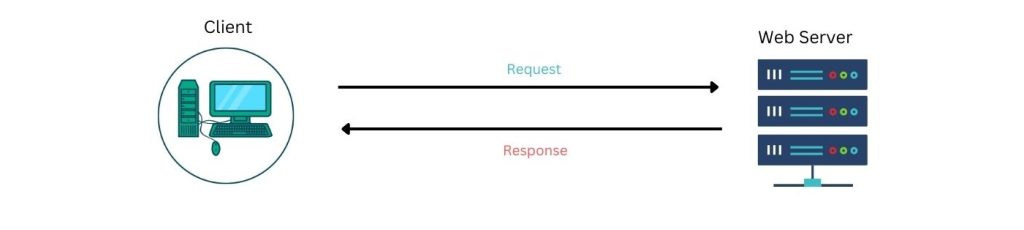
WordPress errors don’t happen too often, given the stable codebase. What’s more, when something does pop up to dampen your day, it’s explicit. The 414 Request-URI Too Large error, for one, tells you exactly what the problem is. From there, you can attempt to fix it.
Much like many other WordPress errors, there are some specific steps you can take to resolve it. In short, you’ll need to adjust some configuration settings to allow for longer URLs. Once you’re finished, the error will be too.
In this article, we will walk you through how to fix the 414 Request-URI Too Large error. It will include the tools and skills you’ll need to solve the problem and list some “pre-steps” before getting under the hood.
Check out our video guide to fixing the 414 Request-URI Too Large error:
What the 414 Request-URI Too Large Error Is (And Why It Happens)
The 414 Request-URL Too Large error is a configuration issue. It’s one of the 400 error codes. They’re troublesome because it often means there’s a critical issue somewhere between your browser and a server.
In this case, a 414 error means that the URL is too long for the server to process, so it throws an exception. This could be an issue when using Urchin Tracking Module (UTM) codes to track conversions. These links can get long depending on the parameters you set, and if they reach the maximum limit of your site’s configuration, you’ll see the error.
As with many WordPress errors, there are many more things going on under the hood to cause a 414. In fact, you can group the causes into three distinct areas:
- Converting a POST request to a GET request with query information that is too long. This is a developer-specific issue that happens at the coding level.
- A redirect loop. We’ve talked about the best practices for redirects in a previous post. If you get into a redirect loop, the resulting URLs get too long, and the error will appear.
- The server could be under attack, and a 414 error at this point will be the least of your worries.
Before we move on, it’s worth noting that for all intents and purposes, a URI and a URL are the same things. While there are some distinct differences between the two, we’re going to use “URL” here to keep things straightforward.
Ever seen this error pop up? 😅 Tackle it with no fear thanks to this guide 💪Click to Tweet
What You’ll Need to Fix the 414 Request-URI Too Large Error
If you’ve encountered the 413 Request Entity Too Large error in the past, you’ll find a 414 error to be similar. Of course, the names show their similarities, as they’re next to each other in the official standards and have almost identical descriptions.
Given this, the list of tools and skills you’d use for fixing a 413 will be the same for a 414 too:
- Administrative access to your server
- One of the many Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) clients available
- The right skills to use SFTP and navigate your server
- A clean and current backup on hand in case you need to restore
- A text editor, though this might not be necessary for you
If you’re a Kinsta customer, you’ll find your SFTP credentials within the MyKinsta dashboard, along with some other handy functionality to get into your server:
It’s also worth noting that we will connect through SFTP here because it’s more secure (hence the name).
What to Do Before You Begin Resolving the 414 Request-URI Too Large Error
Before you crack open the hood on your server and set it to work, you may want to carry out some “pre-steps” first. It could be that there’s a simple workaround that doesn’t involve you tinkering with your configuration files.
What’s more, these checks should be carried out at some point regardless, so getting them taken care of now will help in the long run.
First, a WordPress plugin might generate long URLs as part of its functionality. Full-featured, all-in-one security plugins can be a prime candidate here, especially if they offer lots of functionality.
It’s hard to know at a glance whether a plugin could be at fault, but it’s worth investigating its specific settings for a dedicated option to restrict the length of URLs. If so, toggling this could solve the 414 error within seconds.
Under normal circumstances, though, there are a few other tasks you can carry out to help you diagnose the error:
- Check your server logs for mentions of the error or any other identifying entries.
- Your browser developer tools may give you some indication of the error’s cause — especially your Console.
- Reach out to the site owner or developer (if it’s not you) and let them know the error exists. It could be that they will have a fix or can advise you further on what to do.
Of course, you may want to contact both the site and plugin developers anyway if you’ve found that a plugin is at fault. Even so, if you’ve exhausted all of your outreach and top-level checks, it’s time to venture on.
How to Fix the 414 Request-URI Too Large Error (In 3 Steps)
Once you have your tools together, you’ll need a plan. The fix for the 414 Request-URI Too Large error is to alter a server configuration file. As such, there are three steps you can take.
Let’s start by getting into your server and figuring out which type of server you have.
1. Log In to Your Server (And Determine Your Server Type)
You have to get into the server before you work on it, and this is where your SFTP skills come into play.
We’ve outlined how to get into your site through SFTP in the past, and once you’re in, you’ll need to figure out what type of server you have. There are two main types: Apache and Nginx.
It could be that you already know which server type you run. If so, you can skip to the next step.
If you’re struggling, here’s a quick tip: look for a .htaccess file. It’s found in the root of your server, and if you can see it, this means you’re running an Apache server. Nginx servers use a different configuration file.
That said, it could be that you’re running an Apache server that doesn’t yet have a .htaccess file. As such, there are two other methods you could use:
- Carry out a domain lookup using the Whois Domain Tools site: This might tell you the type of server you’re using, although it’s not a foolproof method.
- Check with your hosting provider about the server type you use. Of course, your host is going to know what server you run. Kinsta customers will always use Nginx servers, although other providers may use Apache or a mix. It’s best to open a ticket with your host to check before you poke around in your site’s backend.
When you’ve determined which type of server you use, you can head onto the next step and find your configuration file.
2. Find the Server Configuration File and Open It in Your Text Editor
As we noted, Apache servers use a .htaccess file for basic server configuration, and it will be located in your root directory. This isn’t the file you need to fix the 414 Request-URI Too Large error, though.
In this case, you’ll need to go deeper into your advanced configuration settings. These are found not at your site’s root folder but the server’s root.
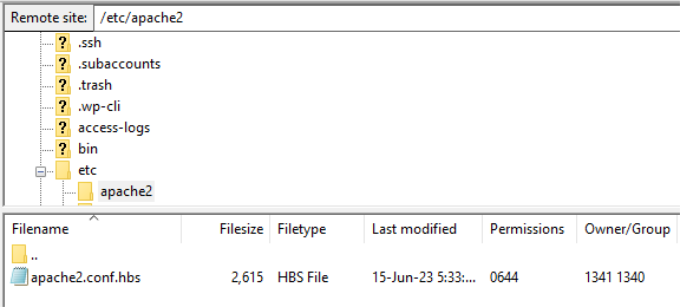
When you log into your site through SFTP, you’ll often come to a directory that contains all of your sites (along with some other files). In many cases, you can go up a couple of levels to a server root directory:
This will give you a few more directories to traverse. Among them will be the etc folder:
The full path of the configuration file will be /etc/apache2/apache2.conf.
For Nginx servers, the process is similar. It’s one we’ve covered in part within our article on adjusting the maximum upload size in WordPress. The path to the configuration file will be /etc/nginx/nginx.conf.
Once you’ve located your file, open it in your favorite text editor. At this point, you’re ready to adjust it.
3. Adjust the Configuration File To Allow for Longer URLs
Much like how Apache and Nginx servers have different configuration files, they also have different settings to adjust. Regardless of your server type, though, you’ll need to open it in an editor if you haven’t already done so. Our preferred approach is to download the file to your computer, work on it, and upload it back to the server.
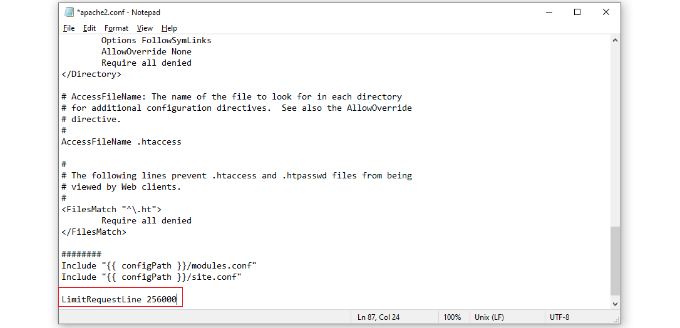
For Apache configuration files, look for the LimitRequestLine setting, or add it to the bottom of your file if it’s not there:
For the value, use at least 128000. If you need to go higher than this, keep to multiples of two (i.e. the next value should be 256000).
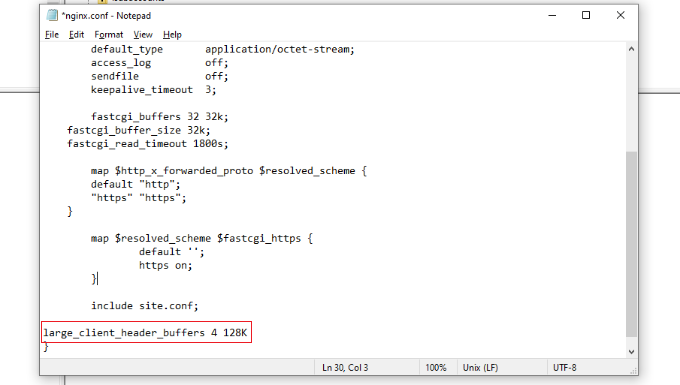
For Nginx servers, you’re looking for the large_client_header_buffers setting. Here, you’ll see two values relating to number and size. For example, large_client_header_buffers 4 8K. The only figure you need to alter here is the size — you can go from 8K to around 128K, although you may need to increase this further (again in multiples of two).
Once you’re done, save your changes and upload your configuration file back to your server. At this point, check your site again, and the 414 Request-URI Too Large error should have gone.
The 414 Request-URI Too Large error may be annoying, but luckily, it tells you exactly what the problem is. 🤷♀️ Learn how to fix it here 👇Click to Tweet
Summary
WordPress errors often have a similar approach for resolving them. You’ll often need to diagnose the error first, though. In the case of the 414 Request-URI Too Large error, the problem is clear: the URLs being passed to the server are too big.
To fix it, you’ll need to change your Apache or Nginx server settings. This doesn’t take too long, and once you’re done, you should be back up and running. While we can’t speak for other hosts, Kinsta’s support team is on hand 24/7 to help you get over the 414 Request-URI Too Large error if you’re stuck. In fact, we’re here whenever you need our help and guidance, so you can get back to running your site.
Have you ever encountered an HTTP 414 error while accessing a website? Have you ever wondered what it is and how to fix it? If so, then this article is for you! In this article, we will provide a complete overview of ‘HTTP 414 URI Too Long’, including detailed explanations of its causes and solutions. So let’s get started!
What Is 414 Http Status Code?
The 414 HTTP status code of the HTTP protocol is a client error response coming from the server when it receives an excessively long request URI. It’s also known as ‘Request-URI too long’ or simply ‘URI Too Long’. The URL, or Uniform Resource Locator, that users type into their browsers to access websites and webpages can sometimes be too long for servers to process. When this happens, the server will return a 414 error message.
Most of the time, 414 errors happen because people are trying to use overly long URLs with lots of unnecessary characters in them – such as extremely long queries filled with unneeded info. This won’t just affect the user’s experience but could potentially lead to issues like slow website loading times down the line due to all the extra information being sent back and forth between browser and server.
In order to prevent these kinds of problems from occurring, developers should make sure that their applications aren’t creating overly complex URLs – by using shorter query strings and avoiding any unnecessary parameters in them. Doing so will ensure that users don’t encounter any unexpected errors while browsing your site or application!
Cause Of 414 Http Status Code Error
Apache servers are usually responsible for receiving an HTTP 414 error when a client attempting to access a web page. This is due to their restrictions on URL length, but there are other potential culprits as well.
First, POST request can often cause this issue due to their inclusion of long query information in the URL. If your website uses POST methods when submitting forms or if you are redirecting users with a URI prefix, then you may run into this problem.
Second, GET request is another potential source of trouble here because they have limits on how much data can be sent within the URL itself. The maximum length varies from browser to browser but most will cut off URLs at around 2000 characters – anything more and you might get an HTTP 414 error message.
Finally, even if all parameters fit within the limit set out by the browsers, certain combinations of parameters may not work as expected and lead to a too-long URI being generated.
Server Side Or Client Side Issue?
The cause of a 414 HTTP status code error can be difficult to pinpoint. It’s important to distinguish between server-side and client-side issues when trying to resolve them. On the server side, the request line or method definition may have been improperly converted, forcing the browser to respond with an error code. This could happen if too much information is included in the request-target, such as long query information that exceeds the maximum limit allowed by servers.
On the other hand, client-side errors may also lead to this issue. In some cases, browsers might not correctly process content from web pages which would result in a similar response. A simple workaround for this type of problem is making sure your browser has up-to-date software installed so that it can properly render webpage contents without any difficulty.
How To Fix 414 Http Status Code Error
Here are some possible solutions to fix the 414 HTTP status code error:
- Shorten the URL: One of the easiest solutions to the 414 error is to shorten the length of the URL being requested. This can be achieved by removing unnecessary parameters or path components from the URL.
- Use HTTP POST method: The HTTP POST method allows you to send large amounts of data to the server in the request body rather than in the URL. This can help to avoid the 414 error in situations where the length of the data being transmitted is too long for the URL.
- Increase server limit: If you have control over the server, you can try to increase the server’s limit for URL length. This can be done by modifying the server configuration or by using a different web server software that supports longer URLs.
- Use URL shortening services: There are many URL shortening services available that can help to shorten long URLs. You can use these services to create shorter URLs that redirect to the original URL, thereby avoiding the 414 error.
- Check for redirection loops: The 414 error can also occur if there is a redirection loop on the server. In this case, the server keeps redirecting the client to the same URL, causing the URL to become too long. You can check for redirection loops and remove them to fix the error.
Other Similar Http Status Codes To 414 Error
Other similar HTTP status codes include 411 Length Required and 413 Payload Too Large which all share similarities to the 414 error due to their implications regarding query information being sent from clients to servers. In addition, some web browsers may also return 403 Forbidden instead of a 414 error as they both relate to restrictions on the client side.
All HTTP status codes by categories
Have you ever encountered a 414 request URI too long error on your WordPress website?
The error is usually caused when there is a critical error between your web browser and a server. You’ll see this error when clicking on a link or any action performed by a WordPress plugin.
In this article, we will show you what is the ‘414 request URI too long’ error and how to fix it.
What is 414 Request URI Too Long Error?
A 414 request URI too long error occurs when a URL or an action you’re requesting is too long for the server to handle.
Do note that there is a difference between URI and URL. A URI or Uniform Resource Identifier can be a resource’s name, location, or both. On the other hand, a URL or Uniform Resource Locator can only be the location of a resource.
Both terms are usually used interchangeably because URL is part of URI. However, the 414 error can be triggered by both components, so let’s look at the causes.
What Causes 414 Request URI Too Long Error?
You might see the 414 error when you click on the link, and the server is unable to process it because it’s too long.
One situation where a link might to very long is using UTM (Urchin Tracking Module) parameters. If you’re using UTM codes to track conversions on your WordPress website and there are a lot of parameters in the URL, then it can cause this error.
Another situation that can cause a 414 error is a redirect loop. This is when a misconfiguration or a setting in a WordPress plugin causes a lot of redirect requests.
As a result, you get incredibly long URLs and 414 requests URI too long error.
Similarly, some plugins can also generate lengthy URIs as part of their functionality. You’re most likely to encounter this error if you have all-in-one WordPress security plugins installed on your site.
In a rare event, a developer-side issue can also trigger a 414 error when a POST request converts into a GET request with query information being too long. Lastly, cyber attacks on your website server can also result in 414 URI too long issues.
That said, let’s see how you can fix the 414 error on your WordPress website.
Fixing 414 Request URI Too Long Error
A quick way to fix this issue is by increasing the size of the URI your website server can process.
Before we move forward, we recommend creating a WordPress backup. That’s because fixing the 414 error involves editing the website configuration files. In case anything goes wrong, you’ll have a backup copy of your site ready to restore.
For more details, please see our guide on how to backup a WordPress site.
Determine if Your Website is Using Apache or Nginx
First, you’ll need to find out the type of server your WordPress website is using. There are 2 main types of servers, which includes Apache and Nginx.
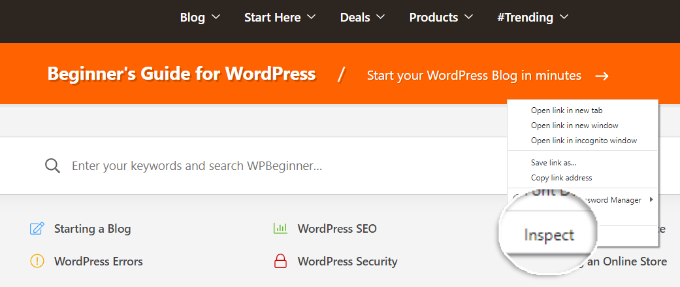
A simple way to do that is by opening your site in a browser. After that, you can right-click on the homepage and select the ‘Inspect’ option.
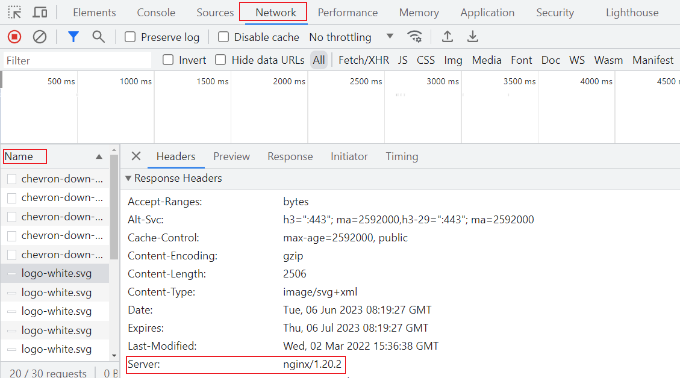
Next, you’ll need to switch to the ‘Network’ tab at the top.
From here, you can select any element under the Name column. After that, you will need to scroll down to the ‘Response Headers’ section and see the ‘Server’ details.
This will show you whether your site is using Nginx or Apache.
If you’re still unsure which server type to use, then you can reach out to your WordPress hosting provider to get more details.
Once you’ve determined the server type, let’s look at how to fix the 414 request URI too long error for Apache and Nginx.
Fixing 414 Request URI Too Long Error in Nginx
First, you’ll need an FTP or file transfer protocol client to access website configuration files.
There are many FTP clients you can use. For this tutorial, we will use Filezilla. If you need help setting up FTP and accessing website files, then please see our guide on how to use FTP to upload files to WordPress.
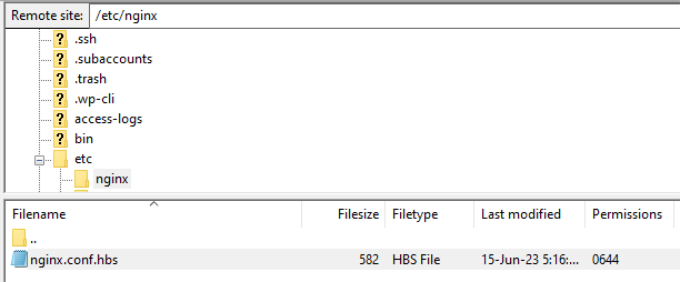
Once you’re logged in, you’ll need to download the ‘nginx.conf’ file. You can access this by following this path: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
After locating the file, go ahead and download it on your computer and then open it in a notepad software.
From here, you can search for large_client_header_buffers 4 8K settings. If it’s not there, then simply add it to the end of the file.
You will see 2 sets of values, which relate to a number and size. Simply edit the size from 8K to 128K. This will increase the URI size and allow the site server to process long URLs.
Once you’re done, simply save the text file and reupload it to your website using the FTP client.
For more details, please see our guide on how to use FTP to upload files to WordPress.
Fixing 414 Request URI Too Long Error in Apache
If you’re using the Apache server type, then the process is similar to that of Nginx. First, you’ll need an FTP client to access website files.
Once you’re logged in, you’ll need to locate the ‘apache2.conf’ file. Simply head to the following path using the FTP client: /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
Next, you’ll need to download the file and open it in notepad software.
After that, you can look for LimitRequestLine 128000 settings. If you don’t see one, then simply add it to the end of the file.
Usually, LimitRequestLine is set to 128000. However, you can increase this to 256000 or higher to remove the 414 error. Just make sure that the value you set is a multiple of 2.
Once you’re done, simply upload the file back to the website using the FTP client. This should help resolve the 414 error on your WordPress website.
We hope this article helped you learn about what is 414 request URI too long error and how to fix it. You may also want to see our guide on WordPress security and the most common WordPress errors.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
Disclosure: Our content is reader-supported. This means if you click on some of our links, then we may earn a commission. See how WPBeginner is funded, why it matters, and how you can support us. Here’s our editorial process.
Editorial Staff at WPBeginner is a team of WordPress experts led by Syed Balkhi with over 16 years of experience in WordPress, Web Hosting, eCommerce, SEO, and Marketing. Started in 2009, WPBeginner is now the largest free WordPress resource site in the industry and is often referred to as the Wikipedia for WordPress.
The server is refusing to service the request because the request-target1 is longer than the server is willing to interpret.
This rare condition is only likely to occur when a client has improperly converted a POST request to a GET request with long query information, when the client has descended into a “black hole” of redirection (e.g., a redirected URI prefix that points to a suffix of itself) or when the server is under attack by a client attempting to exploit potential security holes.
A 414 response is cacheable by default; i.e., unless otherwise indicated by the method definition or explicit cache controls2.
- 1 Content Negotiation RFC7230 Section 5.3
- 2 Calculating Heuristic Freshness RFC7234 Section 4.2.2]3
- Source: RFC7231 Section 6.5.12
414 CODE REFERENCES
Rails HTTP Status Symbol :request_uri_too_long
Go HTTP Status Constant http.StatusRequestURITooLong
Symfony HTTP Status Constant Response::HTTP_REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG
Python2 HTTP Status Constant httplib.REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG
Python3+ HTTP Status Constant http.client.REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG
Python3.5+ HTTP Status Constant http.HTTPStatus.REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG
When is a 414 status code used?
The 414 status code is used when there is a configuration issue. This error code means that the URL is too long for the server to process and the server expects a smaller HTTP path or address.
While there is no maximum length requirement, some browsers may limit the size of HTTP paths or addresses to prevent certain attacks.
Here are a few other instances when an HTTP 414 status code is used:
- Redirect loops that result in long URLs
- Server attacks
- POST request conversions to GET requests with query information that is too long
How to fix a 414 URI Too Large error
Here’s how to fix a 414 URI Too Large error in three steps:
1. Log in to your server
Before you can work on your server, you’ll need to log in and then figure out what type of server you have. If you already know your server type, you can move on to the next step.
Here are a few tips to identify your server type:
- Look for a “htaccess” file in the root of your server — if you see one, it means you have an Apache server
- Use the Whois Domain Tools site to determine your server type
- Ask your hosting provider
2. Find the server configuration file
You’ll need to dig deep into your advanced configuration settings to find a directory that contains all of your site’s files.
You’ll want to find your “etc” folder to find your configuration file. Depending on your server type, you’ll file will look like one of the following:
- Apache: /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
- Nginx: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
3. Adjust the configuration file
Now that you’ve located your file, it’s time to adjust it to fix your HTTP 424 status code error.
First, you’ll need to open your configuration file in an editor. The next steps you take will differ depending on the server type you have.
For Apache servers, follow these steps:
- Look for the LimitRequestLine setting or add it to the bottom of your file if it’s not there
- Use at least 128000 for the value. If you need to go higher, keep the value to multiples of two
For Nginx servers, follow these steps:
- Look for the large_client_header_buffers settings. You’ll see two values relating to number and size.
- Now you can adjust the size. You can use 8K to 128K, and if you need to go bigger, keep it to a multiple of two
Once you’ve adjusted the size to the value you need, simply save your changes and upload your configuration file back to the server.
You can check your site again, and the 414 URI Too Long error should be gone.
Additional resources
- Learn about web development
- Learn about SEO
- Web development services from WebFX
- SEO services from WebFX
- MDN Web Docs
- W3Schools
Return to List of HTTP Status Codes
HTTP response status code 414 URI Too Long is a client error that is returned by the server to indicate that the URI exceeds the length that it allows.
Usage
When the 414 URI Too Long error message is received, the client understands that the server expects a smaller HTTP path or address. While the specification does not stipulate any requirement for length, in practice, browsers may limit the size to prevent certain types of attacks.
For example, many web applications limits the size of the URL for an HTTP GET request to 2,048 characters. This, however, may not be a limit enforced by the server or browser.
Note
Search engines like Google will not index a URL with 414 URI Too Long response status, and consequently, URLs that have been indexed in the past but are now returning this HTTP status code will be removed from the search results.
Example
In the example, the client requests a resource using a URI that is beyond what the server allows.
Request
GET /<…a_long_URI…> HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.re
Response
HTTP/1.1 414 URI Too Long
Code references
.NET
HttpStatusCode.RequestUriTooLong
Rust
http::StatusCode::URI_TOO_LONG
Rails
:request_uri_too_long
Go
http.StatusRequestURITooLong
Symfony
Response::HTTP_REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG
Python3.5+
http.HTTPStatus.REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG
Java
java.net.HttpURLConnection.HTTP_REQ_TOO_LONG
Apache HttpComponents Core
org.apache.hc.core5.http.HttpStatus.SC_REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG
Angular
@angular/common/http/HttpStatusCode.UriTooLong
Takeaway
The 414 URI Too Long status code is a client error that occurs when the URI is larger than the server is willing to accept.
See also
- RFC 7231
Last updated: August 2, 2023