Whether you’re browsing the internet as a user or maintaining and managing a website as a web admin, you’ll encounter certain common errors or HTTP error codes on a daily basis. Some error codes, such as HTTP 499, can cause downtime that can affect businesses of all sizes.
After all, websites are one of the primary ways customers access and interact with products or services.
When a user tries to access a website, but it’s not available due to any reason, they often receive an error message generally represented as an HTTP status code that indicates the type of error.
Like HTTP status codes 100-500, there is plenty of HTTP error codes out there, ranging from 100 to 500. However, for now, we’ll focus on the most frustrating, dreadful, and common HTTP error code – the 499 error.
In this blog, we’ll be explaining what HTTP error 499 actually means, its causes, tips to prevent it, and the best working methods to fix it. Let’s get started!
What is HTTP 499 Status Code Error?
The HTTP 499 error status code is a unique and special case of the 502 Bad Gateway error that is caused by the client side. The 499 error indicates that a client closed the connection before the server could send a response, and the server is still processing the request.
Error 499 is unique because it doesn’t occur from the server end, unlike most errors where the server is often the main culprit due to misconfiguration or some software bug.
But in this particular type of error, the main culprit is the client (web browser or a user agent) that closed the connection before the server could send a response. This means the server was doing its job correctly – processing the request – but the client didn’t wait for the response to be sent back.
This error has not been listed or a part of the official HTTP/1.1 standard, hence it is not well recognized by all web servers.
Similarly, we have two more common errors that fall into the same category: HTTP 404 Not Found error and HTTP 400 Bad Request error, which you must also check out.
Why does the HTTP 499 Status code Occur?
Http 499 status code is specific to only Nginx web servers only and there can be multiple reasons why it can happen. But some of the most common are:
- Network Issues: Network problems can cause lost connections between client and server due to issues like dropped connections or high latency.
- Server-side issue: Server issues like high load or misconfiguration can cause delayed response or failure to respond to client requests.
- Client Side issue: Termination of connection before response due to canceled request or navigating away from the page during loading of the page by the client.
- Firewalls and Anti-virus software: Firewall or Anti-virus software interference can lead to lost connections or blocking of communication between client and server.
- Misconfigured Server: If the server is not properly configured, it won’t be able to handle incoming requests from clients correctly, which may result in Error 499.
To better understand what is triggering error 499, you need to have a basic understanding of how modern web applications work.
In a general web application, a client or your browser sends a request to a web server. Then the web server processes the request and sends a response back to the client.
During the entire communication process between the client and the web server, there are usually security devices installed, such as firewalls or load balancers. These devices play an important role in distributing traffic across multiple servers and filtering out malicious requests.
However, sometimes these devices can be misconfigured and can cause 499 errors to occur. Another common cause for triggering 499 errors is on the client side.
For example, a user may close the browser or switch to another page before the server sends back the response to the browser.
Alternatively, any installed extensions or proxy servers used may also interfere with the communication between the client and the server, causing the 499 error.
These are some of the general and common reasons that might trigger Error 499. However, to determine the exact cause of the error, further investigation is needed, along with trying different troubleshooting methods discussed below.
Now that you understand the meaning of the HTTP 499 status code and some of the main reasons that cause it, let’s check out the top 5 methods that can help you fix it.
1. Purge your browser cache and Reload again
As we mentioned earlier, the HTTP 499 error is not a permanent issue and can sometimes be easily fixed by simply reloading or refreshing the web browser. It is also possible that your server or host may be overburdened with multiple requests, so you should clear your browser cache and try browsing the site again.
Note: Since Chrome has a major Browser market share, here we will be using Chrome for this tutorial.
Step 1: Depending on your browser, navigate to the settings menu. In Google Chrome, you can click on the three vertical dots in the upper right corner of the window.
Step 2: Select “More tools” and Click on “Clear browsing data“.
Step 3: A pop-up window will open on which, you can select all three options under the “Basic” section or just select the “Cached images and files” as shown in the picture below.
Step 4: Click on “Clear data” to initiate the process.
2. Check on a Different Browser or Device
If the error still appears, you can try accessing the website on a different browser or even on a different device to see if the error is specific to the device or configuration.
3. Temporarily disable Plugins or Extensions
Some reports have shown that faulty plugins and extensions can also cause the HTTP status499 error. Therefore, you should check whether a faulty plugin is the main culprit or not.
To do this, Go to your WordPress Dashboard > Plugins and select all the plugins, and then click on Deactivate > Apply from the bulk action menu.
![How to Fix the HTTP NGINX 499 Error? [6 Best Methods] 5 Fixing 499 Error by Disable WordPress Plugins](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/3-1.png)
In case you are unable to log in to your WordPress dashboard for any reason, you can alternatively connect to your site via FTP or a file transfer protocol client such as FileZilla. Go to the wp_content folder > plugins and right-click on the plugin folder you want to edit and rename it to anything you like.
This method will help you deactivate all the installed plugins on your WordPress site. You can then check for the faulty plugins by activating them one by one and trying to access the site simultaneously to see if the error message still appears. Repeat the process until you find the faulty plugin.
4. Check Error Logs
If you have access to the Error logs, look out for the suspicious entries that correspond to the time that the HTTP 499 status error code appears.
Read: 🚩 If you do not have any idea about Error logs, Please check out our Comprehensive dedicated blog on “How to Set up and Use WordPress Error Log?“
5. Disable Firewall or Antivirus Software
Certain firewalls or antivirus software may interfere with communication between the client and the server, resulting in 499 errors. Try disabling your firewall or antivirus software temporarily to see if it resolves the issue.
Therefore, you can try temporarily disabling them and check whether it fixes the issue or not.
For Windows users:
Step 1: First, you need to open your computer’s control panel. To do this, click on the “start” menu on your desktop and type in “control” in the search field.
Step 2: Next, select “System and Security” from the control panel options. This will take you to a new page.
Step 3: On the new page, you’ll see an option for “Windows Defender Firewall.” Click on “Allow an app or feature through Windows Firewall.”
![How to Fix the HTTP NGINX 499 Error? [6 Best Methods] 6 Allowing an app through Windows Firewall](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/11.png)
Step 4: In the next window, you’ll see a list of apps and features that are allowed to communicate through your firewall. To change these settings, click on “Change settings.”
![How to Fix the HTTP NGINX 499 Error? [6 Best Methods] 7 List of allowed apps in Windows Defender Firewall](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/12.png)
Step 5: If you don’t see your DNS client on the list, you can add it by clicking on the plus (+) icon.
Step 6: To temporarily disable your firewall, uncheck the box next to “Windows Defender Firewall” and click on “OK” to save your changes.
Step 7: Alternatively, you can adjust your firewall settings by finding the DNS client or any other application you want to configure and checking or unchecking the boxes next to the desired settings.
Step 8: Once you’re done adjusting your settings, click on “OK” to save your changes.
Note: It’s important to only disable your firewall temporarily if you need to troubleshoot a connectivity issue. Leaving your computer without a firewall can expose it to potential security threats.
6. Contact Your Web Host
If none of the above methods can fix Error 499, the final option is to contact your web host. Sometimes, the request may be canceled due to taking too long to process, causing Error 499. To prevent server overload, web hosts generally use a kill script to forcibly terminate such requests.
The server may be configured to have a response timeout period, and exceeding the set limit may result in a connection being closed and a 499 error occurs. For instance, suppose you have a request that is expected to take 15 seconds to complete, but the server timeout value is set to 10 seconds. This will result in a timeout before completing the request.
Therefore, it is highly recommended to check with your web host about the timeout values set on the server, and if possible, request an extension of the timeout value.
If you are a WPOven user, you don’t need to worry about this issue. Each site is hosted on a Virtual Private Server, and all resources are allocated dedicatedly.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have discussed the 499 error, a frustrating and common error that can cause downtime for websites. We have explained how this error is caused by the client, such as a web browser, closing the connection before the server can send a response.
However, with the right precautions, you can prevent the 499 error from occurring. This includes optimizing your website’s code and configuration, as well as regularly monitoring your server logs for any errors. Additionally, having a reliable web host and a backup plan can also help minimize downtime.
If you do encounter the 499 error, don’t panic! There are several effective methods to fix it, including tweaking your website’s settings or contacting your web host for assistance. By taking these steps, you can quickly resolve the issue and get your website back up and running.
In conclusion, website availability is critical for any business that wants to succeed in today’s digital world. By understanding the causes and solutions of the 499 error, you can ensure that your website is always accessible to your customers. So take the necessary precautions and always stay vigilant to keep your website running smoothly!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Cloudflare 499 error?
The 499 error code is a specific code used by Nginx, indicating that the client has closed the connection while the server is still processing the request.
What is Nginx 499 error code?
The Nginx 499 error code is an HTTP status code exclusive to Nginx web servers, which means the client has closed the connection while the server is still processing the request. Hence it is considered a client-side error.
What is AWS load balancer 499 error?
If the server is unable to respond to the request within the load balancer’s timeout limit, the connection will be terminated, resulting in an error 499 being displayed.
HTTP response status code 499 is an unofficial client error that is specific to both ArcGIS with 499 Token Required and nginx with 499 Client Closed Request.
Usage specific to ArcGIS
When the 499 Token Required status code is received, the server is expecting a token to accompany the HTTP request but it was not submitted. To solve this error, the HTTP request needs to be resubmitted with a valid token.
Usage specific to nginx
When the 499 Client Closed Request status code is generated, it means that the client has closed the HTTP Connection in advance of the server completing the task. As such, the final response cannot be sent and this status code is only available in the nginx logs.
Note
Search engines like Google will not index a URL with 499 response status, and consequently, URLs that have been indexed in the past but are now returning this HTTP status code will be removed from the search results.
Takeaway
The 499 Token Required / Client Closed Request status code is specific to ArcGIS, where the HTTP request required a token that was not included, and nginx, where the client closed the HTTP request prematurely.
See also
- ArcGIS Survey123
- Esri Technical Support for ArcGIS error 499
- nginx HTTP return Codes
Last updated: June 2, 2022
Understand the 499 status code Client Closed Request error: What are the causes and how to fix it.
Table of Contents
- What is the 499 Client Closed Request error?
- How to fix the 499 Client Closed Request error
-
499 error when the website is behind a proxy
- The right way to set the timeouts
- 499 when your server closed the connection
- How to fix the 499 error when your application dies
- 499 when your server is under a DOS or DDOS attack
- How to fix the 499 error when DOS/DDOS attacks:
-
499 error when the website is behind a proxy
- All HTTP Status Codes
What is the 499 Client Closed Request error?
The 499 HTTP is a non-standard status code introduced by Nginx when a client, for instance a browser, closes the connection while Nginx is processing the request.
How to fix the 499 Client Closed Request error
There are various reasons why the client would not process the request and ended up with a 499 error code. In the following sections, we will help you identify the different causes and how to fix them in each case.
499 error when the website is behind a proxy
You may find 499 errors when you have a Load Balancing service between your users and your Nginx. A similar situation occurs when your Nginx site is served by a CDN or is behind a WAF (Web Application Firewall).
The 499 error happens when the front server attending your browser request is an Nginx server in reverse proxy mode, and it sends the request to your server site, but your site process exceeds the waiting time of the front server.
To fix this error, you can:
- Increase the processing capacity of your application server. By increasing the “processing power”, you will reduce the waiting time of the Nginx clients in front of your service.
- If you cannot increase the power of your application server, then increase the timeouts of your proxies (load balancer, CDN, firewall, …).
At Wetopi you can increase the size of your server with a single click.
★ Zero-config: configuration files for all server services are transparently adjusted to the power.
The right way to set the timeouts
If there are proxies on your setup such as a “Load balancer”, a Firewall, a CDN, etc, you should set the timeouts so that you timeout first your application server and then the other proxies to the user.
Example:
User → CDN → Nginx Load Balancer → Nginx application → Php_fpm
It’s recommended to set the timeouts like this:
- n seconds to
Php_fpmtimeout.
Set thephp.inimax_execution_timeand
therequest_terminate_timeoutin yourphp_fpmconfig file.
- n+1 seconds to Nginx application timeout.
Set thefastcgi_read_timeoutin your nginx config.
- n+2 seconds to timeout to Nginx Load Balancer
In your location doing theproxy_passset the timeouts of:proxy_connect_timeoutproxy_send_timeoutproxy_read_timeout - n+3 seconds of timeout for your CDN. NOTE: If you can’t set the timeouts of your CDN, then find what is its timeout and adjust the others according to it.
It provides a correct chain of timeouts: Setting an incremental chain of timeouts lets you find who is reaching the timeout.
499 when your server closed the connection
This could be your case, If:
- your site is running with an Nginx server and,
- the request is passed to an application processor e.g.
php_fpm, or - the request is passed to your API
This setup is configured using the nginx fastcgi_pass directive.
This 499 error code is produced when your server is too slow.
e.g. your WordPress page process takes too long or freezes
To correct this error, you can:
- Increase the processing capacity of your server. By increasing “processing power”, you will reduce the period Nginx waits.
- If you cannot increase your server power, increase Nginx timeouts with the directive:
fastcgi_read_timeout.
How to fix the 499 error when your application dies
If your application dies without an answer, the solution could be in your API or CGI code.
NOTE: This is the least common case, PHP and other processors always throw a note to notify a problem. If the app was throwing an error, Nginx would pass you a 5XX error code, not a 499.
If your application freezes, you have 2 options:
- First, tell the Nginx to wait longer. Increase the timeouts of your Nginx by modifying the
fastcgi_read_timeout. - If waiting longer does not solve the problem, increase the processing capacity of your server.
- If the 499 error occurs on a specific page or request, it could be a “hung” or “code freeze” in your application or content manager. If you use WordPress, check plugin compatibility. If database queries are made, check the good status of tables and indexes.
499 when your server is under a DOS or DDOS attack
There might be a case when someone attacks, and intentionally consumes the server resources. This makes the server unable to process the request and return the result on time.
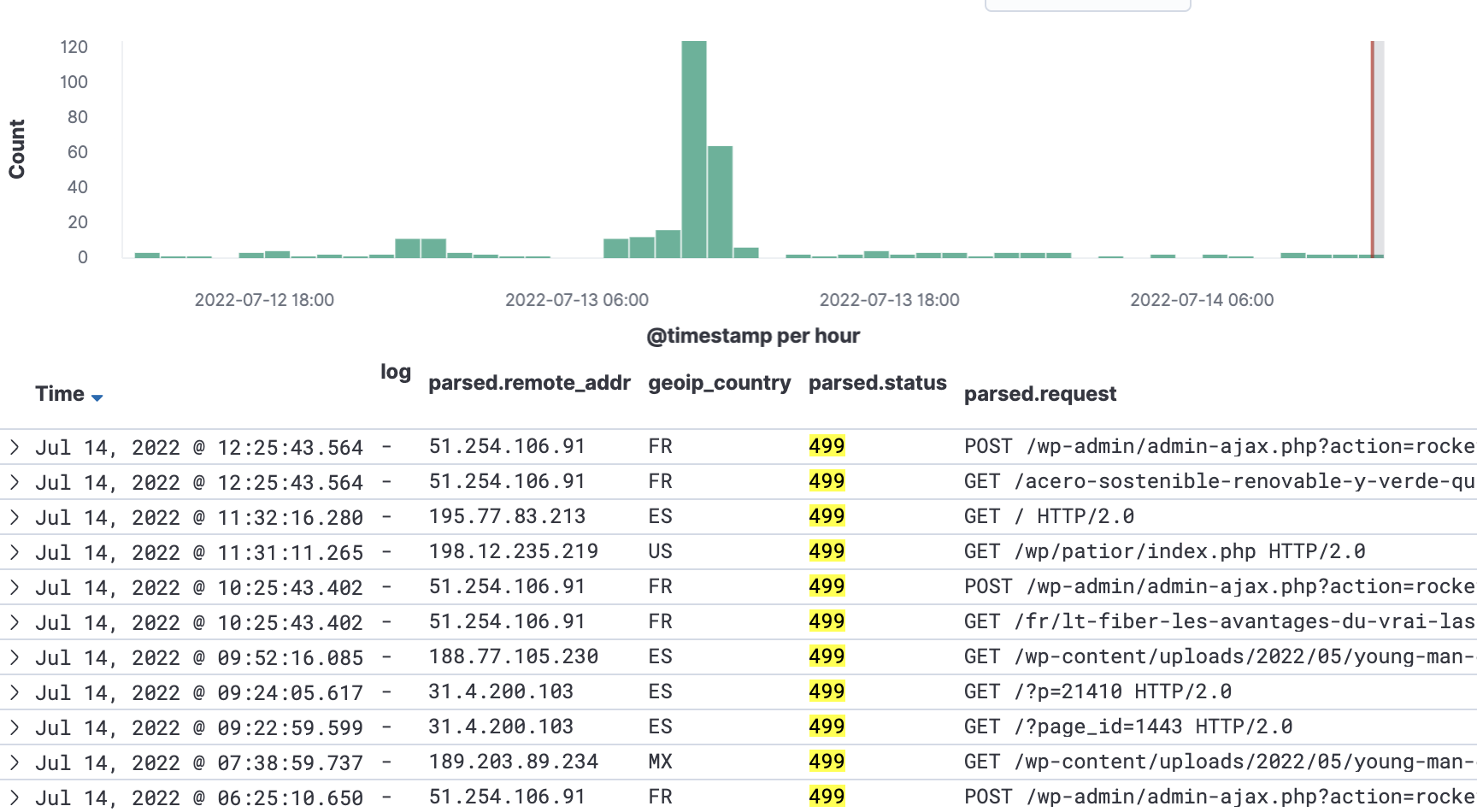
To verify if this is your case: look at your analytics, and search for spikes in traffic with requests giving the 499 status code:
How to fix the 499 error when DOS/DDOS attacks:
In this case, the best solution is a combination of security measures:
- Prevention: avoid non-legit traffic. You can filter malicious traffic with a combination of public and private blacklists.
- Add infrastructure protection against DOS (Denial of Service) and DDOS (Distributed Denial of Service). Find a hosting provider with infrastructure ready to mitigate this kind of attack.
- Add a protection layer, a security proxy, in front of your server, or
- Add an external security service. A well-known one is Cloudflare. They put a distributed infrastructure in front of your server to fight against DDOS attacks.
At Wetopi, as WordPress specialists, we know how important it is to add strong measures of security.
We apply three techniques to filter traffic:Shared security heuristic learning,
Blacklisting from external sources and
Mitigation of DDoS attacks.
We are techies passionate about WordPress. With wetopi, a Managed WordPress Hosting, we want to minimize the friction that every professional faces when working and hosting WordPress projects.
Not a wetopi user?
Free full performance servers for your development and test.
No credit card required.
All HTTP Status Codes
200 OK
201 Created
202 Accepted
203 Non-Authoritative Information
204 No Content
205 Reset Content
206 Partial Content
207 Multi-Status
208 Already Reported
226 IM Used
300 Multiple Choices
301 Moved Permanently
302 Found
303 See Other
304 Not Modified
305 Use Proxy
307 Temporary Redirect
308 Permanent Redirect
400 Bad Request
401 Unauthorized
402 Payment Required
403 Forbidden
404 Not Found
405 Method Not Allowed
406 Not Acceptable
407 Proxy Authentication Required
408 Request Timeout
409 Conflict
410 Gone
411 Length Required
412 Precondition Failed
413 Payload Too Large
414 Request-URI Too Long
415 Unsupported Media Type
416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
417 Expectation Failed
418 I’m A Teapot
421 Misdirected Request
422 Unprocessable Entity
423 Locked
424 Failed Dependency
426 Upgrade Required
428 Precondition Required
429 Too Many Requests
431 Request Header Fields Too Large
444 Connection Closed Without Response
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
499 Client Closed Request
Меню сайта
Компьютеры и железо
Инструменты
Информационные справочники
Облако тегов
1С Google PHP SEO TrustRank Индексация Интернет магазин Поисковая оптимизация Поисковый робот Продвижение блога Продвижение интернет магазина Продвижение сайта Разработка сайта Раскрутка блога Раскрутка интернет магазина Раскрутка сайта Создание блога Создание сайта
BNAME.RU » Код ошибки HTTP 499 Client Closed Request
Что означает ошибка 499 Client Closed Request?
Код используется компанией Nginx. Этот код был введен для определения ситуаций, когда клиент закрывает соединение во время обработки запроса сервером. Таким образом, сервер не может отправить назад заголовок HTTP.
Если Вам помогла информация размещенная на странице «HTTP коды» — Вы можете поддержать наш проект.
«1xx» — Информационные коды HTTP
100 — Continue (Продолжай)
«Продолжить». Этот промежуточный ответ указывает, что запрос… Читать далее
Подробнее
101 — Switching Protocol (Переключение протоколов)
«Переключение протокола». Этот код присылается в ответ на за… Читать далее
Подробнее
102 — Processing (Идёт обработка)
«В обработке». Этот код указывает, что сервер получил запрос… Читать далее
Подробнее
103 — Early Hints (Ранняя метаинформация)
«Ранние подсказки». В ответе сообщаются ресурсы, которые мог… Читать далее
Подробнее
«2xx» — Успешные коды HTTP
200 — OK (Хорошо)
«Успешно». Запрос успешно обработан. Что значит «успешно», з… Читать далее
Подробнее
201 — Created (Создано)
«Создано». Запрос успешно выполнен и в результате был создан… Читать далее
Подробнее
202 — Accepted (Принято)
«Принято». Запрос принят, но ещё не обработан. Не поддержива… Читать далее
Подробнее
203 — Non-Authoritative Information (Информация не авторитетна)
«Информация не авторитетна». Этот код ответа означает, что и… Читать далее
Подробнее
204 — No Content (Нет содержимого)
«Нет содержимого». Нет содержимого для ответа на запрос, но … Читать далее
Подробнее
205 — Reset Content (Сбросить содержимое)
«Сбросить содержимое». Этот код присылается, когда запрос об… Читать далее
Подробнее
206 — Partial Content (Частичное содержимое)
«Частичное содержимое». Этот код ответа используется, когда … Читать далее
Подробнее
207 — Multi-Status (Многостатусный)
Код 207 (Multi-Status) позволяет передавать статусы для неск… Читать далее
Подробнее
208 — Already Reported (Уже сообщалось)
Относится к DAV и был ранее включен в 207 ответ. Там поныне … Читать далее
Подробнее
226 — IM Used (Использовано IM)
Расширение HTTP для поддержки «дельта кодирования» ( delta e… Читать далее
Подробнее
«3xx» — Коды перенаправлений (HTTP Редиректы)
300 — Multiple Choice (Множество выборов)
«Множественный выбор». Этот код ответа присылается, когда за… Читать далее
Подробнее
301 — Moved Permanently (Перемещено навсегда)
«Перемещён на постоянной основе». Этот код ответа значит, чт… Читать далее
Подробнее
302 — Found / Moved Temporarily (Найдено / Перемещено временно)
«Найдено». Этот код ответа значит, что запрошенный ресурс вр… Читать далее
Подробнее
303 — See Other (Смотреть другое)
«Просмотр других ресурсов». Этот код ответа присылается,&nbs… Читать далее
Подробнее
304 — Not Modified (Не изменялось)
«Не модифицировано». Используется для кэширования. Это код о… Читать далее
Подробнее
305 — Use Proxy (Использовать прокси)
«Использовать прокси». Это означает, что запрошенный ресурс … Читать далее
Подробнее
306 — Switch Proxy (Сменить прокси)
Больше не использовать. Изначально подразумевалось, что » по… Читать далее
Подробнее
307 — Temporary Redirect (Временное перенаправление)
«Временное перенаправление». Сервер отправил этот ответ… Читать далее
Подробнее
308 — Permanent Redirect (Постоянное перенаправление)
«Перенаправление на постоянной основе». Это означает, что ре… Читать далее
Подробнее
«4xx» — Коды ошибок на стороне клиента
400 — Bad Request (Некорректный запрос)
«Плохой запрос». Этот ответ означает, что сервер не понимает… Читать далее
Подробнее
401 — Unauthorized (Не авторизован)
«Неавторизовано». Для получения запрашиваемого ответа нужна … Читать далее
Подробнее
402 — Payment Required (Необходима оплата)
«Необходима оплата». Этот код ответа зарезервирован для буду… Читать далее
Подробнее
403 — Forbidden (Запрещено)
«Запрещено». У клиента нет прав доступа к содержимому, поэто… Читать далее
Подробнее
404 — Not Found (Не найдено)
«Не найден». Сервер не может найти запрашиваемый ресурс. Код… Читать далее
Подробнее
405 — Method Not Allowed (Метод не поддерживается)
«Метод не разрешен». Сервер знает о запрашиваемом методе, но… Читать далее
Подробнее
406 — Not Acceptable (Неприемлемо)
Этот ответ отсылается, когда веб сервер после выполнения ser… Читать далее
Подробнее
407 — Proxy Authentication Required (Необходима аутентификация прокси)
Этот код ответа аналогичен коду 401, только аутентификация т… Читать далее
Подробнее
408 — Request Timeout (Истекло время ожидания)
Ответ с таким кодом может прийти, даже без предшествующего з… Читать далее
Подробнее
409 — Conflict (Конфликт)
Этот ответ отсылается, когда запрос конфликтует с текущим со… Читать далее
Подробнее
410 — Gone (Удалён)
Этот ответ отсылается, когда запрашиваемый контент удален с … Читать далее
Подробнее
411 — Length Required (Необходима длина)
Запрос отклонен, потому что сервер требует указание заголовк… Читать далее
Подробнее
412 — Precondition Failed (Условие ложно)
Клиент указал в своих заголовках условия, которые сервер не … Читать далее
Подробнее
413 — Request Entity Too Large (Полезная нагрузка слишком велика)
Размер запроса превышает лимит, объявленный сервером. Сервер… Читать далее
Подробнее
414 — Request-URI Too Long (URI слишком длинный)
URI запрашиваемый клиентом слишком длинный для того, чтобы с… Читать далее
Подробнее
415 — Unsupported Media Type (Неподдерживаемый тип данных)
Медиа формат запрашиваемых данных не поддерживается сервером… Читать далее
Подробнее
416 — Requested Range Not Satisfiable (Диапазон не достижим)
Диапозон указанный заголовком запроса Range не может бы… Читать далее
Подробнее
417 — Expectation Failed (Ожидание не удалось)
Этот код ответа означает, что ожидание, полученное из заголо… Читать далее
Подробнее
418 — I’m a teapot (Я — чайник)
I’m a teapot — Этот код был введен в 1998 году как одна из т… Читать далее
Подробнее
419 — Authentication Timeout (not in RFC 2616) (Обычно ошибка проверки CSRF)
Authentication Timeout (not in RFC 2616) — Этого кода нет в … Читать далее
Подробнее
420 — Enhance Your Calm (Twitter) (Подождите немного (Твиттер))
Возвращается Twitter Search и Trends API, когда клиент отпра… Читать далее
Подробнее
421 — Misdirected Request (Неверный запрос)
Misdirected Request — запрос был перенаправлен на сервер, не… Читать далее
Подробнее
422 — Unprocessable Entity (Необрабатываемый экземпляр)
Запрос имел правильный формат, но его нельзя обработать из-з… Читать далее
Подробнее
423 — Locked (Заблокировано)
Целевой ресурс из запроса заблокирован от применения к нему … Читать далее
Подробнее
424 — Failed Dependency (Невыполненная зависимость)
Не удалось завершить запрос из-за ошибок к предыдущем запрос… Читать далее
Подробнее
425 — Too Early (Слишком рано)
Too Early — сервер не готов принять риски обработки «ранней … Читать далее
Подробнее
426 — Upgrade Required (Необходимо обновление)
Указание сервера, клиенту, обновить протокол. Заголовок отве… Читать далее
Подробнее
428 — Precondition Required (Необходимо предусловие)
Precondition Required — сервер указывает клиенту на необходи… Читать далее
Подробнее
429 — Too Many Requests (Слишком много запросов)
Too Many Requests — клиент попытался отправить слишком много… Читать далее
Подробнее
430 — Would Block (Будет заблокировано)
Код состояния 430 would Block — это код, который сервер мог … Читать далее
Подробнее
431 — Request Header Fields Too Large (Поля заголовка запроса слишком большие)
Request Header Fields Too Large — Превышена допустимая длина… Читать далее
Подробнее
434 — Requested host unavailable (Запрашиваемый адрес недоступен)
Сервер к которому вы обратились недоступен… Читать далее
Подробнее
444 — No Response (Nginx) (Нет ответа (Nginx))
Код ответа Nginx. Сервер не вернул информацию и закрыл соеди… Читать далее
Подробнее
449 — Retry With (Повторить с…)
Retry With — возвращается сервером, если для обработки запро… Читать далее
Подробнее
450 — Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft) (Заблокировано родительским контролем Windows (Microsoft))
Расширение Microsoft. Эта ошибка возникает, когда родительск… Читать далее
Подробнее
451 — Unavailable For Legal Reasons (Недоступно по юридическим причинам)
Unavailable For Legal Reasons — доступ к ресурсу закрыт по ю… Читать далее
Подробнее
499 — Client Closed Request (Клиент закрыл соединение)
Нестандартный код состояния, представленный nginx для случая… Читать далее
Подробнее
«5xx» — Коды ошибок на стороне сервера
500 — Internal Server Error (Внутренняя ошибка сервера)
«Внутренняя ошибка сервера». Сервер столкнулся с ситуацией, … Читать далее
Подробнее
501 — Not Implemented (Не реализовано)
«Не выполнено». Метод запроса не поддерживается сервером и н… Читать далее
Подробнее
502 — Bad Gateway (Плохой шлюз)
«Плохой шлюз». Эта ошибка означает что сервер, во время рабо… Читать далее
Подробнее
503 — Service Unavailable (Сервис недоступен)
«Сервис недоступен». Сервер не готов обрабатывать запрос. За… Читать далее
Подробнее
504 — Gateway Timeout (Шлюз не отвечает)
Этот ответ об ошибке предоставляется, когда сервер действует… Читать далее
Подробнее
505 — HTTP Version Not Supported (Версия HTTP не поддерживается)
«HTTP-версия не поддерживается». HTTP-версия, используемая в… Читать далее
Подробнее
506 — Variant Also Negotiates (Вариант тоже проводит согласование)
Из-за не верной конфигурации, выбранный вариант указывает са… Читать далее
Подробнее
507 — Insufficient Storage (Переполнение хранилища)
Не хватает места для выполнения текущего запроса. Проблема м… Читать далее
Подробнее
508 — Loop Detected (Обнаружено бесконечное перенаправление)
Сервер обнаружил бесконечный цикл при обработке запроса…. Читать далее
Подробнее
509 — Bandwidth Limit Exceeded (Исчерпана пропускная ширина канала)
Данный код статуса, используется в случае превышения веб пло… Читать далее
Подробнее
510 — Not Extended (Не расширено)
У сервера отсутствует расширение, которое пытается использов… Читать далее
Подробнее
511 — Network Authentication Required (Требуется сетевая аутентификация)
Необходимо выполнить аутентификацию, при этом в ответе должн… Читать далее
Подробнее
520 — Unknown Error (Неизвестная ошибка)
Unknown Error, возникает когда сервер CDN не смог обработать… Читать далее
Подробнее
521 — Web Server Is Down (Веб-сервер не работает)
Web Server Is Down, возникает когда подключения CDN отклоняю… Читать далее
Подробнее
522 — Connection Timed Out (Соединение не отвечает)
Connection Timed Out, возникает когда CDN не удалось подключ… Читать далее
Подробнее
523 — Origin Is Unreachable (Источник недоступен)
Origin Is Unreachable, возникает когда веб-сервер недостижим… Читать далее
Подробнее
524 — A Timeout Occurred (Время ожидания истекло)
A Timeout Occurred, возникает при истечении тайм-аута подклю… Читать далее
Подробнее
525 — SSL Handshake Failed (Квитирование SSL не удалось)
SSL Handshake Failed, возникает при ошибке рукопожатия SSL м… Читать далее
Подробнее
526 — Invalid SSL Certificate (Недействительный сертификат SSL)
Invalid SSL Certificate, возникает когда не удаётся подтверд… Читать далее
Подробнее
527 — Error: Railgun Listener to origin error (Ошибка прослушивателя рейлгана для источника)
Нестандартный код CloudFlare — указывает на прерванное соеди… Читать далее
Подробнее
530 — Origin DNS Error (Ошибка исходного DNS)
Нестандартный код CloudFlare. Ошибка HTTP 530 возвращается с… Читать далее
Подробнее
598 — Network read timeout error (Ошибка тайм-аута сетевого чтения)
Используется прокси-серверами Microsoft HTTP для передачи си… Читать далее
Подробнее
599 — Network connect timeout error (Ошибка тайм-аута сетевого подключения)
Используется прокси-серверами Microsoft HTTP для передачи си… Читать далее
Подробнее
Copyright © BNAME.RU 2006 – | Все права защищены.
Последние комментарии
Dane — 18 сентября 2023 15:44
PHP преобразовать первый символ в верхний регистр — функция mb_ucfirst() в многобайтных кодировках и юникода
Saat Anda bermain Starmania, kamu memperoleh bebas berputar-putar di dalam bermain slot serta meja permainan untuk
Eulah — 15 сентября 2023 04:06
PHP преобразовать первый символ в верхний регистр — функция mb_ucfirst() в многобайтных кодировках и юникода
You should enroll early since most of these courses only have limited slots accessible. Everything begins and ends with
Belle — 7 сентября 2023 00:27
PHP преобразовать первый символ в верхний регистр — функция mb_ucfirst() в многобайтных кодировках и юникода
Square also offers a stand that connects to an iPad, bar-code scanner, receipt printer and associated devices for a
Meredith — 31 августа 2023 12:57
PHP преобразовать первый символ в верхний регистр — функция mb_ucfirst() в многобайтных кодировках и юникода
It will also protect you from DDoS assaults and ISP bandwidth throttling. At GamesGames, you’ll be able to check out
Valentina — 21 августа 2023 08:13
PHP преобразовать первый символ в верхний регистр — функция mb_ucfirst() в многобайтных кодировках и юникода
The coins of those video games and the lights and the buzz and the jackpots that folks win in these video games are
Все комментарии
Онлайн статистика
8 посетителей на сайте. Из них:
Гости7
Роботы1
A non-standard status code introduced by nginx for the case when a client closes the connection while nginx is processing the request.
The HTTP 499 status code is not a standard HTTP status code, meaning it is not defined in the HTTP/1.1 specification. This status code is used by the nginx web server to indicate that the client closed the connection before the server could send a response.
The HTTP 499 error typically occurs when a client terminates the connection before the server is able to respond, such as when a user cancels a request or navigates away from a page before it fully loads. In some cases, the error may be caused by a misconfigured server or network issue that disrupts the connection between the client and server.
499 status code example
A 499 status code is not an officially recognized HTTP status code, but it is sometimes used by servers to indicate that a client has closed the connection without receiving a response. Here’s an example of a request and response:
Request
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Response
HTTP/1.1 499 Client Closed Request
Server: nginx/1.19.6
Root causes of a 499 Status Code
The HTTP 499 error is specific to the nginx web server, and it occurs when the client closes the connection before the server can send a response. There are a number of reasons why this could happen, including:
Network issues:
If there is a problem with the network connection between the client and server, such as a dropped connection or high latency, the connection may be lost before the server can respond.
Client-side issues:
If the client navigates away from the page before it fully loads, or cancels the request before the server can respond, the connection may be terminated before a response is received.
Server-side issues:
If the server is experiencing issues, such as a high load or a misconfiguration, it may be unable to respond to the client’s request in a timely manner.
Firewall or security software:
If there is a firewall or security software in place that is blocking the connection or interfering with the communication between the client and server, the connection may be lost.
Misconfigured server:
If the server is misconfigured, it may not be able to properly handle requests and may result in a 499 error.
Server-side timeout:
The server may have a configuration that sets a timeout period for the response, and if it exceeds the limit, it may close the connection and result in a 499 error.
These are just a few examples of what could cause an HTTP 499 error. In order to determine the specific cause of the error, it may be necessary to investigate further using server logs or other troubleshooting methods.
Troubleshooting a 499 Status Code
Since the HTTP 499 error is not a standard HTTP status code, it can be tricky to troubleshoot. However, there are a few general steps that you can take to try to identify and resolve the issue:
- Check the server logs
If you have access to the server logs, check to see if there are any entries that correspond to the time that the HTTP 499 error occurred. This may provide clues as to what caused the error.
- Check the network connection
Verify that the network connection between the client and server is stable and reliable. Check for any network issues, such as dropped packets or high latency, which could cause the connection to be lost.
- Check the browser cache
Clear the browser cache and cookies to ensure that the error is not caused by a cached resource or cookie.
- Disable browser extensions
Disable any browser extensions that could be interfering with the connection, such as ad blockers or security software.
- Try a different browser or device
If the error persists, try accessing the site from a different browser or device to see if the issue is specific to the current configuration.
Does a 499 status code affect SEO?
Since a 499 status code is not an officially recognized HTTP status code and is not a common error, it is unlikely to have any direct impact on SEO. However, if it is a persistent issue on your website, it could affect user experience and lead to lower engagement and higher bounce rates, which could indirectly impact your SEO.
Return to List of HTTP Status Codes

![How to Fix the HTTP NGINX 499 Error? [6 Best Methods] 3 Clear browsing data on Chrome](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/7.png)
![How to Fix the HTTP NGINX 499 Error? [6 Best Methods] 4 Clearing data in Google Chrome](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/8.png)