Все мы, путешествуя по просторам интернета, натыкаемся на различные ошибки при загрузке сайтов. Одна из них, кстати, достаточно часто встречается – я говорю об ошибке сервера 403 Forbidden Error. Сегодня я рассмотрю причины ее возникновения и способы устранения со стороны владельца сайта и его пользователя.
Что означает ошибка 403 и почему она появляется
Ошибка сервера 403 Forbidden означает ограничение или отсутствие доступа к материалу на странице, которую вы пытаетесь загрузить. Причин ее появления может быть несколько, и вот некоторые из них:
- Формат индексного файла неверен.
- Некорректно выставленные права на папку/файл.
- Файлы были загружены в неправильную папку.
Ошибка на стороне пользователя
Обычно ошибка 403 на стороне пользователя указывает на:
-
Ограничения доступа. Веб-сервер может быть настроен для запрета доступа к определенным файлам и директориям. Если пользователь пытается получить доступ к таким ресурсам, сервер отправляет код 403.
-
Аутентификацию. Некоторые веб-страницы требуют аутентификации для доступа. Если пользователь не предоставляет правильные учетные данные, например, логин и пароль, сервер может отправить ошибку.
-
IP-ограничения. Веб-сервер может быть настроен для ограничения доступа к определенным IP-адресам или диапазонам IP-адресов.
-
Расширение файла. На сервере могут быть настроены правила, запрещающие доступ к определенным типам файлов или расширениям.
-
Блокировку брандмауэром или антивирусом. Некоторые брандмауэры или антивирусные программы могут блокировать доступ к определенным сайтам или ресурсам.
Ошибка на стороне владельца сайта
Ошибка 403 может также возникать из-за различных причин со стороны администратора:
-
Ошибка в файле index. Этот документ указывает на главную страницу сайта, название и формат которого должны быть определены правильно. В зависимости от выбранной CMS, они могут отличаться. Так, например, в WordPress корректные наименования – index.html, index.htm или index.php. Вместе с этим важно убедиться, что файл находится в корневой папке домена или поддомена, иначе это также может сказаться на ошибке 403.
-
Расположение файлов сайта. Часто бывает такое, что расположение файлов влияет на появление ошибки 403. Важно, чтобы все находилось на своих местах, которые регламентируются CMS и хостингом.
-
Права доступа. Файловая система имеет 7-балльную систему доступа из трех цифр, где 1 – это права владельца, 2 – группа, 3 – пользователь. Если у посетителя сайта будут ограничены права доступа, то он увидит ошибку 403. Как правило, для папок задается значение 755, для файлов – 644.
-
Проблемы с плагинами. С такой проблемой часто встречаются владельцы CMS WordPress из-за устаревшего ПО или некорректной работы кода расширений. Чтобы убедиться, действительно ли ошибка связана с такой неполадкой, отключите все плагины. Сделать это можно через раздел wp-content – найдите там папку plugins и переименуйте ее на любое другое имя. Если проблема исчезнет, то виной этому один из плагинов.
-
Ошибка в файле .htaccess. Если вы используете Apache Web Server, то попробуйте изменить название файла .htaccess. Такое действие поможет понять, есть ли вина файла в ошибке или нет. Если же код 403 появляется из-за .htaccess, то обратите внимание на директивы: deny, allow, require, redirect, RewriteRule – в них может быть допущена ошибка.
-
Тариф хостинга подобран неправильно. Такое случается, когда вы используете современные технологии, а хостинг их не поддерживает. Например, тариф рассчитан только на PHP 7.4, а вы работаете на PHP 8.0. В таком случае вполне может появляться ошибка 403.
Ограничения на стороне хостинга или провайдера
В некоторых случаях ошибка 403 появляется не по вине пользователя или владельца сайта, а по причине каких-то ограничений со стороны хостинга или провайдера. Рассмотрим наиболее встречаемые:
-
Прекращение работы сайта. Сайт может быть заблокирован хостингом, например, если не оплачен тарифный план или были нарушены правила площадки. Также проблемы могут быть связаны с действиями Роскомнадзора.
-
Устаревший кэш DNS. Обычно это связано с переездом сайта на другой адрес. В таких случаях есть вероятность, что используются устаревшие данные DNS-серверов. Как правило, ошибка уходит сама в течение одних-двух суток.
-
Проблема на стороне провайдера. Если ни одна из вышеперечисленных причин вам не подходит, обратитесь к провайдеру – возможно что-то «сломалось» на его стороне.
Другие причины ошибки 403
Помимо распространенных причин, о которых я уже упоминала выше, существуют и другие, более редкие. Вот несколько из них:
-
Ограничения по времени доступа. Администратор может настроить ограничения по времени доступа к определенным ресурсам. Например, доступ к некоторым страницам или функциональности может быть отключен в конкретное время дня.
-
Блокировка по стране или региону. В некоторых случаях владельцы веб-ресурсов могут настроить блокировку доступа к сайту из определенных стран или регионов. Это может быть сделано по причинам безопасности или для соблюдения правовых ограничений.
-
Превышение лимитов использования. Иногда веб-сервисы или API могут иметь ограничения на количество запросов или использование ресурсов. Если пользователь превышает эти лимиты, сервер может отправить ошибку 403 в ответ на последующие запросы.
-
Ограничения на основе идентификатора пользователя. Веб-сайты, особенно те, которые предоставляют персонализированный контент, могут ограничивать доступ к определенным ресурсам на основе идентификатора пользователя. Например, когда посетитель сайта не является членом определенной группы.
-
Проверка ботов и сканеров. Администраторы могут настроить системы защиты сайта для обнаружения и блокировки автоматических сканеров, вредоносных ботов или спам-роботов. Если сервер обнаруживает подозрительную активность, он может отправлять код 403 в ответ на запросы от таких источников.
Коды ошибок подстатуса для IIS
Основной список кодов ошибок, которые возвращаются службами Microsoft Internet Information Services:
- 403.1 – доступ к выполнению запрещен;
- 403.2 – ставит запрет на чтение;
- 403.3 – запрещает делать запись;
- 403.4 – указывает на то, что нужно использовать SSL-сертификат;
- 403.5 – указывает на то, что нужно использовать SSL-сертификат 128 бит;
- 403.6 – говорит о том, что IP-адрес отклонен;
- 403.7 – требует сертификат;
- 403.8 – говорит о том, что доступ к сайту запрещен;
- 403.9 – указывает на слишком высокий трафик;
- 403.10 – неверная конфигурация;
- 403.11 – говорит о том, что изменен пароль;
- 403.12 – Mapper отказал в доступе;
- 403.13 – означает, что сертификат отозван;
- 403.14 – говорит о том, что листинг каталога отклонен;
- 403.15 – слишком большое число клиентских лицензий;
- 403.16 – указывает на некорректный сертификат;
- 403.17 – срок действия сертификата истек;
- 403.18 – не получается выполнить запрос;
- 403.19 – нельзя выполнить CGI;
- 403.20 – указывает на ошибку входа в систему;
- 403.21 – доступ к источнику запрещен;
- 403.22 – бесконечная глубина запрещена;
- 403.502 – указывает на большое число запросов с одного IP-адреса;
- 403.503 – есть ограничения по IP.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Исправление ошибки сервера 403 Forbidden
Чтобы исправить ошибку сервера 403 Forbidden, обязательно нужен доступ к панели управления вашего хостинга. Все описанные ниже шаги применимы к любой CMS, но примеры будут показаны на основе WordPress.
Проверка индексного файла
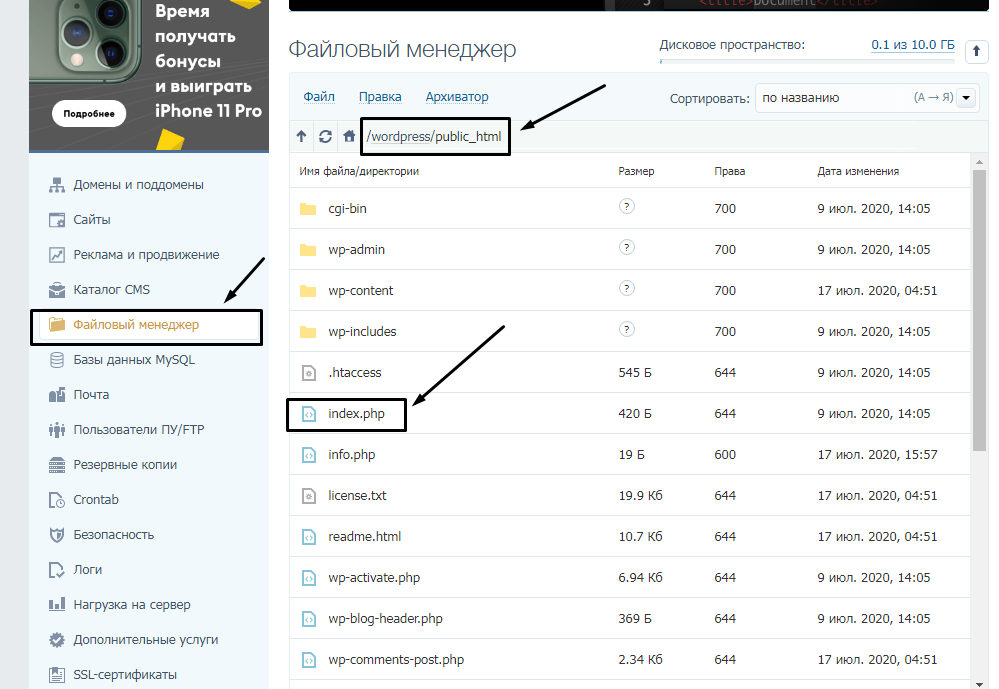
Сначала я проверю, правильно ли назван индексный файл. Все символы в его имени должны быть в нижнем регистре. Если хотя бы один символ набран заглавной буквой, возникнет ошибка 403 Forbidden. Но это больше относится к ОС Linux, которой небезразличен регистр.
Еще не стоит забывать, что индексный файл может быть нескольких форматов, в зависимости от конфигураций сайта: index.html, index.htm, или index.php. Кроме того, он должен храниться в папке public_html вашего сайта. Файл может затеряться в другой директории только в том случае, если вы переносили свой сайт.
Любое изменение в папке или файле фиксируется. Чтобы узнать, не стала ли ошибка итогом деятельности злоумышленников, просто проверьте графу «Дата изменения».
Настройка прав доступа
Ошибка 403 Forbidden появляется еще тогда, когда для папки, в которой расположен искомый файл, неправильно установлены права доступа. На все директории должны быть установлены права на владельца. Но есть другие две категории:
- группы пользователей, в числе которых есть и владелец;
- остальные, которые заходят на ваш сайт.
На директории можно устанавливать право на чтение, запись и исполнение.
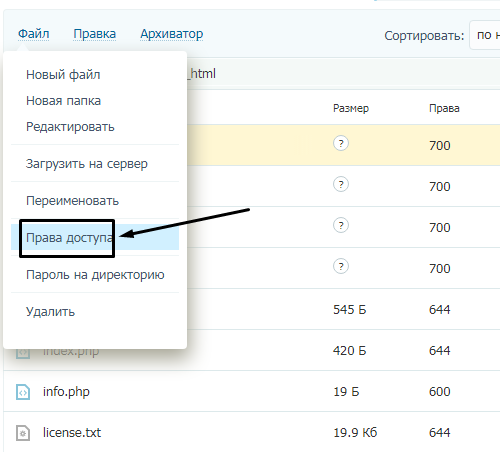
Так, по умолчанию на все папки должно быть право исполнения для владельца. Изменить их можно через панель управления TimeWeb. Для начала я зайду в раздел «Файловый менеджер», перейду к нужной папке и выделю ее. Далее жму на пункт меню «Файл», «Права доступа».
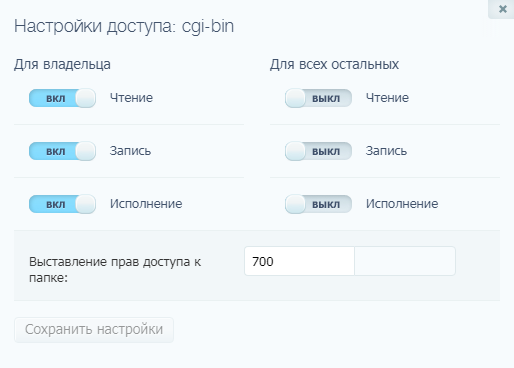
Откроется новое окно, где я могу отрегулировать права как для владельца, так и для всех остальных.
Отключение плагинов WordPress
Если даже после всех вышеперечисленных действий ошибка не исчезла, вполне допустимо, что влияние на работу сайта оказано со стороны некоторых плагинов WordPress. Быть может они повреждены или несовместимы с конфигурациями вашего сайта.
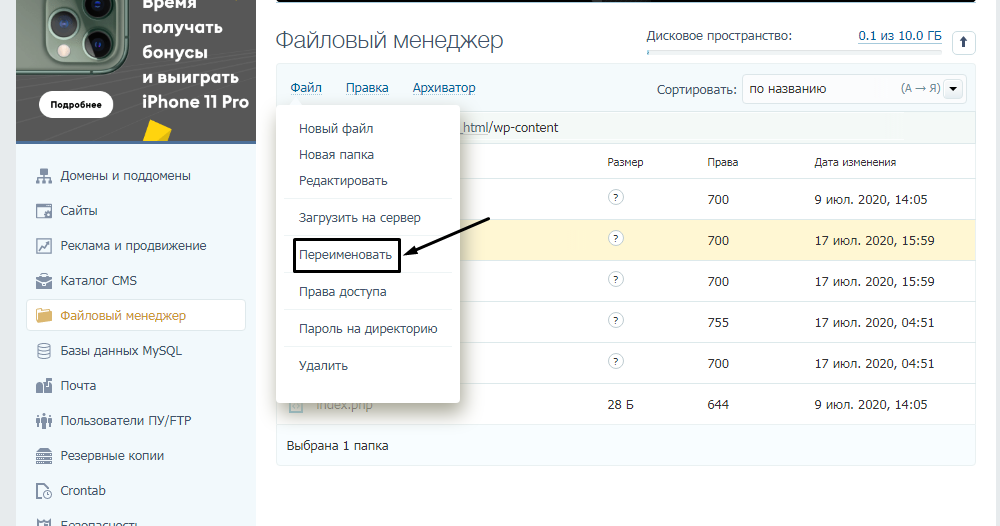
Для решения подобной проблемы необходимо просто отключить их. Но сначала надо найти папку с плагинами. Открываю папку своего сайта, перехожу в раздел «wp-content» и нахожу в нем директорию «plugins». Переименовываю папку – выделяю ее, жму на меню «Файл» и выбираю соответствующий пункт. Название можно дать вот такое: «plugins-disable». Данное действие отключит все установленные плагины.
Теперь нужно попробовать вновь загрузить страницу. Если проблема исчезла, значит, какой-то конкретный плагин отвечает за появление ошибки с кодом 403.
Но что делать, если у вас плагин не один, а какой из них влияет на работу сайта – неизвестно? Тогда можно вернуть все как было и провести подобные действия с папками для определенных плагинов. Таким образом, они будут отключаться по отдельности. И при этом каждый раз надо перезагружать страницу и смотреть, как работает сайт. Как только «виновник торжества» найден, следует переустановить его, удалить или найти альтернативу.
Читайте также
Как решить проблему, если вы – пользователь
Выше я рассмотрела способы устранения ошибки 403 Forbidden для владельцев сайта. Теперь же разберу методы исправления в случаях с пользователем.
- Сначала надо убедиться, что проблема заключается именно в вашем устройстве. Внимательно проверьте, правильно ли вы ввели URL сайта. Может, в нем есть лишние символы. Или, наоборот, какие-то символы отсутствуют.
- Попробуйте загрузить страницу с другого устройства. Если на нем все будет нормально, значит, проблема кроется именно в используемом вами девайсе. Если нет – надо перейти к последнему шагу.
- Еще хороший вариант – немного подождать и обновить страницу. Делается это либо кликом по иконке возле адресной строки браузера, либо нажатием на комбинацию Ctrl + F5. Можно и без Ctrl, на ваше усмотрение.
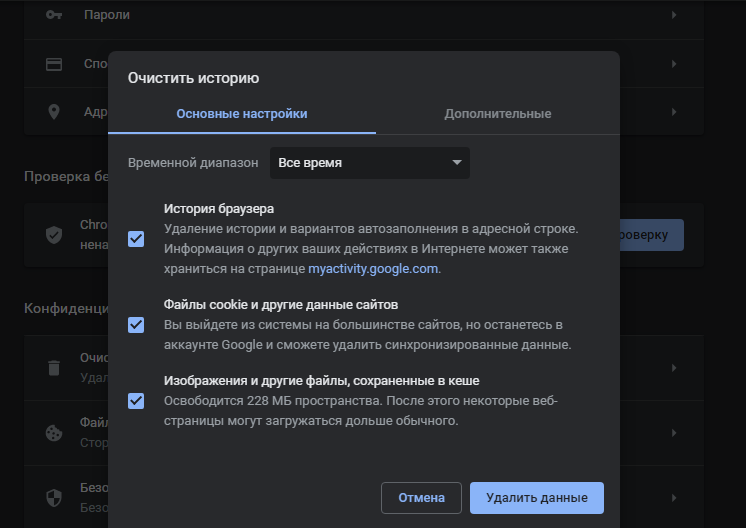
- Если ничего из вышеперечисленного не помогло, надо очистить кэш и cookies. Провести такую процедуру можно через настройки браузера. Для этого необходимо открыть историю просмотров, чтобы через нее перейти к инструменту очистки. Эту же утилиту часто можно найти в настройках, в разделе «Конфиденциальность и безопасность». В новом окне нужно отметить пункты с кэшем и cookies и нажать на кнопку для старта очистки.
- Ошибка 403 Forbidden возникает и тогда, когда пользователь пытается открыть страницу, для доступа к которой сначала надо осуществить вход в систему. Если у вас есть профиль, просто войдите в него и попробуйте вновь загрузить нужную страницу.
- Если вы заходите со смартфона, попробуйте отключить функцию экономии трафика в браузере. Она находится в настройках, в мобильном Google Chrome под нее отведен отдельный раздел.
- Последний шаг – подождать. Когда ни один способ не помогает, значит, неполадки возникли именно на сайте. Возможно, его владелец уже ищет способы решения проблемы и приступает к их исполнению, но это может занять какое-то время. Пользователям остается только дождаться, когда все работы будут завершены.
Еще одна допустимая причина появления ошибки сервера 403 – доступ к сайту запрещен для определенного региона или страны, в которой вы находитесь. Бывает и такое, что сайт доступен для использования только в одной стране. Если вы используете VPN, попробуйте отключить его и перезагрузите страницу. Вдруг получится все исправить.
Если ничего из вышеперечисленного не сработало, рекомендуется обратиться к владельцу сайта. Есть вероятность, что никто не знает о возникшей проблеме, и только ваше сообщение может изменить ситуацию.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
HTTP 403 is an HTTP status code meaning access to the requested resource is forbidden. The server understood the request, but will not fulfill it.if it was correct
Specifications[edit]
HTTP 403 provides a distinct error case from HTTP 401; while HTTP 401 is returned when the client has not authenticated, and implies that a successful response may be returned following valid authentication, HTTP 403 is returned when the client is not permitted access to the resource despite providing authentication such as insufficient permissions of the authenticated account.[a]
Error 403: «The server understood the request, but is refusing to authorize it.» (RFC 7231)[1]
Error 401: «The request requires user authentication. The response MUST include a WWW-Authenticate header field (section 14.47) containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. The client MAY repeat the request with a suitable Authorization header field (section 14.8). If the request already included Authorization credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials.» (RFC 2616)[2]
The Apache web server returns 403 Forbidden in response to requests for URL[3] paths that corresponded to file system directories when directory listings have been disabled in the server and there is no Directory Index directive to specify an existing file to be returned to the browser. Some administrators configure the Mod proxy extension to Apache to block such requests and this will also return 403 Forbidden. Microsoft IIS responds in the same way when directory listings are denied in that server. In WebDAV, the 403 Forbidden response will be returned by the server if the client issued a PROPFIND request but did not also issue the required Depth header or issued a Depth header of infinity.[3]
Reasons for HTTP Status Code 403: Forbidden[edit]
The HTTP status code 403 is used by the server to indicate that access to the requested resource is forbidden. This status code is triggered for various reasons and signifies that while the server understood the request, it refuses to grant access.
A 403 status code can occur for the following reasons:[4]
- Insufficient permissions: The most common reason for a 403 status code is that the user lacks the necessary permissions to access the requested resource. This can mean that the user is not logged in, has not provided valid credentials, or does not belong to the appropriate user group to access the resource.
- Authentication required: In some cases, the server requires authentication to access certain resources. If the user does not provide valid credentials or if the authentication fails, a 403 status code is returned.
- IP restrictions: The server may also restrict access to specific IP addresses or IP ranges. If the user’s IP address is not included in the list of permitted addresses, a 403 status code is returned.
- Server configuration: The server’s configuration can be set to prohibit access to certain files, directories, or areas of the website. This can be due to a misconfiguration or intentional restrictions imposed by the server administrator.
- Blocked by firewall or security software: A 403 status code can occur if a firewall or security software blocks access to the resource. This may happen due to security policies, malware detection, or other security measures.
Examples[edit]
Client request:[5]
GET /securedpage.php HTTP/1.1 Host: www.example.org
Server response:[5]
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden Content-Type: text/html <html> <head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head> <body> <h1>Forbidden</h1> <p>You don't have permission to access /securedpage.php on this server.</p> </body> </html>
Substatus error codes for IIS[edit]
The following nonstandard codes are returned by Microsoft’s Internet Information Services, and are not officially recognized by IANA.[6]
- 403.1 – Execute access forbidden
- 403.2 – Read access forbidden
- 403.3 – Write access forbidden
- 403.4 – SSL required
- 403.5 – SSL 128 required
- 403.6 – IP address rejected
- 403.7 – Client certificate required
- 403.8 – Site access denied
- 403.9 – Too many users
- 403.10 – Invalid configuration
- 403.11 – Password change
- 403.12 – Mapper denied access
- 403.13 – Client certificate revoked
- 403.14 – Directory listing denied
- 403.15 – Client Access Licenses exceeded
- 403.16 – Client certificate is untrusted or invalid
- 403.17 – Client certificate has expired or is not yet valid
- 403.18 – Cannot execute request from that application pool
- 403.19 – Cannot execute CGIs for the client in this application pool
- 403.20 – Passport logon failed
- 403.21 – Source access denied
- 403.22 – Infinite depth is denied
- 403.502 – Too many requests from the same client IP; Dynamic IP Restriction limit reached
- 403.503 – Rejected due to IP address restriction
See also[edit]
- List of HTTP status codes
- URL redirection
Notes[edit]
- ^ See #403 substatus error codes for IIS for possible reasons of why a webserver may refuse to fulfill a request.
References[edit]
- ^
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content. IETF. sec. 6.5.3. doi:10.17487/RFC7231. RFC 7231. - ^ Nielsen, Henrik; Mogul, Jeffrey; Masinter, Larry M.; Fielding, Roy T.; Gettys, Jim; Leach, Paul J.; Berners-Lee, Tim (June 1999). «RFC 2616 — Hypertext Transfer Protocol — HTTP/1.1». Tools.ietf.org. doi:10.17487/RFC2616. Retrieved 2018-04-09.
- ^ a b «HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV)». IETF. June 2007. Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved January 12, 2016.
- ^ HTTP status code 402 How do I solve the problem with the 403 status code?
- ^ a b Example of «Client request» and «Server response» for HTTP status code 403
- ^ IIS 7.0 and later versions define the following HTTP status codes that indicate a more specific cause of an error 403
External links[edit]
- Apache Module mod_proxy – Forward
- Working with SELinux Contexts Labeling files
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content
When I access my localhost of my machine I get the following screen
whereas when I try the same in my server, I getting the following error
HTTP Error 403.4 — Forbidden The page you are trying to access is
secured with Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
I tried replacing http to https, but I am seeing the directory browsing. How to configure the localhost in server to change the screen.
My machine:
OS: Windows 8
IIS version: 8My server machine:
OS: Windows 2012 server
IIS version: 8
Please share your suggestions
asked Oct 11, 2013 at 6:43
It appears you have set «required SSL» for the site and have not assigned a certificate to it.
You have 2 options:
Option 1. Remove «require SSL» from the site using the following instructions:
- Open IIS Manager
- Click on your website
- Click on the «SSL Settings» in the «IIS» section
- Uncheck «Require SSL»
Option 2. Associate a certificate to your site:
Have a look here
answered Oct 11, 2013 at 8:30
TheDaveJayTheDaveJay
7536 silver badges11 bronze badges
2
Remove «require SSL» from the site using the following instructions:
- Open IIS Manager
- Click on your website
- Click on the «SSL Settings» icon
- Uncheck «Require SSL»
answered Aug 24, 2021 at 12:17
It seems you have selected «Require SSL» settings in the IIS. You need to remove it.
Please use the following steps to fix this error.
Open IIS.
Select your website which has the issue.
Click on the SSL Settings.
Untick the «Require SSL» option.
answered Feb 28, 2018 at 12:56
Hiren ParghiHiren Parghi
1,7951 gold badge21 silver badges30 bronze badges
I have installed a renewed SSL certificate on my web server running IIS7.
After installation, I applied website binding to port 443.
My application uses client certificates too, so I have changed the SSL setting to Require ‘client certificate’.
Both client and SSL server certificates are valid but still I am not able to access my application. The error I get is:
403 — Forbidden: Access is denied.
I have enabled client certificate mapping in IIS role settings also but still not getting rid of this 403 error.
I guess client certificate is not able to handshake with server certificate. Please help!
asked Jan 31, 2014 at 6:16
0
In certificate Store verified all server certificate and client cert with its authority hierarchy are available.
also cross check below settings
Application Authentication: Anonymous
Application SSL Setting: Require SSL/ Accept
ApplicationHost.config: enabled OnetoOneMapping under iisClientCertificateMappingAuthentication also added base64 certificate mapped with service accounts
Also based on my past experience we need to ensure we have SChannel registry setting as mentioned in below post.
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/2464556
answered Sep 8, 2016 at 18:41
bijaykbijayk
5563 silver badges18 bronze badges
Simplest workaround just discovered this today. In IIS for your application, Go to Edit Bindings and change your port number. 443 to 4431 or 44301. Any variation you want. In your client computer, type in the new URL using new port number and you will establish a fresh connection to application. Make sure you SSL Settings for IIS Application is set to «Accept» instead of «Require». This means you can click «Cancel» when the pop up asks you to select a certificate you can simply hit «Cancel» and still hit the site. No 403 Error.
Do not spend hours trying to mess with your certificate store, just simply change the port on IIS Server and you’ll be fine.
answered Mar 18, 2019 at 15:28
1
When the web server blocks you from opening the page you are trying to access, a 403 Forbidden error will occur. In most cases of 403 errors, there is usually nothing you can do. However, sometimes your IP can be the cause of the problem.
This article will provide you with basic knowledge about the causes and solutions of the 403 HTTP Status Code both on the end-user side as well as the website administrator.
Table of Contents
- 1 What is a 403 Forbidden Error?
- 2 What is the cause of 403 Forbidden?
- 3 How to fix the 403 Forbidden Error
- 3.1 Check the .htaccess file.
- 3.2 Reset Directory and File Permissions
- 3.3 Disable all WordPress plugins
- 3.4 Upload an Index Page
- 3.5 Edit File Ownership
- 3.6 Malware scanning
- 3.7 Verify the A Record
- 4 How to fix Nginx 403 Forbidden Error
- 4.1 Incorrect Nginx configuration
- 4.2 Wrong files/folders permissions
- 4.3 Incorrectly setting up an index file
- 5 Fix the 403 error as an end-user
- 5.1 Refresh the page
- 5.2 Clear Your Web History/Cache
- 5.3 Double-check the address
- 5.4 Restart the router or get public new IP
- 5.5 Verify that you have permission to access the URL
- 5.6 You can try again later
- 5.7 Contact the website
- 5.8 Get in touch with your ISP
- 5.9 Connect to another VPN server or disconnect from your VPN
- 6 Final lines
What is a 403 Forbidden Error?
The 403 Forbidden error is when you try to access a website or another resource through your web browser without your permission.
This error is known as the “Request is forbidden” because it is the HTTP status code used by the web server to identify this type of error and means that the server understands the request but refuses to authorize it.
This error occurs when the website administrator intentionally blocks the user or it can also be caused by a server error.
The first case is because the web server owner has not set up access for you, so you are not allowed to access the resource. The second case is that the permissions have been incorrectly set up by the web server owner, so you’re being denied access to a resource you shouldn’t.
Website designers can modify the look and feel of the 403 Forbidden error, as well as the 502 bad gateway, 503 Error Service Unavailable, 404 not found errors, or any other server-side error code. That’s why different websites may display 403 pages differently. This error can also be called by different names on different websites.
Technically, a 403 Forbidden is not an error but an HTTP status code returned by the server. In many cases, 403 status code response headers will be returned intentionally (when the webmaster intentionally blocks the user). Here are some possible causes of the 403 error:
- The user is blocked from accessing the entire page/resource or website.
- The user tries to access a directory, but automatic indexing is disabled and there is no index file.
- The user tries to access a file that is only accessible internally.
- Problems with internet resources on the user’s computer.
- Incorrect website address entered
- Changes in the site’s resources.
- The user’s IP is blocked for violating the website’s policy or is banned for other reasons.
- The domain points to the wrong IP address of the server
- The browser is too outdated.
You may see a 403 error in the form of messages like these:
- 403 Forbidden
- HTTP 403
- Blocked
- HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden
- HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden
- Error 403
- Forbidden: This server does not allow you to access this directory.
- Error 403-Forbidden
The following 24 non-standard codes returned by Microsoft Internet Information Services, are still interpreted as 403 error codes on IIS.
Looking at the HTTP header status code returned from the server, we can see exactly why and where the error occurred.
Although these are non-standard Internet Number Authority (IANA) error codes, they are still accepted as 403 Forbidden errors. Here is a list of 24 IIS server error codes 403:
- 403.1 – Execute access forbidden.
- 403.2 – Read access is forbidden.
- 403.3 – Write access forbidden.
- 403.4 – SSL required.
- 403.5 – SSL 128 required.
- 403.6 – IP address rejected.
- 403.7 – Client certificate required.
- 403.8 – Site access denied.
- 403.9 – Forbidden: Too many clients are trying to connect to the web server.
- 403.10 – Forbidden: web server is configured to deny Execute access.
- 403.11 – Forbidden: Password has been changed.
- 403.12 – Mapper denied access.
- 403.13 – Client certificate revoked.
- 403.14 – Directory listing denied.
- 403.15 – Forbidden: Client access licenses have exceeded limits on the web server.
- 403.16 – The client certificate is untrusted or invalid.
- 403.17 – The client certificate has expired or is not yet valid.
- 403.18 – Cannot execute the requested URL in the current application pool.
- 403.19 – Cannot execute CGI applications for the client in this application pool.
- 403.20 – Forbidden: Passport login failed.
- 403.21 – Forbidden: Source access denied.
- 403.22 – Forbidden: Infinite depth is denied.
- 403.501 – Forbidden: Too many requests from the same client IP; Dynamic IP Restriction Concurrent request rate limit reached.
- 403.502 – Forbidden: Too many requests from the same client IP; Dynamic IP Restriction Maximum request rate limit reached.
- 403.503 – Forbidden: the IP address is included in the deny list of IP Restriction
- 403.504 – Forbidden: the hostname is included in the deny list of IP Restriction
What is the cause of 403 Forbidden?
When the server refuses to access a page on a website or the entire website, a 403 Forbidden error occurs.
This error mostly occurs due to misconfiguration of access permissions. Misconfiguration refers to incorrect read, write, or execute permission settings for a file or directory.
Sometimes, 403 errors also occur on the user side because the website administrator intentionally blocks access from 1 IP, an IP range, or an entire region or country.
Error 403 forbidden can also occur when the firewall or any security software or plugins on the server suspects illegal access, so it blocks access. An empty site directory is also likely to return a 403 HTTP header status code if you are trying to access it.
HTTP 403 forbidden errors are strongly associated with file or directory permissions. This will be the focus of the next error remedies. There are also other methods to deal with this, including clearing the browser cache and scanning for malware.
Most of the time you can’t do much if you are an end-user and don’t have server admin rights. Sometimes this error is temporary, sometimes it is not. Whether you’re an end-user or a server administrator, there’s something you can do.
If you are a server administrator, see 7 possible solutions for the HTTP 403 error. Except for method #3 for WordPress, the rest of the solutions are applicable to most websites running on Apache servers.
For sites running on Nginx servers, see the “4. How to fix NGINX 403” error troubleshooting methods.
Check the .htaccess file.
By default, .htaccess files are often hidden in website directories, so you may not see them. The File Manager of hosts running Cpanel will provide the file for you in your public_html directory.
Note that there can be multiple .htaccess files, so the instructions below are instructions for the .htaccess file in the root directory of your website.
.htaccess is a server configuration file that changes Apache Web Server settings. These steps will help you locate this file in the hosting that runs cPanel if you are using it.
- Login to cPanel and find File Manager
- Find the
.htaccessfile in thepublic_htmlfolder. - Click Settings in the upper right corner to enable Show hidden files (dotfiles), if you don’t find this file in the
public_htmlroot directory.
Once you have found the file, check for errors. Right-click on the .htaccess file and select rename to backup.htaccess to create a backup.
Go to your website. If the site works, it’s likely that the .htaccess file is corrupted. Now we need to recreate the .htaccess file by logging into the WordPress admin panel and clicking Settings -> Permalinks.
Click the Save Changes button at the bottom of the page without editing or changing any parameters. This will create a new .htaccess file on your site.
Try the next option if this doesn’t solve the problem.
Reset Directory and File Permissions
Incorrect permissions for files and folders can also be the reason for HTTP 403 errors. Files are often created with default permissions that control what you can do with them. FTP clients allow you to modify folder and file permissions.
First, install an FTP client (we recommend Filezilla – the free version is available on Windows, Linux, and macOS). Configure the parameters of the hosting server on the FTP application. Connect by FTP to the hosting server.
Once it is connected to your website, you can configure it. To change folder permissions, right-click on the public_html folder, then click File permissions.
A Change File attributes window will appear. Enter 755 in the numeric value box. Check the Recurse into subdirectories box. Below that line, tick to Apply to directories only. Click OK to change.
Depending on the number of folders on the server, this may take 1-5 minutes to complete.
Next, we will change the permissions for the files. The steps are the same as for the folder. First, right-click on the public_html folder, then click on File permissions. A Change File attributes table will appear. Enter 644 in the numeric value box.
Check the Recurse into subdirectories box. Below that line, check to Apply to files only. Click OK to change. Depending on the number of files on the server, this may take up to 30 minutes to complete.
Usually changing permissions of files takes longer than changing permissions of folders.
If you can access your hosting account using SSH then you can use the command line to change permissions for folders and files.
Command structure to change permissions for a directory:find /home/huyhoa/public_html -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;Explanation: The above command will find all subdirectories in
/home/huyhoa/public_htmldirectory and change their mod to 755. This command will not execute if it is a file.Command structure to change permissions for files:
find /home/huyhoa/public_html -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;Explanation: the above command will find all files in
/home/huyhoa/public_htmldirectory and their subdirectories and change their mod to 644. This command will not execute if it is a folder.
Once you’ve done this, visit your website to verify that the error has been fixed. If the 403 error still occurs, it may not be caused by the permissions of the files or folders.
It may then be necessary to proceed with method #5 below, which is to change the group and owner for both files and folders.
Disable all WordPress plugins
If your website uses WordPress source code, plugins or themes can be the problem causing 403 errors. Especially security plugins are very likely to cause this error.
If none of the above methods are successful, then it is very likely that you are using an incompatible plugin or your security plugin is blocking access.
To determine if the 403 error is resolved, we will disable the plugins. We recommend deactivating all plugins at once.
This will allow you to quickly identify the problem and start looking for a solution. This is how you can access your hosting account via FTP or use the file manager to access your hosting account to quickly disable all plugins.
Go to public_html->wp-content folder. Locate the plugins folder. To disable all plugins, rename the folder to something like disableplugins. Revisit the website.
If the 403 error does not appear anymore, then the exact 403 error you are getting is due to an incompatible plugin or a security plugin blocking access.
Change the name of the folder to plugins. Now you will need to deactivate the plugins one by one from your WordPress plugins management page. Every time you disable a plugin, check if the site is up and running. Then you should be able to spot the problematic plugin.
Once you’ve found it, update it if necessary, or delete it. If the problem cannot be resolved, contact the plugin’s developer for assistance. You can also contact your hosting provider for assistance.
Upload an Index Page
Every website should have a root directory containing the source code. When servers find this root directory, they look for files that are defined as index files.
Typically, index files are set to index.html, index.html, index.php, index.jsp, index.aspx, index.asp, or default.html. These index files are specified in the server’s configuration file.
When the server accesses the website’s root directory without finding the predefined index files, it will most likely return a 403 error code.
Therefore, for the website to work properly, the root directory is required to have an index file, and upload the index file to your public_html directory.
To do this, use the FTP of your hosting account or file manager. If the server to use is Apache, you can use the .htaccess file to change the default index file configuration.
The code below is an example where Huy Hoa changes the index file from index.html to the default huyhoa.htm, huyhoa.html, huyhoa.php and huyhoa.shtml.
With this order, when called, the server will look for the file huyhoa.htm first, if there is this file it will execute that file, if the file huyhoa.htm does not exist, it will look for the file huyhoa.html, in turn, until the file huyhoa.shtml
DirectoryIndex huyhoa.htm huyhoa.html huyhoa.php /huyhoa.shtml
The command /huyhoa.shtml in the end means that when no files are found, the file huyhoa.shtml will be used in the root directory to execute. If the file huyhoa.shtml also does not exist, a 403 error may be returned.
Edit File Ownership
If you use Linux web hosting, incorrect file ownership could trigger the 403 prohibited error.
Files and folders can typically be assigned to either an Owner or a Group. To modify ownership in these environments, you will need SSH access.
To connect to your VPS, you will also need an SSH terminal. After connecting SSH to your website server via SSH, you can verify ownership using the following SSH command:
ls -1 [file name]
This is the result:
-rwxrw–rw-1 [owner][group]02 Jul 22 18:10 filename.txt
Take a look at the group and owner parts. Your hosting account username should determine the correct ownership. To change file ownership, you can use the chown Linux command.
Here is the syntax for chown.
chown [owner]:[group][filename]
If your username is www, you can use syntax such as this:
chown www:www filename.txt
If you want to change the owner for both the folder and all the files/folders inside it, you can use the command below. This command will change the entire owner and group of the /home/huyhoa directory to the user nginx and group nginx.
chown -R nginx:nginx /home/huyhoa
Contact your hosting provider support team if you are uncomfortable using SSH.
Malware scanning
Malware on the server can also be the cause of the 403 error. Malware can infect websites on the same server and inject unwanted code into the .htaccess file.
Even if you fix this file as instructed in item #2 above, the error won’t go away. To find malware, scan your website.
Sucuri, iThemes Security, and Wordfence are examples of WordPress security plugins that can do this. WordFence and most WordPress security plugins can remove malware.
After the plugin has identified all the infected files, it will give you actionable options like deleting them or restoring them.
You can also restore websites from backup files. If you don’t have a complete backup, you can restore the site using a database backup.
Most hosting providers can provide free data backup (not applicable to VPS hosting and dedicated servers).
Verify the A Record
If your domain name points incorrectly to an IP address, you may get the 403 forbidden error. This is because you don’t have permission to view the content. Double-check that your domain point to the correct IP address.
Your domain could still point to the old web host if you recently moved from one web hosting provider to another. It will result in a 403 error code when the old host cancels your account.
How to fix Nginx 403 Forbidden Error
Nginx 403 forbidden error is a status code that is generated by NGINX and displayed to clients when they attempt to access webservers with insufficient permissions. NGINX protects directory listings and will produce an error 403.
Incorrect Nginx configuration
An NGINX server can get a 403 error for two main reasons:
- Server misconfiguration
- Nginx user does not have execute/read/write permissions for files and directories.
In which the cause of misconfiguration can occur in many categories, such as misconfiguration of the site’s root directory, incorrect configuration of the index file, incorrect configuration of PHP’s running port…
Nginx configuration files can be broken down into various files like Nginx server configuration file, PHP configuration file, MySQL configuration file, SSL configuration file, and site configuration.
For example, the Nginx configuration file will specify which index files should be loaded and in what order of precedence. Nginx will return a 403 Forbidden error if the specified index file is not found in the directory.
403 Forbidden errors in Nginx can also be caused by files or folders that have not been set correctly.
Nginx must have RWX permissions on all paths in order to make files or resources available to the client. This error can be fixed by changing folder permissions to 755 and file permissions to 644.
Details on how to set permissions for folders or files you can be read in “3.2 Reset Directory and File Permissions” above.
Make sure that the Nginx user has full permission to the folders and files. Usually, Nginx will run with the username nginx or www or www.data. With shared hosting systems, often the username you get is also the username that has the same rights to run as the nginx user.
For 403 forbidden errors caused by a misconfiguration on the server, you need to have sufficient server access and knowledge of the commands or the server administrator to be able to handle these errors.
Wrong files/folders permissions
Incorrect file permissions are a major reason for the Nginx 403 Forbidden errors. The default permissions for the directory are 755 and 644 for files, respectively. Any error in these permissions will result in 403 forbidden.
It is also necessary that the Nginx administrator must be the file owner. With this command, you can change ownership of all files to the Nginx administrator.
sudo chown * -R nginx
We also change the permissions for each directory to 755 by using the command.
sudo chmod 755 [directory name]
We can also go to the directory and modify the permissions for all files inside that folder and child folders by using the following command.
sudo chmod 644 *
Incorrectly setting up an index file
Nginx configuration files will determine which index files should be loaded and in what order. This error can be caused by incorrectly setting up the index file. We will use the following example:
server
{
root /home/huyhoa.net/public_html;
index index.html index.htm;
server_name huyhoa.net www.huyhoa.net;
location /
{
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
#fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php-fpm/php81.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
listen 443 ssl;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/huyhoa.net/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/huyhoa.net/privkey.pem;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security max-age=15768000;
resolver 8.8.8.8 1.1.1.1;
ssi on;
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf;
}
server {
listen 80;
access_log off;
error_log off;
server_name huyhoa.net www.huyhoa.net;
return 301 https://huyhoa.net$request_uri;
}
php-fpm configuration file
;listen = 127.0.0.1:9000 listen = /var/run/php-fpm/php81.sock
Configuration file for Nginx
#fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php-fpm/php-fpm.sock;
This line indicates that index.html will load first, followed by index.htm. These files will not be found in the directory and it will cause a 403 forbidden error. In this case, you can fix it by changing the line index index.html index.htm; to index index.php index.html index.htm; so it can find the file index.php and execute
Similar to the above, if you want to load an additional index file, you will need to add it to the list of already recognized index files.
Fix the 403 error as an end-user
Refresh the page
It is worth trying to refresh the page. Sometimes the 403 error can be temporary and a simple refresh may fix it. To refresh most browsers, you can use Ctrl+R, Ctrl+F5 (Windows), or Cmd+R (Mac).
There is also a Refresh button in the address bar. Although it doesn’t always fix the problem, it is easy to do and worth trying.
Clear Your Web History/Cache
A 403 error may also be caused by your browser’s cookies and cache. A cache is used to speed up website loading times. It is possible that the website’s URL has been changed and the actual link to the page is different from the cached one.
The cookies could also be responsible for this error. This could be true if you log in to a website normally but get this error message when you try to log in. This issue can be resolved by clearing the browser cache and cookies.
Clearing the cache can cause your next visit to the site to take longer as your browser will request all files from the site again. Clearing cookies will also sign you out of all logged-in websites.
To clear your Google Chrome cookies and cache, follow these steps:
- Click the three-dot icon in the upper right corner.
- Select Settings.
- Click Clear browsing data in the Privacy and Security section.
Select the appropriate time period to delete data using the drop-down menu. Next, review Cookies and other site data as well as Cached images or files. Finally, click Clear data.
After you have completed the above steps, you can return to the website and log in if required.
In most situations, a 403 forbidden error is because you are blocked from the server side so if this doesn’t work you can try adding method #5.4 below or contact the website support team for help.
Double-check the address
A mistyped URL can also be the reason for the 403 error. You should make sure that the URL you are trying to access is for a file or web page and not a directory.
A typical URL will have a domain part ending in .com / .net.org followed by a / followed by a filename followed by a .html, .php, .asp, or .aspx extension. Directory URLs usually end with “/”. Check that you have entered the correct URL.
Note that now there are thousands of different TLDs, not just limited to Gtlds and countries TLDs like before. You won’t be surprised to see URLs like huyhoa.icu or huyhoa.top or huyhoa.bid…
For security reasons, most servers won’t allow browsing of the directory containing the code, for example with a WordPress website, even though the wp-content directory does exist on the server, but you won’t be able to access it via the link https://huyhoa.net/wp-content/.
If they are configured correctly, you will be redirected to another website or you will come across a blank page with no content.
If the server administrator misconfigures or something goes wrong with the configuration, you may see a 403 error when trying to access these directories.
Restart the router or get public new IP
Some websites or servers have firewall systems to prevent large-scale network attacks or DDOS attacks. These systems often have limitations on the operations that can be performed on the website.
For example, limit access to subpages to 3 operations per second. If you try to open multiple subpages by right-clicking and then open link in new tab and opening too many tabs will result in a spike in data access to the server and the server may think this is a form of DDOS and may temporarily or permanently block access from your side.
Your public IP is a kind of identifier of your identity on the internet. Therefore the website server may block your IP and when you access you will only receive a 403 error.
Therefore, when accessing a certain website and you receive a 403 error message, it is likely that your public IP address has been blocked. Try restarting the router to get the new public IP.
Of course, this would make no sense if your ISP assigns you a fixed IP. However, this is very rare, unless you ask your ISP to assign you a fixed IP (usually this will cost money to have a fixed IP).
If you already have an IP and still get blocked, maybe you should think about the whole IP range or your country has been blocked. At that time, you should think about fake IP using a proxy or using a VPN to connect.
If you are using a different VPN to connect to the website and still receive the 403 error, then this is most likely an error from the website, there is nothing you can do to solve the problem except contact the website owner and ask them to fix the error.
Verify that you have permission to access the URL
You may run into problems if you try to access a website that requires you to sign in before you can view the content. The server is designed to display an error message telling you that you need to be logged in to view the content.
Log in to the site if you can and check if the error goes away. In addition, some websites may block you from accessing part of the website and only allow a small number of pre-declared users to access.
For example, some websites will only allow certain IPs or IP ranges to access the website’s admin area or a sensitive area on the website. When you try to access these areas, the server will return an HTTP 403 Forbidden response status code.
You can try again later
If none of these simple solutions work, you can always put off the problem and return later. Most 403 errors are due to issues with the website involved. It’s possible that someone is already working to fix the problem.
Contact the website
You can also contact the website owner directly. Try to look up the contact information of the website owner and contact them directly to report the error. You can contact them via their social media channels if there is no active contact form on the website. If you know their email or phone number, that’s also a good solution.
Get in touch with your ISP
If the website doesn’t work for you but works for others from another internet service provider in your area, it’s possible that your ISP has blocked the website. Try contacting them and let them know about your problem. While it’s unlikely that they can solve the problem, it might be doable.
Connect to another VPN server or disconnect from your VPN
Nowadays, the use of VPNs has become more popular for many reasons. Especially on smartphone devices. If you’re using a VPN or proxy to mask your public IP, this could be the cause.
VPN users may be blocked by some websites. If you try to connect via VPN, a 403 Forbidden message will appear. You can try disconnecting from your VPN to see if you can access the website.
You can switch to a different VPN server or use a different VPN service, although some websites may not ban all VPN services, they can ban certain VPN service providers or the IP ranges of some VPN Services.
Or maybe that website blocks access from a certain country but is open to other countries. A typical example of this is the websites of some major banks that often block access from countries with high fraud rates.
Final lines
403 Forbidden errors can be frustrating because they prevent you from accessing certain resources. These errors are most commonly caused by incorrect file/folder permissions.
However, there are other causes such as missing index files, faulty plugins, or malware infections. It can be difficult to determine the cause of a 403 error without a lot of servers or IT knowledge.
We are confident that you will be able to fix the 403 errors and recover your site using the methods in this article.
To recap, here are the steps you can take to fix the 403 Forbidden error message from showing on your website.
- You can check the .htaccess file.
- Reset directory and file permissions.
- Disable WordPress plugins
- Upload an index page
- Change ownership
- Verify the A record.
- Be sure to remove all malware.
- Clear your web browser history and cache.
403 is one of many HTTP status codes returned from the server-side when a request is received from the client-side.
Unlike other error codes like 401, 404, 501, and 503 which represent an error on the server-side, the 403 HTTP Status Code error code means that the request is forbidden. This means that the server understands the request but refuses to execute it.
403 forbidden errors basically have an impact on SEO if it is really a server-side error and not you actively blocking. Your website’s rankings will be seriously affected if you don’t fix the error soon.
So, if you actively block, make sure not to block with good bots from search engines.
If you are returning 403 Forbidden errors for the directories you want to block, you can prevent search engines from following links to these locations and specifying NOINDEX.
You can still allow exceptions to these pages by subdirectories or other images, CSS, and static resources to be indexed if they are linked to other indexed.
403 forbidden error can lead search engines to think that you are blocking access and there is no point in indexing or ranking a blocked website. You understand what happened after that, right?
- References: