CURLY_BRACES) or {$ (T_CURLY_OPEN) in tst3.php on line 4
answered May 20, 2017 at 12:07
PeterPeter
1,24719 silver badges33 bronze badges
4
If, despite following all of the above answers (or you can’t edit your php.ini file), you still can’t get an error message, try making a new PHP file that enables error reporting and then include the problem file. eg:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
require_once('problem_file.php');
Despite having everything set properly in my php.ini file, this was the only way I could catch a namespace error. My exact scenario was:
//file1.php
namespace a\b;
class x {
...
}
//file2.php
namespace c\d;
use c\d\x; //Dies because it's not sure which 'x' class to use
class x {
...
}
answered Apr 24, 2015 at 2:55
jxmallettjxmallett
4,0871 gold badge28 silver badges35 bronze badges
2
I would usually go with the following code in my plain PHP projects.
if(!defined('ENVIRONMENT')){
define('ENVIRONMENT', 'DEVELOPMENT');
}
$base_url = null;
if (defined('ENVIRONMENT'))
{
switch (ENVIRONMENT)
{
case 'DEVELOPMENT':
$base_url = 'http://localhost/product/';
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
break;
case 'PRODUCTION':
$base_url = 'Production URL'; /* https://google.com */
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 0);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 0);
ini_set('log_errors', 1); // Mechanism to log errors
break;
default:
exit('The application environment is not set correctly.');
}
}
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:16
If you somehow find yourself in a situation where you can’t modifiy the setting via php.ini or .htaccess you’re out of luck for displaying errors when your PHP scripts contain parse errors. You’d then have to resolve to linting the files on the command line like this:
find . -name '*.php' -type f -print0 | xargs -0 -n1 -P8 php -l | grep -v "No syntax errors"
If your host is so locked down that it does not allow changing the value via php.ini or .htaccess, it may also disallow changing the value via ini_set. You can check that with the following PHP script:
<?php
if( !ini_set( 'display_errors', 1 ) ) {
echo "display_errors cannot be set.";
} else {
echo "changing display_errors via script is possible.";
}
answered Jan 11, 2016 at 12:11
chiborgchiborg
27k14 gold badges98 silver badges116 bronze badges
1
You can do something like below:
Set the below parameters in your main index file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
Then based on your requirement you can choose which you want to show:
For all errors, warnings and notices:
error_reporting(E_ALL); OR error_reporting(-1);
For all errors:
error_reporting(E_ERROR);
For all warnings:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
For all notices:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
For more information, check here.
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:33
Binit GhetiyaBinit Ghetiya
1,9192 gold badges21 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
You can add your own custom error handler, which can provide extra debug information. Furthermore, you can set it up to send you the information via email.
function ERR_HANDLER($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline){
$msg = "<b>Something bad happened.</b> [$errno] $errstr <br><br>
<b>File:</b> $errfile <br>
<b>Line:</b> $errline <br>
<pre>".json_encode(debug_backtrace(), JSON_PRETTY_PRINT)."</pre> <br>";
echo $msg;
return false;
}
function EXC_HANDLER($exception){
ERR_HANDLER(0, $exception->getMessage(), $exception->getFile(), $exception->getLine());
}
function shutDownFunction() {
$error = error_get_last();
if ($error["type"] == 1) {
ERR_HANDLER($error["type"], $error["message"], $error["file"], $error["line"]);
}
}
set_error_handler ("ERR_HANDLER", E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED);
register_shutdown_function("shutdownFunction");
set_exception_handler("EXC_HANDLER");
answered Jun 4, 2017 at 14:41
lintabálintabá
7439 silver badges18 bronze badges
Accepted asnwer including extra options. In PHP files for in my DEVELOPMENT apache vhost (.htaccess if you can ensure it doesn’t get into production):
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
// I've added some extra options that set E_ALL as per https://www.php.net/manual/en/errorfunc.configuration.php.
php_flag log_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_value error_reporting 2147483647
php_value error_log /var/www/mywebsite.ext/logs/php.error.log
answered Jan 8, 2022 at 22:17
This code on top should work:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, try to edit the code on the phone in the file:
error_reporting =on
answered May 9, 2017 at 3:28
Joel WemboJoel Wembo
8146 silver badges10 bronze badges
The best/easy/fast solution that you can use if it’s a quick debugging, is to surround your code with catching exceptions. That’s what I’m doing when I want to check something fast in production.
try {
// Page code
}
catch (Exception $e) {
echo 'Caught exception: ', $e->getMessage(), "\n";
}
answered Mar 27, 2017 at 2:31
XakiruXakiru
2,5861 gold badge15 silver badges11 bronze badges
3
<?php
// Turn off error reporting
error_reporting(0);
// Report runtime errors
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);
// Report all errors
error_reporting(E_ALL);
// Same as error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set("error_reporting", E_ALL);
// Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
?>
While your site is live, the php.ini file should have display_errors disabled for security reasons. However, for the development environment, display_errors can be enabled for troubleshooting.
answered May 24, 2018 at 8:48
pardeeppardeep
3591 gold badge5 silver badges7 bronze badges
0
Just write:
error_reporting(-1);
answered Jan 13, 2017 at 18:56
jewelhuqjewelhuq
1,21015 silver badges19 bronze badges
0
If you have Xdebug installed you can override every setting by setting:
xdebug.force_display_errors = 1;
xdebug.force_error_reporting = -1;
force_display_errors
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3 If this
setting is set to 1 then errors will always be displayed, no matter
what the setting of PHP’s display_errors is.force_error_reporting
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3
This setting is a bitmask, like error_reporting. This bitmask will be logically ORed with the bitmask represented by error_reporting to dermine which errors should be displayed. This setting can only be made in php.ini and allows you to force certain errors from being shown no matter what an application does with ini_set().
answered Oct 19, 2017 at 5:45
If it is on the command line, you can run php with -ddisplay_errors=1 to override the setting in php.ini:
php -ddisplay_errors=1 script.php
answered Oct 24, 2019 at 23:11
gvlasovgvlasov
18.8k21 gold badges74 silver badges110 bronze badges
Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Display all PHP errors
error_reporting(E_ALL); or ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Turn off all error reporting
error_reporting(0);
answered Dec 31, 2019 at 10:07
In Unix CLI, it’s very practical to redirect only errors to a file:
./script 2> errors.log
From your script, either use var_dump() or equivalent as usual (both STDOUT and STDERR will receive the output), but to write only in the log file:
fwrite(STDERR, "Debug infos\n"); // Write in errors.log^
Then from another shell, for live changes:
tail -f errors.log
or simply
watch cat errors.log
answered Nov 26, 2019 at 2:28
NVRMNVRM
11.6k1 gold badge90 silver badges87 bronze badges
2
If you are on a SharedHosting plan (like on hostgator)… simply adding
php_flag display_errors 1
into a .htaccess file and uploading it to the remote folder may not yield the actual warnings/errors that were generated on the server.
What you will also need to do is edit the php.ini
This is how you do it via cPanel (tested on hostgator shared hosting
plan)
After logging into your cPanel, search for MultiPHP INI Editor.
It is usually found under the SOFTWARE section in your cPanel list of items.
On the MultiPHP INI Editor page …you can stay on the basic mode tab and just check the button on the line that says display_errors.
Then click the Apply button to save.
IMPORTANT: Just remember to turn it back off when you are done debugging; because this is not recommended for public servers.
answered Mar 13, 2022 at 17:21
Really Nice CodeReally Nice Code
1,1441 gold badge13 silver badges22 bronze badges
As it is not clear what OS you are on these are my 2 Windows cents.
If you are using XAMPP you need to manually create the logs folder under C:\xampp\php. Not your fault, ApacheFriends ommitted this.
To read and follow this file do.
Get-Content c:\xampp\php\logs\php_error_log -Wait
To do this in VSCode create a task in .vscode\tasks.json
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "Monitor php errors",
"type": "shell",
"command": "Get-Content -Wait c:\\xampp\\php\\logs\\php_error_log",
"runOptions": {
"runOn": "folderOpen"
}
}
]
and have it run on folder load.
answered Dec 3, 2022 at 14:40
theking2theking2
2,2041 gold badge28 silver badges36 bronze badges
В этом руководстве мы расскажем о различных способах того, как в PHP включить вывод ошибок. Мы также обсудим, как записывать ошибки в журнал (лог).
Как быстро показать все ошибки PHP
Самый быстрый способ отобразить все ошибки и предупреждения php — добавить эти строки в файл PHP:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
Что именно делают эти строки?
Функция ini_set попытается переопределить конфигурацию, найденную в вашем ini-файле PHP.
Display_errors и display_startup_errors — это только две из доступных директив. Директива display_errors определяет, будут ли ошибки отображаться для пользователя. Обычно директива dispay_errors не должна использоваться для “боевого” режима работы сайта, а должна использоваться только для разработки.
display_startup_errors — это отдельная директива, потому что display_errors не обрабатывает ошибки, которые будут встречаться во время запуска PHP. Список директив, которые могут быть переопределены функцией ini_set, находится в официальной документации .
К сожалению, эти две директивы не смогут отображать синтаксические ошибки, такие как пропущенные точки с запятой или отсутствующие фигурные скобки.
Отображение ошибок PHP через настройки в php.ini
Если ошибки в браузере по-прежнему не отображаются, то добавьте директиву:
display_errors = on
Директиву display_errors следует добавить в ini-файл PHP. Она отобразит все ошибки, включая синтаксические ошибки, которые невозможно отобразить, просто вызвав функцию ini_set в коде PHP.
Актуальный INI-файл можно найти в выводе функции phpinfo (). Он помечен как “загруженный файл конфигурации” (“loaded configuration file”).
Отображать ошибки PHP через настройки в .htaccess
Включить или выключить отображение ошибок можно и с помощью файла .htaccess, расположенного в каталоге сайта.
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
.htaccess также имеет директивы для display_startup_errors и display_errors.
Вы можете настроить display_errors в .htaccess или в вашем файле PHP.ini. Однако многие хостинг-провайдеры не разрешают вам изменять ваш файл PHP.ini для включения display_errors.
В файле .htaccess также можно включить настраиваемый журнал ошибок, если папка журнала или файл журнала доступны для записи. Файл журнала может быть относительным путем к месту расположения .htaccess или абсолютным путем, например /var/www/html/website/public/logs.
php_value error_log logs/all_errors.log
Включить подробные предупреждения и уведомления
Иногда предупреждения приводят к некоторым фатальным ошибкам в определенных условиях. Скрыть ошибки, но отображать только предупреждающие (warning) сообщения можно вот так:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
Для отображения предупреждений и уведомлений укажите «E_WARNING | E_NOTICE».
Также можно указать E_ERROR, E_WARNING, E_PARSE и E_NOTICE в качестве аргументов. Чтобы сообщить обо всех ошибках, кроме уведомлений, укажите «E_ALL & ~ E_NOTICE», где E_ALL обозначает все возможные параметры функции error_reporting.
Более подробно о функции error_reporting ()
Функция сообщения об ошибках — это встроенная функция PHP, которая позволяет разработчикам контролировать, какие ошибки будут отображаться. Помните, что в PHP ini есть директива error_reporting, которая будет задана этой функцией во время выполнения.
error_reporting(0);
Для удаления всех ошибок, предупреждений, сообщений и уведомлений передайте в функцию error_reporting ноль. Можно сразу отключить сообщения отчетов в ini-файле PHP или в .htaccess:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
PHP позволяет использовать переменные, даже если они не объявлены. Это не стандартная практика, поскольку необъявленные переменные будут вызывать проблемы для приложения, если они используются в циклах и условиях.
Иногда это также происходит потому, что объявленная переменная имеет другое написание, чем переменная, используемая для условий или циклов. Когда E_NOTICE передается в функцию error_reporting, эти необъявленные переменные будут отображаться.
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Функция сообщения об ошибках позволяет вам фильтровать, какие ошибки могут отображаться. Символ «~» означает «нет», поэтому параметр ~ E_NOTICE означает не показывать уведомления. Обратите внимание на символы «&» и «|» между возможными параметрами. Символ «&» означает «верно для всех», в то время как символ «|» представляет любой из них, если он истинен. Эти два символа имеют одинаковое значение в условиях PHP OR и AND.
error_reporting(E_ALL);
error_reporting(-1);
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Эти три строки кода делают одно и то же, они будут отображать все ошибки PHP. Error_reporting(E_ALL) наиболее широко используется разработчиками для отображения ошибок, потому что он более читабелен и понятен.
Включить ошибки php в файл с помощью функции error_log ()
У сайта на хостинге сообщения об ошибках не должны показываться конечным пользователям, но эта информация все равно должна быть записана в журнал (лог).
Простой способ использовать файлы журналов — использовать функцию error_log, которая принимает четыре параметра. Единственный обязательный параметр — это первый параметр, который содержит подробную информацию об ошибке или о том, что нужно регистрировать. Тип, назначение и заголовок являются необязательными параметрами.
error_log("There is something wrong!", 0);
Параметр type, если он не определен, будет по умолчанию равен 0, что означает, что эта информация журнала будет добавлена к любому файлу журнала, определенному на веб-сервере.
error_log("Email this error to someone!", 1, "someone@mydomain.com");
Параметр 1 отправит журнал ошибок на почтовый ящик, указанный в третьем параметре. Чтобы эта функция работала, PHP ini должен иметь правильную конфигурацию SMTP, чтобы иметь возможность отправлять электронные письма. Эти SMTP-директивы ini включают хост, тип шифрования, имя пользователя, пароль и порт. Этот вид отчетов рекомендуется использовать для самых критичных ошибок.
error_log("Write this error down to a file!", 3, "logs/my-errors.log");
Для записи сообщений в отдельный файл необходимо использовать тип 3. Третий параметр будет служить местоположением файла журнала и должен быть доступен для записи веб-сервером. Расположение файла журнала может быть относительным путем к тому, где этот код вызывается, или абсолютным путем.
Журнал ошибок PHP через конфигурацию веб-сервера
Лучший способ регистрировать ошибки — это определить их в файле конфигурации веб-сервера.
Однако в этом случае вам нужно попросить администратора сервера добавить следующие строки в конфигурацию.
Пример для Apache:
ErrorLog "/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log"
В nginx директива называется error_log.
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log;
Теперь вы знаете, как в PHP включить отображение ошибок. Надеемся, что эта информация была вам полезна.
Содержание:
- Способы вывода ошибок PHP
- Виды ошибок в файле .htaccess
- Как включить вывод ошибок через .htaccess
- Примеры практического применения
- Включение журналирования ошибок PHP в .htaccess
- Дополнительные способы вывода ошибок PHP
Ошибки в коде — неотъемлемая часть любого процесса разработки. Чтобы понять, почему не выполняется скрипт, необходимо вывести error-логи PHP на экран.
Следует помнить, что в публичной версии сайта вывод ошибок на экран должен быть отключён.
- Через файл .htaccess, отвечающий за дополнительные параметры сервера Apache.
- Непосредственно через PHP-скрипт.
- Через файл php.ini, содержащий настройки интерпретатора PHP.
Преимущества вывода ошибок в файле .htaccess
- Широкий охват. Параметры распространяются на все элементы дочерних поддиректорий.
- Быстрота и удобство. Обработка ошибок настраивается в несколько команд и в одном месте.
Вывод ошибок на экран лучше делать через файл .htaccess, особенно когда PHP-файлов несколько. Поэтому далее разберём этот способ подробнее.
Виды ошибок PHP в файле .htaccess
- E_ALL — все виды ошибок, кроме E_STRICT до PHP 5.4.0.
- E_ERROR — фатальные ошибки, прекращающие работу скрипта.
- E_WARNING — ошибки-предупреждения. Не являются фатальными, поэтому не вызывают прекращение работы скрипта.
- E_PARSE — ошибки разбора. Могут возникать только во время компиляции.
- E_NOTICE — уведомления о нарушении времени выполнения скрипта.
- E_CORE_ERROR — фатальная ошибка обработчика. Генерируется ядром во время запуска PHP-скрипта.
- E_CORE_WARNING — предупреждения компиляции, возникающие при запуске PHP-скрипта.
- E_COMPILE_ERROR — фатальные ошибки, возникающие на этапе компиляции.
- E_COMPILE_WARNING — предупреждение компилятора PHP-скриптов.
- E_USER_ERROR — ошибки, сгенерированные пользователями.
- E_USER_WARNING — предупреждения, сгенерированные пользователями.
- E_USER_NOTICE — уведомления, сгенерированные пользователями.
Как включить вывод ошибок через .htaccess
Файл .htaccess должен находиться в корневой директории сайта (например, «public_html»). Отредактировать его можно с помощью проводника, доступного в панели хостинга.
Примечание. Если файла .htaccess нет, то его необходимо создать.
Включить отображение ошибок PHP и настроить фильтрацию их вывода можно двумя директивами: «display_errors» и «error_reporting». Первая отвечает за состояние режима показа ошибок («On» или «Off»), а вторая задаёт глубину отображения.
Показать ошибки PHP на экране можно с помощью следующего кода:
php_flag display_errors on php_value error_reporting -1
После сохранения изменённого файла, следует обновить страницу.
Примеры практического применения
Используя указанный код, можно быстро включить или отключить вывод ошибок, а также настроить различные конфигурации для разных режимов работы.
Следующий код скроет ошибки PHP с экрана:
# скрыть ошибки php php_flag display_startup_errors off php_flag display_errors off php_flag html_errors off php_value docref_root 0 php_value docref_ext 0
Иногда нужно фиксировать сбои, но нет возможности вывести ошибки PHP на экран (например, сайт работает в реальном времени). Для этого можно перенаправить вывод информации в лог-файл с помощью следующего кода:
# включить ведение журнала ошибок PHP php_flag log_errors on # месторасположение журнала ошибок PHP php_value error_log /var/www/имя_пользователя/data/www/ваш_www-домен/
Чтобы обработка ошибок в .htaccess выполнялась безопасно надо обязательно защитить папку с log-файлами от внешнего доступа при помощи следующего кода:
# запретить доступ к журналу ошибок PHP <Files PHP_errors.log> Order allow,deny Deny from all Satisfy All </Files>
Можно также настроить фильтрацию. Флаг «integer» указывает на глубину вывода данных (уровень показа). Значение «0» не выведет никаких ошибок. Комбинация «8191» запишет в log-файл сбои всех уровней.
# общая директива для фильтрации ошибок php php_value error_reporting integer
Чтобы текст ошибок не обрезался, можно установить максимальный размер на строку:
# общая директива для установки максимального размера строки log_errors_max_len integer
Выключение записи повторяющихся ошибок сократит объём поступающих данных и улучшит восприятие информации:
# отключить запись повторяющихся ошибок php_flag ignore_repeated_errors on php_flag ignore_repeated_source on
В результате настройки .htaccess для сайта, находящегося в публичном доступе, должны выглядеть так:
# обработка ошибок PHP для публичного ресурса php_flag display_startup_errors off php_flag display_errors off php_flag html_errors off php_flag log_errors on php_flag ignore_repeated_errors off php_flag ignore_repeated_source off php_flag report_memleaks on php_flag track_errors on php_value docref_root 0 php_value docref_ext 0 php_value error_reporting -1 php_value log_errors_max_len 0 <Files /home/path/public_html/domain/PHP_errors.log> Order allow,deny Deny from all Satisfy All </Files>
Во время разработки или отладки файл .htaccess должен содержать следующий код:
# Обработка ошибок PHP во время разработки php_flag display_startup_errors on php_flag display_errors on php_flag html_errors on php_flag log_errors on php_flag ignore_repeated_errors off php_flag ignore_repeated_source off php_flag report_memleaks on php_flag track_errors on php_value docref_root 0 php_value docref_ext 0 php_value error_log /home/path/public_html/domain/PHP_errors.log # [see footnote 3] # php_value error_reporting 999999999 php_value error_reporting -1 php_value log_errors_max_len 0 <Files /home/path/public_html/domain/PHP_errors.log> Order allow,deny Deny from all Satisfy All </Files>
Включение журналирования ошибок PHP в .htaccess
Когда отображение ошибок на странице выключено, необходимо запустить их журналирование следующим кодом:
# включение записи PHP ошибок
php_flag log_errors onphp_value error_log /home/path/public_html/domain/PHP_errors.log
Примечание. Вместо «/home/path/public_html/domain/PHP_errors.log» нужно подставить собственный путь до директории, в которой будет вестись журнал ошибок.
Чтобы запретить доступ к журналу извне, нужно добавить следующий код:
# предотвращаем доступ к логу PHP ошибок <Files PHP_errors.log> Order allow,deny Deny from all Satisfy All </Files>
Дополнительные способы вывода ошибок PHP
Можно добавить оператор «@», чтобы запретить показ ошибок в конкретной инструкции PHP:
$value = @$var[$key];
Вывод ошибок в PHP-скрипте
Чтобы выводить все ошибки, нужно в начале скрипта прописать:
error_reporting(-1);
Если необходимо отображать ошибки PHP только из определённого места скрипта, то можно использовать следующий код:
ini_set('display_errors', 'On'); // сообщения с ошибками будут показываться
error_reporting(E_ALL); // E_ALL - отображаем ВСЕ ошибки
$value = $var[$key]; // пример ошибки
ini_set('display_errors', 'Off'); // теперь сообщений НЕ будет
Примечание. Если заменить значения «On» и «Off» в первой и последней строках на противоположные, то на конкретном участке кода ошибки выводиться не будут.
Через файл php.ini
Включить или выключить показ ошибок на всём сайте/хостинге также можно с помощью файла «php.ini», в котором нужно изменить два следующих параметра:
error_reporting = E_ALL display_errors On
Первая строка отвечает за фильтрацию ошибок (в данном случае показываться будут все типы сбоев), а вторая активирует их отображение на экране. После изменений этого файла необходимо перезапустить сервер Apache.
При отладке скриптов на PHP обычное дело заполучить в браузере «белый экран». Что в большинстве случаев говорит об остановке выполнения PHP кода из-за ошибки. PHP интерпретатор позволяет выводить служебную информацию об ошибках на экран, что существенно облегчает отладку. Но по-умолчанию (в большинстве случаев) такое поведение из соображений безопасности отключено, то есть сообщения об ошибках PHP на экран не выводятся.
В этой статье я расскажу как заставить PHP выводить сообщения об ошибках на экран монитора в окне браузера. Инструкция справедлива для случая когда вы используете веб сервер Apache и если PHP для Вашего сайта подключен как модуль Apache.
Вывод ошибок на экран следует включать только во время отладки сайта. Наличие такого кода может негативно сказаться на безопасности веб-приложения.
Включение вывода ошибок PHP на экран с помощью файла .htaccess
Это очень удобный способ для отладки PHP кода. Работает практически во всех случаях. В папку со скриптом на сайте помещаем файл .htaccess со следующим содержимым:
php_flag display_errors on php_flag display_startup_errors on php_flag error_reporting E_ALL
где:
- display_errors — включает опцию для вывода ошибок на экран вместе с остальным кодом.
- display_startup_errors — включает опцию вывода ошибок, возникающих при запуске PHP, когда еще не работает директива display_errors.
- error_reporting — указывает, какие ошибки выводятся по уровню значимости. При значении директивы E_ALL отображаются все ошибки.
Включение вывода ошибок PHP на экран в коде файла PHP
Этот способ удобен тем, что выводом ошибок на экран вы управляете в самом скрипте PHP. Параметры, заданные с помощью функции ini_set(), имеют более высокий приоритет и перекрывают директивы php.ini и .htaccess. Разместите следующий код в начале PHP файла:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Включение вывода ошибок PHP на экран с помощью файла php.ini
Этот способ актуален когда вы являетесь администратором сервера. В файле php.ini отредактируйте следующие строки (добавьте при необходимости):
display_errors = On display_startup_errors = On error_reporting = E_ALL
Лучший способ вывода PHP ошибок на экран
На мой взгляд обычному пользователю удобнее всего использовать .htaccess, особенно если у вас больше чем один PHP файл. Способ №2 удобен для отладки одного php файла, чтобы не затрагивать уровень вывода ошибок для других php скриптов. Вариант с php.ini подойдет только администраторам сервера, но зато его действие распространяется на все сайты расположенные на данном сервере.
Благодарности
При написании статьи были использованы следующие источники:
- http://drupalace.ru/lesson/vyvod-oshibok-php-na-ekran
- https://help.sweb.ru/entry/137
- http://ramzes.ws/blog/vkljuchit-vyvod-oshibok-php
- http://php.net/manual/ru/function.error-reporting.php
on
June 25, 2020
Errors are undesirable for users and you should do everything in your control to keep users away from them. However, they are of utmost importance for developers. They allow developers to understand the inaccuracies and vulnerabilities in their code by alerting them when their code breaks. They also provide relevant information about what went wrong, where, and what can be done to make amends. Absence of intelligent error reporting can not only make it extremely difficult to debug your project but can also let unnoticed, unresolved inconsistencies bleed into production code.
Most errors in PHP are by default not reported. This might be helpful for web applications in production, where you don’t want users to come across obscure error messages. However, during development, it is imperative to enable error messages — to be alerted about potential inaccuracies in your code before it is released for production.
In this post, we will look at what an error in PHP is, the different types of errors, and how you can enable error reporting in PHP.
Use these links to jump ahead in the tutorial:
What is a PHP error?
Common PHP Error Codes
Turn on Error Reporting in PHP
How to Log Errors in PHP
Conclusion
What is a PHP Error?
An error is an indication of something going wrong in your web application. It is usually encountered when a part of your code has not been properly implemented, for example — mistakes in the syntax, logical inconsistencies, inattention to handling invalid user input, etc. An error in programming paradigms can be as trivial as a missed semicolon or an unclosed parenthesis to something as big as an undefined class function or an unhandled invalid user input.
Let us look at a few common PHP error categories and codes.
Types of PHP Errors
There are primarily four types of errors in PHP —
- Fatal run-time errors
- Warning errors
- Parse errors (Syntax errors)
- Notice errors
Note: We are able to access error messages in the example outputs shown below because error reporting has been turned on for visualization. We will look at how one can enable error messages in the next section.
Fatal run-time errors (E_ERROR | Code 1)
As the name suggests, these errors can not be recovered from. They are encountered when the operation specified in your code can not be performed. As a result, execution is halted.
For example — if you try to call a function that has not been defined, a fatal run-time error would be raised.
<?php
function foo() {
echo "Function foo called.";
}
boo(); // undefined function 'boo'
?>
Warning errors (E_WARNING | Code 2)
A warning error is more subtle in that regard. It does not halt execution — just acts as a friendly reminder of something incorrect in your code, that might pose a bigger problem in the future.
The most common example of a warning error being raised is when you include a missing file in your code.
<?php
include('filename.txt'); // arbitrary file that is not present
echo "Hello world";
?>
Notice how the warning error has not forced the code to halt, allowing the print statement below to be executed.
Parse errors (E_PARSE | Code 4)
Parse errors are encountered as a result of purely syntactical mistakes in one’s code. These errors are generated during compilation, and as a result your code exits before it is run.
Parse error examples include — missing semicolons, unused or unclosed brackets, quotes, etc. Below is an example of the same.
<?php
echo "Hello world";
echo Hello world // no quotes or semicolon used
?>
Notice errors (E_NOTICE | Code 
Notice errors are similar to warning errors in that they are encountered during run-time and they don’t halt code execution. They indicate that something is incorrect in the script that even though doesn’t interrupt execution, should be fixed.
A common example would be trying to use an undefined variable in your code.
<?php
$a = 1;
$c = $a + $b; // undefined variable $b
echo "Hello world";
?>
Turn on Error Reporting in PHP
Error reporting in PHP is usually disabled by default. It can be enabled in three primary ways —
- Directly from code
- By editing the php.ini configuration file
- By editing the .htaccess file.
Before we look into the various methods, a word of caution is necessary. Make sure to disable error reporting for your web application’s production code. You wouldn’t want your users to come across obscure error messages when using your website.
Directly from code
Using the error_reporting() function
To configure error reporting in your PHP project, you can use the error_reporting function. This allows you to manipulate error reporting at run-time.
error_reporting ([ int $level ] ) : intPHP has various types of errors that we looked at earlier in this post. These types can be provided to the error_reporting function as an argument to specify the kinds of errors that should be reported.
To report all PHP errors you can use the function in any of the two ways shown below.
<?php
// Report all PHP errors
error_reporting(E_ALL);
?>
or
<?php
// Report all PHP errors
error_reporting(-1);
?>Both of the above-mentioned methods serve the same purpose, and therefore you can use either of them to enable error reporting for all types of errors.
Let us see this in action using an example —
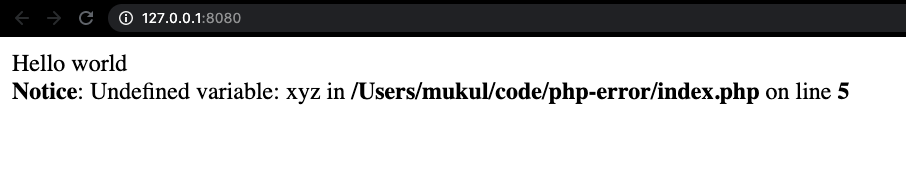
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
echo "Hello world";
// xyz is an undefined variable; should raise an error.
echo $xyz;
?>OUTPUT:
As we can see, a Notice error has been reported. Had we not used the error_reporting function, PHP would have implicitly taken care of it and not reported anything at all.
This only strengthens our above argument about how unresolved issues can go unnoticed if errors are not appropriately reported.
You can also disable error reporting using the function as such —
//Turn off error reporting
error_reporting(0);For reporting only specific kinds of errors, you can provide the required error types as a parameter to the error_reporting function using the bitwise OR operator as shown below —
// Report only selected kinds of errors
error_reporting(E_WARNING | E_ERROR | E_PARSE | E_NOTICE);To enable error reporting for all but one (or more) error levels, you can use the below syntax —
// Report all errors except E_WARNING
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_WARNING);Using the ini_set() function
We can also use the ini_set function to configure error reporting. This function allows us to initialize or modify the various configuration options (specified using a .ini file) directly from our code. This function modifies the configuration options only for the duration of the code (run-time).
You can call this function by adding the following line to your code —
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);We can similarly manipulate error reporting by applying different values for the ‘error_reporting’ option.
// Report selected kinds of errors
ini_set('error_reporting', E_WARNING | E_ERROR | E_PARSE | E_NOTICE);Even though the ini_set function allows us to easily modify the configuration options directly from our code, it is a better practice to keep your PHP configurations in a separate php.ini file on your system. Let’s look at how we can do that in the next section.
By editing the php.ini configuration file
The php.ini serves as a configuration file for your project. It is read when PHP is initialized and can be used for a variety of things — storing environment variables, configuring server ports, error reporting, memory management, etc. You can find a list of the various configuration directives and their default values here.
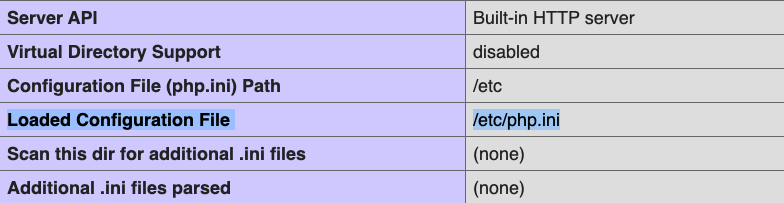
Therefore, to enable error reporting in PHP, you need to edit this configuration file. The php.ini file is usually present in the /etc directory on Linux systems. You can locate the file by printing the output of the phpinfo() function in your code. The file’s path is provided under the ‘loaded configuration file’ row of the output.
Note: If the path mentioned in your output refers to a directory (for example- /etc) and not the file, you can create a new php.ini file inside that directory.
To enable error reporting, you can add either of the following lines to the php.ini file, and restart your server for the effects to take place.
error_reporting = E_ALLor
error_reporting = -1To also report errors encountered during PHP’s startup sequence, you can use the following directive in your php.ini file —
display_startup_errors = 1Some posts on the internet also suggest enabling the ‘display_errors’ option for displaying error messages. In most cases, this is not required since that option is usually turned on by default in PHP.
If it is disabled in your system, you can turn it on by adding the following line in your php.ini file —
display_errors = 1By editing the .htaccess file
The .htaccess (stands for hypertext-access) is a configuration file for manipulating various options provided by Apache-based web-servers.
Even though it can be a little difficult to set up initially based on your operating system, the .htaccess file allows you to exercise control over various server options at the local directory level and the global system level.
To enable error reporting, add the following two lines to your .htaccess file —
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors onEven though (as mentioned above) the display_errors property is by default ON, it is likely that your system admin might have disabled that property globally and you might want to enable it for a local project. Overriding the global property using the local .htaccess file can be a handy approach in such situations.
How to Log Errors in PHP
In large-scale PHP web applications that involve many processes like API requests, data processing etc, it is a good practice to store logs of your output and error messages. Good logging measures allow us to keep track of the inner workings of the system for effective debugging and maintenance. Let’s look at how we can create error logs in PHP.
You need to do two things to store error logs for your project —
- Enable ‘log_errors’ option
- Specify the ‘error_log’ file
Once this has been done, all your errors will be automatically logged to the specified error_log file. Just like error reporting, error logging can be set up from any of these three places — directly from code, from the php.ini configuration file and from the .htaccess file
Directly from code
Using the ini_set function we can configure the relevant PHP options as such —
ini_set('log_errors', 1); // enabling error logging
ini_set('error_log', '/path/my-error-file.log'); // specifying log fileAfter doing this, all our errors would be automatically logged to the specified log file. Let us look at an example —
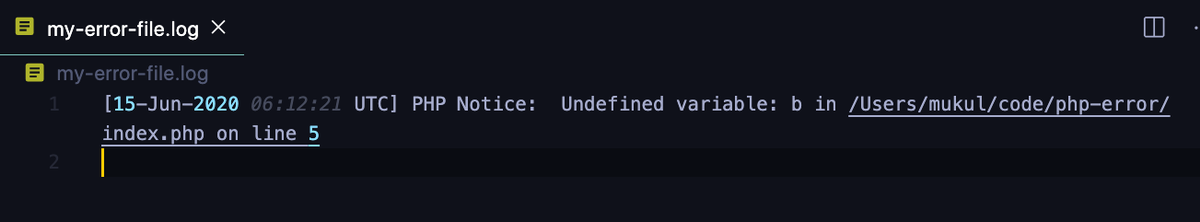
<?php
ini_set('log_errors', 1); // enabling error logging
ini_set('error_log', '/path/my-error-file.log'); // specifying log file
echo $b; // undefined variable should raise error
?>Now, let’s open our project root folder and open the ‘my-error-file.log’ file to see if the error message has been logged.
As you can see, a timestamp has also been added to the error message, as we’d expect any effective logging system to do. All errors further encountered in your code will be appended to this file.
Another alternative to logging errors from your code would be to manually do so using the error_log function. You can use the function as shown below to write to a log file as shown below —
<?php
echo "Hello world";
// manually logging error message ->
error_log('My error message ⚠️', 3, 'my-error-file-2.log');
?>
The first and third arguments of the function represent the error message and the log file respectively. The second argument in the above function (3) is an option that specifies that the error message should be appended to the output of the file.
You can read more about the arguments of the error_log function here.
In this case, as can be seen, one has to specify the error message and the logging file each time. Also, in this method, timestamps are not added to the generated log messages by default.
Using the php.ini configuration file
Enabling logging from the configuration file is pretty straightforward. You only need to add two directives to your php.ini file as shown below —
log_errors = on
error_log = /path/my-error-file.logAfter saving the file, restart your server to enable the automatic error logging to the specified file.
Using the .htaccess file
You can add the following two lines to your .htaccess file to enable error logging —
php_flag log_errors on
php_value error_log /path/my-error-file.logThis also serves the same purpose — enabling error logging, followed by specifying the output log file.
Conclusion
In this post, we learned about what PHP errors are, their different types (fatal errors, warnings, parse errors, and notices), about how important they are, and how you can enable error reporting for your web application. We looked at three different ways of initiating error reporting and storing log files — directly from code, through the php.ini configuration file, and from the server-based .htaccess file.
Now that you know how important it is to be mindful of errors, go ahead and enable error reporting in your project, maintain error logs, and build yourself a full-proof web application! You can also view your PHP errors in ScoutAPM’s dashboard. Also, make sure to disable error displaying when you release your website for production.
After you have enabled error reporting in your project, you might want to learn about how to handle these raised errors (exceptions) in your code. For this, you can refer to our post on Exception Handling in PHP — PHP Advanced Exceptions.
Stay safe! Keep learning! Happy coding!