Did you just try to visit a website only to be met by the HTTP error 431 message? Or, maybe you have your own website and you’re getting complaints from visitors that they see this error when visiting your site?
HTTP status codes like the 431 error can be frustrating because they get in the way of the website that you want to interact with. Thankfully, though, the error code provides you with the information that you need to fix it in the form of those three numbers – 431.
In this post, you’ll learn what this specific error means and what some of the common causes are. Then, we’ll share four troubleshooting steps that you can follow to fix the problem, whether you’re experiencing it on someone else’s website or your own website.
Check Out Our Video Guide to Fixing the 431 Error
What Is HTTP Error 431?
Before we can talk about the HTTP error 431 specifically, we first need to talk about what HTTP is and where these errors come from.
When you visit a website, your web browser needs a way to communicate with the webserver behind that website. It does this using HTTP, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol.
Your web browser sends an HTTP request to the server for certain information – e.g. the website’s code or an image file. Then, the server sends an HTTP response back to the browser.
Along with these requests and responses, browsers and servers also include HTTP status codes, which are numerical codes like 431.
There are tons of different status codes. In fact, we have an entire guide on HTTP status codes. Some HTTP status codes indicate that everything is functioning normally. However, many HTTP status codes indicate some type of error.
As you can probably guess, the HTTP 431 message is one of the error codes. The number 431 indicates the specific HTTP error, which is “Request Header Fields Too Large.”
Essentially, this means that the HTTP request that your browser is making to the server is too large. Or, another way of phrasing it is that the request is too long.
This can happen because the total size of the request headers is too large or it can happen because a single header field is too large.
Because your browser is making a request that is too large/long, the server drops/denies the request instead of delivering the HTTP response that your browser was expecting.
Because your browser doesn’t receive the needed response, it’s unable to render the webpage and shows the HTTP error 431 message instead.
Did you just try to visit a website only to be met by the HTTP error 431 message? This post is for you 👀Click to Tweet
What Causes a 431 Request Header Fields Too Large Error?
In general, HTTP error codes can indicate a problem in two different areas:
- Server-side – there’s something going wrong in the webserver that’s triggering the error code.
- Client-side – there’s something going wrong in the web browser that’s triggering the error.
The HTTP error 431 is a client-side HTTP error. That means the cause of the problem is somewhere in your web browser (because your web browser is the one making the request with large headers). That also means that you’ll need to apply most fixes by adjusting your web browser.
However, the root cause isn’t always your browser’s fault. Sometimes the way that the website is coded can cause your browser to make large requests.
Typically, the HTTP error 431 is caused by issues with cookies, long referrer URLs, or just the total size of the request headers.
If you’re trying to visit someone else’s website, you can try to eliminate these causes by adjusting your web browser.
If you have your own website and you’re trying to diagnose why your site’s visitors are seeing the HTTP error 431, you might need to dig into your site’s code to make it less likely to cause your site’s visitors to have large requests. For example, you might need to adjust how your site uses cookies in visitors’ browsers or configure your server to accept larger requests.
How To Fix HTTP Error 431 (4 Methods)
Now that you know what the HTTP Error 431 Request Header Fields Too Large message means and some of its causes, let’s get into how you can fix this error.
1. Clear Your Cookies and Browser Cache
Pretty much all websites use cookies to identify and store information about individual users. For example, if you log into a website, that website will use a cookie to remember that you’re logged in so that you don’t need to log in again on every single visit.
To learn more about cookies, check out our guide to cookies and PHP sessions.
However, if there are too many cookies, that can lead to large HTTP request headers, which can trigger the HTTP Error 431 Request Header Fields Too Large message.
One common fix, therefore, is to clear the cookies for the site where you’re experiencing issues. Most popular browsers make this pretty easy to do – we’ll show you below.
Here’s how to clear browser cookies in Chrome:
- Enter the following in your browser address bar – chrome://settings/content/all.
- Search for the URL of the site where you’re experiencing issues.
- Click the trash can icon to delete all of the cookies and site data for that site.
The basic method above should also work for other Chromium-based web browsers, such as Brave, Edge, Vivaldi, Opera, and others. However, you’ll need to go through the settings area rather than pasting in the URL.
To clear cookies for a specific site in Safari, follow these instructions:
- Open the Preferences area (Safari > Preferences).
- Select the Privacy tab.
- Click Manage Website Data.
- Search for and select the site where you’re experiencing issues.
- Click the Remove button once you’ve selected the site.
To clear cookies for a specific site in Firefox, follow these instructions:
- Enter the following in your Firefox browser address bar – about:preferences#privacy.
- Scroll down and find the Cookies and Site Data section.
- Click the Manage Data button in that section.
- Search for and select the site where you’re experiencing issues.
- Click the Remove Selected button once you’ve selected the site.
2. Shorten or Remove URL Query Parameters
Trying to visit a site using URLs with long query parameters can also trigger the HTTP error 431.
Query parameters are the part of a URL that comes after the “main” URL. They’re used to pass additional information to the server, but they aren’t actually required to access the page in most cases.
For example, many sites use UTM parameters to track conversions. Here’s an example of a base URL – https://yoursite.com/ — with some additional query parameters:
https://yoursite.com/?utm_source=Facebook&utm_medium=CtW&utm_campaign=PC&fbclid=IwAR3ph8rkY1UfPOzhbrqPWBGqLXFsFeAP48otBX1F0Ao2Y1RYydAJqms_RQU
To see if this is the problem, delete the question mark and everything that comes after it (the bolded portion above). Then, try revisiting the newly cleaned URL and see if the error disappears.
3. Shorten/Edit Your Code (if Writing Custom Code)
These next two tips won’t help if you’re experiencing the error on someone else’s website. But if you’re experiencing the error on your own site (or if your visitors are complaining of experiencing the error), then these tips can help address the root cause.
The first option is to dig into your site’s code and check if your code is generating large request headers. That is, whether your code is forcing visitors’ browsers to send large requests.
These errors are especially common when working with JavaScript. If you check out StackOverflow, you’ll see that most of the people experiencing this error are using technologies such as AngularJS, React, Node.js, etc.
For example, your Node.js app could be asking for more information than is needed, which is generating unnecessarily large request headers. Similarly, remember that spaces in your code count towards the size of the request, so that can be another “invisible” source of large requests.
In some cases, you can also adjust the maximum request size at the server level by editing your server’s configuration code. For example, if you’re using React, you can adjust the max header size in the package.json file – look for this line of code:
"start": "react-scripts --max-http-header-size=1024 start",
4. Adjust Cookie Settings (if Your Site Triggers Errors for Users)
Another way that your site could trigger the HTTP error 431 is the way in which it’s using cookies.
For example, if you’re setting lots of cookies in users’ browsers, that could trigger the error. This is one of the reasons why clearing a site’s cookies is one of the potential fixes.
To avoid this, make sure that you’re not setting too many cookies by accident. This will require digging into your site’s code or hiring an expert with the qualifications to do so.
HTTP status codes like the 431 error can be frustrating because they get in the way of the website that you want to interact with. 😅 This guide is here to help 🚀Click to Tweet
Summary
The HTTP Error 431 Request Header Fields Too Large error is a client-side error that appears when your web browser makes a request to the server with headers that are too large and/or long.
Because the request is too large, the server rejects the request, which is why your web browser displays the HTTP Error 431 message instead of the content that you were expecting.
If you’re experiencing this error when visiting another site, the most common fix is to clear your browser’s cookies for that site. You should also make sure that the URL isn’t too long because of query parameters.
If you’re experiencing this error when visiting your own site (or your visitors are complaining about this error), you’ll likely need to dig into your code to make sure you aren’t generating large request headers or setting too many cookies. In some cases, you might also be able to increase the maximum request header size at the server level by editing your server’s configuration files.
To learn more about HTTPS status codes in general, check out our full guide to HTTP status codes. We also have a number of posts focused on fixing other common HTTP errors, including Internal Server, Bad Requests, Bad Gateway, Not Found Errors.
HTTP response status code 431 Request Header Fields Too Large is returned by the server to indicate that the HTTP headers are too large. This may indicate the total size used by all HTTP headers or instead, only that certain HTTP headers are too big.
Usage
When the 431 Request Header Fields Too Large status code is received, the server is refusing to process the HTTP request because there is too much data specified by the HTTP headers.
Depending on the server, this may refer to the total length of HTTP headers combined or instead, specific ones. In either case, the client may have the option to remove one or more HTTP headers and try the HTTP request again. One possible solution for limiting the number of HTTP headers is to cut or reduce the Cookies that are being transmitted.
Note
Search engines like Google will not index a URL with 431 Request Header Fields Too Large response status, and consequently, URLs that have been indexed in the past but are now returning this HTTP status code will be removed from the search results.
Example
In the example, the client requests a resource and the server responds with the 431 Request Header Fields Too Large status code because the combination of two very large cookie values exceeds the maximum limit set by the server for HTTP headers.
Request
GET /tech-news HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.re
Cookie: first_cookie=<very_long>; second_cookie=<long again!>
Response
HTTP/1.1 431 Request Header Fields Too Large
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 183
<html>
<head>
<title>Request Headers Too Long</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Your request headers are too long. Try retrying the request without cookies.</p>
</body>
</html>
Code references
.NET
HttpStatusCode.RequestHeaderFieldsTooLarge
Rust
http::StatusCode::REQUEST_HEADER_FIELDS_TOO_LARGE
Rails
:request_header_fields_too_large
Go
http.StatusRequestHeaderFieldsTooLarge
Symfony
Response::HTTP_REQUEST_HEADER_FIELDS_TOO_LARGE
Python3.5+
http.HTTPStatus.REQUEST_HEADER_FIELDS_TOO_LARGE
Apache HttpComponents Core
org.apache.hc.core5.http.HttpStatus.SC_REQUEST_HEADER_FIELDS_TOO_LARGE
Angular
@angular/common/http/HttpStatusCode.RequestHeaderFieldsTooLarge
Takeaway
The 431 Request Header Fields Too Large status code is a client error that is sent by the server when the client sends an HTTP request with too much data in the HTTP headers. If the HTTP request can be reduced in size while still making sense, then the HTTP request can be resubmitted with the smaller sized HTTP headers.
See also
- Cookies
- RFC 6585
Last updated: August 2, 2023
In this article, we examine what exactly an HTTP 431 Request Header Too Large error is, why it occurs, and how you can use the latest technological advancements to solve it. We also look at some of the advantages of using these new techniques over outdated methods – so read on to find out more about this exciting development!
What Is HTTP 431 Status Code?
The HTTP 431 Request Header Fields Too Large response status code is an error code used in the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) protocol. This response status code indicates that a server is rejecting a request due to its header fields being too large. It can be caused by proxy servers or other intermediaries, and users may need to take certain troubleshooting steps if it occurs.
This specific error has become more common with the increasing use of web browsers and applications as they tend to include more data within requests than earlier versions did. The combination of this larger data payload along with proxies caching information can lead to an increase in size for some request headers, triggering the 431 response error code.
Cause Of HTTP 431 Error
Some of the common causes of the 431 error include:
- Large request headers: When the client sends a request with header fields that exceed the server’s maximum header size limit, the server rejects the request with the 431 error.
- Security measures: Some security measures, such as firewalls or proxies, may impose limits on the size of HTTP requests, which can cause the 431 error.
- Network issues: Poor network connectivity, low bandwidth, or slow internet speeds can also cause the 431 error.
- Server configuration: If the web server is not configured properly to handle large header fields, it may reject the request with the 431 error.
- Faulty or outdated software: Faulty or outdated software on the client or server-side can also cause the 431 error.
- Malware or viruses: Malware or viruses on the client’s computer can cause requests to be sent with large header fields, which can result in the 431 error.
- Browser extensions: Some browser extensions may modify the request headers and cause them to exceed the server’s maximum header size limit, leading to the 431 error.
- Invalid characters: If the request headers contain invalid or unsupported characters, the server may reject the request with the 431 error.
Server Side Or Client Side Issue?
The HTTP 431 error is typically a server-side issue, although it can also be caused by the client. The error occurs when the server refuses to process the request due to the request header fields being too large. This indicates that the server is not able to handle the request because of its size.
However, the client can also cause the 431 error if it sends a request with header fields that exceed the server’s maximum header size limit. In such cases, the server rejects the request, and the error is returned to the client.
How To Fix HTTP 431 Error Code
Clear browser Cookies And Cache Data To Fix 431 Error
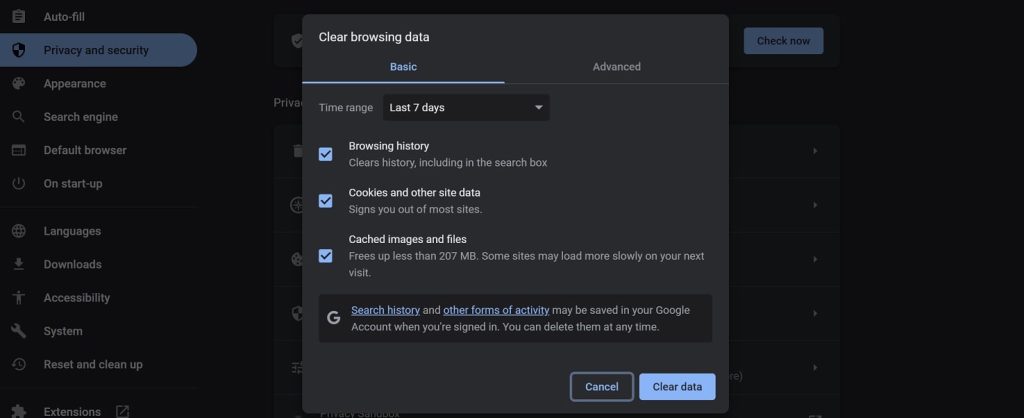
If you clear browsing data such as cookies and cache data can help fix the HTTP 431 error in some cases. Cookies and cache data are stored on the client side and can cause issues with the request headers. Here’s how clearing cookies and cache data can fix the 431 error:
- Clear cookies: Cookies are small files that are stored on the client side and can contain information such as login details or browsing history. If the cookies become corrupted or contain outdated information, they can cause issues with the request headers. Clearing the cookies can help resolve these issues.
- Clear cache data: Cache data is stored on the client-side to speed up the loading time of web pages. If the cache data becomes corrupted or outdated, it can cause issues with the request headers. Clearing the cache data can help resolve these issues.
Clearing cookies and cache data can be done through the browser settings. The exact steps may vary depending on the browser, but here are some general instructions:
- Open the browser settings.
- Find the site data section for clearing browsing data.
- Select the option to clear cookies and cache or site data.
- Choose the time range for which you want to clear the data.
- Click on the clear data button.
This lets users attempt an easier fix before resorting to other more complex methods. After clearing the cookies and browser cache data, try reaccessing the website and check if the HTTP 431 error is resolved.
Try Incognito Mode On Chrome
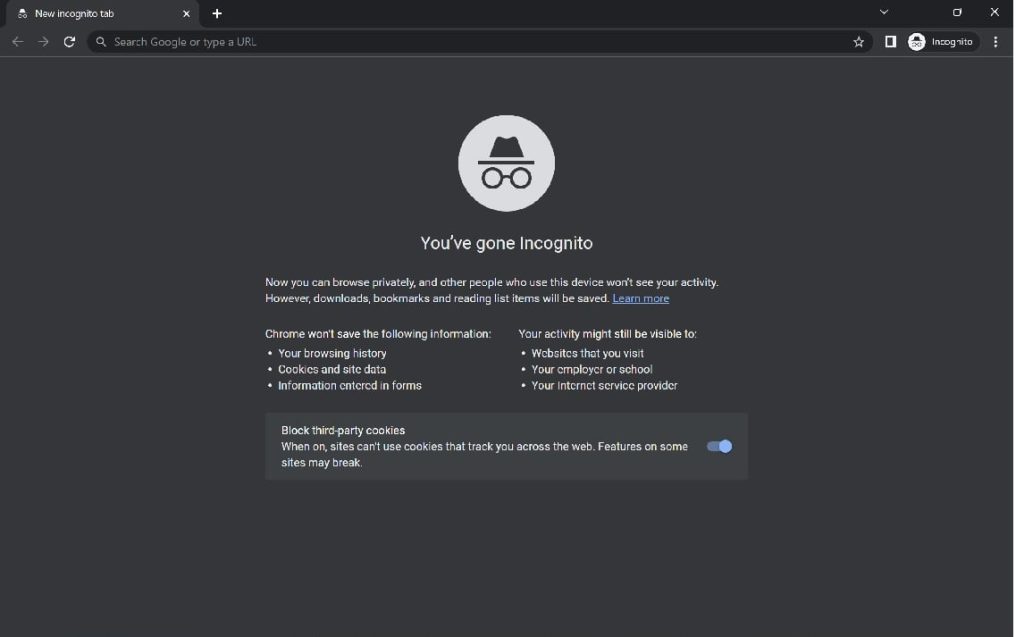
Trying incognito mode on Google Chrome can help fix the HTTP 431 error in some cases. Incognito mode is a feature in Google Chrome that allows you to browse the web privately, without storing any browsing history, cookies, or cache data. Here’s how using incognito mode can fix the http error 431:
- Clear cookies and cache data: Incognito mode automatically clears all cookies, cache data, and other site data when you close the browser. If the cookies and cache data are causing issues with the request headers, using incognito mode can help resolve these issues.
- Disable browser extensions: Browser extensions can modify the request headers and cause them to exceed the server’s maximum header size limit, resulting in the 431 error. Incognito mode disables all browser extensions by default, so if the error is caused by a problematic extension, using incognito mode can help fix the issue.
To use incognito mode in Google Chrome, follow these steps:
- Open Google Chrome.
- Click on the three dots icon in the top right corner of the browser.
- Select “New incognito window” from the drop-down menu.
- A new window will open in incognito mode. You can now try accessing the website again and check if the HTTP 431 error is resolved.
Remove Any Problematic Extensions
Removing any problematic extensions can help fix the HTTP 431 error in some cases. Browser extensions can modify the request headers and cause them to exceed the server’s maximum header size limit, resulting in the 431 error. Here’s how removing problematic extensions can fix the 431 error:
- Identify problematic extensions: If you suspect that an extension is causing the 431 error, you can try disabling all extensions and see if the error persists. If the error goes away after disabling all extensions, you can enable the extensions one by one and test the website to identify the problematic one.
- Remove problematic extensions: Once you have identified the problematic extension, you can remove it from the browser. To remove an extension, follow these steps:
- a. Open Google Chrome.
- b. Click on the three dots icon in the top right corner of the browser.
- c. Select “More tools” from the drop-down menu.
- d. Click on “Extensions”.
- e. Find the problematic extension and click on the remove button.
- f. Confirm the removal of the extension.
- Check if the error is resolved: After removing the problematic extension, try accessing the website again and check if the HTTP 431 error is resolved.
Flush The Dns Cache
Flushing the DNS cache can help fix the HTTP 431 error in some cases. DNS (Domain Name System) cache is a temporary database stored on your computer that contains the IP addresses of websites you’ve recently visited. Flushing the DNS cache clears out this database, which can help resolve issues with accessing websites.
Here’s how flushing the DNS cache can fix the 431 error:
- Open the Command Prompt: To flush the DNS cache, you need to open the Command Prompt. To do this, follow these steps:
- a. Click on the Start menu and type “cmd” in the search bar.
- b. Right-click on “Command Prompt” and select “Run as administrator”.
- Flush the DNS cache: Once the Command Prompt is open, type the following command and press Enter:
ipconfig /flushdnsThis command will flush the DNS cache on your computer. - Restart your computer: After flushing the DNS cache, it’s a good idea to restart your computer to ensure that all changes are applied.
- Check if the error is resolved: After restarting your computer, try accessing the website again and check if the HTTP 431 error is resolved.
Turn Off Any Proxy Server Connections
Turning off any proxy server connections can help fix the HTTP 431 error in some cases. A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your computer and the website you’re trying to access. If the proxy server is configured improperly or is causing issues with the request headers, it can result in the 431 error. Here’s how turning off proxy server connections can fix the 431 error:
- Open the Windows settings: To turn off proxy server connections, you need to access the Windows settings. To do this, follow these steps:
- a. Click on the Start menu and open control panel.
- b. Click on “Network & Internet”.
- Check the proxy server settings: Once you’re in the Network & Internet settings, click on “Proxy” from the left-hand menu. Check if any proxy server settings are enabled. If the “Use a proxy server” option is turned on, it means that a proxy server is being used.
- Turn off the proxy server: To turn off the proxy server, toggle the “Use a proxy server” option to the off position. This will disable the proxy server connection.
- Check if the error is resolved: After turning off the proxy server, try accessing the website again and check if the HTTP 431 error is resolved.
Shorten Or Remove The Url Parameters
Shortening or removing the URL parameters can help fix the HTTP 431 error in some cases. URL parameters are values passed in the URL that can be used by the server to retrieve specific data or perform certain actions. These parameters can increase the size of the request headers, causing the 431 error. Here’s how shortening or removing the URL parameters can fix the 431 error:
- Identify the URL query parameters: To identify the URL parameters, look for question marks (?) in the URL. Anything after the question mark is a URL parameter. For example, in the URL “http://www.example.com/search?q=example”, the parameter is “q=example”.
- Shorten or remove the parameters: Once you have identified the parameters, you can try shortening them or removing them altogether. This can be done by manually editing the URL or by using a URL shortener service.
- Check if the error is resolved: After shortening or removing the URL parameters, try accessing the website again and check if the HTTP 431 error is resolved.
Increase the maximum header size limit
To fix this error, you can try increasing the maximum header size limit on the server. This can be done by modifying the server configuration or settings. The exact steps will depend on the server software being used. Consult the server documentation or seek assistance from the server administrator to make these changes.
Reduce header size
If none of the above worked, reducing the size of request header fields might fix the HTTP 431 error. Here are some instructions on how to reduce the size of header fields:
- Remove unnecessary header fields: Review the request headers and remove any unnecessary header fields. This can help reduce the size of the request headers.
- Compress header fields: Use a compression algorithm such as gzip or deflate to compress the header fields. This can significantly reduce the size of the headers without losing any information.
- Use shorter header field names: Use shorter names for the header fields to reduce their size. For example, instead of using “Accept-Encoding”, use “AE”.
- Combine header fields: Combine multiple header fields into a single field. For example, instead of sending multiple “Cookie” header fields, send a single “Cookie” field with all the necessary information.
- Avoid repeating header fields: Avoid sending the same header fields multiple times. For example, instead of sending multiple “User-Agent” header fields, send a single one.
- Use HTTP/2: HTTP/2 uses a binary format for the header fields, which is more efficient than the text format used in HTTP/1.1. Using HTTP/2 can help reduce the size of the request headers.
- Use POST instead of GET: If possible, use POST instead of GET for sending data in the request. POST requests have a separate body for data, which can help reduce the size of the headers.
Similar Http Status Codes To 431
The 431 HTTP error code indicates a request header is too large. It can be an issue for users, as it restricts their access to content. Fortunately, it’s not the only status code with similar implications.
Similar codes include ‘413 Request Entity Too Large’ and ‘414 URI Too Long’, both of which signify that incoming requests are oversized from a server’s perspective. As such, they require some adjustments by the user in order to gain access again. This could mean shortening or removing URL parameters, among other measures.
All HTTP status codes by categories
431 – код ответа HTTP-заголовка, если точнее, то один из них. Есть много кодов, каждый указывает на определенную проблему. По цифре в сообщении довольно просто определить, какая именно неполадка стала причиной проблемы. В результате любого из кодов не получится загрузить страницу в браузере или любой сайт в целом. Сразу нужно оговориться, что это не всегда зависит от клиента, может быть виноват и сервер.
Суть проблемы
Сообщение HTTP 431 Request Header Fields Too Large само по себе говорит о том, что был отправлен заголовок со слишком большой длиной. В запросе может быть либо один большой заголовок, либо несколько. Чтобы сайт заработал, нужно сократить длину заголовка. Однако его формирование выполняет сайт, а не пользователь, поэтому прямо доступа к редактированию HTTP у нас нет. В значительной части случаев проблема в том, что разработчик неправильно что-то настроил.
Как исправить ошибку 431?
Все, что нужно сделать – очистить кэш и куки в браузере. Первый вариант заключается в том, чтобы удалить все данные этого рода для разных сайтов за определенный промежуток времени. Просто нажимаем CTRL + SHIFT + DEL и увидим окно со всем необходимым. Другой подход сводится к чистке кэша конкретного сайта, если сбой касается только его.
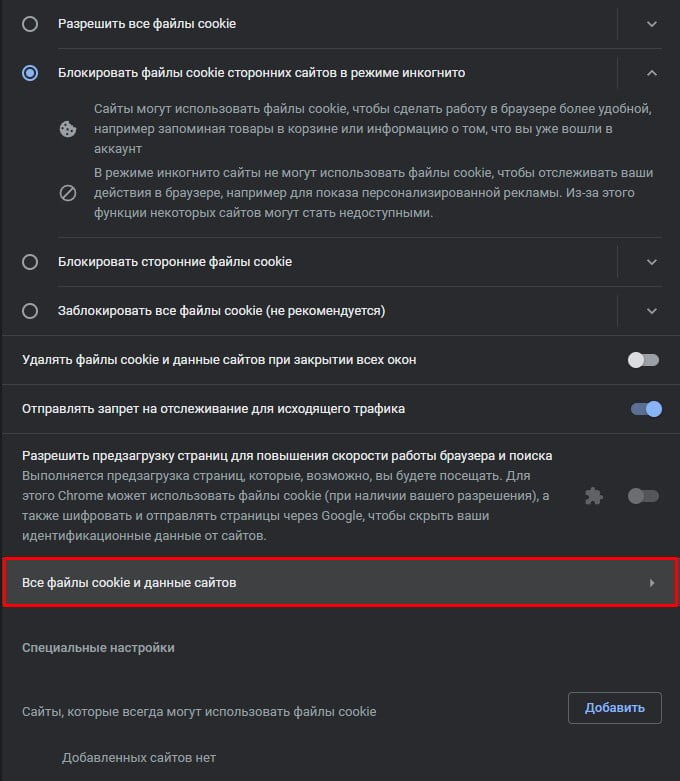
Как очистить cookie сайта:
- Переходим в «Настройки» браузера в раздел «Конфиденциальность и безопасность».
- Выбираем вкладку «Настройки сайтов», а затем переходим сюда – «Файлы сookie и данные сайтов».
- Кликаем на «Все файлы cookie и данные сайтов».
- Ищем тот веб-ресурс, который отправляет назад ошибку HTTP 431.
- Жмем на крестик возле всех сохраненных данных сайта.
- Повторяем запрос на веб-ресурс.
Если в результате чистки куки ошибка HTTP 431 Request Header Fields Too Large не перестанет появляться, сбой спровоцирован какими-то ошибками со стороны сервера. Можно дополнительно проверить, работает ли сайт в режиме Инкогнито и в другом браузере. Обычно нужно просто подождать, пока веб-сайт восстановится.
Updated: 02/14/2023 — 11:19
Time to read: 4 minutes
HTTP error 431 returns the status code: Request header fields too large
You’ve tried to look at content on your own website, and you’ve hit an error. Read through it, and you’ll know that the system thinks «request header fields too large.» But you have no idea what that means.
HTTP errors are meant to give you information about the communication between your device and a website server. But the codes were written for developers, not average people. And even experts can be confused by obscure codes like this one.
Fixing HTTP error 431 is relatively easy once you know what to look for. We’ll walk you through the steps.
Understand the HTTP Language
The acronym HTTP stands for «hypertext transfer protocol,» which was established in 1991. Think of this protocol as the language of requests and responses between devices and servers.
Each time you visit a website, a predictable set of steps happens.
- Browser request: You need data or information from the web server to visit the page.
- Data movement: Buried within that request is information about you, your browser, and more.
- The server’s response: You’re either given access, or you get a code that explains the denial.
Requests are sometimes called «headers.» The HTTP protocol doesn’t specify how long or big these pieces of data can be. But some servers limit size for security reasons.
And that’s where HTTP error 431 comes in.
Unpacking HTTP Error 431
Several types of HTTP errors exist, and they’re numerically grouped. All of the codes in the 400 level involve user errors. These aren’t problems that technically originate with the website or your server. Instead, they involve some kind of request from the user that a website’s server can’t process.
Error 431, which officially says «Request header fields too large,» means the server has dropped the request. The header sent by the user is either too long or too large, and the server denies it.
Web developers can request all kinds of data from users. You might ask for information about these things:
- Preferred languages
- Credentials
- Hosts
- Referring sites
If you ask for too much information, or the data you get back is somehow chunky or lengthy, your user will hit this error code. The page won’t load until the problem is resolved.
Fix Error 431 in 4 Steps
Every HTTP error 431 message is different, and your website could throw up this barrier for reasons that don’t apply to other businesses you know. But for most companies, the problem comes down to one of two factors.
Your visitors could see the code due to cookies or the referring URL is too long.
Try fixing the problem by:
- Eliminating the referrer URL. If you know you have active links on a site with a very long URL, eliminate this query before allowing access.
- Walking through your code. Spaces in your code are applied toward character limits, and they’re not always needed. You could also ask for data you never use or need, which could force users up against your character limits.
- Examining your cookie settings. If you have authorization code mistakes, you could be setting multiple cookies for your users, and that could cause unwelcome HTTP errors.
- Accepting more cookies. If cookies are at the crux of your problem, let more in. Cookies do come with security vulnerabilities, so proceed with care. But if eliminating an error code at all costs is your goal, accepting more cookies could be helpful.
You may need to talk with your server host before making some changes. If you adjust your code to accept more data, but your server doesn’t agree, your users could hit a similar HTTP code involving server access. An open conversation before you adjust code is always wise.
Get Help From Okta
If HTTP errors plague you, we can help. We’ll walk through the problems with you, and we’ll figure out how to give your users access without compromising your security. Contact us to find out more.
References
Brief History of HTTP. High Performance Browser Networking. O’Reilly.
Additional HTTP Status Codes. (April 2012). Internet Engineering Task Force.
Risk Associated With Cookies. (November 2013). Infosec.
5 Tips to Avoid Potential Dangers of Cookies. (November 2020). C Online Mag.